Monoparametric Families of Orbits Produced by Planar Potentials
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- in order to find central potentials that have applications in Celestial Mechanics, e.g., the Newtonian one, and others,
- (ii)
- in order to determine 2D potentials that produce specific families of curves as orbits, e.g., the lemniscate of Bernoulli,
- (iii)
- for finding cubic potentials,
- (iv)
- in order to find homogeneous potentials of zero-degree and other results.
2. The Basic Equation of the 2D Inverse Problem
3. The Methodology for the General Case
One Condition on the Slope Function
- (1)
- (2)
- If 0, then the family of orbits consists of straight lines, and the potential is found from the relation 0 ([14], p. 4).
- (3)
- (4)
4. Central Potentials
Special Cases
- a.
- If we select , then we obtain the cored potential , and the energy of the family of orbits isand the allowed region is the entire plane ( 0).
- b.
- If we select , then we obtain the loagarithmic potential and the energy of the family of orbits isand the allowed region is the entire plane ( 0).
5. Potentials of the Form
Special Cases
6. Cubic Potentials
7. Other Results
Potentials of the Form
8. Integrable Potentials
9. One-Dimensional Potentials
10. Families of Straight Lines
- I.
- ,
- II.
- ,
- III.
- , 0
- IV.
- , 0
11. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szebehely, V. On the determination of the potential by satellite observations. In Proceedings of the International Meeting on Earth’s Rotation by Satellite Observation; Proverbio, G., Ed.; The University of Cagliari: Bologna, Italy, 