A New Hybrid Fermatean Fuzzy Set and Entropy Method for Risk Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Typical FMEA Method
2.2. Typical Intuitionistic Fuzzy Set and Fermatean Fuzzy Set Methods
- (1)
- If , then ;
- (2)
- If , and
- (i)
- , then ;
- (ii)
- , then .
3. Proposed Hybrid Fermatean Fuzzy Set and Entropy Approach
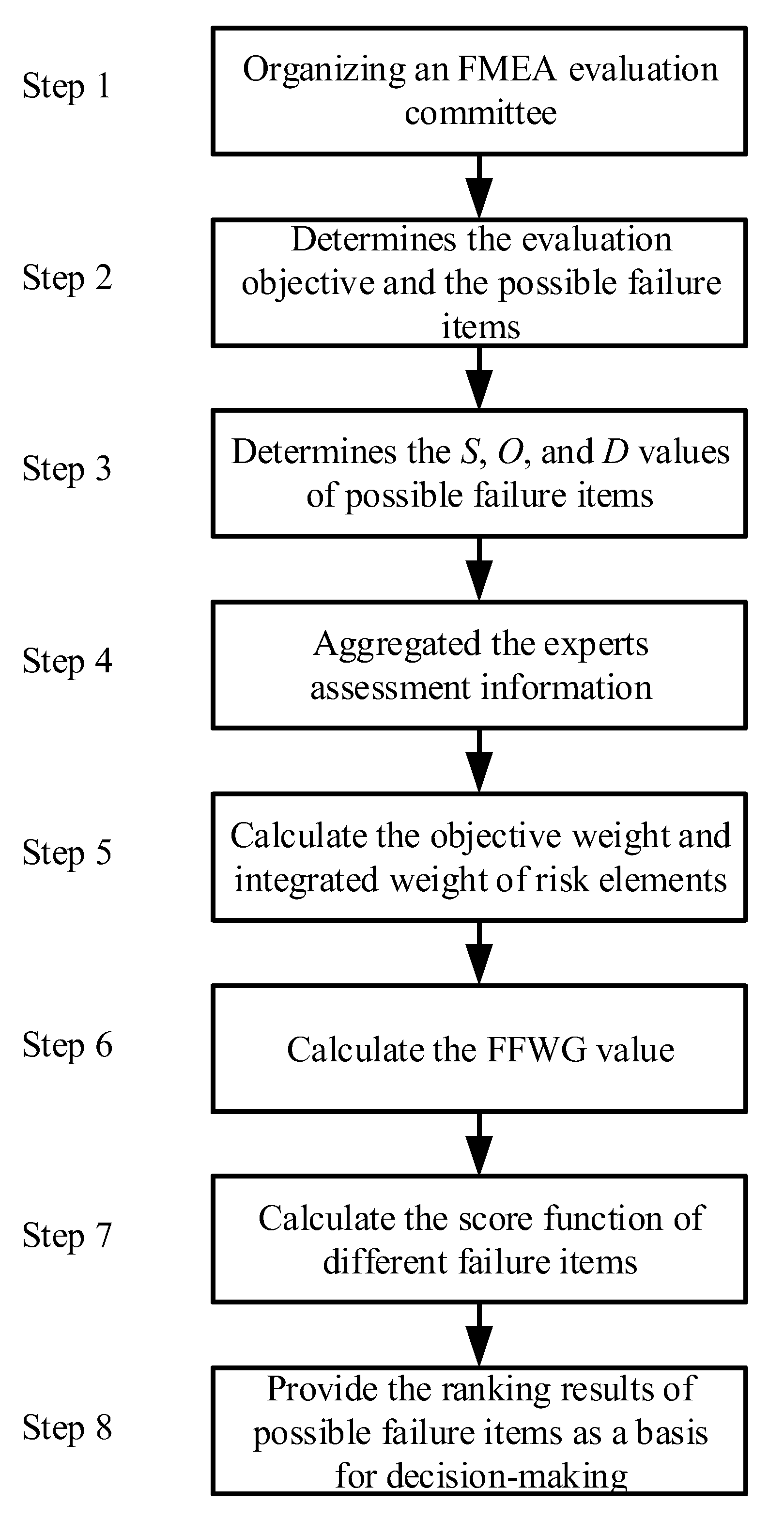
- Step 1:
- Organizing an FMEA evaluation committee.
