Abstract
The deviation of conveyor belts is a key factor that restricts material conveying efficiency of horizontal curves. An evaluation system of the deviation state of curve conveyor belt based on the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model is proposed in this study to investigate the deviation state of the conveyor belt. This system has been used for detection, prediction, deviation correction, and early warning of the conveyor belt deviation state. First, the experiment system of the conveyor belt deviation was built. The conveyor belt deviation images were collected using the machine vision method, and the conveyor belt deviation state data set was established. Second, the mechanical model of curve conveyor belt deviation is presented and solved. The correctable deviation range of the idler frame under different elevations and trough angles was obtained by solving the problem. Third, the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model of conveyor belt deviation based on series-parallel weighing method was put forward. The analysis results showed that the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model is suitable for the prediction of conveyor belt deviation in terms of accuracy, fitting degree, time, and performance. Finally, the deviation state evaluation system was established to realize the visual fusion of the ARIMA–LSTM combined model in the range of correctable deviation of the idler frame. The OCSVM algorithm was used to detect the abnormal deviation of the conveyor belt. The experiment shows that the evaluation system can predict and send out early warning signals according to the detection results, provide corresponding suggestions for adjusting the deviation correction angle, and realize an efficient and intelligent solution for the evaluation of the curved section belt deviation state.
1. Introduction
The horizontal curve belt conveyor has become one of the main pieces of continuous conveying equipment in the field of coal mine and other industrial production because of its characteristics of long distance, large capacity, and high-efficiency conveying. Different from the straight section belt conveyor, the conveyor belt in the curved section turns naturally under the combined force of tension, support force, centripetal force, and other forces. Research shows that the key to improving the material conveying efficiency is to reduce the belt deviation in the curve section [1,2,3,4,5]. However, the deviation phenomenon typically occurs in conveyor belts of some practical projects due to the installation error of the conveyor, manufacturing error, material distribution characteristics, and idler failure [6,7]. The conveyor belt will cause the material to pour after it deviates. Friction between the conveyor belt and roller idler intensifies, and the service life of the conveyor belt roller and idler significantly reduces. Belt deviation may even trigger an emergency stop switch to reduce the delivery efficiency of the system [8,9]. The research shows that most of the faults of the horizontal curve belt conveyor are caused by the belt deviation first. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the deviation state of the conveyor belt at the curved section.
At present, deviation detection of the conveyor belt can be divided into two types: contact and noncontact. Contact deviation detection involves the installation of deviation sensors on racks at both sides of the conveyor belt [10,11]. The sensor will trigger the first-stage knob of the deviation stroke switch and send out an alarm signal when the conveyor belt touches it. Meanwhile, the sensor will trigger the second-stage knob and emergency stop switch button when the conveyor belt continues to deviate. The structure and principle of the deviation device are simple. Sensors are often affected by environmental factors and fail to work due to rust. The machine vision is typically utilized in investigating the noncontact deviation of the conveyor belt. Yang et al. [12] used linear CCD to collect conveyor belt images and detected the edge of the conveyor belt using an image segmentation algorithm to obtain the deviation of the conveyor belt. Yang et al. [13] proposed the gray average method to realize the fast segmentation of the conveyor belt and background. The change rule of the binary image was explored to realize the deviation detection of the conveyor belt. Wang et al. [14] put forward an improved Canny operator detection and morphological processing to detect the edge of the conveyor belt and applied Hough linear detection to locate the conveyor belt. However, the image processing method is complex and impractical. Zhang et al. [7] established a laser-aided method to judge the deviation of the conveyor belt. Although the method of conveyor belt deviation detection based on deep learning introduced by Liu et al. [15] shows superior performance in reliability and anti-interference ability, its calculated deviation degree (DD) error is large. Zhang et al. [16] solved the problem of fast extraction of the edge features of conveyor belt and analysis of the deviation of the conveyor belt under complex backgrounds by improving the target detection network YOLOv5. Based on the detection method, it can be further expanded.
Many scholars have introduced machine learning algorithms into the fault prediction of belt conveyor on the basis of fault detection technology to obtain relevant fault information from the running state of conveyor and forecast the future fault trend. Agata et al. [17] carried out nondestructive testing of conveyor belts using the DiagBelt system and predicted the remaining life of the conveyor belt on the basis of the linear regression model. Hu et al. [18] established the prediction model of belt conveyor faults on the basis of gray least squares support vector machines and applied it to the prediction and early warning of belt conveyor fault characteristic parameters. Liu et al. [19] fused the information of conveyor running state, reliability estimation of idlers, and state detection data to realize the predictive maintenance of the belt conveyor system. Mei et al. [20] put forward an image enhancement algorithm for detecting the edge of the conveyor belt, calculating the DD of the conveyor belt, and estimating and predicting the deviation of the conveyor belt.
To sum up, existing machine vision methods have been successfully used to detect the deviation of conveyor belts in terms of detection speed and performance. However, studies on the prediction and correction of conveyor belt deviation are limited, and ensuring the correction effect of conveyor belt deviation in the curve section is difficult. To ensure the efficient conveying of the conveyor belt at the curve section, this study establishes an evaluation system for the deflection state of the conveyor belt at the curve section based on the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model, evaluates the state of the conveyor belt and puts forward predictive suggestions. This study provides an efficient and intelligent solution for deviation detection, prediction, early warning, and deviation correction of the curve belt conveyor.
2. Construction of Conveyor Belt Deviation Experimental System
2.1. Conveyor Belt Deviation Measurement Test Bed
Figure 1 shows the conveyor belt deviation measurement test bed built in this study to establish the deviation data set of the conveyor belt in the curve section. The image of conveyor belt deviation in the curve section was collected via the machine vision method, and the data were analyzed. The conveyor belt is in the process of dynamic change while running, and directly measuring the deviation of the conveyor belt is impossible. However, the length change of the uncovered idler of the conveyor belt can be measured, and the deviation of the conveyor belt can be obtained indirectly from the length of the bare idler. Adjusting camera bracket 4 can move HD camera 3 in two directions. Camera support 6 is used to adjust the distance at which the high-definition camera acquires the image of the target idler. The portable computer 5 collects and analyzes data of the idler length image obtained by the camera.
