The Investigation of Coupled Vibration of Automobile Transmission System and Its Intelligent Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodologies
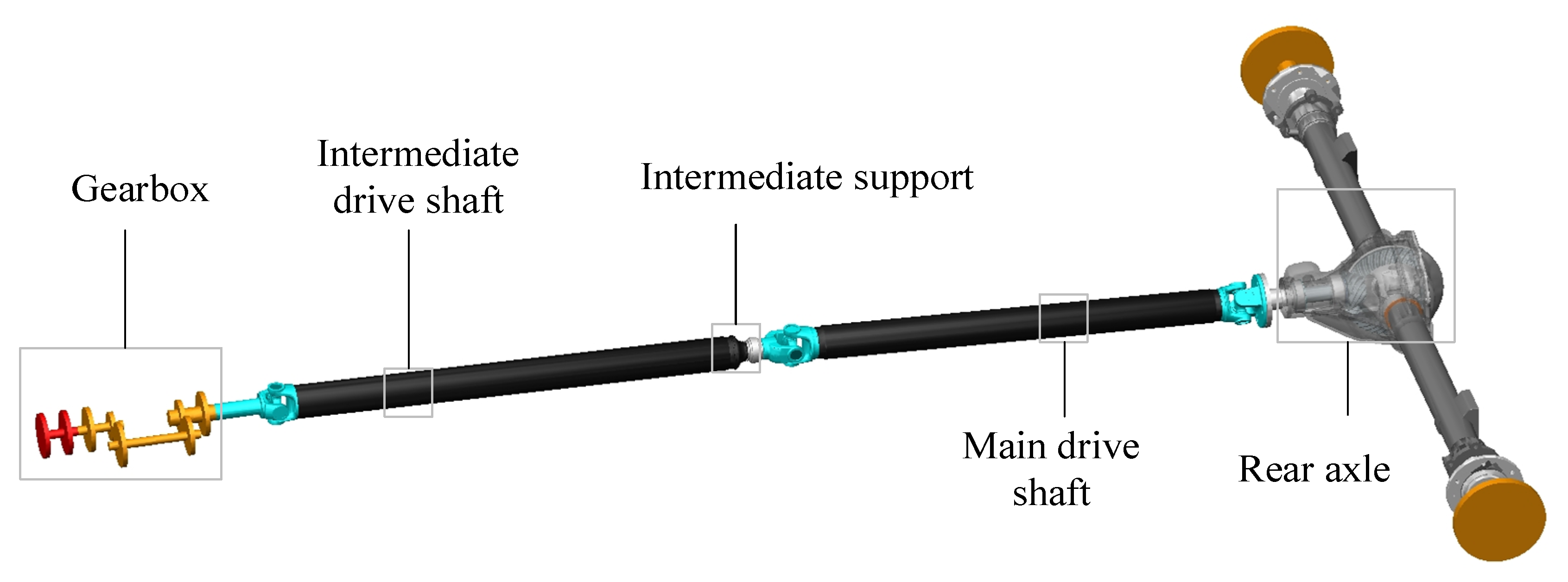
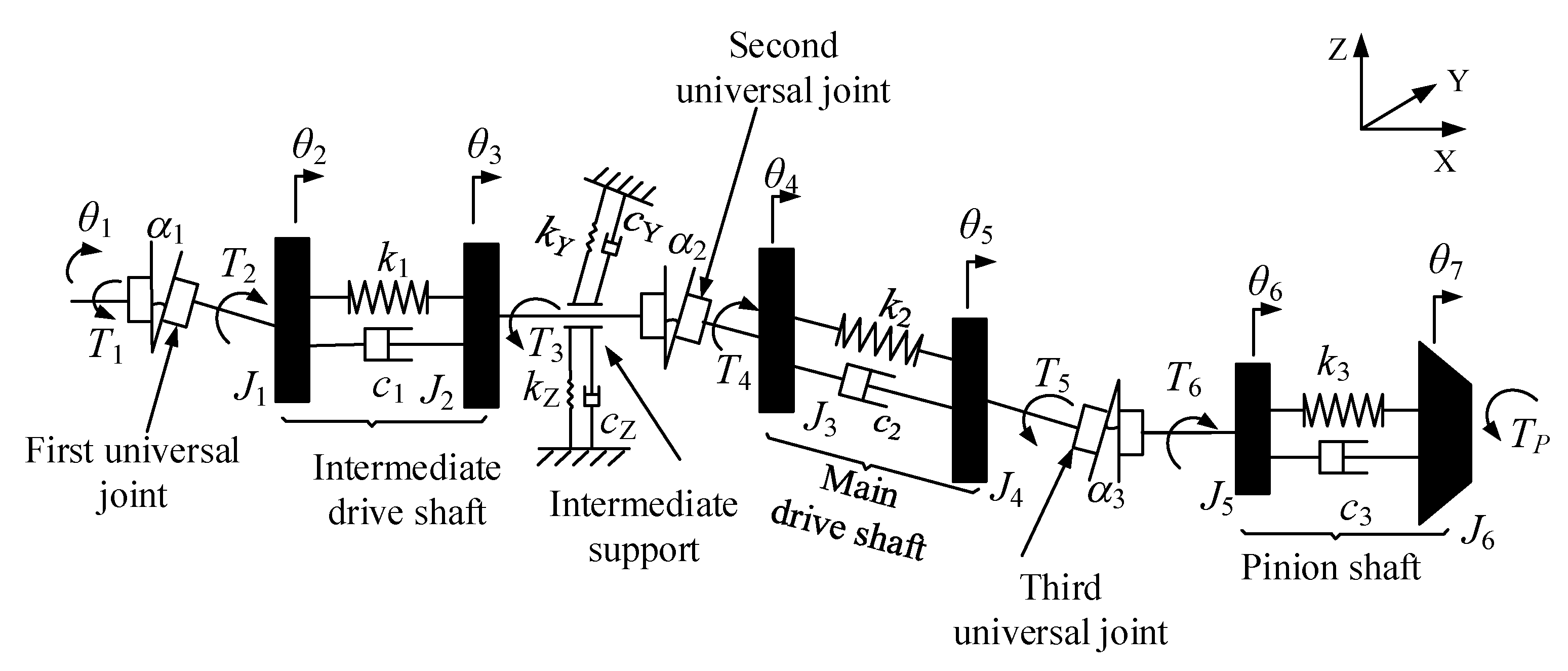
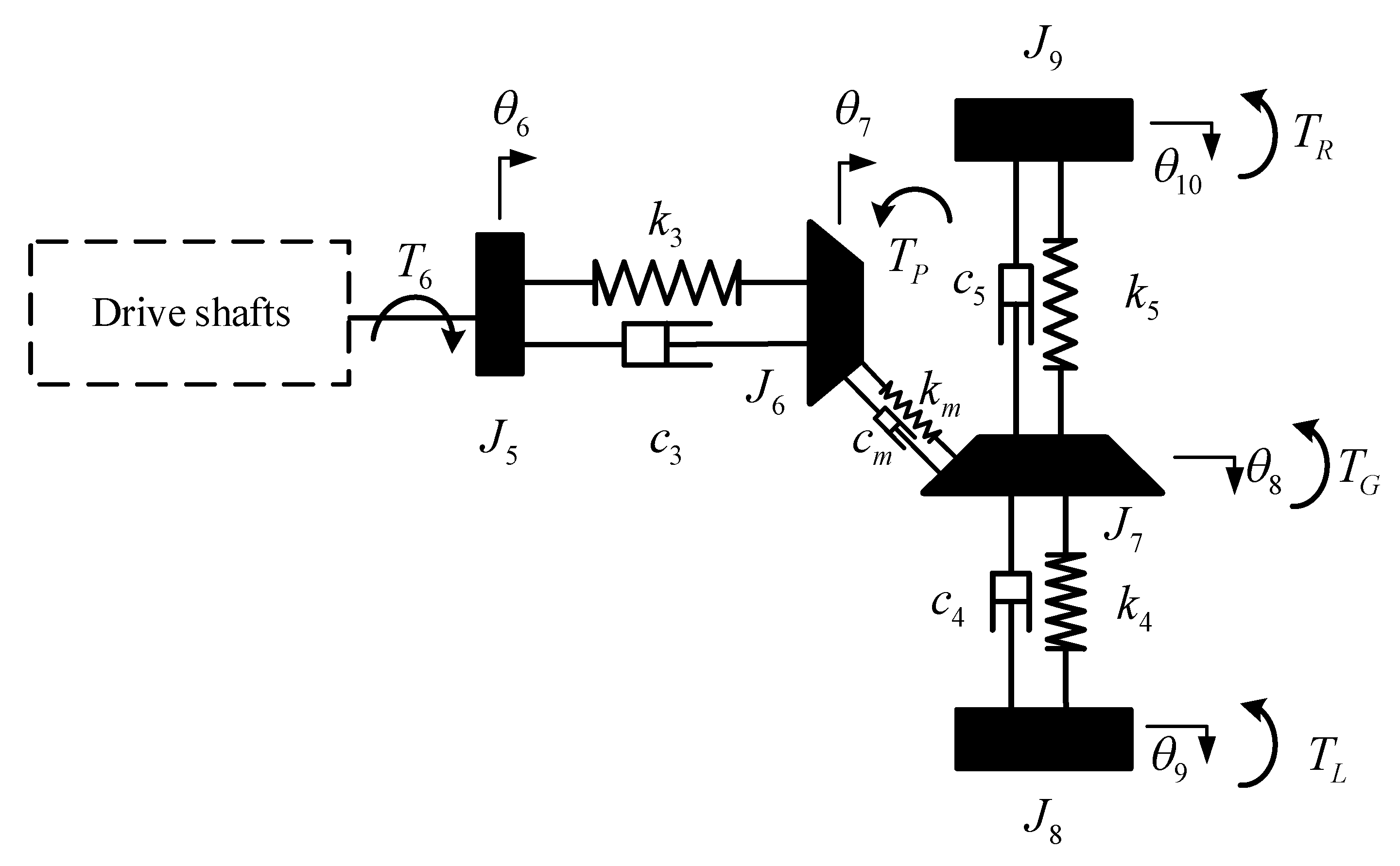
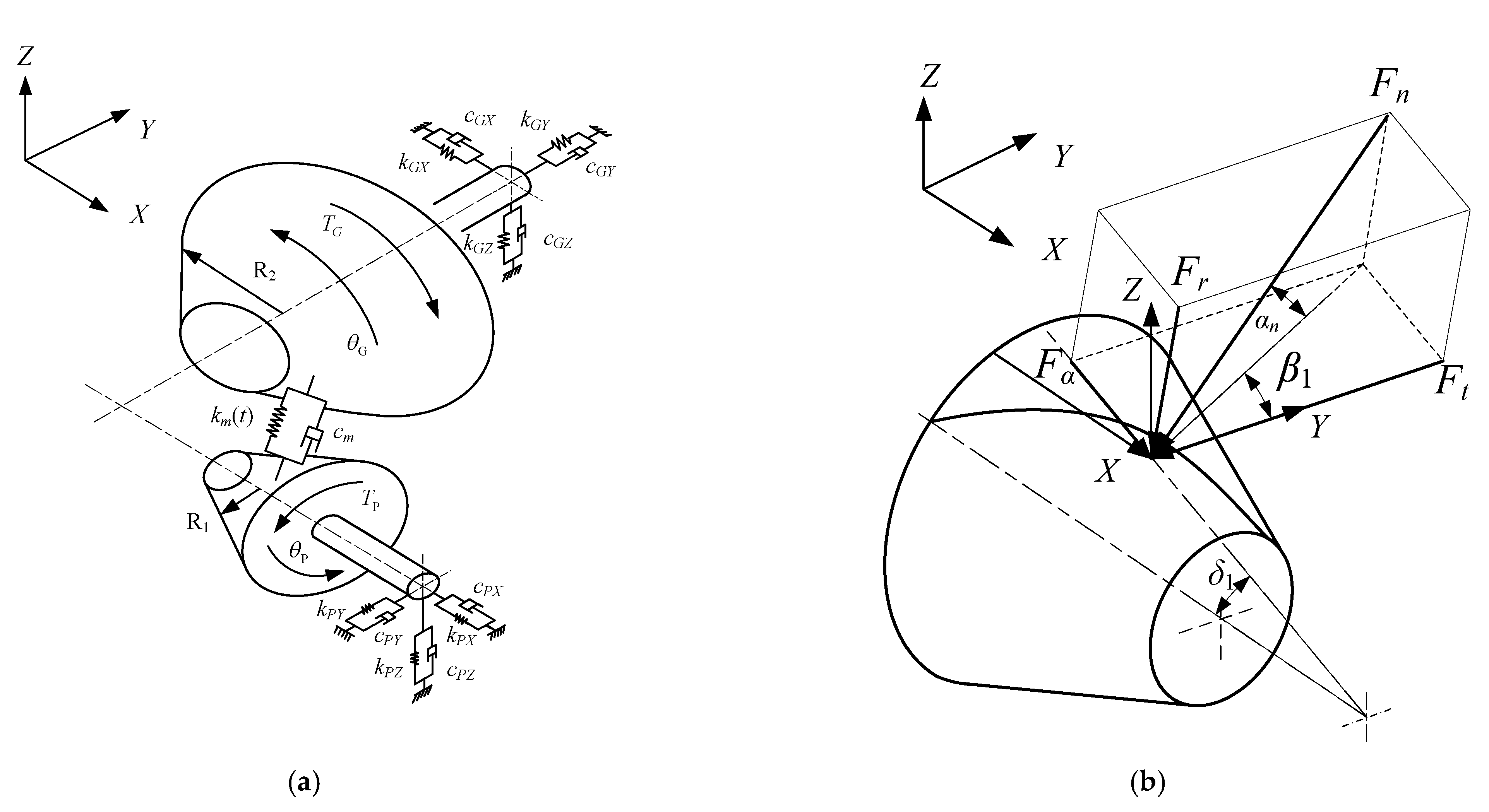
2.1. Mathematical Model of Transmission System
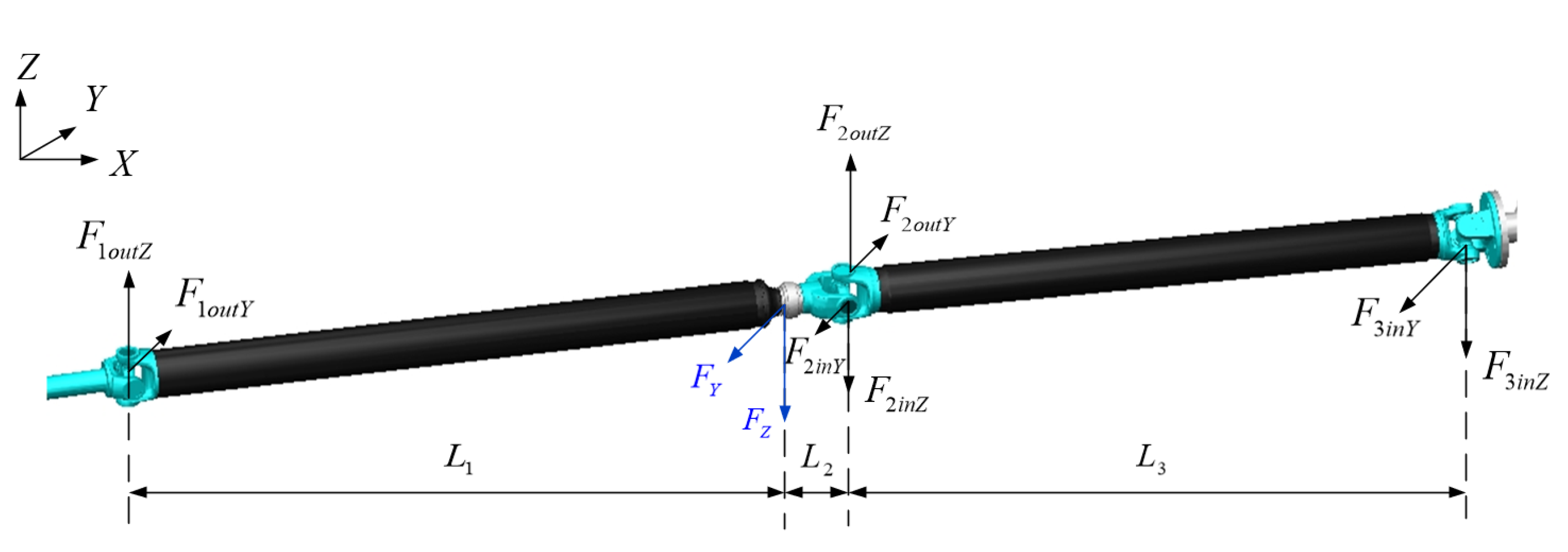
2.1.1. Mathematical Model of Drive Shaft
2.1.2. Mathematical Model of Rear Axle
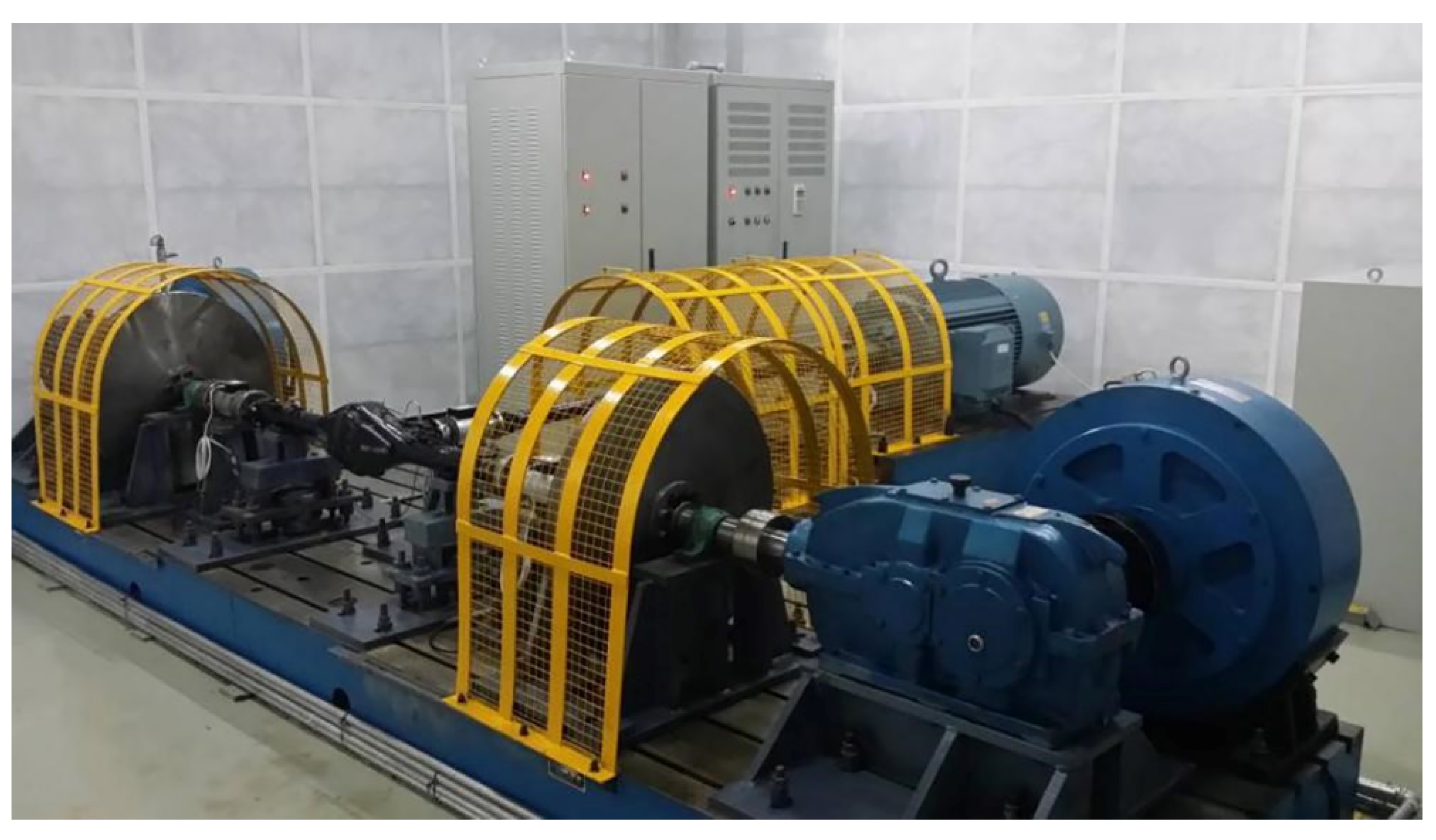
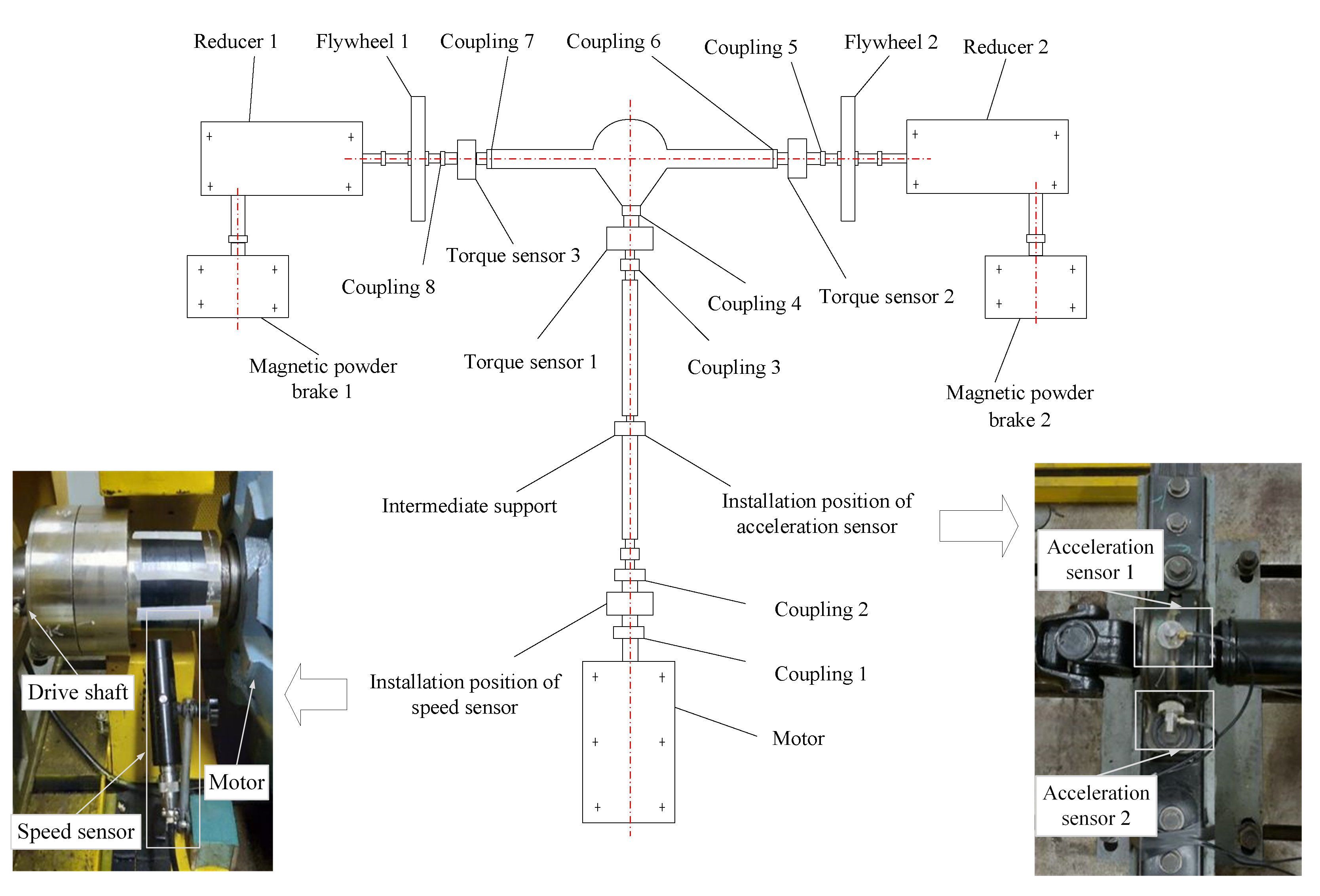
2.2. Experimental Method
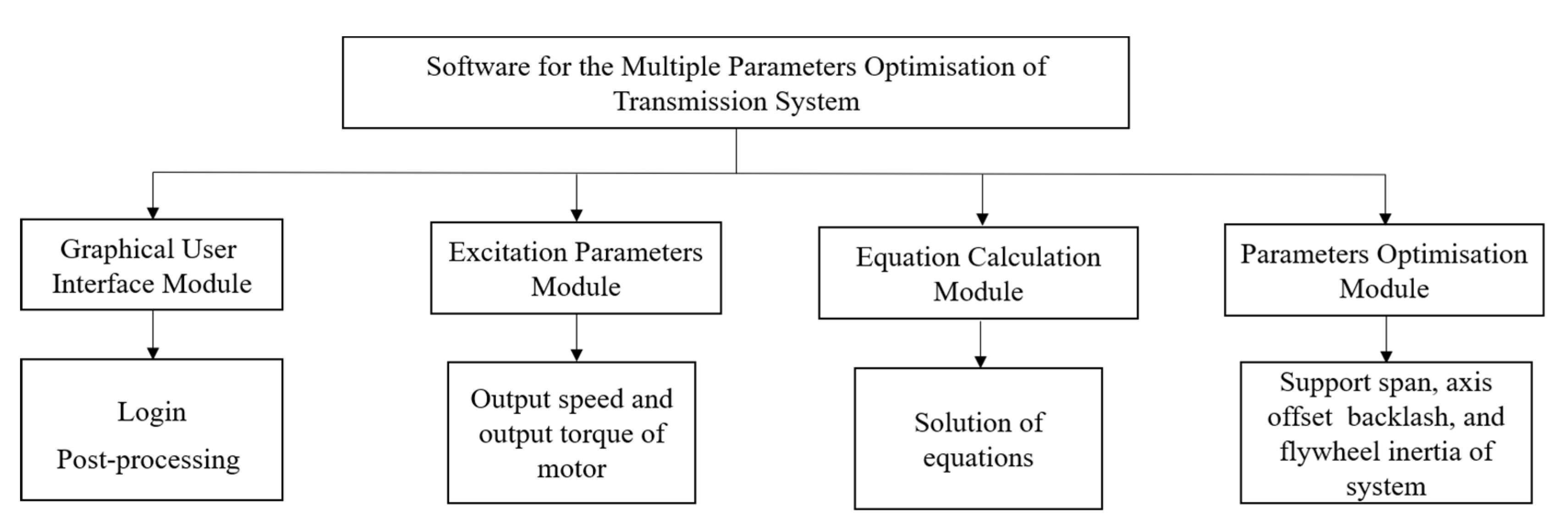
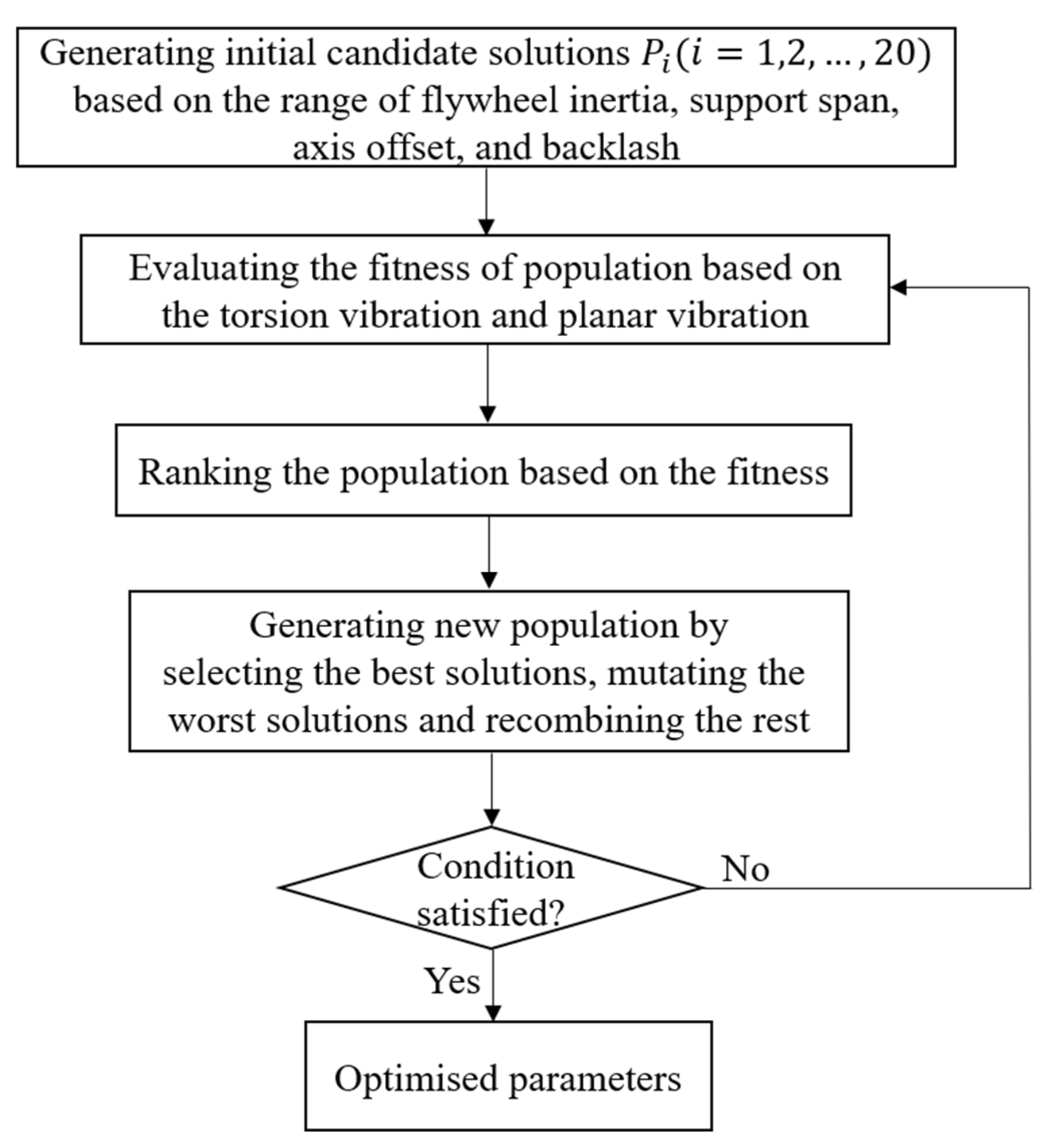
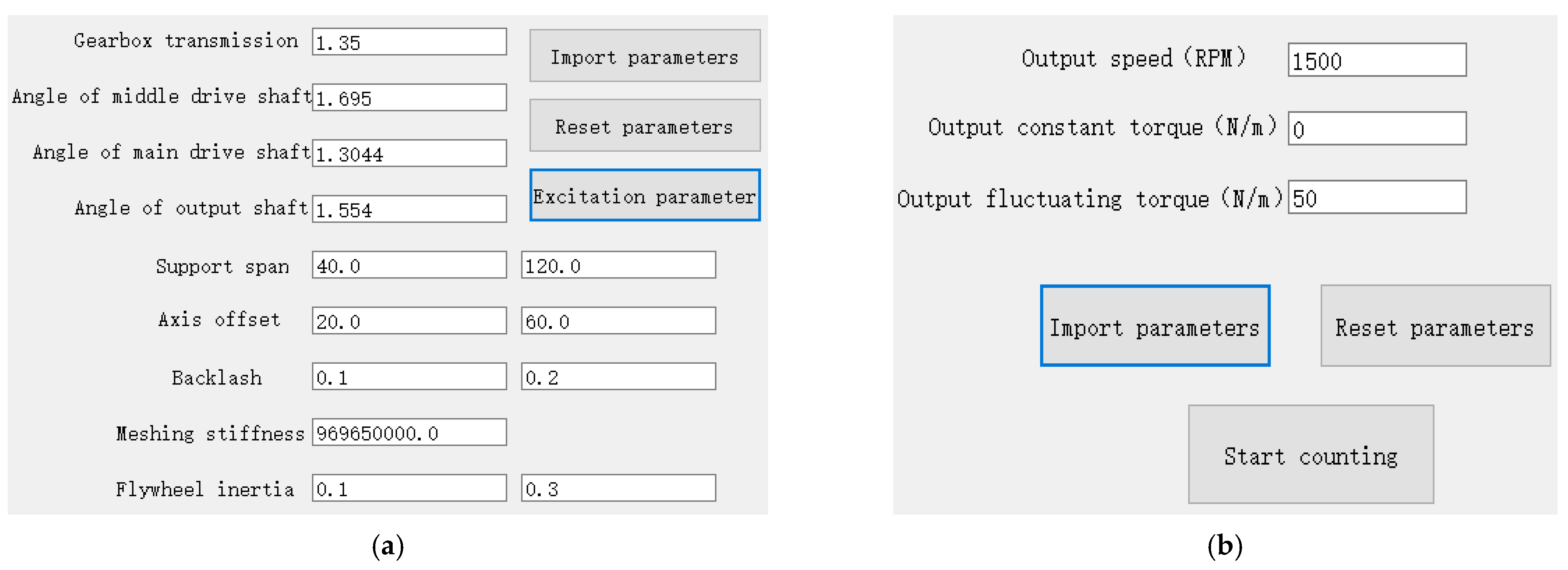
2.3. Optimization Design
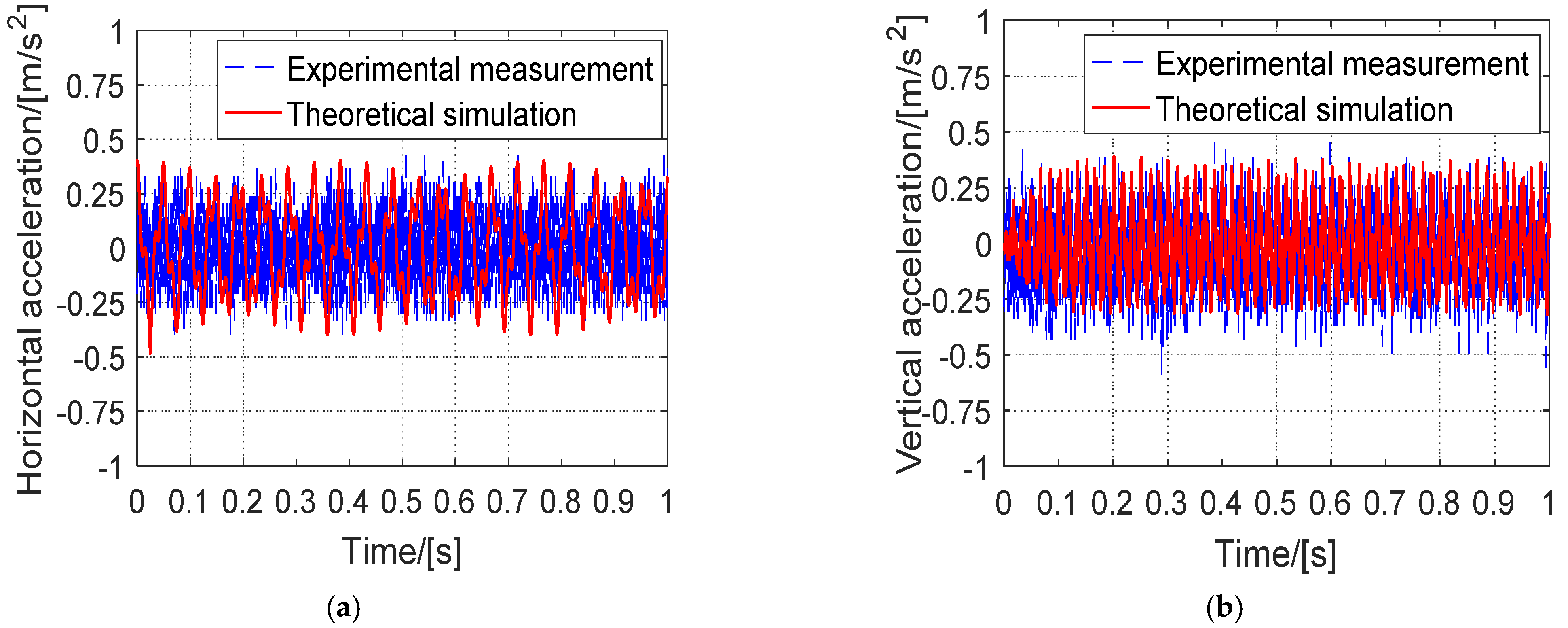
3. Simulations and Experimental Measurements
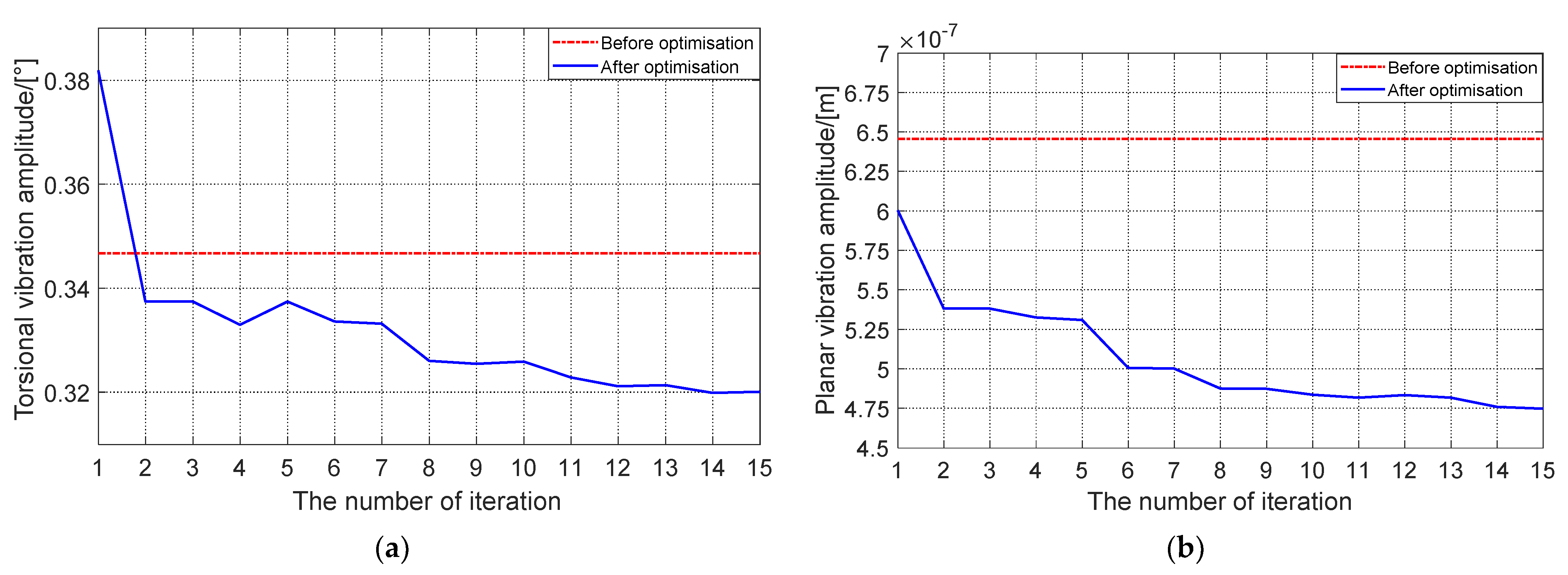
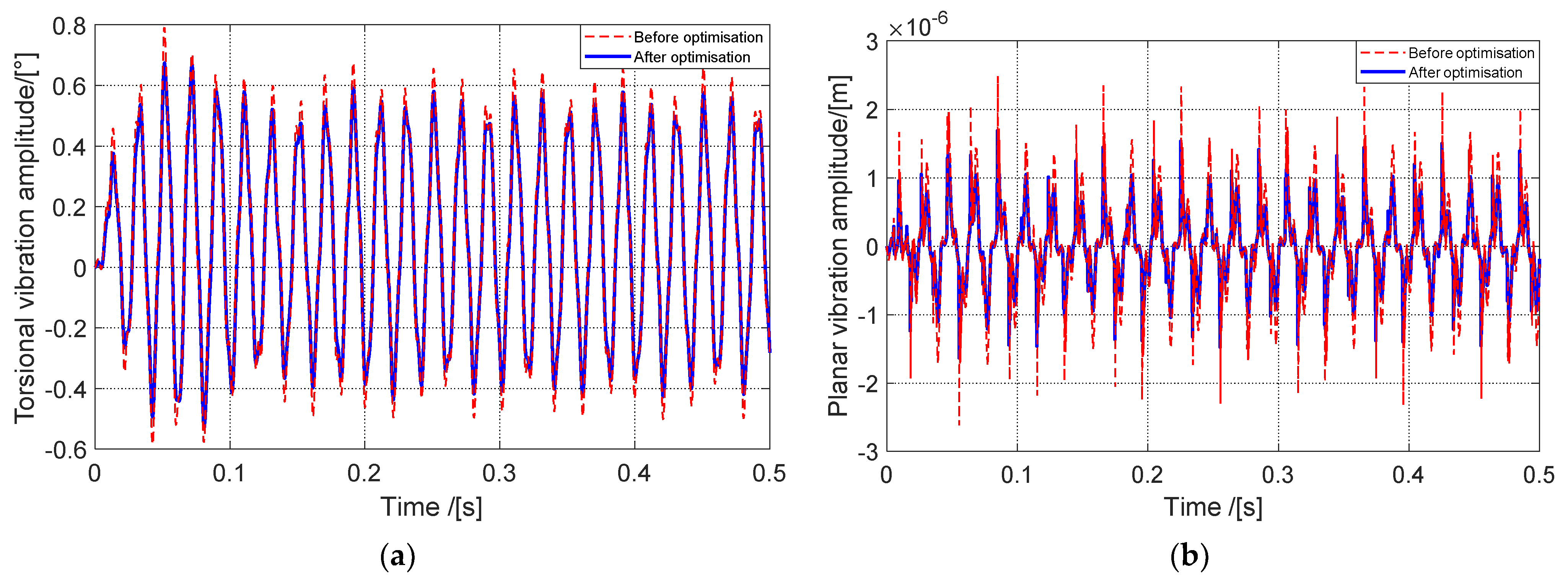
