Abstract
When data exhibit a high frequency of small to medium values and a low frequency of large values, fitting a classical distribution might fail. This is why spliced models defined from different distributions on distinct intervals are proposed in the literature. In contrast to the intensive study of two-spliced distributions, the case with more than two components is scarcely approached. In this paper, we focus on three-spliced distributions and on their ability to improve the modeling of extreme data. For this purpose, we consider a popular insurance data set related to Danish fire losses, to which we fit several three-spliced distributions; moreover, the results are compared to the best-fitted two-spliced distributions from previous studies.
MSC:
60E05; 62P05; 62G07
1. Introduction
Data coming from fields like insurance or finance often exhibit a particular behavior: there are many small to medium values but also a few extreme values. Such behavior prevents the fitting of a classical distribution to the entire data set so that spliced models built of different distributions in subdivided intervals have been proposed to overcome this issue (see the work of Klugman et al. [1] for details). In this sense, Cooray and Ananda [2] called the two-component spliced model composite, and introduced a composite LogNormal–Pareto model, aiming to better capture tails of loss distributions. This composite distribution was extended by Scollnik [3], whose model underlies many subsequent studies: see [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12] to mention just a few. Also, among recent papers dealing with composite models, we mention [13,14,15,16,17,18]; see also the references therein. On the other hand, spliced distributions are also used in other fields dealing with extreme value theory; see the review [19].
In what concerns spliced distributions with more than two components, their study is scarce maybe because the estimation of the thresholds where they change shape is a difficult problem. In particular, three-spliced regression models were considered by [20,21]. In [22], the three-spliced Exponential–LogNormal–Pareto distribution was studied, ref. [23] approached the three-spliced Gamma–LogNormal–Pareto distribution, ref. [24] discussed three three-spliced models (having Weibull as the first component, LogNormal as the second and Pareto/GPD/Burr as the third) in connection with two insurance data sets, while [25] modeled household income data using an Inverse Pareto–Gaussian mixture– Pareto distribution.
In this paper, we first recall the general three-spliced model of [22], then we approach some particular cases with the purpose of modeling a real data set from insurance: the Danish fire losses data. This data set has been intensively studied in the literature in connection with composite distributions starting with [2], and culminating with the comprehensive analysis [7], which compared 256 composite models derived from 16 parametric distributions commonly used in actuarial science. Motivated by this extensive study, in this paper, we propose several three-spliced distributions for modeling the Danish data, built on the basis of the composite distributions that provided the best fits in [7].
Therefore, we define these three-spliced distributions with the purpose of better modeling small, medium and large claims (or data) by separately capturing the behavior of each group, which is consistent with, respectively, lighter-, medium- and heavy-tailed distributions. Also, the choice of the combinations of distributions was made bearing in mind the mentioned behavior of actuarial data.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: in Section 2, we first recall the three-component spliced model, we discuss parameters estimation, and we list the distributions that will be used to define the three-spliced distributions for modeling our data; in connection with these distributions, we briefly present some differentiability conditions because we will consider each three-spliced distribution with and without differentiability conditions at the thresholds. In Section 3, we describe the Danish data set, the distributions fit and compare the results with the ones in [7,24]; we also evaluate and compare some risk measures used in actuarial calculations. We end with a conclusions section followed by two appendices, containing some tables and R code.
2. Three-Component Spliced Distributions
2.1. General Form
A general three-component spliced probability density function (pdf) is defined in [22] by
where are the thresholds where the pdf changes shape. is a pdf with its corresponding cumulative distribution function (cdf), and , while is the right truncation of at , the left-right truncation of at the two thresholds, and the left truncation of at ; therefore, and are also the points where are truncated. The normalizing constants are such that , and represent the probability of each component, e.g., in the case of modeling small, medium and large size claims, represents the proportion of the corresponding type of claim.
A natural requirement for a spliced pdf is the continuity imposed at the thresholds, often followed by the differentiability condition that ensures a smooth pdf. In the next proposition, we present the constraints resulting by imposing such conditions. These constraints are used to reduce the number of estimated parameters, and hence the computational burden of the estimation procedure, e.g., from the first statement of the next proposition, we can see how the normalizing constants can be obtained based on the continuity condition at the two thresholds.
Proposition 1.
(b) Moreover, also imposing differentiability conditions at , i.e., results in the restrictions
Consider the three-spliced pdf (1).
- (a)
- Imposing continuity conditions at the thresholds , i.e., yields
Proof.
(a) The continuity conditions at the thresholds yield (see also [22])
From this first equation, we obtain the second stated formula (of ). From the second equation follows the third stated formula (of ), and inserting these formulas into the condition gives the first stated formula of .
- (b)
- The proof can be found in [22]. □
Let denote the moment-generating function (mgf) of the random variable (rv) X with pdf f, and let denote its initial moment of order n. The following results are proved in [22]:
Proposition 2.
Remark 1.
Random values from the three-component spliced distribution can be generated by using the inversion method on the cdf (2) assuming that and admit inverse functions.
Moreover, from the cdf (2), we obtain the quantiles of a three-spliced distribution as follows:
Proposition 3.
Assume that and admit inverse functions and is the quantile of order , i.e., . Then,
Remark 2.
For large values of p, the quantile is used under the name of Value-at-Risk (VaR) as a risk measure in risk analysis. Based on VaR and developed in connection with heavy-tailed distributions, the Tail-Value-at-Risk (TVaR) is another frequently used risk measure defined for a rv X as In our case, it can be calculated from
hence needing integration. Alternatively, Monte Carlo simulation can be used.
2.2. Parameter Estimation
Let be a random data sample from a three-spliced pdf and the set of parameters to be estimated. The corresponding likelihood function is
Note that to perform maximum likelihood estimation (MLE), in addition to the parameters of , the two thresholds must be estimated. In [22], a complete estimation algorithm is proposed by letting the two threshold estimations sweep the entire data domain, which unfortunately proves to be very time consuming (more precisely, after sorting the data set, MLE solutions are searched by restraining the thresholds in between every two consecutive data such that ; finally, the best solution is kept). Therefore, in [23], some threshold selection methods are revised. Based on these reasons, in the numerical section of this work, we use the following algorithm:
- Step 1.
