Abstract
The Maozaishan Sn deposit, located south of the Dayishan ore field in the Nanling Range, is a newly explored greisen-type Sn deposit. Two muscovite samples from tin-bearing ores yielded 40Ar/39Ar plateau ages of 154.7 ± 1.1 Ma (Mean standard weighted deviation (MSWD) = 0.48) and 152.6 ± 0.7 Ma (MSWD = 0.25), respectively. Zircon U–Pb dating result of fine-grained biotite monzogranite in the Maozaishan mining area shows that these zircon grains can be subdivided into two populations, with ages of 154.2 ± 2.0 Ma (MSWD = 0.51) and 159.6 ± 1.9 Ma (MSWD = 0.09), respectively, indicating that the monzogranite is formed by a multi-stage magmatic event. It is indicated that formation of the Maozaishan Sn deposit is closely related to the Middle Jurassic granitic magmatism. Based on the trace element compositions of zircon grains, the calculated magma temperatures and oxygen fugacity (log(fO2)) values range from 638 °C to 754 °C (mean = 704 °C) and from −18.9 to −15.8 (mean = −17.1), respectively. In addition, these intrusive rocks in the Dayishan ore field belong to highly fractionated granites and are characterized by low oxygen fugacity and crust–mantle origin, which are consistent to these tin-bearing granites in the Nanling Range and in favor of the Sn mineralization.
1. Introduction
South China, as one of the most important metallogenic domains around the world, is famous for the super tungsten–tin (W–Sn) and other rare metal resources [1,2,3,4,5]. In addition, most of the W–Sn resources are hosted in the Nanling Range, which is located in the central South China [6,7,8,9,10]. It was reported that ca. 63% of the Sn reserves are located in the Nanling Range, hosting abundant Sn ore fields (e.g., Guposhan, Jiuyishan, Xianghualing, Xitian, Qitianling, and Dayishan) [7,11,12,13]. Several large- to super large-scale Sn polymetallic deposits were hosted in these ore fields, including Furong, Xintianling, Xianghualing, Da’ao, and Xitian (Figure 1) [7,14,15,16]. Formation of these Sn deposits are closely related to the coeval granitic magmatic intrusions, with ages of 165 to 150 Ma [4,6]. Recently, more and more Sn polymetallic deposits were identified in the Nanling Range, however the relationship between the granitic magmatism and Sn mineralization still needs to be explored.
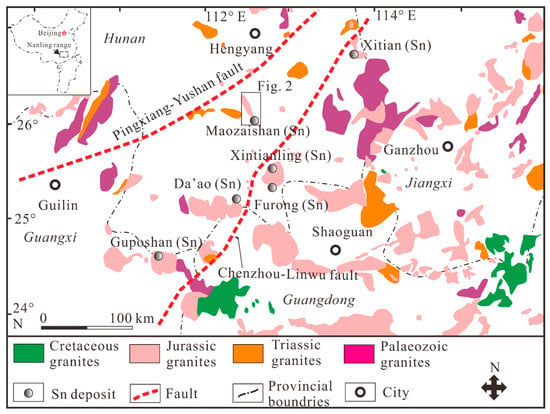
Figure 1.
Geological sketch map of the Nanling Range (modified from [17]), showing the distribution of granitic plutons and related W–Sn deposits.
The Dayishan ore field, located at central Nanling Range, is characterized by large-scale Sn polymetallic mineralization, hosting a series of medium- to large-scale Sn polymetallic deposits, such as Shimaochong (Sn–Cu), Shixingling (Sn–Cu), Tengshan’ao (Sn), and Maozishan (Sn) (Figure 2). However, very limited studies were carried out for these deposits in this ore field, constraining the understanding on the ore genesis of these Sn deposits. Zhang and coauthors [18] first reported a Rb–Sr isochron age of 160 ± 1 Ma for the fluid inclusions in the cassiterite-bearing quartz of the Baishaziling Sn deposit, south of the Dayishan ore field. Recently, Sun and coauthors [19] reported cassiterite U–Pb and molybdenite Re–Os ages of 156.5 ± 2.8 Ma (MSWD = 3.1) and 157.9 ± 7.7 Ma (MSWD = 26), respectively, for the Maozaishan Sn deposit. The obvious large MSWD values make these ages unreliable, since the age might be not convincing if the MSWD value is over 2.5 [20].
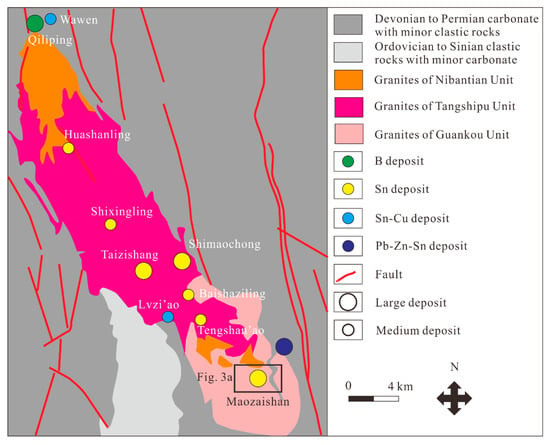
Figure 2.
Schematic geological map of the Dayishan ore field showing the location of Sn polymetallic deposits (modified from [19]).
Therefore, the Maozaishan Sn deposit, north of the Dayishan ore field, was chosen in this study, and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometer (LA-ICP-MS) zircon U–Pb and muscovite 39Ar/40Ar isotopic dating were conducted on the granitoids and tin-bearing ores. In addition, the trace element compositions of the zircon grains from the granites in this deposit were also studied. Based on these analyses, this paper aims to provide some new constraints on the ore- and rock-forming ages, and implications to the Sn mineralization of this ore field.