- Step 2:
- Determination of the evaluation objective and the possible failure items.
- Step 3:
- Determination of the S, O, and D values of possible failure items.
- Step 4:
- Aggregation of the assessment information provided by the experts.
- Step 5:
- The objective weight and integrated weight of the risk elements is calculated.
- Step 6:
- Calculation of the FFWG value.
- Step 7:
- Calculation of the score function of different failure items.
- Step 8:
- Provide the ranking results of possible failure items as a basis for decision-making.
4. Numerical Example
4.1. Case Overview
4.2. Typical Risk Priority Number Method Calculation
4.3. Fuzzy Set Method Solution Typical Intuitionistic Fuzzy Set Calculation
4.4. Typical Fermatean Fuzzy Set Calculation
4.5. Proposed Method Calculation
- Step 4:
- Aggregation of the assessment information of the experts.
- Step 5:
- Calculation of the objective weight and integrated weight of risk elements.
- Step 6:
- Calculation of the FFWG value.
- Step 7:
- Calculation of the score function of different failure items.
- Step 8:
- Providing the ranking results of possible failure items as a basis for decision-making.
4.6. Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed approach is able to deal with both FI and intuitionistic FI provided by experts.
- (2)
- The proposed approach is able to deal with Fermatean FI provided by experts.
- (3)
- The proposed approach fully considers the subjective weights of three different risk elements.
- (4)
- The proposed approach fully considers the objective weights of three different risk elements.
- (5)
- The typical RPN approach, typical IFS method, and typical FFS method are only special cases of the proposed approach.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, K.H.; Wen, T.C.; Chung, H.Y. Soft failure mode and effects analysis using the OWG operator and hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 34, 2625–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S.S.; Solimanzadeh, Y.; Mousavi, S.; Safari, G.H. Risk assessment of physical unit operations of wastewater treatment plant using fuzzy FMEA method: A case study in the northwest of Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.H. A novel risk ranking method based on the single valued neutrosophic set. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2022, 18, 2237–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Bi, Y.W.; Liu, P.D. An evidence theory-based large group FMEA framework incorporating bounded confidence and its application in supercritical water gasification system. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2022, 129, 109580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Guo, Y.J.; Li, F.; Cao, Y.C.; Wang, L.Y.; Ma, Y. Assessment of operation safety risk for south-to-north water diversion project: A fuzzy VIKOR-FMEA approach. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3685–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamustafa, M.; Ceb, S. A new model for the occupational health and safety risk assessment process: Neutrosophic FMEA. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 2023, 38, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, C.; Muhiuddin, G.; Pal, M. Multiple-attribute decision making problems based on SVTNH methods. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 3717–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.M.; Martinez, L. A novel alpha-level sets based fuzzy DEMATEL method considering experts’ hesitant information. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 118925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.M.; Zahran, A.M.; Basheer, R. A novel diagnosis system for detection of kidney disease by a fuzzy soft decision-making problem. Math. Comput. Simul. 2023, 203, 271–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H. Evaluate the orderings of risk for failure problems using a more general RPN methodology. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H. Generalized multi-attribute failure mode analysis. Neurocomputing 2016, 175, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekciog, O.; Koc, K.; Dabanli, I.; Deniz, A. Prioritizing urban water scarcity mitigation strategies based on hybrid multi-criteria decision approach under fuzzy environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Chung, H.Y. A novel AHP-based benefit evaluation model of military simulation training systems. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 956757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.T.; Lin, C.W. Assessing cloud manufacturing applications using an optimally rectified FAHP approach. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 5087–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.Y.; Chang, K.H. A novel general data envelopment analysis based approach for MCDM issues of hydrogen energy under a fuzzy environment. Systems 2022, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Zhang, B.Q.; Ni, W.B. A hybrid model based on SEM and fuzzy TOPSIS for supplier selection. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.T. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymova, L.; Kaczmarek, K.; Sevastjanov, P. An extension of rule base evidential reasoning in the interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy setting applied to the type 2 diabetes diagnostic. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 201, 117100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Xue, Z. Performance evaluation of online recruitment enterprises based on intuitionistic fuzzy set and TOPSIS. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 8526826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Mishra, A.R. Multi-criteria COPRAS method based on parametric measures for intuitionistic fuzzy sets: Application of green supplier selection. Iran. J. Sci. Technol.-Trans. Electr. Eng. 2020, 44, 1645–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogulj, K.; Pamukovic, J.K.; Antucheviciene, J.; Zavadskas, E.K. Intuitionistic fuzzy decision support based on EDAS and grey relational degree for historic bridges reconstruction priority. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 9419–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H. A novel supplier selection method that integrates the intuitionistic fuzzy weighted averaging method and a soft set with imprecise data. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 272, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, C. An integrated CoCoSo-CRITIC-based decision-making framework for quality evaluation of innovation and entrepreneurship education in vocational colleges with intuitionistic fuzzy information. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6071276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Kumam, W.; Alreshidi, N.A. Divergence measures for circular intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 116, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.Y.; Shu, L.; Yang, G.W. Complex intuitionistic fuzzy ordered weighted distance measure. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, K.; Wu, S.L.; Xu, Z.T.; Liu, T.Y. Quality evaluation of wasteless mining in Dongguashan based on intuitionistic fuzzy set and VIKOR. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Yager, R.R. Fermatean fuzzy weighted averaging/geometric operators and its application in multi-criteria decision-making methods. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 85, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Muhiuddin, G.; Santos-Garcia, G. An enhanced VIKOR method for multi-criteria group decision-making with complex Fermatean fuzzy sets. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 7201–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, A.H. Multicriteria decision-making based on distance measures and knowledge measures of Fermatean fuzzy sets. Granul. Comput. 