Genesis of Conventional Reservoirs in Braided Fluvial Tight Sandstones: Evidence from the He 1 Member, Upper Paleozoic, Southern Ordos Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Methods
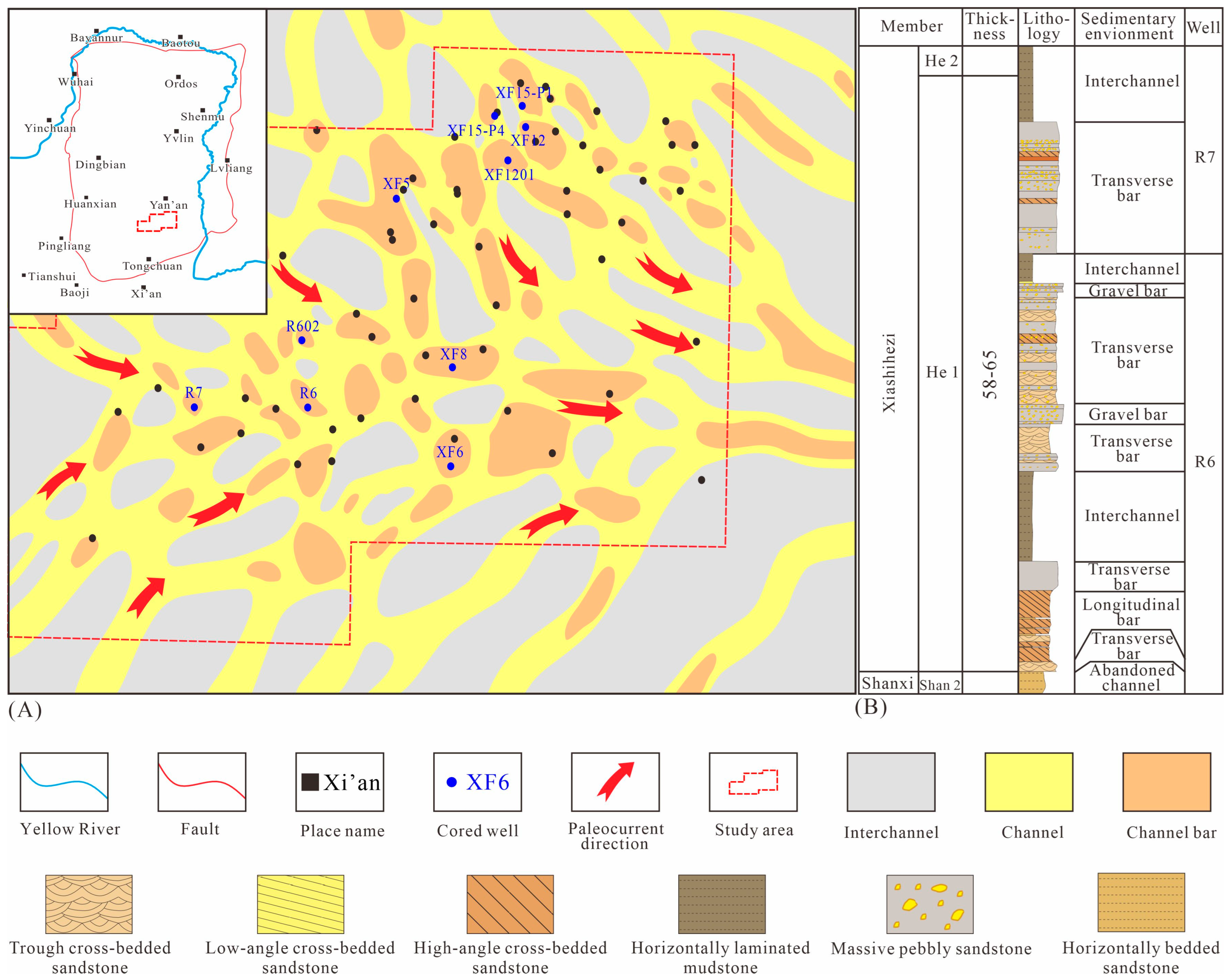
3. Geological Setting
4. Results
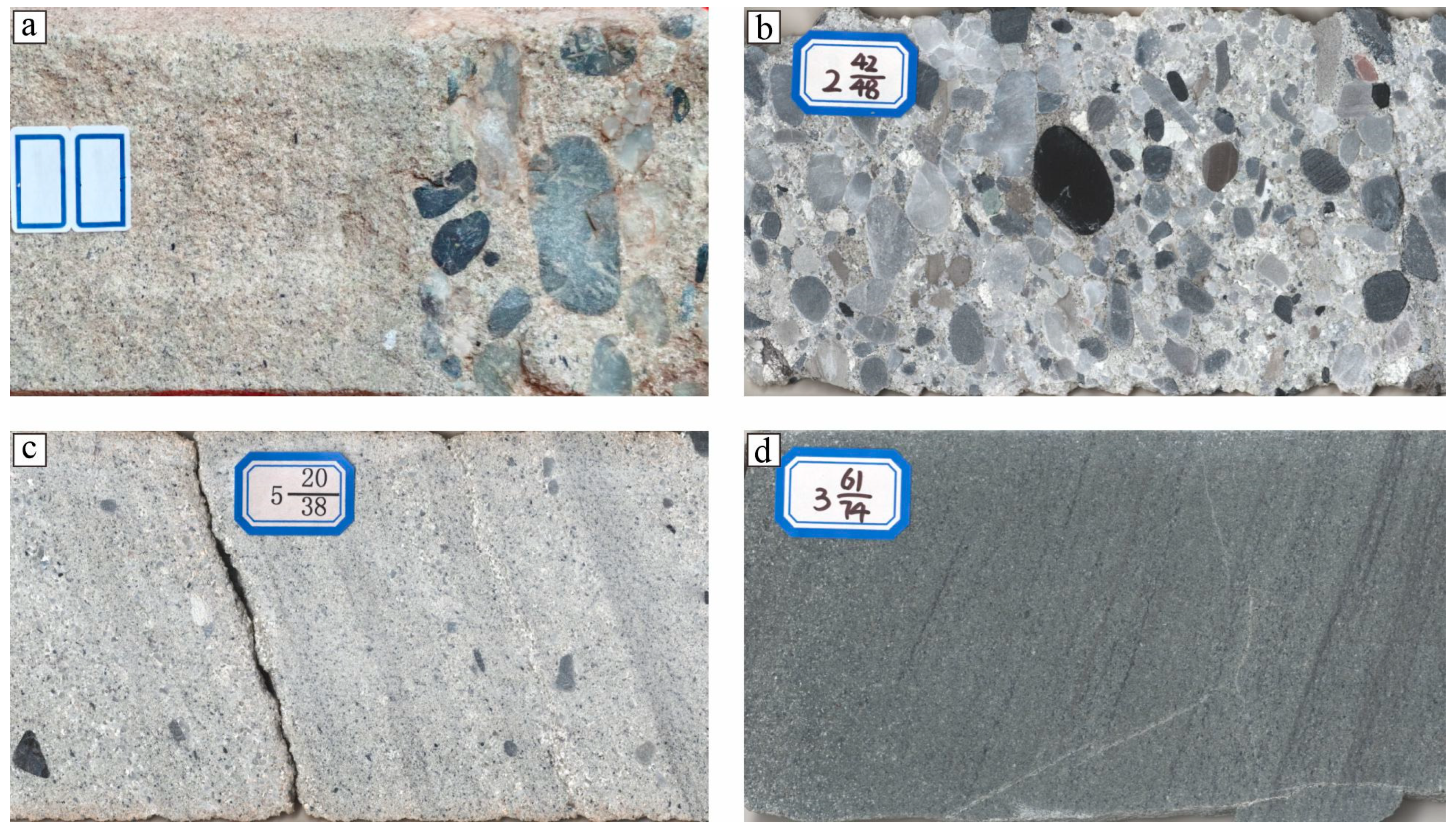
4.1. Sedimentary Microfacies and Characteristics
4.2. Reservoir Quality
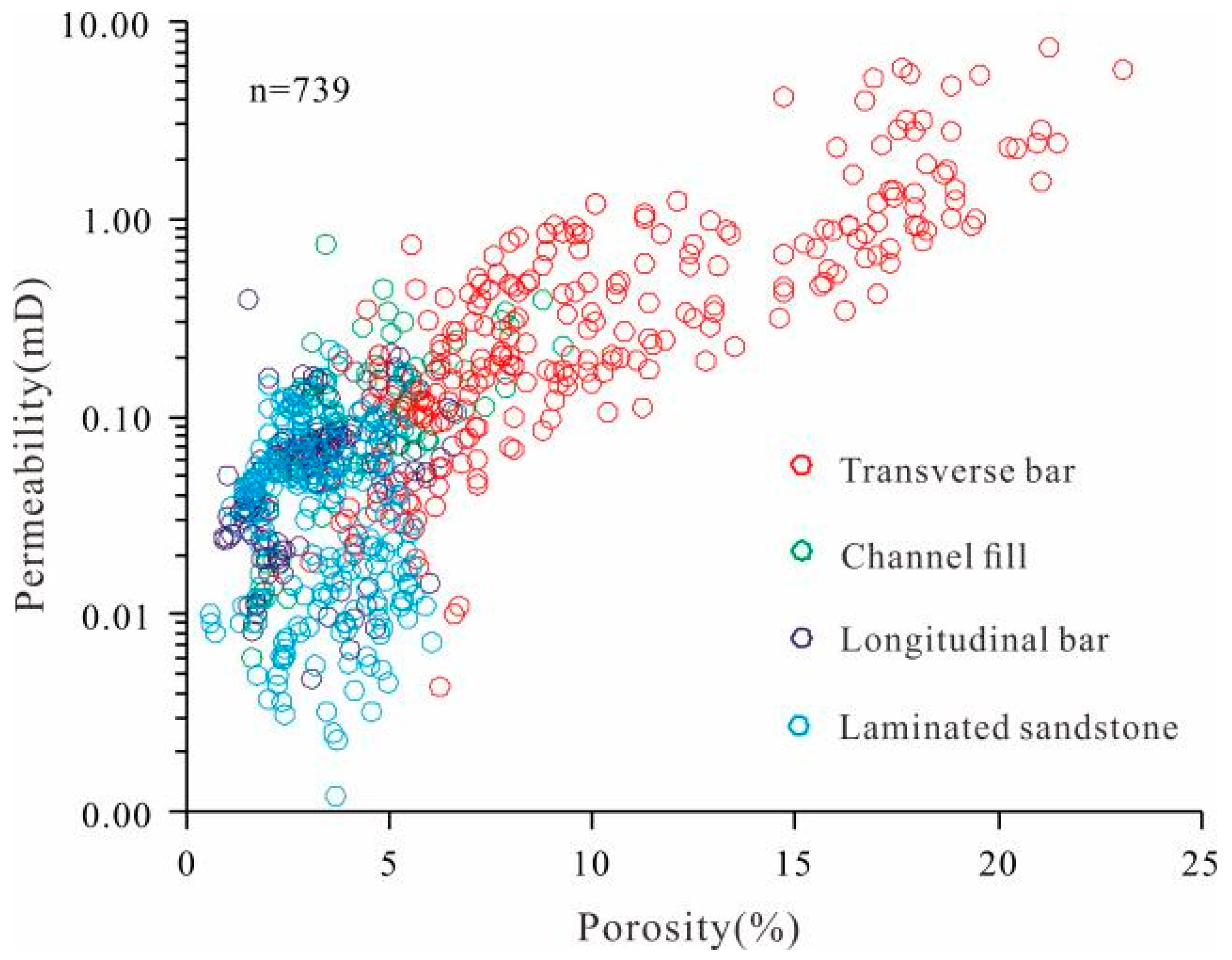
4.2.1. Porosity-Permeability Characteristics
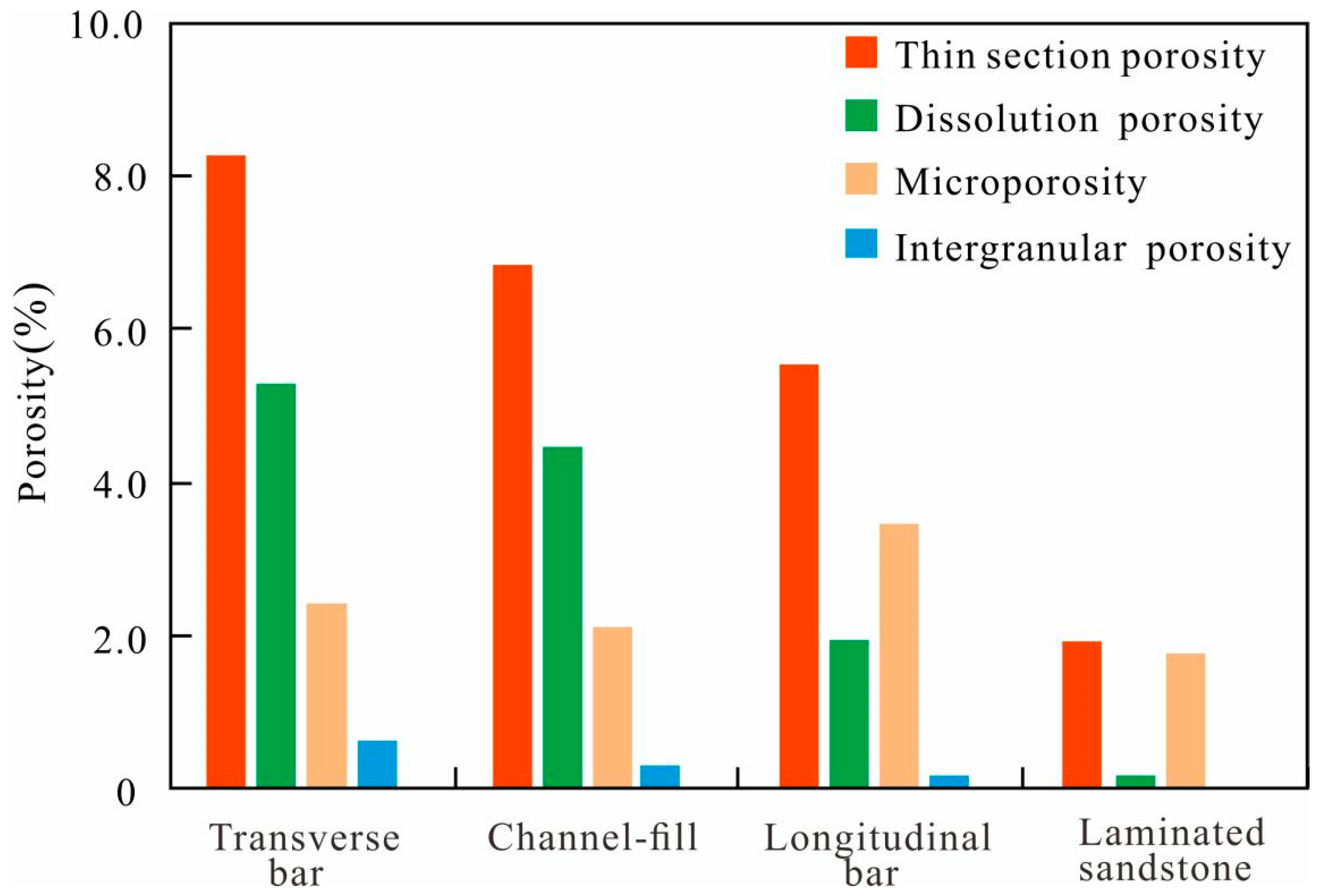
4.2.2. Pore Type
4.2.3. Pore Structure
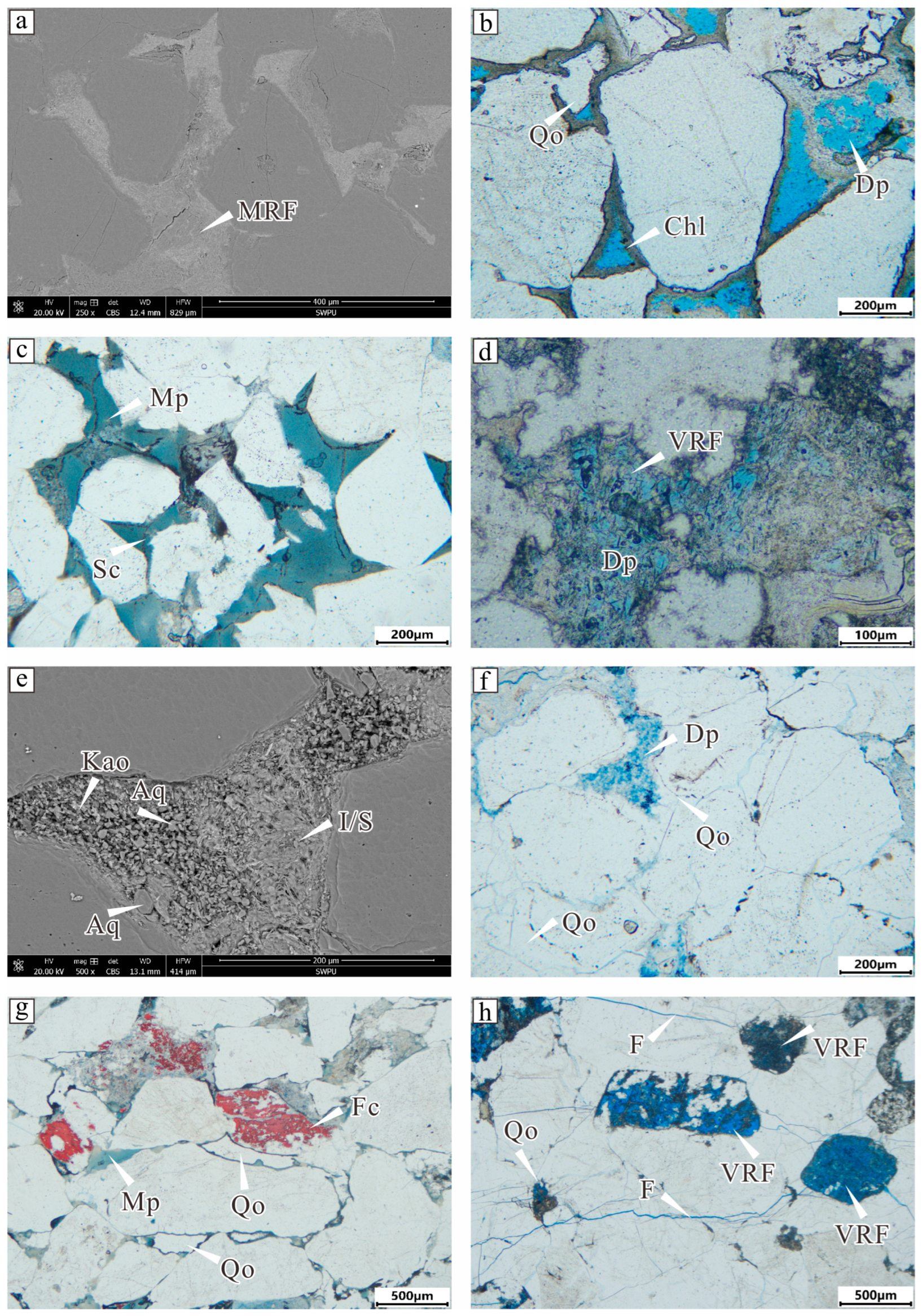
4.3. Petrological Characteristics
4.4. Diagenesis
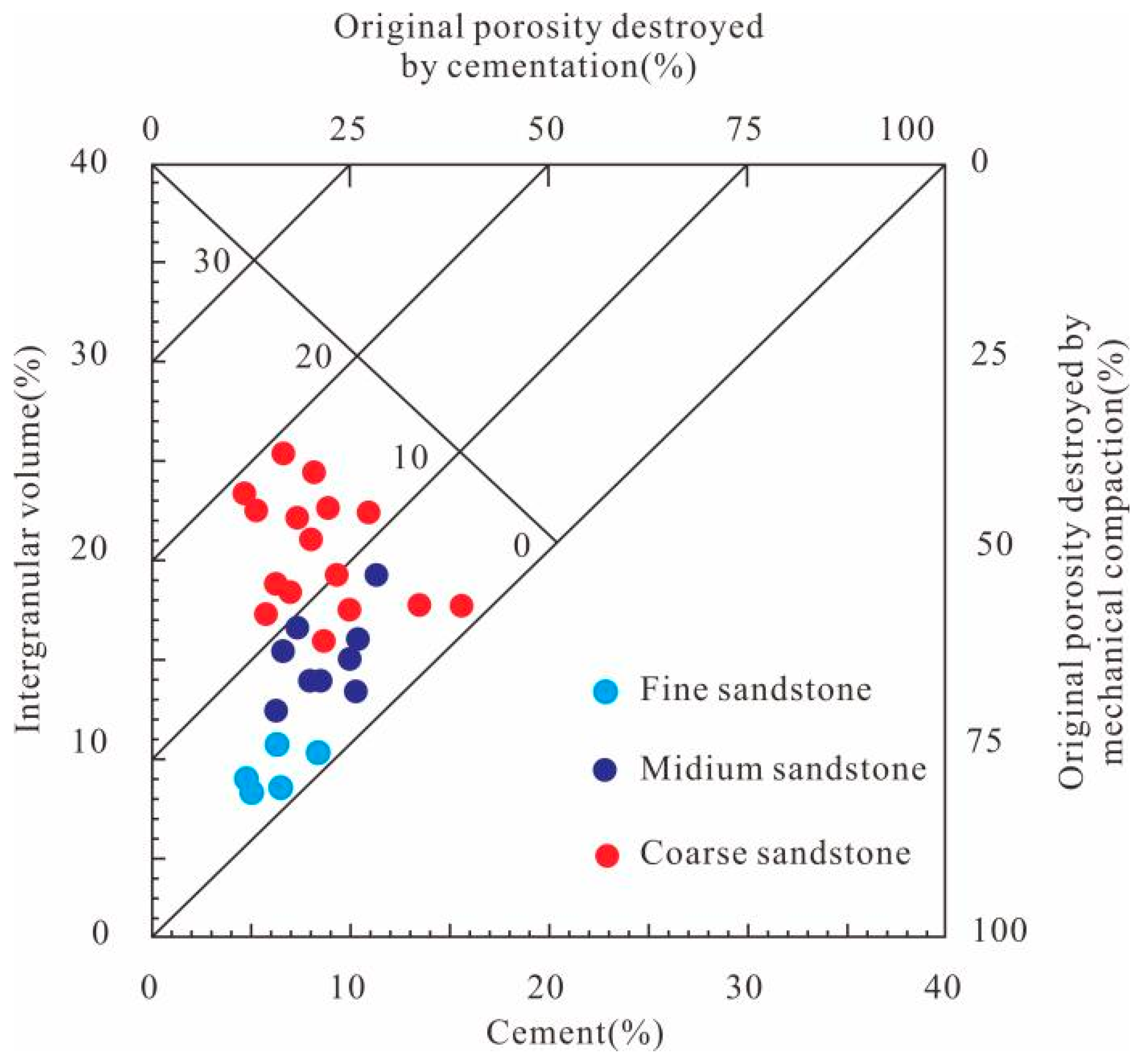
4.4.1. Compaction
4.4.2. Dissolution
4.4.3. Cementation
- (1)
- Chlorite cementation
- (2)
- Silica cementation
4.4.4. Other Diagenetic Alterations
- (1)
- Ferroan calcite replacement and cementation
- (2)
- Fracturing
5. Discussion
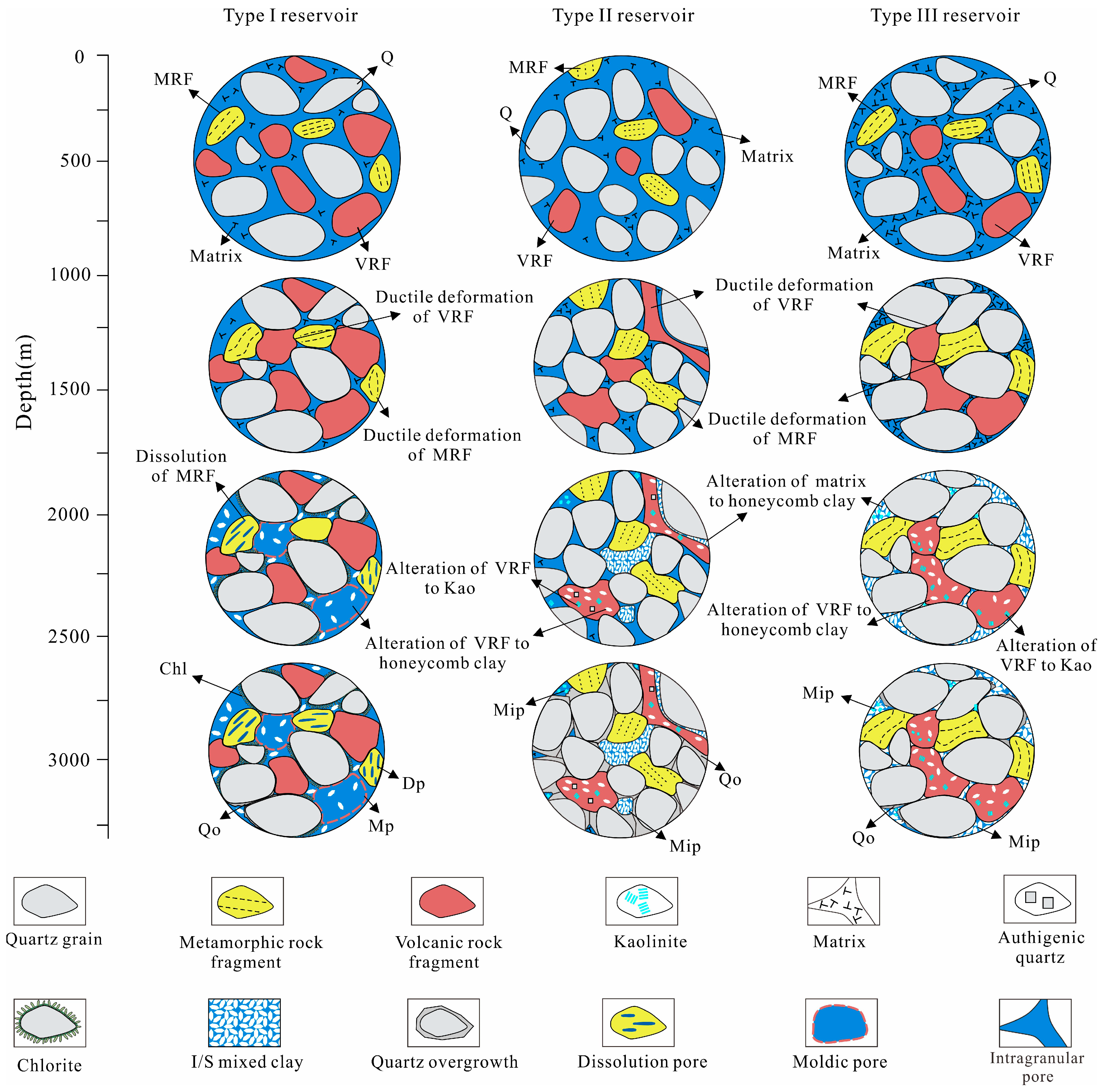
5.1. Reservoir Pore Evolution
5.1.1. Type I Reservoir
5.1.2. Type II Reservoir
5.1.3. Type III Reservoir
5.2. The Relationship Between Volcanic Material and Dissolution
5.2.1. Dissolution Time
5.2.2. Dissolution Material Sources
5.2.3. Differential Dissolution Patterns
5.3. Controls on Quartz Overgrowth
5.3.1. Silica Sources for Quartz Overgrowths
5.3.2. Chlorite Coatings Inhibiting Quartz Overgrowths
5.4. Development Patterns of Conventional Reservoirs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VRF | Volcanic rock fragment |
| MRF | Metamorphic rock fragment |
| I/S | Illite/smectite mixed layers |
| Chl | Chlorite |
| F | Fractures |
| Qo | Quartz overgrowth |
| Aq | Authigenic quartz |
| Fc | Ferroan calcite |
| Sc | Syneresis cracks |
| Kao | Kaolinite |
| Mp | Micropores |
| Q | Quartz grain |
| Dp | Dissolution pore |
| Mo | Moldic pore |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| HPMI | High-pressure mercury injection |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| MICP | Mercury injection capillary pressure |
References
- Fu, J.H.; Fan, L.Y.; Liu, X.S.; Hu, X.Y.; Li, J.H.; Ji, H.K. New Progress, Prospects, and Countermeasures for Natural-Gas Exploration in the Ordos Basin. Pet. Explor. China 2019, 24, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Z.; Guo, B.C.; Zheng, M.; Yang, T. Main Types, Geological Characteristics, and Resource Potential of Tight Sandstone Gas in China. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2012, 23, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.G. Review and Prospect of the Development of China’s Natural Gas Industry. Nat. Gas Ind. 2021, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.L.; Wei, Y.S.; Guo, Z.; Wang, G.T.; Meng, D.; Huang, S.Q. Development Status and Prospects of Tight Sandstone Gas in China. Nat. Gas Ind. 2022, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.T.; Liu, X.P.; Jia, L.; Hu, J.L.