Degradation of Thiol Collectors Using Ozone at a Low Dosage: Kinetics, Mineralization, Ozone Utilization, and Changes of Biodegradability and Water Quality Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
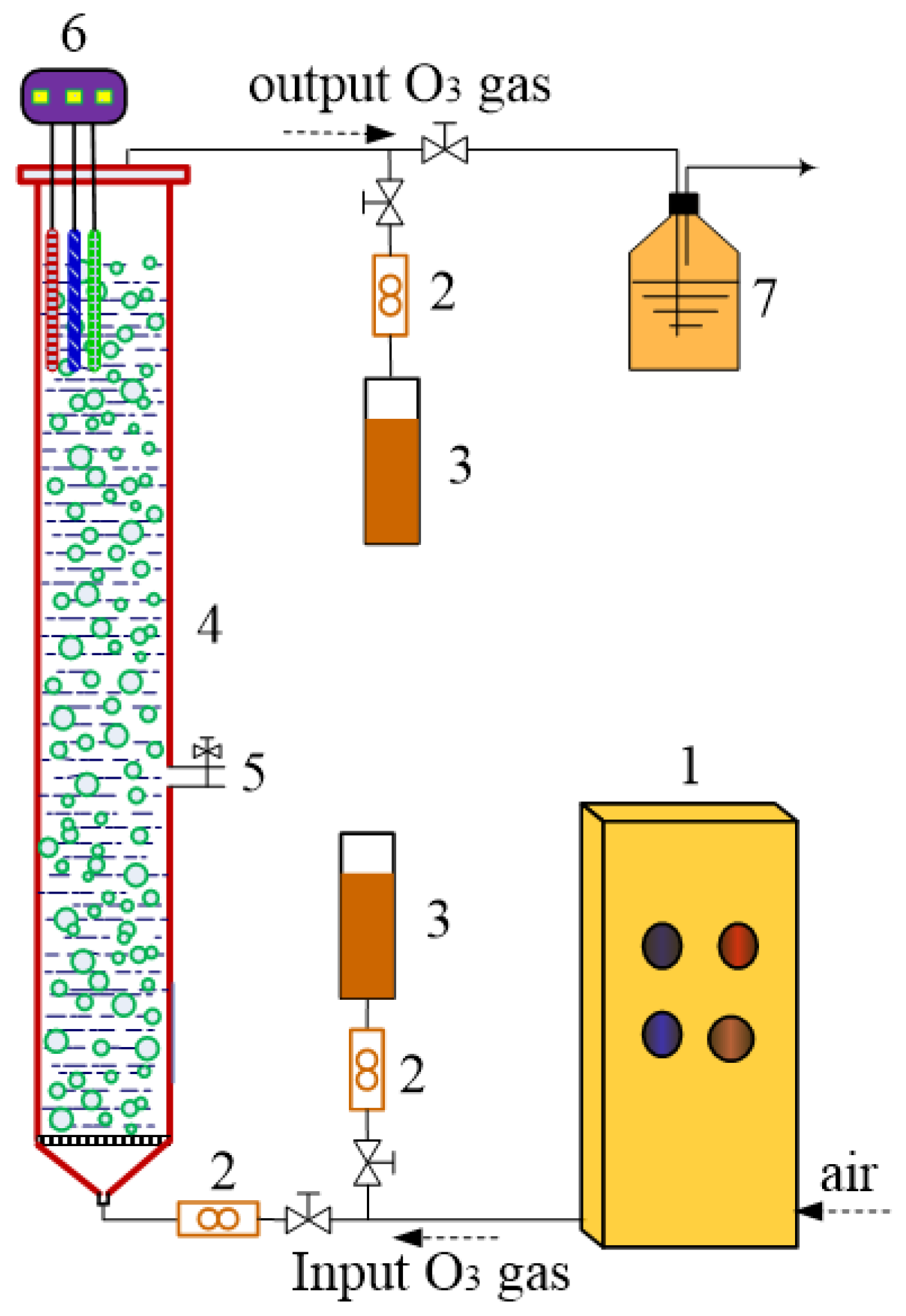
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. Analysis and Calculation
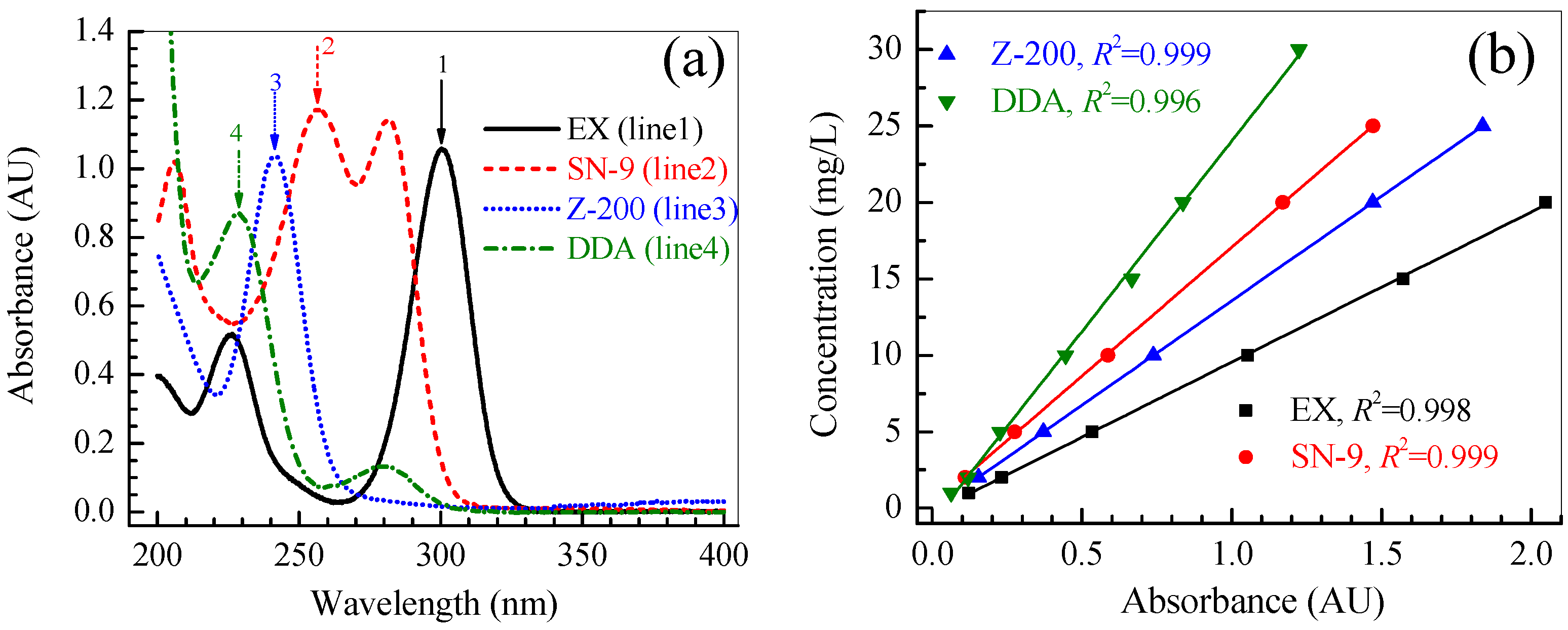
2.3.1. Determination of the Collector Concentration
