3.3. Efficiency Analysis of SPMSM Operation in the Constant-Torque Region
In the SPMSM, the magnets are fixed on the surface of the rotor; therefore, taking into account the fact that the magnetic permeability of PMs is close to the magnetic permeability of air, the inductances along the d and q axes have the same value:
Ld =
Lq =
L = 2 mH. This leads to the presence of only an active component in the electromagnetic torque (6):
In this regard, the energy-efficient SPMSM vector control strategy is the condition
id = 0 [
6]. Under this condition, the input active power (29) will take the form
Based on (34), the input power and flow of the PC will be equal to
,
, and the system of linear equations describing the operation of SPMSM as PC will have the form
Let us determine the kinetic coefficients in the system of Equation (35) using the mathematical model of the PMSM steady-state operation (8) and (9).
Under the condition of
id = 0, from the first equation of system (9), we obtain
Substituting (36) into the first equation of system (9), we get
Substituting (37) into (36) and then the resulting expression into the second equation of system (8), after transformations we get
The second term in parentheses can be neglected due to its smallness.
By substituting the obtained value
iq0 into the second equation of system (9), as well as into the third equation of system (9), we obtain
Equations (39) and (40) are reduced to system of Equation (35):
From the equations of system (41), we obtain the expressions for the kinetic coefficients of the PC, which describe the operation of the vector-controlled SPMSM:
Based on kinetic coefficients (42), expressions for the main dimensionless parameters of this PC can be obtained from (15)–(17):
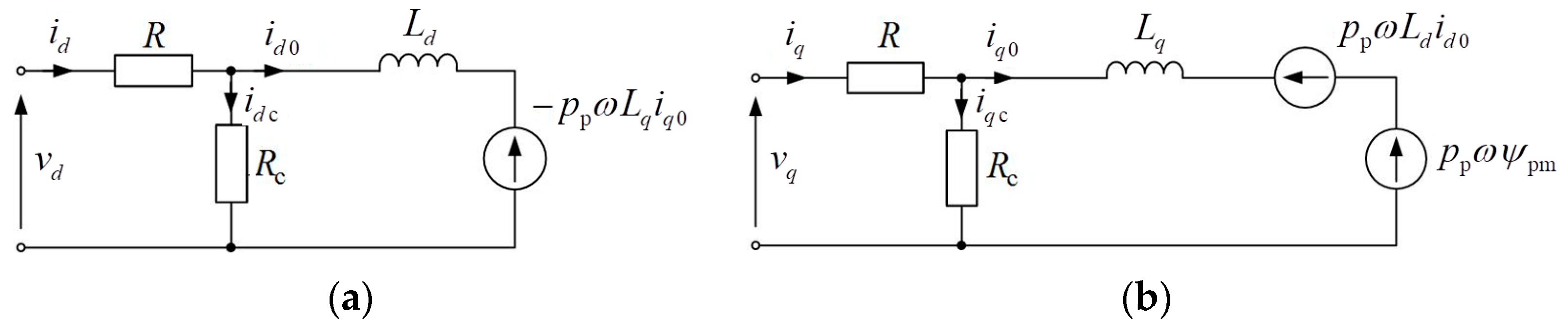
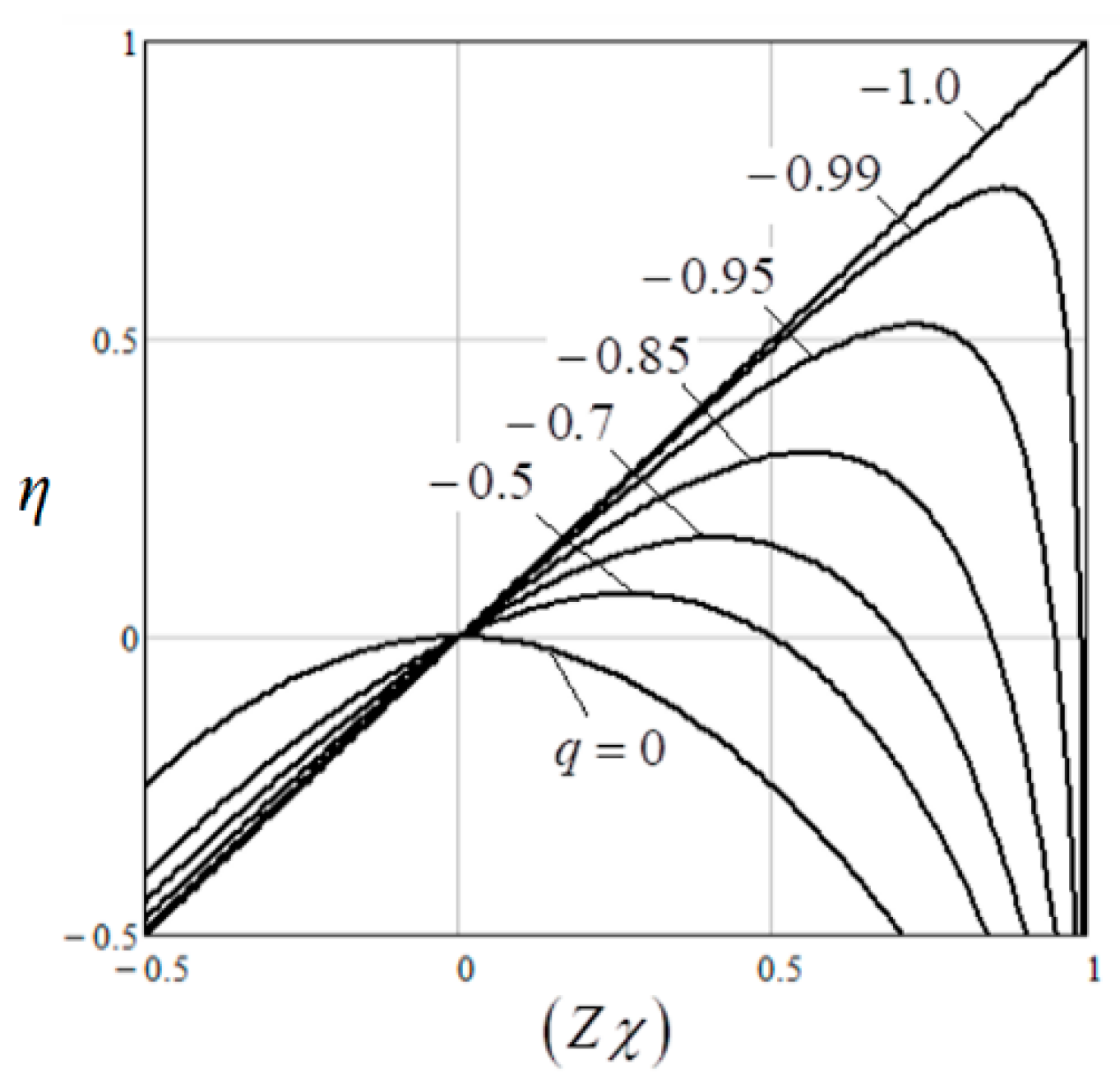
As can be seen from the obtained results (43), the degree of coupling q of the PC modeling the SPMSM vector controlled by the
id = 0 method, for the case without taking into account iron loss, is equal to −1 and does not depend on the mode parameters of the machine. In this case, the SPMSM is modeled by only one substitute scheme determined by the coordinate
q, but without resistance
Rc (
Figure 1b). Therefore, the current
iq completely forms an electromagnetic torque; that is, it is directly linked with the output current. For the case of taking into account iron loss, the resistance
Rc appears in the substitute circuit, through which a part of the input current is closed. In this way, there is already an incomplete coupling between the input and output of the PC, and the degree of coupling is determined using the value
A according to (43). With a decrease in the angular velocity of the machine,
A decreases because, according to (28), the value of the resistance
Rc decreases. For the machine under study, when the relative angular velocity ω
* decreases from 1 to 0.25, the value of q changes from −0.9965 to −0.9898. The maximum energy efficiency of such a machine, according to (20), also decreases from 0.845 to 0.751 (
Figure 3). The value of (
Zχ)
opt also decreases from 0.919 to 0.867.