- Select the initial values for the thresholds (using, for example, graphical diagnostics) and, for each threshold, set up a search grid around its initial value.
- Step 2.
- For in its gridFor in its gridEvaluate the remaining parameters by MLE of the likelihood (5) under the constraints of continuity at the thresholds and differentiability if considered.
- Step 3.
- Among the solutions obtained at Step 2, choose the one that maximizes the log-likelihood function.
- Step 4.
- The algorithm can be reiterated by refining the grids around the last threshold values.
Being based on partial MLE, the algorithm does not necessarily perform full MLE, so variants for improving the estimation should be studied in the future.
Regarding the thresholds selection in Step 1, the histogram can give an idea of where its shape changes. Further, graphical diagnostics like the mean excess function or Hill plots (implemented in the evmix package of R) can be used to detect transitions between different parts of the distribution; we recall that a Pareto tail could be detected if there exists a point beyond which the mean excess plot is linearly increasing. Also, previous information as the estimated thresholds for some two-spliced distributions could be of great help (we used such information in the numerical study).
In what concerns the grids, they can be chosen equispaced around the thresholds, strongly depending on the data: it is recommended to leave a certain amount of data for each of the three components in order to justify the fit of a three-spliced distribution (as pointed out by a referee, estimating parameters within each segment requires a substantial amount of data, which can be challenging to obtain in certain circumstances). Also, the number of values in the grids should be taken such that the computing time is not too long (depending on the computer’s characteristics). Moreover, we preferred to start with grids having larger spans because once a solution was found, we reiterated the algorithm with denser grids around the thresholds of the last solution found.
In Step 2, we used the function optim from R with the default optimization method of Nedler and Mead [26], which works reasonably on non-differentiable functions as was our case for half of the fitted distributions.
Remark 3.
Parameter estimation may present difficulties due to the complexity of the model, potentially leading to unreliable estimates (e.g., potential interaction among different distribution segments may introduce errors in estimations). What we noticed when working on the numerical part is that for a few three-spliced distributions, the algorithm provided some best solutions (sometimes with extreme values of the parameters) that were quite different from the other solutions obtained for the thresholds in the respective grids; this happened especially for the distributions without differentiability at the thresholds. Other problems were reaching the iteration limit (maxithad to be increased) and degeneracy of the Nelder–Mead simplex (see details in the numerical part).
Remark 4.
Other methods suggested in the literature to reduce the grid search are based on empirical quantiles and on the method of moments (however, the resulting system of equations might not have a closed-type solution). On the other hand, to improve the estimation, the MLE procedure was complemented in [24] with a Bayesian analysis via Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation.
Note that if the order of the head, middle and tail distributions is changed, it is expected to obtain different estimated parameters.
2.3. Particular Involved Distributions
In the numerical illustration section, several three-spliced distributions will be fitted to a real data set from insurance: the Danish fire losses. Therefore, the choice of the component distributions is related to this data set and the pdfs of the selected distributions considered for the head, middle, and/or tail of the three-spliced distribution are listed in Table 1. All the distributions are given in terms of shape and scale parameters. Regarding the choice of these eight distributions, we mention that it was based on the detailed discussions of the existing literature and best fits from [7].

Table 1.
Eight positive parametric distributions considered the tail, middle, and/or head distributions in the three-spliced model (abbreviation in brackets).
In total, we fitted 44 three-spliced distributions: 22 with and 22 without differentiability conditions at the two thresholds. We would have liked to try more such distributions, but the computing time is still very long; plus, we can already get an idea based on the selection criteria AIC and BIC.
Two examples. We illustrate the three-spliced distribution with two particular distributions that we fitted to the Danish data set in Section 3: the Weibull–Paralogistic–InverseWeibull and the Paralogistic–Weibull–InverseWeibull. For consistency with the densities notation in Table 1, their parameters are denoted as follows: Weibull, Paralogistic), Inverse Weibull, . For both distributions, we present the pdfs and the restrictions resulting from the differentiability conditions (as discussed above, the continuity conditions yield direct formulas for the normalizing constants, so we do not insist on these ones).
From Table 1 and (1), the pdf of the Weibull–Paralogistic–InverseWeibull distribution is
while the pdf of the Paralogistic–Weibull–InverseWeibull is
In order to impose the differentiability conditions, the following lemma concerning the derivatives of the pdfs from Table 1 involved in Proposition 1 (b) is helpful (the proof is simple so we skip it).
Lemma 1.
Denote the pdf of the distribution by f indexed with the abbreviation of the name. Then, the following relations hold for :
As an illustration, we present the differentiability conditions for the two particular three-spliced distributions considered above as examples. The following proposition easily results from the above lemma.
Proposition 4.
