Design and Analysis of 6-DoFs Upper Limb Assistant Rehabilitation Robot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanism Design
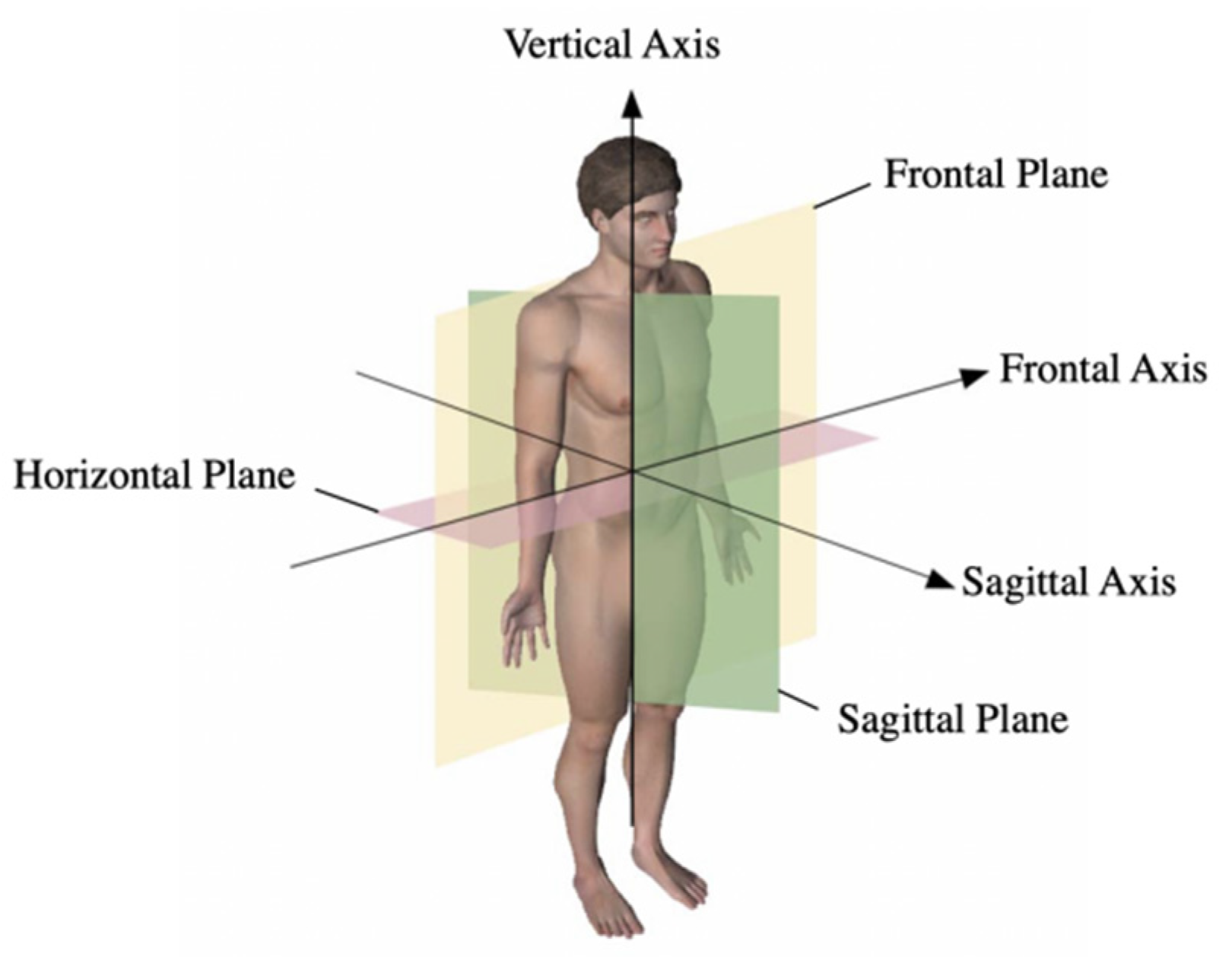
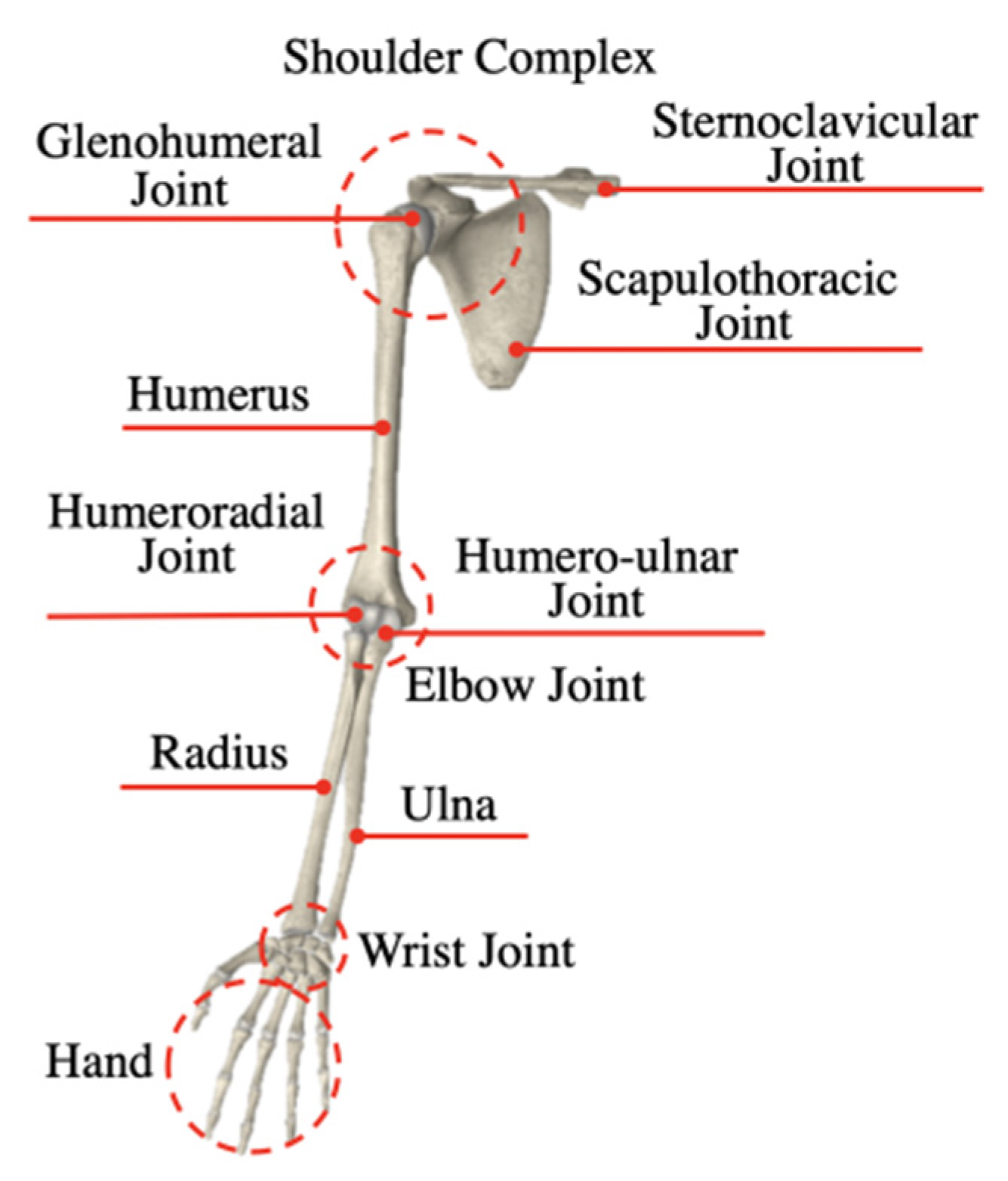
2.1. Analysis of Structure of Human Upper Limbs
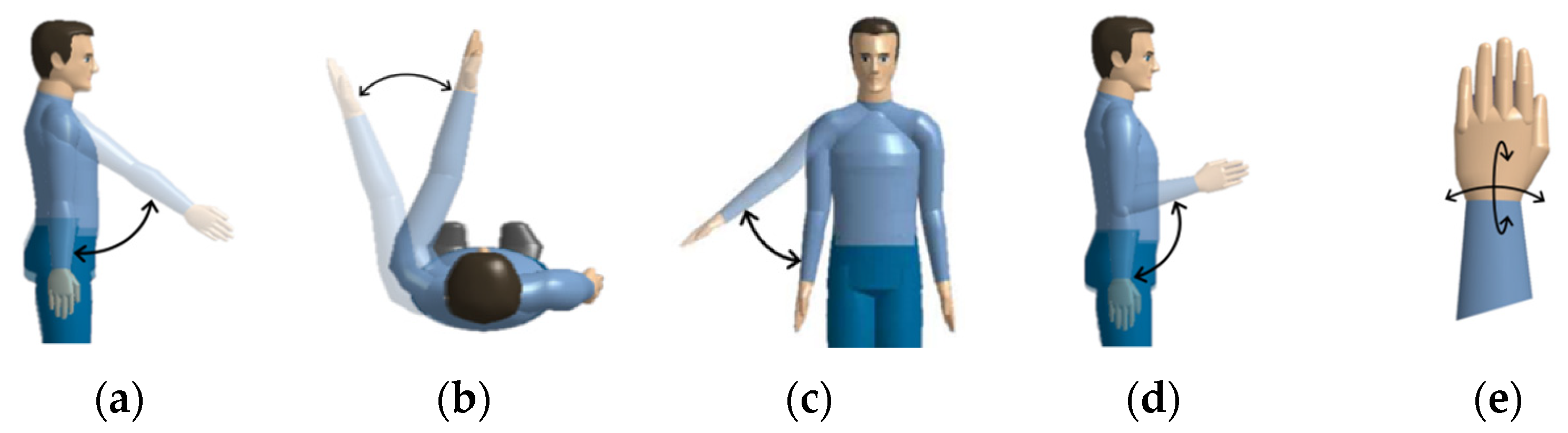
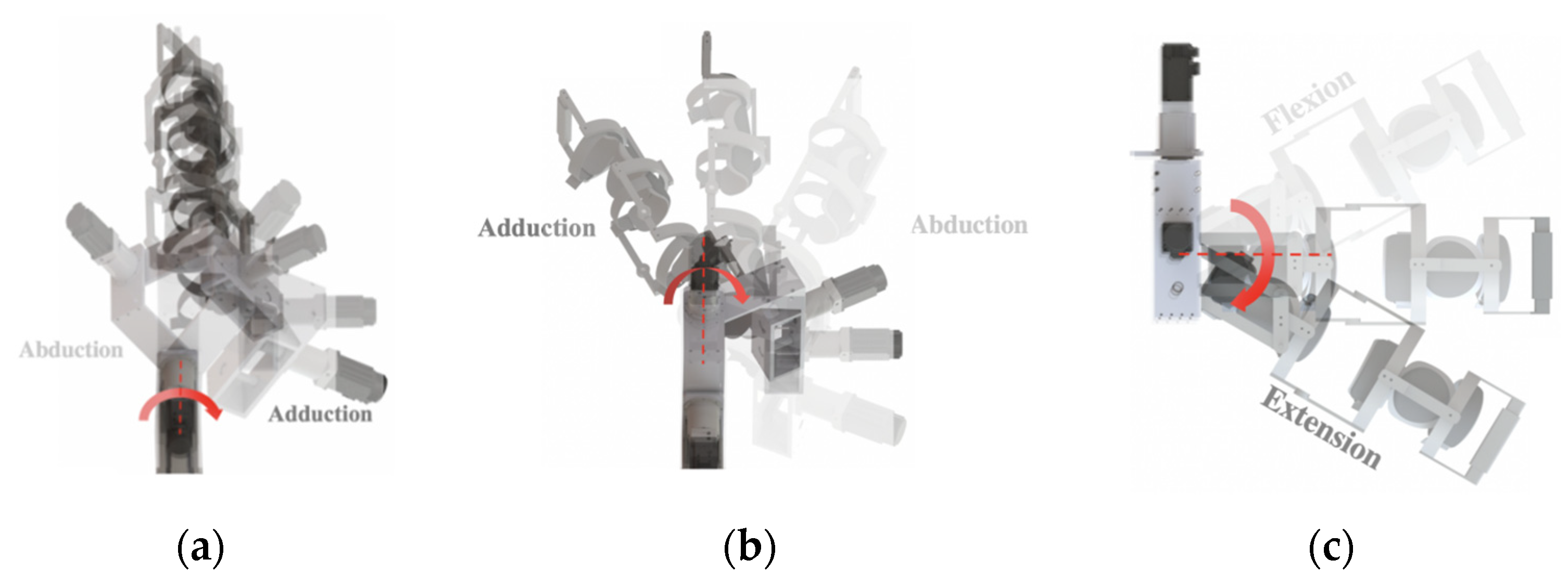
2.2. Analysis of Upper Limb Movement
2.3. Configuration Design
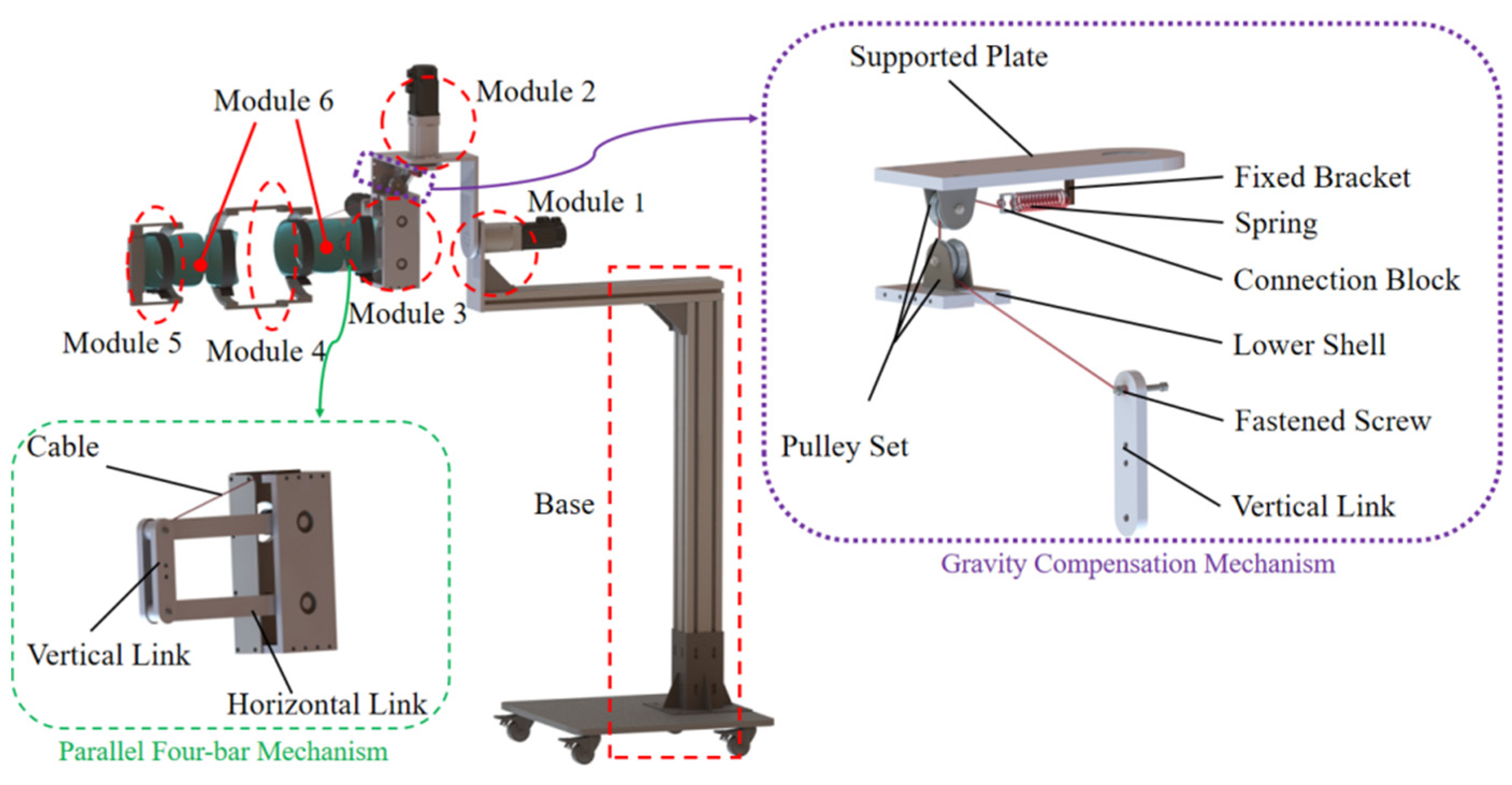
2.4. Overall Structure Design
3. Kinematics and Simulation of the ULRR
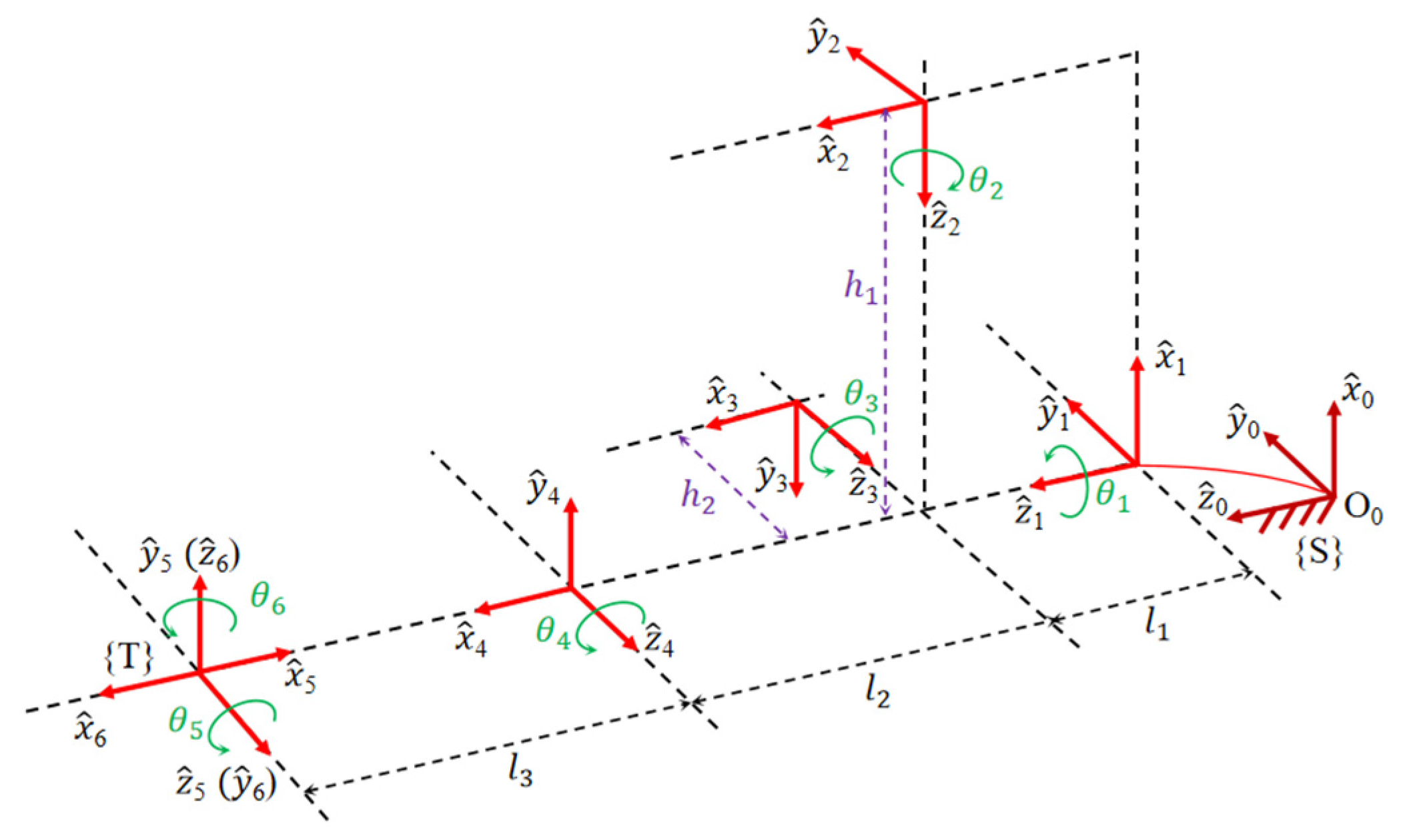
3.1. Kinematic Analysis
3.2. Simulation Analysis
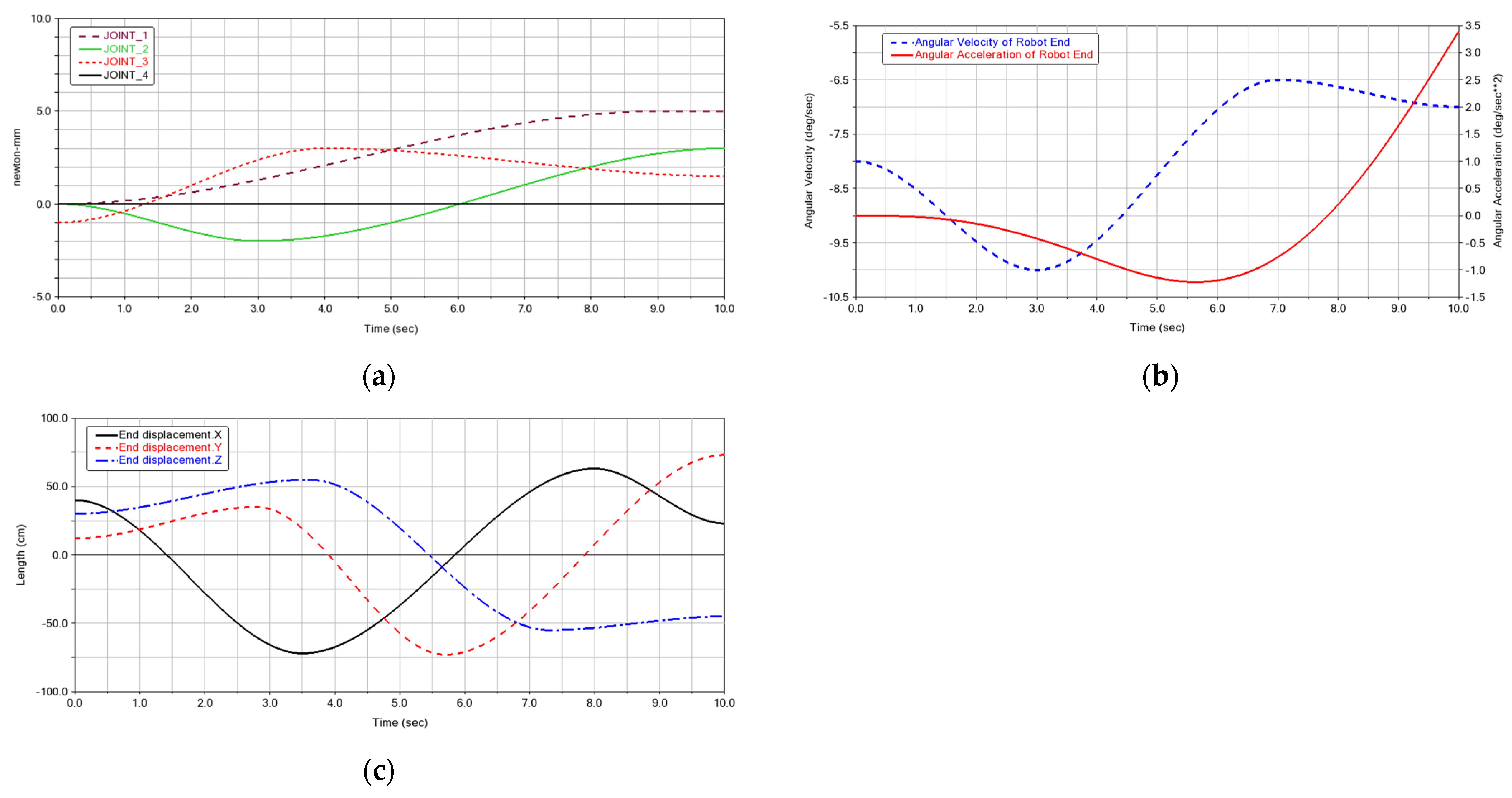
3.2.1. Feasibility and Stationarity Analysis
3.2.2. Verification of the Convenience of the Rehabilitation Process
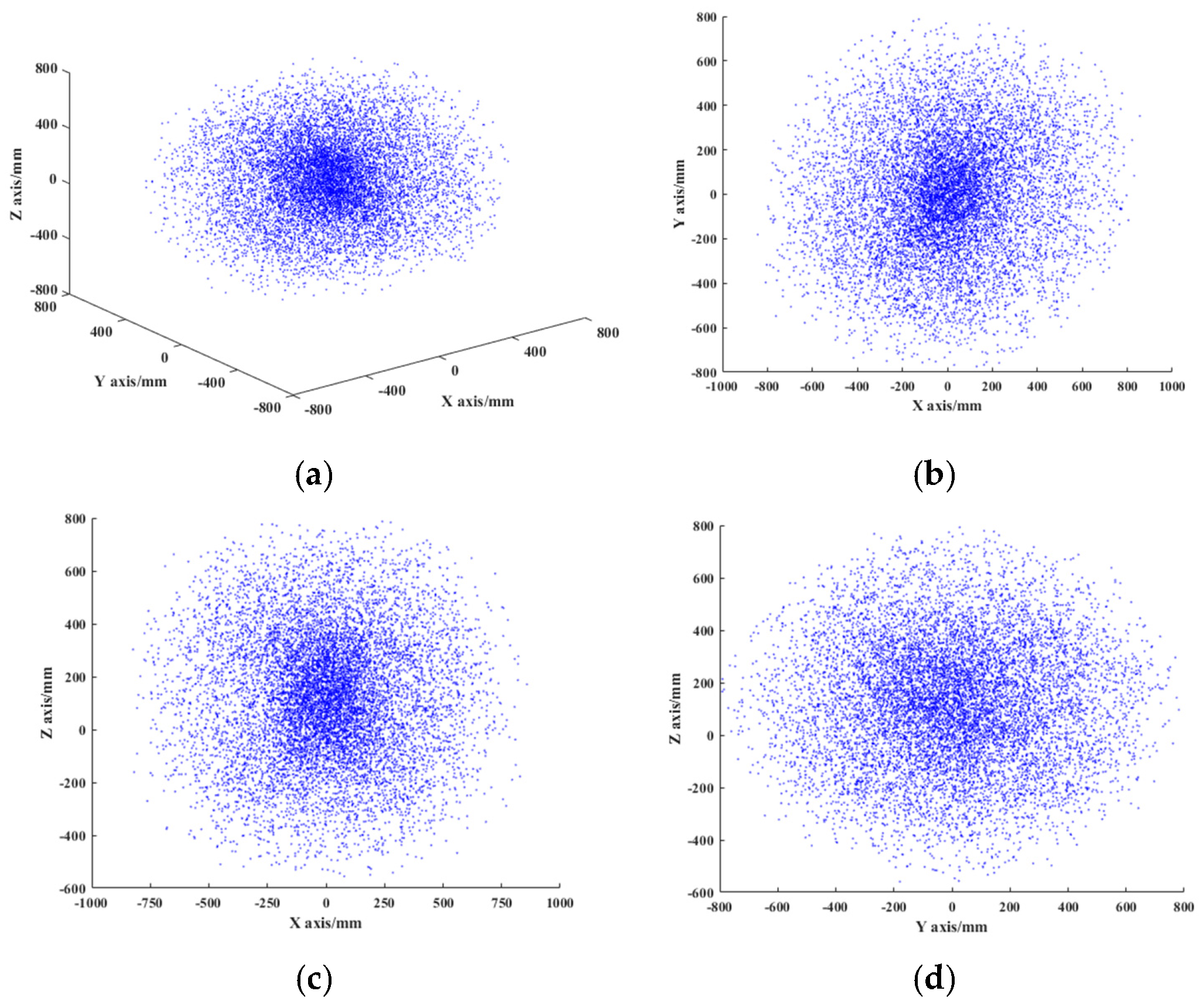
3.3. Workspace of the ULRR
4. Trajectory Planning of the ULRR
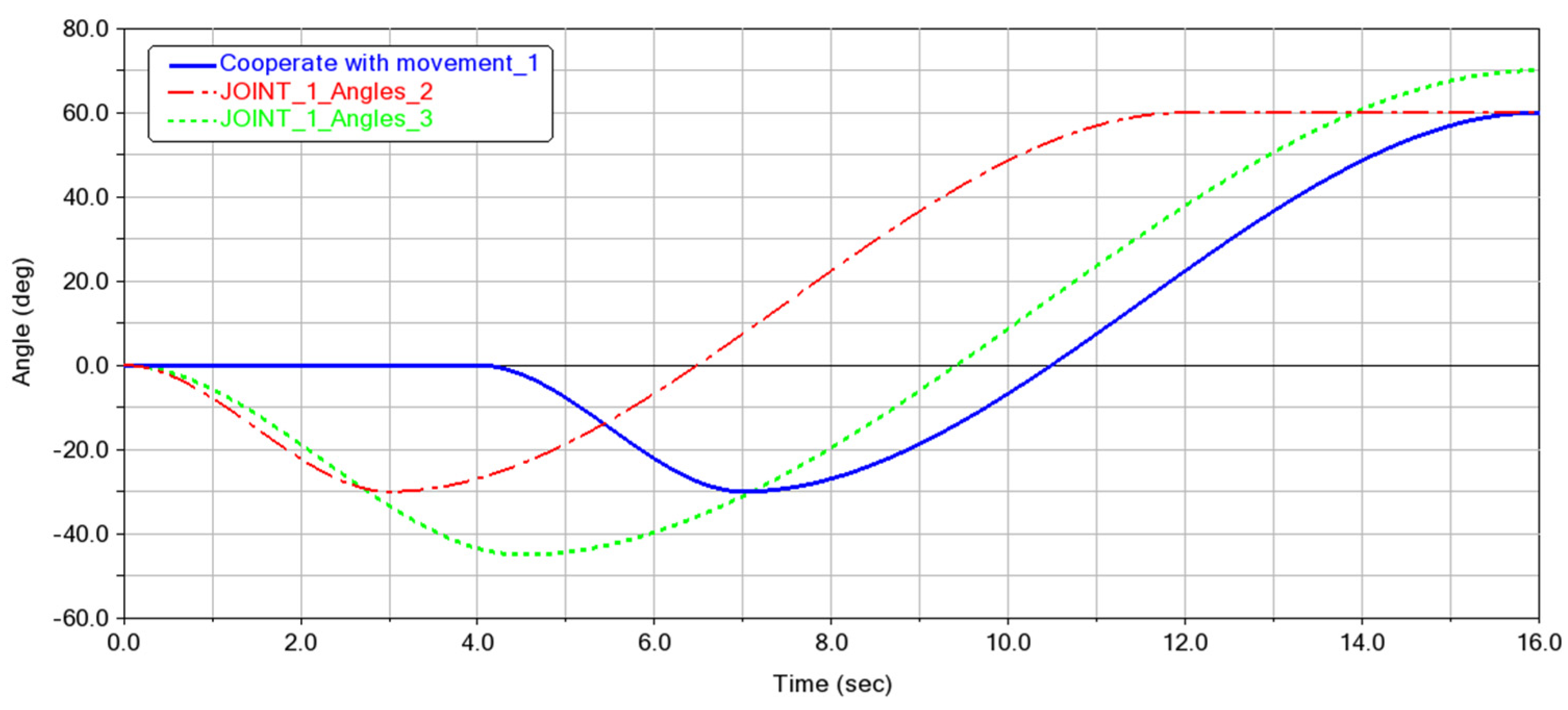
4.1. Trajectory Planning of Joint Space
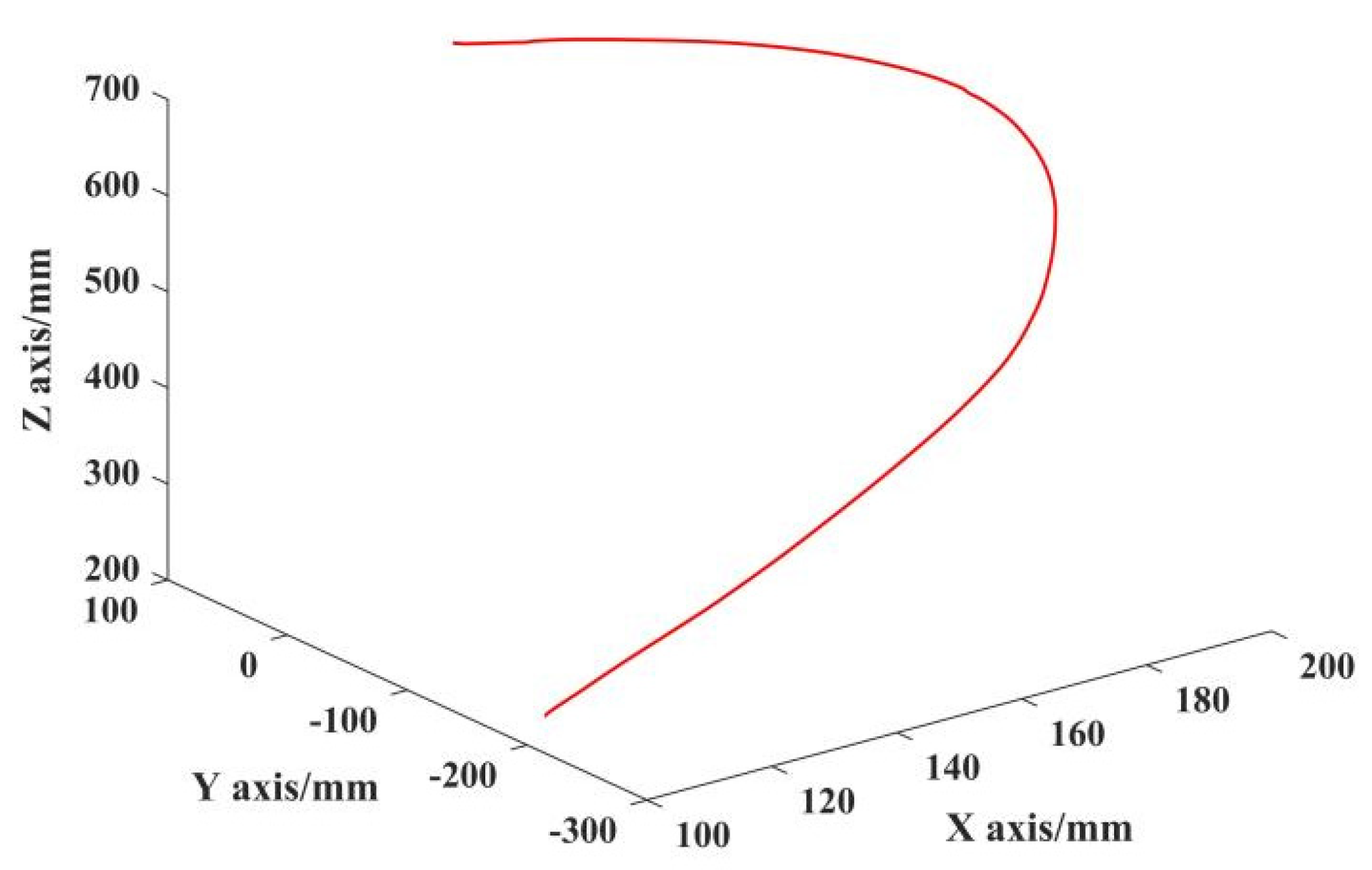
4.2. Trajectory Planning of Cartesian Space
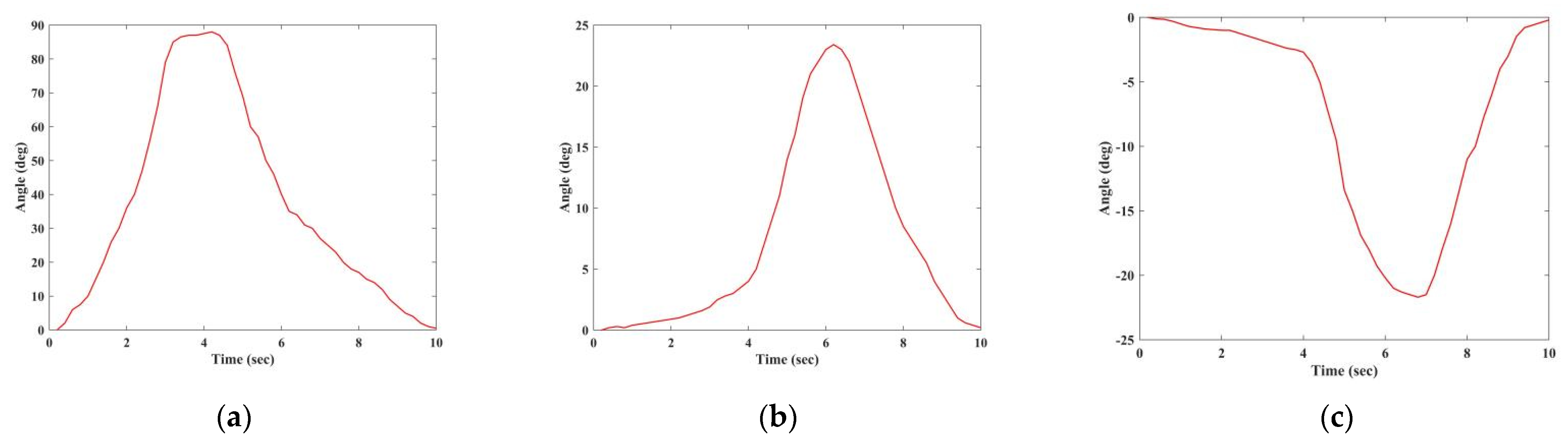
4.3. Simulation of Trajectory Planning
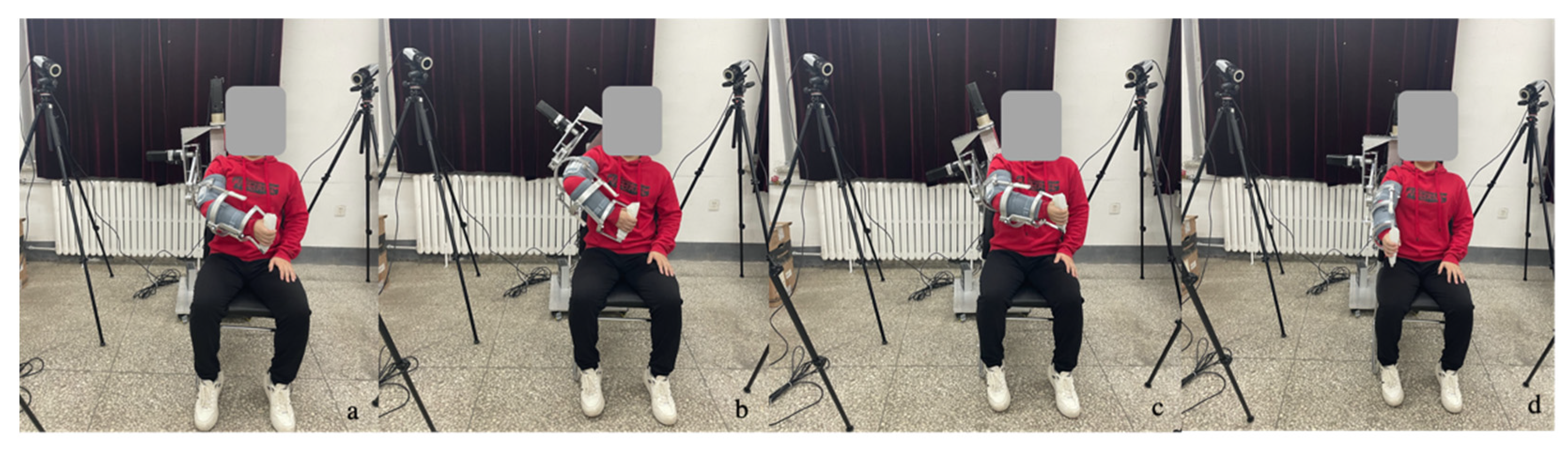
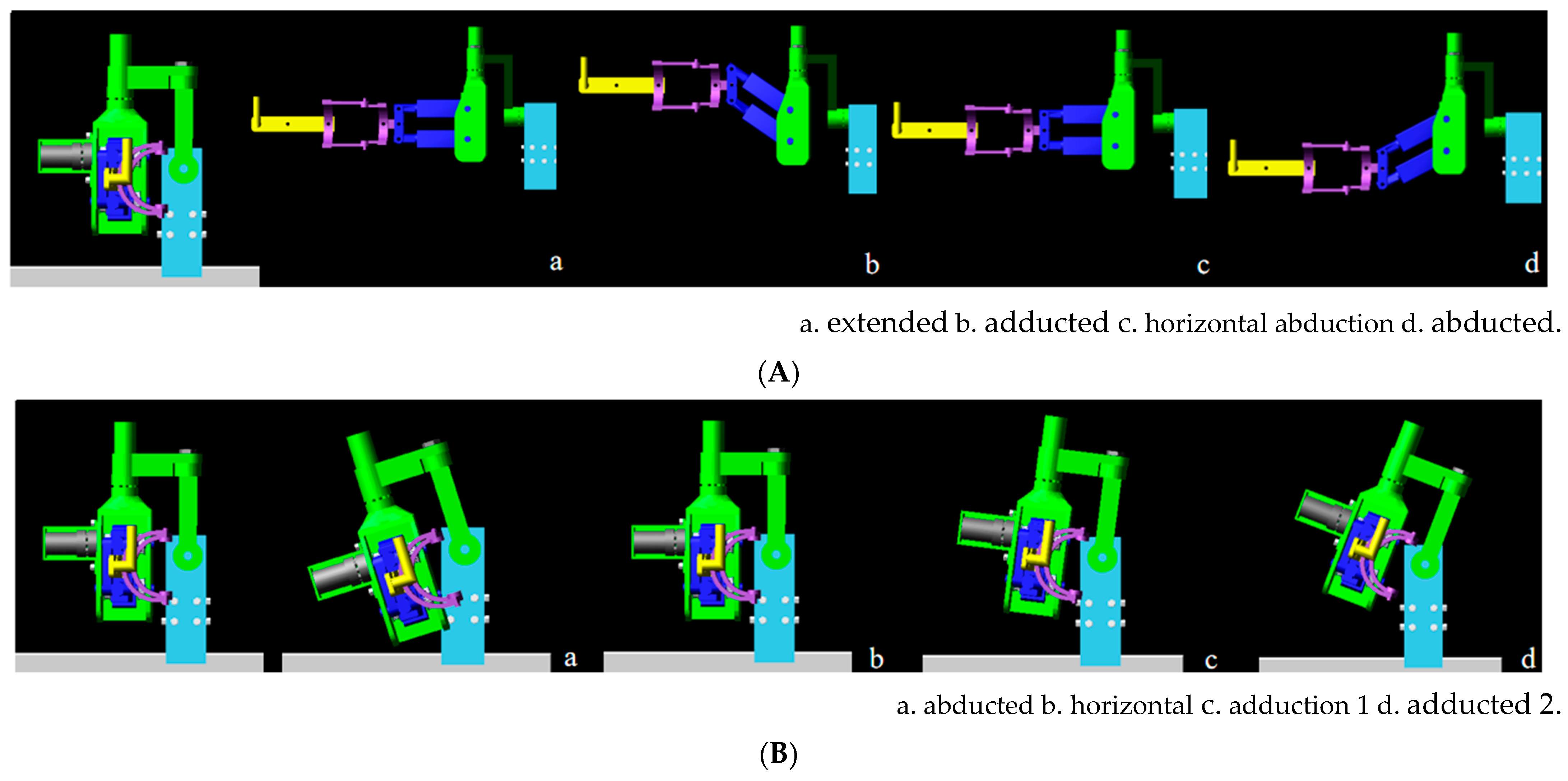