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhou, G.X. Accumulation Patterns and Exploration Targets of Tight Sandstone Gas in the Low-Generation-Intensity Northern Tianhuan Depression, Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2021, 32, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Han, X.G.; Zhao, H.T.; Hu, J.L.; Jing, X.Y.; Chen, Y.H. Gas-Water Distribution Characteristics and Genetic Analysis of Tight Gas Reservoirs in the He 8 Member of the Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 34, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.P. Depositional System and Favorable Reservoir of Shanxi Formation-He 8 Member in Ordos Basin; China University of Geosciences (Beijing): Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Fu, J.H.; Liu, X.S.; Meng, P.L. Accumulation Conditions and Exploration-Development of Tight Gas in the Upper Paleozoic of the Ordos Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2012, 39, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.C.; Liu, J.F.; Guo, R.L.; Li, Y.L.; Yin, H.R.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, F.Q. Development Characteristics and Controlling Factors of High-Quality Reservoirs in the He 8 Member, Southeastern Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2025, 36, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, L.; Wu, J. Study on the Diagenetic Evolution of Tight Sandstones in the Shanxi–Lower Shihezi Interval, Southern Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2021, 32, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, I.; Busch, B.; Koehrer, B.; Adelmann, D.; Hilgers, C. Reservoir quality evolution of upper carboniferous (Westphalian) tight gas sandstones, Lower Saxony Basin, NW Germany. J. Pet. Geol. 2019, 42, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.O.; Harris, N.B.; Ahmed, H.; Baig, M.O.A. Controls on Reservoir Diagenesis in the Lower Goru Sandstone Formation, Lower Indus Basin, Pakistan. J. Pet. Geol. 2016, 39, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano-Paz, D.; Gómez-Dacal, A.R.; Varela, A.N.; Comerio, M.; Muñoz-Olivero, T.M.; Bucher, J.; Richiano, S.; Poiré, D.G. Controls on composition and diagenesis of wave- and river-dominated deltas: Impacts on reservoir properties. An example from the La Anita Formation (Argentina). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 138, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.A.; Hussein, W.S.; Radwan, A.E.; Anani, N.; Abioui, M.; Jain, S.; Shehata, A.A. Petrographic and diagenetic study of siliciclastic Jurassic sediments from the northeastern margin of Africa: Implication for reservoir quality. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 200, 108340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørlykke, K. Relationships between depositional environments, burial history and rock properties. Some principal aspects of diagenetic process in sedimentary basins. Sediment. Geol. 2014, 301, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Li, M.; Pang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, X.; Dai, Q.; Yang, L.; et al. Review of diagenetic facies in tight sandstones: Diagenesis, diagenetic minerals, and prediction via well logs. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.A.; Chunmei, D.; Lin, C.; Gluyas, J.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Munawar, M.J.; Ma, C. Sequence stratigraphy, sedimentary facies and reservoir quality of Es4s, southern slope of Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 448–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Sheng, Y.; Critelli, S.; Civitelli, M.; Mughal, M.S.; Basharat, U. Depositional and diagenetic controls on reservoir properties of the lower Cambrian Khewra Sandstone, eastern salt range, Sub-Himalaya, Pakistan. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 161, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Song, R.; Gluyas, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q. Diagenesis and reservoir quality of carbonates rocks and mixed siliciclastic as response of the Late Carboniferous glacio-eustatic fluctuation: A case study of Xiaohaizi Formation in western Tarim Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 177, 1024–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.; Milad, B.; Elmore, R.D.; Pranter, M.J.; Slatt, R. Diagenetic controls on reservoir quality of a mixed carbonate-siliciclastic system: Sycamore Formation, Sho-Vel-Tum Field, Oklahoma, USA. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 134, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwadebi, A.G.; Taylor, K.G.; Dowey, P.J. Diagenetic controls on the reservoir quality of the tight gas Collyhurst sandstone formation, lower Permian, east Irish Sea basin, United Kingdom. Sediment. Geol. 2018, 371, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quandt, D.; Busch, B.; Hilgers, C. Evolution of Upper Carboniferous tight sandstone reservoirs in the Ruhr and Lower Saxony basins (NW Germany) of the Central European Variscan foreland. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 163, 106774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigi, M.; Jafarian, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Wanas, H.A.; Mattern, F.; Tabatabaei, A. Facies analysis, diagenesis and sequence stratigraphy of the carbonate-evaporite succession of the Upper Jurassic Surmeh Formation: Impacts on reservoir quality (Salman Oil Field, Persian Gulf, Iran). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 129, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assal, E.M.; Farouk, S.; Sarhan, M.A. Sedimentary facies controls on reservoir quality of the Abu Madi Formation, offshore Nile Delta Basin, Egypt. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2023, 9, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.M.; Usman, M.B.; Amao, A.O.; Salisu, A.M.; Al-Ramadan, K.; Abubakar, U.; Mukkafa, S.; Kwami, I.A.; Chiroma, L.U.; Al-Hashem, M.; et al. Linking provenance and diagenesis to reservoir quality evolution of sandstones: The Paleocene-Eocene Kerri-Kerri Formation, northeastern Nigeria. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2025, 172, 107227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunuwadje, S.E.; Macdonald, D.; Bowden, S. Diagenetic and Reservoir Quality Variation of Miocene Sandstone Reservoir Analogues from Three Basins of Southern California, USA. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 31, 930–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghani, M.M.A.; Zairi, M.; Radwan, A.E. Facies analysis, diagenesis, and petrophysical controls on the reservoir quality of the low porosity fluvial sandstone of the Nubian formation, east Sirt Basin, Libya: Insights into the role of fractures in fluid migration, fluid flow, and enhancing the permeability of low porous reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 147, 105986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.L.; Lan, C.L.; Men, C.Q. New braided river model in Sulige Gas Field of Ordos Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2005, 26, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.G.; Zheng, R.C.; Gao, H.C.; Dai, Z.C.; Li, G.J. Sedimentary Facies of the 8th Member of Lower Shihezi Formation in Su6 Area, Sulige Gas Field. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2007, 25, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.P.; Zhao, Z.J.; Li, F.P.; Chen, Z.H.; Shi, L.H.; Liu, L.F. Demenstration and Analysis of Braided River Deposition in the Lower He8 Member in Western Sulige Gas Field. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2015, 12, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Zhang, C.W.; Li, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.F.; Liu, P.; Lu, J.C. Tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the Sulige Gas Field: Development understandings and stable-production proposals. Nat. Gas Ind. 2021, 41, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tang, D.H.; Li, B.T. Sedimentary and reservoir characteristics of Qixia Formation, Qijiang area, southeastern Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Technol. Econ. 2023, 17, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, L.J.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.C. High resolution sequence stratigraphy analysis: Construction of chronostratigraphic sequence framework on facies and reservoir scale. Geoscience 2002, 16, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.X.; Lou, M. Fluvial reservoir characterization and vertical heterogeneity analysis: Taking Liulang Formation of C Oilfield in Xihu Depression as example. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2021, 45, 51–62, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Li, S.L. The Development and Hotspot Problems of Clastic Petroleum Reservoir Sedimentology. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2009, 27, 880–895. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.F.; Bao, H.P.; Kai, B.Z.; Wei, L.B.; Xv, Y.H.; Ma, J.H.; Cheng, X. Critical tectonic modification periods and its geologic features of Ordos Basin and adjacent area. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; Liu, H.J.; Quan, B.; Wang, Z.C.; Qian, K. Late Paleozoic Sedimentary System and Paleogeographic Evolution of Ordos Area. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 1998, 16, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Andrews, P.B.; Lewis, D.W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand. New Zealand J. Geol. Geophys. 1970, 13, 937–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.E.; Jones, S.J. Sedimentary Petrology, 4th ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ding, X.Q.; Hersi, O.S.; Han, M.M.; Zhu, Y. Sedimentary facies and reservoir characteristics of the Western Sulige field Permian He 8 tight sandstones, Ordos Basin, China. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 7818–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.Q.; Hersi, O.S.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.N.; Miao, C.S. Diagenesis of volcanic-rich tight sandstones and conglomerates: A case study from Cretaceous Yingcheng Formation, Changling Sag, Songliao Basin, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.J.; Ma, Q.; Gao, S.L.; Mei, Z.C.; Miao, J.Y. On Provenance of the Permian in the Southeastern Ordos Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2011, 85, 979–986. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.S.; Zhao, W.B.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.L.; Tian, J.C.; Chen, R.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.Y.; Xiao, Y.X. Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology Characteristics of Permian Sandstone and Its Constraints on the Tectonic Evolution of the Southern Ordos Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2023, 41, 1396–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.H.; Li, W.H.; Liu, H.W.; Li, K.Y.; Pang, J.G.; Guo, Y.Q.; Yuan, Z. Provenance analysis of sandstone of the Upper Carboniferous to Middle Permian in Ordos Basin. J. Palaeogeogr. 2009, 11, 629–640. [Google Scholar]
- Javanbakht, M.; Wanas, H.A.; Jafarian, A.; Shahsavan, N.; Sahraeyan, M. Carbonate diagenesis in the Barremian-Aptian Tirgan Formation (Kopet-Dagh Basin, NE Iran): Petrographic, geochemical and reservoir quality constraints. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 144, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørlykke, K.; Jahren, J. Open or closed geochemical systems during diagenesis in sedimentary basins: Constraints on mass transfer during diagenesis and the prediction of porosity in sandstone and carbonate reservoirs. Aapg Bull. 2012, 96, 2193–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, C.; Pe-Piper, G.; Saint-Ange, F.; Piper, D.J.W.; Hawie, N. Predictive Modeling of Reservoir Quality Associated with the Dissolution of K-Feldspar During Diagenesis: Lower Cretaceous, Scotian Basin, Canada. Minerals 2025, 15, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; He, Z.; Gluyas, J.G.; Liu, G.; Liu, T.; Chen, C.; Zou, M. Reservoir quality of the Lower–Middle Permian Shan 2 and He 1 members in the Ordos Basin, China: Implications for depositional and diagenetic processes and the role of volcanic tuffaceous sediment in tight sandstones. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 263, 106050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, G. Sedimentology and Stratigraphy; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 419. [Google Scholar]
