Provenance of Wushan Loess in the Yangtze Three Gorges Region: Insights from Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Late Pleistocene East Asian Monsoon Variations
Abstract
1. Introduction
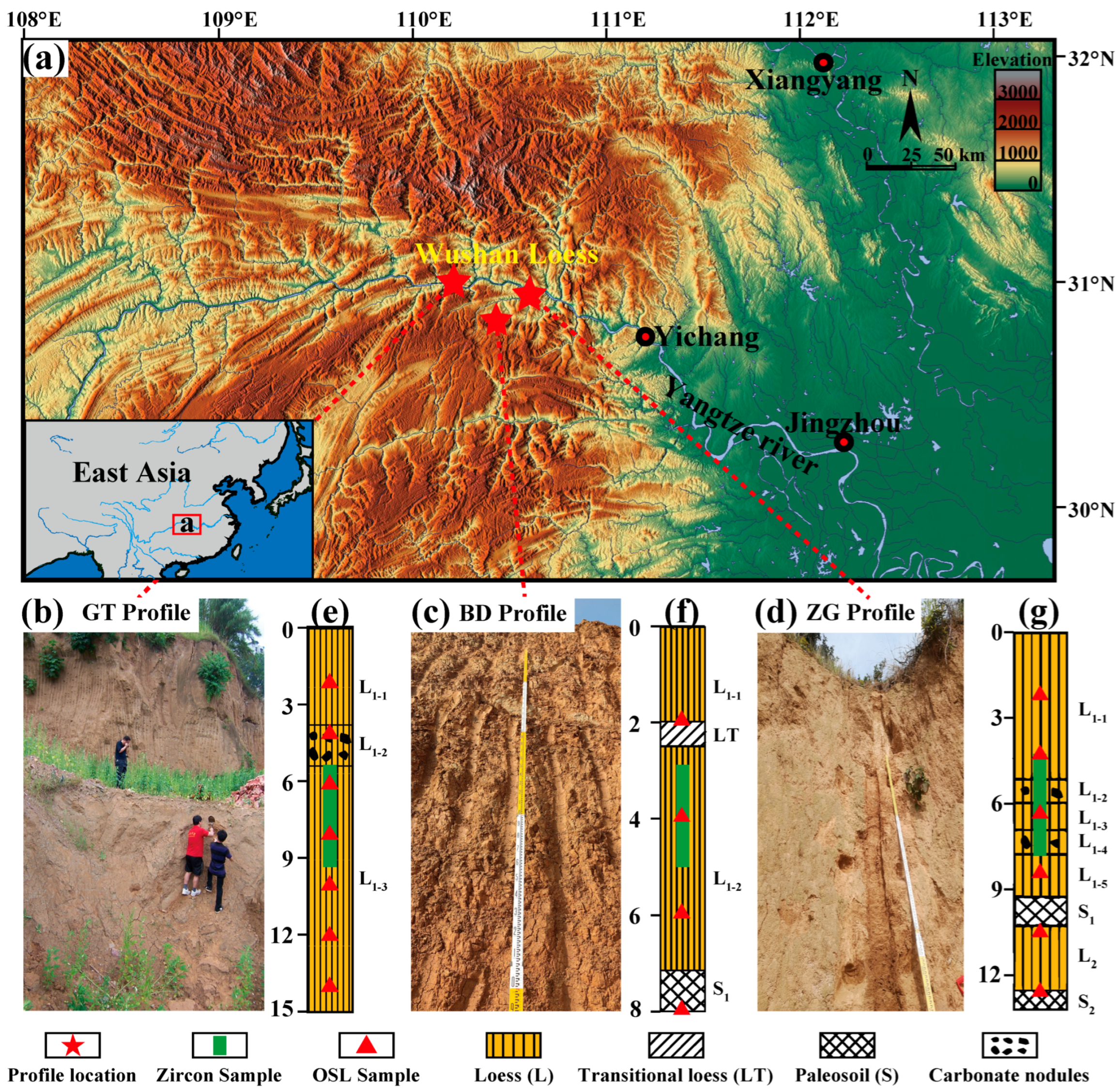
2. Geological Setting
3. Sampling and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Stratigraphy
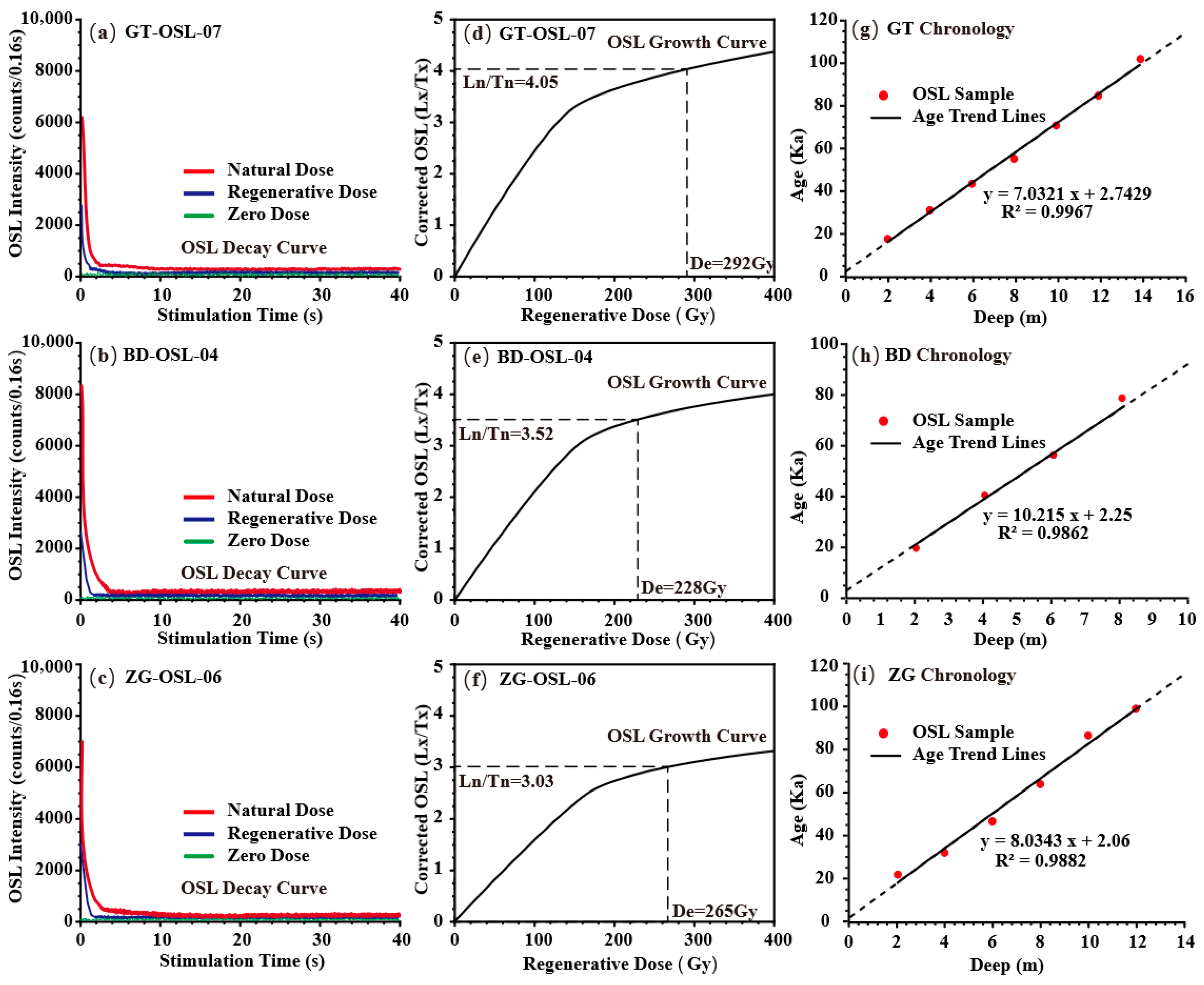
3.2. OSL Chronology
3.3. Grain Size Analysis
3.4. Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology
3.5. Comparative Dataset Compilation
4. Results and Analysis
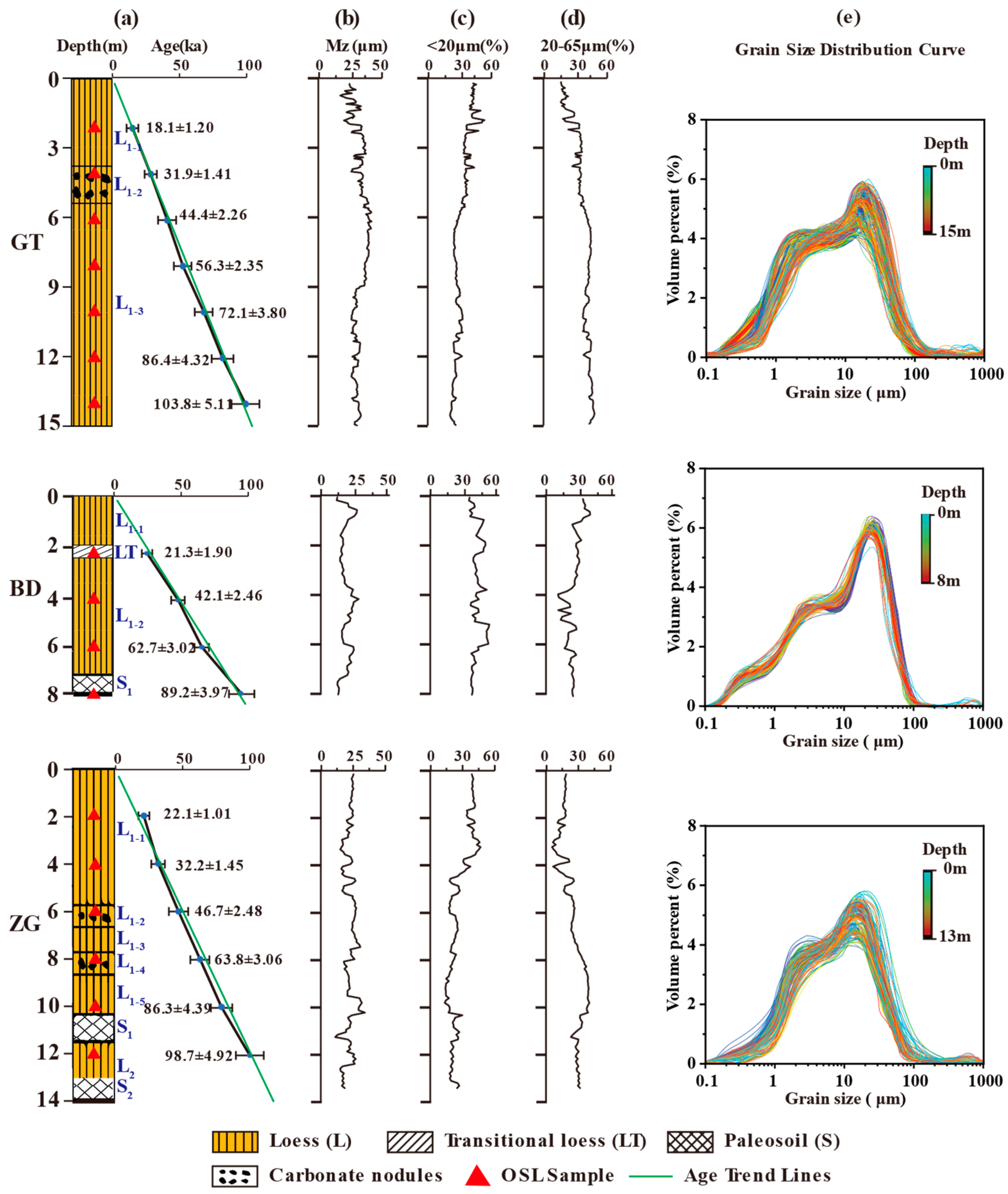
4.1. OSL Chronology of Wushan Loess
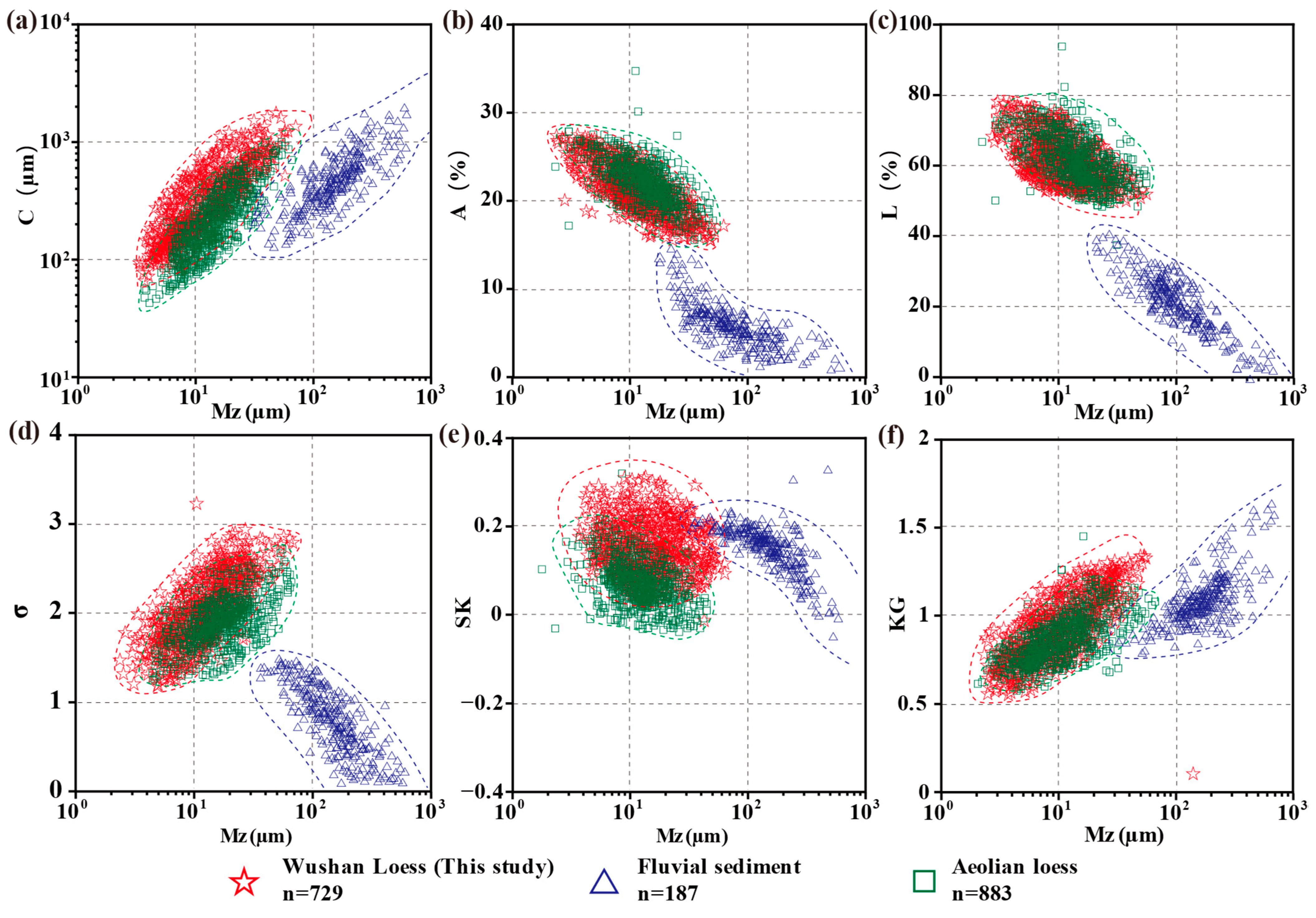
4.2. Grain Size Analysis and Depositional Characteristics
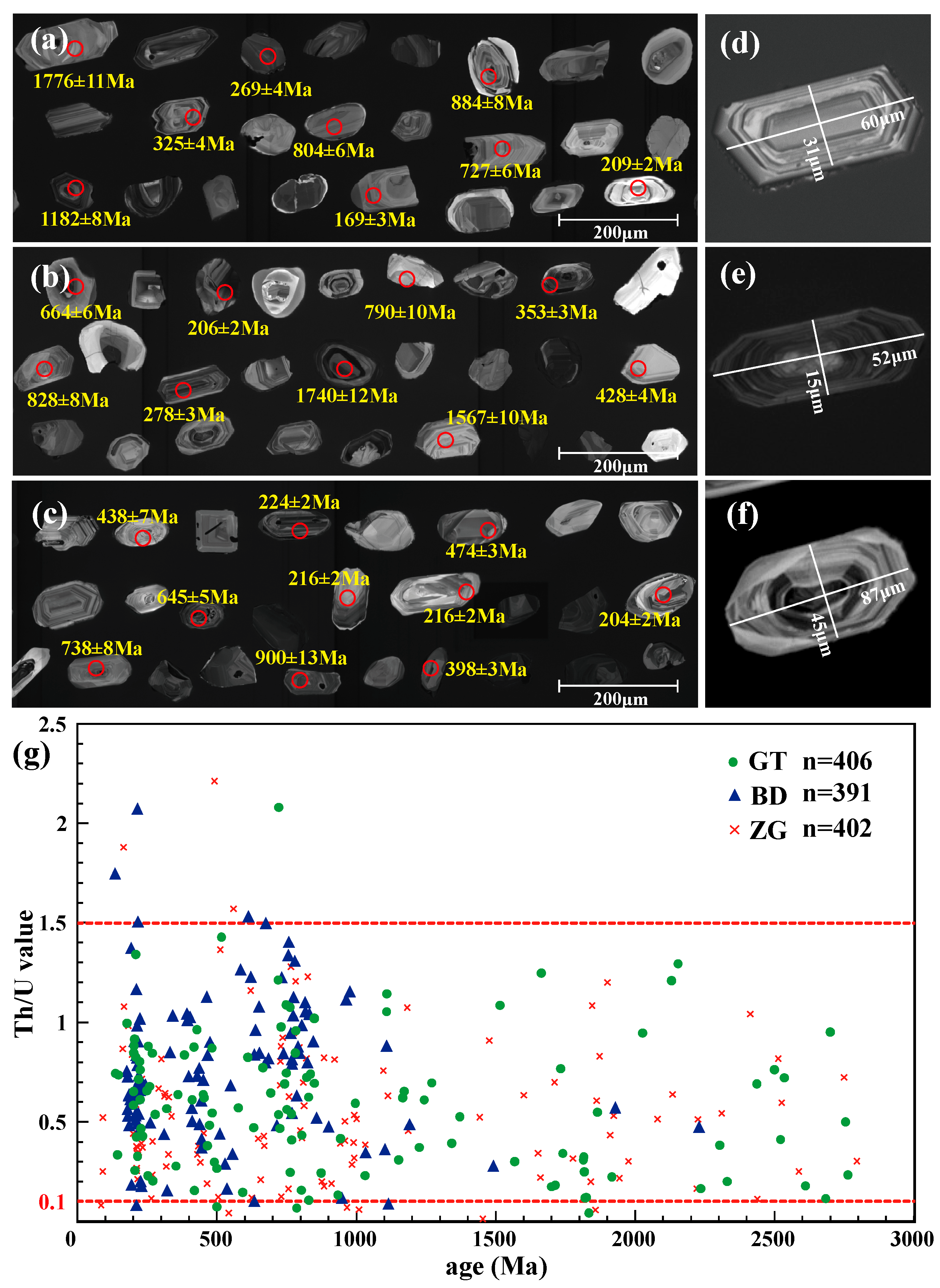
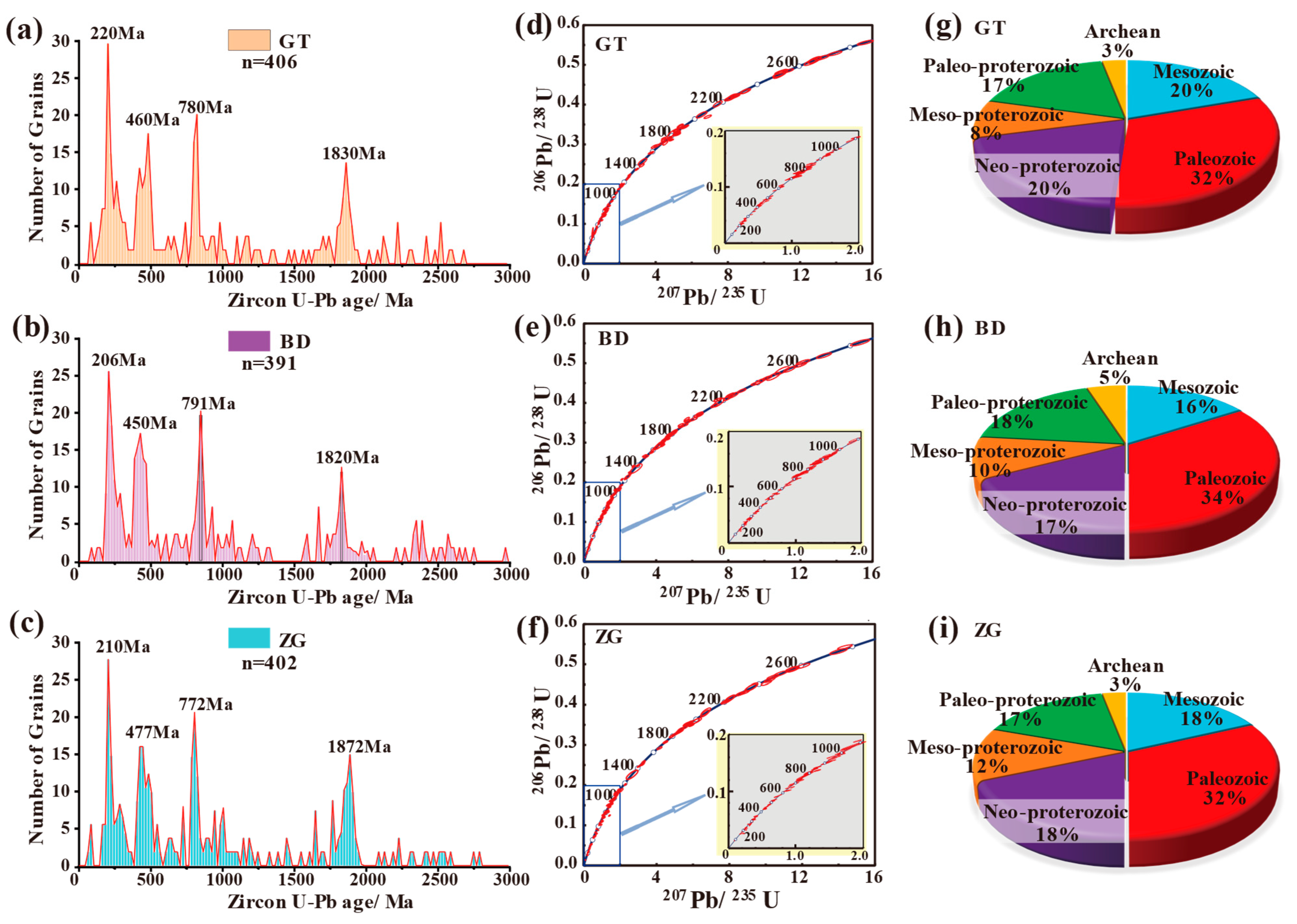
4.3. Detrital Zircon Morphology and U-Pb Ages
5. Discussion
5.1. Grain Size Evidence for Aeolian Genesis of Wushan Loess
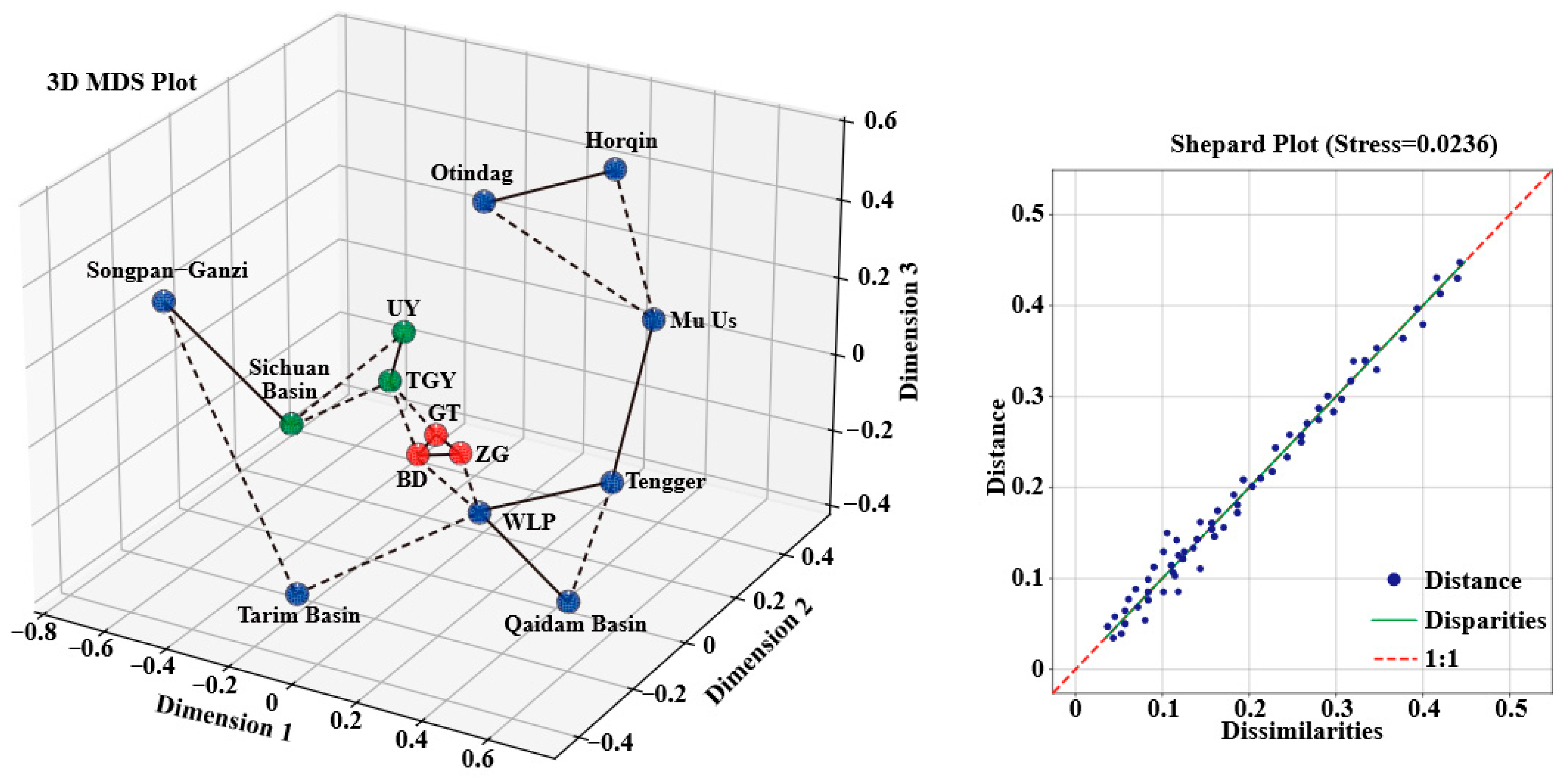
5.2. Mixed Provenance Model Based on U-Pb Age Signatures
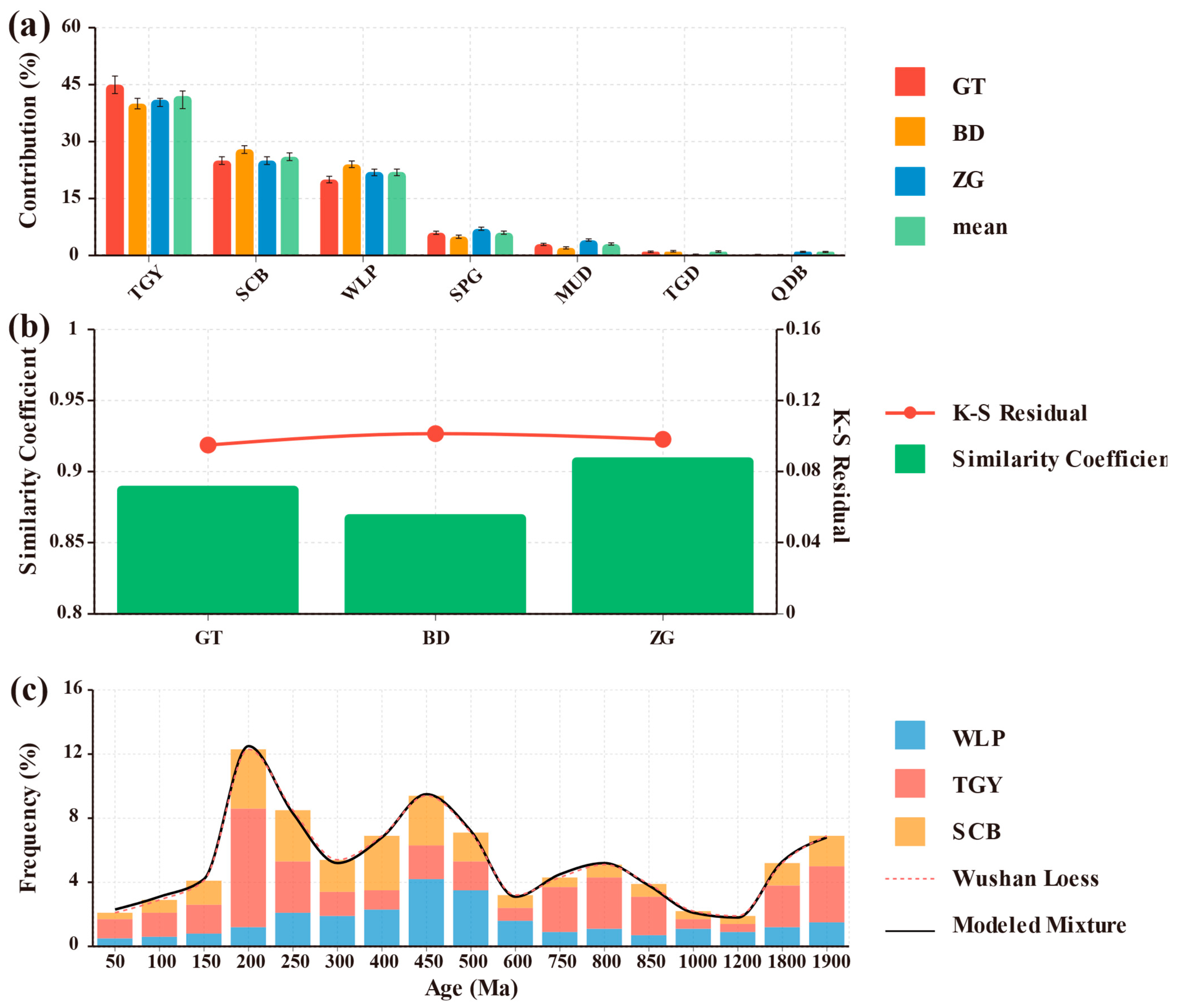
5.3. Quantitative Estimation of Material Sources
5.4. Transport Pathways and Depositional Mechanisms
5.5. Implications for Climate and Atmospheric Circulation Evolution
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OSL | optically stimulated luminescence |
| MIS | Marine Isotope Stage |
| U-Pb | Uranium–Lead |
| Th/U | Thorium/Uranium |
| KDE | Kernel Density Estimation |
| MDS | Multi-Dimensional Scaling |
| NNLS | Non-negative Least Squares |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| LA-ICP-MS | Laser Ablation–Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| CL | Cathodoluminescence |
| TGY | Three Gorges-Yangtze |
| SCB | Sichuan Basin |
| WLP | Western Loess Plateau |
| MUD | Mu Us Desert |
| QB | Qaidam Basin |
| SPG | Songpan-Ganzi |
| TGD | Tengger Desert |
References
- Liu, T.S. Loess and the Environment; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.T.; Ruddiman, W.F.; Hao, Q.Z.; Wu, H.B.; Qiao, Y.S.; Zhu, R.X.; Peng, S.Z.; Wei, J.J.; Yuan, B.Y.; Liu, T.S. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China. Nature 2002, 416, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Ding, Z.; Liu, T.; Rokosh, D.; Rutter, N. 580,000-year environmental reconstruction from aeolian deposits at the Mu Us Desert margin, China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1999, 19, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Pullen, A.; Garzione, C.N.; Peng, W.; Wang, Z. Pre-Quaternary decoupling between Asian aridification and high dust accumulation rates. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pye, K.; Zhou, L.P. Late Pleistocene and Holocene aeolian dust deposition in North China and the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1989, 73, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.L.; Yu, Z.W.; Rutter, N.W.; Liu, T.S. Towards an orbital time scale for Chinese loess deposits. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1994, 13, 39–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejdahl, V.; Bøtter-Jensen, L. Luminescence dating of archaeological materials using a new technique based on single aliquot measurements. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1994, 13, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.R.; Hutton, J.T. Cosmic ray contributions to dose rates for luminescence and ESR dating: Large depths and long-term time variations. Radiat. Meas. 1994, 23, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.C.; An, Z. Correlation between climate events in the North Atlantic and China during the last glaciation. Nature 1995, 375, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, T.; Carter, A.; Watson, T.P.; Vermeesch, P.; Andò, S.; Bird, A.F.; Lu, H.; Garzanti, E.; Cottam, M.A.; Sevastjanova, I. Genetic linkage between the Yellow River, the Mu Us desert and the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 78, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Allé, P.; Corfu, F.; Griffin, W.L.; Meier, M.; Oberli, F.; Von Quadt, A.; Roddick, J.C.; Spiegel, W. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses. Geostand. Newsl. 1995, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Porter, S.C.; An, Z.; Kumai, H.; Yoshikawa, S. Grain size of quartz as an indicator of winter monsoon strength on the Loess Plateau of central China during the last 130,000 yr. Quat. Res. 1995, 43, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltje, G.J. End-member modeling of compositional data: Numerical-statistical algorithms for solving the explicit mixing problem. Math. Geol. 1997, 29, 503–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.J. An Introduction to Optical Dating; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rea, D.K.; Snoeckx, H.; Joseph, L.H. Late Cenozoic eolian deposition in the North Pacific: Asian drying, Tibetan uplift, and cooling of the northern hemisphere. Paleoceanography 1998, 13, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, R.F.; Roberts, R.G.; Laslett, G.M.; Yoshida, H.; Olley, J.M. Optical dating of single and multiple grains of quartz from Jinmium rock shelter, northern Australia: Part I, experimental design and statistical models. Archaeometry 1999, 41, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.R.; Jouzel, J.; Raynaud, D.; Barkov, N.I.; Barnola, J.M.; Basile, I.; Bender, M.; Chappellaz, J.; Davis, M.; Delaygue, G. Climate and atmospheric history of the past 420,000 years from the Vostok ice core, Antarctica. Nature 1999, 399, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.S.; Wintle, A.G. Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol. Radiat. Meas. 2000, 32, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Kutzbach, J.E.; Prell, W.L.; Porter, S.C. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature 2001, 411, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.L.; Sun, J.M.; Yang, S.L.; Liu, T.S. Geochemistry of the Pliocene red clay formation in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for its origin, source provenance and paleoclimate change. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.C. Chinese loess record of monsoon climate during the last glacial-interglacial cycle. Earth Sci. Rev. 2001, 54, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; An, Z.S.; Wu, J.Y.; Shen, C.C.; Dorale, J.A. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China. Science 2001, 294, 2345–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem. Geol. 2002, 192, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.L.; Derbyshire, E.; Yang, S.L.; Yu, Z.W.; Xiong, S.F.; Liu, T.S. Stacked 2.6-Ma grain size record from the Chinese loess based on five sections and correlation with the deep-sea δ18O record. Paleoceanography 2002, 17, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Bloemendal, J.; Rea, D.K.; Vandenberghe, J.; Jiang, F.; An, Z.; Su, R. Grain-size distribution function of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments, and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components. Sediment. Geol. 2002, 152, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bøtter-Jensen, L.; Andersen, C.E.; Duller, G.A.T.; Murray, A.S. Developments in radiation, stimulation and observation facilities in luminescence measurements. Radiat. Meas. 2003, 37, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfu, F.; Hanchar, J.M.; Hoskin, P.W.O.; Kinny, P. Atlas of zircon textures. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 469–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duller, G.A.T. Distinguishing quartz and feldspar in single grain luminescence measurements. Radiat. Meas. 2003, 37, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.S.; Wintle, A.G. The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol: Potential for improvements in reliability. Radiat. Meas. 2003, 37, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Gong, S.L.; Zhao, T.L.; Arimoto, R.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, Z.J. Sources of Asian dust and role of climate change versus desertification in Asian dust emission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.E.; Pearson, N.J.; Griffin, W.L.; Belousova, E.A. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2004, 211, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Duce, R.A. Periodicities of palaeoclimatic variations recorded by loess-paleosol sequences in China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2004, 23, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P. How many grains are needed for a provenance study? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 224, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T. Detrital zircons as tracers of sedimentary provenance: Limiting conditions from statistics and numerical simulation. Chem. Geol. 2005, 216, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, I.; Groenen, P.J.F. Modern Multidimensional Scaling: Theory and Applications, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.L.; Derbyshire, E.; Yang, S.L.; Sun, J.M.; Liu, T.S. Stepwise expansion of desert environment across northern China in the past 3.5 Ma and implications