Analyzing the Causality and Dependence between Exchange Rate and Real Estate Prices in Boom-and-Bust Markets: Quantile Causality and DCC Copula GARCH Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. The Quantile Granger Causality Test
2.2. The Multivariate Quantile Granger Causality Test
2.3. DCC Copula GARCH
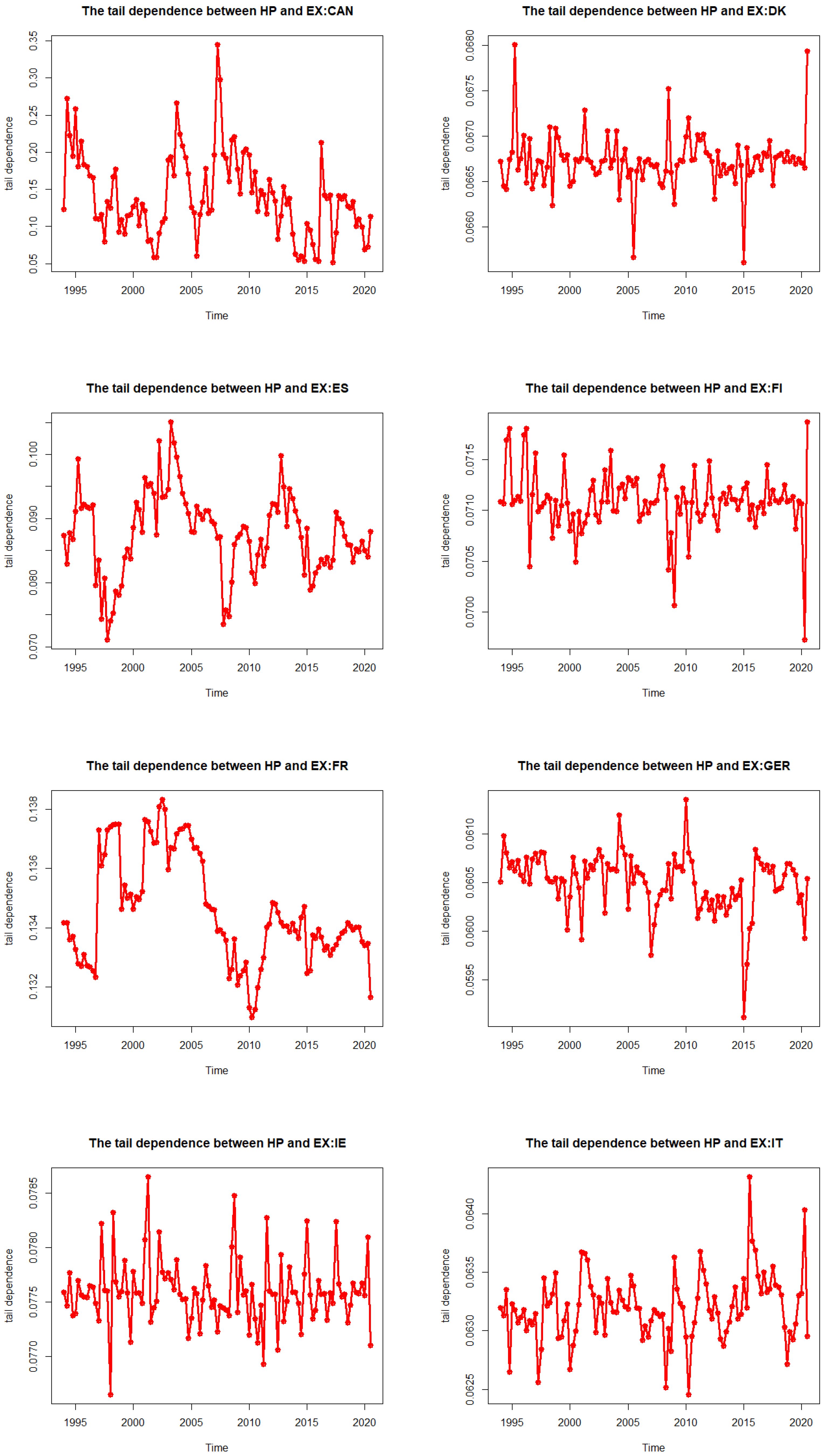
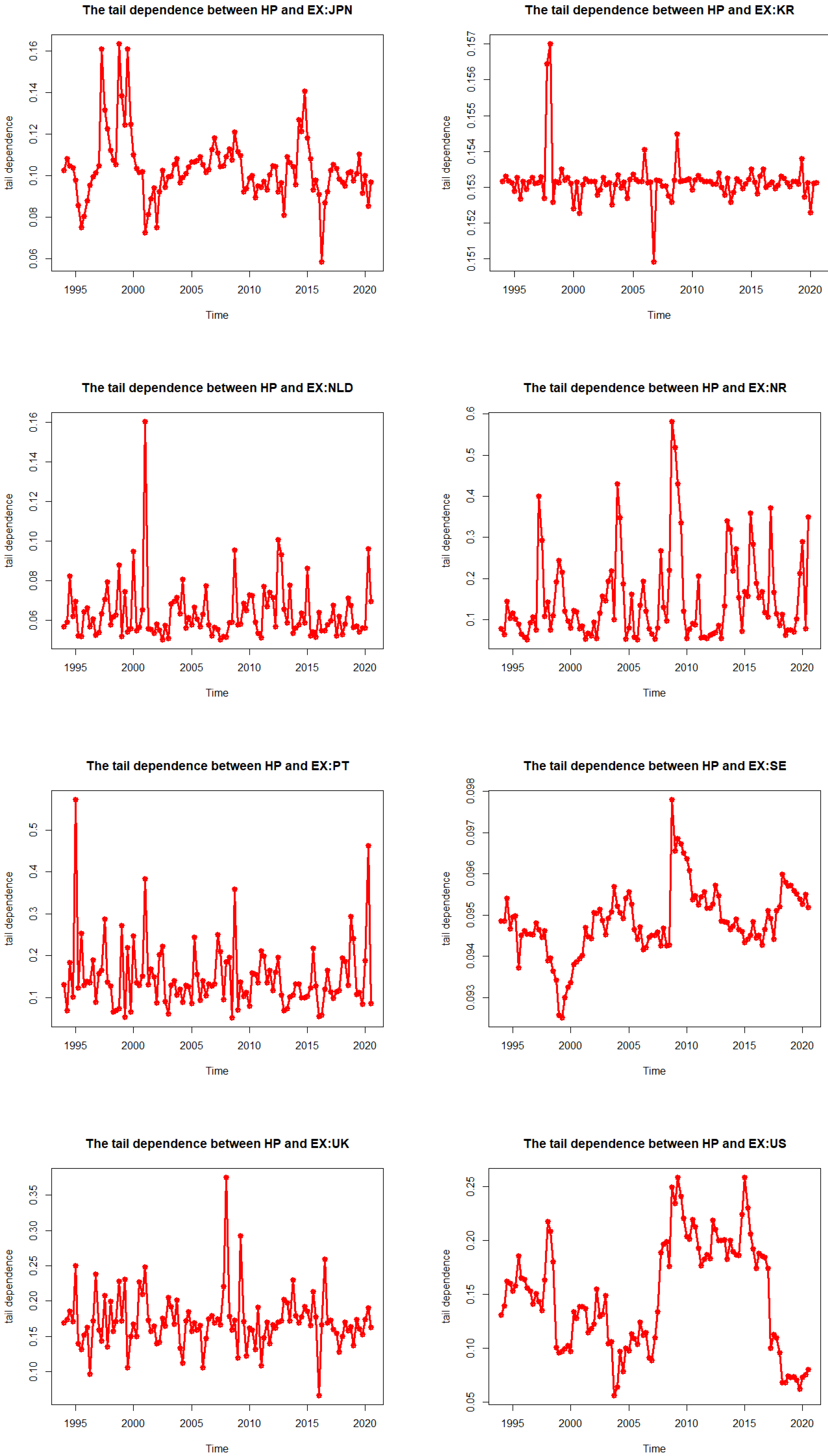
2.4. Tail Dependence Measure
3. Empirical Model and Data
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Summary Statistics and Time Series and Panel Unit Root Test
3.3. The Quantile Granger Causality Test Results
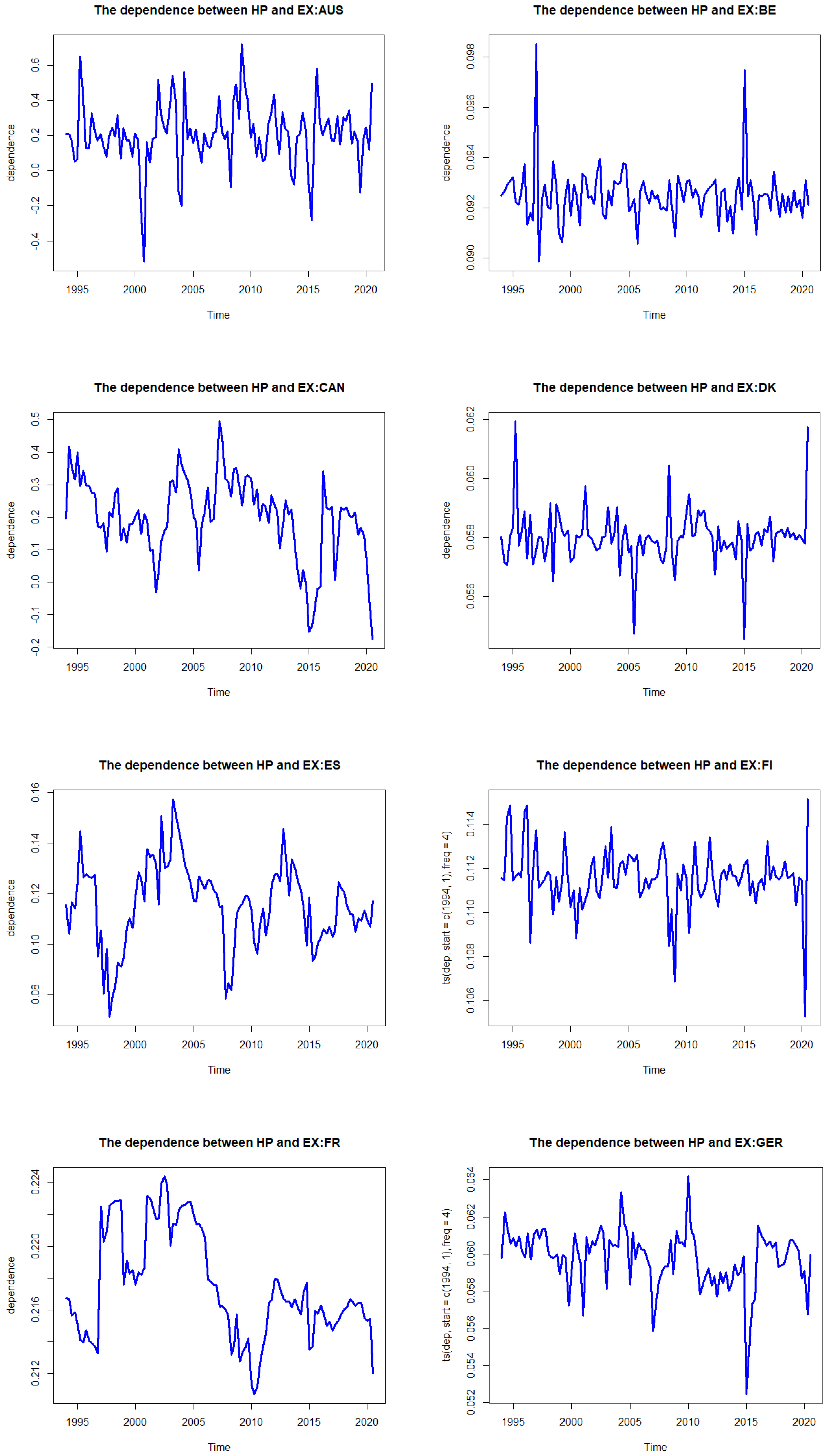
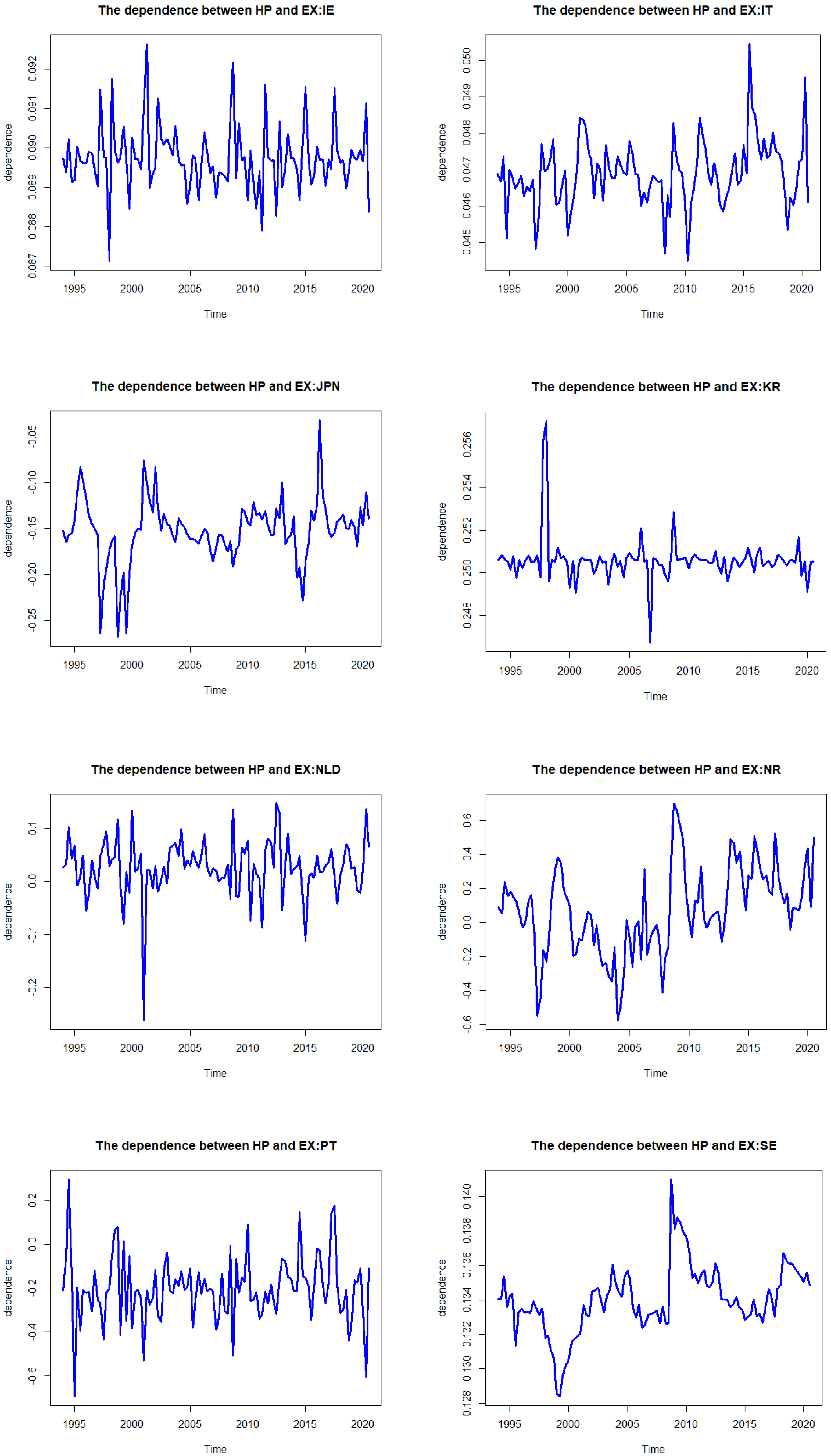
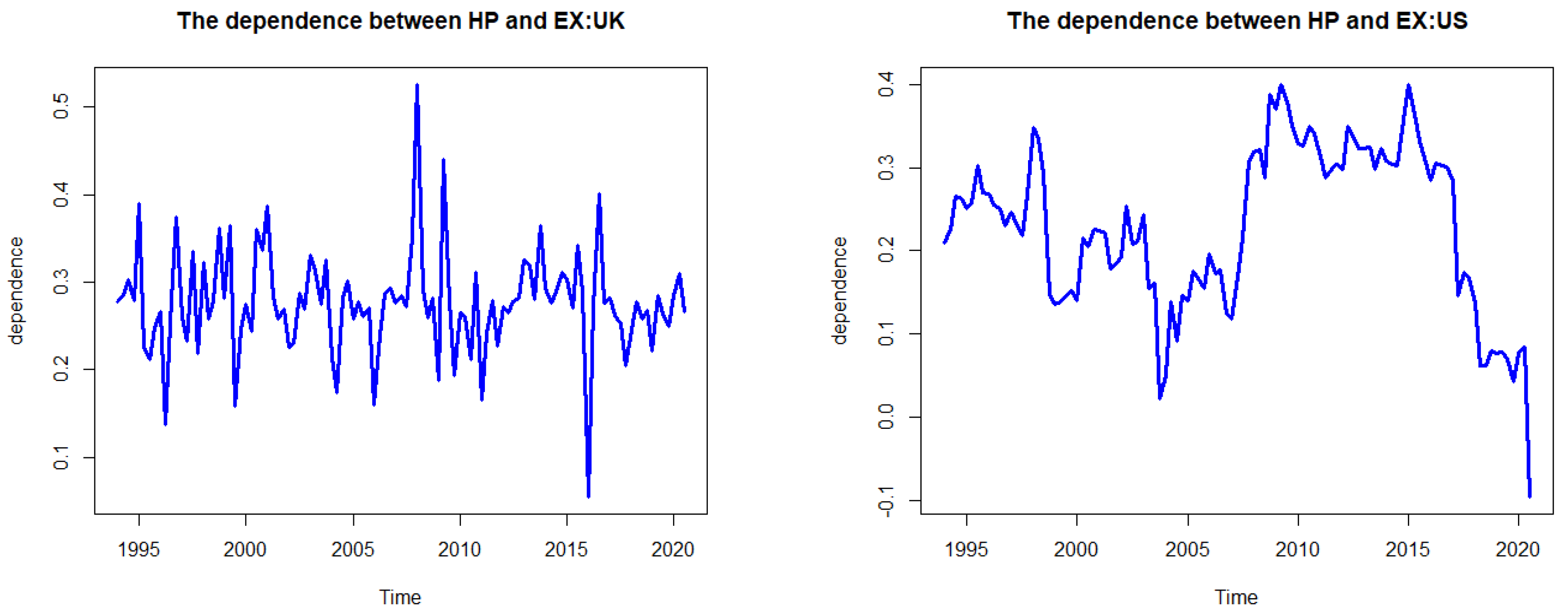
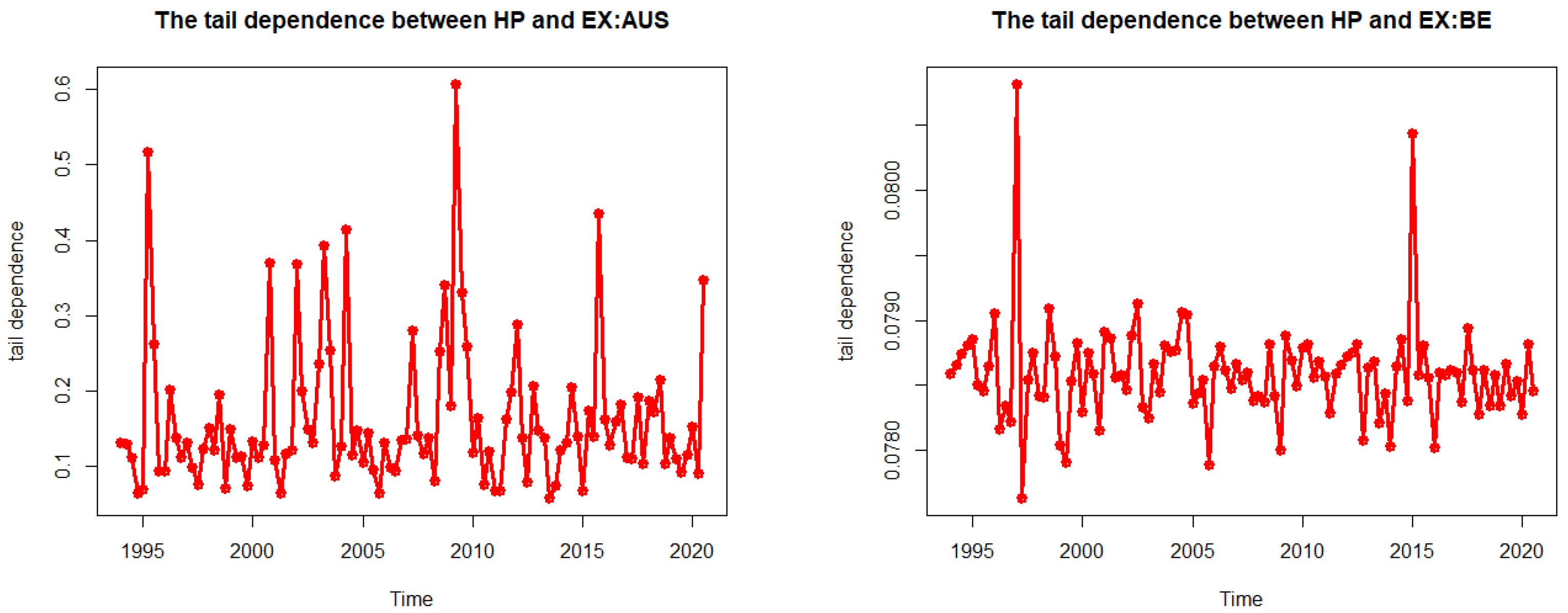
3.4. The DCC Copula GARCH Results
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.C.; Tsai, I.C.; Chang, C.O. House prices and household income: Do they move apart? Evidence from Taiwan. Habitat Int. 2007, 31, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissoondeeal, R.K.; Tsiaras, L. Investigating the Links between UK House Prices and Share Prices with Copulas. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2021, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani-Oskooee, M.; Wu, T.P. Housing prices and real effective exchange rates in 18 OECD countries: A bootstrap multivariate panel Granger causality. Econ. Anal. Policy 2018, 60, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpezzi, S. A simple error correction model of house prices. J. Hous. Econ. 1999, 8, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gete, P. Expectations and the housing boom and bust. An open economy view. J. Hous. Econ. 2020, 49, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N. Housing prices and macroeconomic factors: Prospects within the European Monetary Union. Int. Real Estate Rev. 2003, 6, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallin, J. The long-run relationship between house prices and income: Evidence from local housing markets. Real Estate Econ. 2006, 34, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhed, V.; Zemčík, P. Do house prices reflect fundamentals? Aggregate and panel data evidence. J. Hous. Econ. 2009, 18, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Bhattacharya, R. Regional housing prices in the USA: An empirical investigation of nonlinearity. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2009, 38, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holly, S.; Pesaran, M.H.; Yamagata, T. A spatio-temporal model of house prices in the USA. J. Econom. 2010, 158, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. Testing for cointegration between house prices and economic fundamentals. Real Estate Econ. 2010, 38, 599–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; De Vita, G. Pairwise convergence of district-level house prices in London. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; De Vita, G. Testing for long-run convergence across regional house prices in the UK: A pairwise approach. Appl. Econ. 2013, 45, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Chong, T.T.L.; Park, S.Y. Nonlinear dependence between stock and real estate markets in China. Econ. Lett. 2014, 124, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batayneh, K.I.; Al-Malki, A.M. The relationship between house prices and stock prices in Saudi Arabia: An empirical analysis. Int. J. Econ. Financ. 2015, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Simo-Kengne, B.D.; Gupta, R.; Chang, T. The dynamic relationship between house prices and output: Evidence from US metropolitan areas. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2015, 19, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gete, P.; Reher, M. Mortgage supply and housing rents. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2018, 31, 4884–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizenman, J.; Jinjarak, Y. Real estate valuation, current account and credit growth patterns, before and after the 2008–9 crisis. J. Int. Money Financ. 2014, 48, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thomas, M.; Lee, S. The impact of exchanges rates on international real estate portfolio allocation. J. Real Estate Portf. Manag. 2006, 12, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.I.U.; Zhiqiang, H.U. On correlation between RMB exchange rate and real estate price based on financial engineering. Syst. Eng. Procedia 2012, 3, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumer, L.; Özorhon, B. The exchange rate effect on housing price index and REIT index return rates. Finans. Araştırmalar Çalışmalar Derg. 2020, 12, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kónya, L. Exports and growth: Granger causality analysis on OECD countries with a panel data approach. Econ. Model. 2006, 23, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, J.; Harvey, J.; Hunt, H. Exchange-rate risk mitigation with price-level-adjusting mortgages: The case of the Mexican UDI. J. Real Estate Res. 2003, 25, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troster, V. Testing for Granger-causality in quantiles. Econom. Rev. 2018, 37, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiullah, M.; Chaudhry, S.M.; Shahbaz, M.; Reboredo, J.C. Quantile causality and dependence between crude oil and precious metal prices. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2021, 26, 6264–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, S.; Yuan, D.; Zhu, H. Investor attention and cryptocurrency: Evidence from wavelet-based quantile Granger causality analysis. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2021, 56, 101389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Jung, H. Linear time-varying regression with Copula–DCC–GARCH models for volatility. Econ. Lett. 2016, 145, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarta, S.; McNeil, A.J. The t copula and related copulas. Int. Stat. Rev. 2005, 73, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellner, A. An efficient method of estimating seemingly unrelated regressions and tests for aggregation bias. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1962, 57, 348–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollerslev, T. Generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity. J. Econom. 1986, 31, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, A. Random variables, joint distribution functions, and copulas. Kybernetika 1973, 9, 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, R. Dynamic conditional correlation: A simple class of multivariate generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity models. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2002, 20, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, Y.K.; Tsui, A.K.C. A multivariate generalized autoregressive conditional heteroscedasticity model with time-varying correlations. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2002, 20, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, T.; Czado, C. Evading the curse of dimensionality in nonparametric density estimation with simplified vine copulas. J. Multivar. Anal. 2016, 151, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.L.; Bentler, P.M. Maximum likelihood estimation in covariance structure analysis with truncated data. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 1997, 50, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, F.P. Tail dependence in financial markets: A dynamic copula approach. Risks 2019, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, F.; Trabelsi, N.; Samargandi, N.; Shahzad, S.J.H. Tail Dependence and Risk Spillover from the US to GCC Banking Sectors. Mathematics 2020, 8, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, D.M. Time-varying correlation in housing prices. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2015, 51, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneejuk, P.; Yamaka, W. Predicting contagion from the US financial crisis to international stock markets using dynamic copula with google trends. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastpipatkul, P.; Yamaka, W.; Sriboonchitta, S. Dependence structure of and co-movement between Thai currency and international currencies after introduction of quantitative easing. In Causal Inference in Econometrics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 545–564. [Google Scholar]