1974; pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bozis, G. Generalization of Szebehely’s Equation. Cel. Mech. 1983, 29, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G.; Tsarouhas, G. Conservative fields derived from two monoparametric families of planar orbits. Astron. Astrophys. 1985, 145, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Puel, F. Intrinsic formulation of the equation of Szebehely. Cel. Mech. 1984, 32, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G. Szebehely’s inverse problem for finite symmetrical material concentrations. Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 134, 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Bozis, G.; Grigoriadou, S. Families of planar orbits generated by homogeneous potentials. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 1993, 57, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G.; Anisiu, M.-C.; Blaga, C. Inhomogeneous potentials producing homogeneous orbits. Astron. Nach. 1997, 318, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G.; Ichtiaroglou, S. Boundary Curves for Families of Planar Orbits. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 1993, 58, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G. The inverse problem of dynamics: Basic facts. Inverse Probl. 1995, 11, 687–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriadou, S.; Bozis, G.; Elmabsout, B. Solvable cases of Szebehely’s equation. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 1999, 74, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisiu, M.-C.; Bozis, G.; Blaga, C. Special families of orbits in the direct problem of dynamics. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 2004, 88, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaga, C.; Anisiu, M.-C.; Bozis, G. New solutions in the direct problem of dynamics. PADEU 2006, 17, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Bozis, G.; Anisiu, M.-C.; Blaga, C. A solavable version of the direct problem of dynamics. Rom. Astron. J. 2000, 10, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bozis, G.; Anisiu, M.-C. Families of straight lines in planar potentials. Rom. Astron. J. 2001, 11, 27–43. [Google Scholar]
- Borghero, F.; Bozis, G. Isoenergetic families of planar orbits generated by homogeneous potentials. Meccanica 2002, 37, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisiu, M.-C. An alternative point of view on the equations of the inverse problem of dynamics. Inverse Probl. 2004, 20, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G.; Anisiu, M.-C. A solvable version of the inverse problem of dynamics. Inverse Probl. 2005, 21, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G.; Meletlidou, E. Nonintegrability Detected from Geometrically Similar Orbits. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 1997, 68, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Yoshida, H. A list of all integrable two-dimensional homogeneous polynomial potentials with a polynomial integral of order at most four in the momenta. J. Phys. A Math. Gen 2001, 34, 8611–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Valls, C. Polynomial integrability of Hamiltonian systems with homogeneous potentials of degree -k. Phys. Let. A 2016, 380, 