The differentiability conditions from Proposition 1 imposed to the Weibull–Paralogistic–InverseWeibull distribution yield the following two restrictions for , :
3. Numerical Illustration
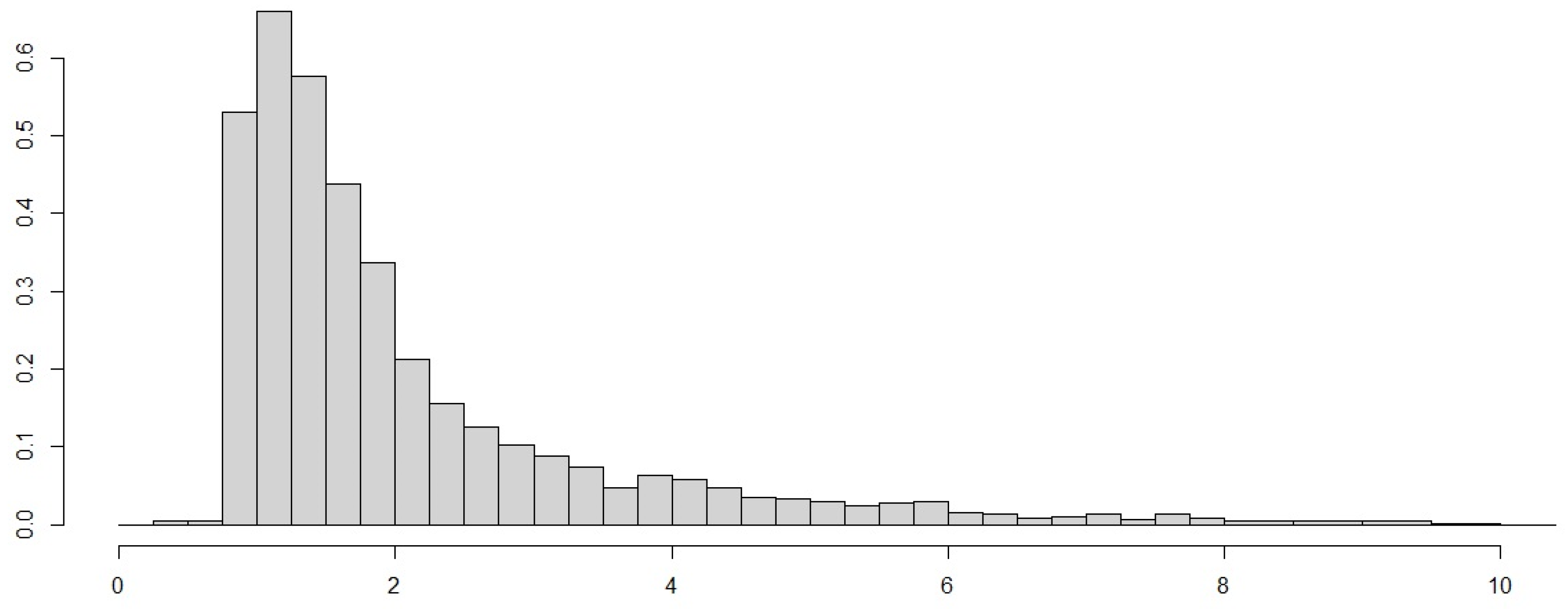
To illustrate the applicability of three-spliced distributions, we consider the Danish fire losses data set consisting of claims available in the SMPracticals package of R 4.4.0 software. This choice is motivated by the fact that this data set was intensively studied in connection with two-spliced distributions, enabling thus comparisons between the fits of various distributions. From the descriptive statistics displayed in Table 2, it can be seen that the data exhibit high right skewness and a very fat tail, hence motivating the fit of spliced distributions to capture the extreme values. Moreover, the histogram in Figure 1 supports the fat tail remark, and also the spliced assumption; see the high gap in the left side at values smaller than 1.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of Danish fire data.
Figure 1.
Histogram of the Danish fire data.
To this data set, we fitted several three-spliced distributions, which, as mentioned in the introduction, are built on the basis of the composite distributions that provided the best fits in [7], also resumed in [8]. Therefore, we combined the 8 distributions presented in Table 1 and obtained the 22 three-spliced distributions from Table 3, each one considered with no differentiability condition and with both differentiability conditions at the thresholds (in total, 44 fitted distributions).

Table 3.
Results of fitting 22 three-spliced models with and without differentiability (ordered according to the BIC of models without differentiability).
For all 22 distributions, we imposed continuity conditions at both thresholds. In a first step, we chose not to impose differentiability conditions in order to obtain a greater flexibility of the pdf, which is necessary to capture, for example, the big jump at the very left side of the histogram. However, in this case, we encountered some problems like degeneracy of the Nelder–Mead simplex and standard errors being unavailable. Also, for a few three-spliced distributions, we obtained substantially smaller BIC values but very bad Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) results (see Table 4), so we reiterated the algorithm, avoiding these extreme situations (for this purpose, we initially kept all the solutions from Step 2 of the algorithm in a list together with the KS values, and based on the log-likelihood and KS, we decided which one is reliable). In a second step, we considered the same 22 distributions but with differentiability conditions at both thresholds.

Table 4.
Results of fitting 4 three-spliced models with the best BIC values but worst KS result (estimated parameters under distribution).
The order in which the spliced distributions are displayed in the tables is based on the BIC order of the spliced distributions with no differentiability; see Table 3. The position of the distributions as the head, middle, or tail was selected following the discussions in [7,24]. More precisely, ref. [24] noticed that the Weibull distribution, having a more flexible shape on the left side, can better capture the smaller claims; therefore, in more than half of our models, Weibull is the head distribution. Alternatively, we considered for the head of several models the Paralogistic as discussed in [7], and the LogNormal. Also, based on the comments of [7], we alternated the Weibull, Paralogistic, LogLogistic and InverseBurr as the middle distributions. A more heavy-tailed distribution should be used for the tail, and, based on their findings, ref. [7] recommended the following ones: InverseWeibull, InverseParalogistic, LogLogistic, Burr and Paralogistic. Among these, as the tail, we used the first three, and added the Pareto one as in [24], which proved to be a good choice.
Also, even if the 20 best-fitting two-spliced distributions in [7] performed better than the models using the LogNormal distribution in the head, we considered the LogNormal as the head distribution in four of our three-spliced models, obtaining good results for the no differentiability models. However, we must mention that we tried several three-spliced distributions with the LogNormal as the middle distribution and without differentiability for models that we do not display here because for all of them, we obtained extreme values of the estimated parameter that necessitate higher precision in the calculation. Nevertheless, we note that [24] obtained good results with the LogNormal as the middle distribution (see Table 6) but including also differentiability conditions and using a more complex estimation algorithm that involves MCMC simulation.
In Table A1 and Table A2 from Appendix A, we display the parameters of the distributions estimated by the method described in Section 2.2, with standard errors under each parameter (in Table A2, the two parameters resulting from the differentiability conditions can be identified by the lack of standard errors beneath them). Concerning the algorithm, based on the previously estimated thresholds (for two-spliced composite distributions) and on the data histogram (see the big jump at the very left side of the histogram), for , we chose a first search grid in the interval 0.8–3 with step 0.1, comprising the thresholds estimated in [24], and the thresholds from Table A2 in [7], all over 0.92. For , a broader grid in the interval 1–20 was considered, avoiding the overlapping; this interval was chosen to be more wide since there is not much information available on a second threshold. Once we found a first solution for , we refined the corresponding grids centered on these solutions, of length 0.5 and with step 0.001, hence obtaining the better solutions displayed in Table A1 and Table A2.
In Appendix B, we added two examples of R code for estimating the parameters with and without differentiability.
Note that the estimated threshold varies between 0.891 and 1.030, mostly around 0.92–0.95, which is consistent with the thresholds reported in Table A2 from [7] and in [24]. Regarding the estimated second threshold , its range is broader from 0.991 to 9.506.
