Evaluation of Hydraulic Characteristics of Electrohydraulic Proportional Valve (EHPV) for an Auto-Steering Tractor Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Agricultural Tractor
2.2. Hydraulic Steering System
2.3. Measurement System
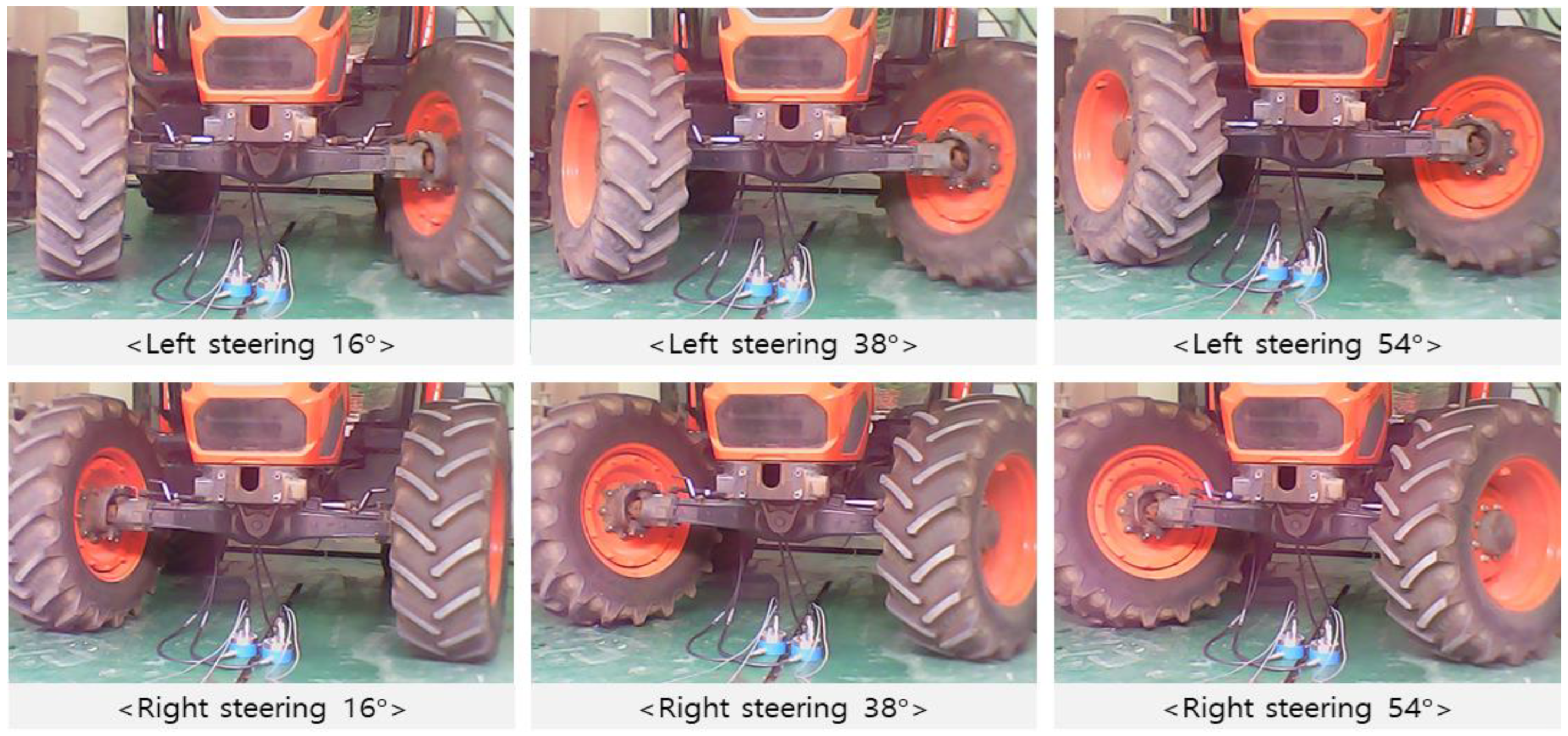
2.4. Experiment Method
2.5. Data Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Profile of the Hydraulic Characteristics for Auto-Steering Tractor EHPV