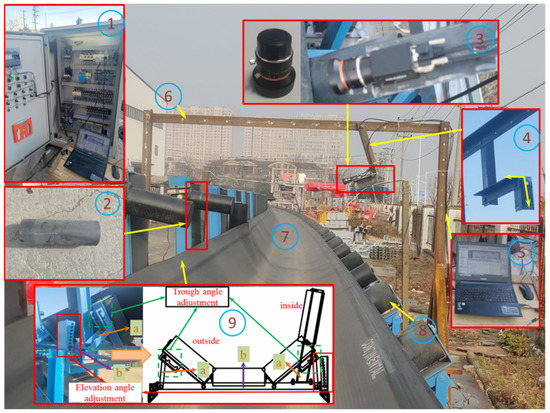
Figure 1.
Conveyor experimental station: (1) Control box; (2) Test idler; (3) HD camera; (4) Adjustable camera support; (5) Laptop; (6) Camera base; (7) Conveyor belt; (8) Carrying idler; (9) Correction device; a: Support frame 1; b: Support frame 2.
The correction device 9 is used to adjust the angle of the test platform, including the support frame 1 (purple arrow in the figure, a) and the support frame 2 (orange arrow in the figure, b). The red box is used to adjust the angle of the elevation angle, and each hole represents 1°. Fix the support frame 1 to the target elevation angle through bolts to complete the elevation angle adjustment. The green box is used to adjust the angle of the trough angle, which can be adjusted by 3 angles. The technician moves the support frame 2 into the trough of the corresponding angle to complete the trough angle adjustment.
The length of the idler is measured by the camera in this experiment. Camera brackets are set up immediately and placed at the head (entering curve section), middle (midpoint), and tail (exiting curve section) parts to collect the image of the length change of the idler as the conveyor is running. The basic parameters of the conveyor belt deviation measurement test platform are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic parameters of test platform.
2.2. Deviation Data Acquisition
Experimental data on conveyor belt deviation were acquired through the professional visual software Vision Master (VM). The length detection process of the idler image shown in Figure 2 is divided into two stages. The change in idler length is regarded as the change of conveyor belt deviation in the first stage. The industrial camera continuously extracts an image, including the edge of the conveyor belt and the length of the exposed idler for a while, and performs gray processing. The length of the bare idler was calculated according to the coordinates of the bare idler obtained from the region of interest (ROI) of the idler in the second stage.
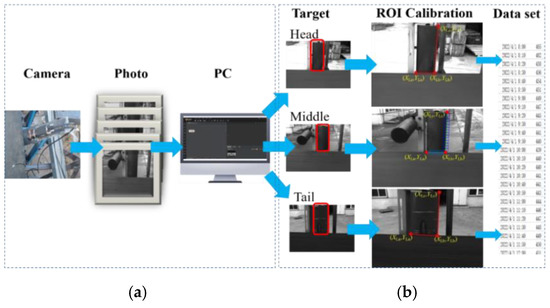
Figure 2.
Idler length acquisition: (a) Phase 1: Image calibration; (b) Phase 2: ROI extraction and calculation.
Considering that different image pixels at the same point may produce distortion in the acquisition process, the average ratio brate between the idler width in all images and the actual idler width was obtained using Equation (1). The actual idler length was calculated using Equation (2).
where lr is idler diameter, and XLmi, YLmi is corner pixel horizontal and vertical coordinates, m = a, b, c. i = 1, 2, …, n.
2.3. Determination of Deviation Detection Position
Equation (1) shows that values of the head, middle, and tail of the curve section are 2.7163, 2.6978, and 3.8465, respectively. The deviation of the conveyor belt in the head, middle, and tail during a working time of 800 s based on Equation (2) is shown in Figure 3. The deviation at the tail of the conveyor belt is larger than that at the middle and head parts under working condition. The maximum deviation to the outside of 18.9611 mm appears in the acceleration stage when the belt speed is 4–5 m/s. The maximum deviation from the middle to the inside of 25.4807 mm appears in the acceleration stage when the belt speed is 3–4 m/s. The maximum deviation to the outside of 13.2936 mm appears in the deceleration stage when the belt speed changes from 5 m/s to 4 m/s. The maximum deviation of the tail to the inside of 44.6203 mm appears in the deceleration stage when the belt speed is 2–3 m/s. The maximum deviation to the outside of 14.1189 mm appears in the deceleration stage when the belt speed changes from 5 m/s to 4 m/s. The maximum deviation of the curve belt conveyor used in this experiment is 60 mm. The limit deviations of the tail, middle, and head conveyor belts are 58.7392, 38.7743, and 39.4459 mm, respectively. The tail of the curve section is prone to free and easy materials in the long-term conveying process. Therefore, the tail of the curve section is used as the collection place of the deviation position of the conveyor belt.
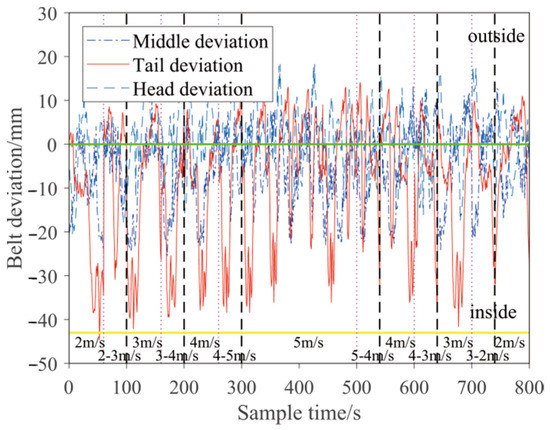
Figure 3.
Head, middle and tail belt deviation status.
3. Establishment of Mechanical Model of Conveyor Belt Deviation in the Curve Section
3.1. Force Equilibrium Equation
A small arc in the curved section was taken as the separation body for force analysis [2,3], and the force of the idler frame is shown in Figure 4a. Forces on the idler frame include the resultant force of belt tension Ftc, conveyor belt and material gravity FG, conveyor belt centrifugal force FQ, supporting force of the idler on the conveyor belt FN, and lateral friction between idler and conveyor belt FR. An included angle exists between the front-end tension T and the back-end tension T + ΔT of the conveyor belt in the curve section. The resultant force Ftc directed to the inside of the conveyor belt is shown in Figure 4b. If Ftc > FN + FR + FQ holds, then the belt will shift to the inside curve [21]. A large radius allows for the centrifugal inertia force to account for a small proportion of the total resultant force when solving the force of the idler group. To simplify the calculation, the centrifugal inertia force is often ignored.
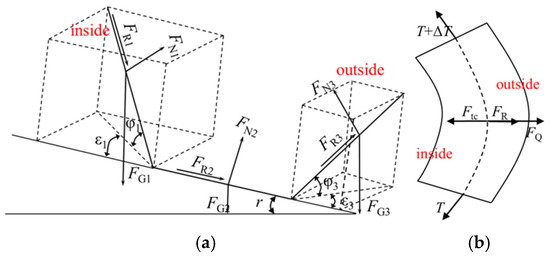
Figure 4.