In what concerns the normalizing constants, we note that the three-spliced distributions without differentiability on positions 9 and 15 have small values of (under 0.1) consistent with higher values of over 9. Also, almost all distributions present values of smaller than 0.1 correlated with small values of (excepting the distributions with the LogNormal as the head and with differentiability conditions).
Regarding the standard errors displayed in Table A1 in parentheses under each estimated parameter of the distributions without differentiability, we note several high values: for the first parameter of the LogNormal used as the head distribution, and for the second parameter of some Weibull distributions used as the head. Since this situation does not happen with the standard errors in Table A2, i.e., for the distributions with differentiability, it seems to be due to the lack of differentiability at threshold .
In Table 3, we present the negative log-likelihood (NLL), number of estimated parameters k, AIC, and BIC values for the 22 distributions with and without differentiability (diff.) conditions; since the distributions are ordered according to the BIC of the distributions without differentiability, in the last column, we display the global BIC order for all 44 distributions. For comparison, in Table 5, we also show the same results for the nine best-fitted two-spliced distributions from [7], and in Table 6, the results for the three three-spliced distributions considered in [24]. We note that 30 of our three-spliced distributions provide a better fit, the first 3 with significant improvement. Also, in general, each one of our spliced distributions with differentiability has higher AIC but smaller BIC (due to a smaller number of estimated parameters) than the same distribution without differentiability. Interestingly, 5 of our top 6 (BIC) distributions contain the Pareto as the tail distribution, while none of the 20 best-fitting two-spliced distributions in [7] contain the Pareto.

Table 5.
Results of the 9 best-fitting two-spliced models (according to the BIC) in [7].

Table 6.
Results of fitting 3 three-spliced models (according to the BIC) in [24].
In Table 7, we also calculate the Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistics and p-values using the R function ks.test for all 22 distributions, where we recall that this test is based on , representing the maximum distance between the empirical distribution function of the sample and the cdf F of the assumed distribution. The smallest such value is provided by the Weibull–InverseBurr–LogLogistic distribution without differentiability (position 36 on BIC scale, unfortunately having a large standard error of the second parameter of the Weibull head distribution). We note that a few spliced distributions have small p-values, especially the ones with the LogNormal as the head distribution and with differentiability (these are also the last ones on the BIC scale); hence, in this case, the LogNormal seems acceptable as the head distribution only without differentiability conditions.

Table 7.
Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) statistics and ranking for the 22 three-spliced models with and without differentiability.
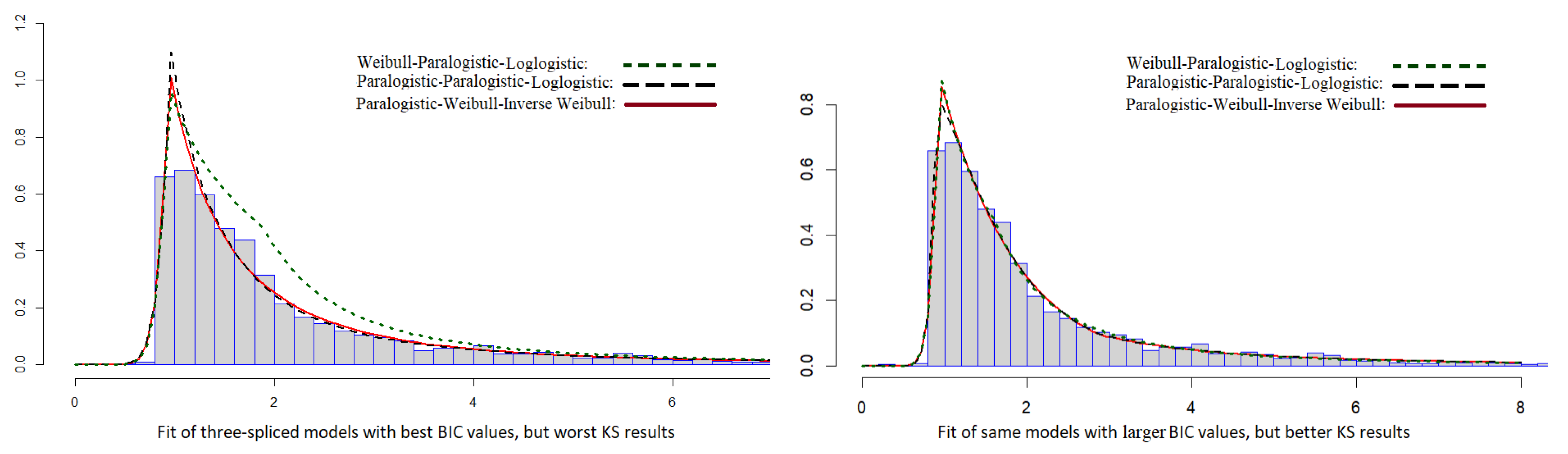
As mentioned above, in Table 4, we display the results for the initial estimation of four three-spliced distributions without differentiability, characterized by substantially smaller BIC values but also by very small KS p-values. In Figure 2, we plot the pdfs of three of these distributions overlapping the data histogram: on the left side, the pdfs corresponding to the distributions in Table 4, and on the right side, the pdfs for the same distributions but re-estimated as in Table A1. We note that the pdfs in the right plot provide a better fit, having a smaller mode. However, note how the Weibull–Paralogistic–LogLogistic (that provides the very best BIC fit) captures the histogram hump between 1.5 and 2.
Figure 2.
Histogram of the Danish fire data with fitted pdfs of 3 three-spliced distributions estimated twice.
We mention that we did not apply the Chi-square test since it proved not to be good enough for highly skewed data as discussed in [7] and the references therein.
Since in actuarial modeling, an important purpose of distribution fitting is to evaluate the risk, in Table 8, we also present the two common risk measures VaR and TVaR evaluated at the 0.95 and 0.99 security levels. For comparison, in Table 9, we display the same risk measures obtained in [7] for the nine best-fitting two-spliced distributions given in Table 5. To calculate the VaR values, we used the quantile Formula (3), while for the evaluation of TVaR, we used the function integrate from R according to Formula (4).

Table 8.
VaR and TVaR at 0.95 and 0.99 security levels for the 22 three-spliced models.