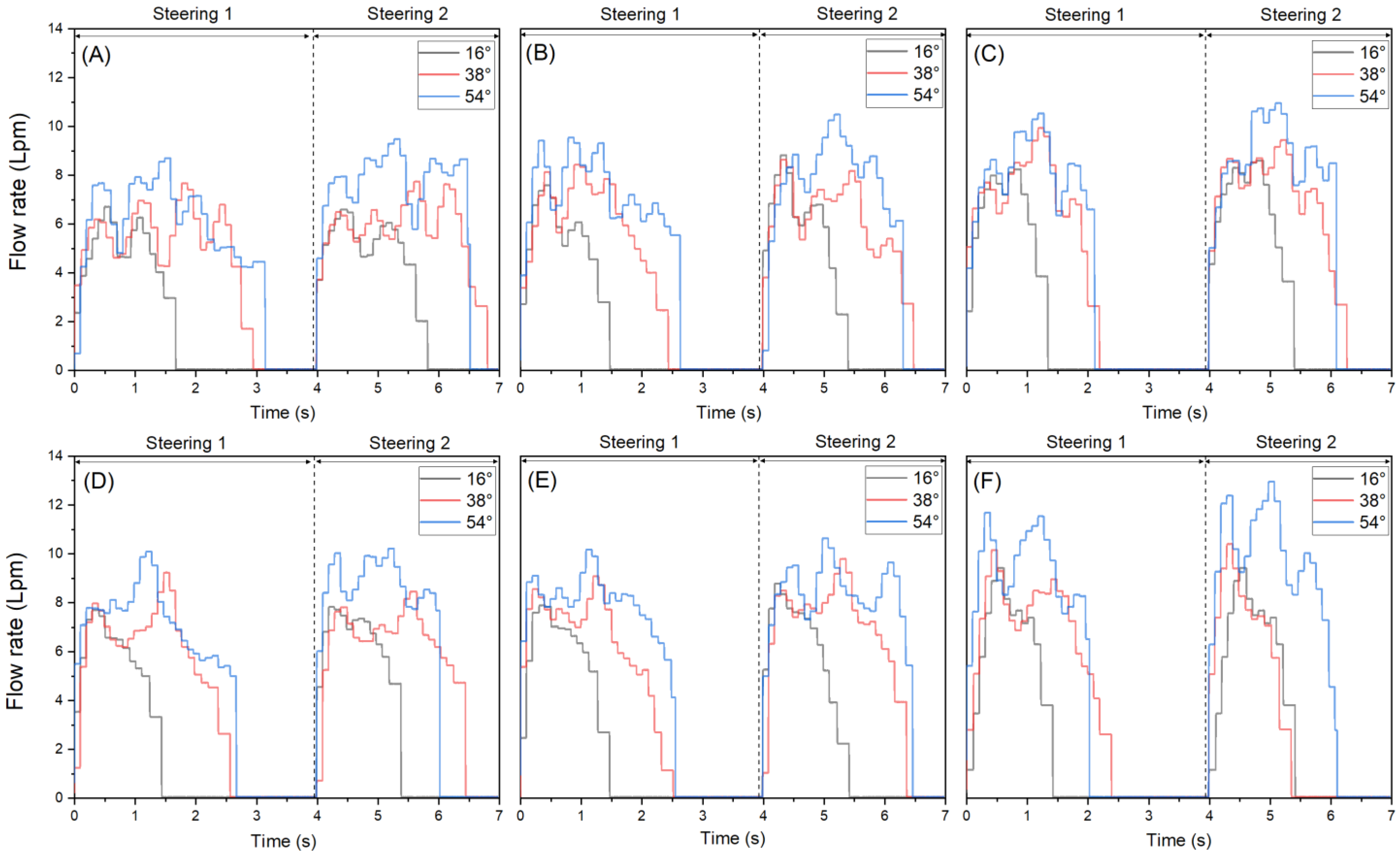
3.1.1. Flow Rate
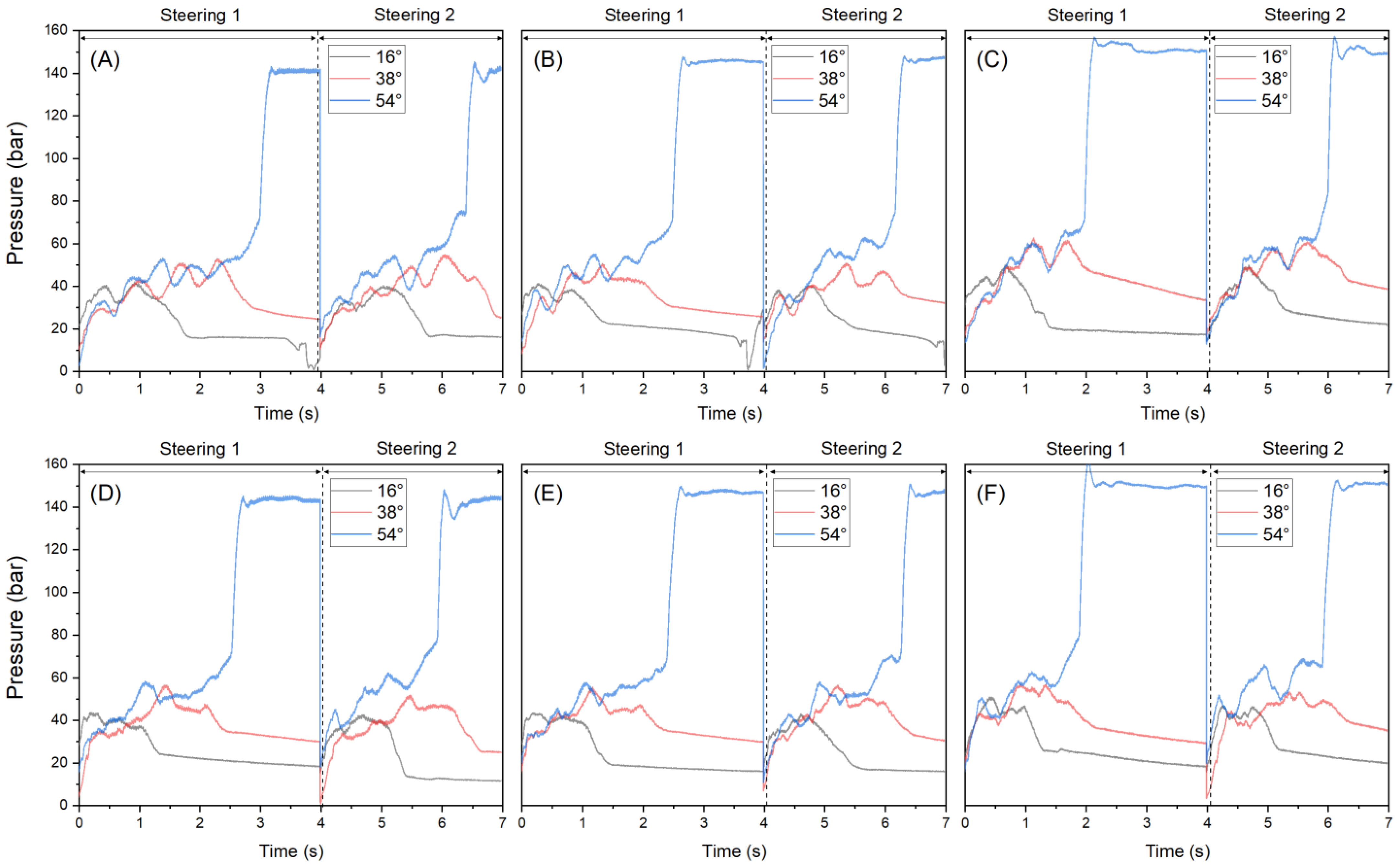
3.1.2. Pressure
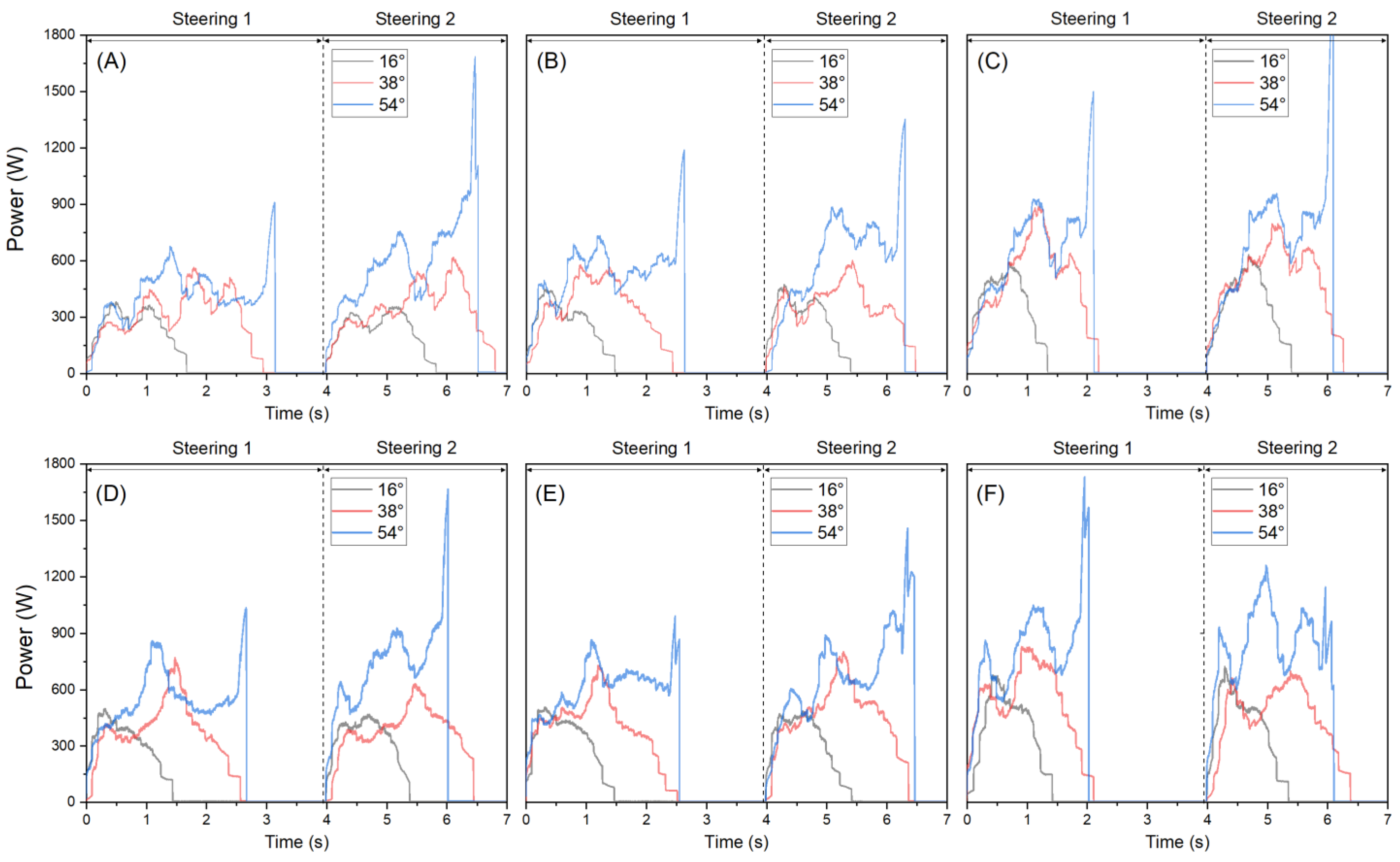
3.1.3. Required Power
3.2. Statistical Analysis of the Hydraulic Characteristics for Auto-Steering Tractor EHPVs
3.2.1. Flow Rate
3.2.2. Pressure
3.2.3. Required Power
