Dynamics of a Double-Impulsive Control Model of Integrated Pest Management Using Perturbation Methods and Floquet Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Derivation of the Impulsive Control Model
3. Dynamics of the Impulsive Model
3.1. Boundedness of the Model Variables
3.2. Existence of the Pest-Free Periodic Orbit
3.3. Stability of the Pest-Free Periodic Solution
- (i)
- Application of biopesticide and chemical pesticide with same time interval , provided that
- (ii)
- Application of biopesticide with time interval and chemical pesticide with time interval , i.e., for different time intervals, where , provided that
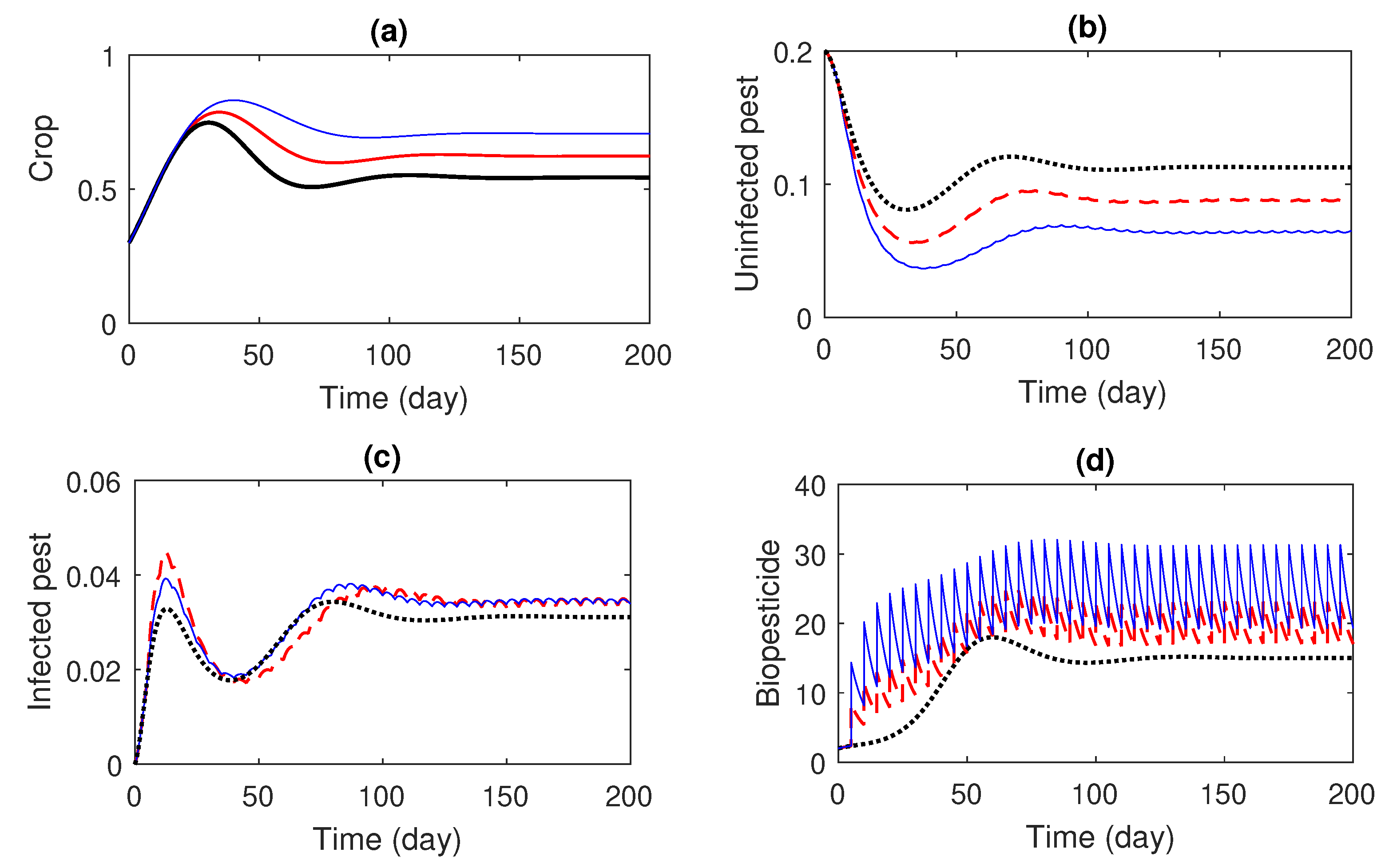
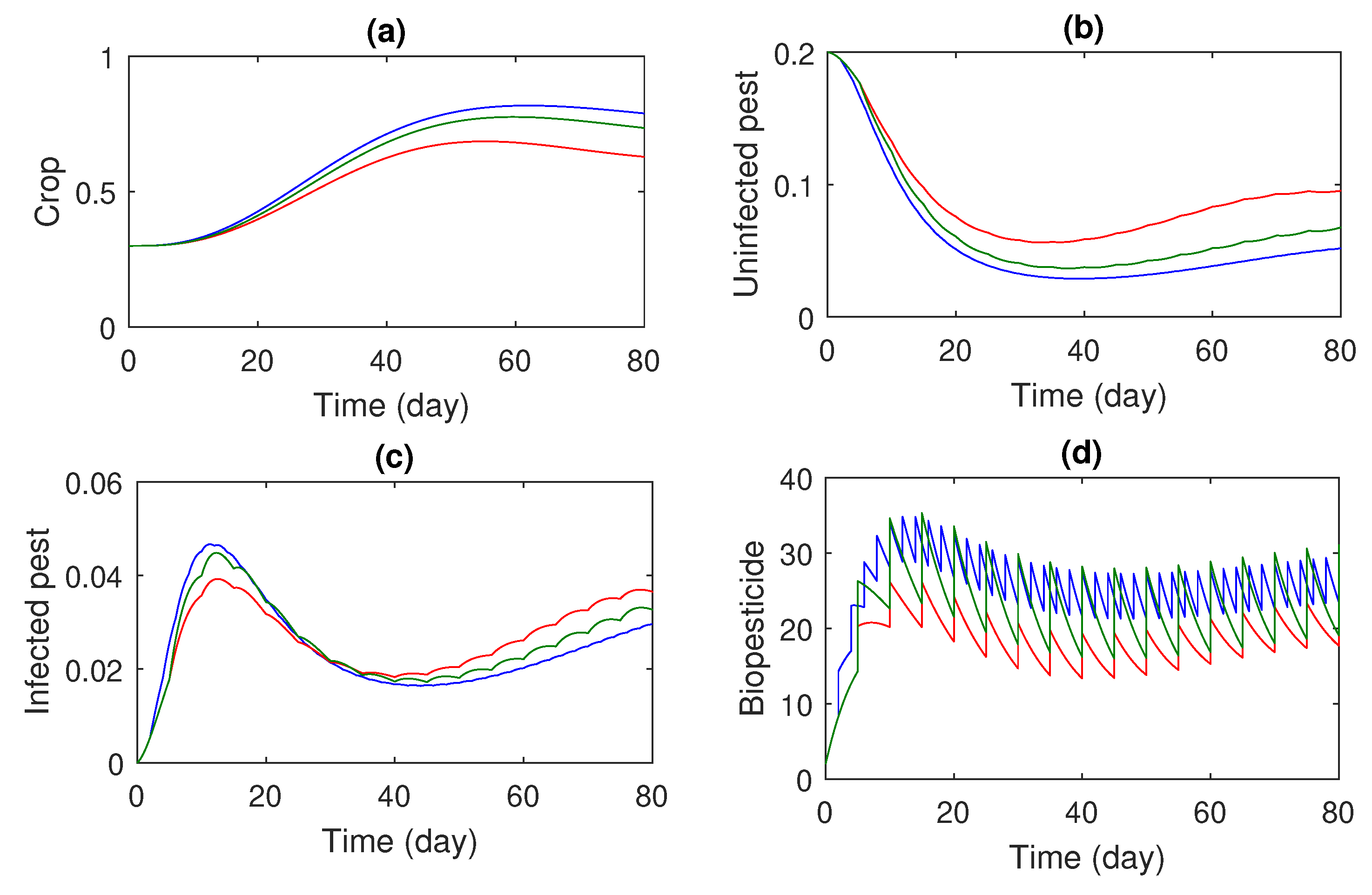
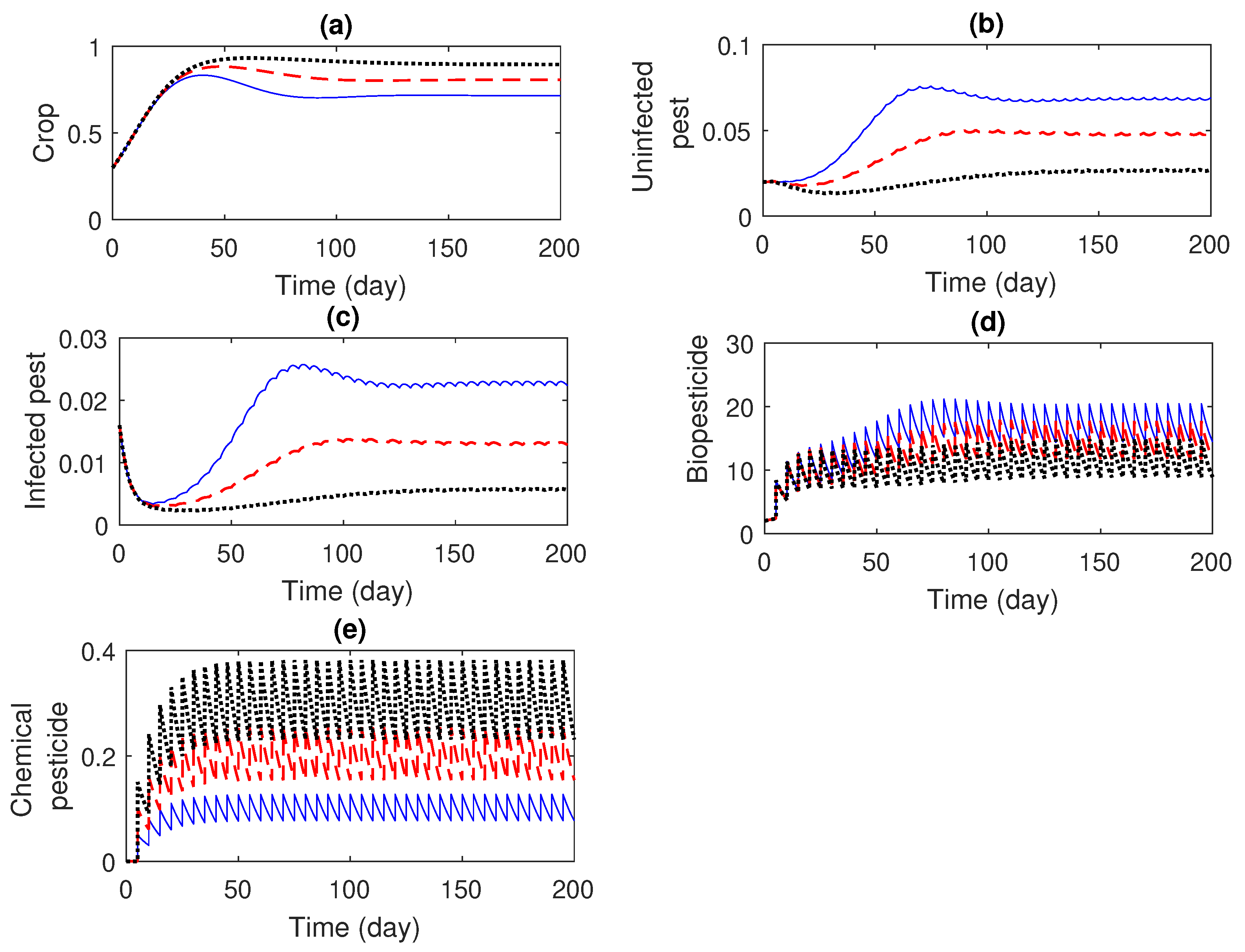
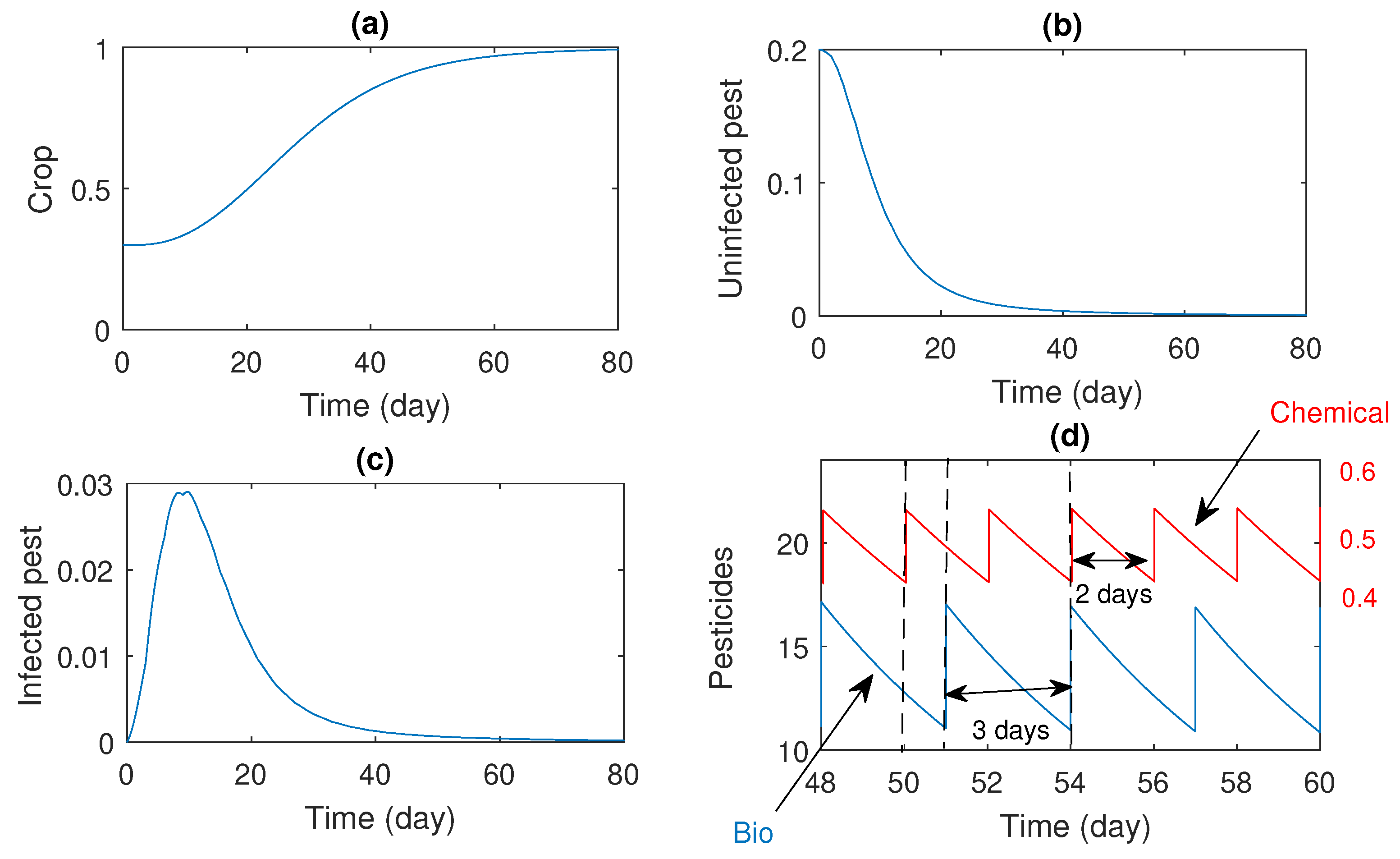
4. Numerical Simulations
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Basir, F.; Banerjee, A.; Ray, S. Role of farming awareness in crop pest management—A mathematical model. J. Theor. Biol. 2019, 461, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndolo, D.; Njuguna, E.; Adetunji, C.O.; Harbor, C.; Rowe, A.; Den Breeyen, A.; Sangeetha, J.; Singh, G.; Szewczyk, B.; Anjorin, T.S.; et al. Research and development of biopesticides: Challenges and prospects. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2019, 6, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Banerjee, G.; Mukherjee, S. Recent trends of modern bacterial insecticides for pest control practice in integrated crop management system. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perring, T.M.; Gruenhagen, N.M.; Farrar, C.A. Management of plant viral diseases through chemical control of insect vectors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Bhattacharya, D.K. Optimization in microbial pest control: An integrated approach. Appl. Math. Model. 