2. Regional Geology
The South China Block (SCB) consists of the Yangtze Block to the northwest and the Cathaysia Block (CAB) to the southeast. The Nanling Range, located in the Cathaysia Block, is the one of the most important ore-forming belts in the SCB [6,10]. Several significant tectonic-magmatic events occurred in this region from the Palaeozoic to Cretaceous, resulting in the widespread Palaeozoic to Cretaceous granitoids, however, the Jurassic granitoids are predominant [6,10,21,22,23,24,25] (Figure 1). The Jurassic granitic intrusions, commonly associated with the W–Sn polymetallic mineralization, intrude into the basement rocks, which are mainly composed of Precambrian weakly metamorphosed rocks and Late Paleozoic sedimentary rocks. In addition, these Late Paleozoic sedimentary rocks, related to the W–Sn polymetallic mineralization, are mainly Devonian and Carboniferous carbonate rocks, and lesser amounts of Upper Triassic to Tertiary sandstone and siltstone [4]. The regional faults are the NE-trending Pingxiang–Yucheng fault and Chenzhou–Linwu fault, however, the latter has a great influence on the spatial distribution of the granitic intrusions and numerous W–Sn polymetallic deposits (Figure 1) [6,26].
The Dayishan ore field is characterized by intensive granitic magmatism and Sn–Cu–Pb–Zn mineralization, hosting a series of medium- to large-scale Sn polymetallic deposits, including Wawen (Sn–Cu), Qiliping (B), Huashanling (Sn), Shimaochong (Sn), Shixingling (Sn), Taizishang (Sn), and Maozaishan (Sn) (Figure 2). Formation of these deposits are associated to the Dayishan pluton, which occupies an area of 300 km2 and intrudes into the Neoproterozoic epimetamorphic rocks and the Devonian–Carboniferous carbonate rocks with minor clastic rocks. The Dayishan granitic pluton can be subdivided into three units (Guankou, Tangshipu, and Nibantian), which are mainly composed of fine- to coarse-grained biotite moyite, fine- to medium-grained biotite (two-mica) monzogranite, and fine- to medium-grained tourmaline-bearing two-mica monzogranite (syenogranite), respectively [19]. In addition, these granites have relatively high contents of SiO2 (69.3–74.7 wt. %), Al2O3 (12.8–14.5 wt. %), and K2O + Na2O (7.66–8.95 wt. %) and high Al2O3/CaO + Na2O + K2O molar ratios (A/CNK = 0.98–1.13), showing peraluminous and calc-alkaline signatures [27]. These granites also have high 10,000 Ga/Al ratios (over 2.6) and Zr + Nb + Ce + Y values (over 350 ppm), indicating an A-type granite affinity [27]. Furthermore, geochronological studies have revealed that these granites were emplaced between the Triassic and Cretaceous [19,27,28].
3. Geology of the Ore Deposit
The medium-scale Maozaishan deposit is one of the Sn deposits in the Dayishan ore field. Three types of Sn ore bodies were identified in this deposit: Greisen-, altered granite-, and pegmatite-type, however, the industrial Sn ore bodies were mainly composed of the greisen-type (Figure 3). The greisen-type Sn ore bodies are veined and/or lentoid, hosted in the fine-grained biotite monzogranite of the Guankou unit. A total of 95 ore veins were identified, with a length of 240–504 m, thickness of 0.76–2.44 m, and Sn grade of 0.20–1.80% (Figure 4a–c). The altered granite- and pegmatite-type Sn ore bodies mainly occur in the central part of the Maozaishan deposit, however, most of them do not have the exploration value. The greisen-type ores are mainly massive with a disseminated structure (Figure 4d–f). Ore minerals consist of cassiterite, pyrite, chalcopyrite, wolframite, sphalerite, arsenopyrite, and marcasite (Figure 4g–l). Gangue minerals are mainly quartz, muscovite, and topaz (Figure 4j). The alteration in this deposit is composed of greisenization, silicification, and so on. Faults in this deposit form an approximately north west (NW)-trending belt, with length of 3100 m and width of 300–900 m. In addition, these faults, related to the Sn mineralization, can be subdivided into three groups: EW-, NWW-, and NEE-trending.
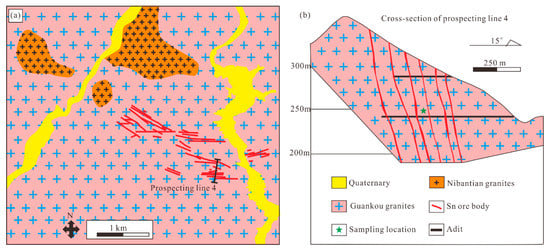
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic geological map and (b) cross-section of prospecting line 4 of the Maozaishan Sn deposit (modified from [19]).
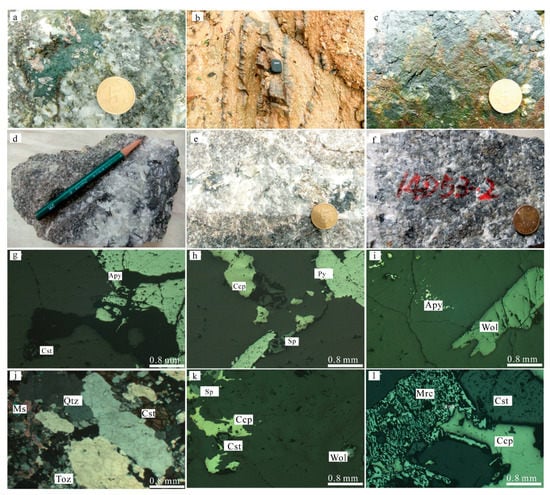
Figure 4.
Photographs of the related ore bodies showing the morphology of greisen-type ores. (a–c) The disseminated and veined greisen-type ore bodies; (d–f) specimens of greisen-type Sn ores; (g–l) micrographs of greisen-type ores. Apy—arsenopyrite; Ccp—chalcopyrite; Cst—cassiterite; Mrc—marcasite; Ms—muscovite; Py—pyrite; Qtz—quartz; Sp—sphalerite; Toz—topaz; Wol—wolframite.