Force analysis diagram. (a) Force of idler group. (b) Force of belt unit.
The resultant force of belt tension is as follows.
Approximate instead of , then . Ignore the second-order differential variables . The above Equation is simplified as follows.
where T is belt tension, is idler spacing, and R is curve radius.
Conveyor belt and material gravity is as follows.
where is mass of handled material per meter. , Q is Conveying capacity. v is belt speed. is the mass of conveying. g is gravitational acceleration, g = 9.8 m/s2. is material gravity distribution coefficient. is belt mass gravity distribution coefficient. i is idler number.
Each force of the conveyor belt in the curved section as well as the belt tension T reduces under no-load working conditions. The three idlers only bear the gravity of the conveyor belt, but ignore the material gravity distribution coefficient Ki. The gravity of the conveyor belt is expressed as follows.
The supporting force of idler to the conveyor belt is
where is trough angle, and r is elevation angle.
The lateral friction force between the idler and conveyor belt is defined as follows.
where is the transverse friction coefficient.
The XY coordinate system is established with the middle idler frame, the X-axis points to the outside of the conveyor belt, and the Y-axis is perpendicular to the ground. Projecting the support force of the idler to the conveyor belt FNi and the friction force of the idler to the conveyor belt FRi on the X-axis is necessary to balance the resultant force Ftc in the negative direction of the X-axis. The projected support force on the X-axis is expressed as follows.
where is the front inclination angle of the idler.
Transverse friction projected on the X-axis is expressed as follows.
Equations (3) and (16) are combined to establish the balance equation of the conveyor belt containing the gravity distribution coefficient on the X-axis of the curved section comprehensively as follows.
3.2. Material and Conveyor Belt Gravity Distribution Coefficient
K is the unknown material gravity distribution coefficient in FN and FR in Equation (17). The useful contact length b of material is calculated according to the horizontal area A of the material on the conveyor belt, as shown in Figure 5a. The vertical area S of the material on the three idlers is then calculated to obtain the gravity distribution coefficient of the material. The stacking section of materials in the curve section changes in different cross-section shapes because of different conveying materials. Here, assuming that the material section at the curve section remains unchanged, the contact length between the material and the conveyor belt is calculated when the material is running b, as shown by the red line in Figure 5b.
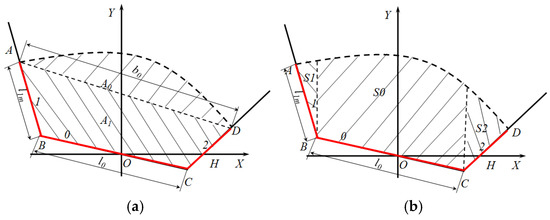
Figure 5.
Material section. (a) Horizontal section. (b) Vertical section.
The total cross-sectional area of the materials during operation is expressed as follows.
where is material loose bulk density.
The area of each horizontal section is calculated as follows.
where is material dynamic accumulation angle. is the maximum length of the horizontal section of material, and is useful to contact length of materials on side idlers.
Only an unknown quantity b exists in Equation (23), and the contact length b of the contact material on the conveyor belt can be obtained. Coordinates of A, B, C, D, and H in Figure 3 are translated according to Equation (24) to (33). The material section equation is then solved according to Equation (39), and the vertical area S of the material is subsequently calculated using Equation (40) to (42). The gravity distribution coefficient of materials on each idler is determined according to the vertical area of materials.
The material arc section equation y = f(x) and its radius can be obtained through the following coordinates.
Arc center coordinate is expressed as follows.
where is arc center angle.
Material section equation is presented as follows.
The cross-sectional area of the material on each idler is expressed as follows.
The gravity distribution coefficient of the material on the idler is calculated as follows.
The relationship of material gravity distribution coefficient is satisfied as follows.
The gravity distribution coefficient of the belt on the idler is expressed as follows.
where , .
The theoretical mechanical model for solving the deviation of the curved conveyor belt was established. Inside Δi and outside Δo deviations were simultaneously solved using Equations (17) and (44), respectively. According to previous design experience, the deviation on the material side is about half of the overall deviation of the conveyor belt to ensure that the deviation of the conveyor belt is Δi + Δo.
3.3. Model Validation
The calculation results of the maximum theoretical deviation of multigroup conveyor models in Refs. [22,23,24] are listed in Table 2 to verify the feasibility and correctness of Equations (17) and (44) further. The calculation results of the deviation mechanics model satisfy the maximum allowable deviation of the conveyor belt, thereby verifying the feasibility of the deviation mechanical model.

Table 2.
Multi-group system verification.
Yang et al. [25] used five idler sets to calculate the belt deviation in the curve section at 52.6403 mm. The deviation of the conveyor belt with three idlers calculated in this study using the deviation mechanical model is 49.1415 mm, with an error of 4.998%, under the same working condition. Tian [26] calculated a maximum deviation of the conveyor belt of 41 mm under the working conditions of a trough angle of 35° and an elevation angle of 5°. The deviation of the conveyor belt calculated by the proposed model is 39.8313 mm, with an error of 2.025%. This finding demonstrates that the deviation mechanical model is correct and feasible.
3.4. Correction Deviation Range of Idler Frame Angle
The engineering investigation revealed that adjusting the angle of the idler frame is an effective measure to solve the deviation of the conveyor belt in the curve section. The correct deviation range of the idler frame includes the maximum deviation, corresponding to different angles of the idler frame. An appropriate adjustment angle can correct not only the deviation of the conveyor belt but also reduce energy consumption. Hence, adjusting the priority of elevation and trough angles before establishing the correctable deviation range of the idler frame is necessary.
Trough and elevation angles in the deviation mechanical model are set as unknown quantities in this study when the method of controlling a single variable is used. The basic parameters of the conveyor belt deviation measurement test bed in Table 1 are substituted to Equations (17) and (44). The analysis results of the influence of the idler frame angle on the correction amount of conveyor belt deviation are shown in Figure 6. Figure 6a presents the relationship between the deviation correction amount of the conveyor belt and the elevation angle under the load condition of the idler frame. The increase of elevation angle is nearly linear and presents a positive correlation with the correction amount of the conveyor belt deviation. The correcting effect of the elevation angle on the conveyor belt is higher when the trough angle is 45°, compared with that at 25° and 35°. Figure 6b illustrates the relationship between the deviation correction amount of the conveyor belt and the elevation angle under no-load working conditions. The rectifying ability of the idler frame decreases gradually with the increase of the trough angle because the trough angle can automatically center, and this centering ability increases with the increase of the angle.