3.3. Evaluation of Hydraulic Characteristics of EHPVs According to Engine Rotational Speed and Steering Angle
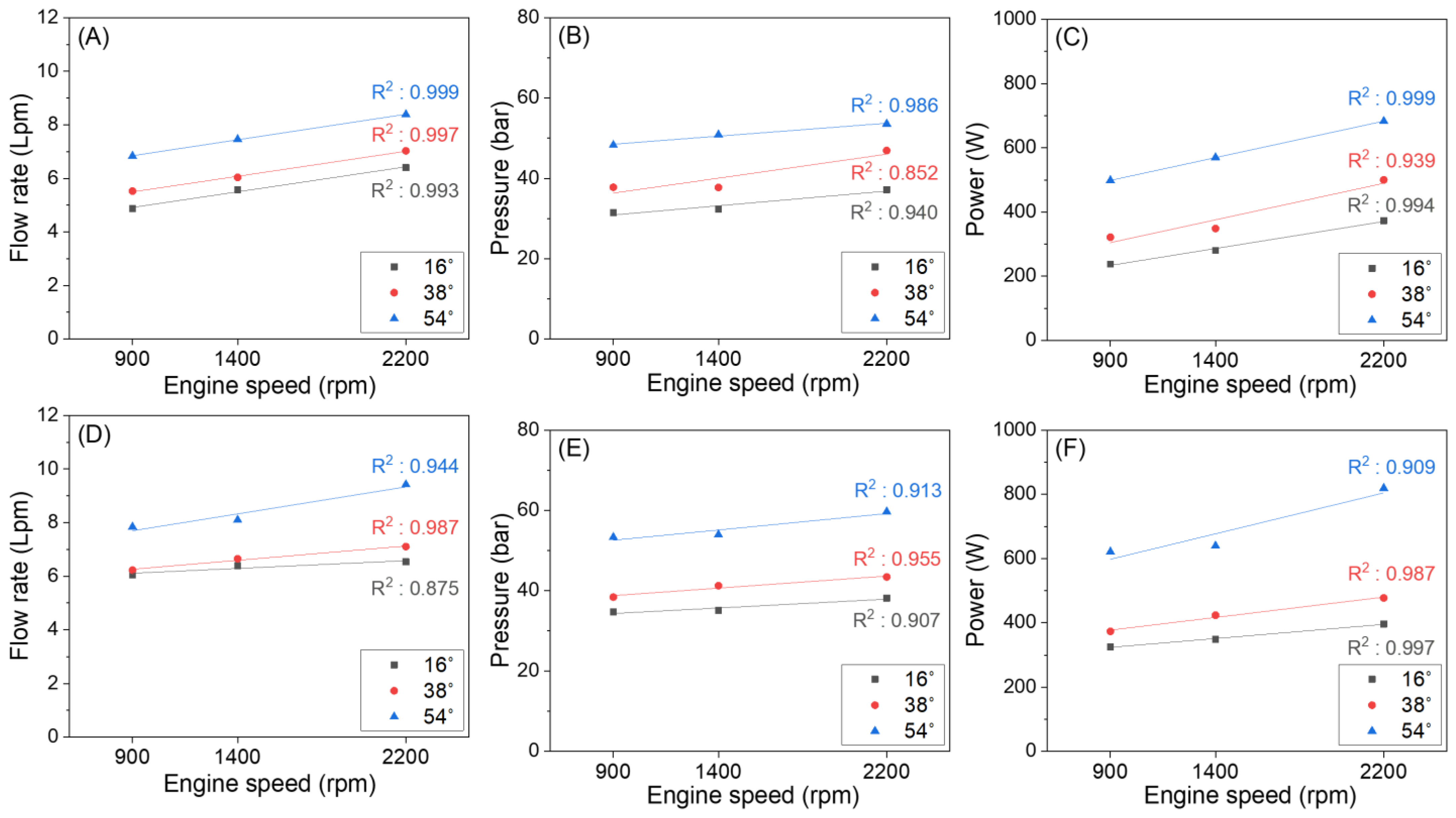
3.3.1. Evaluation of Hydraulic Characteristics following Engine Rotational Speed
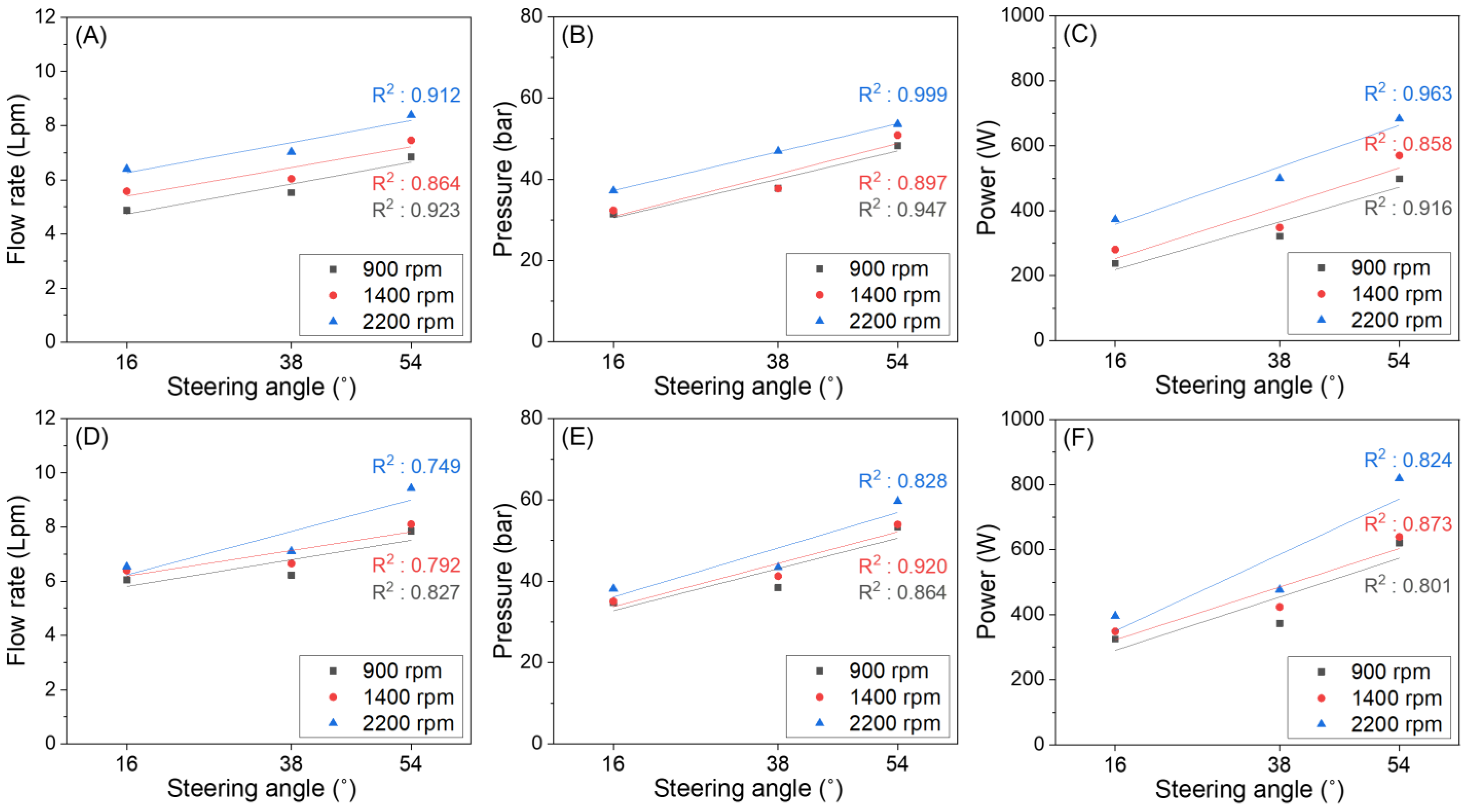
3.3.2. Hydraulic Characteristics Evaluation according to the Steering Angle
3.3.3. Evaluation of the Influence of Working Conditions on the Hydraulic Properties of EHPV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- ANOVA analysis revealed statistically significant differences in the hydraulic characteristics of the EHPV under different engine rotation speeds and steering angle conditions. These results clearly demonstrate that both working conditions have a significant impact on the hydraulic properties of the EHPV.
