Sensor Distribution Optimization for Composite Impact Monitoring Based on AR Model and LPP
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Optimization Problems
- Minimizing the number of sensors.
- Maximizing the effect of state detection.
2.1. Objective Function I: Number of Sensors
2.2. Objective Function II: Minimum Difference among Impact Categories
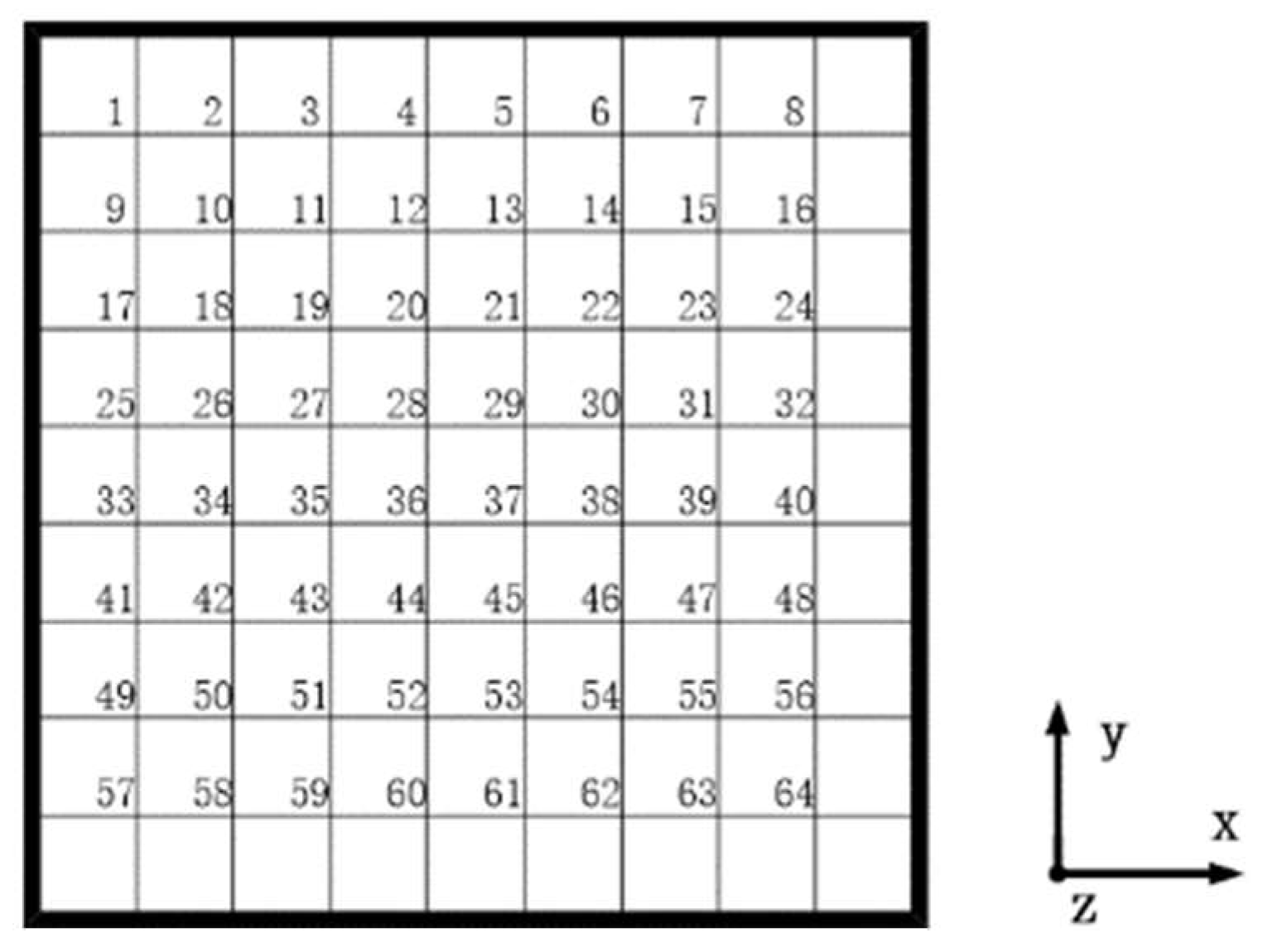
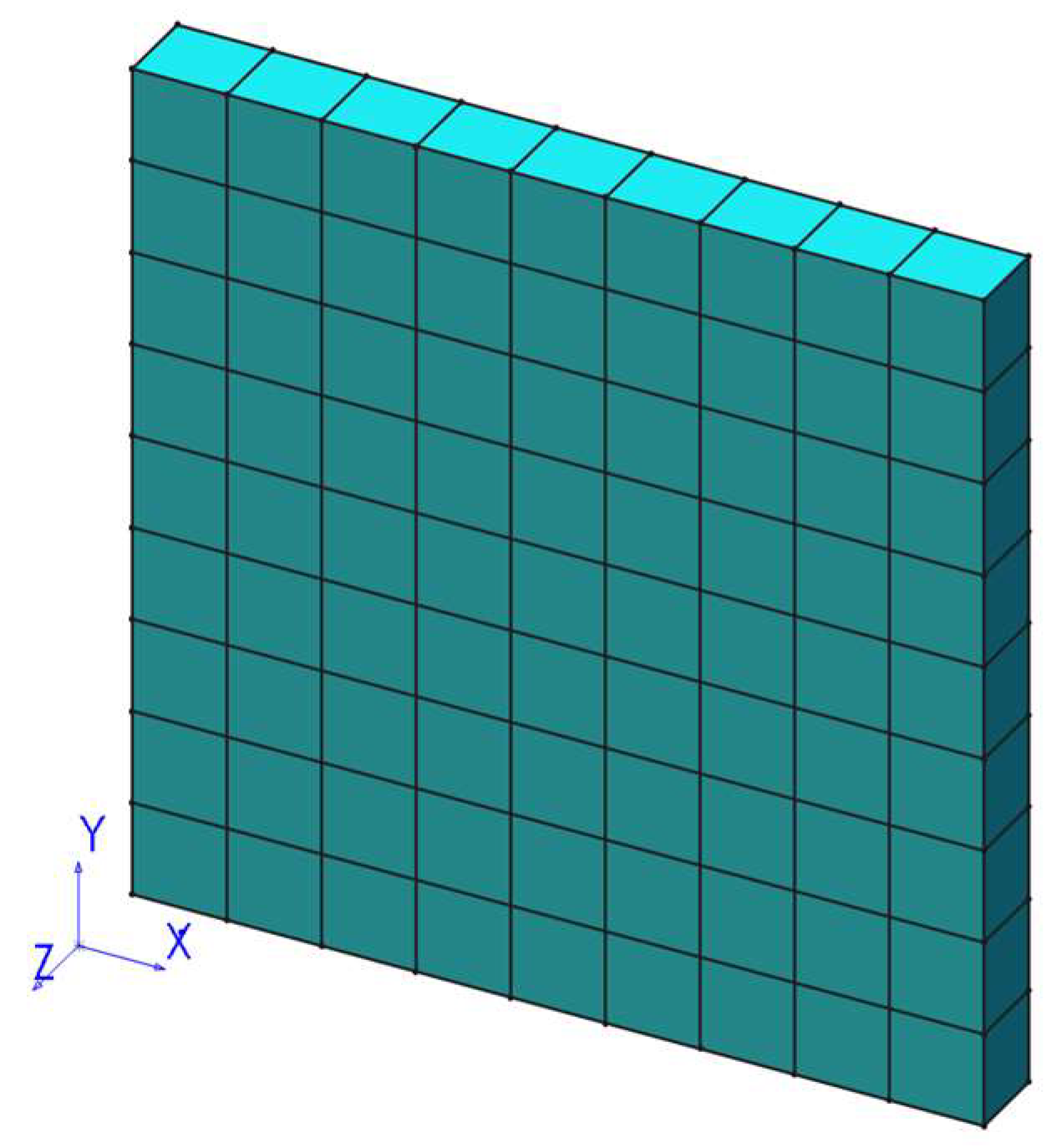
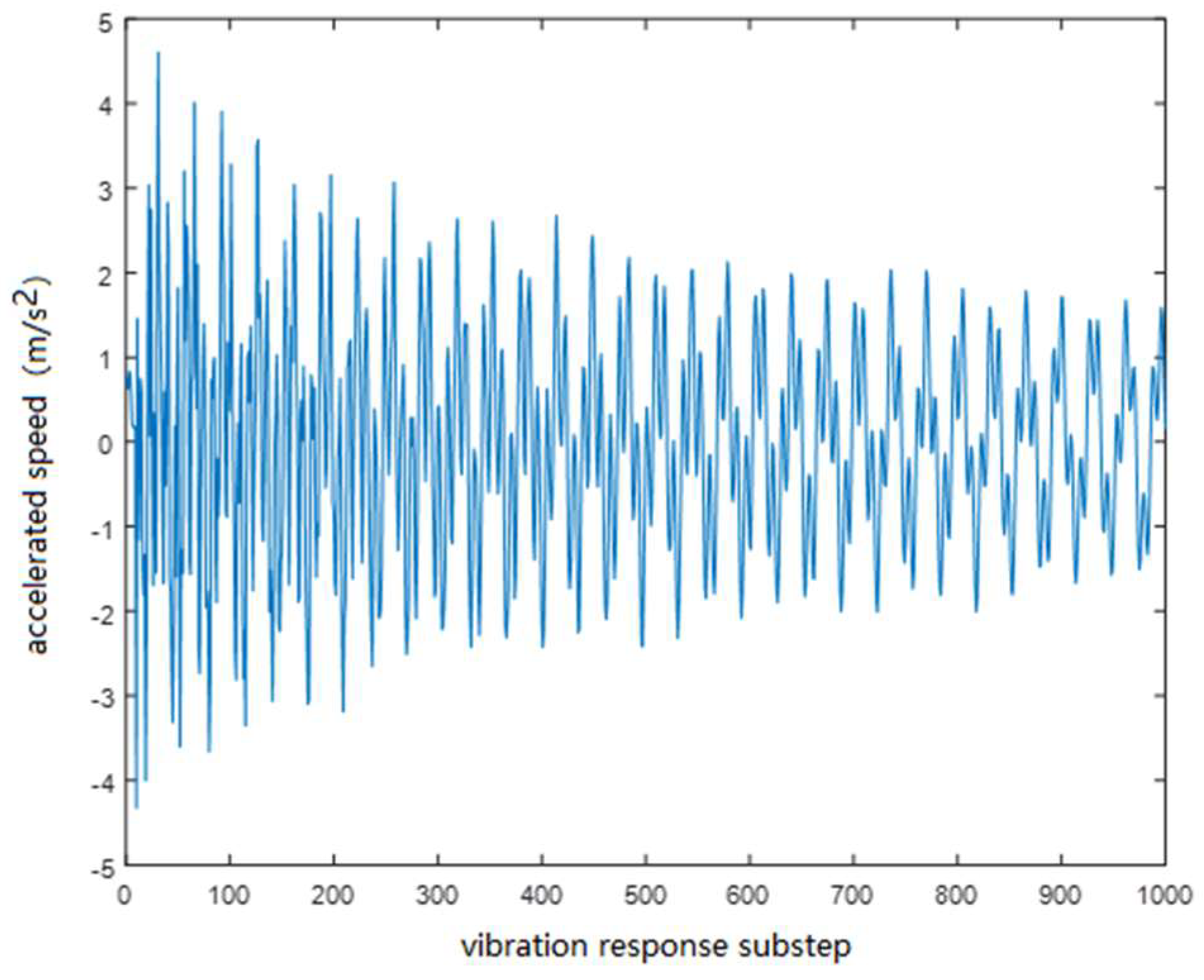
2.2.1. Impact Sample Library Based on Finite Element Simulation
2.2.2. Feature Extraction Based on AR Model
2.2.3. Dimension Reduction Based on LPP
2.2.4. Definition of Objective Function II
3. Sensor Network Optimization Algorithm
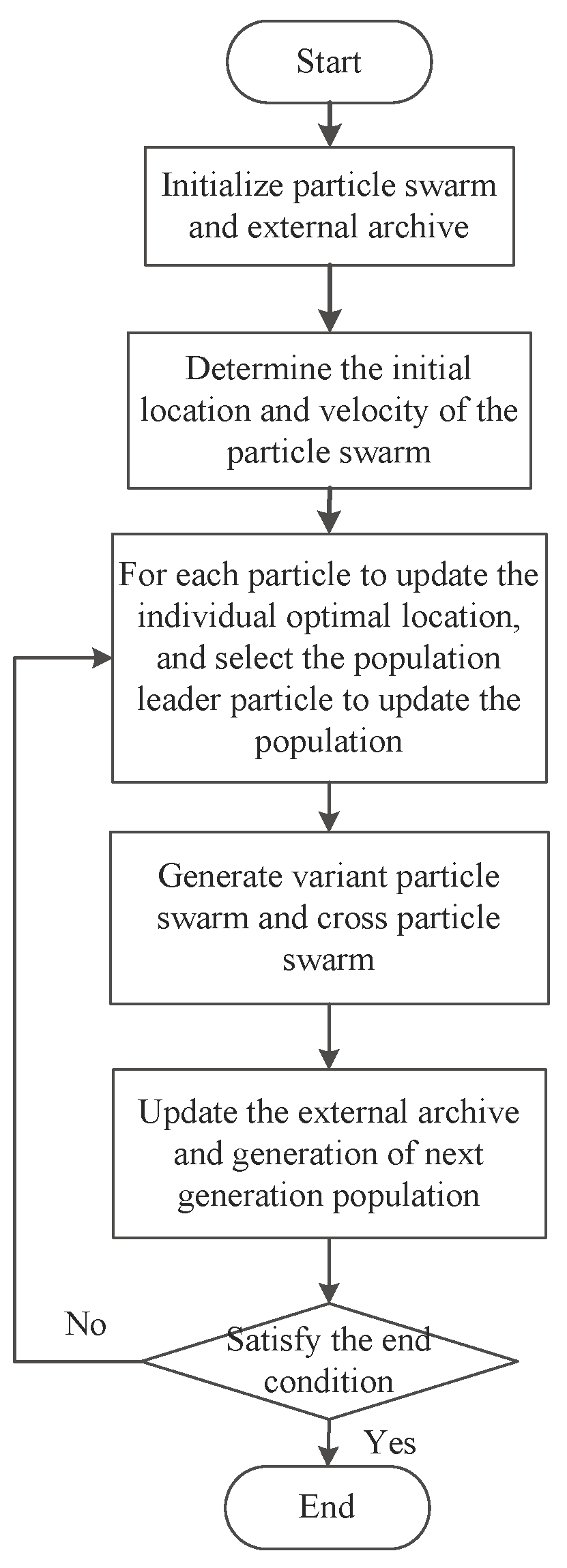
3.1. Multi−Objective Particle Swarm Optimization
3.2. Results and Discussion
4. Method Evaluation
4.1. Experimental System
4.2. Localization Methodology
4.3. Experiment Result and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, C.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Jun, S.-M.; Kim, C.-G. Localizations and force reconstruction of low-velocity impact in a composite panel using optical fiber sensors. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2012, 21, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, Y.; Kim, C.