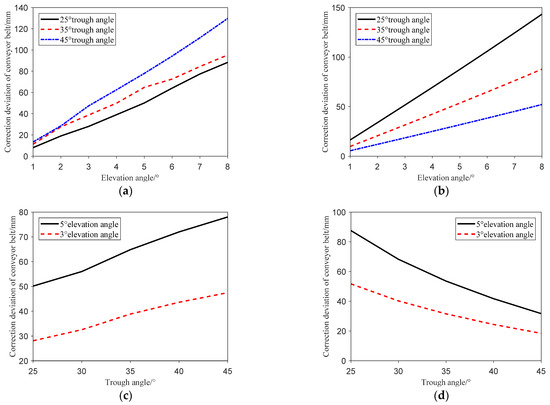
Figure 6.
Relationship between belt deviation and angle under different working conditions. (a) Elevation angle and deviation under load (b) Elevation angle and deviation under no-load. (c) Trough angle and deviation under load (d) Trough angle and deviation under no-load.
Figure 6c depicts the relationship between the deviation correction amount of the conveyor belt and the trough angle under the load condition. The trough angle is approximately, linearly, and positively correlated with the deviation correction amount. The correction amount of conveyor belt deviation is 27.9029 mm under the condition of an elevation angle of 5°. The correction amount of conveyor belt deviation is 19.3501 mm under the condition of an elevation angle of 3°. The trough angle poorly corrects the deviation of the conveyor belt and shows a linear negative correlation trend under the no-load condition (Figure 6d). The correction amount of conveyor belt deviation is 55.917 mm under the condition of an elevation angle of 5°. The correction amount of conveyor belt deviation is 33.204 mm under the condition of an elevation angle of 3°.
In the mechanical model of conveyor belt deviation, the calculation is forward, but it is the opposite in practice. Hence, adjusting the angle of the idler frame is necessary to ensure the normal transportation of materials because the conveyor belt deviated. The relationship between the amount and angle of conveyor belt deviation can be corrected using the idler frame under different working conditions (Figure 6). The correction effect of the elevation angle on conveyor belt deviation is more evident than that of the trough angle. Therefore, adjusting the elevation angle first is recommended when correcting the deviation under actual working conditions. On this basis, the deviation amount of different elevation and trough angles is solved in the deviation mechanical model, and the correctable deviation range of the idler frame under different idler angles is presented in Table 3. These results can provide data for future investigations on the deviation state evaluation system.

Table 3.
Deviation range of the idler angle correction.
4. Establishment of the Prediction Model of Conveyor Belt Deviation
Prediction methods commonly used in machine learning include Prophet, RNN, ARIMA, and LSTM [27,28,29,30]. The Prophet model is commonly used for general trend prediction despite its low accuracy. The susceptibility of the RNN model to the phenomenon of gradient explosion in the process of calculating the gradient of training set leads to a significant difference between the predicted value of the conveyor belt deviation and the actual value. Thus, the RNN model fails to predict the conveyor belt deviation for a long time. However, ARIMA and LSTM present satisfactory accuracy and prediction performance in time series. Therefore, data on conveyor belt deviation in Section 1 are used as training samples of the prediction model in this work, and a prediction model suitable for conveyor belt deviation based on the ARIMA and LSTM prediction models is established.
4.1. ARIMA Prediction Model
Deviation data present a nonlinear trend in the case of conveyor failure because the deviation of the conveyor belt is subject to manual intervention, component life, material characteristics, and other factors during the operation of the conveyor. The auto regressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model presents excellent advantages in processing nonstationary time series data [29]. The parameter p is the autoregressive (AR) term that represents the lag of time series in conveyor belt training concentration, because ARIMA (p, q, d) improves the ARMA (p, q) model. The parameter d is the difference term that represents the order of the time series that differed. The parameter q is the moving average (MA) term that represents the lag of the prediction error. The ARIMA prediction model forecasts the deviation value of the conveyor belt using the sum of the weighted sum of the deviation value indicated at the latest time and the prediction error at the latest time. ARIMA is expressed as follows.
where t is the time value, is the AR coefficient, is the MA coefficient, and is the prediction error.
Deviation data (70%) of the conveyor belt at the tail of the curved Section 1 are taken as the training sample set of the ARIMA prediction model, and the remaining 30% is used as the test sample set. Detecting the stability of the actual deviation training set of the conveyor belt is necessary before using the ARIMA prediction model. The mean standard deviation of the actual deviation training set and the unite root method determines whether the data are stationary time series. The results are shown in Figure 7a. The rolling mean and standard deviation of the length fluctuates randomly up and down within a range. Therefore, the time series data set is initially considered stable. The unit root method is used to determine stable data, and the results are listed in Table 4. The p-value is significantly less than the critical values at 1%, 5%, and 10%. Therefore, processing the data smoothly is unnecessary because conveyor belt data in this experiment are stable at the 99% confidence interval.
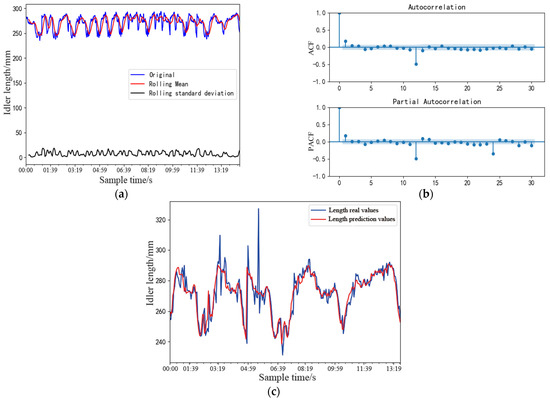
Figure 7.
ARIMA prediction method. (a) Stable series (b) ACF and PACF order. (c) Actual idler length prediction results.

Table 4.
Unit root method.
Orders p and q of the ARIMA prediction model are determined using tailing characteristics of the autocorrelation (ACF) and partial correlation (PACF) coefficient images of stationary time series, as shown in Figure 7b, with p = 1 and q = 1. Finally, the predicted value of the ARIMA prediction model is subjected to differential reverse reduction to obtain the actual idler length value, as shown in Figure 7c. The predicted results of the ARIMA model for the idler length are nearly consistent with the measured data, but the underfitting state also ignores the abnormal deviation. Hence, the ARIMA prediction model is only suitable for forecasting linear data sets because data loss may occur when used in nonlinear data sets. Note that predicting the deviation of the conveyor belt with only a single ARIMA model is impossible.