4. Sample Description and Analytical Methods
The samples in this study, including a fine-grained biotite monzogranite (sample No. 14D30-1) and two cassiterite-bearing greisen-type ores (sample Nos. 14D30-2 and 14D32-1), were collected from the Maozaishan mining area (Figure 3). The fine-grained biotite monzogranite shows porphyroid texture and massive structure, consisting of plagioclase (~45%), K-feldspar (~30%), quartz (~20%), and biotite (~5%) (Figure 5a,b). The accessory minerals are mainly composed of magnetite, zircon, and apatite. Ore minerals of the cassiterite-bearing greisen-type ores are mostly composed of cassiterite, arsenopyrite, pyrite, and chalcopyrite, whereas the gangue minerals are comprised of quartz, muscovite, and chlorite (Figure 5c,d).
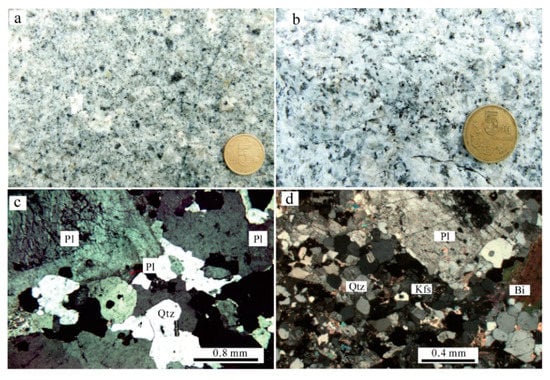
Figure 5.
Hand specimen and micrographs of the fine-grained biotite monzogranite. (a) Hand specimen of the fine-grained biotite monzogranite; (b) Hand specimen of the fine-grained biotite monzogranite; (c) Micrographs of the fine-grained biotite monzogranite; (d) Micrographs of the fine-grained biotite monzogranite; Bi—biotite; Kfs—K-feldspar; Pl—plagioclase; Qtz—quartz.
4.1. In Situ LA-ICP-MS Zircon U–Pb Dating and Trace Element Compositions
Zircon grains from fine-grained biotite monzogranite (sample No. 14D30-1) were first separated following conventional magnetic and heavy liquid techniques. They were hand-picked under a binocular microscope and mounted into epoxy resin blocks and polished to obtain flat surfaces. Before the dating analyses, these zircon grains were photographed using a cathodoluminescence (CL) imaging technique with a scanning electron microscope (TESCAN MIRA 3 LMH FE-SEM, TESCAN, Brno, Czech Republic) at the Sample Solution Analytical Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China. Zircon U–Pb dating was carried out with an Agilent 7700 inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometer (ICP-MS, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), combined with a Coherent 193 laser ablation (LA) system at Sample Solution Analytical Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China. During the analyses, zircon standards, including 91500 and GJ-1, were used as external standards for U–Pb dating. Standard silicate glass (NIST SRM610) was used for external standardization for trace element analysis, and 29Si was used for internal standardization (32.8% SiO2 in zircon). The spot size, energy density, and frequency of the laser were set to 44 µm, 80 mJ, and 5 Hz, respectively, in this study. Each analysis incorporated a background acquisition of approximately 20–30 s followed by 50 s of data acquisition from the sample. In addition, 91500, GJ-1, and NIST SRM610 were analyzed twice, twice, and once, respectively, every ten spots of the zircon grains. The raw ICP-MS data, including the U–Pb and trace element compositions, were processed using ICPMSDataCal software (Version 10.0, [29]), and common lead corrections followed [30]. Concordia diagrams and weighted mean calculations were processed using Isoplot (version 3.0, [31]).
4.2. Muscovite 40Ar–39Ar Dating
The cassiterite-bearing greisen-type ores (sample Nos. 14D30-2 and 14D32-1) were chosen for the Muscovite 40Ar–39Ar dating. First, the muscovite grains were carefully handpicked under a binocular microscope to ensure that the purity of these muscovite grains was at least up to 99.9%. Then, these grains were washed repeatedly in an ultrasonic bath which was filled with deionized water and acetone. Aliquots of approximately10 mg were wrapped in Al foil and stacked in quartz vials. After samples were stacked, the sealed quartz vials were put in a quartz canister, which was wrapped with cadmium foil (0.5 mm in thickness) to act as a slow neutron shield thereby preventing interface reactions during irradiation. The irradiation procedure put the samples in channel B4 of Beijing 49-2 reactor for 50 h at the Chinese Academy of Nuclear Energy Sciences. During irradiation, the vials were rotated at a speed of two cycles per minute to ensure uniformity of the irradiation. The biotite standard ZBH-2506 (132.5 Ma; [32]) was used to monitor the neutron flux. 40Ar/39Ar stepwise heating analyses were performed at the Key Laboratory of Tectonics and Petroleum Resources, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China. Analyses were carried out using an Argus VI mass spectrometer combined with Coherent 50W CO2 laser system. The time of heating was 60 s for every single stage with a laser beam diameter of 2.5 mm, and the time of gas purification was 400 s with two Zr–Al scavengers. The detailed analytical procedures are given by [33]. K2SO4 and CaF2 crystals were analyzed to calculate Ca and K correction factors: (39Ar/37Ar)Ca = 8.984 × 10−4, (36Ar/37Ar)Ca = 2.673 × 10−4, (40Ar/39Ar)K = 5.97 × 10−3. The data-processing software and diagrams of plateau age used the ArArCALC 2.52 software by [34].