- Lucarelli, S.; Andrini, F.U.; Bianchi, A. Euro depreciation and trade asymmetries between Germany and Italy versus the US: Industry-level estimates. Appl. Econ. 2018, 50, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, L.; Lucarelli, S. ECB quantitative easing, euro depreciation and supply chains: Industry-level estimates for Germany, Italy and Greece. New prospects for a Minskyan big bank? PSL Q. Rev. 2021, 74, 15–50. [Google Scholar]
- Maneejuk, P.; Yamaka, W.; Sriboonchitta, S. Mixed-copulas approach in examining the relationship between oil prices and ASEAN’s stock markets. In Proceedings of the International Econometric Conference of Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, 15–16 January 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 531–541. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Max | Min | Mean | Skew | Kurt | Std.Dev | ADF | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 120.848 | 72.955 | 94.389 | 0.234 | −0.770 | 12.838 | −8.395 | 0.000 |
| Belgium | 111.058 | 95.254 | 103.711 | −0.480 | 0.166 | 3.192 | −7.627 | 0.000 |
| Canada | 126.723 | 87.319 | 103.608 | 0.500 | −1.002 | 10.735 | −8.682 | 0.000 |
| Denmark | 110.898 | 97.291 | 103.808 | 0.257 | −0.494 | 2.964 | −8.325 | 0.000 |
| Spain | 110.965 | 92.976 | 101.621 | −0.193 | −1.003 | 4.670 | −6.210 | 0.000 |
| Finland | 119.982 | 98.518 | 105.490 | 1.0548 | 1.225 | 4.540 | −7.739 | 0.000 |
| France | 120.366 | 99.406 | 108.719 | 0.150 | −1.050 | 5.627 | −7.534 | 0.000 |
| Germany | 130.240 | 99.065 | 110.283 | 0.752 | −0.031 | 7.381 | −8.140 | 0.000 |
| Ireland | 129.494 | 91.610 | 106.246 | 0.638 | −0.381 | 8.759 | −7.300 | 0.000 |
| Italy | 110.741 | 90.253 | 103.993 | −0.322 | 0.175 | 3.943 | −8.113 | 0.000 |
| Japan | 213.346 | 98.582 | 139.673 | 0.378 | −0.550 | 26.527 | −4.929 | 0.001 |
| Korea | 119.522 | 69.536 | 99.555 | 0.011 | 0.074 | 9.912 | −8.793 | 0.000 |
| Netherlands | 110.708 | 94.722 | 104.027 | −0.131 | −0.626 | 3.673 | −8.126 | 0.000 |
| Norway | 126.351 | 89.921 | 110.854 | −0.570 | −0.163 | 7.516 | −9.564 | 0.000 |
| Portugal | 106.758 | 94.534 | 101.467 | −0.179 | −0.872 | 2.953 | −9.671 | 0.000 |
| Sweden | 137.776 | 90.436 | 112.254 | 0.083 | −0.528 | 11.368 | −8.135 | 0.000 |
| UK | 115.69 | 83.078 | 98.868 | 0.121 | −1.591 | 10.669 | −7.177 | 0.000 |
| USA | 116.228 | 84.596 | 99.131 | 0.086 | −0.959 | 8.116 | −7.950 | 0.000 |
| Variable | Max | Min | Mean | Skew | Kurt | Std.Dev | ADF | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 112.179 | 40.148 | 74.937 | −0.136 | −1.259 | 23.278 | −4.869 | 0.000 |
| Belgium | 110.800 | 53.832 | 85.191 | −0.447 | −1.445 | 18.479 | −3.691 | 0.000 |