2022, 7, 979–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, J.Y. New distance measure for Fermatean fuzzy sets and its application. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 1903–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Yu, L.Y.; Niu, W.Y.; Liu, Y.; Senapati, T.; Mishra, A.R. MARCOS approach based upon cubic Fermatean fuzzy set and its application in evaluation and selecting cold chain logistics distribution center. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 116, 105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Liu, H.C.; Wang, J.H.; Shi, H. New model for occupational health and safety risk assessment based on Fermatean fuzzy linguistic sets and CoCoSo approach. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2022, 126, 109262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, D.; Sari, I.U.; Senapati, T. Extension of capital budgeting techniques using interval-valued Fermatean fuzzy sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 42, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzadi, G.; Muhiuddin, G.; Butt, M.A.; Ashraf, A. Hamacher interactive hybrid weighted averaging operators under Fermatean fuzzy numbers. J. Math. 2021, 2021, 5556017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Zayas, I.; Anon, F.C.; Virosta, M.S.; del Pozo, J.C.; Montero, C.S.; Baizan, A.N.; Fuster, D. Implementation of the failure modes and effects analysis in a Hospital Radiopharmacy Unit. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. Imagen Mol. 2022, 41, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooranloo, H.S.; Ayatollah, A.S. A model for failure mode and effects analysis based on intuitionistic fuzzy approach. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2016, 49, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.Y.; Meng, Q.P.; Feng, W. Optimization of logistics system with fuzzy FMEA-AHP methodology. Processes 2022, 10, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Tang, Y.C. Managing uncertainty of expert’s assessment in FMEA with the belief divergence measure. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Tsai, I.T. Enhancing FMEA assessment by integrating grey relational analysis and the decision making trial and evaluation laboratory approach. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 31, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksic, B.; Djekic, I.; Miocinovic, J.; Miloradovic, Z.; Memisi, N.; Smigic, N. The application of failure mode effects analysis in the long supply chain-a case study of ultra filtrated milk cheese. Food Control 2022, 138, 109057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H. A new emergency-risk-evaluation approach under spherical fuzzy-information environments. Axioms 2022, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Lee, D.M.; Na, J.W. Automatic failure modes and effects analysis of an electronic fuel injection model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, L.; Schulze, I.; Jaehde, U. Using failure mode and Effects Analysis to increase patient safety in cancer chemotherapy. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2022, 18, 3386–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.Y.; Chen, S.M.; Fan, K.Y. Multiple attribute decision making using improved intuitionistic fuzzy weighted geometric operators of intuitionistic fuzzy values. Inf. Sci. 2020, 535, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chen, X.H. Fermatean fuzzy linguistic set and its application in multicriteria decision making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2019, 34, 878–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Yager, R.R. Fermatean fuzzy sets. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.R.; Rani, P.; Saha, A.; Senapati, T.; Hezam, I.M.; Yager, R.R. Fermatean fuzzy copula aggregation operators and similarity measures-based complex proportional assessment approach for renewable energy source selection. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 5223–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.P.; Wan, S.P.; Dong, J.Y. A Fermatean fuzzy ELECTRE method for multi-criteria group decision-making. Informatica 2022, 33, 181–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.N.; Le, T.Q.; Chang, K.H.; Dang, T.T. Measuring road transport sustainability using MCDM-based entropy objective weighting method. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.C.; Chung, H.Y.; Chang, K.H.; Li, Z.S. A flexible risk assessment approach integrating subjective and objective weights under uncertainty. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 103, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.A.F.; Li, Y.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Shen, Z.F. Service failure risk assessment and service improvement of self-service electric vehicle. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Rating Scales | S | O | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Exceptionally high | Exceptionally high | Exceptionally low |
| 9 | Very high | Very high | Very low |
| 8 | Moderate high | Moderate high | Low |
| 7 | High | High | Slightly low |
| 6 | Slightly high | Slightly high | Average |
| 5 | Average | Average | Slightly high |
| 4 | Slightly low | Slightly low | High |
| 3 | Low | Low | Moderate high |
| 2 | Very low | Very low | Very high |
| 1 | Exceptionally low | Exceptionally low | Exceptionally high |
| Phases | Basic and Reliable Service | Reason for Service Failure | Failure Item | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Register phase | Properly manage user data | Misuse of information | 1 | |
| Register phase | Equality agreement service | Protocol pitfalls | 2 | |
| Application phase | Start part | Delivering reliable electric vehicles | Delivering defective electric vehicles | 3 |
| Application phase | Start part | High-quality repair service | Low-quality repair service | 4 |
| Application phase | Start part | Convenient and hassle-free charging service | Defective charging service | 5 |
| Application phase | Start part | Attribution of responsibility is certain | Attribution of responsibility is uncertain | 6 |
| Application phase | Drive part | Professional safety certification | Lack of professional safety certification | 7 |
| Application phase | Drive part | Reasonable and transparent fees | Unreasonable charges | 8 |
| Application phase | Drive part | Adequate safety equipment | Insufficient safety equipment | 9 |
| Application phase | Drive part | Sufficient insurance claims | Insufficient insurance claims | 10 |
| Application phase | Stop part | Safe and convenient parking service | Parking problem | 11 |
| Application phase | Stop part | Complete security alert | Incomplete security alert | 12 |
| Application phase | Stop part | Violations resolved quickly | The complexity of dealing with breaches | 13 |
| Account log out phase | Efficient deposit refunds | Deposit refunds are troublesome | 14 | |
| Account log out phase | Resolve disputes fairly | Dealing with arguments is unfair | 15 | |
| Account log out phase | Excellent customer service | Bad customer service | 16 |
| Linguistic Level | S | O | D | FFN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | Exceptionally low | Exceptionally low | Exceptionally high | (0.10, 0.95) |
| L2 | Very low | Very low | Very high | (0.20, 0.90) |
| L3 | Low | Low | Moderate high | (0.30, 0.85) |
| L4 | Slightly low | Slightly low | High | (0.40, 0.80) |
| L5 | Average | Average | Slightly high | (0.50, 0.70) |
| L6 | Slightly high | Slightly high | Average | (0.60, 0.60) |
| L7 | High | High | Slightly low | (0.70, 0.50) |
| L8 | Moderate high | Moderate high | Low | (0.80, 0.40) |
| L9 | Very high | Very high | Very low | (0.85, 0.30) |
| L10 | Exceptionally high | Exceptionally high | Exceptionally low | (0.95, 0.20) |
