Computation of the Deuteron Mass and Force Unification via the Rotating Lepton Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
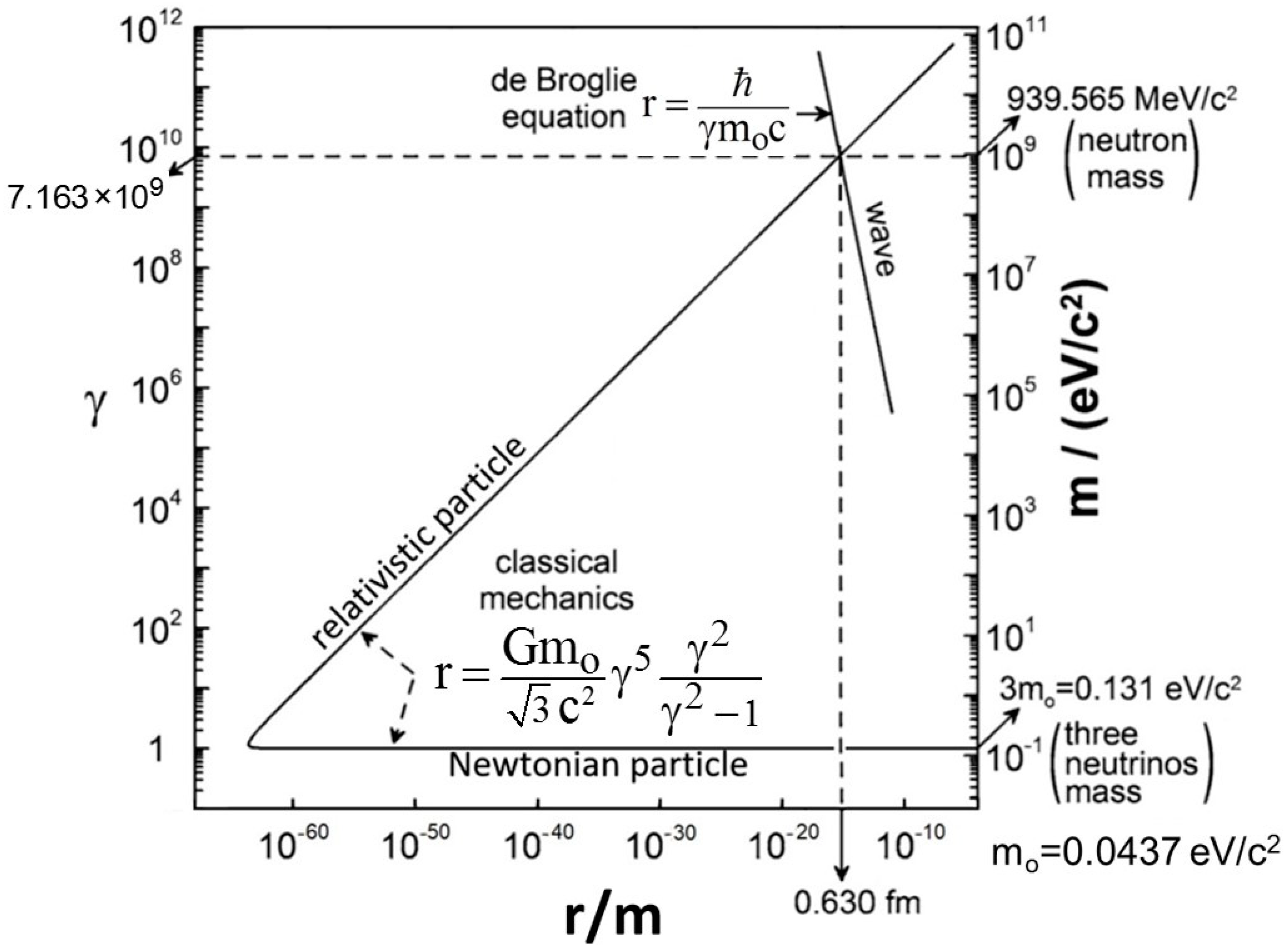
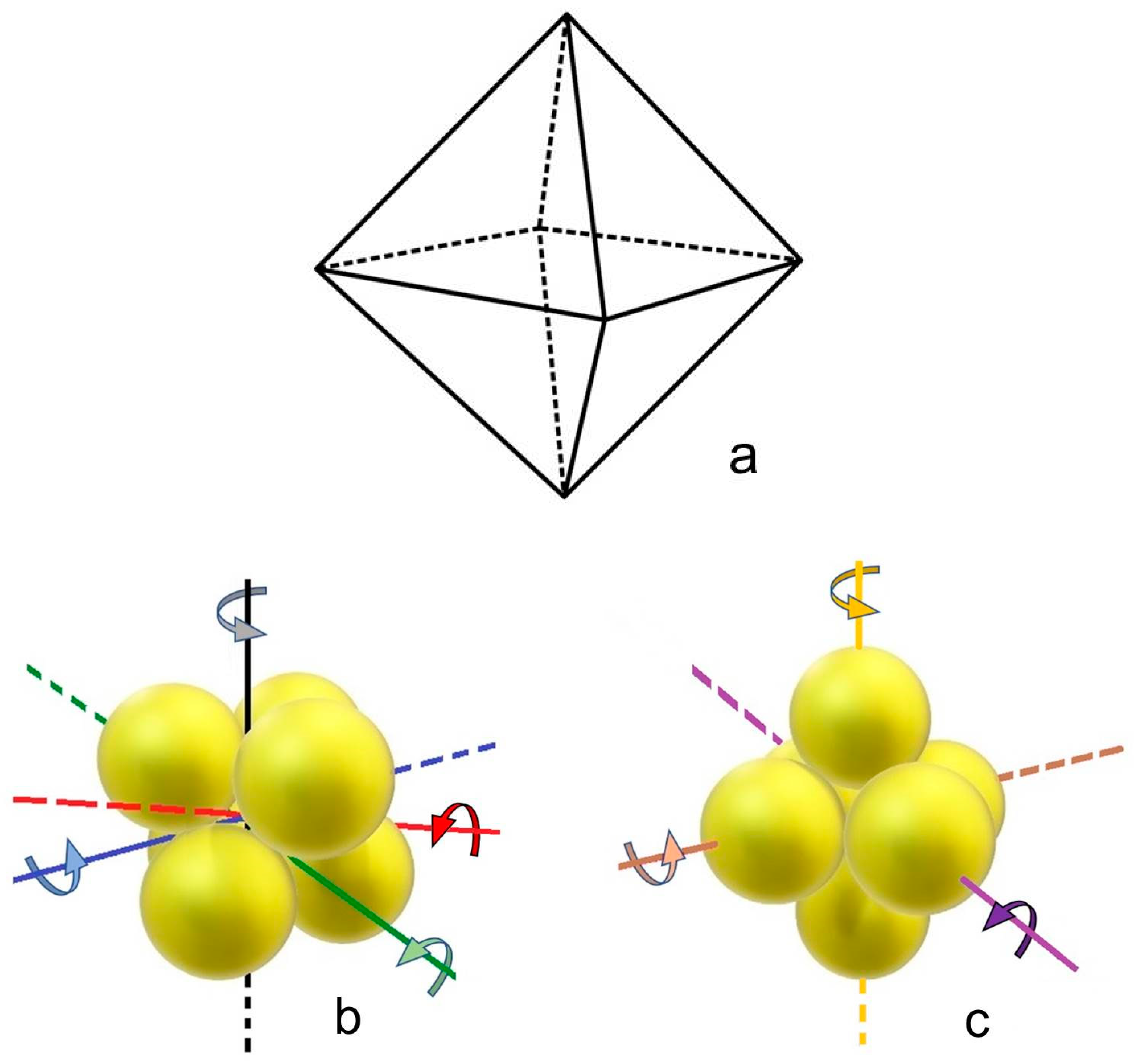
2. The Rotating Lepton Model (RLM)
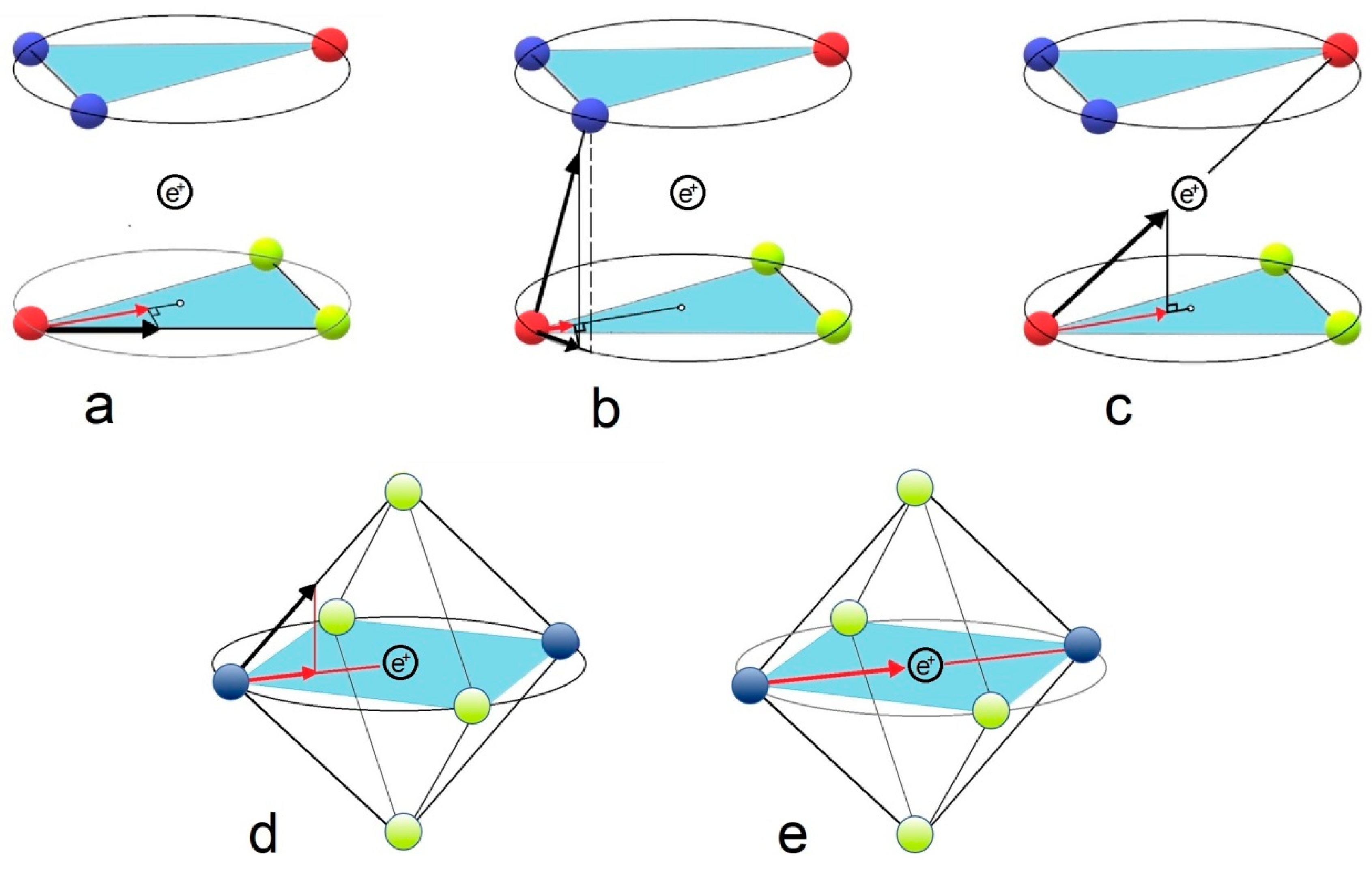
3. The Deuteron Model
4. Mathematical Modeling and Mass Computation
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary/Nomenclature/Abbreviations
| QCD | Quantum chromodynamics |
| RLM | Rotating lepton model |
| m1, m2, m3 | Rest neutrino eigenmasses |
| mn | Neutron mass |
| me | Electron mass |
| mμ | Muon mass |
| mPl | Planck mass |
| γ | Lorentz factor = |
| mo | Rest mass |
| v | Particle speed |
| r | Rotational radius |
| G | Gravitational constant, 6.6743 × 10−11 m3/(kgs2) |
| mg | Gravitational mass |
| mi | Inertial mass |
| c | Speed of light in vacuum |
| Reduced Planck’s constant | |
| eV/c2 | Mass unit, 1.783 × 10−36 kg |
| Mean γ value | |
| F1 | Centripetal force in the equatorial rotation |
| F2 | Centripetal force in the top–bottom rotation |
| md | Total deuteron mass |
| md,r | Mass of the rotating components of the deuteron |
| mo,d | Neutrino rest mass in the deuteron |
| mo,n | Neutrino rest mass in the neutron |
| 1 | Equatorial rotation |
| 2 | Top–bottom rotation |
| d | Deuteron |
| Quantum chromodynamics (QCD) | The strong force theory of the standard model (SM). |
| Rotating lepton model (RLM) | It has the same goals as QCD, but has no adjustable parameters. |
| Deuteron | The nucleus of the deuterium, comprising a proton and a neutron. |
| Quarks | Building blocks of hadrons, identified as relativistic rotating neutrinos in the RLM. |
| Strong force | Force binding the constituents of hadrons. |
| Relativistic gravity | Newtonian gravity, also accounting for special relativity. |
