In Situ Effectiveness of Alkaline and Cementitious Amendments to Stabilize Oxidized Acid-Generating Tailings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Joutel Mine Site
2.2. Amendments Formulation
2.3. Field Cell Construction
2.4. Physical, Chemical, and Mineralogical Analyses
3. Results
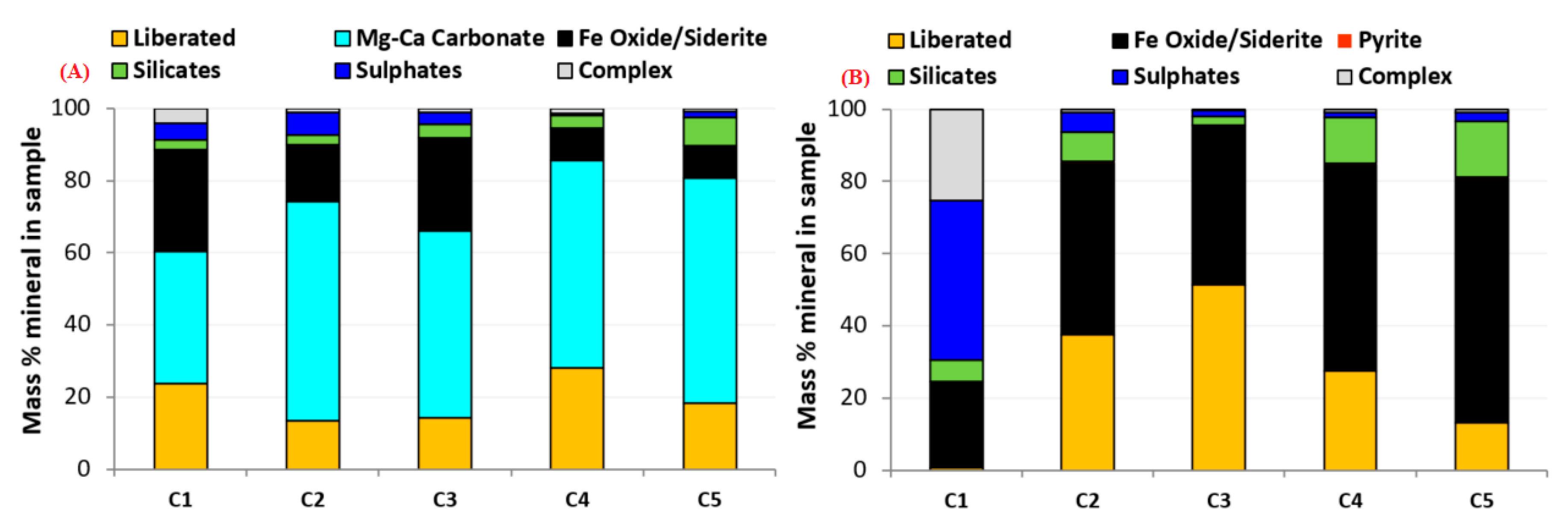
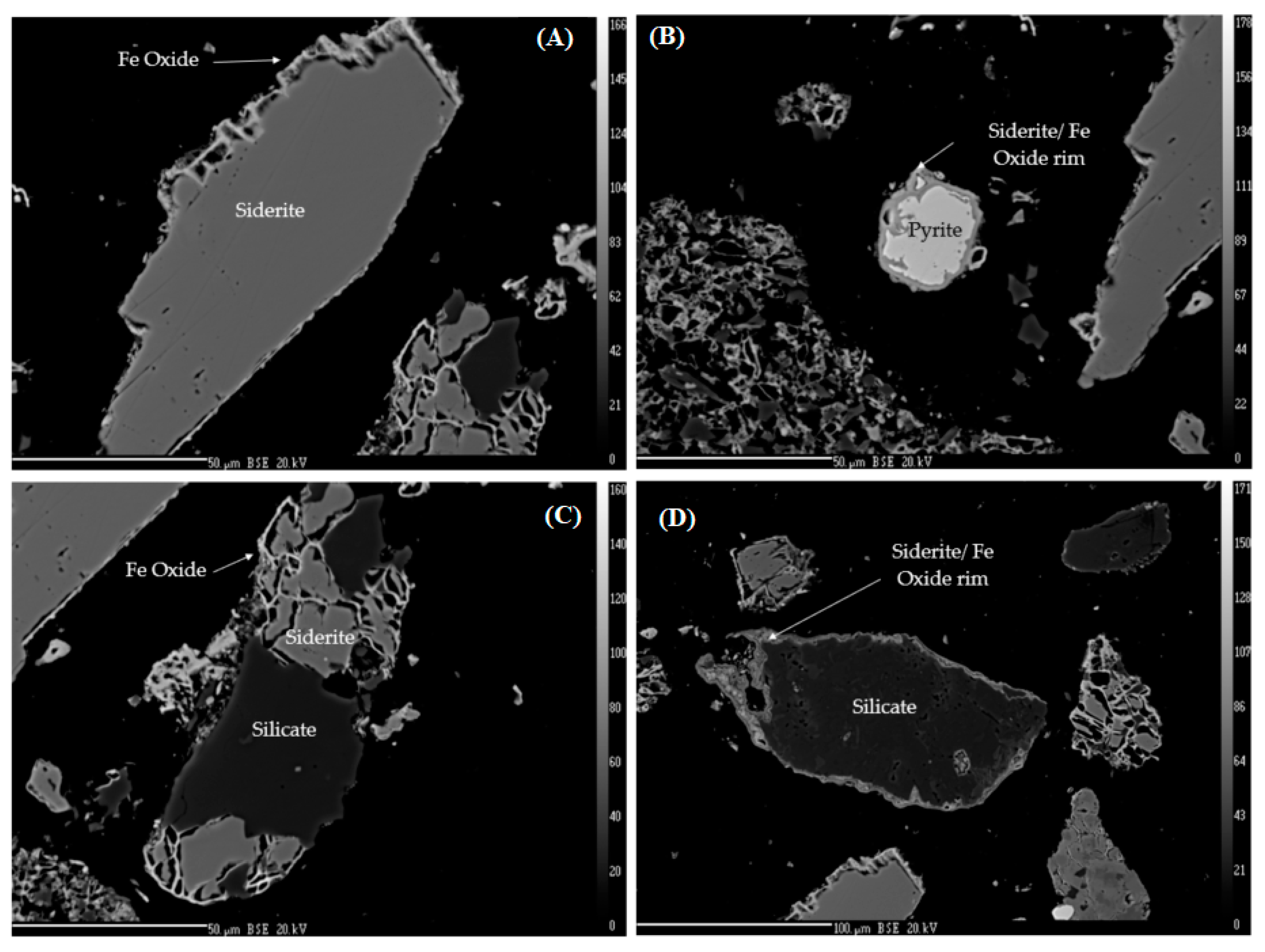
3.1. Chemical, Mineralogical, Static Test, and Physical Characterizations of Solid Samples
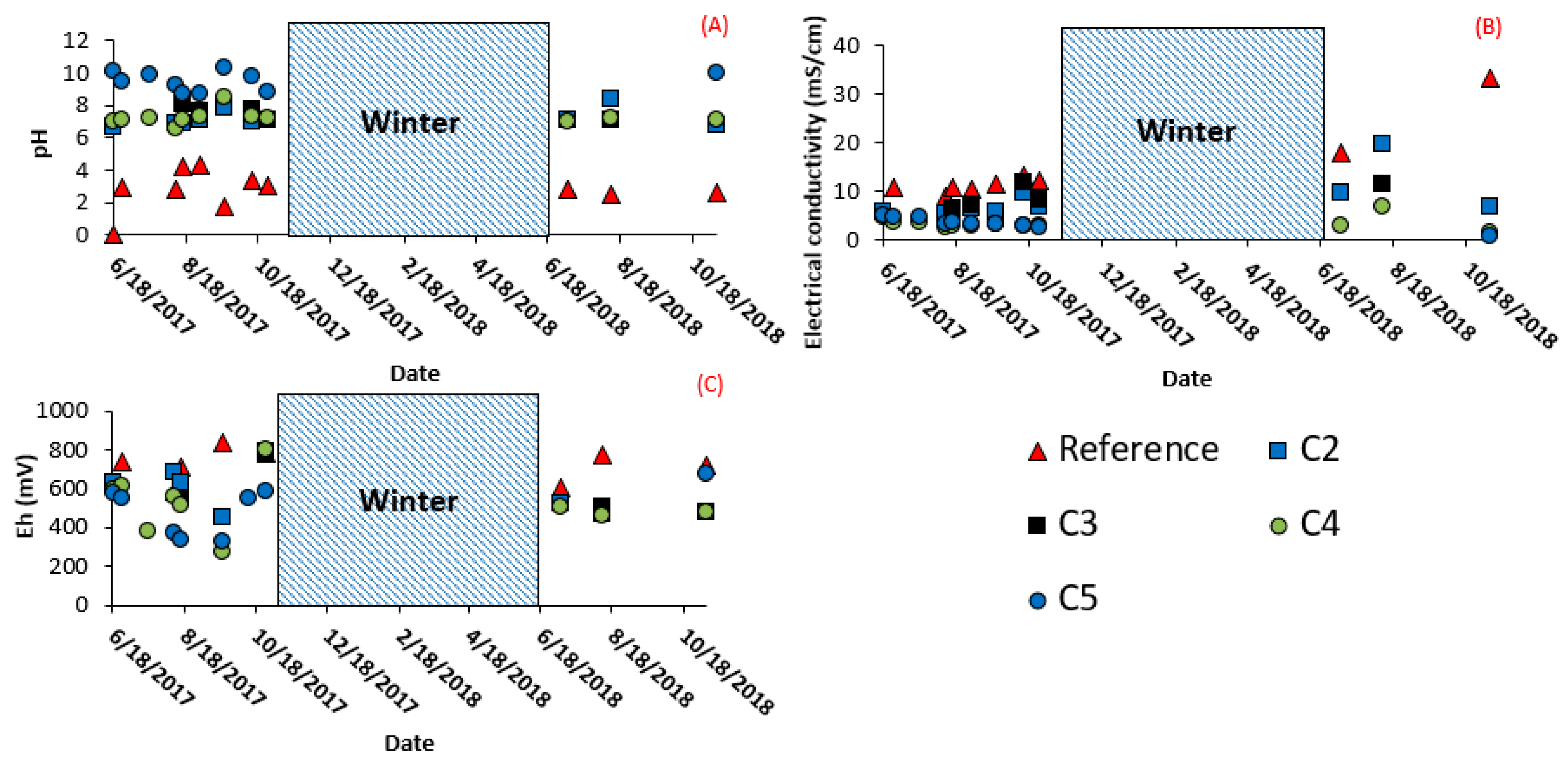
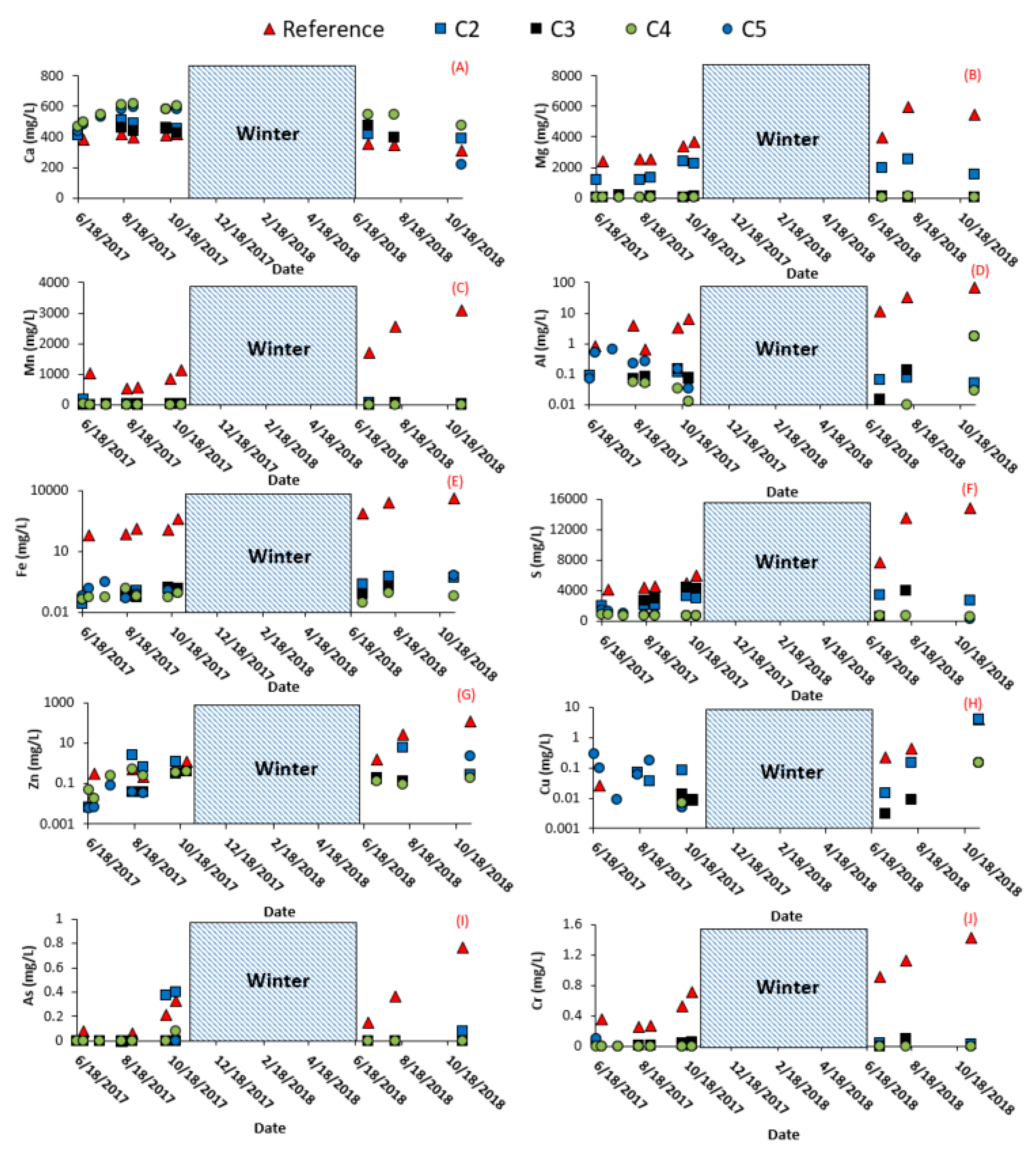
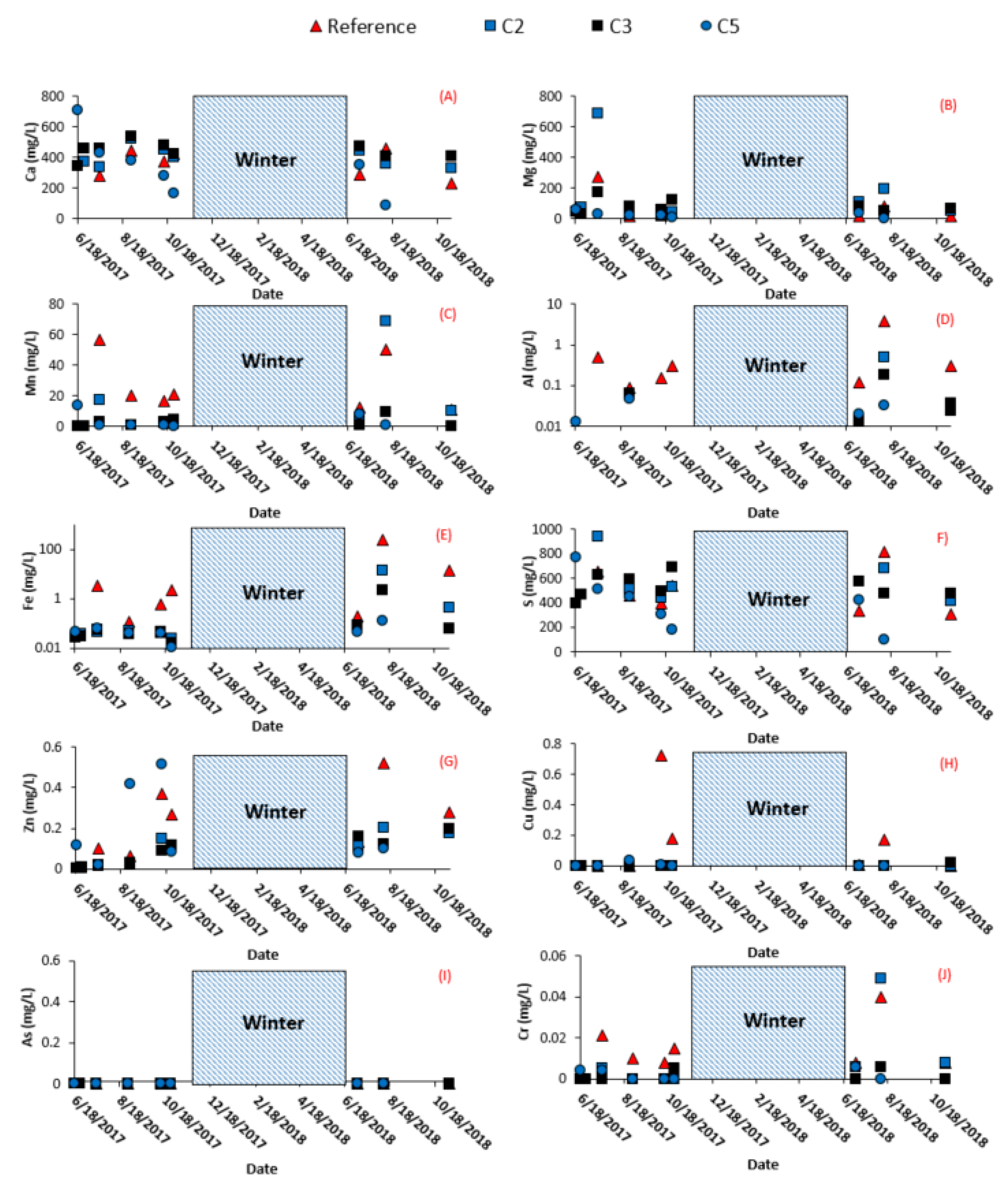
3.2. Field Cell Monitoring
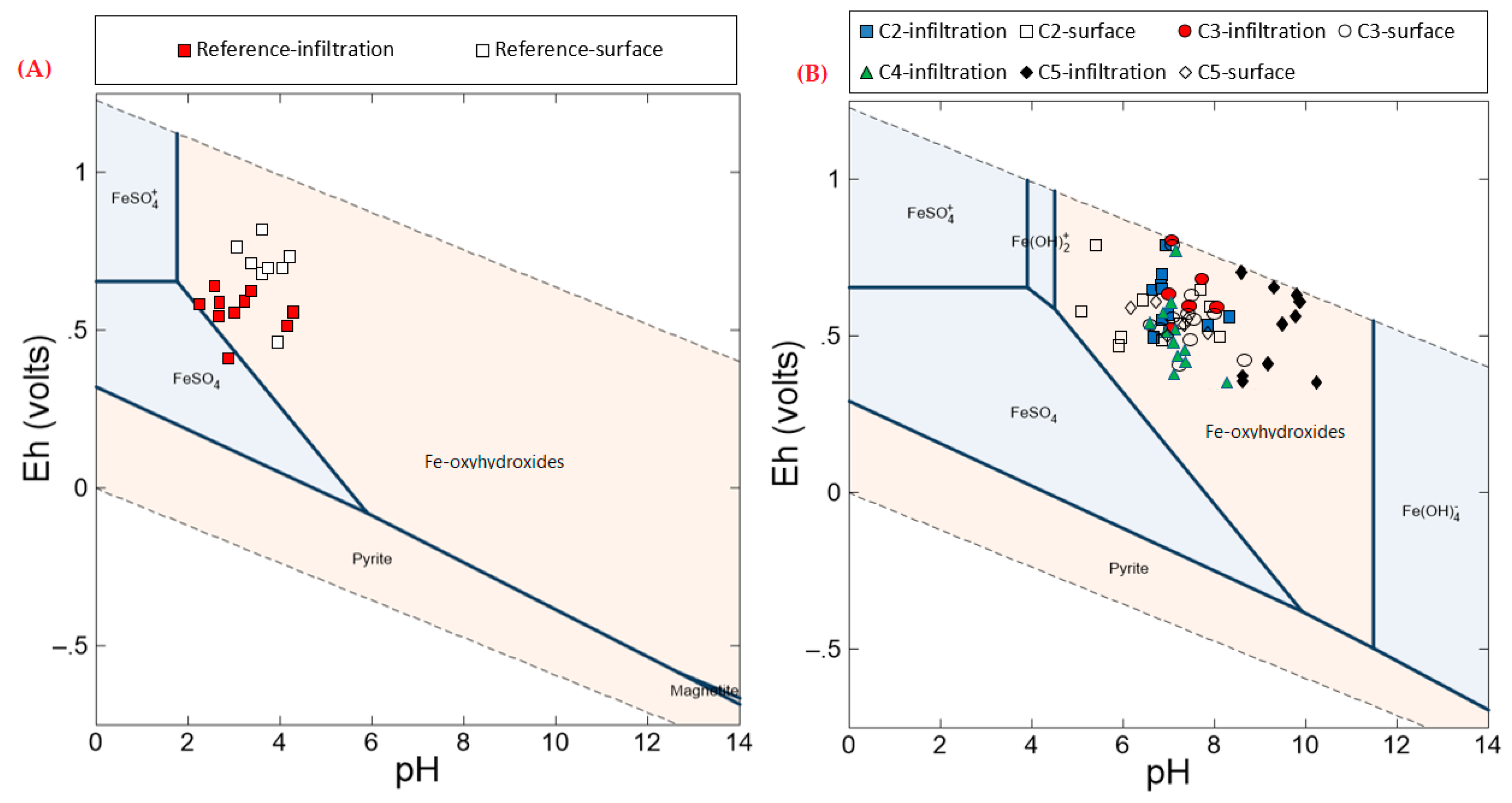
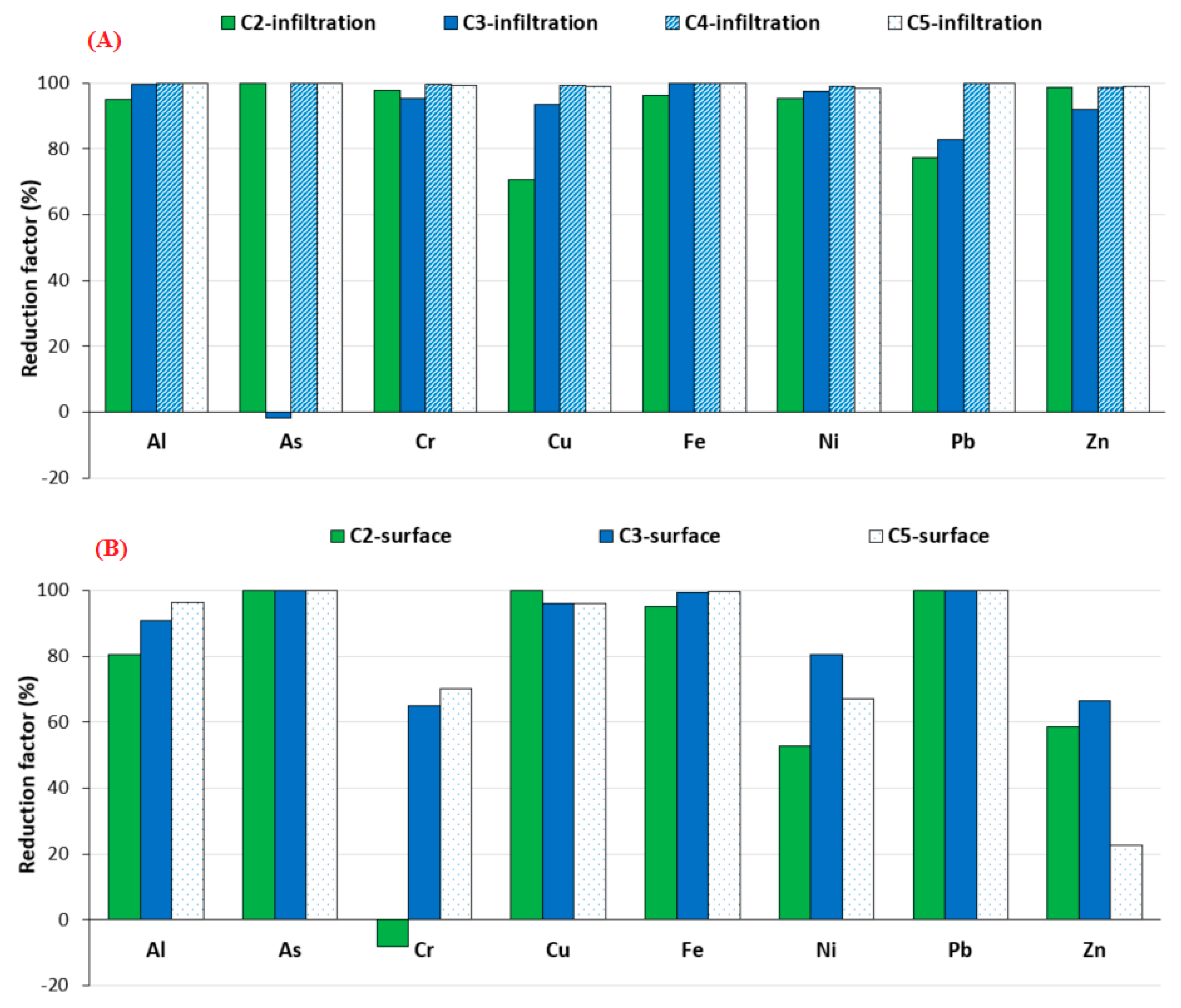
3.2.1. Vertical Infiltration
3.2.2. Surface and Subsurface Runoff
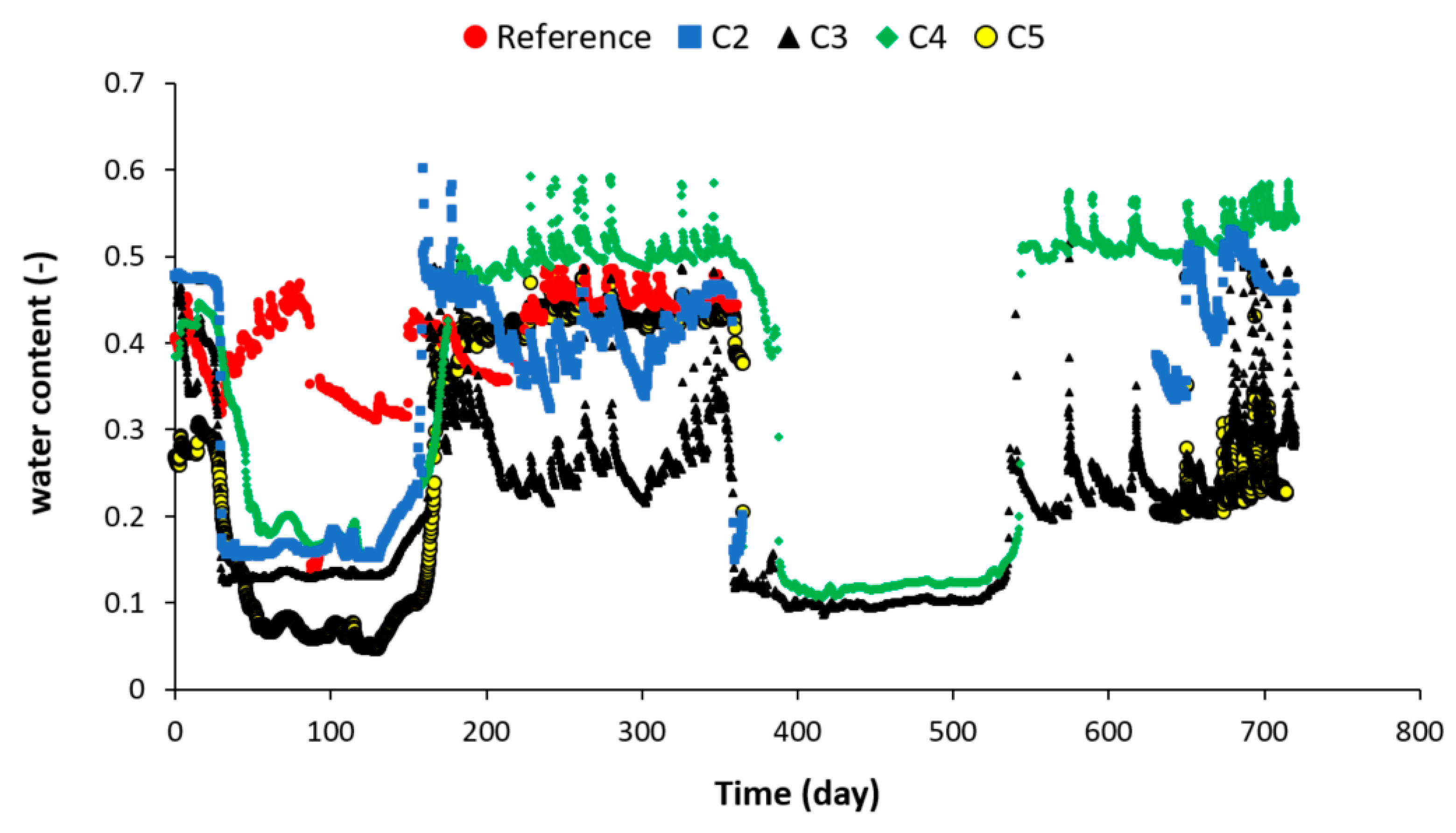
3.3. Water Content Evolution
3.4. Field Cell Dismantlement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez, L.; Gómez, R.; Sánchez, V.; Villaseñor, J.; Alonso-Azcárate, J. Performance of waste-based amendments to reduce metal release from mine tailings: One-year leaching behaviour. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 209, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Wen, J.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, T.; Huang, F.; Qin, H.; Tian, S. A comparative study for the stabilisation of heavy metal contaminated sediment by limestone, MnO2 and natural zeolite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tyrer, M.; Hills, C.; Yang, X.; Carey, P. Immobilisation of heavy metal in cement-based solidification/stabilisation: A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shen, Z.; Al-Tabbaa, A. PC-based and MgO-based binders stabilised/solidified heavy metal-contaminated model soil: Strength and heavy metal speciation in early stage. Géotechnique 2018, 68, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciglia, P.P.; Romano, S.; Vagliasindi, F.G. Stabilisation/Solidification of soils contaminated by mining activities: Influence of barite powder and grout content on γ-radiation shielding, unconfined compressive strength and 232Th immobilisation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 174, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.; Trakal, L.; Sillerova, H.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L.; Hough, R.; Beesley, L. Mobility of As, Cr and Cu in a contaminated grassland soil in response to diverse organic amendments; a sequential column leaching experiment. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 88, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Jin, F.; Al-Tabbaa, A. The performance of blended conventional and novel binders in the in-situ stabilisation/solidification of a contaminated site soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlKattan, M.; Oelkers, E.H.; Dandurand, J.