4. Optimization Based on the Mathematical Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.G.; Sun, X.R.; Xu, J.L. A case study of intelligent manufacturing for key components of vehicles. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Mechanical, Electric and Industrial Engineering (MEIE2021), Kunming, China, 22–24 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Zou, L. Study on the torsional vibration of a hybrid electric vehicle powertrain with compound planetary power-split electronic continuous variable transmission. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2014, 228, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.Y.; Yin, Z.H.; Shangguan, W.B. Analysis and optimization for contact forces and transmission efficiency of an automotive ball joint. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2020, 234, 3207–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Xu, J.H.; Gou, H.W. A Research Review on the Key Technologies of Intelligent Design for Customized Products. Engineering 2017, 3, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.Y.; Tan, B.H.; Ding, F. An experimental investigation of resonance sources and vibration transmission for a pure electric bus. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2019, 234, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Wu, Z.Y.; Lu, J. Investigation of the effect of rotation speed on the torsional vibration of transmission system. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2019, 13, JAMDSM0079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.P.; Xia, C.G.; Chen, S.D. Parametric Investigation of Dual-Mass Flywheel Based on Driveline Start-up Torsional Vibration Control. Shock Vib. 2019, 2019, 3171698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Lie, Y.J.; Jia, B. Research on coupled vibrations of driveshaft–rear axle system based on nonlinear hybrid model. J. Vib. Control 2021, 10775463211002628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Yang, X.T.; Sun, X.Q. Optimal Design of Shift Point Strategy for DCT Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. Machines 