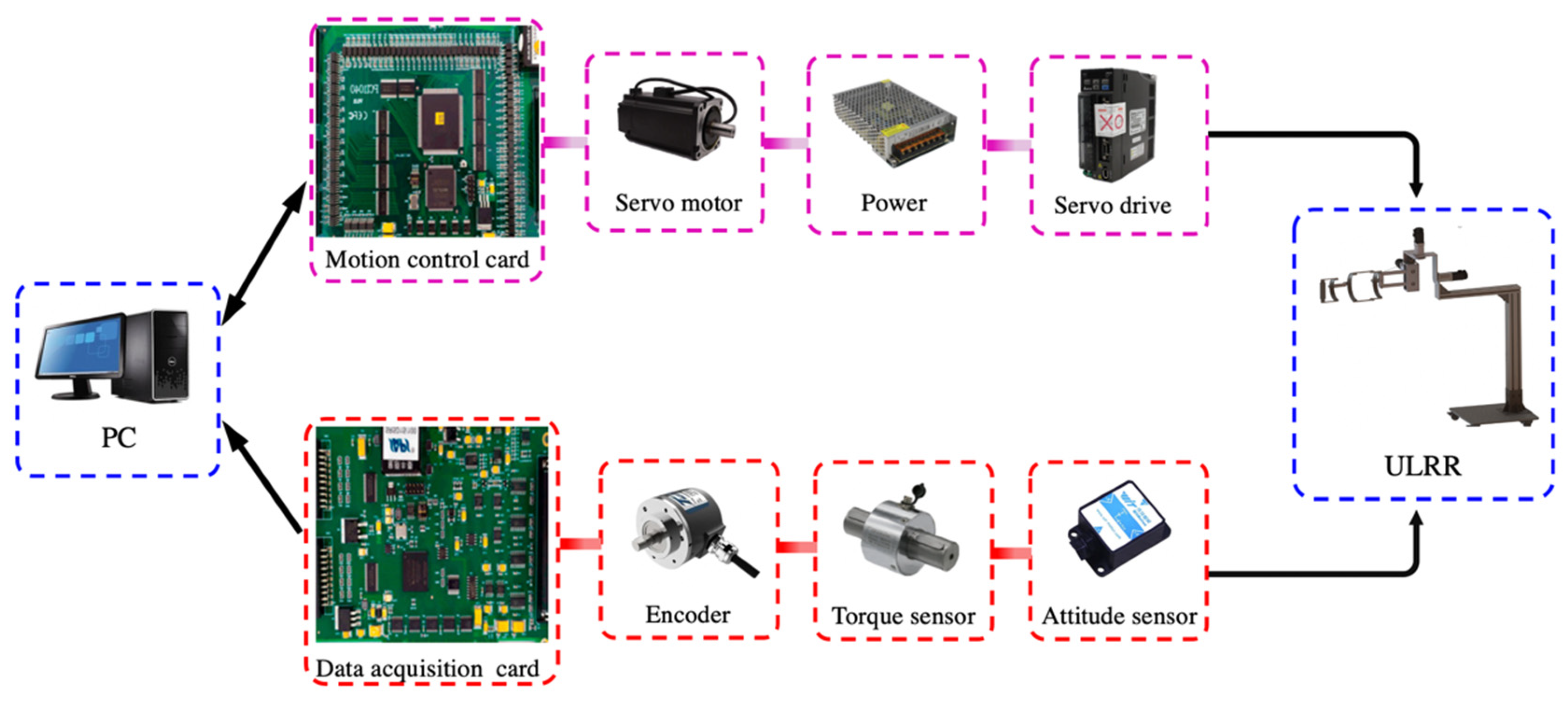
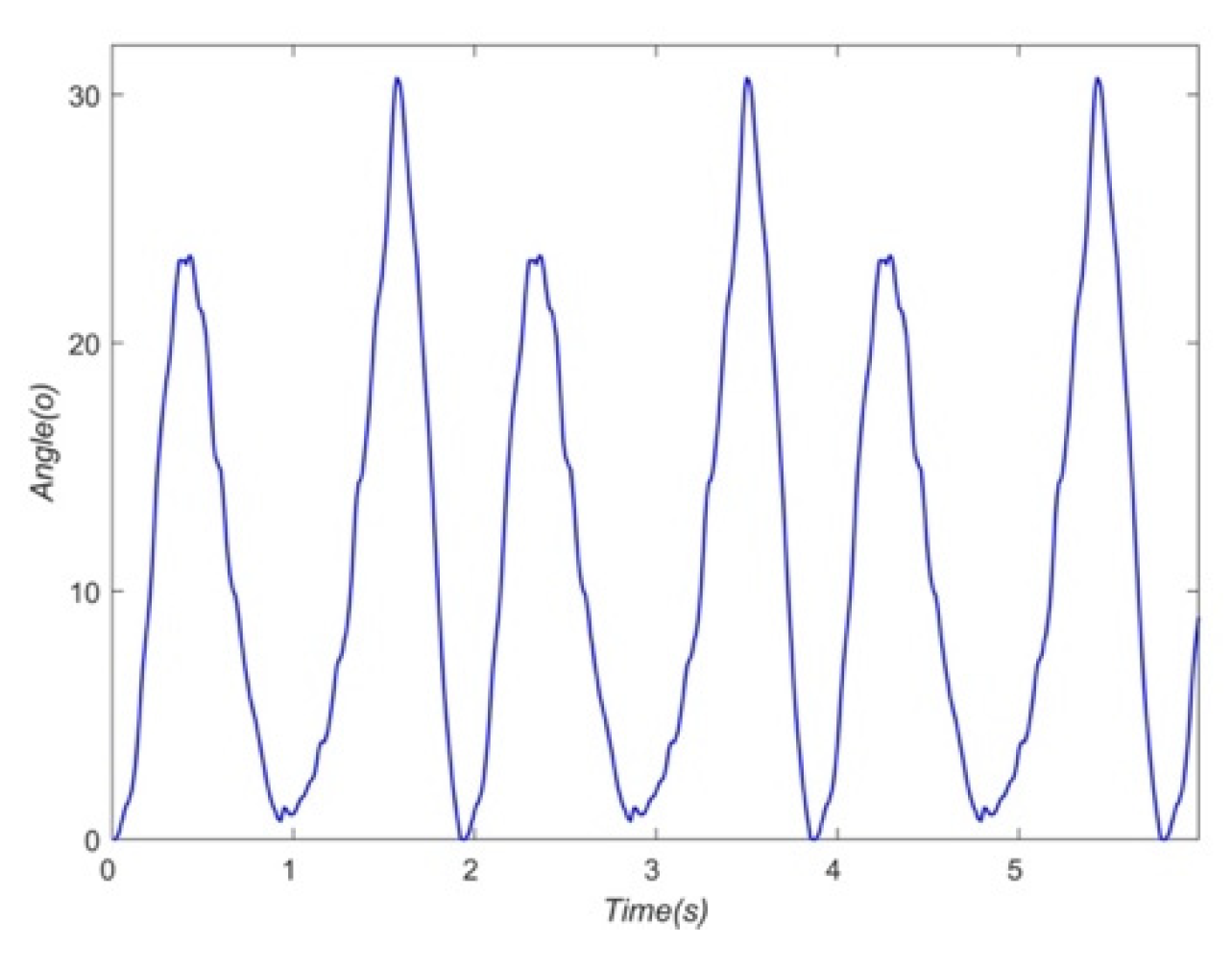
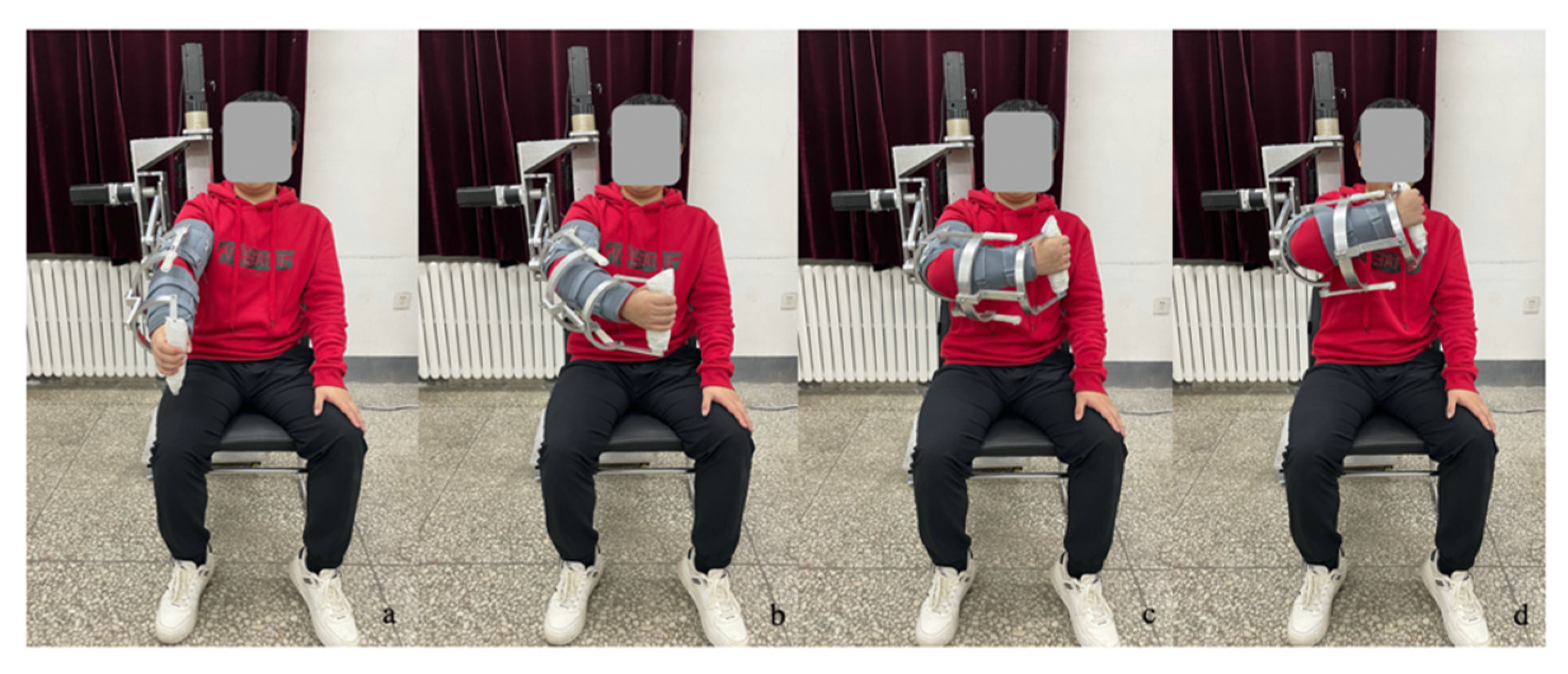
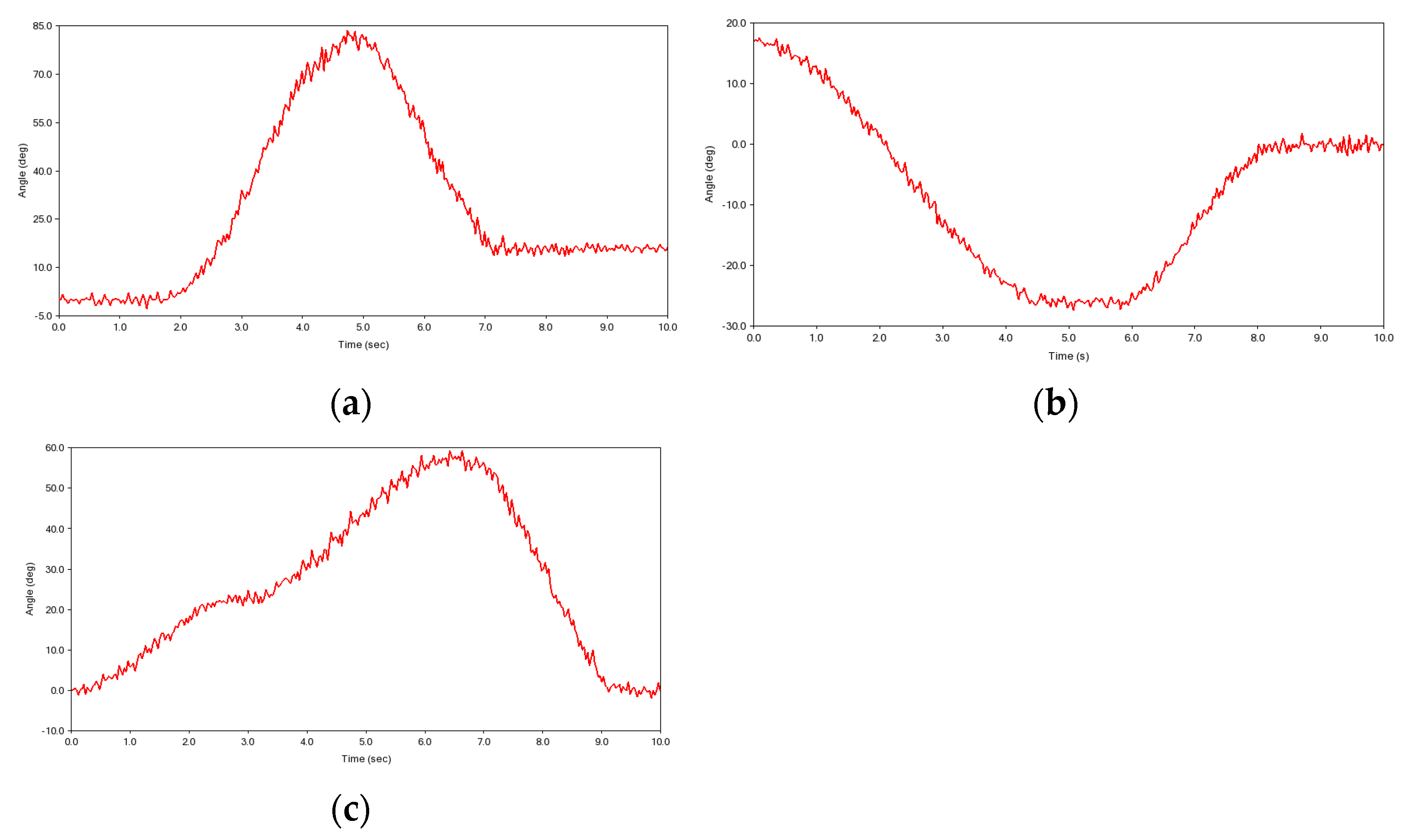
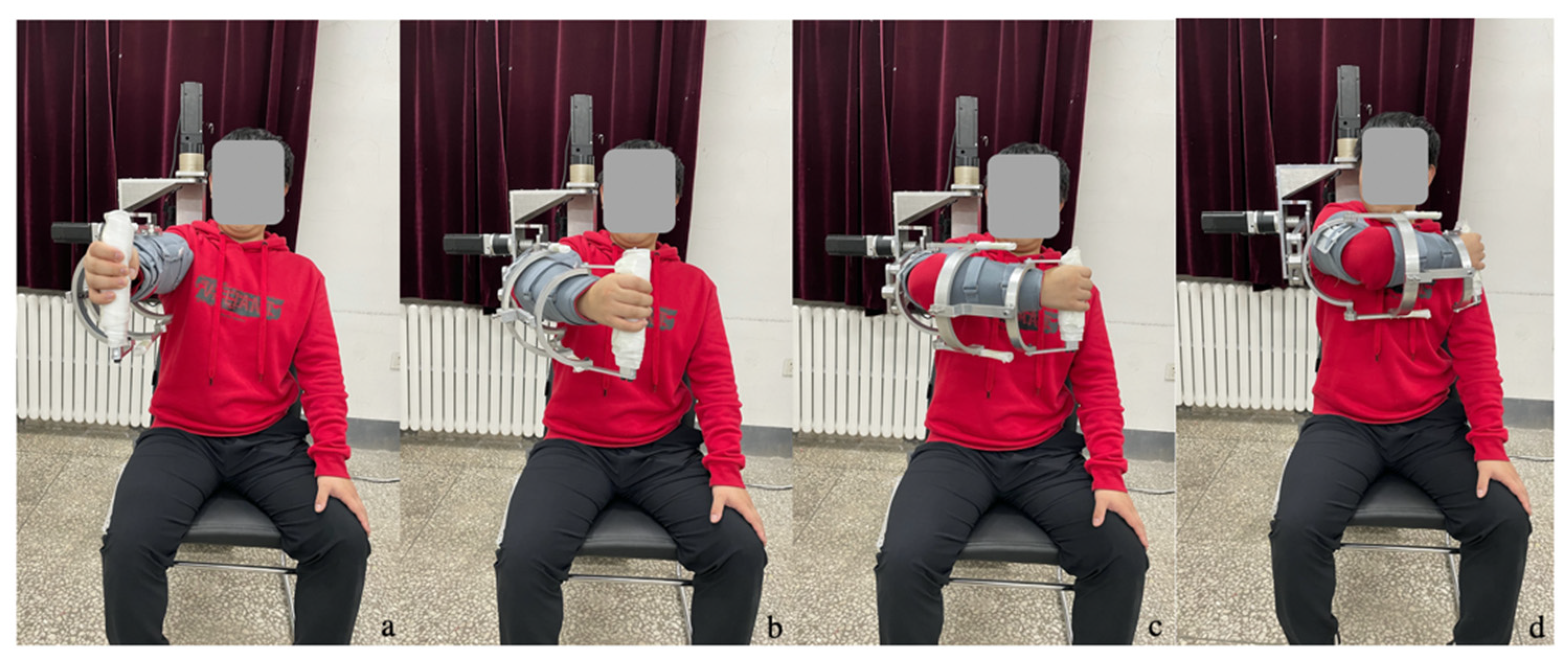
5. Rehabilitation Training Experiment
5.1. Training experiment of the A/A motion of SJ in FP
5.2. Training Experiment of Multi-Joint Compound
5.3. Training Experiment of Active Rehabilitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, J.S.; Khan, S.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Sidney, S. Changes in Mortality in Top 10 Causes of Death from 2011 to 2018. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 36, 2517–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milot; Marie-Hélène; Cramer, S.C. Recovery after Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 654–659. [Google Scholar]
- Mandeville, R.M.; Brown, J.M.; Sheean, G.L. A neurophysiological approach to nerve transfer to restore upper limb function in cervical spinal cord injury. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 43, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BlankA, A.; French, J.A.; Pehlivan, A.U.; O’Malley, M.K. Current Trends in Robot-Assisted Upper-Limb Stroke Rehabilitation: Promoting Patient Engagement in Therapy. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2014, 2, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Wang, T.; Yu, J. Design and analysis of shoulder joint exoskeleton rehabilitation mechanism based on gear and rack transmission. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 055122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yochelson, M.R.; Dennisonsr, A.C.; Kolarova, A.L. Stroke Rehabilitation, 6th ed.; Elsevier: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2021; pp. 2–47. [Google Scholar]
- Marco, G.; Alexander, D.W.; Simon, B.; Verena, K.M.; Tobias, N.; Rober, R. A robotic system to train activities of daily living in a virtual environment. Med. Biol. Eng. 2011, 49, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Agrawal, S.K. Design of a Cable-Driven Arm Exoskeleton (CAREX) for Neural Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Agrawal, S.K. Transition from mechanical arm to human arm with CAREX: A cable driven ARm EXoskeleton (CAREX) for neural rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 2457–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.C.; Zhang, K.J.; Sun, S.Q.; Gao, Z.G.; Zhang, L.K.; Yang, Z.L. An upper-limb power-assist exoskeleton using proportional myoelectric control. Sensors 2014, 14, 6677–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, M.A.; Bai, S.; Bak, T. A Review on Design of Upper Limb Exoskeletons. Robotics 2020, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Takeda, Y. Kineto-Static Analysis of a Wrist Rehabilitation Robot with Compliance and Passive Joints for Joint Misalignment Compensation. Machines 2020, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Saini, M.; Anand, S.; Kumar, N.; Srivastava, M.V.P.; Mehndiratta, A. Robotic Exoskeleton for Wrist and Fingers Joint in Post-Stroke Neuro-Rehabilitation for Low-Resource Settings. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 2369–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.J.; Su, C.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Chen, Z.T.; Chai, T.Y. Nonlinear disturbance observer-based control design for a robotic exoskeleton incorporating fuzzy approximation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5763–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Niu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Niu, J.; Sun, L. Mechanical Design and Analysis of the