4.2. LSTM Prediction Model
Long short-term memory (LSTM) is an improvement of RNN that solves the problem of gradient disappearance and explosion in long time series training [25]. LSTM is calculated as follows.
where is input gate, is forgotten gate, is cell status, is output gate, W is weight coefficient matrix, b is offset, is the sigmoid function, tanh is the tangent function, and is the final prediction results.
LSTM determines the output value of each forward unit through Equations (47)–(51) and then reversely calculates the error of each unit. The gradient of the weight matrix is calculated according to the error calculated at the upper level. The weight matrix is optimized through the Adam optimization algorithm, and the iterative method is used for point-by-point prediction.
Deviation data of the conveyor belt (80%) at the tail of the curved Section 1 are taken as the training sample set of the LSTM deviation prediction model, and the remaining 20% is used as the test sample set. Figure 8a–c present the prediction results of conveyor belt deviation via LSTM, three-step LSTM, and multi-LSTM models, respectively. Figure 8c illustrates that the multi-LSTM prediction model is unsuitable for determining the fitting degree and prediction effect and exhibits an over- or underfitting state. The fitting results of LSTM and three-step LSTM are consistent with the measured values. However, the weak local fitting effect of the short prediction sequences requires further improvement.
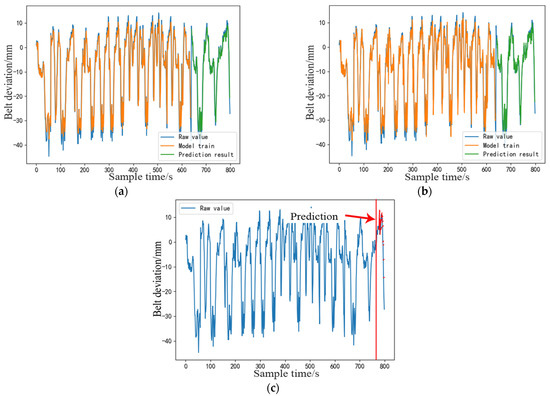
Figure 8.
LSTM prediction method. (a) LSTM. (b) Three-LSTM. (c) Multi-LSTM.
4.3. ARIMA–LSTM Combined Prediction Model Based on Series–Parallel Weighting
According to the prediction results in Section 4.1 and Section 4.2, the ARIMA and LSTM models can complete basic prediction with some defects. On this basis, the ARIMA and LSTM prediction model is recombined in this work using series-parallel weighting. The error term of the ARIMA model is revised and predicted through the LSTM model. The revised predicted value of the ARIMA model and the predicted value of the LSTM model are then weighted and summed via the parallel connection. Finally, the predicted value of conveyor belt deviation is obtained after modified combined weighting. The calculation method of the ARIMA–LSTM combined forecasting model is presented as follows.
where is the predicted value of the combined model, are the weighting coefficients of LSTM and ARIMA prediction models, and . and are the predicted values of the LSTM and ARIMA prediction models at time t.
The prediction error of the combined prediction model is expressed as follows.
where is actual value of belt deviation. , are the prediction errors of the LSTM prediction model and ARIMA prediction model at time t, respectively.
The squared value of the prediction error is calculated as follows.
The sum of squares of prediction errors of the combined model is assumed as follows.
The weighted coefficient vector of the combined prediction model is expressed as follows: . The error matrix is presented as follows.
where , .
The sum of squares of prediction errors of the combined model is calculated as follows.
Unit column vector is as follows: . The constrains of weighting coefficients are determined as follows.
If the error variance of the combined forecasting model reaches the minimum under the constraint condition, then its minimum value is expressed as follows.
Both sides of Equation (59) are multiplied by to solve under minimum variance, where .
Equations for solving the weighting coefficient and the sum of squares of prediction errors are expressed as follows.
The prediction deviation value of the conveyor belt at time t can be obtained by substituting into Equation (52). The ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model based on series-parallel combined weighting is shown in Figure 9, where X represents the input data of conveyor belt deviation, C represents the state of LSTM cells at the current time, H represents the hidden output of LSTM cells at the current time, and P represents the data output.
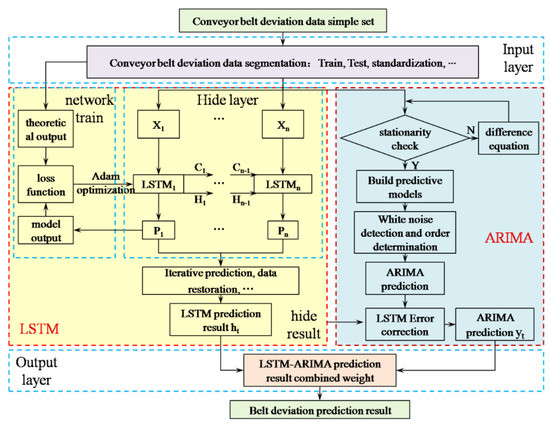
Figure 9.
ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model.
The composite model is completely established in a Python environment. Deviation data of the conveyor belt (80%) at the tail of the curved Section 1 are taken as the training sample set of the combined prediction model, and the remaining 20% is used as the test sample set. The prediction results of the combined model are shown in Figure 10. The fitting curve of the combined model is closer to the actual value, and the local prediction curve has not been fitted or under fitted. The combination prediction model retains the advantages of the ARIMA and LSTM models to predict the deviation trend of the conveyor belt in the curve section accurately.
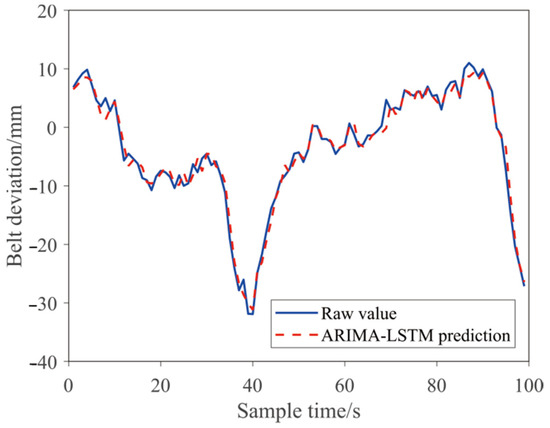
Figure 10.
ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction method.