-G. Impact localization on composite wing using 1D array FBG sensor and RMS/correlation based reference database algorithm. Compos. Struct. 2015, 125, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieczonka, L.; Aymerich, F.; Staszewski, W.J. Impact Damage Detection in Light Composite Sandwich Panels. Procedia Eng. 2014, 88, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Han, X.; Fei, Q. Localization of low-velocity impact by using fiber brag grating sensors based on wavelet packet energy eigenvector. J. Vib. Shock. 2017, 36, 184–189. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Xiong, Z.; Jia, H.; Liang, D. Impact localization algorithm on wing model using optical fiber sensors based on time-difference identification. J. Optoelectron. 2017, 28, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D. Research on structure health monitoring ultrasonic guided wave based on machine learning method. Fiber Compos. 2020, 37, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, M. Optimal placement of sensors based on improved artificial fish swam algorithm. J. Nanchang Univ. Eng. Ed. 2019, 41, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhart, R.; Kennedy, J. A New Optimizer Using Particle Swarm Theory. In Proceedings of the 1995 6th International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, Nagoya, Japan, 4–6 October 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, K.S.C.; Maalej, M.; Quek, S.T. An Application of a Plastic Optical Fiber Sensor and Genetic Algorithm for Structural Health Monitoring. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2006, 17, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczak, A.L.; Wang, H.; Darabi, H.; Jafari, M.A. Genetic algorithm convergence study for sensor network optimization. Inf. Sci. 2001, 133, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Bakhary, N.; Kueh, A.; Yassin, A.M. Optimal sensor placement for mode shapes using improved simulated annealing. Smart Struct. Syst. 2014, 13, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.-H.; Li, H.-N.; Gu, M.; Zhang, X.-D. Sensor Placement Optimization in Structural Health Monitoring Using Niching Monkey Algorithm. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2014, 14, 1440012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.-H.; Shih, H.-C.; Liao, B.-Y.; Chu, S.-C. A ladder diffusion algorithm using ant colony optimization for wireless sensor networks. Inf. Sci. 2012, 192, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chang, S.; Kim, J. Consensus Achievement of Decentralized Sensors Using Adapted Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Céspedes-Mota, A.; Castañón, G.; Martínez-Herrera, A.F.; Cárdenas-Barrón, L.E. Optimization of the Distribution and Localization of Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Differential Evolution Approach. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello, C.A.C.; Reyes-Sierra, M. Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimizers: A Survey of the State-of-the-Art. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Res. 2006, 2, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, C.; Shashikala, T.; Neetesh, K. FZ enabled Multi-objective PSO for multicasting in IoT based Wireless Sensor Networks. Inf. Sci. 2019, 498, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Xu, Y. Application research of Ballastless track health monitoring scheme based on BIM technology. J. East China Jiaotong Univ. 2022, 39, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Rail transit infrastructure monitoring and analysis of vibration response. J. East China Jiaotong Univ. 2021, 38, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Huang, L.; Peng, J. Sensor distribution optimization for structural impact monitoring based on NSGA-II and wavelet decomposition. Sensors 2018, 18, 42–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bugharbee, H.; Trendafilova, I. A fault diagnosis methodology for rolling element bearings based on advanced signal pretreatment and autoregressive modelling. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 369, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zheng, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Hua, H. Using AR model and fractal geometry for condition monitoring of working machinery. J. Mech. Strength 2001, 23, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. A Bayesian analysis of the minimum AIC procedure. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1978, 30, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhong, A.; Yang, J.; Zhang, D. LPP solution schemes for use with face recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 4165–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.-F.; Ng, S.-C.; Cheung, C.-C.; Lui, A.K. A new strategy for finding good local guides in MOPSO. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Li, R. Traffic identification method based on multiple probabilistic neural network mode. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
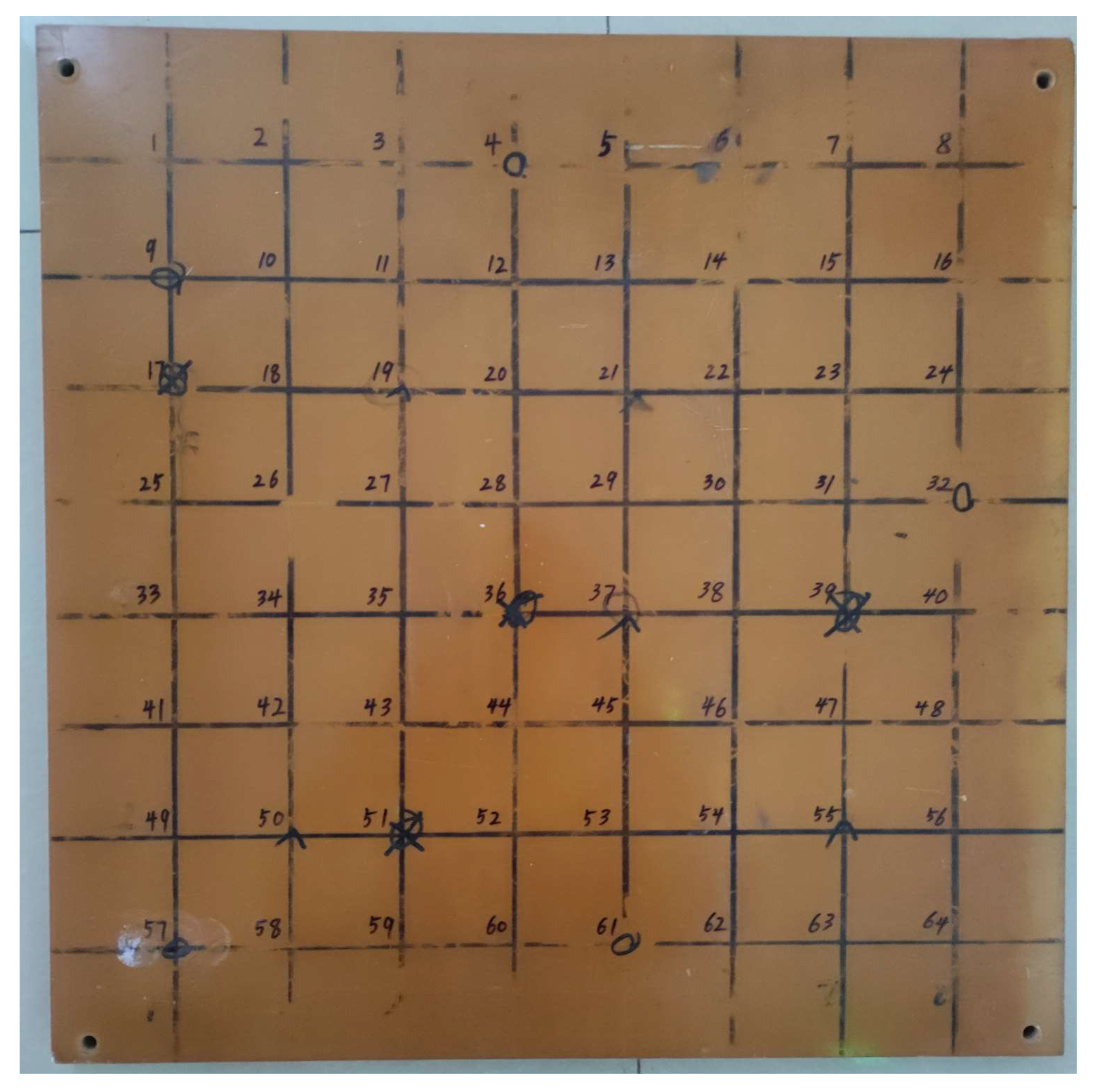
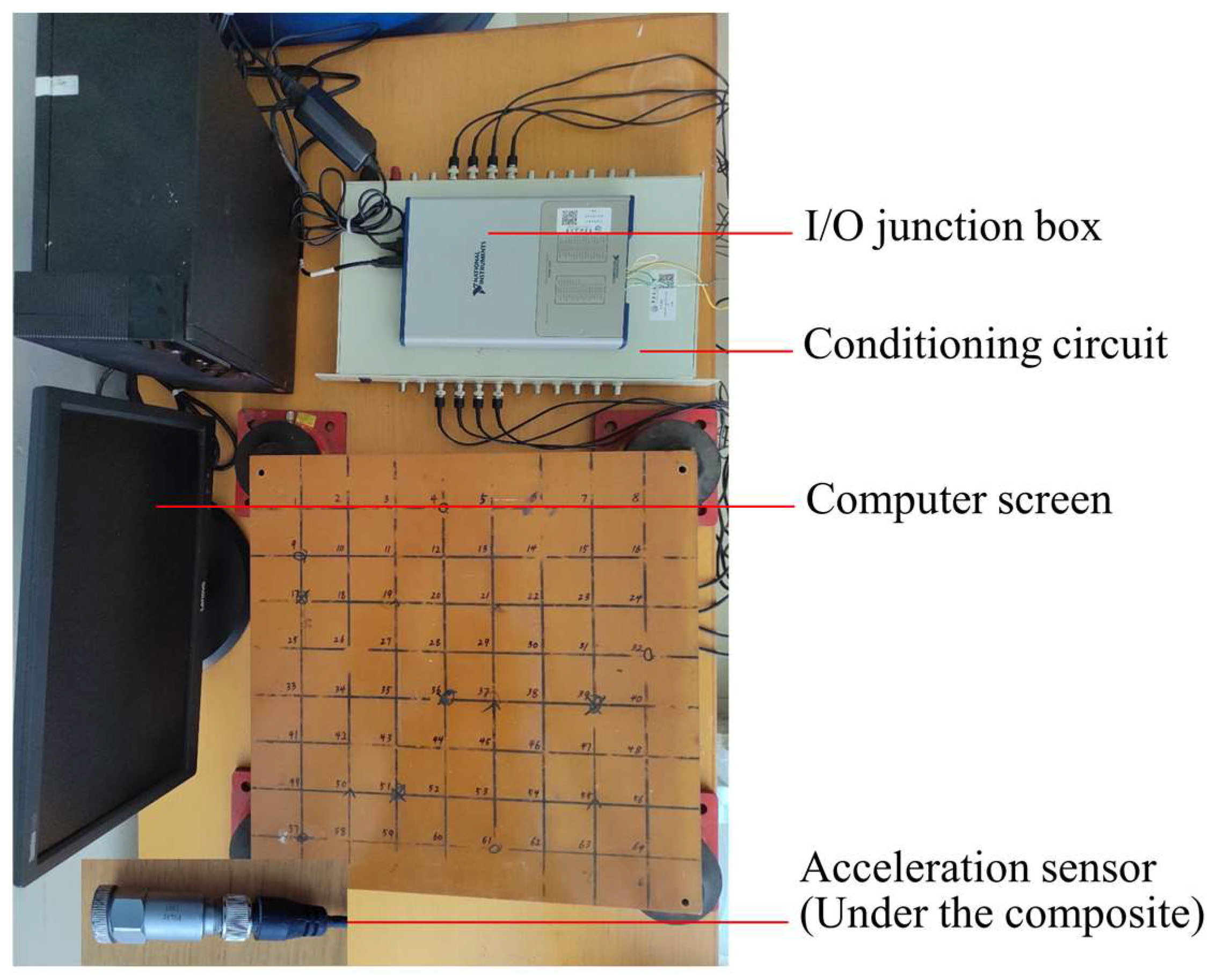

| Equipment | Parameter |
|---|---|
| thickness and area | 15 mm × 500 mm × 500 mm |
| elastic modulus | |
| Poisson ratio | |
| shear elasticity | |
| density |
| Parameter | Numeric |
|---|---|
| individual number of initial population | 800 |
| maximum inertia weight | 0.4 |
| minimum inertia weight | 0.95 |
| maximum value of self−learning factor | 2.5 |
| maximum value of group learning factor | 2.5 |
| mutation probability | 0.1 |