5. Results
5.1. Zircon U–Pb Dating
Zircon grains from the fine-grained biotite monzogranite sample had a length of 50–250 µm and width of 50–150 µm, with aspect ratios of 2:1 to 5:1. In addition, these zircon grains were euhedral or subhedral in shape and gray-black in CL imaginings (Figure 6). CL images show that these zircons have intense internal oscillatory zoning features, indicating a magmatic origin [35]. In addition, CL images also show that some of the zircon grains have cores, and these zircon cores might be from the magma source of the fine-grained biotite monzogranite. These zircon grains have Th and U contents of 441–2283 ppm and 163–756 ppm, respectively, with Th/U ratios of 0.33–0.51 (Table S1). Several zircon grains have relatively big errors (spot Nos. 04, 05, and 20), which were eliminated in the process of dating calculation. The 207Pb/235U and 206Pb/238U isotopic ratios were 0.1630–0.1843 and 0.0238–0.0256, respectively. Based on the 206Pb/238U ages, these zircon grains can be subdivided into two populations: 152–156 Ma (population 1) and 157–161 Ma (population 2). Isotopic ratios of population 1 are mainly plotted on or near the concordia curve (Figure 7a), yielding a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 154.2 ± 2.0 Ma (MSWD = 0.51, Figure 7b). Isotopic ratios of population 2 are also plotted on or near the concordia curve (Figure 7c), yielding a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 159.6 ± 1.9 Ma (MSWD = 0.09, Figure 7d).
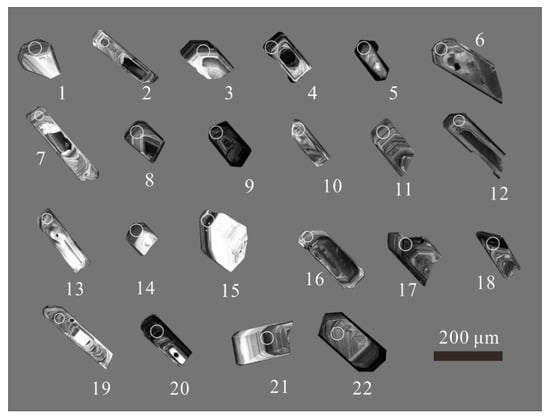
Figure 6.
Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircon grains of the fine-grained biotite monzogranite.
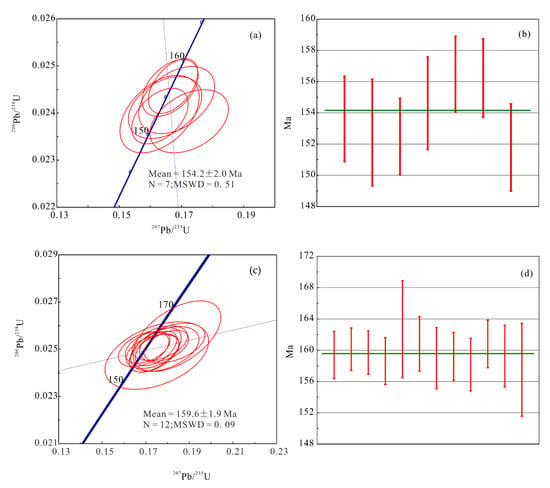
Figure 7.
Concordia diagrams of zircon U–Pb geochronological data for the fine-grained biotite monzogranite in the Maozaishan deposit. (a) Concordia diagram of zircons (Population 1); (b) Weight mean average plot of zircons (Population 1); (c) Concordia diagram of zircons (Population 2); (d) Weight mean average plot of zircons (Population 2);
5.2. Trace Element Compositions of Zircons
Trace element compositions of the zircon grains from the fine-grained biotite monzogranite are given in Table S2. Some zircon grains (spot Nos. 04, 05 and 20) are not discussed in this study, since the concordant degree of these three spots was below 90%.
Most of these zircon grains have high contents of heavy rare earth elements (HREEs; 472–1032 ppm) and relatively low contents of light rare earth elements (LREEs; 10–173 ppm), with LREE/HREE ratios of 0.02–0.23. They contain variable rare earth element (REEs) contents with ΣREE values of 483–1117 ppm. They also have negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu* = 0.04–0.16) and positive Ce anomalies (Ce/Ce* ratios of 0.98–214) (Figure 8). Some zircon grains contain a relatively high LREE content, which is different from the normal magmatic zircon grains and similar to the hydrothermal zircons [36]; however, these abnormal zircon grains show no feature of hydrothermal reformation in CL images. Therefore, the reason why these abnormal zircon grains contain high LREE contents remains unclear, and more studies are needed. In addition, these zircon grains also have relatively high Sn contents of ~0.74 ppm.
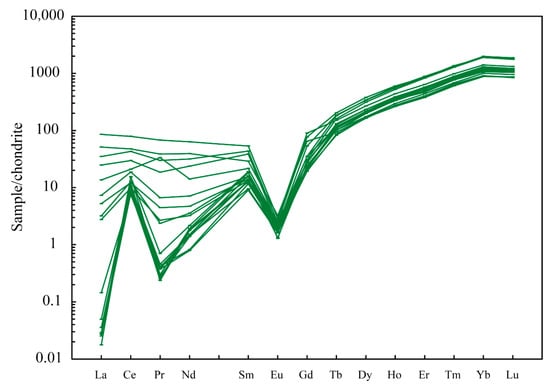
Figure 8.
Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (REE) chemistry of zircon grains for fine-grained biotite monzogranite in the Maozaishan deposit. The chondrite values are from [37].
5.3. Muscovite 40Ar–39Ar Dating
The Ar–Ar isotopic dating results for two muscovite samples are given in Table S3. The age spectra exhibit that the flat plateau of the samples (14D30-2 and 14D32-1) are featured by the release of 80.9% and 99.8% of 39ArK, respectively, indicating that K and radiogenic 40Ar in these samples are homogeneous and the K–Ar isotopic system for two muscovite samples were not affected by heating disturbances.
Twelve laser heating stages were carried out for sample 14D30-2, and stages four to 12 (840–1400 °C) obtained a flat age spectrum, yielding a well-defined plateau age of 154.7 ± 1.1 Ma (MSWD = 0.48, Figure 9a), consistent with the inverse isochron age of 154.6 ± 2.9 Ma (MSWD = 5.1, Figure 9b).