- (2)
- The required power exhibited the highest coefficient of variation. By minimizing flow rate fluctuations, it is possible to reduce power fluctuations and enhance the stability of the EHPV.
- (3)
- Through the results of the regression analysis, it was revealed that the engine rotation speed and steering angle had a linear relationship with the hydraulic characteristics of the EHPV and that the steering angle had a greater effect on the hydraulic characteristics.
- (4)
- The design specifications of the flow control valve in the EHPV have a substantial influence on its hydraulic characteristics. Excessive control flow rate may lead to increased power fluctuations, while insufficient control flow rate could compromise steering performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Freedonia Group. Freedonia Group Global Agricultural Equipment; The Freedonia Group: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.T.; Kim, Y.H.; Baek, S.M.; Kim, Y.J. Technology Trend on Autonomous Agricultural Machinery. J. Drive Control 2022, 19, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Z.; Moon, H.C.; Kim, J.H. Off-Road Machinery System Engineering; Development of a Path Generation and Tracking Algorithm for a Korean Auto-guidance Tillage Tractor. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentz, A.; Dima, C.; Wellington, C.; Herman, H.; Stager, D. A system for semi-autonomous tractor operations. Auton. Robot. 2002, 13, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Research and Markets. Autonomous Tractors Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2023–2028; IMARC: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Zhao, L.; Miao, H. Steering tracking control based on assisted motor for agricultural tractors. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.H.; Seo, I.H.; Chung, S.O.; Kim, K.D. Development of Steering Control System based on CAN for Autonomous Tractor System. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 37, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Jeon, C.W.; Han, X.Z.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J. Application of Electrohydraulic Proportional Valve for Steering Improvement of an Autonomous Tractor. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 47, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Shen, W.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, H. A Review of Key Technologies for Friction Nonlinearity in an Electro-Hydraulic Servo System. Machines 2022, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stosiak, M.; Karpenko, M.; Prentkovskis, O.; Deptuła, A.; Skačkauskas, P. Research of vibrations effect on hydraulic valves in military vehicles. Def. Technol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitov, A.; Slavov, T.; Kralev, J. Robustness Analysis of an Electrohydraulic Steering Control System Based on the Estimated Uncertainty Model. Information 2021, 12, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Heo, S.J. Effects of Design Parameters of Power Steering System for Passenger Cars on the Vehicle Steering Characteristics. Trans. Korean Soc. Automot. Eng. 1996, 4, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.J.; Ha, J.W.; Choi, D.S.; Kim, H.J. Development of a self-leveling system for the bucket of an agricultural front-end loader using an electro hydraulic proportional valve and a tilt sensor. J. Drive Control 2015, 12, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikwar, S.; Tewari, V.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Verma, C.R.; Rao, M.S. Simulation of components of a power shuttle transmission system for an agricultural tractor. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 114, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tewari, V.K.; Bharti, C.K.; Ranjan, A. Modeling, simulation and experimental validation of flow rate of electro-hydraulic hitch control valve of agricultural tractor. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2021, 82, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Park, W.Y. Development of tractor three-point hitch control system using proportional valve. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 36, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaresi, S.M.; Taroni, F.L.; Previdi, F.; Bittanti, S. Control system design on a power-split CVT for high-power agricultural tractors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2004, 9, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, H.; Liang, W.; Yuefeng, D.; Zhenghe, S.; Enrong, M.; Zhongxiang, Z. Design and experiment on integrated proportional control valve of automatic steering system. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Jiang, H. An electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system for heavy vehicles. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1687814016679566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Ye, C.; Zhang, W. Design optimization and experimental performance test of dynamic flow balance valve. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2020, 14, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Im, D.; Cho, S.J.; Park, Y.J. A Study on the Prediction of Driving Performance of Agricultural Tractors Driving on Dry Sand. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 47, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensh, S.; Tewari, V.K.; Upadhyay, G. An instrumentation system to measure the loads acting on the tractor PTO bearing during rotary tillage. J. Terramech. 2021, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, T.J.; Park, S.U.; Choi, Y.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J. Analysis of Power Requirement of 78 kW Class Agricultural Tractor According to the Major Field Operation. Trans. Korean Soc. Mech. Eng.-A 2019, 43, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, Y.M. PTO Torque and Draft Analyses of an Integrated Tractor-Mounted Implement for Round Ridge Preparation. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 47, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, M.; Hansson, P.A. PM—Power and machinery: Effects of engine control strategies and transmission characteristics on the exhaust gas emissions from an agricultural tractor. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 83, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
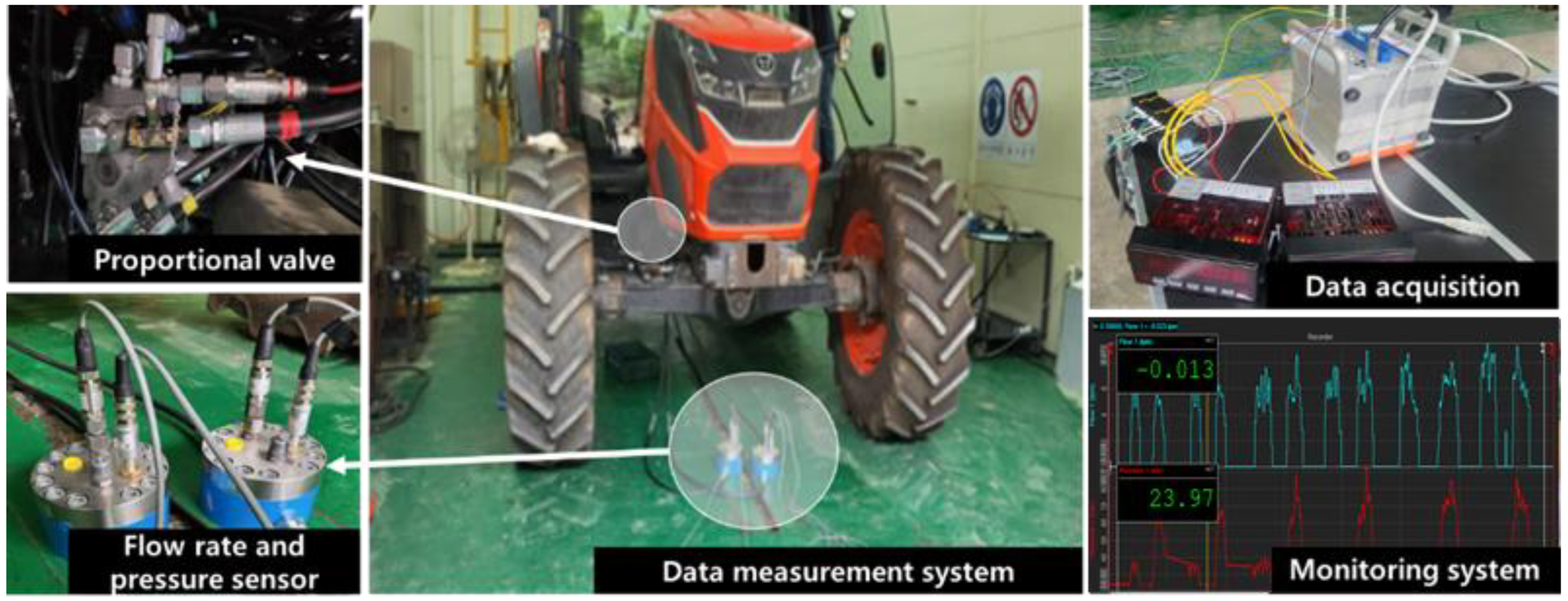
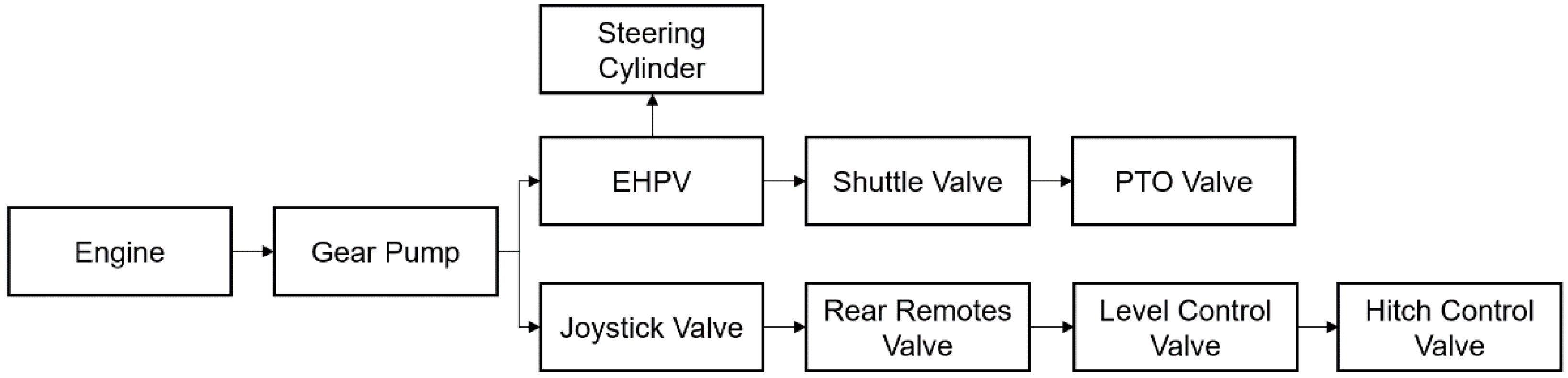


| Parameters | Specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Dimension (length × width × height) (mm) | 4290 × 2250 × 2770 | |
| Engine-rated power (kW) | 93.2 (at 2200 rpm) | |
| Engine maximum torque (Nm) | 500 (at 1400 rpm) | |
| Empty weight (kg) | 4070 | |
| Steering pump | Displacement (cc/rev) | 21 |
| Efficiency (%) | Approximately 95 (at no loads) | |
| The gear ratio of engine pump | 1:1 | |
| Hydraulic oil | Specific gravity | 0.865 |
| Viscosity (cSt) | 53.79 (at 40 °C) | |
| 9.428 (at 100 °C) | ||
| Item | Specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| EHPV | Maximum flow rate (Lpm) | 60 |
| Control flow rate (Lpm) | 25 | |
| Maximum pressure (bar) | 220 | |
| Item | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Flow rate sensor (Hysense QG100) | Measuring principle: displacement |
| Viscosity range: 10–500 mm2/s (cSt) | |
| Output signal: 4–20 mA | |
| Range: 0.7–70 Lpm | |
| Supply voltage: 12–24 VDC | |
| Environmental temperature: max. +80 °C | |
| Accuracy: 0.4% | |
| Pressure sensor (Hysense PR130) | Measuring principle: piezo-resistive |
| Pressure type: relative pressure | |
| Output signal: 4–20 mA/0–10 VDC | |
| Range: 250 bar | |
| Weight: 85 g | |
| Accuracy: 0.5% | |
| Data acquisition (Q.brixx A107) | 4 universal analog input channels |
| Fast, high-accuracy digitalization 24-bit ADC, 10 kHz sample rate per channel | |
| Power supply: 10–30 VDC | |
| Environmental temperature: −20 °C–60 °C | |