- Morad, S.; Ketzer, J.M.; De Ros, L.F. Spatial and temporal distribution of diagenetic alterations in siliciclastic rocks: Implications for mass transfer in sedimentary basins. Sedimentology 2000, 47, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Gier, S.; Krois, P. Porosity-preserving chlorite cements in shallow-marine volcaniclastic sandstones: Evidence from Cretaceous sandstones of the Sawan gas field, Pakistan. Aapg Bull. 2009, 93, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, S.N. Preservation of Anomalously High Porosity in Deeply Buried Sandstones by Grain-Coating Chlorite: Examples from the Norwegian Continental Shelf. Aapg Bull. 1993, 77, 1260–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, R.H.; Griffiths, J.; Wooldridge, L.J.; Utley, J.E.P.; Lawan, A.Y.; Muhammed, D.D.; Simon, N.; Armitage, P.J. Chlorite in sandstones. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 204, 103105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, C. Chlorite and associated influence on reservoir properties in tight sandstones of the Upper Shaximiao Formation, SW Sichuan Basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2025, 293, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowey, P.J.; Hodgson, D.M.; Worden, R.H. Pre-requisites, processes, and prediction of chlorite grain coatings in petroleum reservoirs: A review of subsurface examples. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 32, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.Y.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, Q. The Influence and Formation Environment of Chlorite Coatings in the Clastic Rock. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2015, 33, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.Y.; Miao, C.S.; Li, R.I.; Zhu, J.F.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.N. Influencing factors of tight clastic reservoir physical properties and main controlling factors of high-quality reservoirs: Taking the Yingcheng Formation of Longfengshan sub-sag in Changling Fault Depression of Songliao Basin as an example. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2022, 33, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.Q.; Zhang, S.N.; Ge, P.L.; Yi, C. Diagenetic System of the Yanchang Formation Reservoirs in the Southeastern Ordos Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2011, 29, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.M.; Jones, S.J.; Gluyas, J.; Al-Ramadan, K. Impact of Grain-Coating Clays on Porosity Preservation in Paleocene Turbidite Channel Sandstones: Nelson Oil Field, UK Central North Sea. Minerals 2022, 12, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Components | Type I Reservoir (n = 18) | Type II Reservoir (n = 21) | Type III Reservoir (n = 19) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max, % | Min, % | Aver, % | Max, % | Min, % | Aver, % | Max, % | Min, % | Aver, % | ||
| Fragments | Quartz | 90.6 | 66.5 | 71.6 | 87.9 | 50.5 | 69.9 | 75.86 | 46.3 | 63.6 |