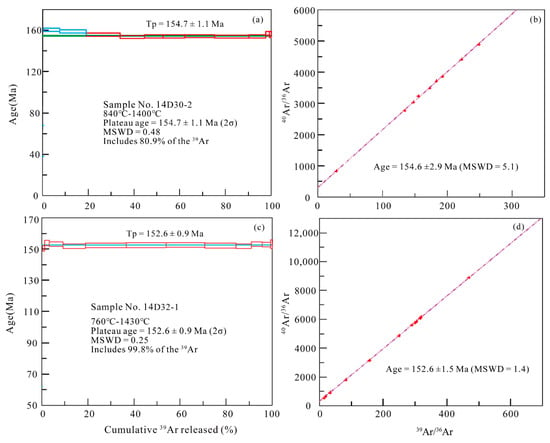
Figure 9.
39Ar–40Ar age spectra and isochron for muscovite samples of the greisen-type Sn ores from the Maozaishan deposit. (a) 39Ar–40Ar spectra of muscovite sample (No. 14D30-2); (b) Isochron age for of muscovite sample (No. 14D30-2); (c) 39Ar–40Ar spectra of muscovite sample (No. 14D32-1); (d) Isochron age for of muscovite sample (No. 14D32-1).
6. Discussion
6.1. Timing of Mineralization and Granitic Magmatism
The Dayishan composite pluton comprises a series of granitic rocks, including hornblende-bearing biotite granodiorite (monzogranite), two-mica (biotite) monzogranite (syenogranite), and tourmaline-bearing two-mica monzogranite (syenogranite), whose ages were 278–210 Ma, 181–156 Ma, and 148–128 Ma, respectively [27,28,38]. These ages indicate that the Dayishan composite pluton was formed by multi-stages of magmatism ranging from the Triassic to Cretaceous, however, it was proposed that the Middle Jurassic magmatism was closely related to the Sn mineralization in the Dayishan ore field [18,19]. In this study, high-precision LA-ICP-MS U–Pb dating results show that the fine-grained biotite monzogranite in the Maozaishan mining area has two ages of 154.2 ± 2.0 Ma (population 1) and 159.6 ± 1.9 Ma (population 2), with relatively low MSWD values of 0.51 and 0.09, respectively, indicating these ages are reliable. Furthermore, most of the zircon grains of population 2 have a larger size than population 1 (Figure 6), revealing that these zircon grains of population 2 might be likely the xenocrysts which were commonly crystallized in the early stage of magmatism in the magma chamber. These ages indicate that these granites might be the product of a multi-stage magmatic event. In this study, two Ar–Ar ages of hydrothermal muscovite from the greisen-type ore were obtained, with ages of 154.7 ± 1.1 Ma (MSWD = 0.48) and 152.6 ± 0.9 Ma (MSWD = 0.25). The low MSWD values and high release 39ArK of the two samples indicate that these ages are reliable, which could be regarded as the ore-forming ages of the Maozaishan Sn deposit, revealing that the Maozaishan deposit was formed in the Middle Jurassic. In addition, these Ar–Ar ages were consistent to the zircon age of population 1, revealing that the formation of the Maozaishan deposit is related to the final emplacement of the magma.
The Nanling Range, one of the largest Sn metallogenic domains in China, hosts the largest Sn resource and reserve (ca. 63%) [22]. In addition, the large-scale Sn mineralization in this region is closely related to the Middle Jurassic granitic magmatism, although some Triassic and Cretaceous mineralized events have been reported [39,40,41,42]. The ages of Sn-dominated polymetallic mineralization in the Dayishan ore field, including the Maozaishan deposit, are consistent with the period of large-scale W–Sn polymetallic mineralization event in Nanling Range (165–150 Ma) [6].
6.2. Physico-Chemical of Condition of the Granitic Magma
Zircon, one of the common accessory minerals in the granitoids, contains some specific elements, including Ti, Hf, Nb, and REEs, which could provide significant information on the physico-chemical conditions of the magmatic melt [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56]. It was proposed that the Ti behavior in the zircon grains were sensitive to the temperatures of the melt [50,51]. Due to this property, Ti contents could provide credible constraints on the crystallization temperatures of zircon grains [50,51,55]. In addition, some elements in zircon grains show multiple valence under a specific chemical condition, for example, Ce occurs as Ce4+ and Ce3+ under oxidizing and reducing conditions, respectively. Therefore, Ce could be used as the valid tracer to reflect the redox condition of the melt [43,44,49]. Based on the model proposed by Ferry and Watson [55] and Trail et al. [44], Ti-in-zircon temperatures and oxygen fugacity of the zircon grains from fine-grained biotite monzogranite were calculated, respectively, and the results are shown in Table S2. These zircon grains have relatively high temperatures of 638–754 °C (mean = 704 °C) and relatively low logf(O2) values of −18.9 to −15.8 (mean = −17.1). Furthermore, the samples were mainly plotted on the field between the IW (iron-wüstite) and FMQ (Fe2SiO4-Fe3O4 + SiO2) buffers, indicating a relatively low oxygen fugacity for this melt (Figure 10).
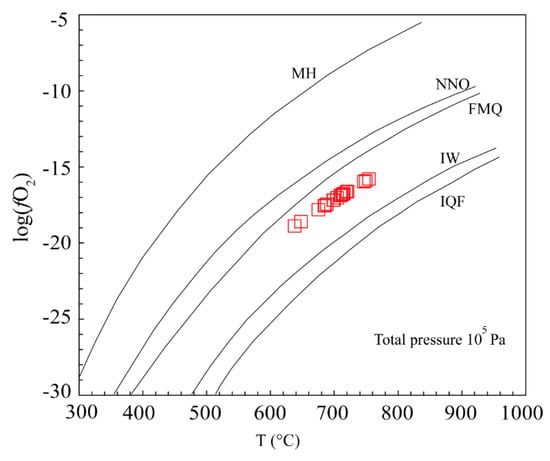
Figure 10.
