Global Dynamics of an Age-Structured Tuberculosis Model with Vaccine Failure and Nonlinear Infection Force
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The TB Model and Its Fundamental Properties
2.1. The TB Model
2.2. Well-Posedness
2.3. Asymptotic Smoothness
- (1)
- ;
- (2)
- for some , has compact closure for each .
- (1)
- ;
- (2)
- uniformly in ;
- (3)
- uniformly in ;
- (4)
- uniformly in .
3. Existence of Equilibrium States
4. Uniform Persistence and Global Stability
4.1. Uniform Persistence
4.2. Global Stability
5. Parameter Estimation and Sensitivity Analysis
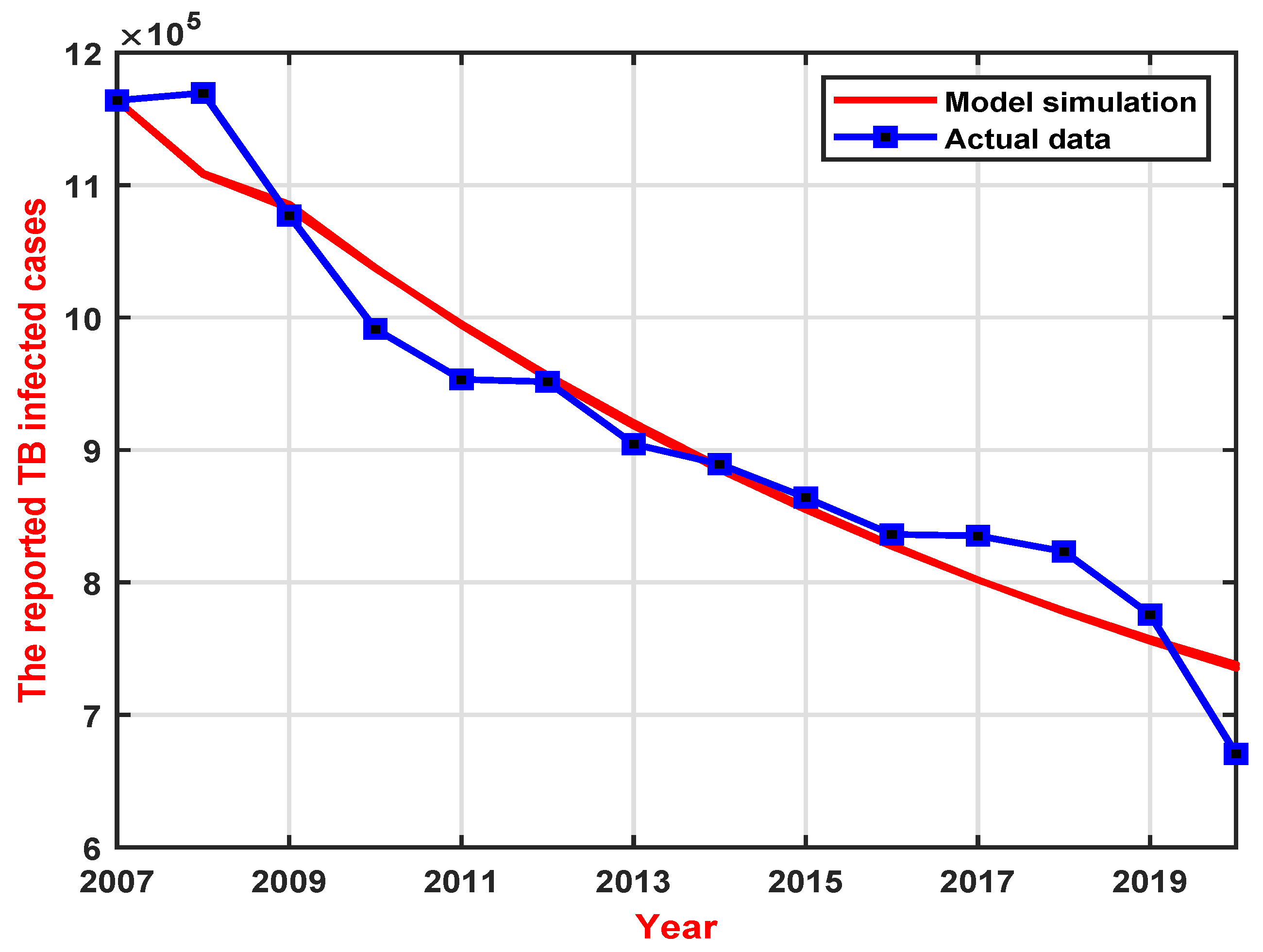
5.1. Parameter Estimation
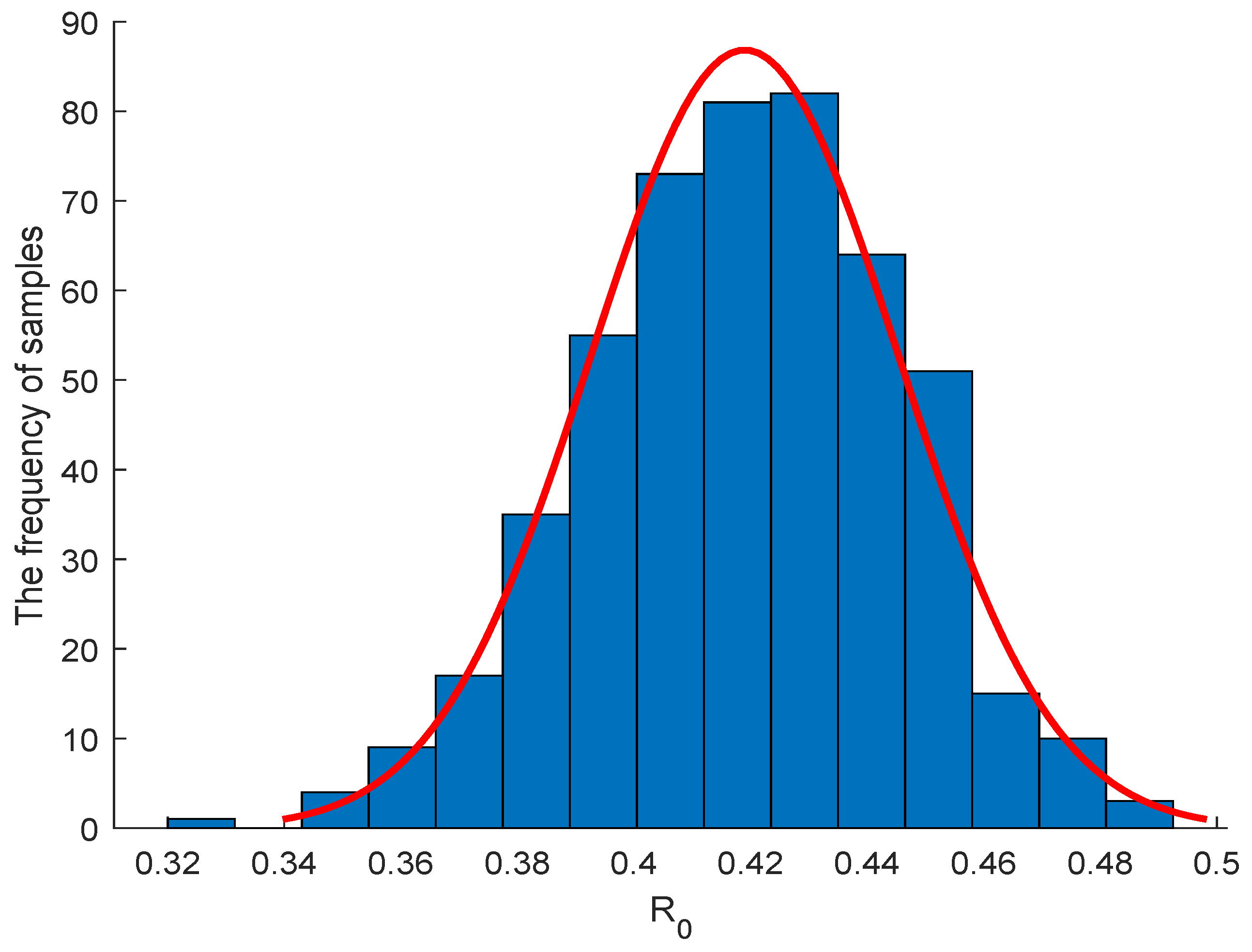
5.2. Sensitivity Analysis
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240061729 (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Guo, Z.K.; Xiang, H.; Huo, H.F. Analysis of an age-structured tuberculosis model with treatment and relapse. J. Math. Biol. 2021, 82, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.K.; Khajanchi, S.; Kar, T. Transmission dynamics of tuberculosis with multiple re-infections. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 130, 109450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jung, E.; Lee, S.M. Optimal intervention strategy for prevention tuberculosis using a smoking-tuberculosis model. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 380, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, D. The dynamics of a stochastic vaccinated tuberculosis model with treatment. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 527, 121274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcaglar, C.; Shabbeer, A.; Vandenberg, S.L.; Yener, B.; Bennett, K.P. Epidemiological models of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex infections. Math. Biosci. 2012, 236, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Jung, E. Optimal Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Strategy from a Mathematical Model Based on Real Data. Bull. Math. Biol. 2014, 76, 1566–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, H.F.; Zou, M.X. Modelling effects of treatment at home on tuberculosis transmission dynamics. Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 9474–9484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Analysis of an in-host tuberculosis model for disease control. Appl. Math. Lett. 2020, 99, 105983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Basic TB Facts. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/default.htm (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Burman, W.J.; Bliven, E.E.; Cowan, L.; Bozeman, L.; Nahid, P.; Diem, L.; Vernon, A. Relapse associated with active disease caused by Beijing strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trollfors, B.; Sigurdsson, V.; Dahlgren-Aronsson, A. Prevalence of Latent TB and Effectiveness of BCG Vaccination Against Latent Tuberculosis: An Observational Study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 109, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Cords, O.; Liu, Q.; Acuna-Villaorduna, C.; Bonnet, M.; Fox, G.J.; Carvalho, A.C.C.; Chan, P.C.; Croda, J.; Hill, P.C.; et al. Infant BCG vaccination and risk of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis throughout the life course: A systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e1307–e1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiabudiawan, T.P.; Reurink, R.K.; Hill, P.C.; Netea, M.G.; van Crevel, R.; Koeken, V.A. Protection against tuberculosis by Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination: A historical perspective. Med 2022, 3, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerantzas, C.A.; Jacobs, W.R. Origins of Combination Therapy for Tuberculosis: Lessons for Future Antimicrobial Development and Application. mBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseiniporgham, S.; Sechi, L.A. A Review on Mycobacteriophages: From Classification to Applications. Pathogens 2022, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Tuberculosis: Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/tuberculosis-multidrug-resistant-tuberculosis-(mdr-tb) (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Global analysis of tuberculosis dynamical model and optimal control strategies based on case data in the United States. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 422, 126983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S. Global stability in a tuberculosis model of imperfect treatment with age-dependent latency and relapse. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2017, 14, 1337–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, M.; Milner, F. The Basic Approach to Age-Structured Population Dynamics; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.K.; Huo, H.F.; Xiang, H. Analysis of an age-structured model for HIV-TB co-infection. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 2022, 27, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.K.; Huo, H.F.; Xiang, H. Global dynamics of an age-structured malaria model with prevention. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 1625–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Sekine, H. A mathematical model for Chagas disease with infection-age-dependent infectivity. Math. Biosci. 2004, 190, 39–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, I.; Tiwari, P.K.; Samanta, S.; Elmojtaba, I.M.; Al-Salti, N.; Chattopadhyay, J. A simple SI-type model for HIV/AIDS with media and self-imposed psychological fear. Math. Biosci. 2018, 306, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Threshold dynamics of an SIRS model with nonlinear incidence rate and transfer from infectious to susceptible. Appl. Math. Lett. 2017, 70, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, R.P.; McCluskey, C.C. Global stability for an SEI model of infectious disease with immigration. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 243, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X. Global dynamics for an age-structured epidemic model with media impact and incomplete vaccination. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2016, 32, 136–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zou, S.; Yang, J. Global analysis of an SIR epidemic model with infection age and saturated incidence. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2016, 30, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.L.; Thieme, H.R. Dynamical Systems and Population Persistence; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Magal, P.; Zhao, X.Q. Global Attractors and Steady States for Uniformly Persistent Dynamical Systems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 2005, 37, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, J.K.; Waltman, P. Persistence in Infinite-Dimensional Systems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1989, 20, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, C.J.; Pilyugin, S.S. Global analysis of age-structured within-host virus model. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 2013, 18, 1999–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasalle, J.P. Some Extensions of Liapunov’s Second Method. Ire Trans. Circuit Theory 1960, 7, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/tuberculosis#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/ (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Xue, L.; Jing, S.; Wang, H. Evaluating Strategies For Tuberculosis to Achieve the Goals of WHO in China: A Seasonal Age-Structured Model Study. Bull. Math. Biol. 2022, 84, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Fang, Z.; Luo, S.; Lin, S.; Xu, L.; Yan, B.; Liu, X.; Xia, L.; Fan, X.; Lu, S. The effect of BCG vaccination and risk factors for latent tuberculosis infection among college freshmen in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 122, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: http://www.chinacdc.cn/ (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Haario, H.; Laine, M.; Mira, A.; Saksman, E. DRAM: Efficient adaptive MCMC. Stat. Comput. 2006, 16, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MCMC Toolbox for Matlab. Available online: https://mjlaine.github.io/mcmcstat/index.html#org0701d35 (accessed on 18 August 2023).
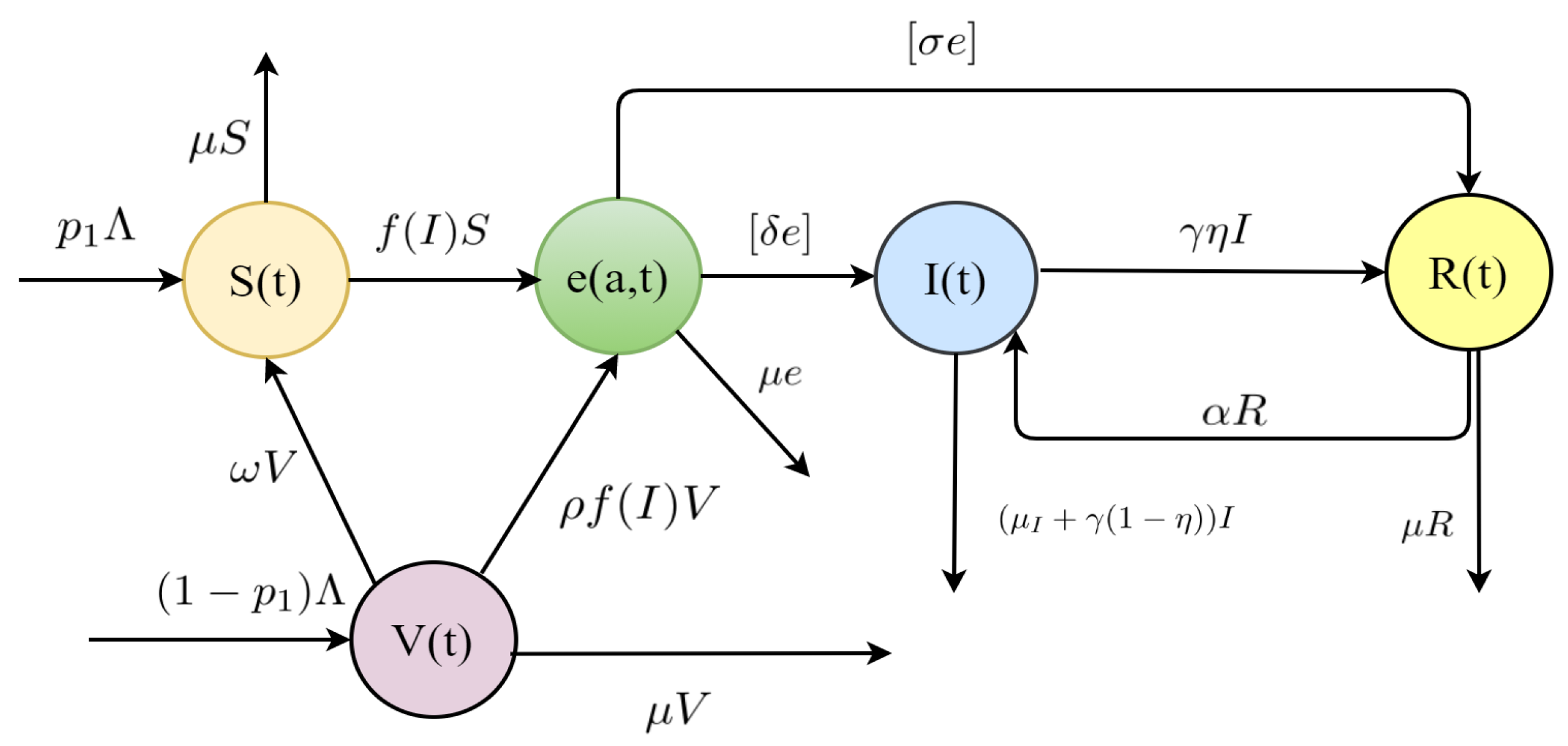

| Notations | Definitions |
|---|---|
| the rate of recruitment of susceptible individuals | |
| the constant natural death rate of individuals in every compartment | |
| the coverage rate of the BCG vaccine | |
| the rate of vaccine-induced protection wanes | |
| the reduction coefficient of the contagion rate | |
| the rate distribution of latent individuals entering the infectious subclass | |
| the rate distribution of latent individuals entering the recovered subclass | |
| the rate of treatment | |
| the death rate of the infectious individuals | |
| the proportion of effective treatment | |
