Oscillatory Behavior of the Solutions for a Parkinson’s Disease Model with Discrete and Distributed Delays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Existence of Oscillatory Solutions
- (i)
- Re () = 0, Im() , and or
- (ii)
- Re () > 0, and Re () > max {||, ||, , ||}, or
- (iii)
- Im () = 0, > 0.
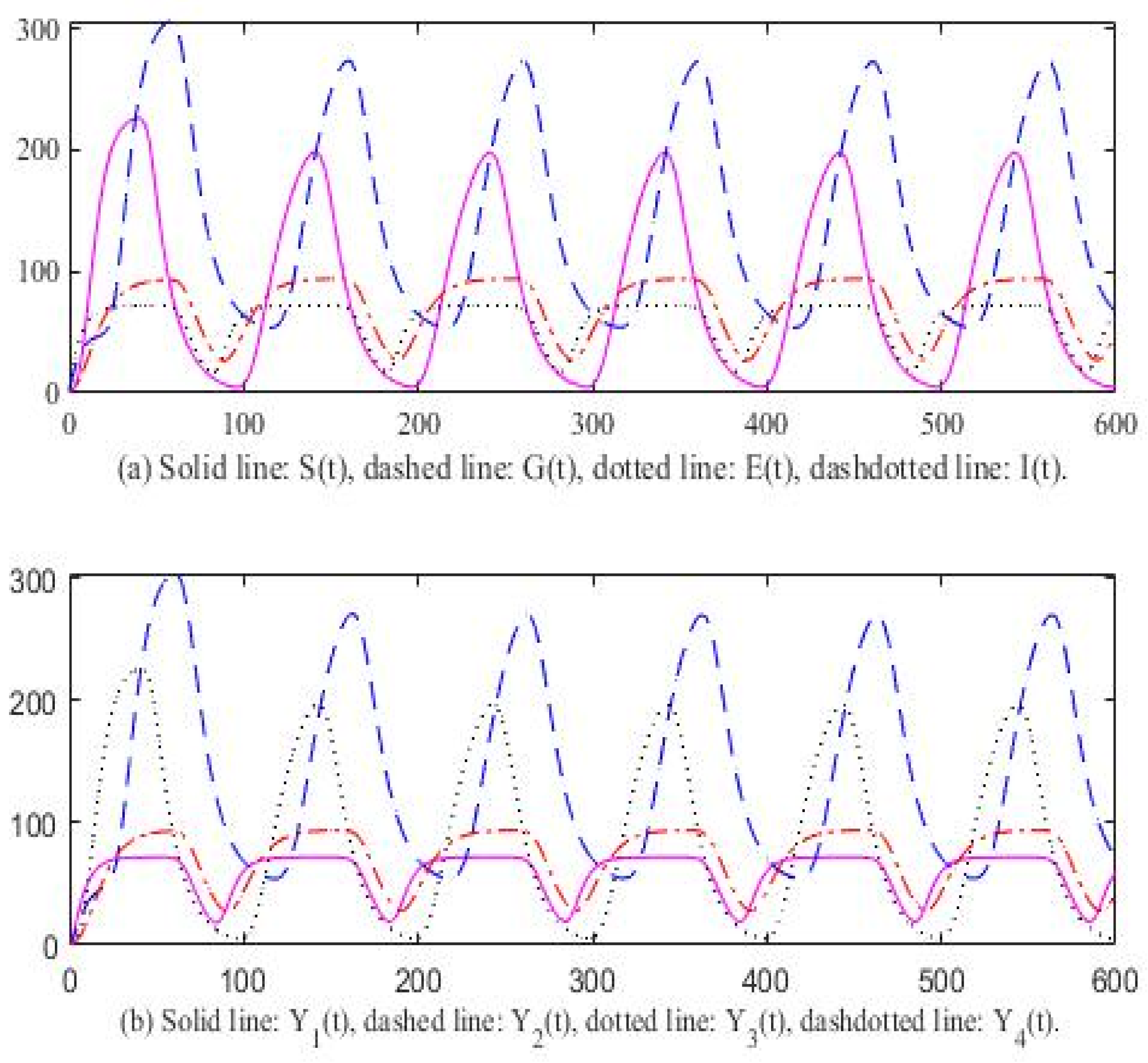
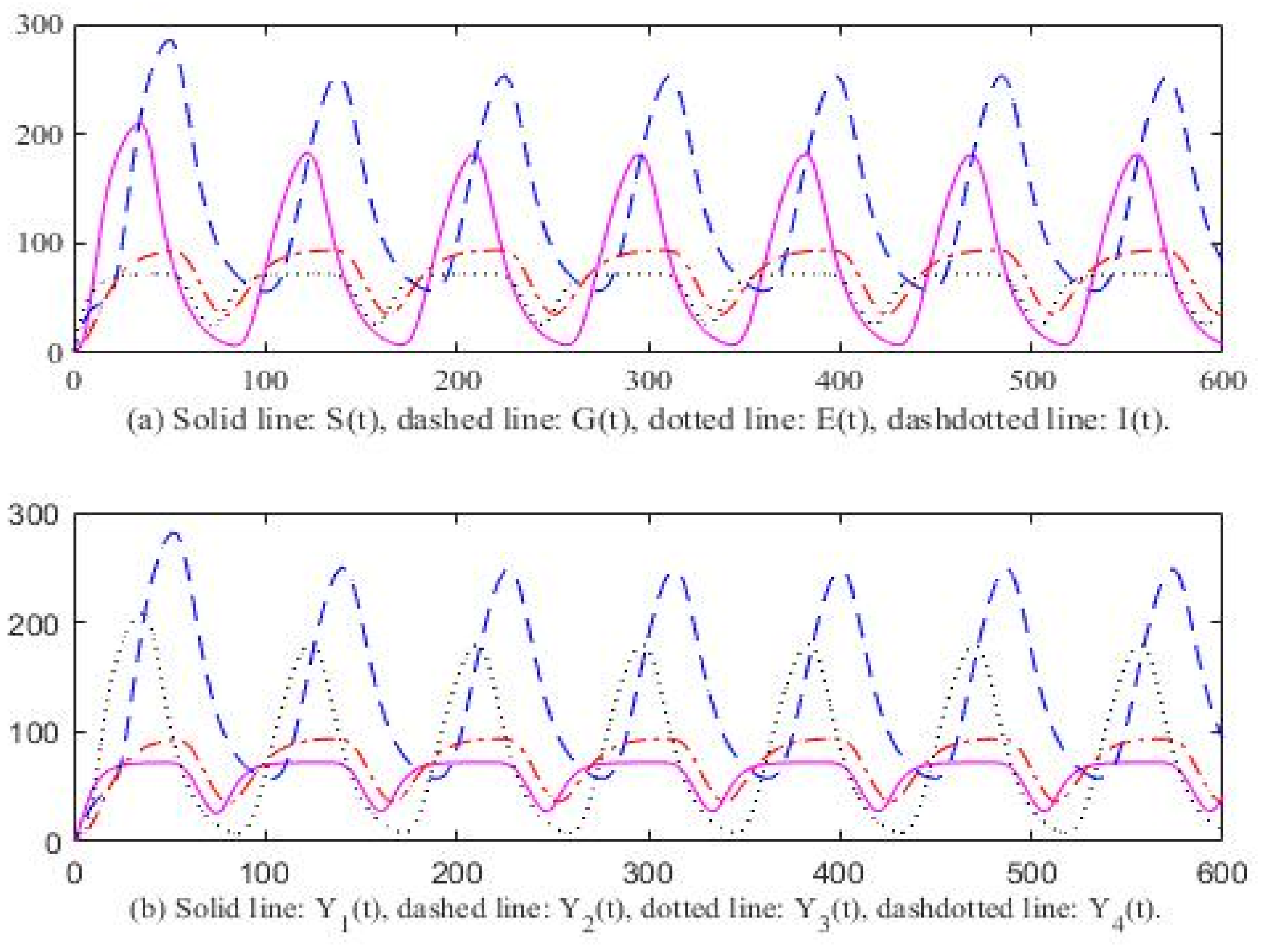
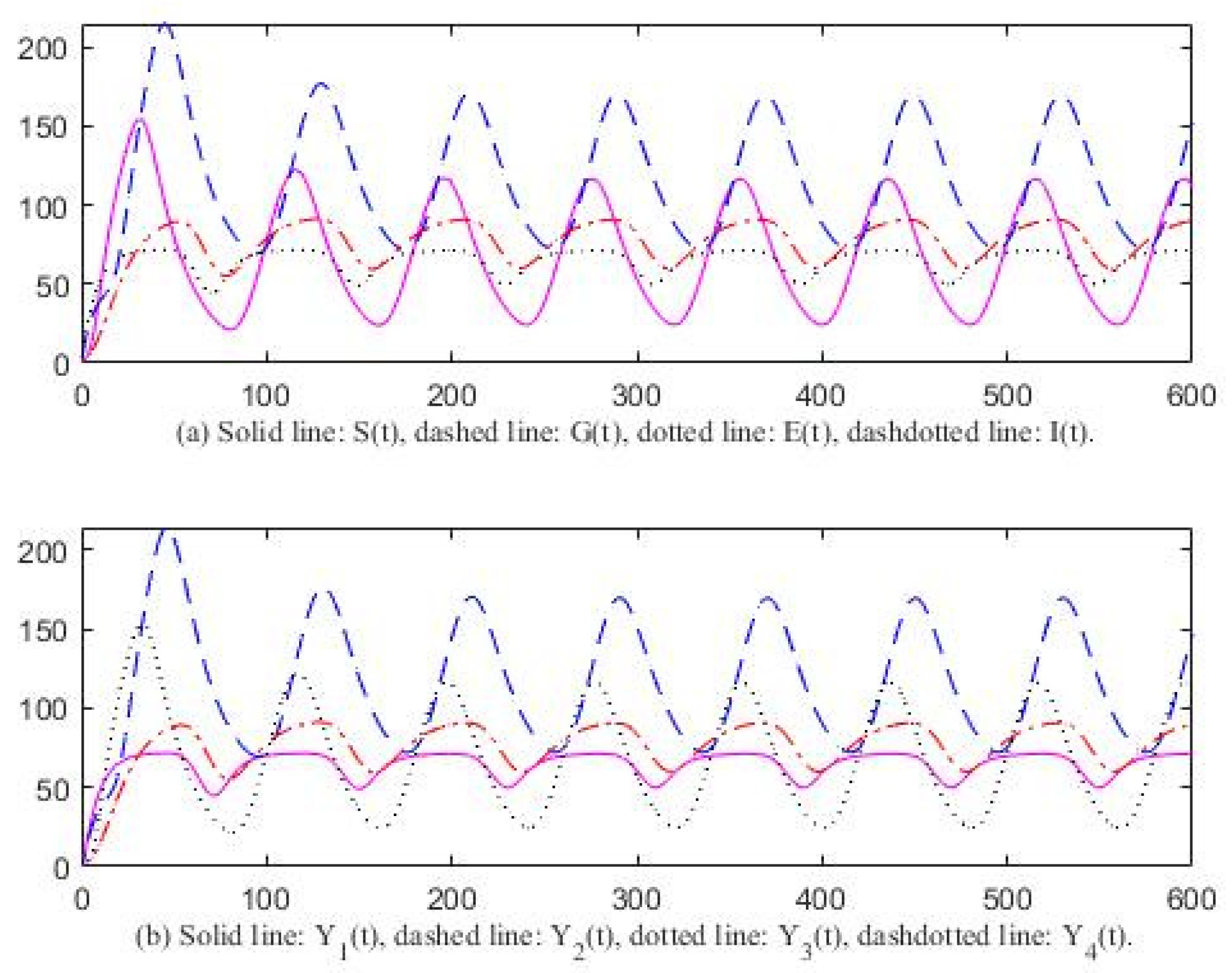
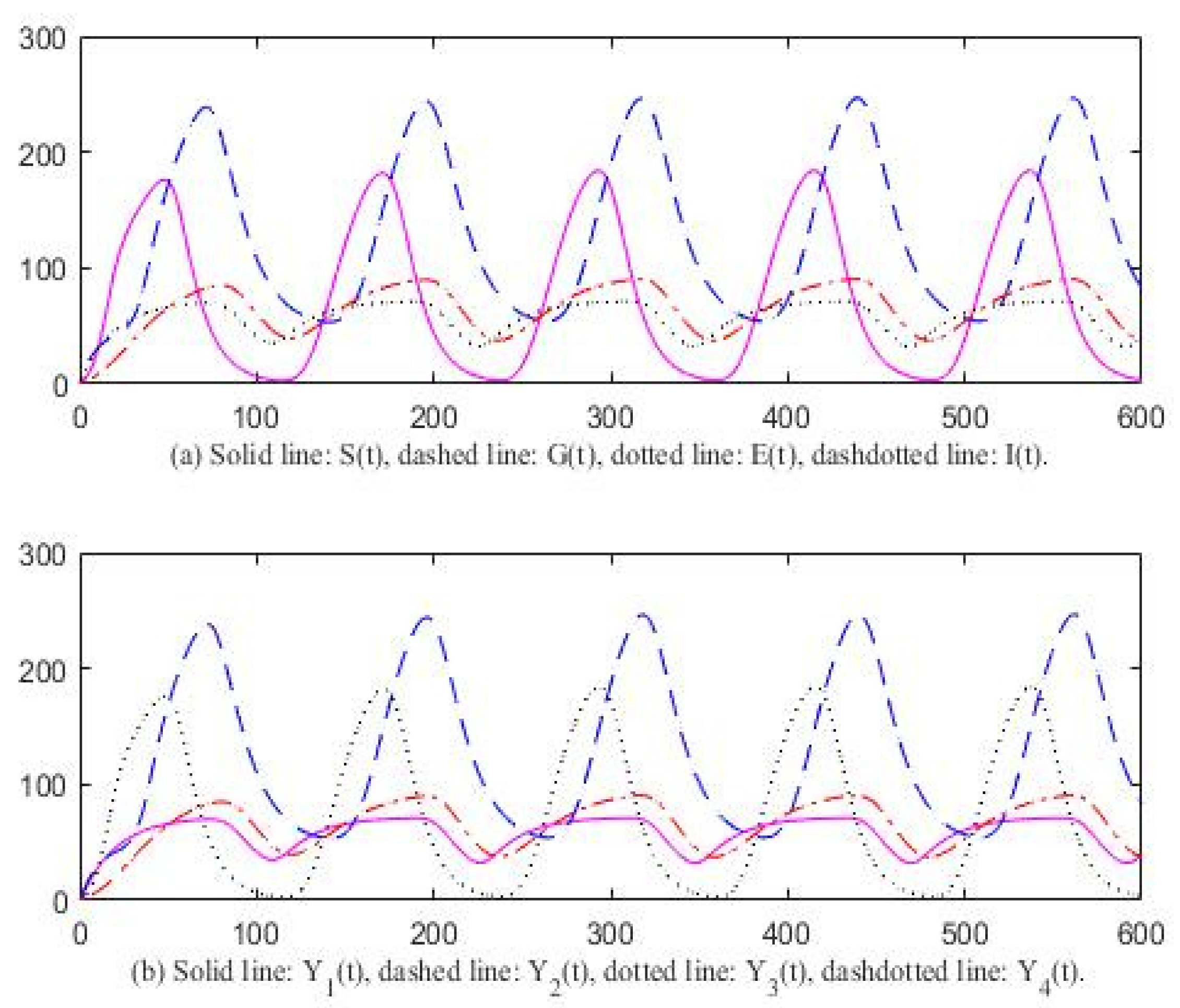
3. Computer Simulation Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuwairqi, S.M.; Badrah, A.A. Modeling the dynamics of innate and adaptive immune response to Parkinson’s disease with immunotherapy. AIMS Math. 2023, 8, 1800–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, B.; Zhu, L.; Lin, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, D. The possible mechanism of direct feedback projections from basal ganglia to cortex in beta oscillations of Parkinson’s disease: A theoretical evidence in the competing resonance model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 120, 107142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, B.; Zhu, L.; Lin, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, D. Hopf bifurcation analysis for Parkinson oscillation with heterogeneous delays: A theoretical derivation and simulation analysis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2022, 114, 106614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaslik, E.; Kokovics, E.A.; Radulescu, A. Stability and bifurcations in Wilson-Cowan systems with distributed delays, and an application to basal ganglia interactions. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2022, 104, 105984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, B.; Zhou, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, D. Hopf bifurcation mechanism analysis in an improved cortex-basal ganlia network with distributed delays: An application to Parkinson’s disease. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 166, 113022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiza, H.A.; Sohaly, M.A.; Elfouly, M.A. Small two-delay differential equations for Parkinson’s disease models using Taylor series transform. Indian J. Phys. 2023, 97, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrah, A.; Tuwairqi, S.A. Modeling the dynamics of innate immune response to Parkinson disease with therapeutic approach. Phys. Biol. 2022, 19, 056004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, R.; Chang, C.Y.; Raja, M.A.; Chaudhar, N.I. Design of intelligent neuro-supervised networks for brain electrical activity rhythms of Parkinson’s disease model. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terman, D.; Rubin, J.E.; Yew, A.C.; Wilson, C.J. Activity patterns in a model for the subthalamopallidal network of the basal ganglia. J. Neurosci. 2020, 22, 2963–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Kang, Y.; Ghori, M.B. Emergence of beta oscillations of a resonance model for Parkinson’s disease. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 8824760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Xu, X.; Horn, A.; Li, N.; Ling, Z.; Brown, P.; Wang, S. Intra-operative characterization of subthalamic oscillations in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grado, L.L.; Johnson, M.D.; Netoff, T.I. Bayesian adaptive dual control of deep brain stimulation in a computational model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, 1006606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Xu, M.