The value of the SPMSM operating point
Zχ, in turn, depends on the values of two main variables—the angular velocity of the machine
ω and the load torque
TL, which directly affect the value of
vq. The value of the latter was calculated from Equations (6), (8) and (9) under the following conditions:
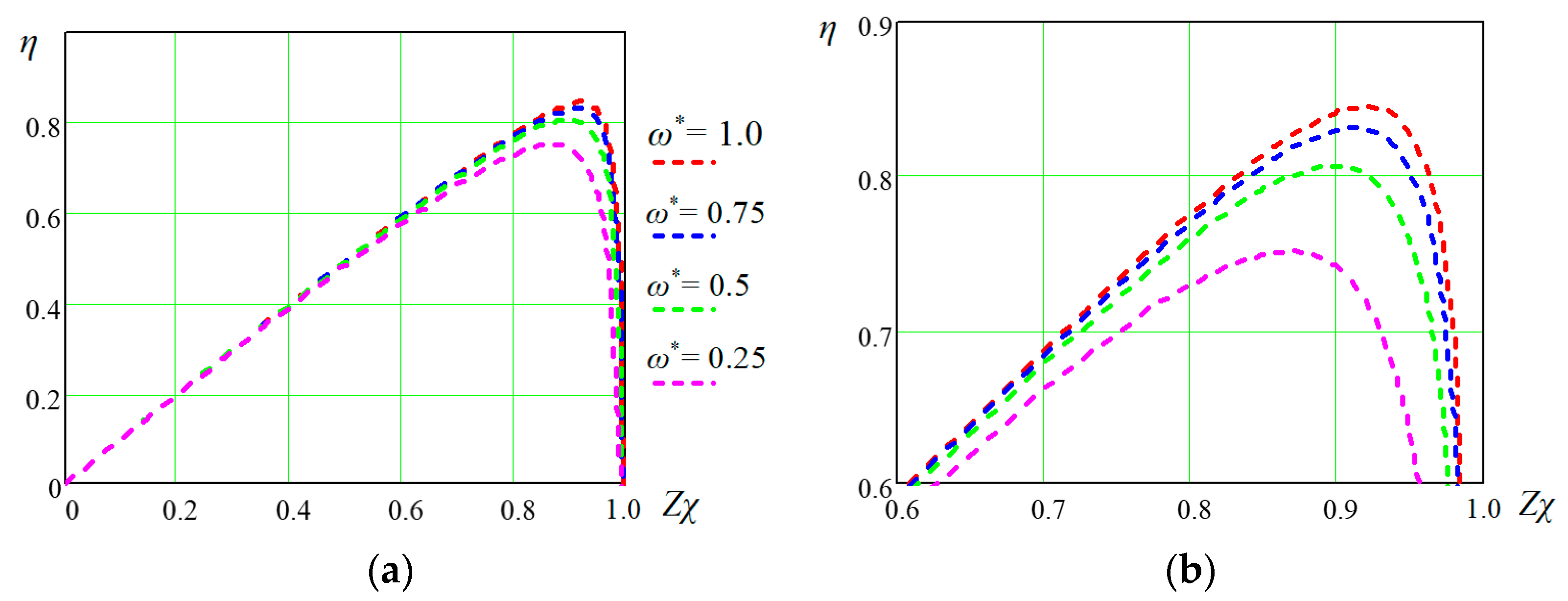
Figure 4 shows how the dimensionless indicator
Zχ of the operating mode of the studied machine depends on the fixed values of the main variables
ω and
TL. As can be seen from this figure, the optimal value of (
Zχ)
opt, and therefore the maximum efficiency of the machine, is achieved only with a certain combination of values
ω and
TL. The following relationship between the variables ω and
TL corresponds to the (
Zχ)
opt curve:
In
Figure 4 both above and below the curves shown (
Zχ)
opt, the energy efficiency of the SPMSM decreases, and the lower part corresponds to the left side of the
η(
Zχ) characteristics shown in
Figure 3, and the upper part is on the right side of the
η(
Zχ) characteristics. As can be seen from
Figure 4, the greatest deviation of the obtained dependences
Zχ(
ω) and
Zχ(
TL) from the corresponding optimal curves (
Zχ)
opt is observed at low values of both
ω and
TL, and the best approximation of the specified dependences to (
Zχ)
opt occurs for the average values of
ω and
TL. The obtained regularity can be clearly seen from the efficiency map, which is constructed using the dependencies obtained above for the studied SPMSM in
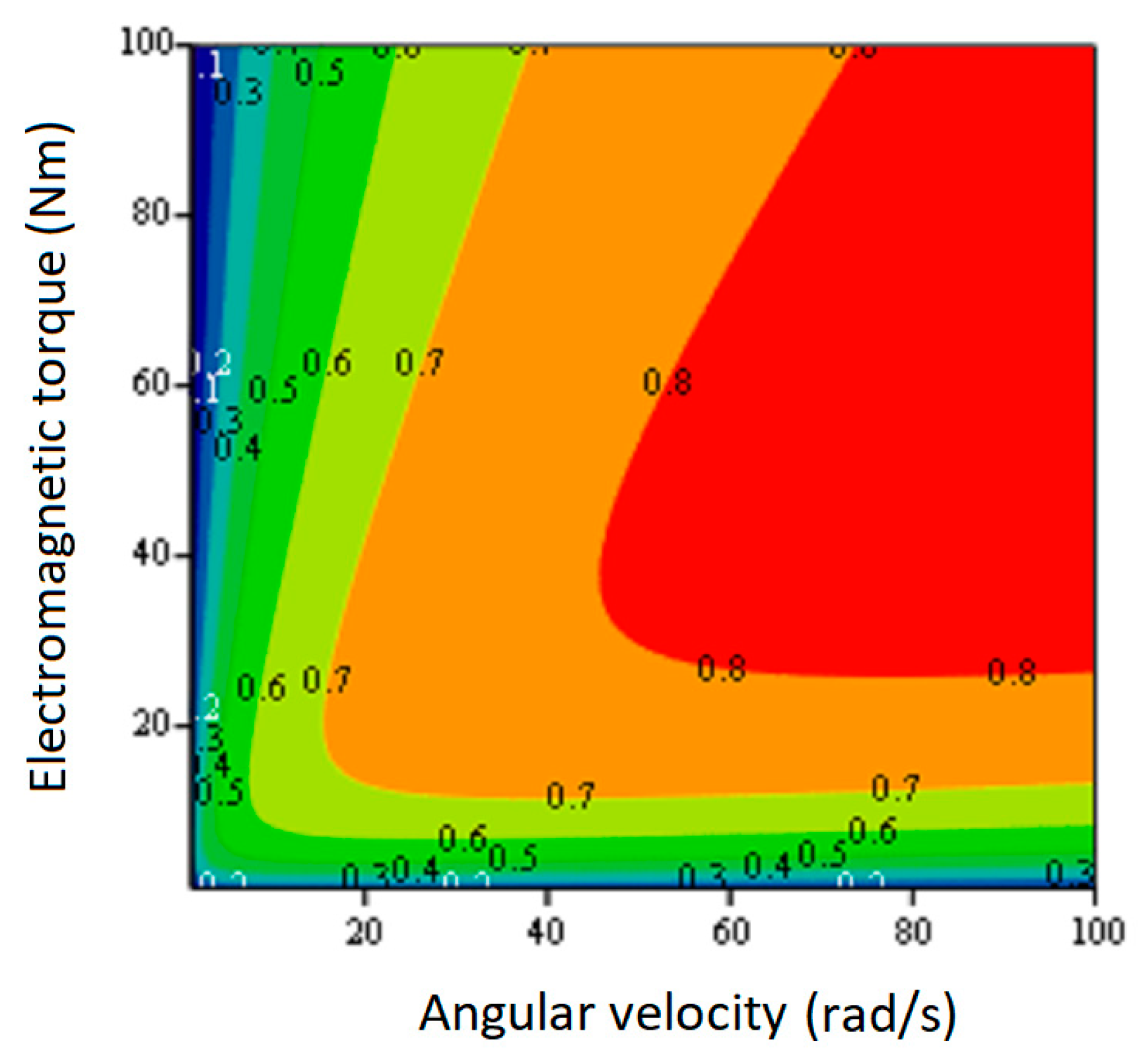
Figure 5.
Therefore, the energy efficiency of SPMSM taking into account iron loss and the operating according to the criterion id = 0 directly depends on the parameters of the drive—angular velocity and load torque. High efficiency can be ensured only with the indicated combinations of these parameters. Unfortunately, there are no other options to change the SPMSM performance map.
3.4. Efficiency Optimization of the IPMSM Operation in the Constant-Torque Region
As can be seen from the nonlinear mathematical model of IPMSM for its steady-state operation—from systems of Equations (8) and (9), as well as from complex expressions for the input force and flow (31)—analytical expressions are obtained for the kinetic coefficients of the PC that describe the operation of this machine, which is impossible. Therefore, the research method for this case remains only numerical. Since the system is clearly nonlinear, the PC parameters will change depending on the working point of the machine—the set values of the angular velocity ω0 and the load torque TL0. For a given pair of values of these variables, it is necessary to linearize the system and obtain the PC parameters.
As is known [
9], already in the constant torque control region of the IPMSM angular velocity regulation, the energy efficiency of its operation also depends on the value of the armature current component
id. Even for the classic case—without taking into account iron loss—it is not possible to obtain analytical expressions for the dependencies of the optimal values of the components of the armature current on the value of only the load torque—the MTPA curve [
35]. If iron loss is also taken into account, even with the help of such a simple model, which is used in this work, it will not be possible to obtain such analytical dependencies. Therefore, for the purpose of numerical energy optimization of the IPMSM taking into account iron loss, it is necessary to introduce one more variative variable. As the analysis showed, it is easiest to choose the component of the armature current
id0, which determines the reactive component of the electromagnetic torque. Therefore, further calculations should be carried out as a function of this variable.