3876–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Lara, L.; Llibre, J. The cored and logarithmic potentials: Periodic orbits and integrability. J. Math. Phys. 2012, 53, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, A.; Przybylska, M. Integrability of Hamiltonian systems with algebraic potentials. Phys. Let. A 2016, 380, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorizzi, B.; Grammaticos, B.; Ramani, A. A new class of integrable systems. J. Math. Phys. 1983, 24, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorizzi, B.; Grammaticos, B.; Ramani, A. Integrability of Hamiltonians with third- and fourth-degree polynomial potentials. J. Math. Phys. 1983, 24, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Hietarinta, J. Direct methods for the search of second invariants. Phys. Rep. 1987, 147, 87–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorizzi, B.; Grammaticos, B.; Ramani, A. Integrable Hamiltonian systems with velocity-dependent potentials. J. Math. Phys. 1985, 26, 3070–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icthiaroglou, S.; Voyatzis, G. Integrable potentials with logarithmic integrals of motion. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1988, 21, 3537–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G. A transformed equation for a vanishing Poisson bracket. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1989, 22, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozis, G. Two-dimensional integrable potentials with quartic invariants. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1992, 25, 3329–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icthiaroglou, S.; Meletlidou, E. On monoparametric families of orbits sufficient for integrability of planar potentials with linear or quadratic invariants. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1990, 23, 3673–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriadou, S. The inverse problem of dynamics and Darboux’s integrability criterion. Inverse Probl. 1999, 15, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
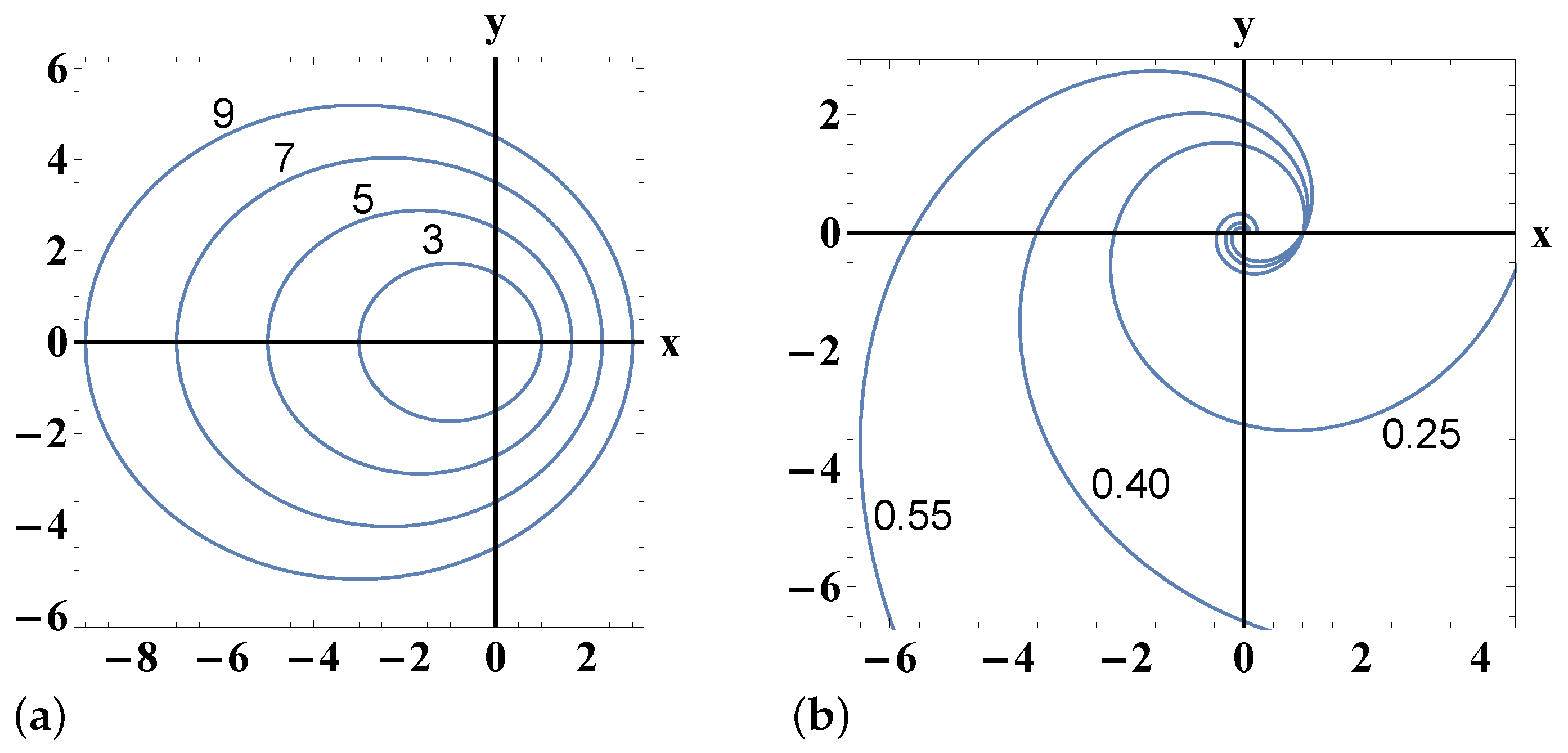
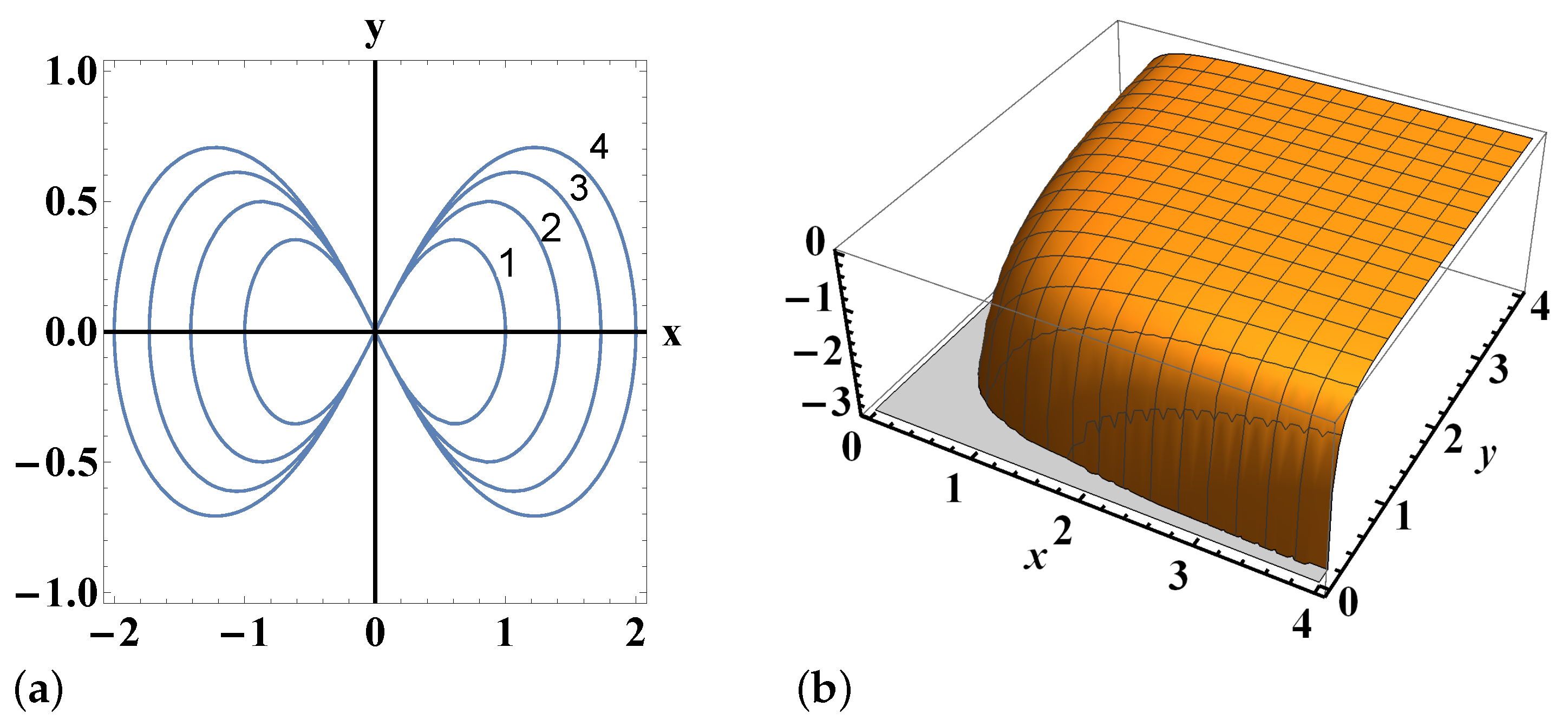
| Family of Orbits | Potential V(x,y) | Energy | Allowed Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| y > 0 | |||
| (0) | the entire plane |
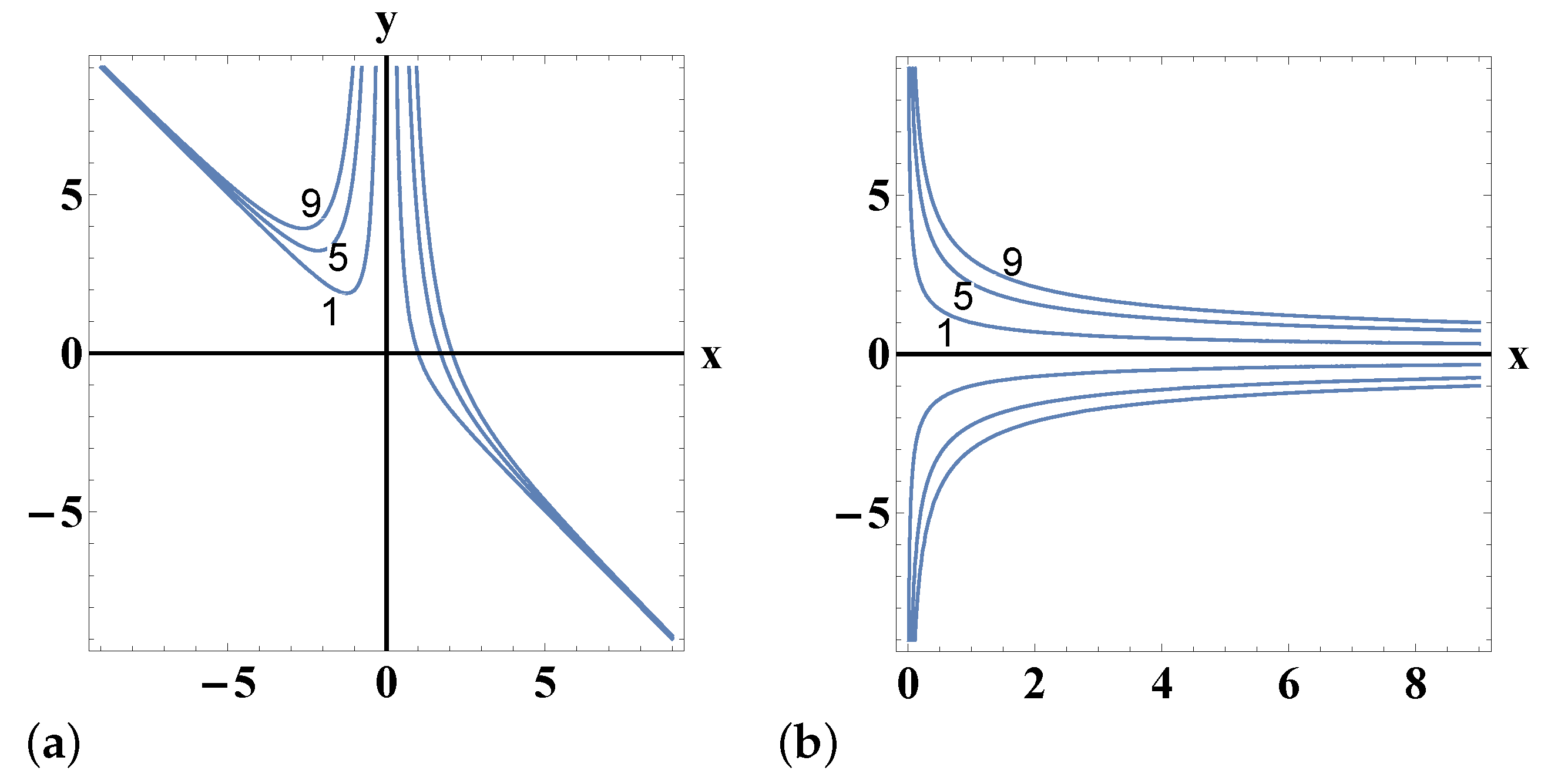
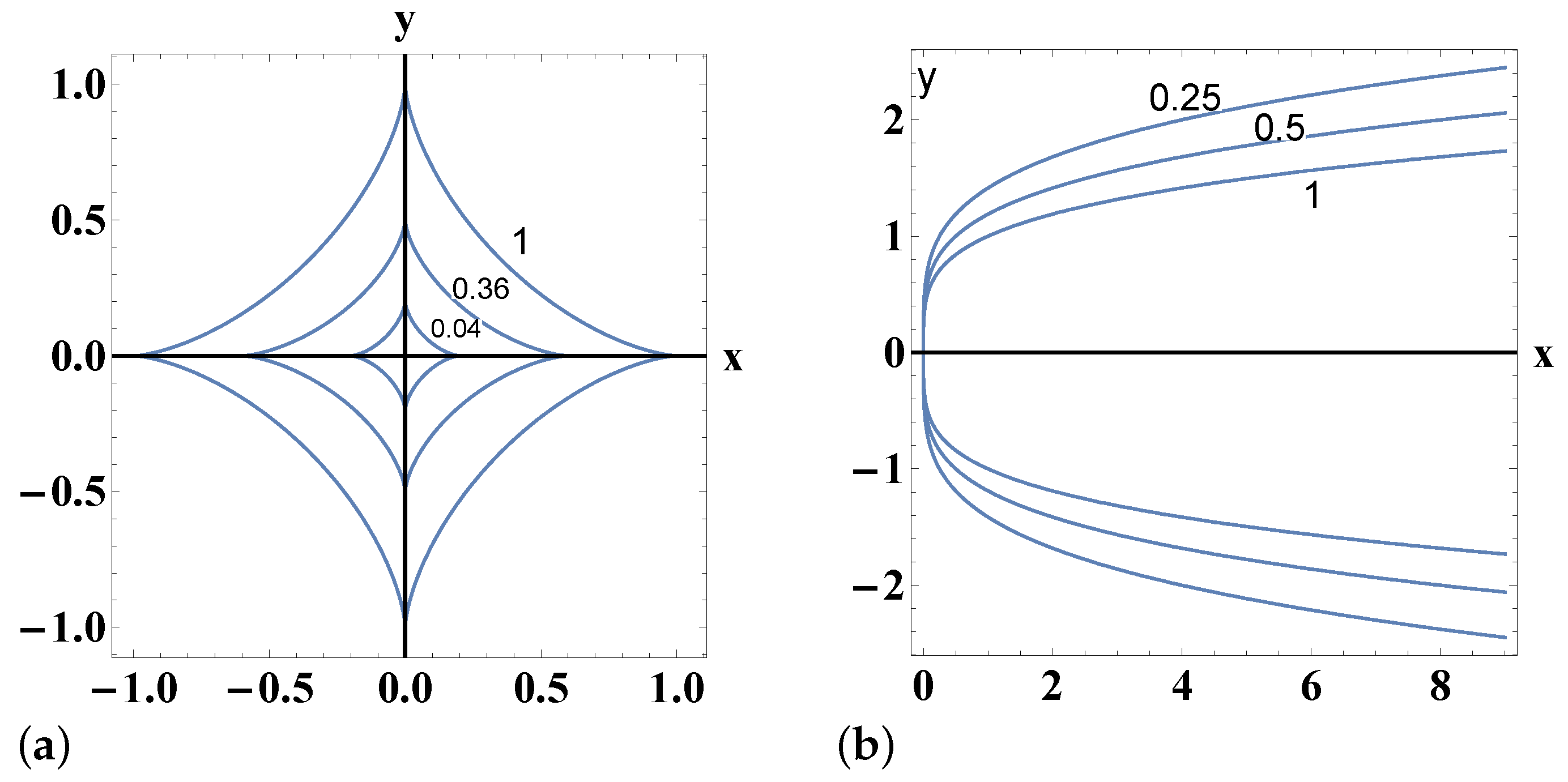
| Family of Orbits | Potential V(x,y) | Energy | Allowed Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 0 | |||
| < 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotoulas, T. Monoparametric Families of Orbits Produced by Planar Potentials. Axioms 2023, 12, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050423
Kotoulas T. Monoparametric Families of Orbits Produced by Planar Potentials. Axioms. 2023; 12(5):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050423
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotoulas, Thomas. 2023. "Monoparametric Families of Orbits Produced by Planar Potentials" Axioms 12, no. 5: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050423
APA StyleKotoulas, T. (2023). Monoparametric Families of Orbits Produced by Planar Potentials. Axioms, 12(5), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050423