| Failure Item | S | O | D | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | |
| 1 | L5 | L5 | L7 | L6 | L5 | L5 | L6 | L4 | L4 | L3 | L4 | L5 |
| 2 | L3 | L2 | L2 | L3 | L3 | L4 | L3 | L4 | L4 | L3 | L4 | L4 |
| 3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L6 | L6 | L6 | L6 | L7 | L7 | L8 | L7 | L6 |
| 4 | L4 | L5 | L5 | L6 | L6 | L7 | L6 | L7 | L6 | L6 | L6 | L7 |
| 5 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L3 | L2 | L1 | L1 | L1 | L5 | L4 | L6 | L4 |
| 6 | L3 | L5 | L4 | L4 | L7 | L6 | L7 | L7 | L1 | L1 | L2 | L1 |
| 7 | L5 | L5 | L4 | L6 | L8 | L8 | L7 | L9 | L3 | L3 | L4 | L3 |
| 8 | L4 | L6 | L5 | L5 | L5 | L4 | L6 | L4 | L3 | L3 | L4 | L2 |
| 9 | L4 | L2 | L2 | L4 | L7 | L6 | L7 | L8 | L4 | L5 | L4 | L3 |
| 10 | L5 | L3 | L4 | L4 | L7 | L6 | L7 | L8 | L4 | L3 | L4 | L4 |
| 11 | L7 | L6 | L6 | L6 | L5 | L5 | L4 | L6 | L2 | L1 | L2 | L1 |
| 12 | L4 | L3 | L3 | L5 | L3 | L4 | L4 | L3 | L3 | L4 | L2 | L2 |
| 13 | L6 | L6 | L7 | L5 | L3 | L2 | L4 | L3 | L2 | L2 | L3 | L3 |
| 14 | L6 | L6 | L6 | L6 | L7 | L6 | L8 | L6 | L3 | L4 | L2 | L3 |
| 15 | L7 | L6 | L7 | L7 | L6 | L6 | L7 | L5 | L2 | L4 | L3 | L2 |
| 16 | L5 | L6 | L6 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L4 | L4 | L4 | L5 | L4 | L5 |
| Failure Item | S | O | D | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | |
| 1 | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.06) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.50, 0.70) |
| 2 | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) |
| 3 | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.80, 0.40) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) |
| 4 | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) |
| 5 | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.10, 0.95) | (0.10, 0.95) | (0.10, 0.95) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.40, 0.80) |
| 6 | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.10, 0.95) | (0.10, 0.95) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.10, 0.95) |
| 7 | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.80, 0.40) | (0.80, 0.40) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.85, 0.30) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) |
| 8 | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.20, 0.90) |
| 9 | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.80, 0.40) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) |
| 10 | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.80, 0.40) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) |
| 11 | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.10, 0.95) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.10, 0.95) |
| 12 | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.20, 0.90) |
| 13 | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.30, 0.85) |
| 14 | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.80, 0.40) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.30, 0.85) |
| 15 | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.70, 0.50) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.20, 0.90) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.30, 0.85) | (0.20, 0.90) |
| 16 | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.60, 0.60) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.50, 0.70) | (0.40, 0.80) | (0.50, 0.70) |
| Failure Item | S | O | D | RPN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.750 | 5.000 | 4.000 | 115.000 |
| 2 | 2.500 | 3.500 | 3.750 | 32.813 |
| 3 | 5.250 | 6.250 | 7.000 | 229.688 |
| 4 | 5.000 | 6.500 | 6.250 | 203.125 |
| 5 | 3.000 | 1.250 | 4.750 | 17.813 |
| 6 | 4.000 | 6.750 | 1.250 | 33.750 |
| 7 | 5.000 | 7.875 | 3.250 | 127.969 |
| 8 | 5.000 | 4.750 | 3.000 | 71.250 |
| 9 | 3.000 | 7.000 | 4.000 | 84.000 |
| 10 | 4.000 | 7.000 | 3.750 | 105.000 |
| 11 | 6.250 | 5.000 | 1.500 | 46.875 |
| 12 | 3.750 | 3.500 | 2.750 | 36.094 |
| 13 | 6.000 | 3.000 | 2.500 | 45.000 |
| 14 | 6.000 | 6.750 | 3.000 | 121.500 |
| 15 | 6.750 | 6.000 | 2.750 | 111.375 |