Table 9.
VaR and TVaR at the 0.95 and 0.99 security levels for the 9 best-fitting composite models in [7].
Note that even if most of our three-spliced distributions slightly underevaluate the empirical VaR0.95 risk measure, almost all of them slightly overevaluate the empirical VaR0.99 and overevaluate TVaR0.95. All our three-spliced distributions overevaluate the empirical TVaR0.99, some strongly probably due to a too heavy tail (see the LogNormal–Weibull–Pareto without differentiability).
To conclude, the best overall fitting might not provide the best fit of the tail, which is of great importance in risk modeling, where a moderate overestimation of, for example, actuarial quantities is preferable to underestimation.
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Motivated by a real insurance data set that includes small to extreme values, in this paper, we considered three-spliced distributions with the aim of better modeling small, medium, and large data. After briefly recalling some properties, we discussed an estimation procedure that, to reduce the computing time, is based on a grid search for the two unknown thresholds. The procedure was applied on the insurance data set by fitting 22 three-spliced distributions considered with and without differentiability at the two thresholds. By not considering the differentiability conditions, we hoped to obtain a better fit; however, we noticed that the lack of differentiability can create estimation problems, and for this data set, it did not necessarily produce better fits in terms of BIC.
By comparing the results with the best two-spliced models previously fitted to the same data set, we concluded that three-spliced distributions can indeed improve the fitting. Still, we note the fact that there are many more ways to combine distributions into a three-spliced model than into a two-spliced model, while the computing time needed to fit a three-spliced distribution is much longer than for a two-spliced one, especially in the case without differentiability at thresholds (see Appendix B).
Therefore, when deciding to use three-spliced models, it is better to have a good knowledge of their components, which could be achieved by first fitting some two-spliced distributions. Related to this aspect, as future work, we plan to improve the estimation procedure in order to reduce the computing time. We mention that we recently became aware of the work [24], which made use of MCMC simulation to complement the MLE procedure, so we will consider this as a future work direction.
Also, as future work, it would be interesting to study three-spliced models having negative support.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.V.; Methodology, A.B. and R.V.; Software, A.B. and R.V.; Validation, A.B. and R.V.; Formal Analysis, A.B. and R.V.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, A.B. and R.V.; Writing—R.V.; Supervision, R.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available in the SMPracticals package version 1.4-3.1 of R software.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the positive comments and help of the anonymous referees in substantially improving the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Tables

Table A1.
Estimated parameters for 22 three-spliced models without differentiability (standard error under parameter value).
Table A1.
Estimated parameters for 22 three-spliced models without differentiability (standard error under parameter value).
| Head | Middle | Tail | , | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weibull 13.301, 5.696 (0.818, 2.966 ) | LogLogistic 0.434, 0.027 (0.629, 0.376) | Pareto a = 1.414 (0.037) | 0.925 1.612 | 0.063, 0.432 0.505 |
| Weibull 14.625, 1.412 (0.995, 0.894) | Weibull 0.891,1.033 (0.631, 0.318) | Pareto a = 1.416 (0.038) | 0.908 1.607 | 0.053, 0.439 0.508 |
| LogNormal 34.971, 1.563 (36.022, 0.799) | Weibull 1.357, 1.144 (0.159, 0.092) | Pareto a = 1.372 (0.048) | 0.908 2.381 | 0.053, 0.661 0.286 |