| Residual strong force | The force binding nucleons with other nucleons. |
References
- Griffiths, D. Introduction to Elementary Particles, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, A. Zür Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper. Ann. Der Physik. 1905, 4, 891–921, English Translation On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies by Jeffery, G.B. and Perrett, W. 1923. Available online: http://fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/www (accessed on 22 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- French, A.P. Special Relativity; W.W. Norton & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Vayenas, C.G.; Souentie, S. A Bohr-Einstein-de Broglie Model for the Formation of Hadrons. In Gravity, Special Relativity and the Strong Force; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vayenas, C.G.; Souentie, S.; Fokas, A. A Bohr-type model of a composite particle using gravity as the attractive force. Physica A 2014, 405, 360–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vayenas, C.G.; Fokas, A.S.; Grigoriou, D. On the structure, masses and thermos-dynamics of the W± bosons. Physica A 2016, 450, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, P.G.; Krotkov, R.; Dicke, R.G. The equivalence of inertial and passive gravitational mass. Ann. Phys. 1964, 26, 442–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokas, A.S.; Vayenas, C.G.; Grigoriou, D.P. On the mass and thermodynamics of the Higgs boson. Physica A 2018, 492, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayenas, C.G.; Grigoriou, D.P. Hadronization via gravitational confinement. In Proceedings of the Particle Physics at the Year of 25th Anniversary of the Lomonosov Conferences, Moscow, Russia, 24–30 August 2017; Studenikin, A., Ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019; pp. 