| crossover probability | 0.25 |
| First Pareto Solution Set | Second Pareto Solution Set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designed Threshold | Objective Function I | Sensor No. | Objective Function II | Objective Function I | Sensor No. | Objective Function II |
| 5 | 5 | 10 13 29 30 42 | 0.0106096652 | 5 | 9 23 36 44 52 | 0.0106096643 |
| 4 | 11 14 37 38 | 0.00817384898 | 4 | 11 14 20 27 | 0.00817384895 | |
| 3 | 7 18 37 | 0.00540325603 | 3 | 16 28 54 | 0.00540325602 | |
| 2 | 11 21 | 0.00207577165 | 2 | 44 54 | 0.00207577163 | |
| 1 | 59 | 3.35 × 10−11 | 1 | 21 | 1.08 × 10−11 | |
| 3 | 3 | 7 18 37 | 0.00540325603 | 3 | 16 28 54 | 0.00540325602 |
| 2 | 11 21 | 0.00207577165 | 2 | 44 54 | 0.00207577163 | |
| 1 | 59 | 3.35 × 10−11 | 1 | 21 | 1.08 × 10−11 | |
| 1 | 1 | 59 | 3.35 × 10−11 | 1 | 21 | 1.08 × 10−11 |
| First Pareto Solution Set | Second Pareto Solution Set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designed Threshold | Objective Function I | Sensor No. | Objective Function II | Objective Function I | Sensor No. | Objective Function II |
| 5 | 5 | 33 53 60 95 99 | 0.00428453616 | 5 | 6 52 55 90 95 | 0.00425298431 |
| 4 | 64 67 82 89 | 0.00353586021 | 4 | 19 37 67 89 | 0.00351594635 | |
| 3 | 6 27 89 | 0.00222758237 | 3 | 60 68 82 | 0.00222758192 | |
| 2 | 34 37 | 0.00138900543 | 2 | 82 89 | 0.00106970087 | |