| Accuracy: 0.01% typical |
| Engine Speed (rpm) | Descriptive Statistics | Left Steering | Right Steering | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA 16 * | SA 38 | SA 54 | SA 16 | SA 38 | SA 54 | ||
| 900 | Max. | 6.69 | 7.72 | 9.47 | 7.81 | 9.22 | 10.21 |
| Min. | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.60 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 4.87 ± 1.28 Cc | 5.52 ± 1.42 Cb | 6.84 ± 1.71 Ca | 6.04 ± 1.42 Cc | 6.22 ± 1.74 Cb | 7.84 ± 1.48 Ca | |
| CV | 0.263 | 0.256 | 0.250 | 0.235 | 0.280 | 0.189 | |
| 1400 | Max. | 8.81 | 8.62 | 10.48 | 8.77 | 9.78 | 10.63 |
| Min. | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.30 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 5.57 ± 1.81 Bc | 6.04 ± 1.73 Bb | 7.46 ± 1.73 Ba | 6.39 ± 1.49 Bc | 6.65 ± 2.09 Bb | 8.10 ± 1.30 Ba | |
| CV | 0.324 | 0.286 | 0.232 | 0.264 | 0.314 | 0.160 | |
| 2200 | Max. | 8.58 | 9.93 | 10.95 | 10.40 | 10.14 | 12.95 |
| Min. | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.64 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 6.41 ± 1.85 Ac | 7.03 ± 1.93 Ab | 8.39 ± 1.57 Aa | 6.54 ± 2.36 Ac | 7.10 ± 2.27 Ab | 9.42 ± 2.02 Aa | |
| CV | 0.289 | 0.275 | 0.187 | 0.361 | 0.319 | 0.214 | |
| Engine Speed (rpm) | Descriptive Statistics | Left Steering | Right Steering | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA 16 * | SA 38 | SA 54 | SA 16 | SA 38 | SA 54 | ||
| 900 | Max. | 41.7 | 54.5 | 143.1 | 43.2 | 56.2 | 145.2 |
| Min. | 10.0 | 9.4 | 2.1 | 14.1 | 0.1 | 15.2 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 31.4 ± 6.5 Cc | 37.8 ± 9.2 Bb | 48.3 ± 20.2 Ca | 34.7 ± 6.5 Bc | 38.4 ± 9.7 Cb | 53.3 ± 19.1 Ba | |
| CV | 0.208 | 0.244 | 0.418 | 0.188 | 0.252 | 0.357 | |
| 1400 | Max. | 40.9 | 50.3 | 147.2 | 43.1 | 56.3 | 150.6 |
| Min. | 17.6 | 7.7 | 0.9 | 16.4 | 6.4 | 10.4 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 32.3 ± 5.6 Bc | 37.7 ± 9.2 Bb | 50.9 ± 22.1 Ba | 35.0 ± 6.5 Bc | 41.2 ± 8.3 Bb | 53.9 ± 22.6 Ba | |
| CV | 0.173 | 0.201 | 0.435 | 0.185 | 0.200 | 0.419 | |
| 2200 | Max. | 49.4 | 62.3 | 156.1 | 50.5 | 56.6 | 161.1 |
| Min. | 13.6 | 15.9 | 12.3 | 15.2 | 2.7 | 15.5 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 37.2 ± 7.7 Ac | 46.9 ± 10.5 Ab | 53.6 ± 23.3 Aa | 38.1 ± 8.0 Ac | 43.4 ± 9.2 Ab | 59.7 ± 23.0 Aa | |
| CV | 0.208 | 0.225 | 0.435 | 0.211 | 0.212 | 0.385 | |
| Engine Speed (rpm) | Descriptive Statistics | Left Steering | Right Steering | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA 16 * | SA 38 | SA 54 | SA 16 | SA 38 | SA 54 | ||
| 900 | Max. | 378 | 615 | 1684 | 496 | 767 | 1665 |
| Min. | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 238 ± 89 Cc | 321 ± 130 Cb | 498 ± 220 Ca | 324 ± 112 Cc | 373 ± 146 Bb | 621 ± 217 Ca | |
| CV | 0.375 | 0.403 | 0.441 | 0.346 | 0.390 | 0.349 | |
| 1400 | Max. | 470 | 598 | 1351 | 502 | 799 | 1456 |
| Min. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 280 ± 115 Bc | 349 ± 132 Bb | 570 ± 219 Ba | 349 ± 125 Bc | 423 ± 168 Bb | 639 ± 202 Ba | |
| CV | 0.409 | 0.380 | 0.384 | 0.358 | 0.396 | 0.316 | |
| 2200 | Max. | 629 | 914 | 1980 | 719 | 825 | 1724 |
| Min. | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 18 | |
| Avg. ± std. | 373 ± 158 Ac | 520 ± 180 Ab | 683 ± 293 Aa | 396 ± 187 Ac | 477 ± 186 Ab | 819 ± 241 Aa | |
| CV | 0.423 | 0.346 | 0.429 | 0.473 | 0.410 | 0.294 | |
| Items | Steering | Steering Angle | Equation | Pearson’s r | R2 | Adj. R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow rate | LS | 16 | y = 0.00117Se* + 3.8633 | 0.996 | 0.993 | 0.985 |
| 38 | y = 0.00117Se + 4.4476 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.995 | ||
| 54 | y = 0.00119Se + 5.7754 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||
| RS | 16 | y = 0.00036Se + 5.7805 | 0.935 | 0.875 | 0.750 | |
| 38 | y = 0.00067Se + 5.6560 | 0.993 | 0.987 | 0.973 | ||
| 54 | y = 0.00126Se + 6.5640 | 0.972 | 0.944 | 0.888 | ||