2021, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Zha, Y.W.; Liu, T. Research on Adaptive Control of Air-Borne Bolting Rigs Based on Genetic Algorithm Optimization. Machines 2021, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.D.; He, Z.C.; Li, G.Y. Uncertainty analysis and optimization of automotive driveline torsional vibration with a driveline and rear axle coupled model. Eng. Optim. 2018, 50, 1871–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, N. Parameters optimization of two-speed powertrain of electric vehicle based on genetic algorithm. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2020, 12, 1687814020901652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.C.; Jin, Z.C.; Liu, D.W. Multi-Objective Lightweight Optimization of Parameterized Suspension Components Based on NSGA-II Algorithm Coupling with Surrogate Model. Machines 2021, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Zhu, J.W.; Wan, L. Effects of intermediate support stiffness on nonlinear dynamic response of transmission system. J. Vib. Control 2020, 26, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.Q.; Li, Y.N.; Zan, C.L. Dynamic Modeling and Analysis of Nonlinear Compound Planetary System. Machines 2022, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lim, T.C.; Li, M.F. Dynamics of a hypoid gear pair considering the effects of time-varying mesh parameters and backlash nonlinearity. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 308, 302–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.Y.; Qin, D.T.; Liu, C.Z. Investigation of electromechanical coupling vibration characteristics of an electric drive multistage gear system. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 121, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, S.D.; Saribay, Z.B.; Cigeroglu, E. Nonlinear time-varying dynamic analysis of a spiral bevel geared system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 92, 1901–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshidianfar, A.; Saghafi, A. Global bifurcation and chaos analysis in