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriou, D.P.; Vayenas, C.G. Schwarzschild geodesics and the strong force. In Proceedings of the Particle Physics at the Year of 25th Anniversary of the Lomonosov Conferences, Moscow, Russia, 24–30 August 2017; Studenikin, A., Ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019; pp. 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Vayenas, C.G.; Tsousis, D.; Grigoriou, D. Computation of the masses, energies and internal pressures of hadrons, mesons and bosons via the Rotating Lepton Model. Physica A 2020, 545, 123679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayenas, C.G.; Tsousis, D.; Grigoriou, D.; Parisis, K.; Aifantis, E.C. Hadronization via gravitational confinement of fast neutrinos: Mechanics at fm distances. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 2022, 102, e202100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayenas, C.G.; Grigoriou, D.; Tsousis, D. Mass generation via gravitational confinement of fast neutrinos. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.09760v5. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, R.N.; Antusch, S.; Babu, K.S.; Barenboim, G.; Chen, M.-C.; De Gouvêa, A.; De Holanda, P.; Dutta, B.; Grossman, Y.; Joshipura, A.; et al. Theory of neutrinos: A white paper. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2007, 70, 1757–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, T. Discovery of neutrino oscillations. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 1607–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkert, V.D.; Elouadrhiri, L.; Girod, F.X. The pressure distribution inside the proton. Nature 2018, 557, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aifantis, E.C. A concise