| 16 | 5.250 | 4.750 | 4.500 | 112.219 |
| Failure Item | S | O | D | IFWG | Score Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (0.584, 0.416) | (0.505, 0.495) | (0.404, 0.596) | (0.492, 0.508) | −0.016 |
| 2 | (0.252, 0.748) | (0.352, 0.648) | (0.376, 0.624) | (0.322, 0.678) | −0.356 |
| 3 | (0.532, 0.468) | (0.628, 0.372) | (0.709, 0.291) | (0.619, 0.381) | 0.237 |
| 4 | (0.505, 0.495) | (0.654, 0.346) | (0.628, 0.372) | (0.592, 0.408) | 0.184 |
| 5 | (0.304, 0.696) | (0.126, 0.874) | (0.482, 0.518) | (0.264, 0.736) | −0.471 |
| 6 | (0.404, 0.596) | (0.678, 0.322) | (0.126, 0.874) | (0.326, 0.674) | −0.349 |
| 7 | (0.505, 0.495) | (0.794, 0.206) | (0.326, 0.674) | (0.508, 0.492) | 0.016 |
| 8 | (0.505, 0.495) | (0.482, 0.518) | (0.304, 0.696) | (0.420, 0.580) | −0.161 |
| 9 | (0.307, 0.693) | (0.709, 0.291) | (0.404, 0.596) | (0.445, 0.555) | −0.110 |
| 10 | (0.404, 0.596) | (0.709, 0.291) | (0.376, 0.624) | (0.476, 0.524) | −0.048 |
| 11 | (0.628, 0.372) | (0.505, 0.495) | (0.151, 0.849) | (0.363, 0.637) | −0.273 |
| 12 | (0.381, 0.619) | (0.352, 0.648) | (0.280, 0.720) | (0.335, 0.665) | −0.330 |
| 13 | (0.606, 0.394) | (0.304, 0.696) | (0.252, 0.748) | (0.359, 0.641) | −0.282 |
| 14 | (0.600, 0.400) | (0.687, 0.313) | (0.304, 0.696) | (0.500, 0.500) | 0.000 |
| 15 | (0.678, 0.322) | (0.606, 0.394) | (0.280, 0.720) | (0.486, 0.514) | −0.027 |
| 16 | (0.532, 0.468) | (0.482, 0.518) | (0.452, 0.548) | (0.488, 0.512) | −0.025 |
| Failure Item | S | O | D | FFWG | Score Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (0.575, 0.625) | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.400, 0.788) | (0.486, 0.701) | −0.230 |
| 2 | (0.250, 0.875) | (0.350, 0.825) | (0.375, 0.813) | (0.320, 0.837) | −0.554 |
| 3 | (0.525, 0.675) | (0.625, 0.575) | (0.700, 0.500) | (0.612, 0.579) | 0.036 |
| 4 | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.650, 0.550) | (0.625, 0.575) | (0.588, 0.605) | −0.018 |
| 5 | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.125, 0.938) | (0.475, 0.725) | (0.261, 0.833) | −0.560 |
| 6 | (0.400, 0.788) | (0.675, 0.525) | (0.125, 0.938) | (0.323, 0.729) | −0.354 |
| 7 | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.788, 0.400) | (0.325, 0.838) | (0.504, 0.617) | −0.107 |
| 8 | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.475, 0.725) | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.415, 0.756) | −0.360 |
| 9 | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.700, 0.500) | (0.400, 0.788) | (0.438, 0.694) | −0.251 |
| 10 | (0.400, 0.788) | (0.700, 0.500) | (0.375, 0.813) | (0.472, 0.684) | −0.215 |
| 11 | (0.625, 0.575) | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.150, 0.925) | (0.361, 0.719) | −0.325 |
| 12 | (0.375, 0.800) | (0.350, 0.825) | (0.275, 0.863) | (0.330, 0.829) | −0.533 |
| 13 | (0.600, 0.600) | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.250, 0.875) | (0.356, 0.764) | −0.401 |
| 14 | (0.600, 0.600) | (0.675, 0.525) | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.495, 0.645) | −0.146 |
| 15 | (0.675, 0.525) | (0.600, 0.600) | (0.275, 0.863) | (0.481, 0.648) | −0.160 |
| 16 | (0.525, 0.675) | (0.475, 0.725) | (0.450, 0.750) | (0.482, 0.716) | −0.255 |
| Weight | S | O | D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | NMD | MD | NMD | MD | NMD | |
| Subjective weight | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 |
| Objective weight | 0.197 | 0.227 | 0.348 | 0.546 | 0.456 | 0.227 |
| Integrated weight | 0.265 | 0.280 | 0.340 | 0.440 | 0.395 | 0.280 |
| Failure Item | S | O | D | FFWG | Score Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (0.575, 0.625) | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.400, 0.788) | (0.475, 0.701) | −0.237 |
| 2 | (0.250, 0.875) | (0.350, 0.825) | (0.375, 0.813) | (0.329, 0.835) | −0.547 |
| 3 | (0.525, 0.675) | (0.625, 0.575) | (0.700, 0.500) | (0.624, 0.578) | 0.050 |
