Abstract
In this work, we consider the monotone inclusion problem in real Hilbert spaces and propose a simple inertial method that does not include any evaluations of the associated resolvent and projection. Under suitable assumptions, we establish the strong convergence of the method to a minimal norm solution. Saddle points of minimax problems and critical points problems are considered as the applications. Numerical examples in finite- and infinite-dimensional spaces illustrate the performances of our scheme.
MSC:
65K05; 65K10; 47H10; 47L25
1. Introduction
Since Minty [1], and the many others to follow, such as [2,3,4], introduced the theory of the monotone operator, a large number of theoretical and practical developments have been presented. Pascali and Sburian [5] pointed out that the class of monotone operators is important, and due to the simple structure of the monotonicity condition, it can be handled easily. The monotone inclusion problem is one of the highlights due to its important significance in convex analysis and convex optimization problems, which includes convex minimization, monotone variational inequality, convex and concave minimax problems, linear programming problems and many others. For further information and applications, see, e.g., Bot and Csetnek [6], Korpelevich [7], Khanc et al. [8], Sicre et al. [9], Xu [10], Yin et al. [11] and the many references therein [12,13,14,15].
Let H be a real Hilbert space and be a given operator with domain . The monotone inclusion problem is formulated as finding a point such that
We denote the solution set of (1) by .
One of the simplest classical algorithms for solving the monotone inclusion problem (1) is the proximal point method of Martinet [16]. Given a maximal monotone mapping and its associated resolvent , the proximal point algorithm generates a sequence according to the update rule:
The proximal point algorithm, also known as the regularization algorithm, is a first-order optimization method that requires the function and gradient (subgradient) evaluations, and thus attracts much interest. For more relevant improvements and achievements on the regularization methods in Hilbert spaces, one can refer to [17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
One important application of monotone inclusions is the convex minimization problem. Given is a nonempty, closed and convex set and a continuously differentiable function f, the constrained minimization aims to find a point such that
Using some operator theory properties, it is known that solves (3) if and only if for some . This relationship translates to the projected gradient method:
where is the metric projection onto C and is the gradient of f.
The projected gradient method calls for the evaluation of the projection onto the feasible set C as well as the gradient evaluation of f. This guarantees a reduction in the objective function while keeping the iterates feasible. With the set C as above and an operator , an important problem worth mentioning is the monotonic variational inequality problem, consisting of finding a point such that
Using the relationship between the projection , the resolvent and the normal cone of the set C, that is,
we obtain the iterative step rule for solving (4)
Indeed, the mentioned optimization methods above now “dominate” in modern optimization algorithms based on first-order information (such as function values and radial/subgradient), and it can be predicted that they will become increasingly important as the scale of practical application problems increases. For excellent works, one can refer to Teboulle [24], Drusvyatskiy and Lewis [25], etc. However, it is undeniable that they are highly dependent on the structure of the given problem, and computationally, these methods rely on the ability to compute resolvents/projections per iteration; taking algorithm (5), for instance, the complexity of each step depends on the computation of the projection to the convex set C.
Hence, in this work, we wish to combine the popular inertial technology (see, e.g., Nesterov [26], Alvarez [27] and Alvarez–Attouch [28]) and establish a strong convergence iterative method that does not use resolvents or projections, and has good convergence properties due to the inertial technique.
The outline of this paper is as follows. In Section 2, we collect the definitions and results needed for our analysis. In Section 3, the resolvent/projection-free algorithm and its convergence analysis are presented. Later, in Section 4, we present two applications of the monotone inclusion problem, saddle points of the minimax problem and the critical points problem. Finally, in Section 5, numerical experiments illustrate the performances of our scheme in finite- and infinite-dimensional spaces.
2. Preliminaries
Let C be a nonempty, closed and convex subset of a real Hilbert space H equipped with the inner product . Denote the strong convergence to x of by , the -weak limit set of by
We recall two useful properties of the norm:
for all and such that .
Definition 1.
Let H be a real Hilbert space. An operator is called inverse strongly monotone (μ-ism) (or μ-cocoercive) if there exists a number such that
Definition 2.
Let C be a nonempty, closed convex subset of H. The operator is called the metric projection of H onto C: for every element , there is a unique nearest point in C, such that
The characterization of the metric projection is
Lemma 1
(Xu [29], Maingé [30]). Assume that and are nonnegative real sequences such that
where is a sequence in and is a real sequence. Provided that
(a) , ; ;
(b) .