Therefore, it is advisable to build the IPMSM mathematical model taking into account iron loss, for successive numerical calculations, based on the systems of Equations (8) and (9) and expressions (31) in the following view:
Having the set parameters of the working point of the machine
ω =
ω0 and
TL =
TL0, as a result of cyclic calculations according to expressions (46)–(52) for points in the range
id0 = 0–(−100) A, the final dependences
va(
id0) and
ia(
id0), which characterize the input power of the PC depending on the value of the component of the armature current
id0, are obtained at a given output power
Po(
ω0,
TL0). Thus, for each value of
id0, there is a pair of the PC input and output coordinates—flow
X and force
J. However, these values are not enough to determine three kinetic coefficients from two equations in system (32). To obtain one more point of the linear PC, it is necessary to linearize the obtained dependences of the input force
va(
id0) and the input flow
ia(
id0) of the PC based on the output coordinates of the force ω and the flow
TL at the given point (
ω0,
TL0). To obtain such linear dependences, similar calculations were carried out according to expressions (46)–(52), but for points equidistant to the left and right of the given point at some insignificant distances: once by the value of
ω0 for
TL =
TL0 and the second time by the value of
TL0 for
ω =
ω0. Four linear dependences of the input flow and force on the output flow and force at the given point (
ω0,
TL0) were found based on the pairs of values
va(
id0) and
ia(
id0) obtained at these points and depending on
id0. Attempts to apply points from the obtained linear dependencies to determine the kinetic coefficients showed that if even two points from different dependencies are taken, then the values of the kinetic coefficients
Lio and
Loi determined from the two equations of system (32) will be different. Therefore, only one linearized dependence was taken—
va(
id0) as the function of
ω, which the least of all obtained differs from the linear character that leads to the smallest calculation error. The angular coefficient of the tangent to the curve at the point
ω0 is determined based on the received values of the armature input voltage module (48) from the left
and right
of the given value
ω0:
Using the obtained value
, it is possible to determine the necessary one more operating point of the PC—the value of the input voltage
va(
id0) at
ω = 0:
The value of the kinetic coefficients was carried out in the following order.
From the second equation of system (32) for
ω = 0, the following is obtained:
From the first equation of system (32) for the working point of the PC, the following is found:
From the second equation of system (32) for the working point of the PC, the following is determined
With the use of kinetic coefficients (55)–(57) according to expressions (15)–(17), dependences on the main parameters of the PC and the indicator of the energy efficiency of the studied IPMSM taking into account iron loss were obtained: q(id0), Zχ(id0) and η(id0).
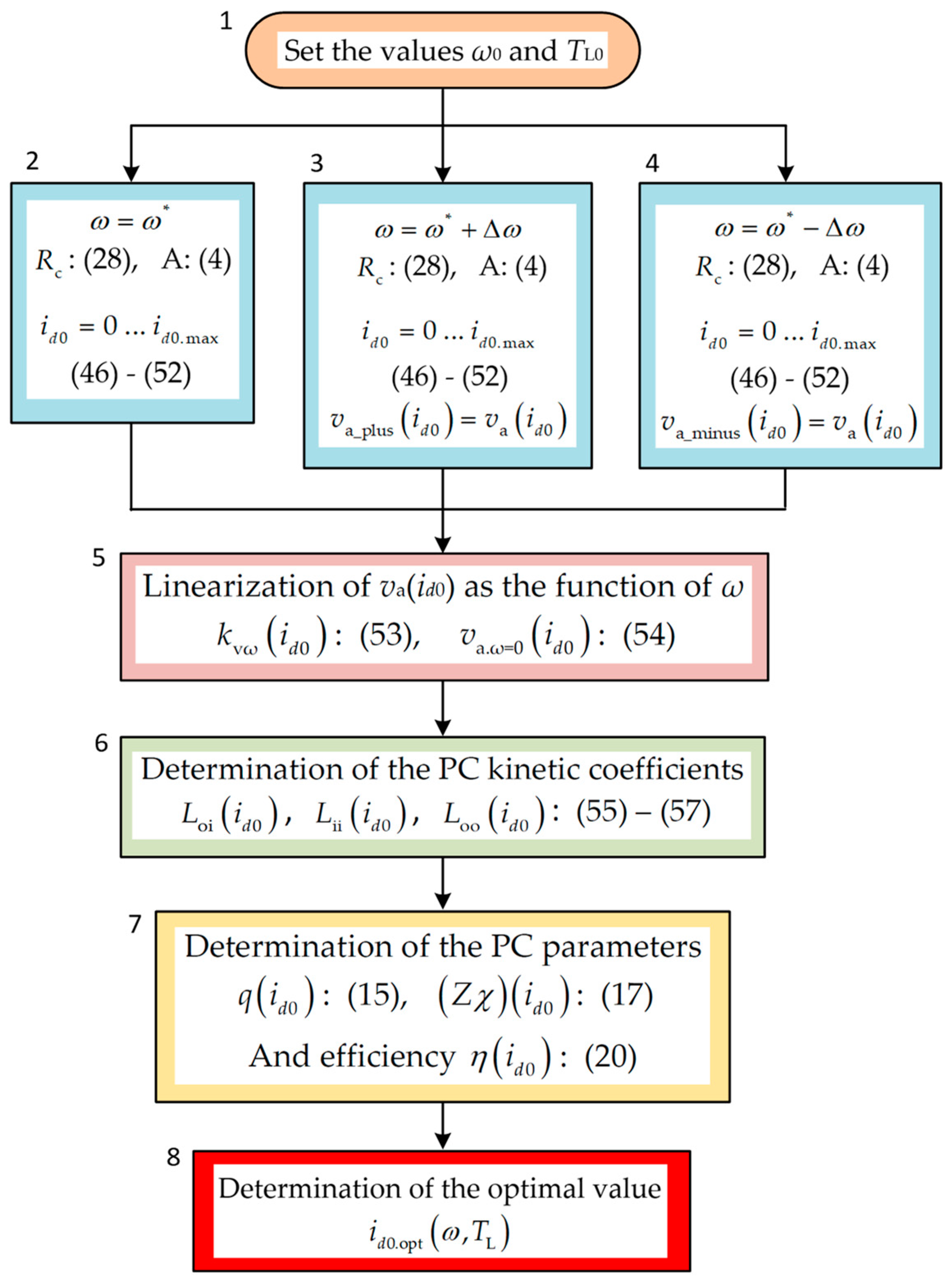
According to the described algorithm, a program was created in the Mathcad environment that allows you to calculate the specified parameters and performance indicators of the PC, which models the operation of the studied IPMSM taking into account iron loss for different operating points of the machine depending on the component of the armature current
id0. The flow chart of this algorithm is presented in
Figure 6. The algorithm works as follows.
In block 1, the operating parameters of the machine are specified—the set values of the angular velocity ω0 and the load torque TL0. In blocks 2–4, in cycles for a given range of values of the d-component of the armature current, identical calculations of the dependencies on id0 of the main electrical variables of the machine are carried out according to expressions (46)–(52). These calculations differ only in the values of the angular velocity—for a given value of ω0 and for the values shifted from it to the left and right by the amount Δω (in the work, Δω = 5 s−1 is used). According to the results of these calculations, in block 5, a multiple, id0-dependent, linearization of the dependence of the armature voltage module based on the machine angular velocity is carried out according to expression (53), and the coordinates of another working point of the PC, which models the IPMSM, are found based on the obtained linear dependence according to (54). Next, in block 6, according to expressions (55)–(57), the id0-dependent values of the kinetic coefficients of the PC are found. Based on these values, block 7 also determines the main parameters of the PC—q and Zχ, which also depend on id0, as well as the energy efficiency of the machine operation η(id0). From the latter, in block 8, the optimal value of id0.opt, for which the efficiency is maximum, can be obtained.
To check the correctness of the algorithm, the first computational experiment was conducted for the variant for which the results can be determined analytically—for the IPMSM without taking into account iron loss. Having set three orders of magnitude higher than the real value of
Rc in the model, the results were obtained for the nominal angular velocity of the machine and for the values of the load torque of 0.25
Tn, 0.5
Tn, 0.75
Tn and 1.0
Tn, which are shown in
Figure 7.