| Canada | 133.800 | 48.077 | 78.426 | 0.489 | −1.001 | 26.360 | −5.272 | 0.000 |
| Denmark | 121.965 | 46.888 | 88.228 | −0.253 | −1.071 | 21.957 | −3.780 | 0.000 |
| Spain | 165.874 | 69.145 | 108.657 | 0.301 | −1.006 | 28.799 | −3.494 | 0.000 |
| Finland | 105.900 | 56.315 | 88.791 | −0.776 | −0.854 | 15.853 | −4.061 | 0.000 |
| France | 114.000 | 50.697 | 86.695 | −0.526 | −1.507 | 22.641 | −2.935 | 0.000 |
| Germany | 133.100 | 87.800 | 101.454 | 0.949 | 0.542 | 10.492 | −8.966 | 0.000 |
| Ireland | 160.800 | 46.900 | 103.179 | −0.159 | −0.791 | 30.737 | −3.494 | 0.000 |
| Italy | 136.350 | 85.067 | 107.844 | 0.400 | −1.169 | 15.418 | −10.435 | 0.000 |
| Japan | 146.017 | 92.900 | 111.782 | 0.816 | −0.834 | 16.292 | −4.216 | 0.001 |
| Korea | 112.522 | 72.840 | 94.370 | −0.875 | −0.148 | 9.052 | −4.628 | 0.000 |
| Netherlands | 134.100 | 56.552 | 104.868 | −0.944 | −0.188 | 20.939 | −3.494 | 0.000 |
| Norway | 110.100 | 32.00 | 73.843 | −0.162 | 1.342 | 24.906 | −6.055 | 0.000 |
| Portugal | 144.800 | 93.300 | 120.694 | −0.398 | −0.780 | 13.672 | −3.494 | 0.000 |
| Sweden | 123.300 | 35.549 | 73.518 | 0.096 | −1.211 | 26.440 | −4.887 | 0.000 |
| UK | 112.300 | 38.900 | 82.271 | −0.655 | −1.059 | 24.405 | −4.363 | 0.000 |
| US | 127.800 | 73.900 | 96.687 | 0.115 | −1.054 | 14.926 | −3.493 | 0.000 |
| Variable | Max | Min | Mean | Skew | Kurt | Std.Dev | LLC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 124.316 | 90.558 | 105.983 | 0.133 | −0.466 | 8.077 | −5.993 | 0.000 | |
| 128.095 | 60.045 | 93.413 | −0.120 | −0.750 | 20.258 | −8.234 | 0.000 | |
| 62,991.91 | 25,384.09 | 35,024.32 | −0.233 | 2.228 | 4943.922 | −4.083 | 0.000 | |
| 22.832 | 0.073 | 21.908 | 0.830 | 2.768 | 2.739 | −5.031 | 0.000 |
| Country | GEX Cause GHP | GHP Cause GEX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Causality | p-Value | Causality | |
| Australia | 0.121 | Yes | 0.211 | Yes |
| Belgium | 0.023 | No | 0.301 | Yes |
| Canada | 0.121 | Yes | 0.108 | Yes |
| Denmark | 0.503 | Yes | 0.232 | Yes |
| Spain | 0.221 | Yes | 0.122 | Yes |
| Finland | 0.343 | Yes | 0.003 | No |
| France | 0.245 | Yes | 0.005 | No |
| Germany | 0.434 | Yes | 0.003 | No |
| Ireland | 0.107 | Yes | 0.293 | Yes |
| Italy | 0.201 | Yes | 0.193 | Yes |
| Japan | 0.105 | Yes | 0.762 | Yes |
| Korea | 0.321 | Yes | 0.201 | Yes |
| Netherlands | 0.294 | Yes | 0.184 | Yes |
| Norway | 0.056 | No | 0.501 | Yes |
| Portugal | 0.301 | Yes | 0.211 | Yes |
| Sweden | 0.104 | Yes | 0.401 | Yes |
| UK | 0.000 | No | 0.000 | No |
| USA | 0.000 | No | 0.329 | Yes |
| Country | GEX Cause GHP | GHP Cause GEX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Causality | p-Value | Causality | |
| Australia | 0.000 | No | 0.008 | No |
| Belgium | 0.344 | Yes | 0.490 | Yes |