2.3.2. Determination of COD, BOD5, TOC, and Concentration of SO42− ions
2.3.3. Analysis of Water Quality Parameters
2.3.4. Analysis of Gaseous O3 Concentration
3. Results and Discussion
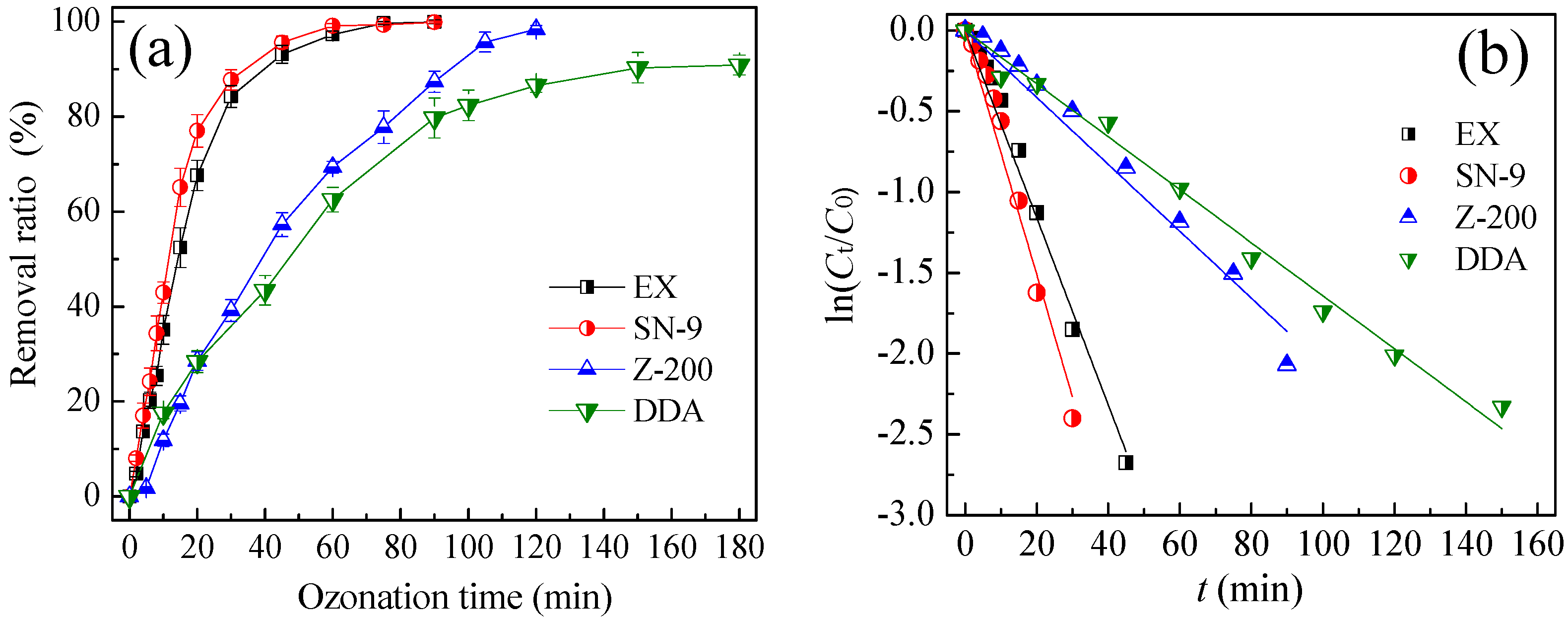
3.1. Degradation Kinetics of Thiol Collectors
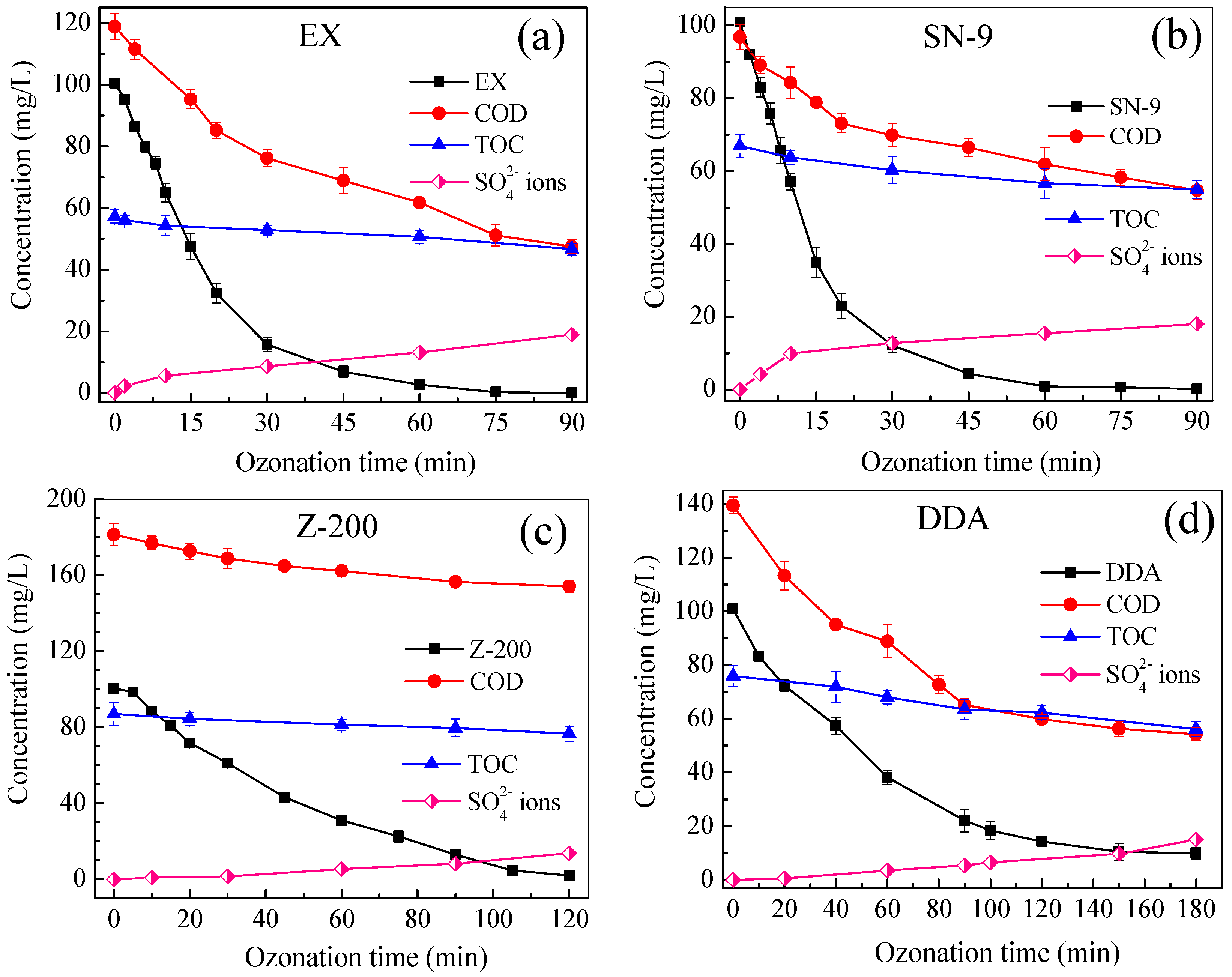
3.2. Carbon and Sulfur Mineralization of Thiol Collectors
3.3. Variation of Biodegradability
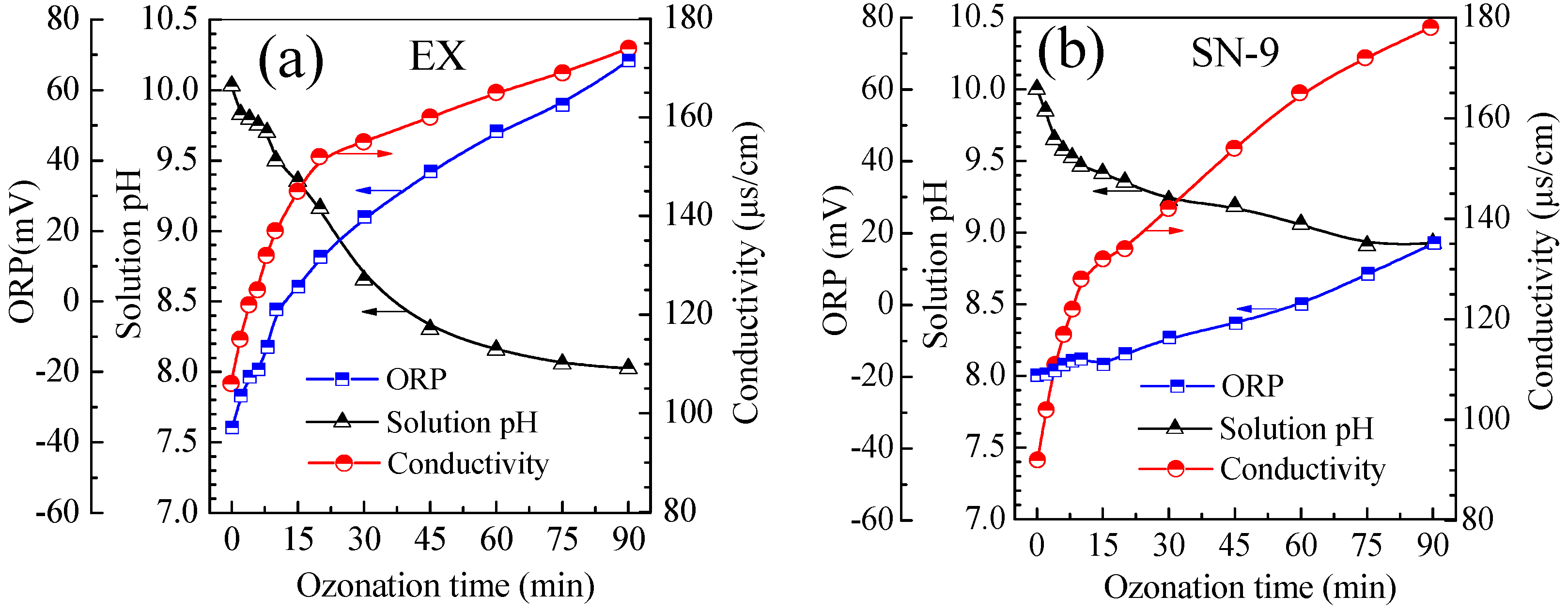