4.4. Comparison of Fitting Degree of Different Prediction Models
Figure 11a shows the loss function of the ARIMA–LSTM combined model, as well as RNN and LSTM models. The error degree between the RNN model and the measured value of conveyor belt deviation is larger than that of LSTM and the ARIMA–LSTM combined model. Figure 11b presents the fitting curve of the LSTM, ARIMA, and ARIMA–LSTM combined models with actual values. Figure 11c illustrates the error between predicted and actual values of the ARIMA, LSTM, and ARIMA–LSTM combined models. The error of the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model is smaller than that of the ARIMA and LSTM models. The results showed that the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model achieves higher prediction accuracy and stronger generalization ability than the single prediction model.
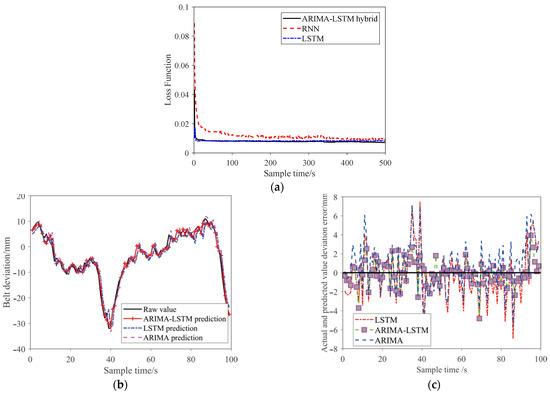
Figure 11.
Comparison of different prediction models. (a) Loss function. (b) Comparison with single and hybrid model. (c) Prediction error.
4.5. Performance Comparison of Different Prediction Models
Willmott et al. [31] demonstrated that mean absolute error (MAE) is a natural average error index that can describe the average error of model performance accurately. Chai et al. [32] indicated that root mean squared error (RMSE) can highlight the advantages and disadvantages of the prediction model. RMSE is very sensitive to sudden changes in the deviation between predicted and actual values of conveyor belt deviation and can reflect the prediction accuracy of conveyor belt deviation. RMSE is the key index of the conveyor belt deviation prediction model. MAE represents the average absolute error between predicted and actual deviation values of the conveyor belt and the basic index for investigating the deviation of the conveyor belt. Compared with a single performance index, scholars typically choose the combined performance index to reflect the performance of the prediction model comprehensively. RMSE and MAE are selected as evaluation indexes in this work. RMSE and MAE of the prediction model are calculated using Equations (62) and (63), respectively.
where is the actual belt deviation value, is the deviation prediction value of different prediction models, and n is the number of sample time points.
Figure 12 shows the MAE and RMSE values for different prediction models. The combination models of LSTM, three-LSTM, and ARIMA–LSTM demonstrate high precision in predicting the conveyor belt deviation. However, the prediction trend of the ARIMA–LSTM combined model shows a high fitting degree with the actual deviation trend. Meanwhile, RMSE is larger than MAE because RMSE amplifies the error between the predicted value of conveyor belt deviation and the actual value, while MAE reflects the actual error value. Therefore, small RMSE and MAE values of the prediction model indicate an enhanced prediction performance.
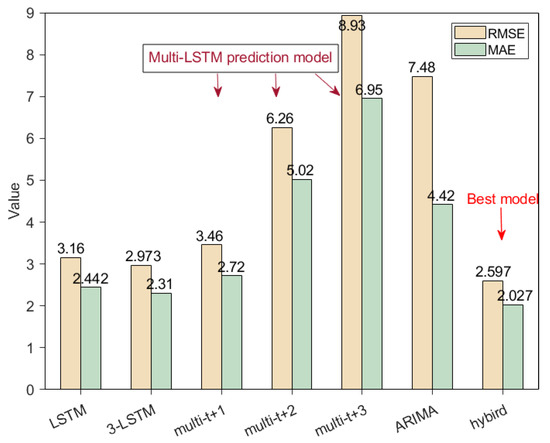
Figure 12.
Performance comparison of different prediction models.
Compared with the three-LSTM and LSTM models, the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model demonstrated a decrease in RMSE by 14.48% and 21.68% and MAE by 20.47% and 13.96%, respectively. Table 5 shows the comparison of the average error rate and the total time of the ARIMA, LSTM, and ARIMA–LSTM prediction models. The average error rate of the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model is significantly lower than that of other single prediction models. The average error rate of the ARIMA–LSTM model is 24.34% higher than that of the LSTM model. The ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model is suitable for predicting the deviation degree of the conveyor belt given its accuracy, fitting degree, time, and performance.

Table 5.
Comparison of accuracy and training time of different prediction models.
5. Establishment of Conveyor Belt Condition Evaluation System
5.1. Application of the Prediction Model in the Correctable Deviation Range
The correct deviation range of the idler angle obtained in Table 3 is fused with the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model to observe the distribution of conveyor belt deviation prediction results in the range of correctable deviation further (Figure 13). The pink line denotes the prediction result of the combined model at an elevation angle of 3°. The deviation degree of the conveyor belt exceeded the maximum deviation range allowed by the current angle of the idler frame when t is equal to 14 and 43 s. This feature may reduce the service life of the conveyor belt with the extension of working hours. Therefore, adjusting the angle of the idler frame in time is necessary to avoid a high degree of deviation of the conveyor belt. The black line in Figure 13 denotes the prediction results of conveyor belt deviation under an elevation angle of 5°. The limit deviation range of the conveyor belt is within the range of 5° and can be corrected, but the correction effect of the conveyor belt is achieved when the elevation angle is 4°. Therefore, reasonable suggestions for adjusting the angle are provided for detecting abnormal points in the prediction results.
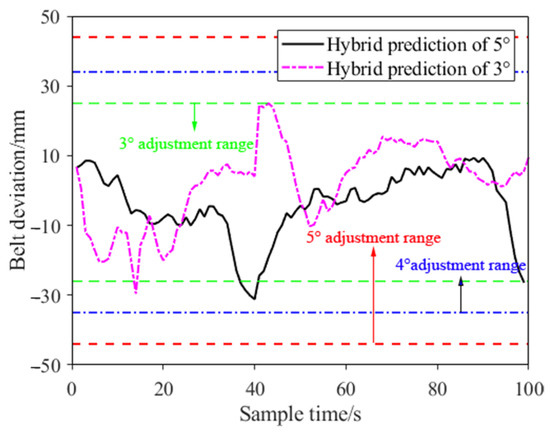
Figure 13.
Fusion of combined model and correctable deviation range (Green line is 3°adjustment range, blue line is 4°adjustment range, red line is 5°adjustment range).