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D. A bidirectional Hopf bifurcation analysis of Parkinson’s oscillation in a simplified basal ganglia model. J. Theor. Biol. 2022, 536, 110979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darcy, N.; Lofredi, R.; Fatly, B.A.; Neumann, W.J.; Hubl, J.; Brucke, C.; Krause, P.; Schneider, G.; Kuhn, A. Spectral and spatial distribution of subthalamic beta peak activity in Parkinson’s disease patients. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 356, 114150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.E.; Espay, A.J. Disease modification in Parkinson’s disease: Current approaches, challenges, and future considerations. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, C.; Anjum, R. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms, translational models and management. Strateg. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.E.; Mally, K. Axon degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 246, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovonou, A.; Bolduc, C.; Linan, V.S.; Gora, C.; Peralta, M.R.; Levesque, M. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: Bridging the gap between disease hallmarks and research questions. Trans. Neurodegener. 2023, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Luo, S. Joint modeling of multivariate longitudinal measurements and survival data with applications to Parkinson’s disease. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2016, 25, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, D.; Martin, M. Quality of life and Parkinson’s disease: Translation and validation of the US Parkinson’s disease questionnaire (PDQ-39). Qual. Life Res. 1999, 8, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Chelliah, V.; Chen, C.; Graaf, P.H. Mathematical biology models of Parkinson’s disease. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2019, 8, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buatois, S.; Retout, S.; Frey, N.; Ueckert, S. Item response theory as an efficient tool to describe a heterogeneous clinical rating scale in de novo idiopathic Parkinson’s disease patients. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, I.A.; Kuznetsov, A.V. What can trigger the onset of Parkinson’s disease—A modeling study based on a compartmental model of alpha-synuclein transport and aggregation in neurons. Math. Biosci. 2016, 278, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braatz, E.M.; Coleman, R.A. A mathematical model of insulin resistance in Parkinson’s disease. Comput. Biol.Chem. 2015, 56, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, M.; Middleton, R.; Wellstead, P. Feedback motif for the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. IET. Syst. Biol. 2012, 6, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poliquin, P.O.; Chen, J.; Cloutier, M.; Trudeau, L.E.; Jolicoeur, M. Metabolomics and in-silico analysis reveal critical energy deregulations in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flagmeier, P.; Meisl, G.; Vendruscolo, M.; Galvagnion, C. Mutations associated with familial Parkinson’s disease alter the initiation and amplification step of α-synuclein aggregation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10328–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotharius, J.; Brundin, P. Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: Dopamine, vesicles and α-synuclein. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotegher, N.; Duchen, M.R. Crosstalk between lysosomes and mitochondria in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelders, G.; Baekelandt, V.; Perren, A. Linking neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 4784268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafee, N. A bifurcation problem for a functional differential equation of finitely retarded type. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1971, 35, 312–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Plamondon, R. An oscillatory criterion for a time delayed neural ring network model. Neural Netw. 2012, 29, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, C. Oscillatory Behavior of the Solutions for a Parkinson’s Disease Model with Discrete and Distributed Delays. Axioms 2024, 13, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13020075
Feng C. Oscillatory Behavior of the Solutions for a Parkinson’s Disease Model with Discrete and Distributed Delays. Axioms. 2024; 13(2):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13020075
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Chunhua. 2024. "Oscillatory Behavior of the Solutions for a Parkinson’s Disease Model with Discrete and Distributed Delays" Axioms 13, no. 2: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13020075
APA StyleFeng, C. (2024). Oscillatory Behavior of the Solutions for a Parkinson’s Disease Model with Discrete and Distributed Delays. Axioms, 13(2), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13020075