-L.; Schott, J. An experimental study of calcite and limestone dissolution rates as a function of pH from −1 to 3 and temperature from 25 to 80 °C. Chem. Geol. 1998, 151, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatahi, B.; Khabbaz, H. Influence of Chemical Stabilisation on Permeability of Municipal Solid Wastes. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2015, 33, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Illikainen, M.; Kuokkanen, T.; Lassi, U. Stabilization/solidification of fly ash from fluidized bed combustion of recovered fuel and biofuel using alkali activation and cement addition. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doye, I.; Duchesne, J. Neutralisation of acid mine drainage with alkaline industrial residues: Laboratory investigation using batch-leaching tests. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, M.; Duchesne, J.; Lamontagne, A.; Isabel, D. Using red mud bauxite for the neutralization of acid mine tailings: A column leaching test. Can. Geotech. J. 2006, 43, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 327–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleri, M.A.; Whetstone, G.T. In situ stabilisation/solidification: Project lifecycle. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravotta III, C.A.; Trahan, M.K. Limestone drains to increase pH and remove dissolved metals from acidic mine drainage. Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 581–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, R.P.; Figueiredo, B.R.; de Mello, J.W.V.; Santos, J.C.Z.; Zandonadi, L.U.; Andrade, R.P.; Mello, J.W.V. Control of geochemical mobility of arsenic by liming in materials subjected to acid mine drainage. J. Soils Sediments 2008, 8, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkou, R.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B. Laboratory Evaluation of the Use of Alkaline Phosphate Wastes for the Control of Acidic Mine Drainage. Mine Water Environ. 2009, 28, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Jiang, N.J.; Liu, S.Y.; Jin, F.; Singh, D.N.; Puppala, A.J. Engineering properties and microstructural characteristics of cement-stabilized zinc-contaminated kaolin. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 51, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Poon, C.S.; Sun, H.; Lo, I.M.; Kirk, D.W. Heavy metal speciation and leaching behaviors in cement based solidified/stabilized waste materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 82, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehdi, M.; Tariq, A. Stabilization of sulphidic mine tailings for prevention of metal release and acid drainage using cementitious materials: A review. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 6, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogbara, R.B.; Yi, Y.