| Canada | 0.108 | Yes | 0.000 | No |
| Denmark | 0.693 | Yes | 0.390 | Yes |
| Spain | 0.000 | No | 0.440 | Yes |
| Finland | 0.202 | Yes | 0.842 | Yes |
| France | 0.839 | Yes | 0.108 | Yes |
| Germany | 0.224 | Yes | 0.421 | Yes |
| Ireland | 0.409 | Yes | 0.213 | Yes |
| Italy | 0.156 | Yes | 0.224 | Yes |
| Japan | 0.772 | Yes | 0.302 | Yes |
| Korea | 0.394 | Yes | 0.221 | Yes |
| Netherlands | 0.000 | No | 0.209 | Yes |
| Norway | 0.834 | Yes | 0.200 | Yes |
| Portugal | 0.247 | Yes | 0.498 | Yes |
| Sweden | 0.690 | Yes | 0.702 | Yes |
| UK | 0.509 | Yes | 0.287 | Yes |
| USA | 0.873 | Yes | 0.654 | Yes |
| Country | GEX Cause GHP | GHP Cause GEX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Causality | p-Value | Causality | |
| Australia | 0.023 | No | 0.223 | Yes |
| Belgium | 0.001 | No | 0.824 | Yes |
| Canada | 0.774 | Yes | 0.002 | No |
| Denmark | 0.002 | No | 0.001 | No |
| Finland | 0.292 | Yes | 0.229 | Yes |
| France | 0.301 | Yes | 0.493 | Yes |
| Germany | 0.224 | Yes | 0.000 | No |
| Ireland | 0.092 | No | 0.254 | Yes |
| Italy | 0.392 | Yes | 0.119 | Yes |
| Japan | 0.743 | Yes | 0.394 | Yes |
| Korea | 0.224 | Yes | 0.320 | Yes |
| Netherlands | 0.302 | Yes | 0.983 | Yes |
| Norway | 0.924 | Yes | 0.291 | Yes |
| Portugal | 0.000 | No | 0.390 | Yes |
| Spain | 0.021 | No | 0.000 | No |
| Sweden | 0.091 | No | 0.083 | No |
| UK | 0.000 | No | 0.000 | No |
| USA | 0.345 | Yes | 0.011 | No |
| Parameter | μ | Log- Likelihood | Q (1) | ARCH (1)-LM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia Belgium Canada Denmark Spain Finland France Germany Ireland Italy Japan Korea Netherlands Norway Portugal Sweden UK USA | 0.001 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.001 * (0.001) −0.001 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.001) −0.003 * (0.002) 0.002 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.001) −0.001 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.000) −0.001 * (0.001) −0.001 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.001) | 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) | 0.001 * (0.013) 0.006 * (0.028) 0.277 * (0.179) 0.004 * (0.044) 0.001 * 0.002 0.115 * (0.326) 0.001 * (0.002) 0.000 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.001) 0.263 * (0.097) 0.000 * (0.014) 0.467 * (0.547) 0.000 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.007) 0.006 * (0.019) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.008) 0.000 * (0.005) | 0.996 * (0.015) 0.990 * (0.032) 0.583 * (0.174) 0.993 * (0.050) 0.997 * 0.002 0.840 * (0.357) 0.998 * (0.002) 0.998 * (0.001) 0.998 * (0.001) 0.562 * (0.090) 0.995 * (0.018) 0.264 * (0.275) 0.997 * (0.001) 0.999 * (0.006) 0.989 * (0.022) 0.998 * (0.000) 0.999 * (0.007) 0.999 * (0.005) | 300.745 428.020 331.006 415.697 420.142 399.687 425.977 397.402 378.668 404.200 288.104 308.411 399.928 336.605 463.464 339.252 342.664 347.242 | 0.915 0.814 0.739 0.994 0.462 0.484 0.618 0.752 0.340 0.963 0.846 0.379 0.757 0.376 0.215 0.136 0.758 0.654 | 0.564 0.511 0.720 0.139 0.359 0.334 0.791 0.174 0.609 0.508 0.668 0.640 0.712 0.804 0.454 0.942 0.937 0.550 |