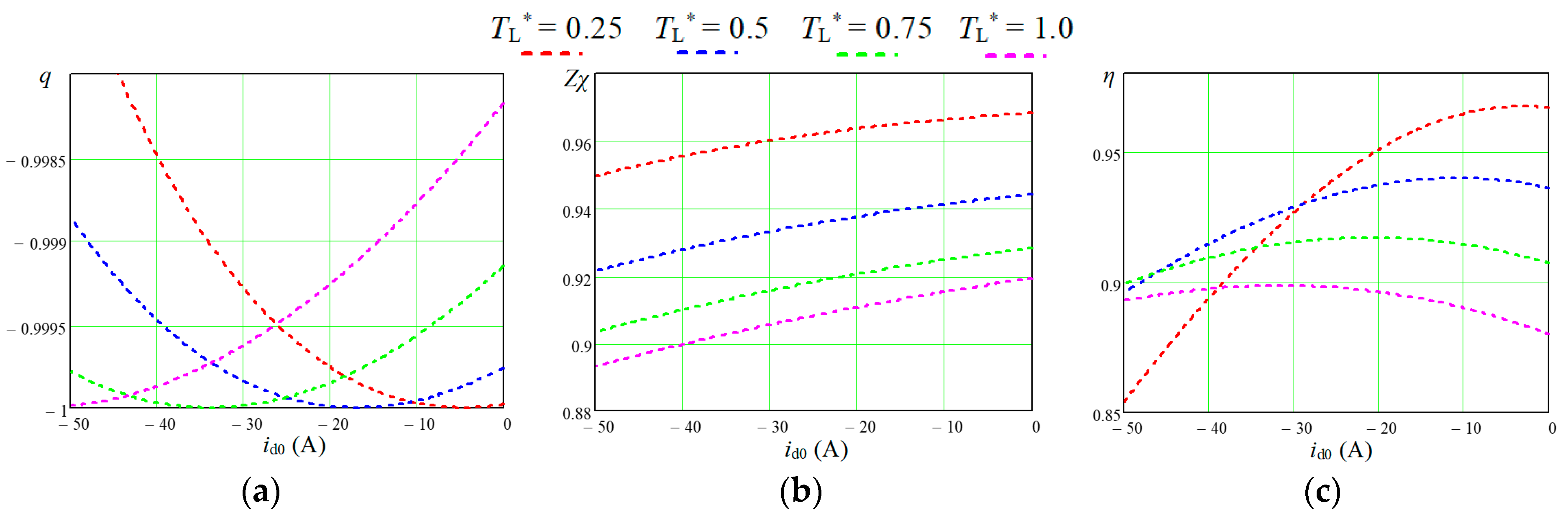
From the dependences
η(
Zχ) shown in
Figure 7, the value of the current component
id0, at which the maximum energy efficiency is achieved, were obtained, which are listed in
Table 2. Since in the case of not taking into account iron loss,
id0 =
id, these values should correspond to the values of the MTPA curve. In [
24], the dependence on p. u. between the electromagnetic torque and the component of the armature current
id for the IPMSM at the points of the MTPA curve is given as
where the relative values are normalized to the corresponding base values
For the calculation, a numerical dependence was obtained from expression (55) in [
24]:
Calculated using (58)–(60) for the studied IPMSM,
id values from the MTPA curve are given in
Table 2. The deviation obtained according to the developed algorithm from the corresponding values obtained analytically does not exceed 1.5 A for medium and high loads, which is less than 10% for medium loads and less than 5% for the nominal motor load torque. This is an acceptable result for these studies and indicates the adequacy of the proposed research method and algorithm for calculating the parameters and performance indicators of the IPMSM taking into account iron loss.
From
Figure 7, it can be seen that even without taking into account in the IPMSM iron loss, the degree of coupling decreases.
q = −1, i.e., full coupling for each loads occurs only for the one value of
id0, i.e., for a certain optimal ratio between the components of the armature current
id0 and
iq0. With other ratios between these components, which also provide the required electromagnetic torque of the machine, the coupling between the input and output will already be incomplete. This can be explained by the different contribution of the components of the armature current to the production of the electromagnetic torque according to (6) and the two substitute circuits that work in this case (
Figure 1). With differences from the optimal ratios between the components of the armature current, there is a “slippage” of power in one of the circuits or in two circuits together.
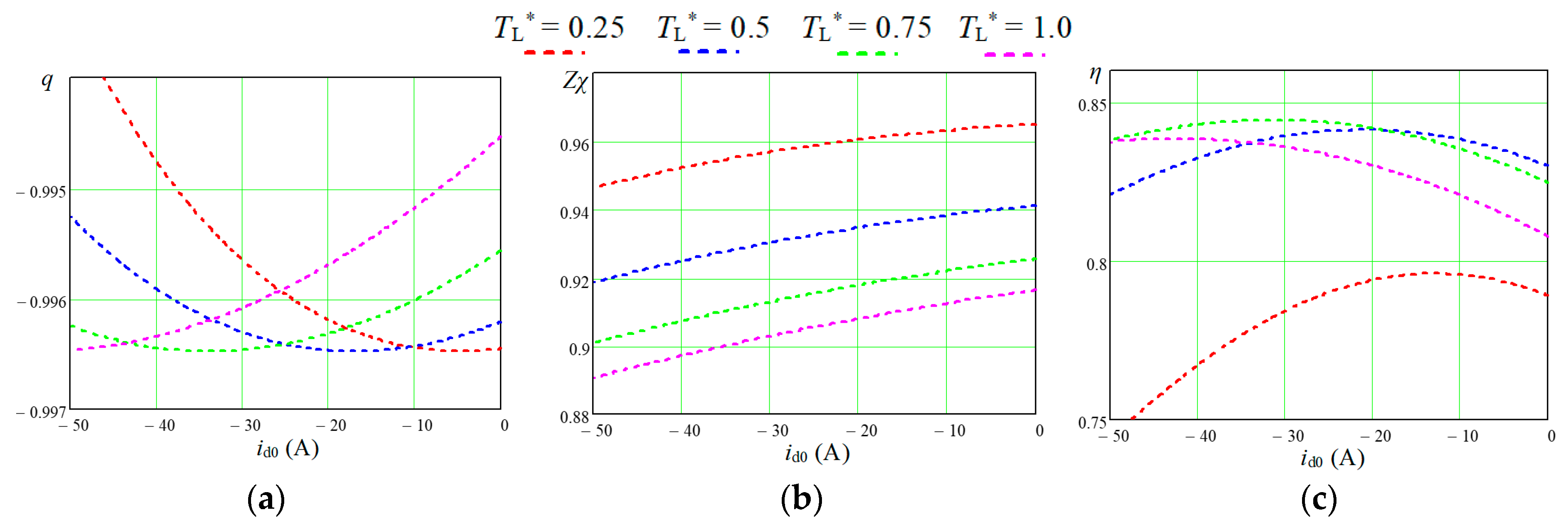
In
Figure 8, similar to those shown in
Figure 7, dependencies were obtained from the developed calculation program for the studied IPMSM taking into account iron loss.
A comparison of the results shown in
Figure 8 with the similar ones shown in
Figure 6, which makes it possible to draw the following conclusions. Taking into account the iron loss leads to a decrease in the modulus of the PC degree of coupling, which simulates the operation of the machine (
Figure 8a) and a shift of its maximum towards higher values of the id0 current component. The values of the maximum energy efficiency under medium and high loads of the drive (
TL* = 0.5–1.0) are reduced by taking into account the iron loss by 5–9% compared to the option without taking into account these losses (
Figure 8c). In the case of low drive load (
TL* = 0.25),
η is reduced by as much as 17%, which is explained by the relative increase in the effect on
η of losses in steel compared to reduced losses in copper. The points of maximum energy efficiency are also shifted towards larger values of the
id0 current component, which are very close to similar values of this current, at which the maximum value of the degree of coupling is ensured. Similar regularities also occur for other values of the IPMSM angular velocity.
Thus, the presence of one more variable coordinates—the d-component of the armature current—makes it possible to ensure the operation of the IPMSM taking into account the iron loss at the points of maximum energy efficiency. The developed technique makes it possible to obtain optimal values of id0.opt for each pair of values of the operating point of the drive—angular velocity and load torque.
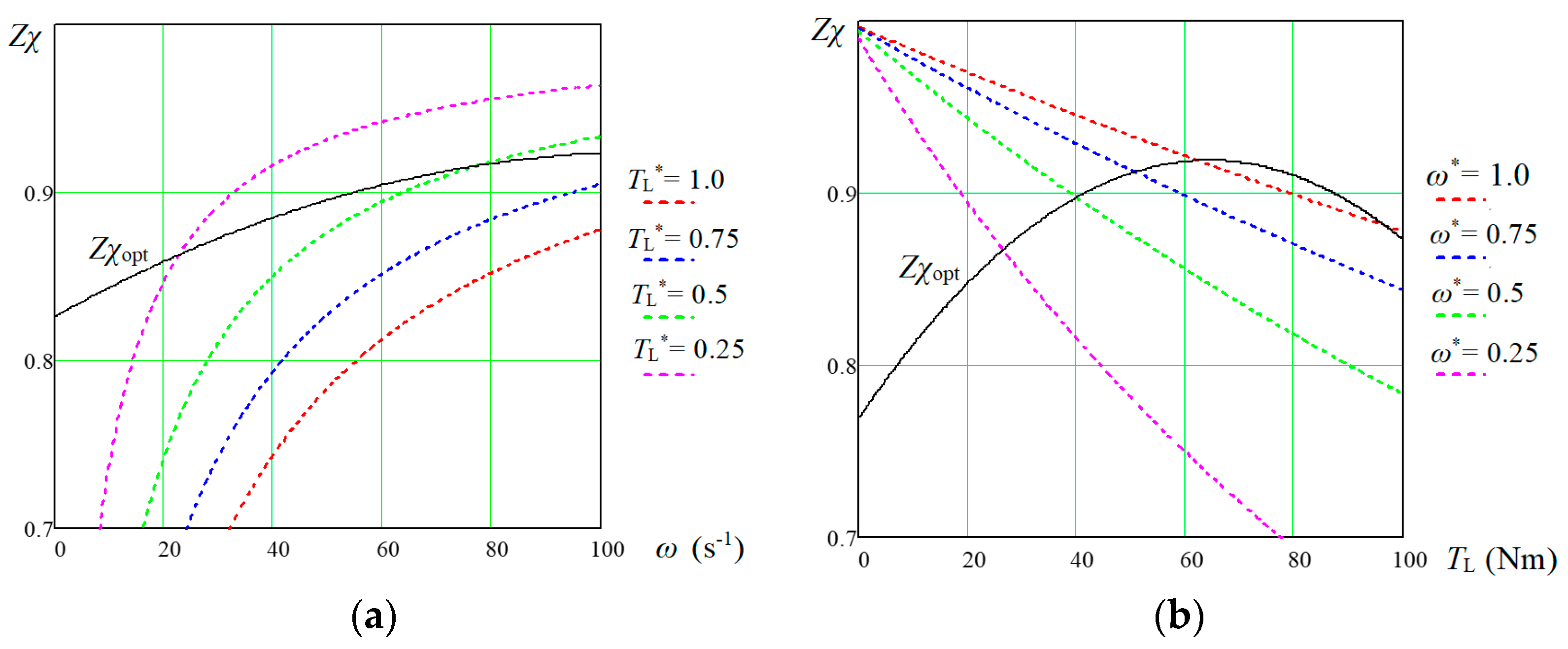
The developed algorithm (
Figure 6) and the corresponding program in Mathcad make it possible to obtain the optimal values of
id0.opt for each pair of the machine variables that characterizes the drive operating point—angular velocity and load torque. As a result of the calculations carried out for 20 operating points of the studied IPMSM, the dependencies
id0.opt(
ω,
TL) are constructed in
Figure 9a.