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Process envelopes for stabilisation/solidification of contaminated soil using lime–slag blend. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Pouliot, S. Influence of disposal configurations on hydrogeological behaviour of sulphidic paste tailings: A field experimental study. Int. J. Process. 2014, 131, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, B.; Benzaazoua, M.; Maqsoud, A.; Bussière, B. Long term hydro-geochemical behaviour of surface paste disposal in field experimental cells. In Proceedings of the Conference Canadienne de Ge’otechnique, GeoRegina, CD-Rom, Regina, Slovakia, 28 September–2 October 2014; Volume 1, p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Komnitsas, K.; Bartzas, G.; Paspaliaris, I. Efficiency of limestone and red mud barriers: Laboratory column studies. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylona, E.; Xenidis, A.; Paspaliaris, I. Inhibition of acid generation from sulphidic wastes by the addition of small amounts of limestone. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstrom, H.; Ljungberg, J.; Ohlander, B. Role of carbonates in mitigation of metal release from mining waste. Evidence from humidity cells tests. Environ. Geol. 1999, 37, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, J.; Reardon, E. Determining controls on element concentrations in cement kiln dust leachate. Waste Manag. 1998, 18, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, P.; Ayora, C.; Torrentó, C.; Nieto, J.-M. The behavior of trace elements during schwertmannite precipitation and subsequent transformation into goethite and jarosite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 4130–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asta, M.P.; Ayora, C.; Román-Ross, G.; Cama, J.; Acero, P.; Gault, A.G.; Charnock, J.M.; Bardelli, F. Natural attenuation of arsenic in the Tinto Santa Rosa acid stream (Iberian Pyritic Belt, SW Spain): The role of iron precipitates. Chem. Geol. 2010, 271, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, M.M.; O Leckie, J. Competitive adsorption of cd, cu, zn, and pb on amorphous iron oxyhydroxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1981, 83, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Jambor, J.L.; Weisener, C.G. The geochemistry of acid mine drainage. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Belzile, N.; Maki, S.; Chen, Y.-W.; Goldsack, D. Inhibition of pyrite oxidation by surface treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 196, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.-F.; Dang, Z.; Chen, Y.-W.; Belzile, N. The passivation of pyrrhotite by surface coating. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, A.L.; Dipple, G.M.; Power, I.M.; Mayer, K.U. Influence of surface passivation and water content on mineral reactions in unsaturated porous media: Implications for brucite carbonation and CO2 sequestration. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 148, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.U.; Jeon, B.H.; Park, S.S.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, D.K.; Choi, U.-K.; Kim, S.J. Inhibition of pyrite oxidation by surface coating: A long-term field study. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelou, V.P.; Zhang, Y.L. A review: Pyrite oxidation mechanisms and acid mine drainage prevention. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 25, 141–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedem. Diversité Microbiologique Dans La Production De Drainage Minier Acide À La halde Sud De La Mine Doyon. Mend/Medem 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Southam, G. Geomicrobiology of sulfide mineral oxidation. Rev. Mineral. 1997, 35, 361–390. [Google Scholar]
- Lamontagne, A. Étude De La Méthode D’empilement Des Stériles Par Entremêlement Par Couches Pour Contrôler Le Drainage Minier Acide. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Laval, Quebec City, QC, Cannada, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mackie, A.L.; Walsh, M.E. Investigation into the use of cement kiln dust in high density sludge (HDS) treatment of acid mine water. Water Res. 2015, 85, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchesne, J.; Laforest, G. Remediation of electric arc furnace dust leachate by the use of cementitious materials: A column-leaching test. Chin. J. Geochem. 2006, 25, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichrak, H.; Mostafa, B.; Abdelkabir, M.; Bruno, B. Effect of cementitious amendment on the hydrogeological behavior of a surface paste tailings’ disposal. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2016, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Yanful, E.K. A review of binders used in cemented paste tailings for underground and surface disposal practices. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Marion, P.; Picquet, I.; Bussière, B. The use of pastefill as a solidification and stabilization process for the control of acid mine drainage. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Aubertin, M. Les effets d’amendements alcalins sur des résidus miniers sulfureux entreposés en surface: Cas des dépôts en pâte. Déchets Sci. Tech. 2009, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccu, R.; Ghiani, M.; Serci, A.; Fadda, S.; Peretti, R.; Zucca, A. Heavy metal immobilization in the mining-contaminated soils using various industrial wastes. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussy, S.; Benzaazoua, M.; Blanc, D.; Moszkowicz, P.; Bussière, B. Arsenic stability in arsenopyrite-rich cemented paste backfills: A leaching test-based assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Alkali activation of fly ash: Effect of the SiO2/Na2O ratio. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 106, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Jung, M.C. Solidification of arsenic and heavy metal containing tailings using cement and blast furnace slag. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33 (Suppl. 1), 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-K. Hydration and solidification of hazardous wastes containing heavy metals using modified cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyronnard, O.; Benzaazoua, M. Alternative by-product based binders for cemented mine backfill: Recipes optimisation using Taguchi method. Miner. Eng. 2012, 29, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Kennedy, C.; Parwani, R.; Graham, S. The role of hardpan formation on the reactivity of sulfidic mine tailings: A case study at Joutel mine (Québec). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Genty, T. Spatial Mapping of Acidity and Geochemical Properties of Oxidized Tailings within the Former Eagle/Telbel Mine Site. Minerals 2019, 9, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussière, B.; Mbonimpa, M.; Molson, J.W.; Chapuis, R.P.; Aubertin, M. Field experimental cells to evaluate the hydrogeological behaviour of oxygen barriers made of silty materials. Can. Geotech. J. 2007, 44, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzahzah, H.; Benzaazoua, M.B.; Bussiere, P.B. A quantitative approach for the estimation of the “fizz rating” parameter in the acid-base accounting tests: A new adaptations of the Sobek test. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 153, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Jambor, J.L.; Weisener, C.G. The geochemistry of acid mine drainage. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 9, 612. [Google Scholar]
- Blowes, D.W.; Jambor, J.L.; Alpers, C.N. The Environmental Geochemistry of Sulfide Mine-Wastes; Mineralogical Association of Canada: Québec, QC, Canada, 1994; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Jambor, J. Mineralogy of mine wastes and strategies for remediation. In Environmental Mineralogy; Vaughan, D.J., Wogelius, R.A., Eds.; European Mineralogical Union: Jena, Germany, 2013; Volume 13, pp. 295–338. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Belem, T.; Bussière, B. Chemical factors that influence the performance of mine sulphidic paste backfill. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Ouellet, J.; Servant, S.; Newman, P.; Verburg, R. Cementitious backfill with high sulfur content Physical, chemical, and mineralogical characterization. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Germann, P. Macropores and water flow in soils. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussière, B.; Aubertin, M.; Julien, M. Couvertures avec effets de barrière capillaire pour limiter le drainage minier acide: Aspects théoriques et pratiques. Vecteur Environ. 2001, 34, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, E.C.; Bybordi, M. The vertical movement water in stratified porous material: 1. Infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. Hydraulics of Groundwater; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker, S. Flow in porous media I: A theoretical derivation of Darcy’s law. Transp. Porous Media 1986, 1, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getter, K.L.; Rowe, D.B.; Andresen, J.A. Quantifying the effect of slope on extensive green roof stormwater retention. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 31, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, T.; Zhang, W. Effects of Rainfall, Vegetation, and Microtopography on Infiltration and Runoff. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermang, J.; Norton, L.; Huang, C.; Cornelis, W.; Da Silva, A.; Gabriels, D. Characterization of Soil Surface Roughness Effects on Runoff and Soil Erosion Rates under Simulated Rainfall. Soil Sci. Soc. J. 2015, 79, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambor, J. Mineralogy of sulfide-rich tailings and their oxidation products. Environ. Geochem. Sulfide Mine Wastes 1994, 22, 59–102. [Google Scholar]
- Jambor, J.; Dutrizac, J.; Groat, L.; Raudsepp, M. Static tests of neutralization potentials of silicate and aluminosilicate minerals. Environ. Geol. 2002, 43, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lapakko, K.A. Evaluation of neutralization potential determinations for metal mine waste and a proposed alternative. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on the Abatement of Acidic Drainage, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 24–29 April 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Dagenais, A. Comparison of kinetic tests for sulfide mine tailings. In Proceedings of the Tailings and Mine Waste 01, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 6–19 January 2001; Balkema: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2001; pp. 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Dagenais, A.-M.; Archambault, M. Kinetic tests comparison and interpretation for prediction of the Joutel tailings acid generation potential. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 1086–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowes, D.W.; Jambor, J.L.; Hanton-Fong, C.J.; Lortie, L.; Gould, W. Geochemical, mineralogical and microbiological characterization of a sulphide-bearing carbonate-rich gold-mine tailings impoundment, Joutel, Québec. Appl. Geochem. 1998, 13, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussière, B.; Benzaazoua, M.; Aubertin, M.; Mbonimpa, M. A laboratory study of covers made of low-sulphide tailings to prevent acid mine drainage. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, C.L.; Ciminelli, V.S.; Osseo-Asare, K. The role of carbonate ions in pyrite oxidation in aqueous systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, H.E.; Walker, S.R.; Parsons, M.B. Mineralogical characterization of mine waste. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.V.; Gillham, R.W.; Reardon, E.J. Pyrite oxidation in carbonate-buffered solution: 1. Experimental kinetics. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussy, S.; Benzaazoua, M.; Blanc, D.; Moszkowicz, P.; Bussière, B. Assessment of arsenic immobilization in synthetically prepared cemented paste backfill specimens. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bouzahzah, H.; Bussière, B.; Villarraga-Gómez, H. Determination of the available acid-generating potential of waste rock, part I: Mineralogical approach. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 99, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Bouzahzah, H. Determination of the available acid-generating potential of waste rock, part II: Waste management involvement. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 100, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erguler, Z.A.; Erguler, G.K. The effect of particle size on acid mine drainage generation: Kinetic column tests. Miner. Eng. 2015, 76, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cell | Formulation |
|---|---|
| C1 | Reference (oxidized tailings) |
| C2 | 5 wt % limestone |
| C3 | 10 wt % limestone |
| C4 | 5 wt % (1/2 OPC + 1/2 FA) |
| C5 | 5 wt % OPC |
| Characterization | Parameter | Units | MT | Limestone | OPC | FA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical characteristics | D10 | µm | 1.8 | 50 | 4.2 | 82 |
| D30 | 4.7 | 250 | 11.3 | 180 | ||
| D90 | 30.4 | 4500 | 46.7 | 1500 | ||
| initial water content | wt % | 15 | 6.1 | dry | 3.52 | |
| Chemical composition | Al | % | 2.02 | 0.295 | 2.75 | 4.69 |
| Ca | 3.72 | 33.82 | 49.07 | 7.58 | ||
| Mg | 0.15 | 2.350 | 1.18 | 1.05 | ||
| Mn | 0.42 | 0.031 | 0.06 | 0.42 | ||
| Na | 1.07 | 0.125 | 0.16 | 1.96 | ||
| K | 0.26 | 0.245 | 0.43 | 1.85 | ||
| Fe | 27.24 | 0.483 | 2.23 | 2.24 | ||
| Si* | 17.76 | 7.76 | 14.82 | |||
| Li | ≤0.0005 | ≤0.0005 | ≤0.0005 | 0.002 | ||
| Pb | 0.013 | ≤0.0005 | ≤0.0005 | ≤0.0005 | ||
| As | 0.091 | ≤0.0005 | 0.005 | ≤0.0005 | ||
| Cr | 0.0024 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.006 | ||
| Cu | ≤0.001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.007 | ≤0.0001 | ||
| Zn | 0.01 | ≤0.0055 | 0.05 | 0.07 | ||
| S (total) | 6.80 | 0.93 | 1.74 | 0.43 | ||
| S (sulfates) | 0.27 | - | - | - | ||
| C | 2.2 | - | - | - | ||
| Static tests | NP | kg CaCO3/t | 183 | 880 | - | - |