| Parameter | μ | Log-Likelihood | Q (1) | ARCH (1)-LM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia Belgium Canada Denmark Spain Finland France Germany Ireland Italy Japan Korea Netherlands Norway Portugal Sweden UK USA | 0.004 * (0.002) 0.003 * (0.000) 0.004 * (0.001) 0.004 * (0.001) −0.002 * (0.004) 0.000 * (0.001) −0.003 * (0.002) −0.001 * (0.001) 0.002 * (0.005) −0.008 * (0.002) −0.002 * (0.001) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.005 * (0.003) 0.005 * (0.001) −0.001 * (0.002) 0.005 * (0.001) 0.004 * (0.002) 0.004 * (0.002) | 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) 0.000 * (0.000) | 0.000 * (0.010) 0.008 * (0.022) 0.456 * (0.207) 0.346 (0.180) 0.223 * (0.098) 0.589 * (0.297) 0.475 * (0.208) 0.169 * (0.038) 0.148 * (0.055) 0.354 * (0.177) 0.314 * (0.151) 0.165 * (0.134) 0.090 * (0.025) 0.220 * (0.0701) 0.000 * (0.024 *) 0.000 * (0.007) 0.389 * (0.138) 0.265 * (0.116) | 0.995 * (0.011) 0.985 * (0.027) 0.543 * (0.144) 0.477 0.123 0.665 * (0.057) 0.410 * (0.073) 0.463 * (0.034) 0.763 * (0.062) 0.741 * (0.069) 0.398 * (0.133) 0.685 * (0.097) 0.834 * (0.069) 0.664 * (0.061) 0.638 * (0.085) 0.999 * (0.018) 0.999 * (0.007) 0.610 * (0.110) 0.706 * (0.095) | 404.508 424.184 425.671 409.341 413.902 422.550 466.536 429.898 361.837 468.160 484.814 434.012 447.000 392.873 425.741 417.912 404.876 504.900 | 0.069 0.061 0.399 0.565 0.684 0.622 0.899 0.819 0.725 0.717 0.806 0.889 0.507 0.722 0.858 0.735 0.981 0.775 | 0.195 0.400 0.776 0.624 0.843 0.649 0.845 0.863 0.692 0.590 0.808 0.968 0.922 0.857 0.586 0.644 0.571 0.743 |
| Country | Coef | SE | p-Value | Mean (Dep) | Mean (Tail) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | a | 0.252 | 0.117 | 0.032 | 0.355 | 0.160 |
| b | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| Belgium | a | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.929 | 0.145 | 0.079 |
| b | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| Canada | a | 0.110 | 0.096 | 0.252 | 0.325 | 0.140 |
| b | 0.655 | 0.374 | 0.080 | |||
| Denmark | a | 0.001 | 0.062 | 0.988 | 0.091 | 0.067 |
| b | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| Spain | a | 0.012 | 0.074 | 0.871 | 0.181 | 0.088 |
| b | 0.753 | 0.493 | 0.127 | |||
| Finland | a | 0.001 | 0.026 | 0.970 | 0.112 | 0.071 |
| b | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| France | a | 0.002 | 0.036 | 0.967 | 0.335 | 0.135 |