End-Effector Finger Rehabilitation Robot (EFRR) for Stroke Patients. Machines 2021, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huo, W.G.; Xu, W.X.; Samer, M.; Yacine, A. Control of upper-limb power-assist exoskeleton using a human-robot interface based on motion intention recognition. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Irube, K.; Takeda, Y. Kineto-Static Analysis and Design Optimization of a 3-DOF Wrist Rehabilitation Parallel Robot with Consideration of the Effect of the Human Limb. Machines 2021, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomer, C.; Baldoví, A.; Torromé, S.; Navarro, M.D.; Moliner, B.; Ferri, J.; Noé, E. Efficacy of Armeo® Spring during the chronic phase of stroke. Study in mild to moderate cases of hemiparesis. Neurología 2013, 28, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijbels, D.; Lamers, I.; Kerkhofs, L.; Alders, G.; Knippenberg, E.; Feys, P. The Armeo Spring as training tool to improve upper limb functionality in multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2011, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicuri, C.; Porcellini, G.; Merolla, G. Robotics in shoulder rehabilitation. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergin, M.A.; Patoglu, V. ASSISTON-SE: A self-aligning shoulder-elbow exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 2479–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, M.; Sonobe, M.; Mihara, M. Tracking Training and Its Assessment Using 3D Rehabilitation System for Upper Limbs “EMUL” and Brain Function Imaging Method “MRS”. In Proceedings of the JSME Annual Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (Robomec), Asahikawa, Japan, 13–16 June 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Yokoo, T. Compilation of Joint Motion Database using Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot (Rehabilitation Robotics and Mechatronics (2)). In Proceedings of the JSME Annual Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (Robomec), Hamamatsu, Japan, 27–29 May 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, A.U.; Rose, C.; O’Malley, M.K. System characterization of RiceWrist-S: A forearm-wrist exoskeleton for upper extremity rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitle, K.D.; Pehlivan, A.U.; O’Malley, M.K. A robotic exoskeleton for rehabilitation and assessment of the upper limb following incomplete spinal cord injury. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 4960–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadivar, Z.; Sullivan, J.L.; Eng, D.P. RiceWrist Robotic Device for Upper Limb Training: Feasibility Study and Case Report of Two Tetraplegic Persons with Spinal Cord Injury. Int. J. Biol. Eng. 2012, 2, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, A.U.; Sergi, F.; Erwin, A. Design and validation of the RiceWrist-S exoskeleton for robotic rehabilitation after incomplete spinal cord injury. Robotica 2014, 32, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, D.A. Essentials of Kinesiology for the Physical Therapist Assistant, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2019; pp. 175–249. [Google Scholar]
- Qie, X.; Kang, C.; Zong, G.; Chen, S. Trajectory Planning and Simulation Study of Redundant Robotic Arm for Upper Limb Rehabilitation Based on Back Propagation Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Joint | DoFs | Human | Robot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | F/E in the SP | 0–180°/0–60° | 0–120°/0–45° |
| A/A in the HP | 0–75°/0–90° | 0–45°/0–90° | |
| A/A in the FP | 0–50°/0–180° | 0–45°/0–135° | |
| Elbow | F/E | 0–135° | 0–100° |
| Wrist | RUD | 0–20°/0–35° | 0–20°/0–30° |
| F/E | 0–50°/0–40° | 0–50°/0–40° |
| Joint | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.864023 × 104 | 6.244685 × 104 | 3.370621 × 104 |
| 2 | 2.783526 × 104 | 2.500916 × 104 | 1.038952 × 104 |
| 3 | 0.577064 × 104 | 0.452236 × 104 | 0.237761 × 104 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Pang, Z.; Gao, M.; Duan, Z. Design and Analysis of 6-DoFs Upper Limb Assistant Rehabilitation Robot. Machines 2022, 10, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111035
Li S, Wang Z, Pang Z, Gao M, Duan Z. Design and Analysis of 6-DoFs Upper Limb Assistant Rehabilitation Robot. Machines. 2022; 10(11):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111035
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuang, Zhanli Wang, Zaixiang Pang, Moyao Gao, and Zhifeng Duan. 2022. "Design and Analysis of 6-DoFs Upper Limb Assistant Rehabilitation Robot" Machines 10, no. 11: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111035
APA StyleLi, S., Wang, Z., Pang, Z., Gao, M., & Duan, Z. (2022). Design and Analysis of 6-DoFs Upper Limb Assistant Rehabilitation Robot. Machines, 10(11), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111035