nonlinear vibration of spur gear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2013, 75, 783–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Li, G.Y.; Zheng, L. Influence of Asymmetric Mesh Stiffness on Dynamics of Spiral Bevel Gear Transmission System. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 124148. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Inertia (Kg·m2) | Stiffness (N/m) | Damping (N·s/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intermediate drive shaft | |||
| Main drive shaft | |||
| Pinion shaft |
| Parameters | Pinion | Gear |
|---|---|---|
| The number of teeth | 10 | 41 |
| Pitch cone angle (°) | 12.75 | 76.50 |
| Average pressure angle (°) | 21.25 | 21.25 |
| Average spiral angle (°) | 47.97 | 28.27 |
| Radius of pitch circle (mm) | 18.8 | 71.7 |
| Parameters | Stiffness (N/m) | Damping (N·s/m) | Equivalent Mass (kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinion | 8.6 × 108 | 1050 | 1.037 | |||
| 1.6 × 109 | 1050 | 1.037 | ||||
| 1.6 × 109 | 1050 | 1.037 | ||||
| Gear | 2.8 × 109 | 1000 | 6.162 | |||
| 6.9 × 108 | 1000 | 6.162 | ||||
| 2.8 × 109 | 1000 | 6.162 | ||||
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Output power of motor (kW) | 160 |
| Rated torque of motor (N·m) | 509 |
| Rated speed of motor (RPM) | 2979 |
| Moment of inertia of motor (kg·m2) | 1.7256 |
| Mass of motor (kg) | 1105 |
| Input power of reducer (kW) | 86 |
| Input speed of reducer (RPM) | 1000 |
| Output speed of reducer (RPM) | 125 |
| Rated torque of magnetic powder brake (N·m) | 5000 |
| Sampling frequency of speed sensor (Hz) | 40,000 |
| Sensitivity of acceleration sensor 1 (pc/s2) | 4.77 |
| Sensitivity of acceleration sensor 2 (pc/s2) | 4.94 |
| Mass of flywheel (kg) | 328 |
| Moment of inertia of flywheel (kg·m2) | 27 |
| Parameters | Current Values | Selection Ranges of Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Flywheel inertia (kg·m2) | 0.2 | 0.1~0.3 |
| Support span (mm) | 82.5 | 40~120 |
| Axis offset (mm) | 38 | 20~60 |
| Backlash (mm) | 0.15 | 0.1~0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Xiang, D.; Zeng, C.; Huang, F. The Investigation of Coupled Vibration of Automobile Transmission System and Its Intelligent Design. Machines 2022, 10, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060428
Liu X, Xiang D, Zeng C, Huang F. The Investigation of Coupled Vibration of Automobile Transmission System and Its Intelligent Design. Machines. 2022; 10(6):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060428
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaogang, Dongshan Xiang, Chunhui Zeng, and Fengyun Huang. 2022. "The Investigation of Coupled Vibration of Automobile Transmission System and Its Intelligent Design" Machines 10, no. 6: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060428
APA StyleLiu, X., Xiang, D., Zeng, C., & Huang, F. (2022). The Investigation of Coupled Vibration of Automobile Transmission System and Its Intelligent Design. Machines, 10(6), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060428