T versus log(fO2) plot for the zircon grains from the fine-grained biotite monzogranite in the Maozaishan deposit (modified from [46]). MH: Fe3O4-Fe2O3; NNO: Ni-NiO; FMQ: Fe2SiO4-Fe3O4 + SiO2; IW: Fe-FeO; IQF: Fe + SiO2-Fe2SiO4.
6.3. Implications to the Sn Mineralization
Generally, tin (Sn) mineralization is commonly related to felsic magmatism, since Sn is enriched in these melts via partial melting of metal-rich crust components [54,55,56,57,58,59]. It was highlighted that these factors of the felsic melt, including the fractionated signature, source, and redox condition, play crucial roles in controlling the Sn mineralization [57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65]. Firstly, the worldwide cases have proved that highly fractionated granites are favorable for Sn mineralization, since Sn tends to be enriched in the late stage melt [12,13,59]. Secondly, magma, originated from these crustal rocks, including meta-sedimentary- and/or meta-volcanic-rocks, would be in favor of Sn mineralization, however, the mantle sources could also attribute to the Sn mineralization [66]. Thirdly, the low oxygen fugacity melts are essential for Sn mineralization, since Sn tends to be enriched in the residual melt at low oxygen fugacity conditions because of the Sn behavior in melt [59,61,67,68,69,70].
The fine grained biotite monzogranites, outcropping in the Maozaishan mining area, are characterized by high contents of SiO2 (69.3–74.7%) and Na2O + K2O (7.90–8.95%), high Rb/Sr ratios of 2.64–11.0, and high differentiation index (DI) values of 84–90 (total values of six normative minerals, including quartz, orthoclase, albite, nepheline, leucite, and kalsilite), indicating that they belong to the highly fractionated granites [27]. Furthermore, the low log(fO2) values of these granites, ranging from −18.9 to −15.8, indicate that the low oxygen fugacity of the ore-forming related melt in this deposit is in favor of Sn enrichment and mineralization [59,67,68,69,70]. In addition, these granites have εNd(t) values of −6.94 to −5.19, two stages Nd model ages of 1.41–1.37 Ga (TDM2Nd), εHf(t) values of −9.35 to −1.16, and two stages Hf model ages of 1.79–1.28 Ga (TDM2Hf), which are similar to those of the tin-bearing granites (εNd(t) values of −10 to −3, TDM2Nd of 1.7–1.1Ga, peak εHf(t) values of −7 to −3, and peak TDM2Hf ages of 1.6–1.2 Ga) and differ from those of the tungsten-bearing granites (εNd(t) values of −12 to −8, TDM2(Nd) of 1.9–1.7 Ga, peak εHf(t) values of −12 to −8, and peak TDM2Hf ages of 2.0–1.8 Ga) in the Nanling Range [6,27]. It was proposed that the tin-bearing granites in the Nanling Range were sourced from the partial melting of the Proterozoic basement rocks of the South China Block with mantle-derived magma invoked, whereas the tungsten-bearing granites were originated from the partial melting of the Proterozoic basement rocks of the South China Block with few or no involvement of mantle materials [6]. Therefore, these granitic rocks in this ore field show the common isotopic feature with those tin-bearing granites in the Nanling Range, indicating that they might be also the product of the crust–mantle interaction. In addition, these ore-forming related melts might be enriched in Sn, since zircon grains have a relatively high Sn content (up to 0.74 ppm).
Consequently, these highly fractionated Middle Jurassic granites of the Dayishan pluton with low oxygen fugacity and crust–mantle origin are similar to those Sn-related granites in the Nanling Range (e.g., Jiuyishan, Xitian, Qitianling, and Guposhan) [6,11,12,13]. These unique properties of these granites result in the formation of the Maozaishan deposit and other large-scale Sn deposits in the Nanling Range, making this region a significant Sn metallogenic domain in China.
7. Conclusions
1. Muscovite 40Ar/39Ar dating results suggest that the Maozaishan Sn deposit was formed at ca. 154 Ma, which is closely related to the coeval granitic magmatism. Zircon U−Pb dating results indicate that the ore-forming related granites were the result of multi-stage magmatism.
2. Ore related melt is characterized by high temperatures (638−754 °C) and low oxygen fugacity, with calculated (Ti-in-Zircon) temperatures (from 638 °C to 754 °C) and log(fO2) from −18.9 to −15.8.
3. These ore-forming related granites in the Dayishan ore field are characterized by highly fractionated signatures, low oxygen fugacity, and crust–mantle origin, which are in favor of the Sn mineralization.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/9/12/773/s1, Table S1: LA-ICP-MS zircon U–Pb dating data of the granites from the Maozaishan deposit, Table S2: LA-ICP-MS trace element compositions of the zircon grains of the granites in the Maozaishan deposit (ppm), Table S3: 40Ar/39Ar laser stepwise heating analytical data for two muscovite samples from the Maozaishan deposit.