| Feldspar | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 4.8 | 0.0 | 2.3 | |
| Volcanic rock fragment | 7.7 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 10.6 | 3.1 | 4.4 | |
| Metamorphic rock fragment | 16.2 | 7.9 | 12.5 | 24.6 | 5.6 | 16.8 | 35.2 | 12.2 | 17.8 | |
| Mica | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 6.2 | 1.3 | 4.1 | |
| Cements | Calcite | 4.8 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 5.6 | 0.4 | 2.2 | 10.3 | 0.4 | 2.3 |
| Chlorite | 8.4 | 3.5 | 5.6 | 6.7 | 2.2 | 3.5 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.1 | |
| Illite | 1.8 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 4.2 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 5.3 | 0.2 | 3.5 | |
| Kaolinite | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 3.1 | 0.0 | 1.6 | |
| Quartz overgrowth | 2.1 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 8.3 | 0.6 | 4.1 | 3.3 | 0.2 | 0.9 | |
| Parameters | Type I Reservoir (n = 18) | Type II Reservoir (n = 21) | Type III Reservoir (n = 19) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compaction Index (IGV) (%) | 28.7 ± 3.2 | 23.5 ± 2.8 | 18.9 ± 2.1 |
| Dissolution-induced Porosity Enhancement Rate (%) | 8.5 ± 1.8 | 5.2 ± 1.3 | 2.1 ± 0.9 |
| Quartz Overgrowth Coverage (%) | 15.2 ± 1.8 | 42.7 ± 8.9 | 28.4 ± 7.1 |
| Chlorite Coating Coverage (%) | 78 ± 12 | 42 ± 15 | 23 ± 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Lin, F.; Zhang, X.; Han, S.; Zhu, Y. Genesis of Conventional Reservoirs in Braided Fluvial Tight Sandstones: Evidence from the He 1 Member, Upper Paleozoic, Southern Ordos Basin, China. Minerals 2025, 15, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111104
Ding X, Wang Y, Gao J, Lin F, Zhang X, Han S, Zhu Y. Genesis of Conventional Reservoirs in Braided Fluvial Tight Sandstones: Evidence from the He 1 Member, Upper Paleozoic, Southern Ordos Basin, China. Minerals. 2025; 15(11):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111104
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Xiaoqi, Yi Wang, Jingyun Gao, Feilan Lin, Xiang Zhang, Shujie Han, and Ying Zhu. 2025. "Genesis of Conventional Reservoirs in Braided Fluvial Tight Sandstones: Evidence from the He 1 Member, Upper Paleozoic, Southern Ordos Basin, China" Minerals 15, no. 11: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111104
APA StyleDing, X., Wang, Y., Gao, J., Lin, F., Zhang, X., Han, S., & Zhu, Y. (2025). Genesis of Conventional Reservoirs in Braided Fluvial Tight Sandstones: Evidence from the He 1 Member, Upper Paleozoic, Southern Ordos Basin, China. Minerals, 15(11), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111104