| 1 | 63 | 2.3215 × 10−11 | 1 | 96 | 1.9516 × 10−11 | |
| 3 | 3 | 6 27 89 | 0.00222758237 | 3 | 60 68 82 | 0.00222758192 |
| 2 | 34 37 | 0.00138900543 | 2 | 82 89 | 0.00106970087 | |
| 1 | 63 | 2.3215 × 10−11 | 1 | 96 | 1.9516 × 10−11 | |
| 1 | 1 | 63 | 2.3215 × 10−11 | 1 | 96 | 1.9516 × 10−11 |
| Equipment | Model Number | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| acceleration sensor | CA−YD−188T | with a range of −10 g to 10 g, sensitivity is 500 mV/g, frequency response is 0.6~5000. |
| conditioning circuit | YE3826A | 12−channel analog input channel, custom cable connector kits and mounting accessories. |
| I/O junction box | NI−USB−6356 | 16 analog inputs at 16 bits, 1 MS/s (multichannel), 1.25 MS/s (single channel). |
| Sensor Network | Half Load Impact | Full Load Impact | Average Recognition Rate | Single Impact Recognition Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (11, 21) | 66.25% | 62.19% | 64.22% | 14.09 ms |
| (7, 18, 37) | 75.86% | 73.59% | 74.73% | 19.66 ms |
| (11, 14, 37, 38) | 86.09% | 83.98% | 85.04% | 21.39 ms |
| Method | Optimize Database | Feature Extraction | Data Dimensionality Reduction | Optimization Algorithm for Sensor Networks | Impact Category Recognition Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ANSYS | AR | LPP | MOPSO | PNN |
| B | ANSYS | Energy analysis of Wavelet Band | PCA | MOPSO | PNN |