| AP | kg CaCO3/t | 195 | - | - | - | |
| Mineralogical composition | Quartz | wt % | 27.84 | 2.07 | Not applicable | 5.32 |
| Calcite | 7.82 | 75.76 | 15.51 | |||
| Dolomite | 0.60 | 22.17 | ||||
| Muscovite | 1.03 | |||||
| Siderite | 11.41 | 3.65 | ||||
| Orthoclase | 0.99 | 8.34 | ||||
| Biotite | 0.23 | 7.52 | ||||
| Albite | 12.78 | 20.51 | ||||
| Gypsum | 1.45 | |||||
| Goethite | 22.29 | |||||
| Pyrite | 12.22 | |||||
| Labradorite | 0.30 | 22.88 | ||||
| Chlorite | 0.74 | |||||
| Corundum | 0.41 | |||||
| Anhydrite | 1.83 |
| Elements (ppm) | Al | As | Ba | Be | Bi | Ca | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Fe | K | Li | Mg | Mn | Mo | Na | Ni | Pb | S | Ti | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection limit (ppm) | 60 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 60 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 200 | 25 | 55 |
| C1 | 20,200 | 910 | 38 | <5 | 108 | 37,230 | 39 | <5 | 24 | <10 | 272,400 | 2600 | <5 | 1515 | 4237 | 8 | 10,700 | 25 | 128 | 75,350 | 627 | 99 |
| C2 | 18,250 | 783 | 36 | <5 | 108 | 50,910 | 37 | <5 | 24 | <10 | 256,300 | 2580 | <5 | 7839 | 6104 | 7 | 9360 | 27 | 102 | 71,600 | 317 | 96 |
| C3 | 15,360 | 654 | 31 | <5 | 109 | 106,000 | 30 | <5 | 22 | <10 | 221,000 | 2530 | <5 | 10,940 | 5122 | 9 | 7810 | 23 | 99 | 66,060 | 486 | 85 |
| C3-duplicate | 15,150 | 673 | 32 | <5 | 105 | 100,900 | 30 | <5 | 22 | <10 | 208,900 | 2520 | <5 | 11,100 | 5082 | 9 | 8090 | 24 | 98 | 64,600 | 501 | 83 |
| C4 | 21,930 | 399 | 66 | <5 | 104 | 33,660 | 37 | <5 | 36 | <10 | 291,200 | 2210 | <5 | 9660 | 7698 | 6 | 12,900 | 21 | 105 | 57,920 | 865 | 115 |
| C5 | 21,970 | 426 | 49 | <5 | 100 | 40,720 | 38 | <5 | 40 | <10 | 281,800 | 2110 | <5 | 7711 | 6775 | 8 | 12,600 | 21 | 136 | 43,100 | 756 | 107 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Genty, T. In Situ Effectiveness of Alkaline and Cementitious Amendments to Stabilize Oxidized Acid-Generating Tailings. Minerals 2019, 9, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9050314
Elghali A, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B, Genty T. In Situ Effectiveness of Alkaline and Cementitious Amendments to Stabilize Oxidized Acid-Generating Tailings. Minerals. 2019; 9(5):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9050314
Chicago/Turabian StyleElghali, Abdellatif, Mostafa Benzaazoua, Bruno Bussière, and Thomas Genty. 2019. "In Situ Effectiveness of Alkaline and Cementitious Amendments to Stabilize Oxidized Acid-Generating Tailings" Minerals 9, no. 5: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9050314
APA StyleElghali, A., Benzaazoua, M., Bussière, B., & Genty, T. (2019). In Situ Effectiveness of Alkaline and Cementitious Amendments to Stabilize Oxidized Acid-Generating Tailings. Minerals, 9(5), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9050314