| Weibull 14.469, 3.349 (0.981, 1.048 ) | Weibull 1.449, 1.168 (0.168, 0.083) | InverseWeibull 1.487, 1.036 (0.096, 0.547) | 0.907 2.380 | 0.052, 0.660 0.288 |
| Weibull 13.170, 1.307 (0.798, 9.987) | LogLogistic 0.494, 0.039 (0.157, 0.016) | InverseParalogistic 1.414, 0.010 (0.037, 8.948 ) | 0.928 1.630 | 0.065, 0.437 0.498 |
| Weibull 13.126, 1.434 (0.924, 1.286) | Paralogistic 0.760, 0.202 (1.924, 3.421) | LogLogistic 1.413, 4.791 (0.037, 8.948 ) | 0.928 1.611 | 0.064, 0.431 0.505 |
| Weibull 13.195, 2.161 (0.805, 26.465) | Paralogistic 0.551, 1.239 (0.109, 8.948 ) | InverseWeibull 1.413, 1.177 (3.932 , 0.301) | 0.927 1.607 | 0.064, 0.429 0.507 |
| LogNormal 37.297, 1.618 (61.381, 1.180) | Weibull 1.438, 1.166 (0.156, 0.080) | InverseParalogistic 1.501, 0.666 (0.099, 0.323) | 0.908 2.422 | 0.053, 0.666 0.281 |
| Weibull 13.183, 1.533 (0.804, 1.954) | LogLogistic 1.806, 0.894 (0.088, 0.084) | InverseWeibull 2.022, 10.462 (0.240, 1.291) | 0.928 9.506 | 0.065, 0.890 0.045 |
| Weibull 15.881, 1.875 (1.169, 11.988) | Paralogistic 2.154, 1.745 (0.157, 0.089) | InverseParalogistic 1.483, 0.544 (0.098, 0.335) | 0.891 2.350 | 0.044, 0.662 0.294 |
| LogNormal 20.985, 1.231 (18.962, 0.546) | Weibull 1.329, 1.120 (0.159, 0.097) | LogLogistic 1.454, 0.564 (0.103, 0.470) | 0.912 2.467 | 0.056, 0.670 0.274 |
| Paralogistic 15.860, 1.649 (1.180, 0.938) | LogLogistic 2.670, 1.205 (0.221, 0.047) | InverseWeibull 1.478, 0.930 (0.098, 0.596) | 0.891 2.474 | 0.043, 0.682 0.275 |
| Weibull 15.808, 7.666 (1.178, 2.965 ) | LogLogistic 2.700, 1.206 (0.230, 0.046) | LogLogistic 1.473, 0.558 (0.100, 0.429) | 0.891 2.399 | 0.043, 0.670 0.287 |
| Weibull 13.254, 5.734 (0.839, 2.097 ) | Weibull 0.362, 0.417 (0.615, 1.469) | LogLogistic 1.408, 0.050 (0.074, 0.377) | 0.924 1.529 | 0.062, 0.398 0.540 |
| LogLogistic 13.775, 7.703 (0.858, 2.965 ) | LogLogistic 1.834, 0.928 (0.088, 0.081) | InverseWeibull 1.990, 10.049 (0.233, 1.283) | 0.920 9.216 | 0.061, 0.893 0.046 |
| LogNormal 11.608, 0.960 (8.851, 0.356) | Weibull 1.231, 1.039 (0.156, 0.114) | InverseWeibull 1.556, 1.553 (0.094, 0.463) | 0.928 2.586 | 0.064, 0.677 0.259 |
| Paralogistic 15.145, 3.873 (0.905, 0.498) | Paralogistic 1.867, 1.593 (0.115, 0.116) | LogLogistic 1.524, 1.018 (0.115, 0.541) | 0.901 2.914 | 0.050, 0.732 0.218 |
| Paralogistic 1.082, 0.964 (0.127,0.120) | Weibull 13.417, 7.272 (0.016, 0.015) | InverseWeibull 1.540, 1.617 (0.106, 0.611) | 0.922 2.888 | 0.061, 0.718 0.221 |
| Weibull 13.682, 1.858 (0.841, 7.220) | InverseBurr 3.833 , 6.060, 2.261 (8.948 , 1.397, 0.051) | InverseParalogistic 1.494, 0.638 (0.097, 0.324) | 0.917 2.309 | 0.059, 0.642 0.299 |
| Weibull 14.443, 2.939 (0.963, 432.610) | InverseBurr 0.027, 4.704, 2.203 (0.079, 1.536, 0.221) | LogLogistic 1.448, 0.438 (0.103, 0.479) | 0.912 2.295 | 0.055, 0.642 0.303 |
| Weibull 15.309, 1.469 (1.076, 1.339) | InverseBurr 0.103, 4.120, 2.043 (0.145, 1.204, 0.311) | InverseWeibull 1.506, 1.200 (0.095, 0.517) | 0.901 2.419 | 0.049, 0.669 0.282 |
| InverseBurr 6.594, 2.399, 5.262 (5.201, 1.830, 4.813) | LogLogistic 2.623, 1.202 (0.245, 0.049) | InverseWeibull 1.418, 0.442 (0.121, 1.013) | 0.893 2.426 | 0.045, 0.674 0.281 |

Table A2.
Estimated parameters for 22 three-spliced models with differentiability (standard error under estimated parameter value).
Table A2.
Estimated parameters for 22 three-spliced models with differentiability (standard error under estimated parameter value).
| Head | Middle | Tail | , | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weibull 16.452, 0.946 (0.884, —) | LogLogistic 2.338, 1.112 (0.111, —) | Pareto a = 1.410 (0.036) | 0.944 2.022 | 0.081, 0.552 0.367 |
| Weibull 16.300, 0.948 (0.853, —) | Weibull 1.335,1.088 (0.124, —) | Pareto a = 1.410 (0.037) | 0.947 1.867 | 0.083, 0.507 0.410 |
| LogNormal 0.096, 0.179 (—, 0.007) | Weibull 0.970, 0.810 (0.136, —) | Pareto a = 1.409 (0.039) | 1.025 2.041 | 0.144, 0.494 0.362 |
| Weibull 16.841, 0.941 (0.818, —) | Weibull 1.474, 1.141 (1.001 , 1.001 ) | InverseWeibull 1.406, 3.881 (1.001 , —) | 0.940 1.797 | 0.078, 0.490 0.432 |