5.2. Anomaly Detection of Conveyor Belt Deviation Based on OCSVM
Anomaly detection aims to identify irregularities. Common anomaly detection algorithms include local outlier factor (LOF) [33] based on density distribution, DBSCAN based on clustering [34,35], isolation forest (IF) based on the tree [36,37], and one class support vector machine (OCSVM) semi-supervised learning algorithm based on classification [38]. The standard of anomaly detection is different for each method. The basic idea of detecting conveyor belt deviation anomalies is to identify the prediction results via the combined prediction model. The conveyor belt deviation anomaly is a typical two-classification problem, that is, “normal” or “deviation.”
The OCSVM algorithm based on classification is utilized for detecting abnormal points of conveyor belt deviation in the prediction results. OCSVM was compared with IF, non-supervised (N-S) LOF, semi-supervised (S-S) LOF, and DBSCAN. Precision, recall, F1-score, and weight average are commonly used in anomaly detection. The evaluation results are shown in Figure 14. Figure 14a presents the evaluation index obtained after training the five detection methods in the case of a sample set of 800. Compared with IF, LOF, and DBSCAN, OCSVM presents the best detection performance, with evaluation indexes of 0.89, 0.94, 0.89, and 0.85. Figure 14b illustrates the evaluation index obtained when the test set is 100. The test results showed that OCSVM is better than other detection algorithms in the test samples and its evaluation index is 0.98.
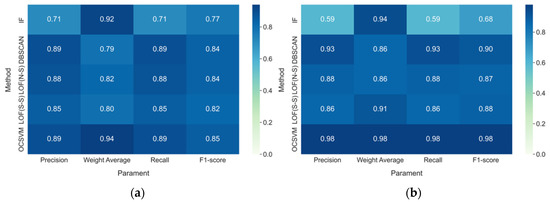
Figure 14.
Anomaly detection method. (a) Train (sample: 800). (b) Test (prediction sample: 100).
The detection of deviation anomalies of the conveyor belt from the deviation prediction results requires not only high accuracy of anomaly detection but also the very fast speed of anomaly detection. The total detection times of the five anomaly detection algorithms are listed in Table 6. The longest anomaly detection time of the unsupervised LOF algorithm is 11.56 s, while OCSVM only needs 1.849 s to detect outliers in the deviation prediction results accurately and rapidly. Therefore, the OCSVM algorithm can be applied to detect abnormal points of conveyor belt deviation accurately and efficiently in this study.

Table 6.
Time comparison of anomaly detection algorithms.
5.3. Establishment of Visual Interactive Interface
The interactive interface of the evaluation system for the deviation state of the curve conveyor belt is established in this work to observe the distribution of prediction results in the range of correctable deviation further and obtain intuitive suggestions for angle adjustment (Figure 15). The interactive interface includes real-time trend prediction, trend error distribution, conveyor status information, and early warning prompts. The conveyor belt deviation state evaluation system will constantly compare the deviation prediction results with the maximum correctable range of the current angle of the idler frame. If the abnormal algorithm fails to detect whether the maximum correctable range of the current angle of the idler frame has been exceeded, then it will indicate a prompt of “No need to adjust the angle for the time being!” The system will provide an early warning at the interface of “The conveyor belt has deviated. Please refer to the recommended angle adjustment value of the system.” when continuous abnormal points are detected and persistently exceed the maximum correction range of the idler frame. Technicians can adjust the angle of the idler frame in time according to the recommended angle adjustment suggestion prompted by the interactive interface. The visual interactive interface can reduce not only the labor intensity but also sufficiently shorten the time of adjusting the angle of the idler frame. This method provides an intelligent and efficient solution for deviation detection, prediction, early warning and deviation correction, and adjustment suggestions for the curve conveyor belt.
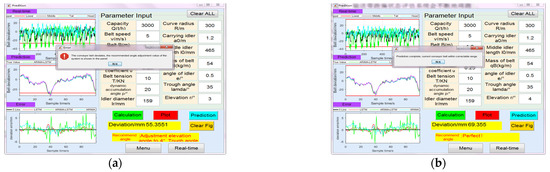
Figure 15.
Interactive interface. (a) Deviation of conveyor belt and early warning (b) Normal state of conveyor belt.
5.4. Experimental Verification
The feasibility of this method is verified with the help of the experimental platform, as shown in Figure 16. Figure 16a shows the deviation state of the conveyor belt under the actual operating conditions. The red line is the maximum acceptable deviation range, and the yellow line is the actual operating track of the conveyor belt. It can be seen that the conveyor belt has exceeded the currently acceptable maximum deviation range, and continuous operation will cause unpredictable damage to the conveyor system. At the same time, the deviation state evaluation method in this study (Figure 16b) also shows that the current angle is not suitable for continuous operation, and it is recommended to adjust the elevation angle to 4° to ensure the smooth operation of the horizontal curve belt conveyor. Figure 16c shows that the conveyor belt condition evaluation system prompts that the current elevation angle can correct the conveyor belt deviation after the elevation angle is adjusted to 4°. Figure 16d shows the deviation of the conveyor belt when the technician adjusts the elevation angle of the idler frame to 4°. The deviation range of the conveyor belt gradually returns to the correctable deviation range, which also proves the feasibility of the deviation state evaluation method in this study after 15–20 s of startup and operation.
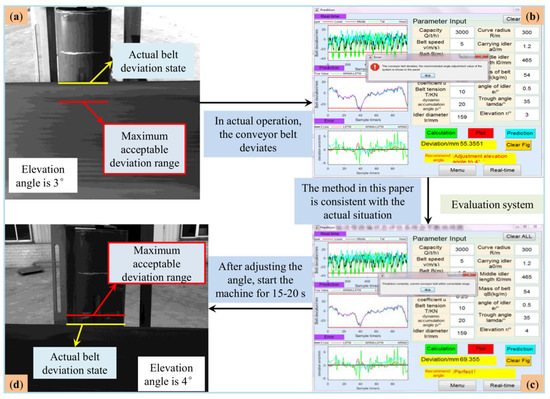
Figure 16.
Case analysis. (a) Conveyor belt status when not adjusted. (b) System calculation results. (c) System Recommendations. (d) Conveyor belt status after adjustment.
6. Conclusions
A state evaluation system of conveyor belt deviation based on the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model is established in this study to realize the state evaluation of the conveyor belt deviation in the curve section. The proposed system can predict and warn operators according to deviation detection data of the conveyor belt and provide intelligent and efficient suggestions for correcting the deviation angle adjustment. This work can help promote the efficient and intelligent development of the curved conveyor belt, reduce the production costs, and realize green and sustainable development. Compared with a previous study, the main contributions of this study can be summarized as follows.