for monsoon evolution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 237, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Yan, M.; Van der Voo, R.; Rea, D.K.; Song, C.; Parés, J.M.; Gao, J.; Nie, J.; Dai, S. Late Cenozoic deformation and uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from high-resolution magnetostratigraphy of the Guide Basin, Qinghai Province, China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2005, 117, 1208–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, S.H. Internal dose rate to K-feldspar grains from radioactive elements other than potassium. Radiat. Meas. 2005, 40, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Hao, Q.; Yin, Q.; Yuan, B.; Liu, T. Grain-size features of a Miocene loess-soil sequence at Qinan: Implications on its origin. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, T. The age of the Taklimakan Desert. Science 2006, 312, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Clemens, S.C.; Liu, Q.; Ji, J.; Tada, R. East Asian monsoon variability over the last seven glacial cycles recorded by a loess sequence from the northwestern Chinese Loess Plateau. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7, Q12Q02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Clemens, S.C.; An, Z.; Yu, Z. Astronomical timescale and palaeoclimatic implication of stacked 3.6-Myr monsoon records from the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2006, 25, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintle, A.G.; Murray, A.S. A review of quartz optically stimulated luminescence characteristics and their relevance in single-aliquot regeneration dating protocols. Radiat. Meas. 2006, 41, 369–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.M. Assessing the effectiveness of the double-SAR protocol in isolating a luminescence signal dominated by quartz. Radiat. Meas. 2007, 42, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Günther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.; Chen, H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, N.J.; Densmore, A.L.; Seward, D.; Fowler, A.; Wipf, M.; Ellis, M.A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Extraordinary denudation in the Sichuan Basin: Insights from low-temperature thermochronology adjacent to the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113, B04409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, J.; Košler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Horstwood, M.S.A.; Morris, G.A.; Nasdala, L.; Norberg, N. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, K.J.; Murray, A.S.; Jain, M.; Bøtter-Jensen, L. Laboratory fading rates of various luminescence signals from feldspar-rich sediment extracts. Radiat. Meas. 2008, 43, 1474–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ding, Z. Advance-retreat history of the East-Asian summer monsoon rainfall belt over northern China during the last two glacial-interglacial cycles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 274, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Yin, J.; Lu, Y. Late Quaternary environmental changes and organic carbon density in the Hunshandake Sandy Land, eastern Inner Mongolia, China. Glob. Planet. Change 2008, 61, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, L.; Hu, S.; Cheng, X. Magnetic Fabric of Aqueous and Aeolian Sediments in the Middle Yangtze River. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 82, 857–863. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.T.; Berger, A.; Yin, Q.Z.; Qin, L. Strong asymmetry of hemispheric climates during MIS-13 inferred from correlating China loess and Antarctica ice records. Clim. Past 2009, 5, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Guo, Z.; Kahmann, A.J.; Oldknow, C. Geochemical characteristics of the Miocene eolian deposits in China: Their provenance and climate implications. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2009, 10, Q04004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; He, F.; Brady, E.C.; Tomas, R.; Clark, P.U.; Carlson, A.E.; Lynch-Stieglitz, J.; Curry, W.; Brook, E. Transient simulation of last deglaciation with a new mechanism for Bølling-Allerød warming. Science 2009, 325, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K.; Tsoar, H. Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Smalley, I.; O’Hara-Dhand, K.; Wint, J.; Machalett, B.; Jary, Z.; Jefferson, I. Rivers and loess: The significance of long river transportation in the complex event-sequence approach to loess deposit formation. Quat. Int. 2009, 198, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, L.; Kang, C.; Hu, S.; Huo, J.; Yan, L.; Cheng, X. Magnetic Fabric Characteristics of the Sandy Sediments in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River and Their Indicative Significance of Palaeowind Field. Acta Geophys. Sin. 2009, 52, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Clemens, S.C.; Prell, W.L.; Sun, Y. Orbital-scale timing and mechanisms driving Late Pleistocene Indo-Asian summer monsoons: Reinterpreting cave speleothem δ18O. Paleoceanography 2010, 25, PA4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; An, Z.; Clemens, S.C.; Bloemendal, J.; Vandenberghe, J. Seven million years of wind and precipitation variability on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 297, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P.; Fenton, C.R.; Kober, F.; Wiggs, G.F.S.; Bristow, C.S.; Xu, S. Sand residence times of one million years in the Namib Sand Sea from cosmogenic nuclides. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Fan, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y. Petrogenesis of late Triassic post-collisional basaltic rocks of the Lancangjiang tectonic zone, southwest China, and tectonic implications for the evolution of the eastern Paleotethys. Lithos 2010, 120, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Ding, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Lu, H. A ~6 Ma chemical weathering history, the grain size dependence of chemical weathering intensity, and its implications for provenance change of the Chinese loess–red clay deposit. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, K.; Tada, R.; Tani, A.; Sun, Y.; Isozaki, Y.; Toyoda, S.; Hasegawa, H. Millennial-scale oscillations of the westerly jet path during the last glacial period. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Wang, L.; Oldfield, F.; Peng, S.; Qin, L.; Song, Y.; Xu, B.; Qiao, Y.; Bloemendal, J.; Guo, Z. Delayed build-up of Arctic ice sheets during 400,000-year minima in insolation variability. Nature 2012, 490, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Kirby, E.; Furlong, K.P.; van Soest, M.; Xu, G.; Shi, X.; Kamp, P.J.J.; Hodges, K.V. Two-phase growth of high topography in eastern Tibet during the Cenozoic. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, H.; Vandenberghe, J.; Zheng, S.; van Balen, R. Late Miocene uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau inferred from basin filling, planation and fluvial terraces in the Huang Shui catchment. Glob. Planet. Change 2012, 88, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K. The nature, origin and accumulation of loess. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1995, 14, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, J. Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment: A powerful proxy for process identification. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 121, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P. Multi-sample comparison of detrital age distributions. Chem. Geol. 2013, 341, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrels, G. Detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology applied to tectonics. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 42, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, A.; Stevens, T.; Rittner, M.; Vermeesch, P.; Carter, A.; Andò, S.; Garzanti, E.; Lu, H.; Nie, J.; Zeng, L. Quaternary dust source variation across the Chinese Loess Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 435, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Stevens, T.; Rittner, M.; Stockli, D.; Garzanti, E.; Limonta, M.; Bird, A.; Andò, S.; Vermeesch, P.; Saylor, J. Loess Plateau storage of Northeastern Tibetan Plateau-derived Yellow River sediment. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P.; Garzanti, E. Making geological sense of ‘Big Data’ in sedimentary provenance analysis. Chem. Geol. 2015, 409, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malusà, M.G.; Resentini, A.; Garzanti, E. Hydraulic sorting and mineral fertility bias in detrital geochronology. Gondwana Res. 2016, 31, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C. Provenance and tectonic-paleogeographic evolution: Constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb ages of Late Triassic-Early Jurassic deposits in the northern Sichuan basin, central China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 127, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P.; Resentini, A.; Garzanti, E. An R package for statistical provenance analysis. Sediment. Geol. 2016, 336, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Fitzsimmons, K.E.; Chang, H.; Orozbaev, R.; Li, X. Eolian dust dispersal patterns since the last glacial period in eastern Central Asia: Insights from a loess-paleosol sequence in the Ili Basin. Clim. Past 2018, 14, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chang, H.; Qin, X.; Burr, G.S.; Liu, W. Aridification in the Asian Interior Recorded by Mineral Assemblages in Tarim Basin since the Late Miocene and Its Link to Global Cooling. Minerals 2022, 12, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Jolivet, M.; Cheng, F. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Central Qilian Shan (Northwest China) Constrained by Fission-Track Ages of Detrital Grains from the Huangshui River. Minerals 2023, 13, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liu-Zeng, J.; Wu, L.; Cleber, S.J.; Liu, D.; Dai, J.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Meso–Cenozoic Exhumation in the South Qinling Shan (Central China) Recorded by Detrital Apatite Fission-Track Dating of Modern River Sediments. Minerals 2023, 13, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Hu, C.; Wu, R.; Qin, L.; Xiang, R.; An, Z.; Lu, H. How Was the Late Neogene Red Clay Formed in the Ordos Plateau (Northwest China)? Minerals 2024, 14, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Guan, K.; Lin, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. The Geochemical Characteristics of Zircon and K-Feldspar Grains from the Lower Yellow and Yangtze Rivers: Implications for Provenance Tracing Studies in the Western Pacific Ocean. Minerals 2025, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, J.S.; Kramers, J.D. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two-stage model. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1975, 26, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, H.; Pye, K. Dust transport and the question of desert loess formation. Sedimentology 1987, 34, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, E.; Billard, A.; Van Vliet-Lanoe, B.; Lautridou, J.P.; Cremaschi, M. Loess and palaeoenvironment: Some results of a European joint programme of research. J. Quat. Sci. 1988, 3, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample ID | Grain Size (μm) | Sample Level (m) | U (ppm) | Th (ppm) | K (%) | Water Content (%) | Dose Rate D (Gy/ka) | Equivalent Dose De (Gy) | Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT-OSL-01 | 38–63 | 1.7 | 1.939 | 7.074 | 1.296 | 18.69% | 1.99 ± 0.10 | 35.96 ± 5.03 | 18.1 ± 1.20 |
| GT-OSL-02 | 38–63 | 3.8 | 2.089 | 7.174 | 1.47 | 13.61% | 2.24 ± 0.09 | 71.58 ± 7.16 | 31.9 ± 1.41 |
| GT-OSL-03 | 38–63 | 5.9 | 2.094 | 7.837 | 1.615 | 19.62% | 2.27 ± 0.08 | 100.6 ± 9.05 | 44.4 ± 2.26 |
| GT-OSL-04 | 38–63 | 8.3 | 2.113 | 7.425 | 1.474 | 11.69% | 2.28 ± 0.07 | 128.24 ± 11.54 | 56.3 ± 2.35 |
| GT-OSL-05 | 38–63 | 9.8 | 2.161 | 7.371 | 1.488 | 14.31% | 2.23 ± 0.06 | 160.9 ± 19.31 | 72.1 ± 3.80 |
| GT-OSL-06 | 38–63 | 12.1 | 2.763 | 8.599 | 1.412 | 18.35% | 2.28 ± 0.05 | 196.86 ± 25.59 | 86.4 ± 4.32 |