Then, the limit of the sequence exists and .
Lemma 2
(see, e.g., Opial [31]). Let H be a real Hilbert space and such that there exists a nonempty, closed and convex set satisfying the following:
(1) For every , exists;
(2) Any weak cluster point of belongs to S.
Then, there exists such that converges weakly to .
Lemma 3
(see, e.g., Maingé [30]). Let be a sequence of real numbers that does not decrease at infinity, in the sense that there exists a subsequence of such that for all . Also consider the sequence of integers defined by
Then, is a nondecreasing sequence verifying and, for all ,
3. Main Result
We are concerned with the following monotone inclusion problem: finding such that
where A is a monotone-type operator on H.
Remark 1.
Clearly, if for some , then is a solution of (9) and the iteration process is terminated in finite iterations. In general, the algorithm does not stop in finite iterations, and thus we assume that the algorithm generates an infinite sequence.
Convergence Analysis
For the convergence analysis of our algorithm, we assume the following assumptions:
(A1) A is a continuous maximal monotone operator with cocoercive coefficient from H to H;
(A2) The solution set of (9) is nonempty.
Theorem 1.
Suppose that the assumptions (A1)–(A2) hold. If the sequences , are in and satisfy the following conditions:
(B1) , and ;
(B2)
Then, the recursion generated by Algorithm 1 converges strongly to an element p which is closest to in Ω, that is, .
| Algorithm 1 Convergence Analysis |
Initialization: Choose , and such that , select arbitrary starting points , and set . Iterative Step: Given the iterates and for each , choose such that , compute
Stopping Criterion: If , then stop. Otherwise, set and return to Iterative Step. |
Proof.
First, we prove that is bounded. Without the loss of the generality, let p be the closest element to 0 in because . It follows from the cocoercivity of A with coefficient that
Taking into account the definition of in the recursion (10), we have
and
which implies that Furthermore, we have
In view of the assumption on , we obtain , which entails that there exists some positive constant such that ; therefore,
namely, the sequence is bounded, and so are and .
By using again the formation of , we obtain
Here, two cases should be considered.
Case I. Assume that the sequence is decreasing, namely, there exists such that for each , and then there is the limit of and It turns out from (14) and the condition that
which implies that and .
Furthermore, by the setting of , we have and , which together with yields that
Because is bounded, it follows from Eberlein–Shmulyan’s theorem, for arbitrary point , that there exits a subsequence of such that converges weakly to q. By , and A is continuous, we have
which entails that . In view of the fact that the choice of q in was arbitrary, we conclude that , which makes Lemma 2 workable, that is, converges weakly to some point in .
Now, we claim that , where .
For this purpose, let , and then we have
which yields that
In addition, by using again the formation of , we obtain
and substituting the above inequality in (15), we have
where .
Owing to , we can infer that for each , so we have
In addition, from the assumption on , we have
and from , we have
and therefore (16) enables Lemma 1 to be applicable to, namely, .
Case II. If the sequence is not decreasing at infinity, in the sense that there exists a subsequence of such that . Owing to Lemma 3, we can induce that and , where is an indicator defined by and as .
Taking into account the fact that the formula (14) still holds for each , that is,
In addition, from the theorem’s assumptions and that
Transposing again, we have
which amounts to
Consequently, the sequence converges strongly to p, which is the closest point to 0 in . This completes the proof. □
Remark 2.
If the operator A is accretive with cocoercivity or maximal monotone, then all the above results hold.
4. Applications
4.1. Minimax Problem
Suppose and are two real Hilbert spaces, the general convex–concave minimax problem in a Hilbert space setting is illustrated as follows:
where Q and S are nonempty, closed and convex subsets of Hilbert spaces and , respectively, and is convex in x (for each fixed and concave in (for each fixed ).
A solution of the minimax problem (21) is interpreted as a saddle point, satisfying the following inequality
which amounts to the fact that is a minimizer in Q of the function , and is a maximizer in S of the function .
Minimax problems are an important modeling tool due to their ability to handle many important applications in machine learning, in particular, in generative adversarial nets (GANs), statistical learning, certification of robustness in deep learning and distributed computing. Some recent works can be seen in, e.g., Ataş [32], Ji-Zhao [33] and Hassanpour et al. [34].
For example, if we consider the standard convex programming problem,
where f and are convex functions. Using the Lagrange function L, the problem (22) can be reformulated as the following minimax problem (see, e.g., Qi and Sun [35]):
It can be seen that in (23) is a convex–concave function on , where
and the Kuhn–Tucker vector of (22) is exactly the saddle point of Lagrangian function in (23).