Given the smooth character of the curves obtained in
Figure 9, the amount of research conducted was enough to create a look-up table (LUT) from which, through interpolation, it will be possible to determine the optimal value of
id0.opt for any pair of
ω and
TL values in the range from zero to nominal. Using such an LUT-ME, as well as the created program, the values of the studied IPMSM’s operation efficiency were calculated in the entire range of changes in angular velocity and load torque, in which the amplitude of the linear armature voltage
Vl-l.m does not exceed the specified nominal value
VDC = 150 V. The value of this voltage depending on the angular velocity and load torque of the studied IPMSM are shown in
Figure 9b. As can be seen from this figure, the motor can operate at an angular velocity greater than the nominal value of 100 s
−1, but with a small load, and the lower the load, the higher the angular velocity it can achieve. So, with a load torque of
TL = 25 Nm, the motor can develop an angular velocity up to 125 s
−1 with maximum efficiency.
So, as can be seen from the obtained results, the developed method of energy efficiency analysis allows one to evaluate the capabilities of the IPMSM with respect to the operating region with a constant torque, but with an angular velocity greater than the nominal one, as shown in [
36].
Figure 10 presents the efficiency map obtained for the studied IPMSM taking into account iron loss, which operates at the points of ME at optimal values of the
id0.opt current component. A comparison of the obtained efficiency map for the IPMSM with the efficiency map for SPMSM (
Figure 5) shows the advantages of the first over the second in higher efficiency especially with loads close to the nominal one.
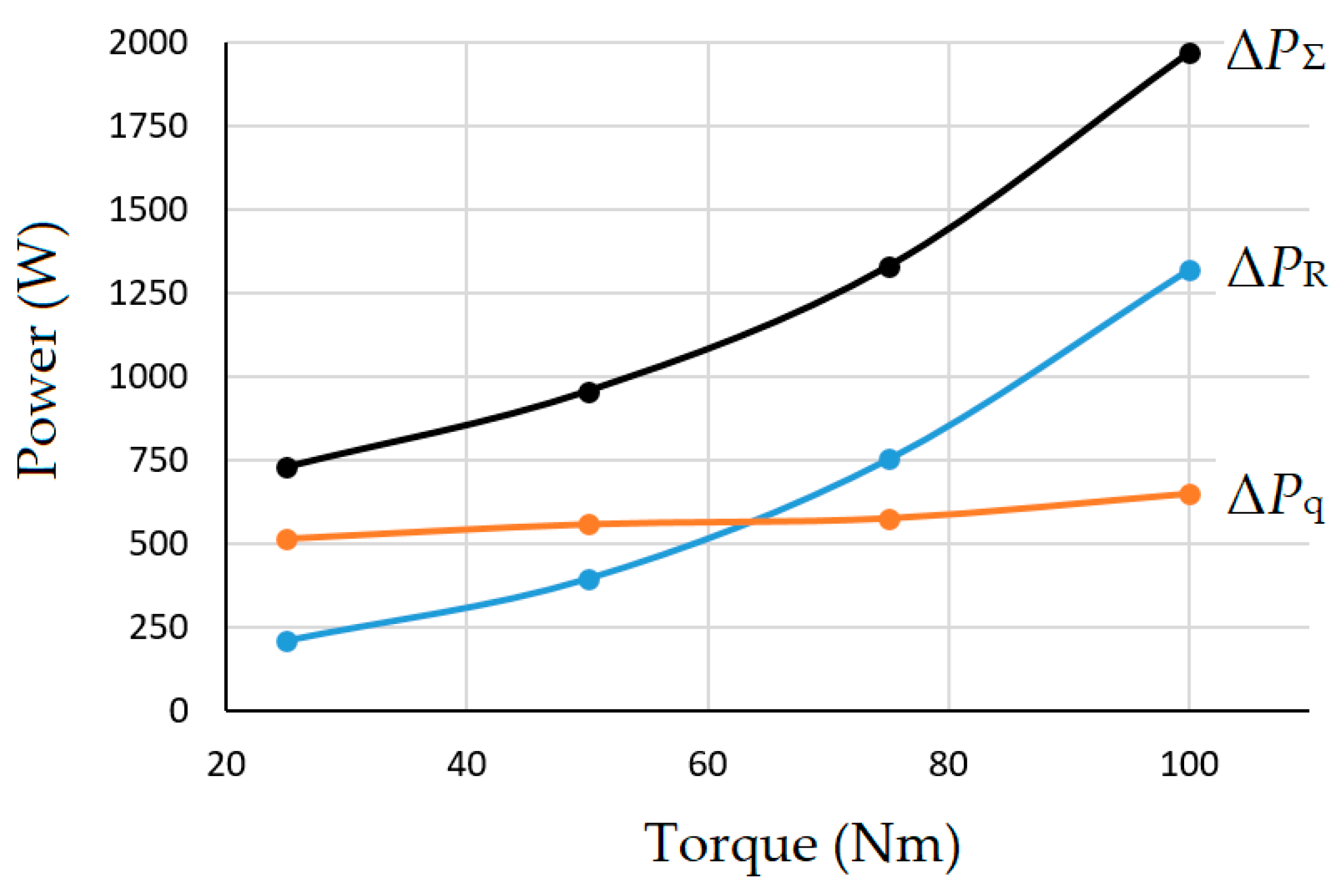
Based on the given results of the IPMSM operation with different loads at the nominal angular velocity, it is possible to easily calculate, based on (25) and (26), the power loss components caused by the imbalance in the power conversion process Δ
PR and incomplete coupling of the PC Δ
Pq. The calculation procedure is as follows. From
Figure 8b, the values of the current component
id0.opt for each load are obtained. For each
id0.opt from
Figure 8a,b, the values of
q and
Zχ are defined, which are used to find the power loss components in p. u. using (25) and (26). For each of the loads, the value of the input force
Xi =
vs(
id0.opt) and the kinetic coefficient
Lii(
id0.opt) are determined from the program. Based on the obtained data, the absolute values of the components of power losses were found using the same expressions (25) and (26). Their dependence on the IPMSM load is shown in
Figure 11.
As can be seen from the obtained results, the losses from incomplete coupling ΔPq, which are caused primarily by losses in steel, at a constant motor angular velocity, depend very little on the drive load, while the losses from the imbalance of the process ΔPR, which are the heating losses in the armature windings, rapidly increase with an increase in the load torque of the drive. At the rated values of the IPMSM angular velocity and the load torque, the total losses ΔPΣ amount of 1973 W, which is the nominal value of the losses in the studied machine.
3.5. Efficiency Analysis of the IPMSM Operation in the Constant-Power Region
The numerical simulation algorithm of the IPMSM taking into account iron loss operation developed with the use of the LNTD is quite suitable for modeling their operation in the region of angular velocity regulation with a constant power. The difference between the IPMSM operation in this region compared to the one of constant torque is the presence of a limitation on the armature voltage that is caused by the value of the DC voltage
VDC of the voltage invertor power supply. In addition, there is also in place here a limitation of the armature current in the long-term operating mode that is caused by the heating of the machine. These restrictions are described by the following inequalities [
5]:
where
vs.max is the maximum value of the armature voltage amplitude in the two-phase reference frame and
is.max is the maximum value of the armature current amplitude in the two-phase reference frame in the long-term motor operating mode.
The
vs.max value is related to
VDC based on the following relationship:
Simulation of the studied IPMSM operation in the constant-power region was conducted with the use of the developed calculation program in the MathCad 15 environment similarly to the constant torque region.