| Number of Sensors | Method A | Method B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Network | Average Recognition Rate | Sensor Network | Average Recognition Rate | |
| 2 | (11,21) | 64.22% | (28,30) | 25.27% |
| 3 | (7,18,37) | 74.73% | (11,25,29) | 59.14% |
| 4 | (11,14,37,38) | 85.04% | (27,30,50,55) | 76.95% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Tan, J.; Ding, Y.; Huang, P.; Tang, G.; Zhan, J. Sensor Distribution Optimization for Composite Impact Monitoring Based on AR Model and LPP. Machines 2022, 10, 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121154
Li P, Tan J, Ding Y, Huang P, Tang G, Zhan J. Sensor Distribution Optimization for Composite Impact Monitoring Based on AR Model and LPP. Machines. 2022; 10(12):1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121154
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peng, Jianbin Tan, Ying Ding, Peiwei Huang, Gan Tang, and Jinqing Zhan. 2022. "Sensor Distribution Optimization for Composite Impact Monitoring Based on AR Model and LPP" Machines 10, no. 12: 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121154
APA StyleLi, P., Tan, J., Ding, Y., Huang, P., Tang, G., & Zhan, J. (2022). Sensor Distribution Optimization for Composite Impact Monitoring Based on AR Model and LPP. Machines, 10(12), 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121154