| Pressure | LS | 16 | y = 0.00457Se + 26.7773 | 0.970 | 0.940 | 0.880 |
| 38 | y = 0.00746Se + 29.6195 | 0.923 | 0.852 | 0.703 | ||
| 54 | y = 0.00401Se + 44.8996 | 0.993 | 0.986 | 0.972 | ||
| RS | 16 | y = 0.00275Se + 31.8236 | 0.952 | 0.907 | 0.814 | |
| 38 | y = 0.00375Se + 35.3689 | 0.977 | 0.955 | 0.911 | ||
| 54 | y = 0.00511Se + 47.9787 | 0.955 | 0.913 | 0.826 | ||
| Power | LS | 16 | y = 0.10518Se + 139.2046 | 0.997 | 0.994 | 0.988 |
| 38 | y = 0.14224Se + 176.6751 | 0.969 | 0.939 | 0.878 | ||
| 54 | y = 0.14189Se + 370.8443 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||
| RS | 16 | y = 0.05528Se + 273.3504 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.995 | |
| 38 | y = 0.07910Se + 305.7478 | 0.994 | 0.987 | 0.975 | ||
| 54 | y = 0.15918Se + 454.3579 | 0.953 | 0.909 | 0.818 |
| Items | Steering | Engine Speed | Equation | Pearson’s r | R2 | Adj. R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow rate | LS | 900 | y = 0.05046As* + 3.9264 | 0.961 | 0.923 | 0.846 |
| 1400 | y = 0.04788As + 4.6329 | 0.930 | 0.864 | 0.729 | ||
| 2200 | y = 0.05076As + 5.4468 | 0.955 | 0.912 | 0.824 | ||
| RS | 900 | y = 0.07287As + 5.0645 | 0.910 | 0.827 | 0.655 | |
| 1400 | y = 0.04290As + 5.5012 | 0.890 | 0.792 | 0.585 | ||
| 2200 | y = 0.04488As + 5.0854 | 0.866 | 0.749 | 0.498 | ||
| Pressure | LS | 900 | y = 0.43440As + 23.5246 | 0.973 | 0.947 | 0.894 |
| 1400 | y = 0.47379As + 23.2502 | 0.947 | 0.897 | 0.794 | ||
| 2200 | y = 0.43272As + 30.3204 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||
| RS | 900 | y = 0.54714As + 27.3615 | 0.929 | 0.864 | 0.728 | |
| 1400 | y = 0.48524As + 25.9252 | 0.959 | 0.920 | 0.840 | ||
| 2200 | y = 0.46994As + 25.2074 | 0.910 | 0.828 | 0.657 | ||
| Power | LS | 900 | y = 6.67659As + 112.0829 | 0.957 | 0.916 | 0.832 |
| 1400 | y = 7.34466As + 135.2262 | 0.926 | 0.858 | 0.715 | ||
| 2200 | y = 8.01223As + 230.1733 | 0.981 | 0.963 | 0.925 | ||
| RS | 900 | y = 7.4635As + 170.6954 | 0.895 | 0.801 | 0.603 | |
| 1400 | y = 7.39471As + 204.1820 | 0.934 | 0.873 | 0.745 | ||
| 2200 | y = 10.69033As + 179.1830 | 0.908 | 0.824 | 0.649 |
| Items | Steering | Equation | R2 | Adj. R2 | SE * | SC ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se *** | As **** | ||||||
| Flow rate | LS | y = 0.0012Se + 0.0497As + 2.906 | 0.937 | 0.916 | 0.3169 | 0.610 | 0.751 |
| RS | y = 0.0009Se + 0.0575As + 3.858 | 0.790 | 0.720 | 0.5861 | 0.391 | 0.798 | |
| Pressure | LS | y = 0.0053Se + 0.4470As + 17.675 | 0.942 | 0.923 | 2.2896 | 0.369 | 0.898 |
| RS | y = 0.0039Se + 0.5058As + 20.091 | 0.872 | 0.830 | 3.7797 | 0.240 | 0.903 | |
| Power | LS | y = 0.1300Se + 7.3440As − 35.494 | 0.928 | 0.904 | 45.6628 | 0.500 | 0.823 |
| RS | y = 0.0988Se + 8.7457As + 25.401 | 0.823 | 0.764 | 80.9260 | 0.333 | 0.844 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lim, R.-G.; Sim, T.; Kim, T.-J.; Kim, W.-S. Evaluation of Hydraulic Characteristics of Electrohydraulic Proportional Valve (EHPV) for an Auto-Steering Tractor Application. Machines 2023, 11, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11070674
Min Y-S, Kim Y-J, Lim R-G, Sim T, Kim T-J, Kim W-S. Evaluation of Hydraulic Characteristics of Electrohydraulic Proportional Valve (EHPV) for an Auto-Steering Tractor Application. Machines. 2023; 11(7):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11070674
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Yi-Seo, Yong-Joo Kim, Ryu-Gap Lim, Taeyong Sim, Taek-Jin Kim, and Wan-Soo Kim. 2023. "Evaluation of Hydraulic Characteristics of Electrohydraulic Proportional Valve (EHPV) for an Auto-Steering Tractor Application" Machines 11, no. 7: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11070674
APA StyleMin, Y.-S., Kim, Y.-J., Lim, R.-G., Sim, T., Kim, T.-J., & Kim, W.-S. (2023). Evaluation of Hydraulic Characteristics of Electrohydraulic Proportional Valve (EHPV) for an Auto-Steering Tractor Application. Machines, 11(7), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11070674