| 4 | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.650, 0.550) | (0.625, 0.575) | (0.597, 0.596) | 0.001 |
| 5 | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.125, 0.938) | (0.475, 0.725) | (0.267, 0.849) | −0.592 |
| 6 | (0.400, 0.788) | (0.675, 0.525) | (0.125, 0.938) | (0.302, 0.692) | −0.304 |
| 7 | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.788, 0.400) | (0.325, 0.838) | (0.492, 0.576) | −0.071 |
| 8 | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.475, 0.725) | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.402, 0.751) | −0.358 |
| 9 | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.700, 0.500) | (0.400, 0.788) | (0.448, 0.659) | −0.196 |
| 10 | (0.400, 0.788) | (0.700, 0.500) | (0.375, 0.813) | (0.472, 0.651) | −0.170 |
| 11 | (0.625, 0.575) | (0.500, 0.700) | (0.150, 0.925) | (0.330, 0.716) | −0.332 |
| 12 | (0.375, 0.800) | (0.350, 0.825) | (0.275, 0.863) | (0.324, 0.828) | −0.534 |
| 13 | (0.600, 0.600) | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.250, 0.875) | (0.335, 0.777) | −0.432 |
| 14 | (0.600, 0.600) | (0.675, 0.525) | (0.300, 0.850) | (0.475, 0.624) | −0.135 |
| 15 | (0.675, 0.525) | (0.600, 0.600) | (0.275, 0.863) | (0.455, 0.640) | −0.168 |
| 16 | (0.525, 0.675) | (0.475, 0.725) | (0.450, 0.750) | (0.477, 0.717) | −0.260 |
| Failure Item | Typical RPN Method [36] | Typical IFS Method [45] | Typical FFS Method [28] | Proposed Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPN | Ranking | Score Function | Ranking | Score Function | Ranking | Score Function | Ranking | |
| 1 | 115.000 | 5 | −0.016 | 5 | −0.230 | 7 | −0.237 | 8 |
| 2 | 32.813 | 15 | −0.356 | 15 | −0.554 | 15 | −0.547 | 15 |
| 3 | 229.688 | 1 | 0.237 | 1 | 0.036 | 1 | 0.050 | 1 |
| 4 | 203.125 | 2 | 0.184 | 2 | −0.018 | 2 | 0.001 | 2 |
| 5 | 17.813 | 16 | −0.471 | 16 | −0.560 | 16 | −0.592 | 16 |
| 6 | 33.750 | 14 | −0.349 | 14 | −0.354 | 11 | −0.304 | 10 |
| 7 | 127.969 | 3 | 0.016 | 3 | −0.107 | 3 | −0.071 | 3 |
| 8 | 71.250 | 10 | −0.161 | 10 | −0.360 | 12 | −0.358 | 12 |
| 9 | 84.000 | 9 | −0.110 | 9 | −0.251 | 8 | −0.196 | 7 |
| 10 | 105.000 | 8 | −0.048 | 8 | −0.215 | 6 | −0.170 | 6 |
| 11 | 46.875 | 11 | −0.273 | 11 | −0.325 | 10 | −0.332 | 11 |
| 12 | 36.094 | 13 | −0.330 | 13 | −0.533 | 14 | −0.534 | 14 |
| 13 | 45.000 | 12 | −0.282 | 12 | −0.401 | 13 | −0.432 | 13 |
| 14 | 121.500 | 4 | 0.000 | 4 | −0.146 | 4 | −0.135 | 4 |
| 15 | 111.375 | 7 | −0.027 | 7 | −0.160 | 5 | −0.168 | 5 |
| 16 | 112.219 | 6 | −0.025 | 6 | −0.255 | 9 | −0.260 | 9 |
| Information and Weight Considerations | Typical RPN Method [36] | Typical IFS Method [45] | Typical FFS Method [28] | Proposed Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Considerations for FI | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Considerations for intuitionistic FI | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Considerations for Fermatean FI | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Subjective weight | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Objective weight | No | No | No | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, K.-H.; Chung, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-N.; Lai, Y.-D.; Wu, C.-H. A New Hybrid Fermatean Fuzzy Set and Entropy Method for Risk Assessment. Axioms 2023, 12, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12010058
Chang K-H, Chung H-Y, Wang C-N, Lai Y-D, Wu C-H. A New Hybrid Fermatean Fuzzy Set and Entropy Method for Risk Assessment. Axioms. 2023; 12(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Kuei-Hu, Hsiang-Yu Chung, Chia-Nan Wang, Yu-Dian Lai, and Chi-Hung Wu. 2023. "A New Hybrid Fermatean Fuzzy Set and Entropy Method for Risk Assessment" Axioms 12, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12010058
APA StyleChang, K.-H., Chung, H.-Y., Wang, C.-N., Lai, Y.-D., & Wu, C.-H. (2023). A New Hybrid Fermatean Fuzzy Set and Entropy Method for Risk Assessment. Axioms, 12(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12010058