| the relapse rate |
| Year | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
| Cases | 1,163,959 | 1,169,540 | 1,076,938 | 991,350 | 953,275 | 951,508 | 904,434 |
| Year | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Cases | 889,381 | 864,015 | 836,236 | 835,193 | 823,342 | 775,764 | 670,538 |
| Parameters | Value | Source | Parameters | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01518682 | Fitting | Fitting | |||
| 0.047465098 | Fitting | 1,805,707 | Fitting | ||
| 0.086799875 | Fitting | 0.010890517 | Fitting | ||
| 0.000960051 | Fitting | 0.200034765 | Fitting | ||
| Fitting | 129,832,691 | Fitting | |||
| Parameters | Mean | Std | 95% CI | Gewekes Z-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.015224 | 0.0017461 | [0.01521682, 0.015232125] | 0.99492 | |
| 0.047357 | 0.0054654 | [0.047333118, 0.047381024] | 0.9904 | |
| 0.08693 | 0.010083 | [0.0868855, 0.086973908] | 0.98351 | |
| 0.00095903 | 0.00011069 | [0.000958544, 0.000959514] | 0.99975 | |
| 0.090725 | 0.010535 | [0.090678698, 0.09077104] | 0.99583 | |
| 0.99636 | ||||
| 0.98896 | ||||
| 1,801,600 | 209,190 | [1,800,674, 1,802,508] | 0.99182 | |
| 0.010882 | 0.0012476 | [0.010876, 0.010887] | 0.98807 | |
| 0.19972 | 0.023108 | [0.1996197, 0.199822] | 0.9752 | |
| [130,309,596, 130,441,079] | 0.99426 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Zhang, L. Global Dynamics of an Age-Structured Tuberculosis Model with Vaccine Failure and Nonlinear Infection Force. Axioms 2023, 12, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090805
Guo Z, Zhang L. Global Dynamics of an Age-Structured Tuberculosis Model with Vaccine Failure and Nonlinear Infection Force. Axioms. 2023; 12(9):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090805
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhongkai, and Liang Zhang. 2023. "Global Dynamics of an Age-Structured Tuberculosis Model with Vaccine Failure and Nonlinear Infection Force" Axioms 12, no. 9: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090805
APA StyleGuo, Z., & Zhang, L. (2023). Global Dynamics of an Age-Structured Tuberculosis Model with Vaccine Failure and Nonlinear Infection Force. Axioms, 12(9), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090805