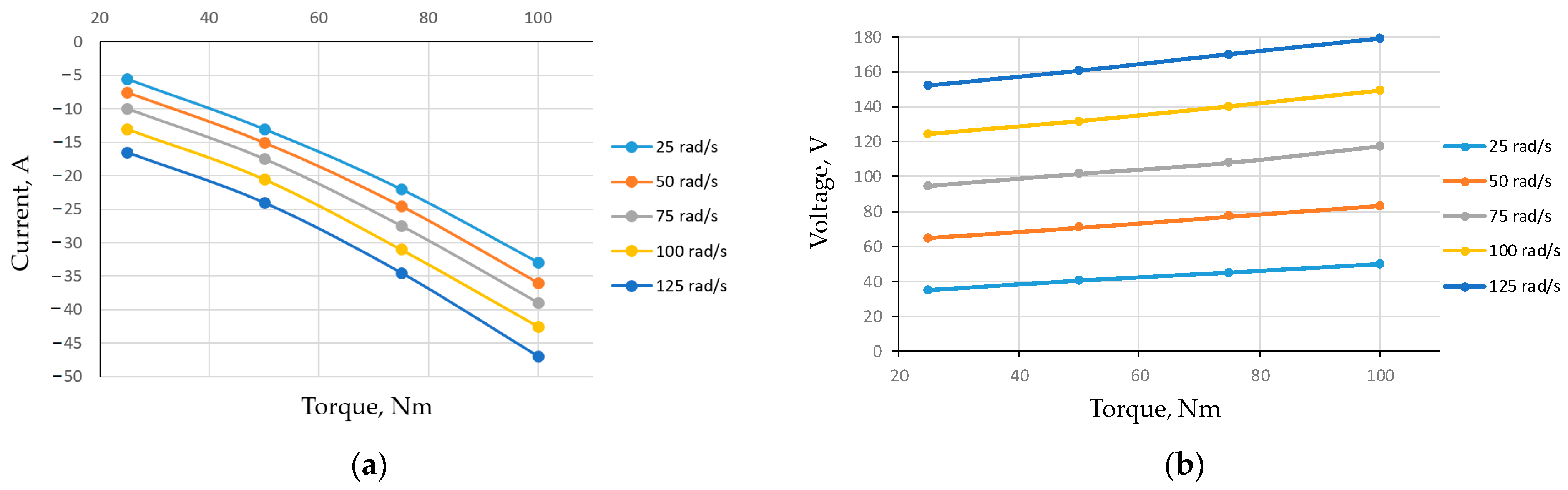
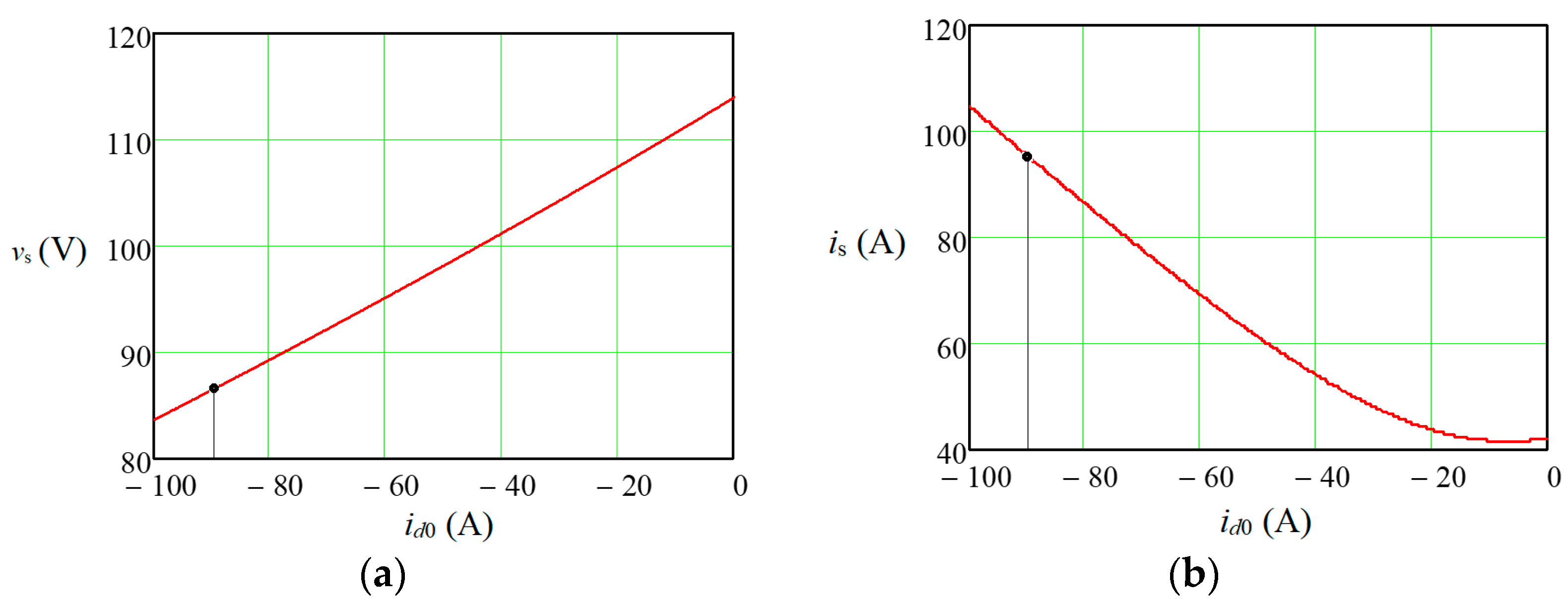
At the beginning, for the nominal operating mode of the machine—the nominal values of the angular velocity and the load torque—the Vs.max and Is.max values were determined by (61) and (62): Vs.max = 87 V and Is.max = 93.5 A. According to (63), the required value for this is VDC = 150 V.
Further studies were carried out for the relative angular velocity of the IPMSM equal to
ω* = 1.5. The research methodology consisted of reducing the motor load torque to such a value that the voltage
vs decreased to
vs.max. As a result, the value of the load torque
TL = 38 Nm, which was permissible from the point of view of the current limitation, was obtained (
Figure 12). At the same time, the optimal
id0 value for ensuring the specified maximum torque was −90 A. Dependencies of the main parameters and characteristics for the PC, which models the studied IPMSM operation based on the value of such an armature current component
id0 during machine operation in the constant power region with an angular velocity of 150 s
−1 for the maximum value of a load torque of 38 Nm are shown in
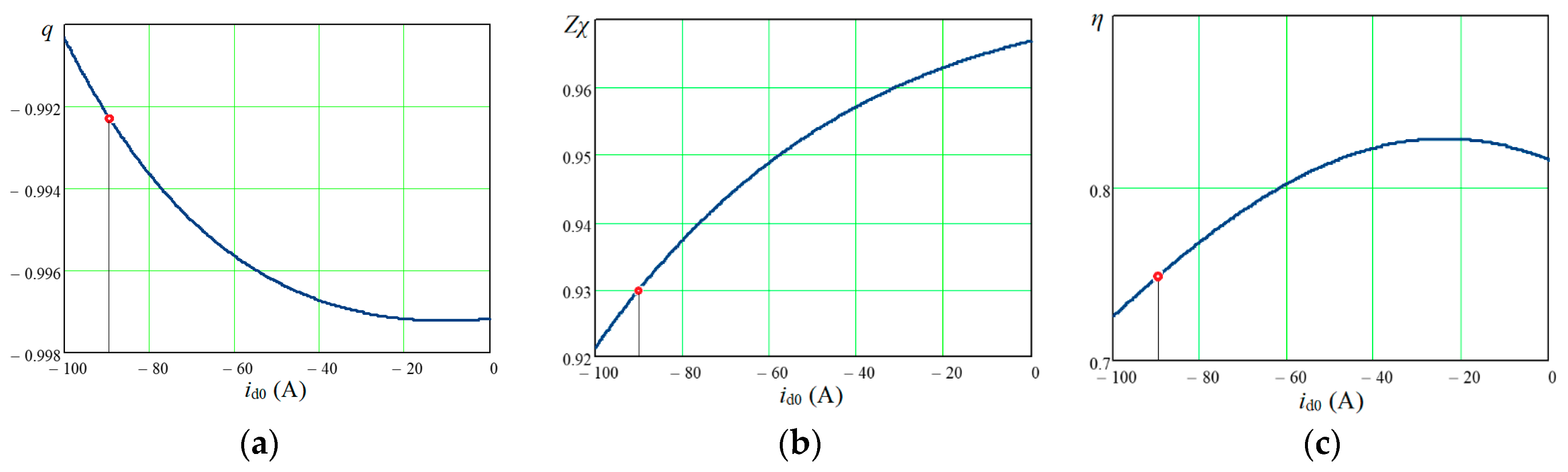
Figure 13. As can be seen from the figure, at the operating point, the degree of coupling is
q = −0.9923, and the energy efficiency of the IPMSM is
η = 0.750. At the same time, for the optimal value
id0 = −23 A, for this load,
η = 0.828. However, for such a regime, the required value of
vs is 107 V, which is significantly more than the nominal value (
Figure 12a).
Analyzing the dependencies in
Figure 13, it can be concluded that the operation of the IPMSM in the constant-power control region is characterized by a significant shift in the operating point from the point of maximum energy efficiency. This is explained by the need to set such a value of the armature current component
id0, which would provide the task of increased angular velocity while limiting the value of the armature voltage at the nominal level. When the angular velocity increases, the armature voltage remains unchanged, but the armature current increases (
Figure 12b), which leads to a decrease in energy efficiency. The higher the given angular velocity, the larger the i
d0 value will be, and the lower the energy efficiency will be. That is, when working in the constant-power region, the
id0 value is assigned a different task than energy optimization, as it was in the constant-torque control region. Hence, accordingly, there is a decrease in the energy efficiency of the machine. When the load torque decreases below the permissible value of 38 Nm for a given angular velocity, the energy efficiency decreases even more. Thus, at the same angular velocity of the machine of 150 s
−1, the decrease in
TL to 18 Nm leads to a decrease of
id0 to −70 A, but
η decreases already to 0.657.