review of gradient models in mechanics and physics. Front. Phys. 2020, 7, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aifantis, E.C. Gradient Extension of Classical Material Models: From Nuclear & Condensed Matter Scales to Earth & Cosmological Scales. In Size-Dependent Continuum Mechanics Approaches; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2021; pp. 417–452. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, S. Dreams of a Final Theory; Pantheon Books: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Penrose, R. The Road to Reality: A Complete Guide to the Laws of the Universe; Vintage: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hawking, S. A Brief History of Time; Transworld Publishers Ltd.: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vayenas, C.G.; Grigoriou, D.; Tsousis, D.; Parisis, K.; Aifantis, E.C. Computation of the Deuteron Mass and Force Unification via the Rotating Lepton Model. Axioms 2022, 11, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11110657
Vayenas CG, Grigoriou D, Tsousis D, Parisis K, Aifantis EC. Computation of the Deuteron Mass and Force Unification via the Rotating Lepton Model. Axioms. 2022; 11(11):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11110657
Chicago/Turabian StyleVayenas, Constantinos G., Dimitrios Grigoriou, Dionysios Tsousis, Konstantinos Parisis, and Elias C. Aifantis. 2022. "Computation of the Deuteron Mass and Force Unification via the Rotating Lepton Model" Axioms 11, no. 11: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11110657
APA StyleVayenas, C. G., Grigoriou, D., Tsousis, D., Parisis, K., & Aifantis, E. C. (2022). Computation of the Deuteron Mass and Force Unification via the Rotating Lepton Model. Axioms, 11(11), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11110657