| Weibull 16.604, 0.944 (0.901, —) | LogLogistic 2.363, 1.120 (0.112, —) | InverseParalogistic 1.411, 1.764 (0.036, 8.948 ) | 0.942 2.007 | 0.079, 0.550 0.371 |
| Weibull 16.318, 0.947 (0.773, —) | Paralogistic 1.884, 1.546 (8.948 , 8.948 ) | LogLogistic 1.410, 7.320 (8.948 , —) | 0.946 1.945 | 0.082, 0.530 0.388 |
| Weibull 16.893, 0.940 (0.948, —) | Paralogistic 2.041, 1.632 (0.166, 0.118) | InverseWeibull 1.415, 0.154 (0.072, —) | 0.938 1.799 | 0.077, 0.492 0.431 |
| LogNormal 0.112, 0.184 (—, 7.636 ) | Weibull 0.749, 0.557 (0.113, —) | InverseParalogistic 1.420, 3.600 (0.041, 1.001 ) | 1.030 2.302 | 0.148, 0.545 0.307 |
| Weibull 15.979, 0.951 (0.738, —) | LogLogistic 2.148, 1.058 (8.948 , 8.948 ) | InverseWeibull 1.427, 1.154 (8.948 , —) | 0.950 2.230 | 0.086, 0.594 0.320 |
| Weibull 16.422, 0.946 (0.870, —) | Paralogistic 1.885, 1.548 (0.088,—) | InverseParalogistic 1.412, 4.156 (0.037, 8.948) | 0.945 1.946 | 0.082, 0.531 0.387 |
| LogNormal 0.104, 0.182 (—, 7.416 ) | Weibull 0.979, 0.813 (0.141, —) | LogLogistic 1.409, 1.322 (0.039, 1.001 ) | 1.030 2.021 | 0.147, 0.486 0.367 |
| Paralogistic 15.571, 1.145 (8.948 , 8.948 ) | LogLogistic 2.139, 1.040 (8.948 , —) | InverseWeibull 1.416, 1.254 (8.948 , —) | 0.959 2.189 | 0.091, 0.580 0.329 |
| Weibull 16.515, 0.945 (0.893, —) | LogLogistic 2.360, 1.118 (0.112, —) | LogLogistic 1.410, 2.013 (0.036, 8.948 ) | 0.943 2.005 | 0.080, 0.549 0.371 |
| Weibull 16.231, 0.949 (0.844, —) | Weibull 1.296, 1.073 (0.121, —) | LogLogistic 1.412, 5.428 (0.037, 1.001 ) | 0.948 1.895 | 0.084, 0.514 0.402 |
| LogLogistic 16.577, 0.965 (0.718, —) | LogLogistic 2.325, 1.099 (0.035, 8.948 ) | InverseWeibull 1.407, 2.408 (0.035, —) | 0.963 2.009 | 0.095, 0.535 0.370 |
| LogNormal 0.104, 0.182 (—, 7.334 ) | Weibull 0.977, 0.810 (8.948 , 8.948 ) | InverseWeibull 1.408, 1.453 (8.948 , —) | 1.030 2.022 | 0.147, 0.487 0.366 |
| Paralogistic 16.278, 1.127 (0.754, —) | Paralogistic 1.864, 1.531 (8.948 , 8.948 ) | LogLogistic 1.412, 3.506 (8.948 , —) | 0.948 1.962 | 0.084, 0.533 0.383 |
| Paralogistic 11.533, 1.389 (0.815, 0.148) | Weibull 14.359, 0.989 (0.693, —) | InverseWeibull 1.537, 0.830 (0.049, —) | 0.902 0.991 | 0.045, 0.070 0.885 |
| Weibull 15.747, 0.955 (0.806, —) | InverseBurr 0.057, 3.466, 2.089 (—, 0.864, 0.376) | InverseParalogistic 1.421, 1.214 (0.038, 8.948 ) | 0.955 1.953 | 0.090, 0.525 0.385 |
| Weibull 17.828, 0.932 (1.038, —) | InverseBurr 0.049, 6.765, 1.906 (—, 4.658, 0.092) | LogLogistic 1.413, 0.114 (0.080, 0.317) | 0.931 1.603 | 0.073, 0.423 0.504 |
| Weibull 15.832, 0.954 (0.874, —) | InverseBurr 0.291, 2.761, 1.651 (—, 1.137, 1.123) | InverseWeibull 1.413, 5.797 (0.042, 8.948 ) | 0.953 1.977 | 0.087, 0.534 0.379 |
| InverseBurr 0.592, 23.222, 0.993 (—, 4.265, 7.457 ) | LogLogistic 1.702, 0.797 (8.948 , 8.948 ) | InverseWeibull 1.463, 3.400 (8.948 , —) | 0.972 3.633 | 0.103, 0.735 0.162 |
Appendix B. R Code
In Figure A1, we present an example of R code to estimate the six parameters of a three-spliced distribution without differentiability, while Figure A2 shows the results obtained in about 30 min.
Note that this code is the same for any distribution with six parameters to be estimated, the only difference consisting in changing the functions names in . Also, this code can be easily adapted for other three-spliced distributions with a different number of parameters to be estimated (in our case, we also have distributions with five and seven such parameters).
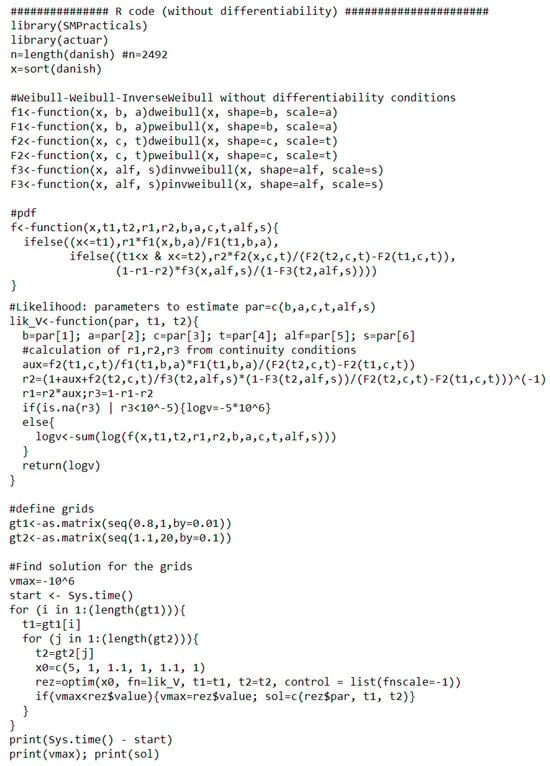
Figure A1.
R code for estimation without differentiability.
Figure A1.
R code for estimation without differentiability.

Figure A2.
Result of R code for estimation without differentiability.
Figure A2.
Result of R code for estimation without differentiability.


Figure A3.
R code for estimation with differentiability.
Figure A3.
R code for estimation with differentiability.
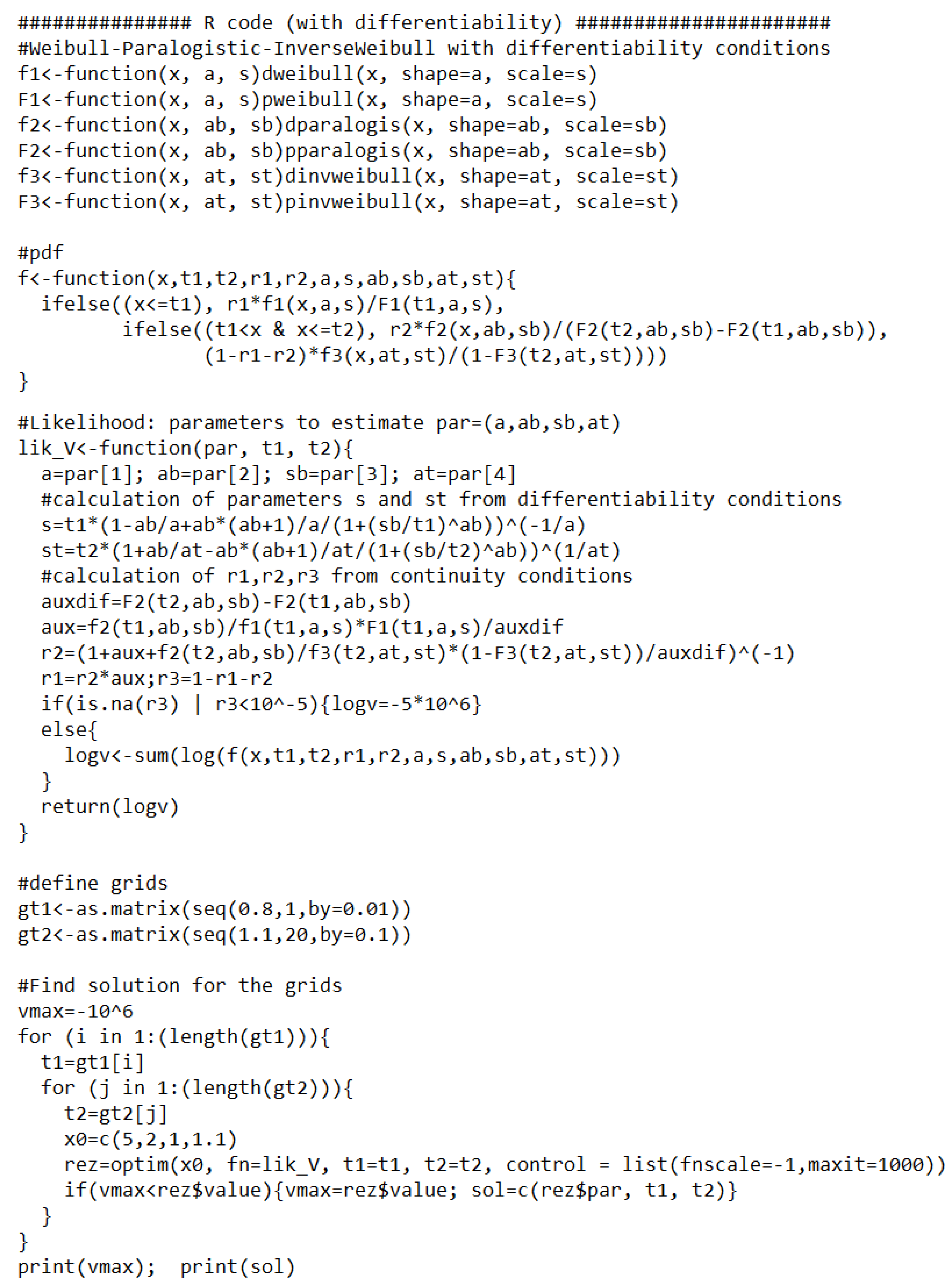

Figure A4.