| GT-OSL-07 | 38–63 | 14.2 | 2.857 | 8.806 | 1.283 | 16.51% | 2.24 ± 0.04 | 237.04 ± 33.19 | 103.8 ± 5.11 |
| BD-OSL-01 | 38–63 | 1.8 | 2.713 | 7.733 | 1.284 | 15.77% | 2.23 ± 0.09 | 47.55 ± 6.18 | 21.3 ± 1.90 |
| BD-OSL-02 | 38–63 | 4.1 | 2.54 | 7.889 | 1.266 | 17.76% | 2.14 ± 0.07 | 89.9 ± 8.99 | 42.1 ± 2.46 |
| BD-OSL-03 | 38–63 | 6.2 | 2.447 | 6.918 | 1.005 | 19.09% | 1.81 ± 0.06 | 113.62 ± 10.23 | 62.7 ± 3.02 |
| BD-OSL-04 | 38–63 | 8.1 | 2.404 | 6.766 | 0.993 | 15.79% | 1.83 ± 0.05 | 162.8 ± 19.54 | 89.2 ± 3.97 |
| ZG-OSL-01 | 38–63 | 1.9 | 2.296 | 7.127 | 1.185 | 15.67% | 2.03 ± 0.08 | 44.84 ± 5.83 | 22.1 ±1.01 |
| ZG-OSL-02 | 38–63 | 3.9 | 3.058 | 8.104 | 1.081 | 17.70% | 2.11 ± 0.08 | 67.89 ± 6.79 | 32.2 ± 1.45 |
| ZG-OSL-03 | 38–63 | 6.1 | 2.756 | 8.517 | 1.782 | 18.87% | 2.59 ± 0.09 | 120.89 ± 10.88 | 46.7 ± 2.48 |
| ZG-OSL-04 | 38–63 | 7.9 | 1.965 | 6.569 | 1.461 | 17.06% | 2.08 ± 0.06 | 132.51 ± 11.93 | 63.8 ± 3.06 |
| ZG-OSL-05 | 38–63 | 10.2 | 1.83 | 7.916 | 1.557 | 14.33% | 2.25 ± 0.06 | 194.34 ± 25.26 | 86.3 ± 4.39 |
| ZG-OSL-06 | 38–63 | 12.3 | 2.238 | 8.113 | 1.179 | 16.07% | 2.02 ± 0.04 | 197.21 ± 27.61 | 98.7 ± 4.92 |
| Profiles | <4 μm (%) | 4–20 μm (%) | 20–63 μm (%) | >63 μm (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT n = 298 | Maximum | 17.82 | 34.95 | 44.73 | 11.50 |
| Minimum | 14.35 | 29.12 | 40.28 | 8.25 | |
| Mean | 16.25 | 32.18 | 41.87 | 9.70 | |
| BD n = 166 | Maximum | 13.67 | 31.84 | 51.89 | 12.60 |
| Minimum | 10.43 | 26.15 | 46.32 | 7.10 | |
| Mean | 12.34 | 29.15 | 48.91 | 9.60 | |
| ZG n = 265 | Maximum | 16.94 | 30.78 | 52.65 | 8.63 |
| Minimum | 13.21 | 25.47 | 47.19 | 5.13 | |
| Mean | 15.43 | 28.27 | 49.68 | 6.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Su, J.; Jia, M. Provenance of Wushan Loess in the Yangtze Three Gorges Region: Insights from Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Late Pleistocene East Asian Monsoon Variations. Minerals 2025, 15, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111180
Hu X, Zhang Y, Li C, Li G, Liu J, Li Y, Su J, Jia M. Provenance of Wushan Loess in the Yangtze Three Gorges Region: Insights from Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Late Pleistocene East Asian Monsoon Variations. Minerals. 2025; 15(11):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111180
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xulong, Yufen Zhang, Chang’an Li, Guoqing Li, Juxiang Liu, Yawei Li, Jianchao Su, and Mingming Jia. 2025. "Provenance of Wushan Loess in the Yangtze Three Gorges Region: Insights from Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Late Pleistocene East Asian Monsoon Variations" Minerals 15, no. 11: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111180
APA StyleHu, X., Zhang, Y., Li, C., Li, G., Liu, J., Li, Y., Su, J., & Jia, M. (2025). Provenance of Wushan Loess in the Yangtze Three Gorges Region: Insights from Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Late Pleistocene East Asian Monsoon Variations. Minerals, 15(11), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111180