2010, 34, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Bhattacharya, D.K. Pest control through viral disease: Mathematical modeling and analysis. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 238, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fest, C.; Schmidt, K. The Chemistry of Organophosphorus Pesticides; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenteren, J.C.V. Integrated pest management in protected crops. In Integrated Pest Management; Dent, D., Ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1995; pp. 311–320. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1573950400276916864 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Flint, M.L. Integrated Pest Management for Walnuts; University of California Statewide Integrated Pest Management Project; Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1987; Volume 3270, p. 3641. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, V.M. The bioeconomics of pest control. Iowa State J. Res. 1975, 49, 467–472. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/224978255.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Liu, B.; Teng, Z.; Chen, L. Analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling II functional response concerning impulsive control strategy. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2006, 193, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez Chávez, J.; Jungmann, D.; Siegmund, S. Modeling and analysis of integrated pest control strategies via impulsive differential equations. Int. J. Differ. Equ. 2017, 2017, 1820607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Nieto, J.J. The dynamics of an epidemic model for pest control with impulsive effect. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2010, 11, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Basir, F.; Noor, M.H. A Model for Pest Control using Integrated Approach: Impact of latent and gestation Delays. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 108, 1805–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraha, T.; Al Basir, F.; Obsu, L.L.; Torres, D.F.M. Pest control using farming awareness: Impact of time delays and optimal use of biopesticides. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 146, 110869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, J.; Basir, F.A.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ghosh, M.; Roy, P.K. A mathematical model for pest management in Jatropha curcas with integrated pesticides—An optimal control approach. Ecol. Complex. 2019, 37, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Chen, L. Modelling and analysis of integrated pest management strategy. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 2004, 4, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez Chavez, J.; Jungmann, D.; Siegmund, S. A comparative study of integrated pest management strategies based on impulsive control. J. Biol. Dyn. 2018, 12, 318–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, P.; Kaur, M. Stability analysis of an eco-epidemiological SIN model with impulsive control strategy for integrated pest management considering stage-structure in predator. Int. J. Math. Model. Numer. Optim. 2022, 12, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Yuen, P. Extinction and permanence of the predator-prey system with general functional response and impulsive control. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 88, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic behaviour of a predator-prey system with impulsive control strategy. Int. J. Dyn. Syst. Differ. Equ. 2022, 12, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.; Chauhan, S.; Dhar, J. Controlling pest by integrated pest management: A dynamical approach. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2020, 5, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Dynamics analysis of stage-structured wild and sterile mosquito interaction impulsive model. J. Biol. Dyn. 2022, 16, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, J.; Al Basir, F.; Cao, X.; Roy, P.K. Integrated pest management for Jatropha Carcus plant: An impulsive control approach. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2021, in press. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Tang, S.; Cheke, R.A. Dynamic complexity of a predator-prey model for IPM with nonlinear impulsive control incorporating a regulatory factor for predator releases. Math. Model. Anal. 2019, 24, 134–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.A.; Ramachandran, R.; Cao, J.; Alzabut, J.; Niezabitowski, M.; Balas, V.E. Stability analysis and comparative study on different eco-epidemiological models: Stage structure for prey and predator concerning impulsive control. Optim. Control. Appl. Methods 2022, 43, 842–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, Q.D.; Liu, B. A pest control model with birth pulse and residual and delay effects of pesticides. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2019, 2019, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Kang, B.-L.; Tao, F.-M.; Hu, G. Modelling the effects of pest control with development of pesticide resistance. Acta Math. Appl. Sin. Engl. Ser. 2021, 37, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzabut, J. An Integrated Eco-Epidemiological Plant Pest Natural Enemy Differential Equation Model with Various Impulsive Strategies. 2022. Available online: http://earsiv.ostimteknik.edu.tr:8081/xmlui/handle/123456789/207 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, L. A impulsive infective transmission SI model for pest control. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2007, 30, 1169–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Basir, F.; Chowdhury, J.; Das, S.; Ray, S. Combined impact of predatory insects and bio-pesticide over pest population: Impulsive model-based study. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2022, 7, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Jiang, X.; Chen, L. A predator-prey model with disease in the prey and two impulses for integrated pest management. Appl. Math. Model. 2009, 33, 2248–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausmeier, C.A. Floquet theory: A useful tool for understanding nonequilibrium dynamics. Theor. Ecol. 2008, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Basir, F.; Chowdhury, J.; Torres, D.F.M. Dynamics of a Double-Impulsive Control Model of Integrated Pest Management Using Perturbation Methods and Floquet Theory. Axioms 2023, 12, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12040391
Al Basir F, Chowdhury J, Torres DFM. Dynamics of a Double-Impulsive Control Model of Integrated Pest Management Using Perturbation Methods and Floquet Theory. Axioms. 2023; 12(4):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12040391
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Basir, Fahad, Jahangir Chowdhury, and Delfim F. M. Torres. 2023. "Dynamics of a Double-Impulsive Control Model of Integrated Pest Management Using Perturbation Methods and Floquet Theory" Axioms 12, no. 4: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12040391
APA StyleAl Basir, F., Chowdhury, J., & Torres, D. F. M. (2023). Dynamics of a Double-Impulsive Control Model of Integrated Pest Management Using Perturbation Methods and Floquet Theory. Axioms, 12(4), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12040391