Result of R code for estimation with differentiability.
Figure A4.
Result of R code for estimation with differentiability.

In Figure A3, we present an example of R code to estimate the four parameters of a three-spliced distribution with differentiability, while the results are shown in Figure A4 obtained in about 34 s (this is faster because there are only four parameters to estimate). On the other hand, it is more complicated to adapt this code to other three-spliced distributions because the parameters calculated from the differentiability conditions change with the distribution.
Note that the computing times above are for grids of dimensions 21 × 190. However, we used larger grids, and the computing time increased, especially when we also stored the results in a list containing also KS values as explained before.
We mention that we used a laptop Intel(R)Core(TM) i7-1255U, 1.76 GHz.
References
- Klugman, S.A.; Panjer, H.H.; Willmot, G.E. Loss Models: From Data to Decisions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 715. [Google Scholar]
- Cooray, K.; Ananda, M.M. Modeling actuarial data with a composite lognormal-Pareto model. Scand. Actuar. J. 2005, 2005, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollnik, D.P. On composite lognormal-Pareto models. Scand. Actuar. J. 2007, 2007, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, S.A.; Hamzah, N.A.; Maghsoudi, M.; Nadarajah, S. Modeling loss data using composite models. Insur. Math. Econ. 2015, 61, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderin-Ojeda, E. On the Composite Weibull–Burr Model to describe claim data. Commun. Stat. Case Stud. Data Anal. Appl. 2015, 1, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderin-Ojeda, E.; Kwok, C.F. Modeling claims data with composite Stoppa models. Scand. Actuar. J. 2016, 2016, 817–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, B.; Miljkovic, T. Extending composite loss models using a general framework of advanced computational tools. Scand. Actuar. J. 2019, 2019, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambakuyana, W.A.; Shongwe, S.C. Composite and Mixture Distributions for Heavy-Tailed Data—An Application to Insurance Claims. Mathematics 2024, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutali, S.; Vernic, R. On the composite Lognormal–Pareto distribution with uncertain threshold. Commun.-Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2020, 51, 4492–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajah, S.; Bakar, S. New composite models for the Danish fire insurance data. Scand. Actuar. J. 2014, 2014, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynkens, T.; Verbelen, R.; Beirlant, J.; Antonio, K. Modelling censored losses using splicing: A global fit strategy with mixed Erlang and extreme value distributions. Insur. Math. Econ. 2017, 77, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollnik, D.P.; Sun, C. Modeling with Weibull-Pareto models. N. Am. Actuar. J. 2012, 16, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Majid, M.H.; Ibrahim, K. On Bayesian approach to composite Pareto models. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradhye, G.; Tzougas, G.; Bhati, D. A Copula-Based Bivariate Composite Model for Modelling Claim Costs. Mathematics 2024, 12, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderín-Ojeda, E.; Gómez-Déniz, E.; Vázquez-Polo, F.J. Conditional tail expectation and premium calculation under asymmetric loss. Axioms 2023, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.C.; Tzougas, G.; Wüthrich, M.V. Mixture composite regression models with multi-type feature selection. N. Am. Actuar. J. 2023, 27, 396–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ananda, M.M. A generalized family of exponentiated composite distributions. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ananda, M.M. A new insight into reliability data modeling with an exponentiated composite Exponential-Pareto model. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarrott, C. Univariate extreme value mixture modeling. In Extreme Value Modeling and Risk Analysis; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2016; pp. 41–67. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, K.; Ma, S. Three-part model for fractional response variables with application to Chinese household health insurance coverage. J. Appl. Stat. 2013, 40, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.; Valdez, E.A. Fat-tailed regression modeling with spliced distributions. N. Am. Actuar. J. 2018, 22, 554–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca, A.; Vernic, R. On the three-spliced Exponential-Lognormal-Pareto distribution. Analele ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Ovidius Constanţa. Ser. Mat. 2022, 30, 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Baca, A.; Vernic, R. Extreme values modeling using the Gamma-Lognormal-Pareto three-spliced distribution. In Changes and Innovations in Social Systems: 505 (Studies in Systems, Decision and Control); Hoskova-Mayerova, S., Flaut, C., Flaut, D., Rackova, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, J. Claims Modelling with Three-Component Composite Models. Risks 2023, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.H.A.; Ibrahim, K.; Masseran, N. Three-Part Composite Pareto Modelling for Income Distribution in Malaysia. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex algorithm for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).