(1) The correctable deviation range was established. The mechanical model of conveyor belt deviation in the curve section was established and verified in this work. The priority of angle adjustment of the idler frame was determined, and the range of deviation correction of the idler frame was established.
(2) The ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model was established. The ARIMA and LSTM models were combined through the series-parallel weighted method and their prediction performance was compared. The results showed that RMSE and MAE values of the combined prediction model reduced by 14.48% and 13.96%, respectively. Compared with LSTM, the average error rate increased by 24.34%. The ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model is suitable for the prediction of conveyor belt deviation in the curved section in terms of accuracy, fitting degree, time, and performance.
(3) The evaluation system of the conveyor belt deviation state in the curved section was established. The correct deviation range of the idler angle was combined with the ARIMA–LSTM combined prediction model in this system. The OCSVM algorithm was used to detect the abnormal deviation of the conveyor belt accurately and efficiently. A visual interactive interface was then established to realize the application and visual fusion of the combined prediction model in the correctable deviation range of the idler frame. The system can predict the belt deviation according to deviation detection data, send out a warning signal according to the prediction results, and provide the corresponding angle adjustment suggestion.
(4) The method in this study was verified by an experimental platform. The experimental results show that the method based on data prediction is feasible for the curved conveyor belt condition evaluation. This study provides an efficient and intelligent solution for the state evaluation of the curve belt deviation.
Author Contributions
This article was written by Y.W. who completed the manuscript, X.S. reviewed and edited the manuscript, and W.M. supervised it. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 52075356), Shanxi Province Graduate Education Reform Research Project of Shanxi (grant no. 2021YJJG257), and the School-level graduate education innovation project of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology (grant no. XCX212070, SY2022034).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
We declare that no conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
References
- Grimmer, K.-J.; Kessler, F. The design of belt conveyors with horizontal curves. Bulk Solids Handl. J. 1992, 12, 557–563. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, F.; Grabner, K.; Grimmer, K.-J. “bico-Tec” A new type of belt conveyor with horizontal curve. Bulk Solids Handl. J. 1993, 13, 741–747. [Google Scholar]
- Leberwirth, H. Design of belt conveyors with horizontal curves. Bulk Solids Handl. J. 1994, 14, 283–285. [Google Scholar]
- Tooker, G.E. Suspension idler is used in the horizontal curves. Bulk Solids Handl. J. 1988, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Du, H. Resistance Analysis of Belt Conveyor during Horizontal Turning Section. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 201–203, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lin, Y. Typical failure analysis and processing of belt conveyor. J. Procedia Eng. 2011, 26, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. Analysis for Controlling Belt Deviation in Conveyor System. Am. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. Surv. 2013, 1, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y. The present and future development of belt conveyer. J. Coal Mine Mach. 2004, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J. Research of mine conveyor belt deviation detection system based on machine vision. J. Min. Sci. 2021, 57, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miao, C.; Li, X.; Xu, G. Research on Deviation Detection of Belt Conveyor Based on Inspection Robot and Deep Learning. Complexity 2021, 2021, 3734560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Miao, C.; Li, X.; Mei, X. On-line conveyor belts inspection based on machine vision. Optik 2014, 125, 5803–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Miao, C.Y.; Kang, K.; Li, X. Machine vision inspection technique for conveyor belt deviation. J. North Univ. China Nat. Sci. Ed. 2012, 33, 667–671. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Dai, M. Belt vision localization algorithm based on machine vision and belt conveyor deviation detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 34rd Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC), Jinzhou, China, 6–8 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, M. A computer vision based conveyor deviation detection system. J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Edge Detection for Conveyor Belt Based on the Deep Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference, Wenzhou, China, 17–22 November 2018; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Jia, Y., Du, J., Zhang, W., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, K.; Cao, Y.; Li, M.; Hao, N.; Zhang, Y. A deep learning-based method for deviation status detection in intelligent conveyor belt system. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirjanów-Błażej, A.; Jurdziak, L.; Burduk, R.; Błażej, R. Forecast of the remaining lifetime of steel cord conveyor belts based on regression methods in damage analysis identified by subsequent DiagBelt scans. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 100, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zong, M. Fault Prediction Method of Belt Conveyor Based on Grey Least Square Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA), Beihai, China, 16–17 January 2021; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; He, D.; Lodewijks, G.; Pang, Y.; Mei, J. Integrated decision making for predictive maintenance of belt conveyor systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 188, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Miao, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Rapid inspection technique for conveyor belt deviation. J. Mech. Eng. Res. Dev. 2016, 39, 653–662. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Song, W.; Liu, J. Dynamic Design and Computer Imitation of Belt Conveyor with Horizontal Curves. Adv. Eng. Forum 2011, 2–3, 833–837. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, L. The Design and Application of Long Distance Belt Conveyor with Horizontal Curves. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xv, L.; Qiu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Hu, S. Design of turning radius of long distance belt conveyor of Changjiu Limestone Mine. Opencast Min. Technol. 2019, 34, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Study of Design Technology for Long Distance Horizontal Curve Belt Conveyor. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. Research on Design and Calculation Theory of Belt Conveyor with Horizontal Curves. Master’s Thesis, Northeastern University, Shenyang, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L. Research on Key Technologies of Long Distance Horizontal Turning Belt Conveyor. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, Taiyuan, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.; Fan, S. Probabilistic electric load forecasting: A tutorial review. Int. J. Forecast. 2016, 32, 914–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Du Yanli, N.I. Exploring LSTM based recurrent neural network for failure time series prediction. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2018, 44, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Kazemi, H.; Tahmasebi, P. A comparative machine learning study for time series oil production forecasting: ARIMA, LSTM, and Prophet. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 164, 105126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, M.; Li, R. Deep learning for household load forecasting—A novel pooling deep RNN. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5271–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?—Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breunig, M.M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Ng, R.T.; Sander, J. LOF: Identifying density based local outliers. In Proceedings of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Dallas, TX, USA, 15–18 May 2000; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 29, pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, Oregon, 2–4 August 1996; 96, pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hooshin, H.; Hanmid, S. A fast DBSCAN algorithm for big data based on efficient density calculation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 203, 117501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Ting, K.M.; Zhou, Z.-H. Isolation forest. In Proceedings of the 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Pisa, Italy, 15–19 December 2008; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Karczmarek, P.; Kiersztyn, A.; Pedrycz, W.; Al, E. K-means-based isolation forest. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 195, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.J.; Li, L.F. Robust least squares one-class support vector machine. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).