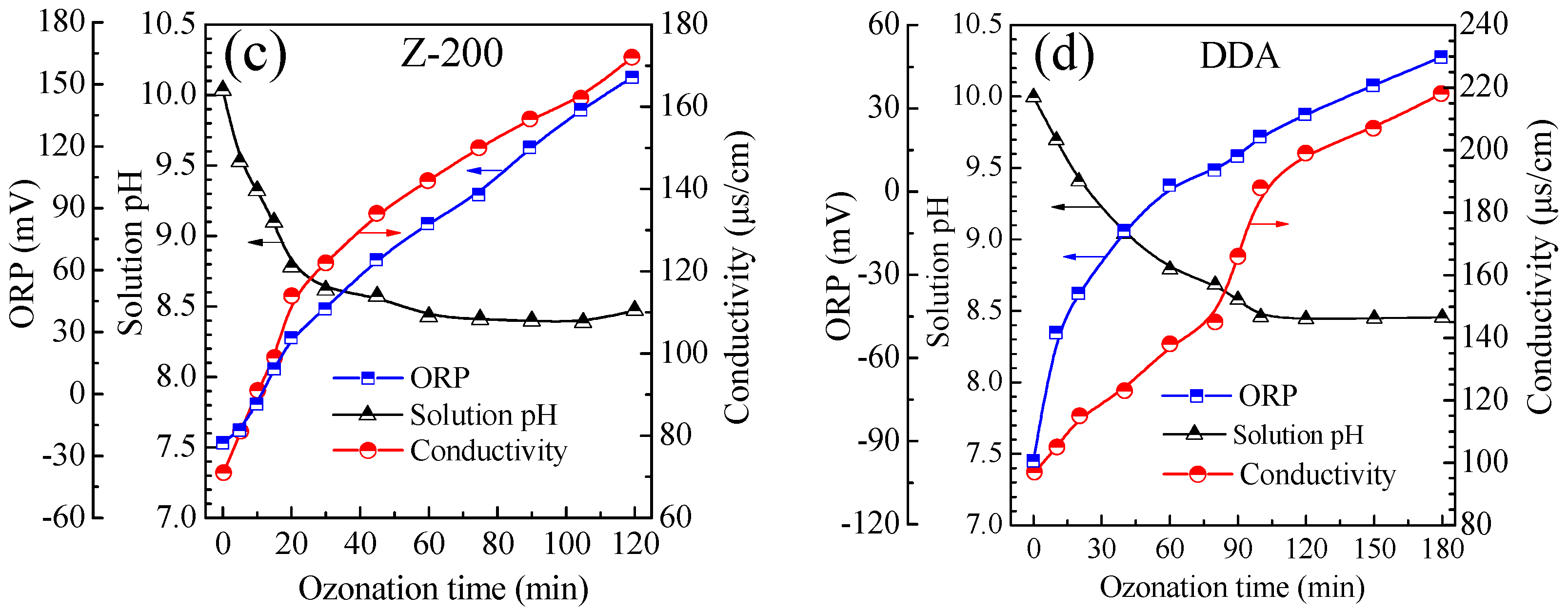
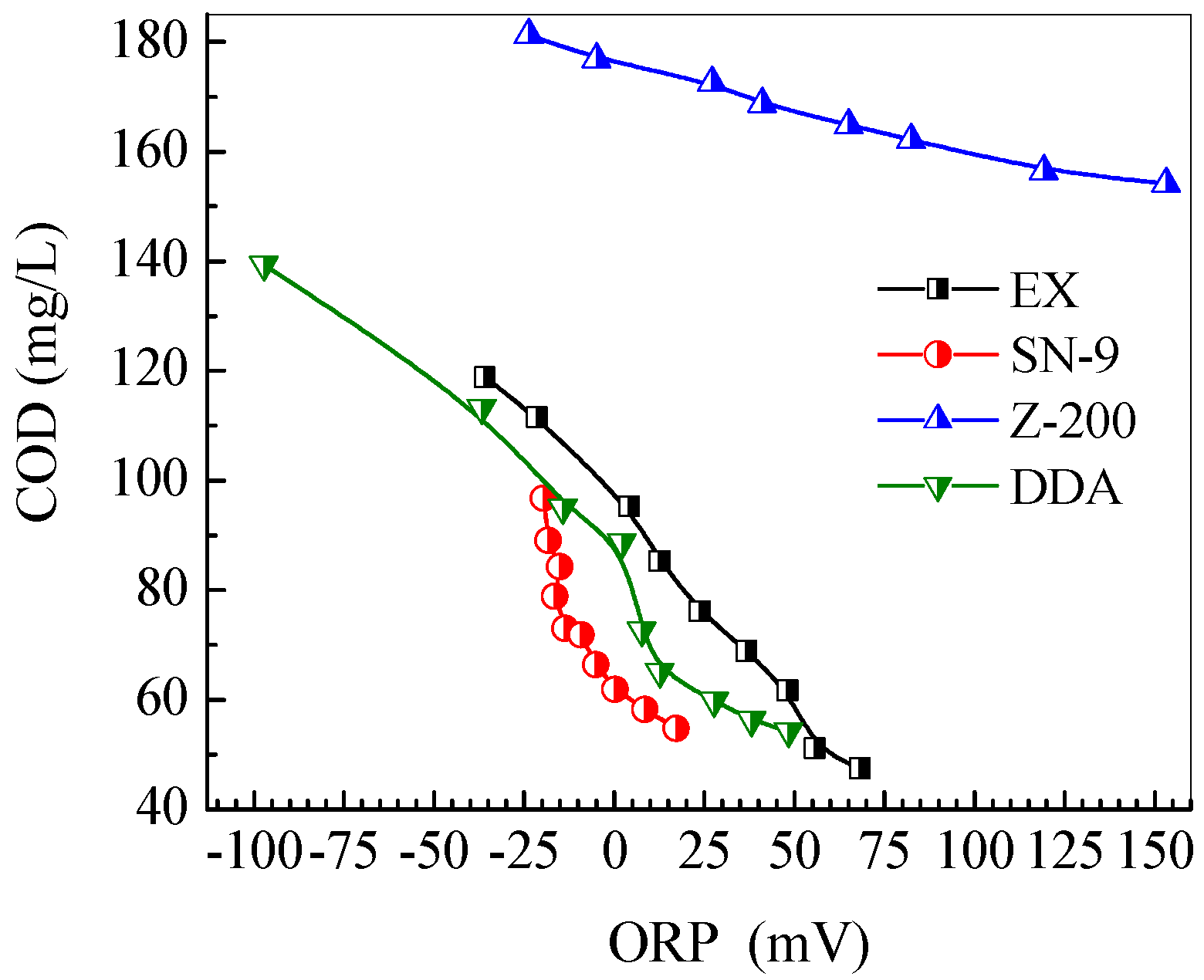
3.4. Evolution of Solution pH, ORP and Conductivity
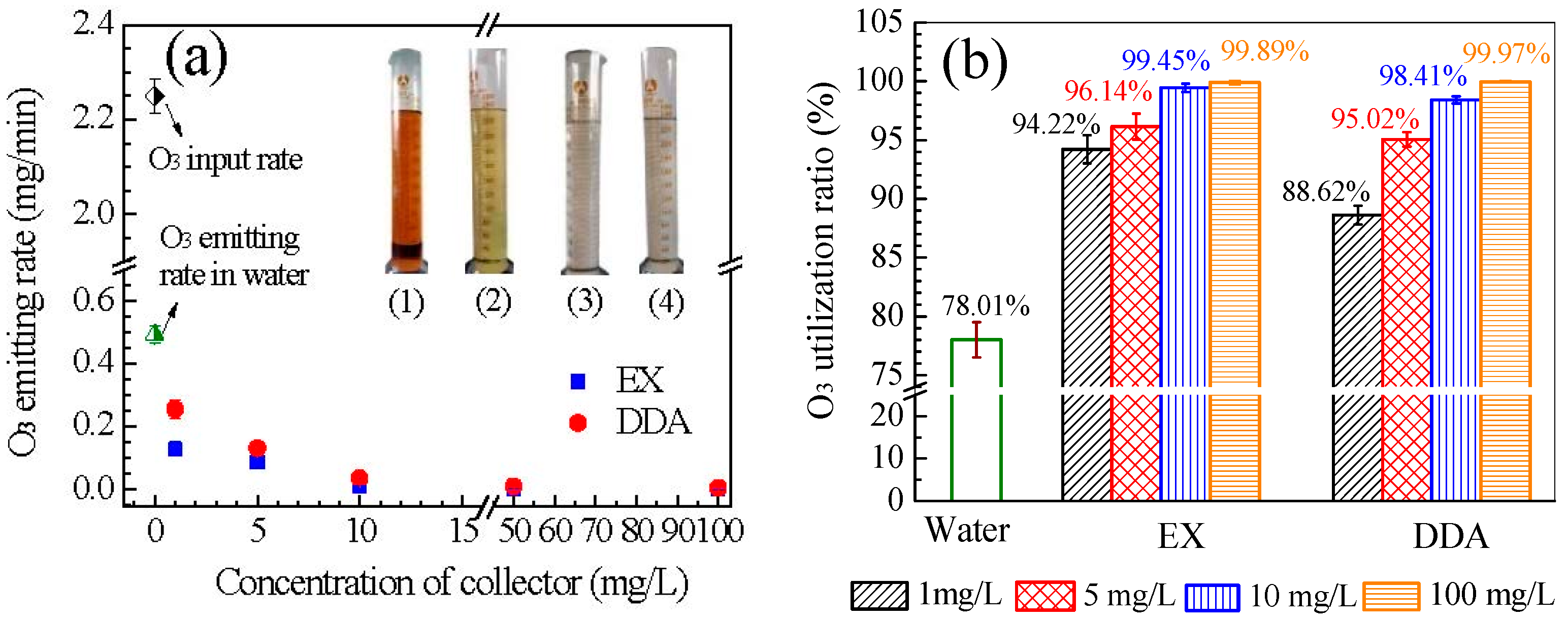
3.5. Ozone Utilization
3.6. Analysis of Energy Consumption Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bulatovic, S.M. Handbook of Flotation Reagents: Chemistry, Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Somasundaran, P.; Moudgil, B.M. Reagents in Mineral