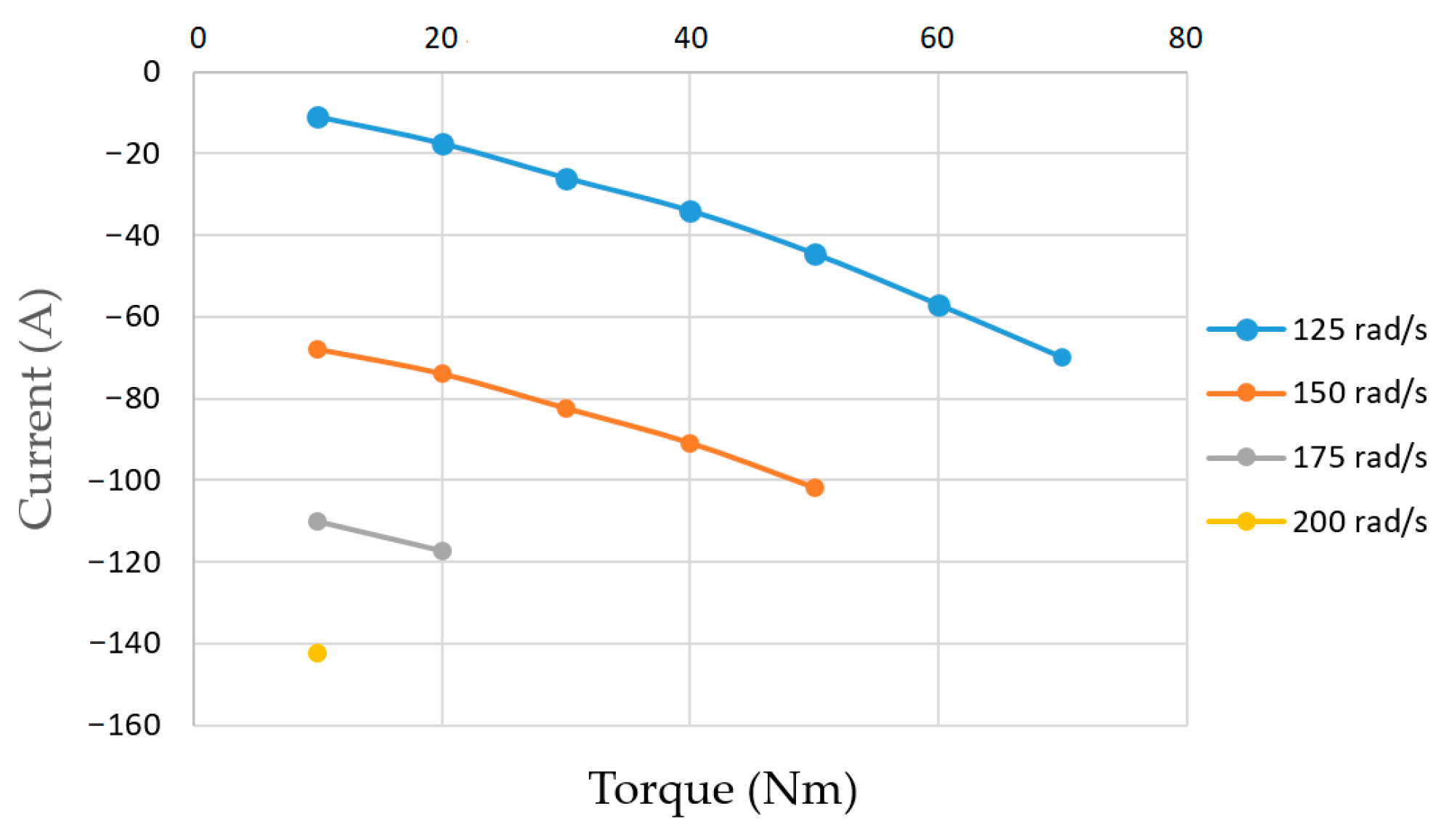
According to the method described above, using the developed program, the values of the
d-component of the armature current were obtained, which ensure the armature voltage
vs.max = 87 V for a number of operating points of the studied IPMSM during its operation at high angular velocities in the FW region. These points are shown in
Figure 14, according to which, similar to the IPMSM operation in the region of angular velocity regulation with a constant torque (
Figure 9a), the corresponding LUT FW is formed.
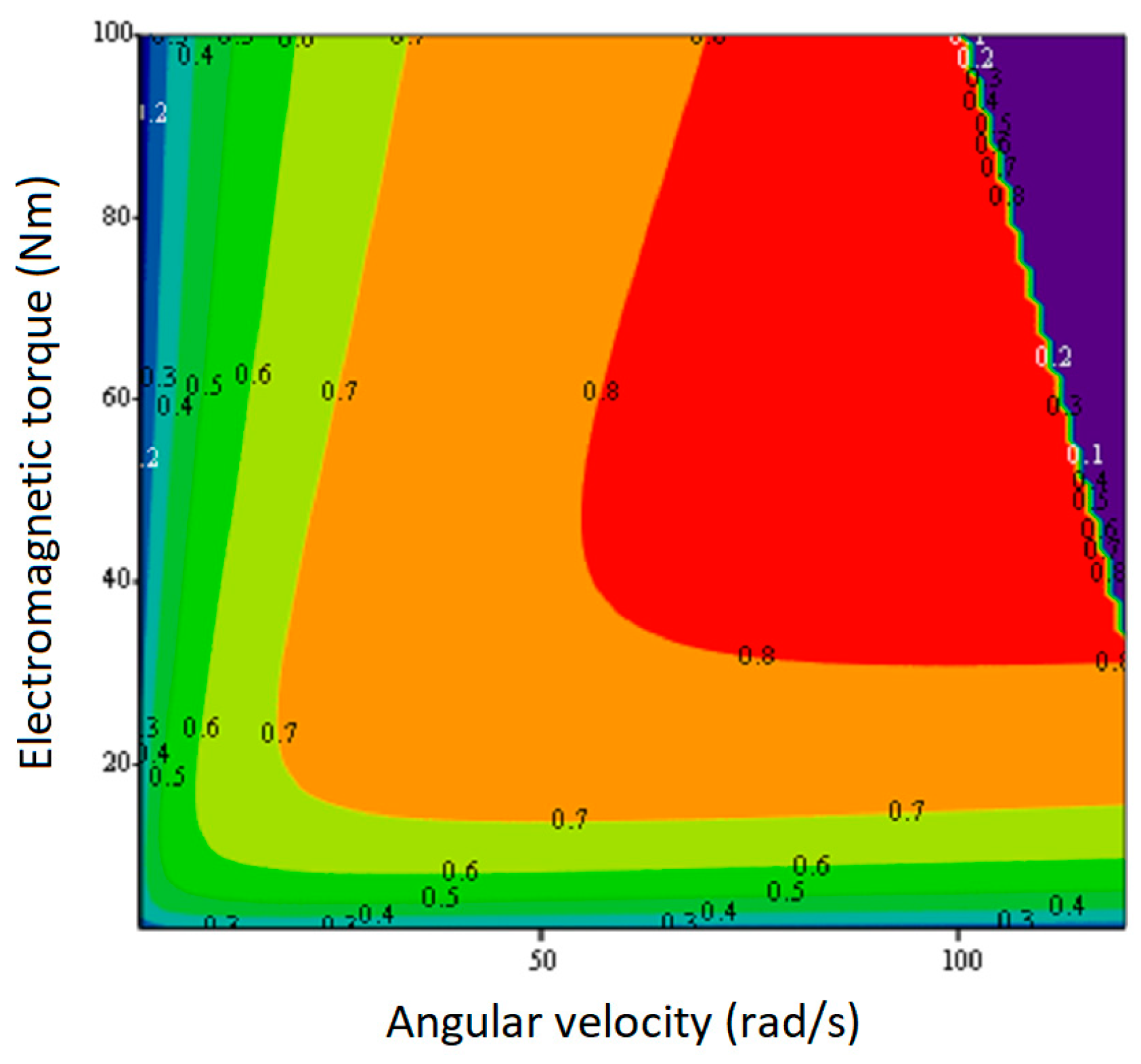
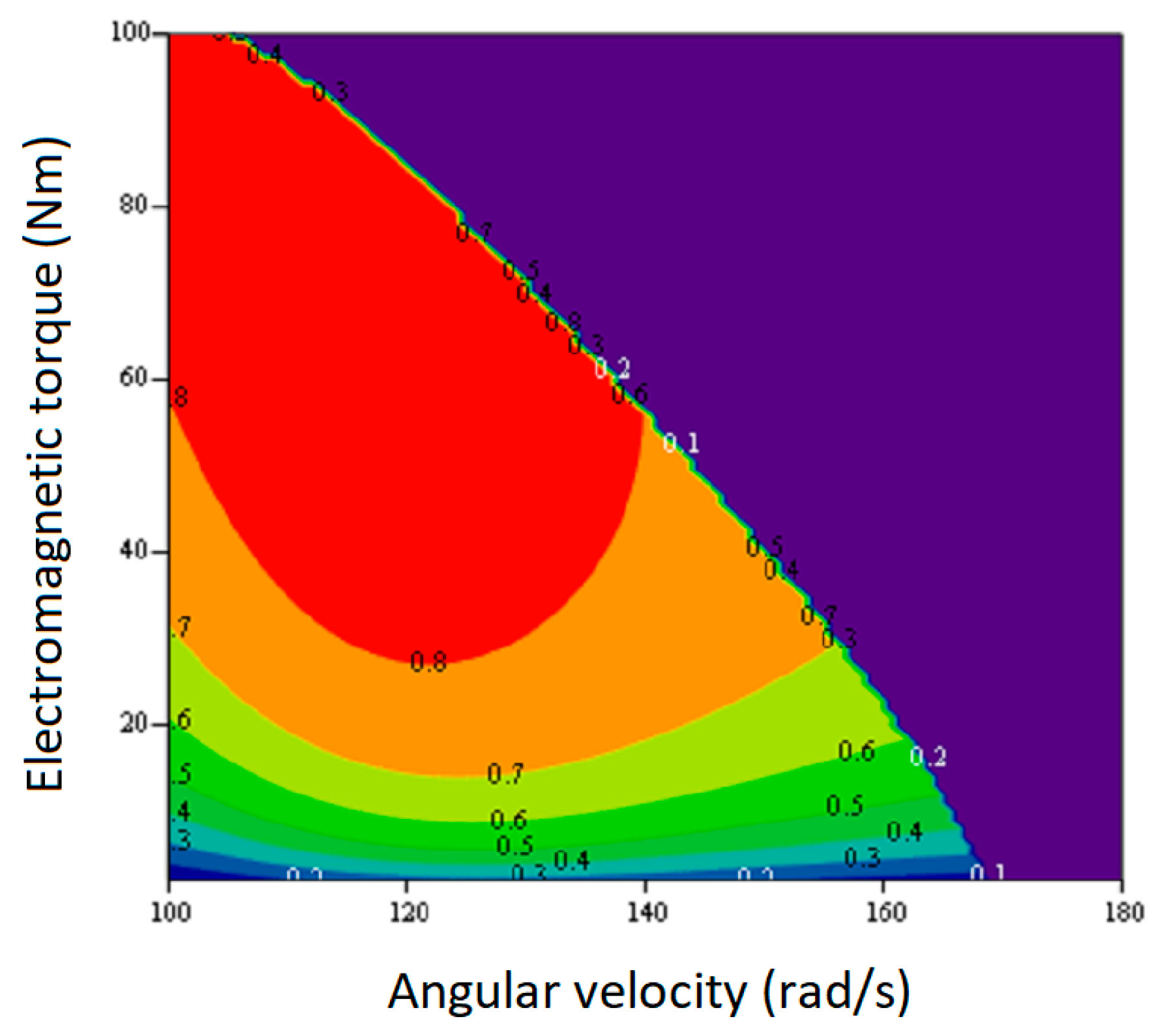
Using this LUT FW, as well as the created program, the efficiency values of the studied IPMSM were calculated, and a corresponding efficiency map of its operation in the FW region was obtained that is shown in
Figure 15. From the side of high speeds and load torques of the machine, this efficiency map is limited by the curve that corresponds to the rated total power losses of the studied IPMSM for the steady state of its operation, which are 1973 W. Total power losses in copper and iron of the machine were calculated in the program using the expressions for the components of relative power losses (25) and (26):
In (61), all parameters Lii, q and (Zχ) were calculated using the software as functions of the coordinates of the machine working point (ω,TL), and the input force of the PC was V.
From the obtained efficiency map, it can be seen that the operation of the studied IPMSM, taking into account the iron loss, is characterized by a fairly high efficiency in the FW region only at relatively low angular velocities and at the maximum load torques for these velocities.
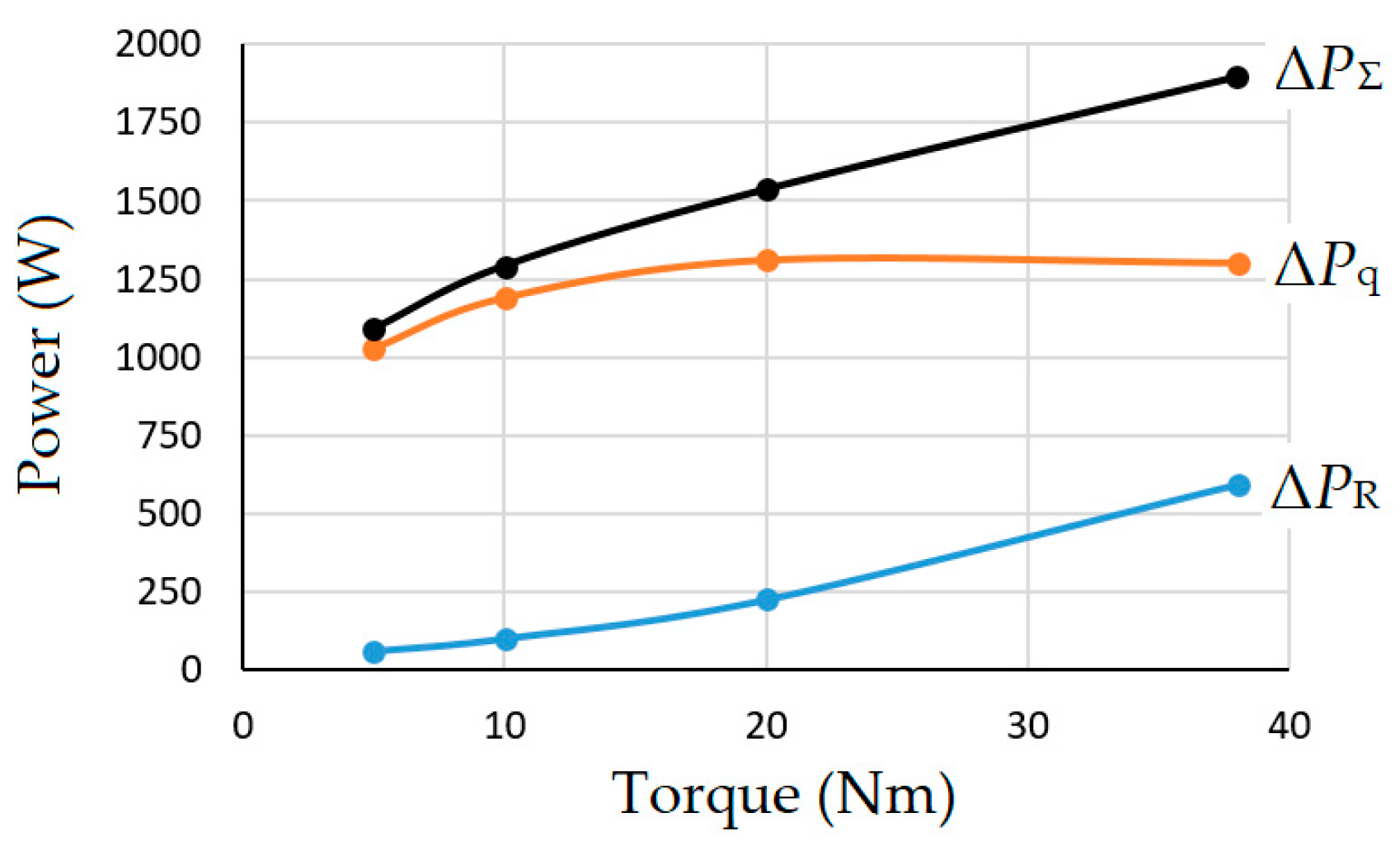