Another nice example is the Tchebychev approximating problem that consists of finding such that
that is, for given , finding approaching , where and Q is the space composed of the functions .
It is known that L has a saddle point if and only if
If L is convex–concave and differentiable, let and present the derivatives of L on x and , respectively, and then we have , where .
Note that is maximal monotone for the unconstrained case (i.e., ), and finding a saddle point of L equals to solving the equation . For more details on the minimax problem and its solutions, one can refer to the von Neumann works from the 1920s and 1930s [36,37] and Ky Fan’s minimax theorem [38].
Now, we consider minimax problems (21) under the unconstrained case, and let the solution set of the minimax problem be nonempty. So, by taking , we can obtain the saddle point of the minimax problem in from the following results.
Theorem 2.
Let and be two real Hilbert spaces. Suppose that the function L is convex–concave and differentiable such that . Under the setting of the parameters in Algorithm 1, if the sequences , , are in and satisfying the conditions as in Theorem 1, then the sequence generated by the following scheme
converges strongly to the least norm element , where and are two arbitrary initial points.
Proof.
Noting that is maximal monotone, so letting A be in Algorithm 1, and following Theorem 1, we have the result. □
Indeed, if we denote , then the recursions (24) specifically can be rewritten as follows for arbitrary initial points , , , ,
and the sequence pair converges strongly to an element which is closest to .
4.2. Critical Points Problem
In this part, we focus on finding the critical points of the functional defined by
where H is a real Hilbert space, the function is a proper, convex and lower semi-continuous function and is a convex locally Lipschitz mapping.
A point is said to be a critical point of if and if it satisfies
where is the generalized directional derivative of at in the direction which is defined by
Critical point theory is a powerful theoretical tool, which has been greatly developed in recent years and has been widely used in many fields, such as differential equations, operations research optimization and so on. For some recent works on the applications of critical point theory, we can refer to Trushnikov et al. [39], Turgut et al. [40] and therein.
A typical instance is finding the solution of the impulsive differential equation model existing in the fields of medicine, biology, rocket and aerospace motion and optimization theory which can be transformed into finding the critical point of some functional.
Specifically, we consider the following impulsive differential equation:
where , , , , . In addition, there exist and such that holds for all .
Let and the norm is induced by the inner product , .
Denote , and the functional on H is defined as
and then the periodic solution of the system (27) corresponds to the critical point of the functional F one to one.
If the functional F in (26) satisfies the Palais–Smale compact conditions and F is bounded from below, then there exists a critical point such that (see, e.g., Motreanu and Panagiotopoulos [41]). From Fermat’s theorem, one can refer that the critical point is a solution of the inclusion (see, e.g., Moameni [42]),
where is the generalized derivative of defined as
From Clarke [43], carries bounded sets of H into bounded sets of and is hemicontinuous. Moreover, we can infer that is a monotone mapping because is convex, which makes Browder ([17], Theorem 2) applicable, namely, is a maximal monotone mapping. Denoted by is the critical points set of the problem (26). By taking , we have the following result.
Theorem 3.
Let H be a real Hilbert space. Suppose that is of the form (26), bounded from below and satisfying the Palais–Smale compact conditions such that . Under the setting of the parameters in Algorithm 1, if , , are the sequences in satisfying the conditions as in Theorem 1, then the sequence generated by the following schemes
converges strongly to an element which is closest to .
5. Numerical Examples
In this section, we present numerical examples in finite- and infinite-dimensional spaces to illustrate the applicability, efficiency and stability of Algorithm 1. All the codes for the results are written in Matlab R2016b and are performed on an LG dual-core personal computer.
Example 1.
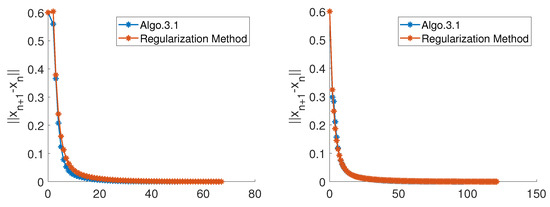

Here, we test the effectiveness of our algorithm in finite-dimensional space which does not need super high dimensions. For the purpose, let , and define the monotone operators A as follows:
it is easy to verify that the cocoercivity coefficient , so we set .