Author Contributions
Y.L. conceived and designed the experiments; J.G., Z.Z., and Y.N. took part in the field campaigns; J.F. took part in the discussion; J.G. and Z.Q. analyzed the data; J.G. and Y.L. wrote the paper.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the China Geological Survey (grant no. DD20190154).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hu, R.; Chen, W.T.; Xu, D.; Zhou, M. Reviews and new metallogenic models of mineral deposits in South China: An introduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, M.; Pirajno, F. Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Guo, C.L.; Yuan, S.D.; Cheng, Y.B.; Chen, Y.C. Spatial–temporal distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in south China and their metallogenic settings. Geol. J. China Univ. 2008, 14, 510–526. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Guo, C.L.; Chen, Y.C. Large-scale tungsten–tin mineralization in the Nanling region, South China: Metallogenic ages and corresponding geodynamic processes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, W.W. Introduction to the special issue of Mesozoic W–Sn deposits in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 101, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Du, J.G.; Wu, Q.H.; Kong, H.; Li, H.; Wan, Q.; Xi, X.S.; Gong, Y.S.; Zhao, H.R.; et al. Formation and geodynamic implication of the Early Yanshanian granites associated with W–Sn mineralization in the Nanling Range, South China: An overview. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 1744–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Y.; Wu, Q.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Kong, H.; Li, H.; Xi, X.S.; Huang, Q.H.; Liu, B. Geochronology and Genesis of the Xitian W-Sn Polymetallic Deposit in Eastern Hunan Province, South China: Evidence from Zircon U–Pb and Muscovite Ar–Ar Dating, petrochemistry, and Wolframite Sr–Nd–Pb Isotopes. Minerals 2018, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Xiang, Y. Petrogenesis of Jurassic tungsten-bearing granites in the Nanling Range, South China: Evidence from whole-rock geochemistry and zircon U–Pb and Hf–O isotopes. Lithos 2017, 278, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Ireland, T.; Tian, X.; Hu, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.; Xu, D. Generation of Late Mesozoic Qianlishan A2-type granite in Nanling Range, South China: Implications for Shizhuyuan W–Sn mineralization and tectonic evolution. Lithos 2016, 266, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Zhu, J.; Lu, J.; Ma, D. Multiple-aged granitoids and related tungsten-tin mineralization in the Nanling Range, South China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 2045–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Ma, X. Petrogenesis of the Late Mesozoic Guposhan composite plutons from the Nanling Range, South China: Implications for W–Sn mineralization. Am. J. Sci. 2014, 314, 235–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Z.; Wu, X.B.; Cao, J.Y.; Hu, B.; Zhang, X.W.; Gong, Y.S.; Liu, W.D. Geochronology, Petrology, and Genesis of Two Granitic Plutons of the Xianghualing Ore Field in South Hunan Province: Constraints from Zircon U–Pb Dating, Geochemistry, and Lu–Hf Isotopic Compositions. Minerals 2018, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Jiang, S.; Yang, S.; Dai, B.; Lu, J. Mineral chemistry, trace elements and Sr–Nd–Hf isotope geochemistry and petrogenesis of Cailing and Furong granites and mafic enclaves from the Qitianling batholith in the Shi-Hang zone, South China. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Peng, J.; Hao, S.; Li, H.; Geng, J.; Zhang, D. In situ LA-MC-ICP-MS and ID-TIMS U–Pb geochronology of cassiterite in the giant Furong tin deposit, Hunan Province, South China: New constraints on the timing of tin–polymetallic mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 43, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Peng, J.; Hu, R.; Li, H.; Shen, N.; Zhang, D. A precise U–Pb age on cassiterite from the Xianghualing tin–polymetallic deposit (Hunan, South China). Miner. Depos. 2008, 43, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.D.; Zhang, D.L.; Du, A.D.; Qu, W.J. Re–Os dating of molybdenite from the Xintianling giant tungsten–molybdenum deposit in southern Hunan Province, China and its geological implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Kang, L.; Peng, J.; Zhong, H.; Gao, J.; Liu, L. In-situ elemental and isotopic compositions of apatite and zircon from the Shuikoushan and Xihuashan granitic plutons: Implication for Jurassic granitoid-related Cu–Pb–Zn and W mineralization in the Nanling Range, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 93, 382–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Luo, H.; Wu, Z.H.; Fan, X.W.; Xiong, J.; Yang, J.; Mou, J.Y. Rb–Sr isochron age and its geological significance of Baishaziling tin deposit in Dayishan ore field, Hunan Province. Earth Sci. 2014, 39, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, G.; Lü, Z.; Huang, Z.; Yu, X. Geological and geochronological constraints on the formation of the Jurassic Maozaishan Sn deposit, Dayishan orefield, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 94, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.; Hart, S.R.; Wendt, I. Realistic use of two-error regression treatments as applied to Rb–Sr data. Rev. Geophys. 1972, 10, 551–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gong, Y.; Pi, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, G.; Xiong, S.; Yao, S. Jurassic magmatism related Pb–Zn–W–Mo polymetallic mineralization in the central Nanling Range, South China: Geochronologic, geochemical, and isotopic evidence from the Huangshaping deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 91, 877–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, S.B.; Xu, J.X.; Zhang, J.J.; Zeng, Z.L.; Chen, F.W.; Li, H.Q.; Guo, C.L.; et al. Assessment on mineral resource in Nanling region and suggestion for further prospecting. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 81, 882–890. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C. The characteristic target-pattern regional ore zonality of the Nanling region, China (I). Geosci. Front. 2011, 2, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cao, J.; Kong, H.; Shao, Y.; Li, H.; Xi, X.; Deng, X. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the early Mesozoic Xitian granitic pluton in the middle Qin-Hang Belt, South China: Constraints from zircon U–Pb ages and bulk-rock trace element and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic compositions. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 128, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Santosh, M.; Huang, G. Zircon U–Pb geochronology and geochemistry of granites in the Zhuguangshan complex, South China: Implications for uranium mineralization. Lithos 2018, 308, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, F.; Peng, T.P. Mezosic mafic magmatism in Hunan-Jiangxi provinces and the lithospheric extension. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.X.; Xu, Z.W.; Zuo, C.H.; Lu, J.J.; Wang, R.C.; Miu, B.H.; Lu, R. Emplacement Time and Material Source of the Southern Dayishan Granitic Batholith (Taipingshan Body), Guiyang City, Hunan Province. Geol. Rev. 2017, 63, 395–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.Y.; Pan, Z.F.; Hou, Z.Q.; Li, J.D.; Che, Q.J.; Chen, H.M. Ore body distribution pattern, ore-controlling factors and prospecting potentiality in the Dayishan tin deposit. Geol. Prospect. 2005, 41, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, Z.; Gao, C.; Zong, K.; Wang, D. Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycling-induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U–Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons from Mantle Xenoliths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T. Correction of common lead in U–Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem. Geol. 2002, 192, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.S. Age determinations of 40Ar–40K, 40Ar–40Ar and radiogenic 40Ar released characteristics on K–Ar geostandards of China. Chin. J. Geol. 1983, 4, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.N.; Bai, X.J.; Liu, W.G.; Mei, L.F. Automatic 40Ar/39Ar dating technique using multicollector ArgusVI MS with home-made apparatus. Geochimica 2015, 44, 477–484. [Google Scholar]