To analyze the energy regularities of IPMSM operation in the FW region of angular velocity regulation, for the last experiment, the components of power losses due to the imbalance process Δ
PR and the PC incomplete coupling Δ
Pq on the drive load torque
TL were calculated according to the algorithm described in
Section 3.4 (
Figure 16). For a given angular velocity of 150 s
−1, the
TL varied from 5 Nm to the maximum permissible value of 38 Nm.
The nature of the components of power losses in the IPMSM during its operation in the FW region with constant power regulation obtained in
Figure 16 is radically different from the nature of these losses in the region with constant torque regulation shown in
Figure 11. Although the total value of power losses at the maximum load of the drive differs slightly, in the constant power region, the iron loss clearly prevails over the copper loss. As in the previous case, the iron loss slightly depends on the drive load, since the motor angular velocity is unchanged, but in the constant power region, this loss is approximately twice as large as that in the constant-torque region. Loss in copper is also higher in the constant-power region than in the constant-torque region for the same value of the load torque. This is explained by the significant value of the current component
id0, at the level of (−65)–(−90) A, compared to this component in the range (−13)–(−43) A in the constant-torque region. As a result of the significant losses and the low value of the electromagnetic torque of the motor, despite its higher angular velocity, the efficiency of the IPMSM in the constant-power region decreases (from 0.365 to 0.745 in the computational experiment) compared to the constant-torque region (from 0.795 to 0.845).