Next, let us compare our Algorithm 1 with the regularization method. Specifically, the regularization algorithm (RM) is considered as
As for the components, both our Algorithm 1 and the regularization method (RM), initial points , are generated randomly by Matlab, inertial coefficient is chosen to satisfy that if , then ; otherwise, , where , , . The experimental results are listed in Figure 1. Moreover, the iterations and convergence rate of Algorithm 1 for different values of are presented in Table 1.

Figure 1.
Algorithm 1 and the Regularization Method.

Table 1.
Example 1 Numerical Results for Algorithm 1 and Regularization Method.
Example 2.
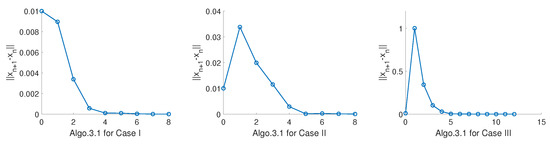

Now, we measure our Algorithm 1 in with . Define the mappings A by for all , and then it can be shown that A is -cocoercive monotone mapping. All the parameters , θ, , and are chosen as in Example 1. The stop criterion is . We test Algorithm 1 for the following three different initial points:
Case I: ;
Case II:
Case III:
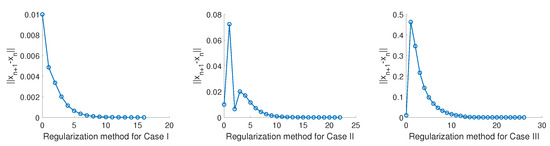
In addition, we also test the regularization method as illustrated in Example 1, and the tendency of the sequence is proposed in Figure 2 and Figure 3 and Table 2.

Figure 2.
Algorithm 1 for Case I, Case II, Case III in Example 2.

Figure 3.
Regularization Method for Case I, Case II, Case III in Example 2.

Table 2.
Example 2 Numerical Results for Algorithm 1 and Regularization Method.
6. Conclusions
The proximal point method (regularization method) and projection-based method are two classical and significant methods for solving monotone inclusions, variational inequalities and related problems.
However, the evaluations of resolvents/projections in these methods heavily rely on the structure of the given problem, and in the general case, this might seriously affect the computational effort of the given method. Thus, motivated by the ideas of Chidume et al. [44], Alvarez [28], Alvarez–Attouch [27] and Zegeye [45], we present a simple strong convergence method that avoids the need to compute resolvents/projections.
We present several theoretical applications such as minimax problems and critical point problems, as well as some numerical experiments illustrating the performances of our scheme.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This article was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12071316) and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0177).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Minty, G.J. Monotone (nonlinear)operators in Hilbert spaces. Duke Math. J. 1962, 29, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browder, F. The solvability of nonlinear functional equations. Duke Math. J. 1963, 30, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, J.; Lions, J. Quelques résultats de Višik sur les problèmes elliptiques non linéares par les méthodes de Minty-Browder. Bull. Soc. Math. Fr. 1965, 93, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minty, G.J. On a monotonicity method for the solution of non-linear equations in Banach spaces. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1963, 50, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascali, D.; Sburian, S. Nonlinear Mappings of Monotone Type; Editura Academia Bucuresti: Bucharest, Romania, 1978; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Bot, R.I.; Csetnek, E.R. An inertial forward-backward-forward primal-dual splitting algorithm for solving monotone inclusion problems. Numer. Algorithms 2016, 71, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpelevich, G.M. The extragradient method for finding saddle points and other problems. Ekonomika i Matematicheskie Metody 1976, 12, 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Suantai, S.; Cholamjiak, W. Shrinking projection methods involving inertial forward–backward splitting methods for inclusion problems. Rev. Real Acad. Cienc. Exactas Fis. Nat. A Mat. 2019, 113, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicre, M.R. On the complexity of a hybrid proximal extragradient projective method for solving monotone inclusion problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2020, 76, 991–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.K. A regularization method for the proximal point algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2006, 36, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.H.; Jian, J.B.; Jiang, X.Z.; Liu, M.X.; Wang, L.Z. A hybrid three-term conjugate gradient projection method for constrained nonlinear monotone equations with applications. Numer. Algorithms 2021, 88, 389–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berinde, V. Iterative Approximation of Fixed Points; Lecture Notes in Mathematics; Springer: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chidume, C.E. An approximation method for monotone Lipshitz operators in Hilbert spaces. J. Austral. Math. Soc. Ser. 1986, A 41, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačurovskii, R.I. On monotone operators and convex functionals. Usp. Mat. Nauk. 1960, 15, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zarantonello, E.H. Solving Functional Equations by Contractive Averaging; Technical Report #160; U. S. Army Mathematics Research Center: Madison, WI, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Martinet, B. Regularisation d’inequations variationnelles par approximations successives. Rev. Fr. Inform. Rech. Oper. 1970, 4, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Browder, F.E. Nonlinear maximal monotone operators in Banach space. Math. Annalen 1968, 175, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, R.E., Jr. A strongly convergent iterative method for the solution of 0∈Ux for a maximal monotone operator U in Hilbert space. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1974, 48, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boikanyo, O.A.; Morosanu, G. A proximal point algorithm converging strongly for general errors. Optim. Lett. 2010, 4, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibzadeh, H. Some Remarks on the Proximal Point Algorithm. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2012, 153, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockafellar, R.T. Monotone operators and the proximal point algorithm. SIAM J. Control Optim. 1976, 14, 877–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehu, Y. Single projection algorithm for variational inequalities in Banach spaces with applications to contact problems. Acta Math Sci. 2020, 40B, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.H.; Shahzad, N. Strong convergence of a proximal point algorithm with general errors. Optim. Lett. 2012, 6, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teboulle, M. A simplified view of first order methods for optimization. Math. Program. Ser. B 2018, 170, 67–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusvyatskiy, D.; Lewis, A.S. Error bounds, quadratic growth, and linear convergence of proximal methods. Math. Oper. Res. 2018, 43, 919–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, Y. Introductory Lectures on Convex Optimization; Cluwer: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, F. Weak convergence of a relaxed and inertial hybrid projection-proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators in Hilbert spaces. SIAM J. Optim. 2004, 14, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Attouch, H. An inertial proximal method for maximal monotone operators via discretization of a nonlinear oscillator with damping. Set-Valued Anal. 2001, 9, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.K. Iterative algorithms for nonliear operators. J. Lond. Math. Soc. 2002, 66, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingé, P.E. Approximation methods for common fixed points of nonexpansive mappingn Hilbert spaces. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2007, 325, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opial, Z. Weak convergence of the sequence of successive approximations for nonexpansive mappings. Bull Amer Math Soc. 1967, 73, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataş, İ. Comparison of deep convolution and least squares GANs for diabetic retinopathy image synthesis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 14431–14448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.M.; Zhao, P. Image restoration based on the minimax-concave and the overlapping group sparsity. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, H.; Hosseinzadeh, E.; Moodi, M. Solving intuitionistic fuzzy multi-objective linear programming problem and its application in supply chain management. Appl. Math. 2023, 68, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.Q.; Sun, W.Y. Nonconvex Optimization and Its Applications; Book Series (NOIA, Volume 4), Minimax and Applications; Kluwer Academic Publishers: London, UK, 1995; pp. 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Von Neumann, J. Zur Theorie der Gesellschaftsspiele. Math. Ann. 1928, 100, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann, J. Uber ein bkonomisches Gleichungssystem und eine Verallgemeinerung des Brouwerschen Fixpunktsatzes. Ergebn. Math. Kolloqu. Wien 1935, 8, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, K. A minimax inequality and applications. In Inequalities, III; Shisha, O., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1972; pp. 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Trushnikov, D.N.; Krotova, E.L.; Starikov, S.S.; Musikhin, N.A.; Varushkin, S.V.; Matveev, E.V. Solving the inverse problem of surface reconstruction during electron beam surfacing. Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test. 2023, 59, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, O.E.; Turgut, M.S.; Kirtepe, E. A systematic review of the emerging metaheuristic algorithms on solving complex optimization problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 14275–14378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motreanu, D.; Panagiotopoulos, P.D. Minimax Theorems and Qualitative Properties of the Solutions of Hemivariational Inequalities; Nonconvex Optimization and Its Applications; Kluwer Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Moameni, A. Critical point theory on convex subsets with applications in differential equations and analysis. J. Math. Pures. Appl. 2020, 141, 266–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, F. Functional Analysis Calculus of Variations and Optimal Control; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 193–209. [Google Scholar]
- Chidume, C.E.; Osilike, M.O. Iterative solutions of nonlinear accretive operator equations in arbitrary Banach spaces. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 1999, 36, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, H. Strong convergence theorems for maximal monotone mappings in Banach spaces. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2008, 343, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).