| b | 0.924 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| Germany | a | 0.001 | 0.153 | 0.995 | 0.060 | 0.061 |
| b | 0.611 | 7.354 | 0.934 | |||
| Ireland | a | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.140 | 0.076 |
| b | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| Italy | a | 0.001 | 0.141 | 0.994 | 0.074 | 0.063 |
| b | 0.449 | 5.484 | 0.935 | |||
| Japan | a | 0.044 | 0.196 | 0.821 | 0.236 | 0.103 |
| b | 0.567 | 0.594 | 0.339 | |||
| Korea | a | 0.001 | 0.074 | 0.989 | 0.384 | 0.153 |
| b | 0.001 | 13.290 | 1.000 | |||
| Netherlands | a | 0.059 | 0.103 | 0.571 | 0.071 | 0.064 |
| b | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| Norway | a | 0.233 | 0.112 | 0.037 | 0.310 | 0.150 |
| b | 0.497 | 0.258 | 0.054 | |||
| Portugal | a | 0.223 | 0.159 | 0.159 | 0.336 | 0.149 |
| b | 0.001 | 0.382 | 0.998 | |||
| Sweden | a | 0.001 | 0.046 | 0.983 | 0.209 | 0.095 |
| b | 0.855 | 1.525 | 0.575 | |||
| UK | a | 0.081 | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.419 | 0.172 |
| b | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| USA | a | 0.047 | 0.043 | 0.273 | 0.352 | 0.149 |
| b | 0.881 | 0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| DCC-Copula (Normal Copula) AIC = 278.829 BIC = 300.092 | ||||||
| CCC-Copula (Normal Copula) AIC = 293.093 BIC = 317.023 | ||||||
| DCC-Copula (Student-t Copula) AIC = 257.098 BIC = 280.189 | ||||||
| CCC-Copula (Student-t Copula) AIC = 285.229 BIC = 302.109 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamaka, W.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Maneejuk, P.; Dinh, H.Q. Analyzing the Causality and Dependence between Exchange Rate and Real Estate Prices in Boom-and-Bust Markets: Quantile Causality and DCC Copula GARCH Approaches. Axioms 2022, 11, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11030113
Yamaka W, Liu J, Li M, Maneejuk P, Dinh HQ. Analyzing the Causality and Dependence between Exchange Rate and Real Estate Prices in Boom-and-Bust Markets: Quantile Causality and DCC Copula GARCH Approaches. Axioms. 2022; 11(3):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11030113
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamaka, Woraphon, Jianxu Liu, Mingyang Li, Paravee Maneejuk, and Hai Q. Dinh. 2022. "Analyzing the Causality and Dependence between Exchange Rate and Real Estate Prices in Boom-and-Bust Markets: Quantile Causality and DCC Copula GARCH Approaches" Axioms 11, no. 3: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11030113
APA StyleYamaka, W., Liu, J., Li, M., Maneejuk, P., & Dinh, H. Q. (2022). Analyzing the Causality and Dependence between Exchange Rate and Real Estate Prices in Boom-and-Bust Markets: Quantile Causality and DCC Copula GARCH Approaches. Axioms, 11(3), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11030113