- Koppers, A. ArArCALC—software for 40Ar/39Ar age calculations. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.; Schaltegger, U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P. Trace-element composition of hydrothermal zircon and the alteration of Hadean zircon from the Jack Hills, Australia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. An examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks. In The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell Science Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Su, J.B.; Li, J.H.; Dong, S.W. Zircon U–Pb dating of Dayishan and Tashan Plutons in Hunan Province and its tectonic implications. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2015, 36, 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, W.W.; Lu, L.; Wang, H. Constraints of multiple dating of the Qingshan tungsten deposit on the Triassic W(-Sn) mineralization in the Nanling region, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 94, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.H.; Chen, K.X.; Chen, K.X.; Liu, G.Q.; Fu, J.M.; Yin, J.P. Geological characteristics and Re–Os dating of molybdenites in Hehuaping tin–polymetallic deposit, Southern Hunan Province. Miner. Depos. 2006, 25, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Li, X.F.; Feng, Z.H.; Bai, Y. 40Ar/39Ar dating of muscovite from greisenized granite and geological significance in Limu tin deposit. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2009, 29, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Mao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, X.; Hao, D. An Early Cretaceous W–Sn deposit and its implications in southeast coastal metallogenic belt: Constraints from U–Pb, Re–Os, Ar–Ar geochronology at the Feie’shan W–Sn deposit, SE China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S.; Wu, K. Oxygen fugacity and porphyry mineralization: A zircon perspective of Dexing porphyry Cu deposit, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 206, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, D.; Watson, E.B.; Tailby, N.D. Ce and Eu anomalies in zircon as proxies for the oxidation state of magmas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 97, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, D.; Watson, E.B.; Tailby, N.D. The oxidation state of Hadean magmas and implications for early Earth’s atmosphere. Nature 2011, 480, 79–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, H.P.; Wones, D.R. Stability relations of the ferruginous Biotite. J. Petrol. 1962, 3, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, A.D.; Berry, A.J. An experimental study of trace element partitioning between zircon and melt as a function of oxygen fugacity. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 95, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A.P.; Wooden, J.L. Coupled elemental and isotopic analyses of polygenetic zircons from granitic rocks by ion microprobe, with implications for melt evolution and the sources of granitic magmas. Chem. Geol. 2010, 277, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.R.; Palin, J.M.; Campbell, I.H. Relative oxidation states of magmas inferred from Ce(IV)/Ce(III) in zircon: Application to porphyry copper deposits of northern Chile. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2002, 144, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B.; Harrison, T.M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1983, 64, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B.; Harrison, T.M. Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest Earth. Science 2005, 308, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.F.; McDowell, S.M.; Mapes, R.W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance. Geology 2003, 31, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; He, B. Implications from zircon-saturation temperatures and lithological assemblages for Early Permian thermal anomaly in northwest China. Lithos 2013, 182, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, L.A.; Watson, E.B. Rutile saturation in hydrous siliceous melts and its bearing on Ti-thermometry of quartz and zircon. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2007, 258, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.M.; Watson, E.B. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2007, 154, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehnke, P.; Watson, E.B.; Trail, D.; Harrison, T.M.; Schmitt, A.K. Zircon saturation re-revisited. Chem. Geol. 2013, 351, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štemprok, M. Solubility of tin, tungsten and molybdenum oxides in felsic magmas. Miner. Depos. 1990, 25, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K. Sedimentary Crust and Metallogeny of Granitoid Affinity: Implications from the Geotectonic Histories of the Circum-Japan Sea Region, Central Andes and Southeastern Australia. Resour. Geol. 2012, 62, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, R.L.; Kroner, U. Phanerozoic tin and tungsten mineralization—Tectonic controls on the distribution of enriched protoliths and heat sources for crustal melting. Gondwana Res. 2016, 31, 60–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnen, R.L.; Lichtervelde, M.; Černý, P. Granitic pegmatites as sources of strategic metals. Elements 2012, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B. Metallogeny of tin: Magmatic differentiation versus geochemical heritage. Econ. Geol. 1982, 77, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneresse, J. Element mobility in melts during successive intrusions of crustal-derived magmas and Sn–W mineralization. Resour. Geol. 2006, 56, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Förster, H.J.; Rickers, K.; Webster, J.D. Formation of extremely F-rich hydrous melt fractions and hydrothermal fluids during differentiation of highly evolved tin-granite magmas: A melt/fluid-inclusion study. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2005, 148, 582–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiter, K.; Müller, A.; Leichmann, J.; Gabašová, A. extural and chemical evolution of a fractionated granitic system: The Podlesí stock, Czech Republic. Lithos 2005, 80, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Mao, J.; Yang, Z. Geology and vein tin mineralization in the Dadoushan deposit, Gejiu district, SW China. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillitoe, R.H. Tin mineralisation above mantle hot spots. Nature 1974, 248, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.; Jungyusuk, N.; Khositanont, S.; Höhndorf, A.; Kuroda, Y. The tin-tungsten ore system of Pilok, Thailand. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1994, 10, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnen, R.L.; Pichavant, M.; Holtz, F.; Burgess, S. The effect of fO2 on the solubility, diffusion, and speciation of tin in haplogranitic melt at 850 °C and 2 kbar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnen, R.L.; Pichavant, M.; Holtz, F. The combined effects of fO2, and melt composition on SnO2, solubility and tin diffusivity in haplogranitic melts. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4965–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B. Metallogeny of Tin (Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990; 211p. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).