Technology; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.F. Teratogenic toxicity of butyl xanthate to frog embryos. Environ. Sci. Acta 1990, 10, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.X.; Forsling, W. The degradation kinetics of ethyl xanthate as a function of pH in aqueous solution. Miner. Eng. 1997, 10, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppinen, J.; Aaltonen, A.; Sihvonen, T.; Leppinen, J.; Sirén, H. Xanthate degradation occurring in flotation process waters of a gold concentrator plant. Miner. Eng. 2015, 80, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.R.; Finch, J.A. A review of water reuse in flotation. Miner. Eng. 1989, 2, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielczarski, J. The role of impurities of sphalerite in the adsorption of ethyl xanthate and its flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1986, 16, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, R.; Massinaei, M.; Zeraatkar Moghaddam, A. Removal of the residual xanthate from flotation plant tailings using modified bentonite. Miner. Eng. 2018, 119, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.X.; Tian, J.; Ren, J.; Xu, P.T.; Dai, Y.K.; Sun, S.Y.; Wu, C. Oxidation of aniline aerofloat in flotation wastewater by sodium hypochlorite solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.Q.; Sun, W.; Ouyang, K.; Zhang, L.M.; Hu, Y.H. Decomposition of sodium butyl xanthate (SBX) in aqueous solution by means of OCF: Ozonator combined with flotator. Miner. Eng. 2015, 70, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.F.; Feng, J.; Yang, T.W.; Yang, H.F. Comparison of alky xanthates degradation in aqueous solution by the O3 and UV/O3 process: Efficiency, mineralization and ozone utilization. Miner. Eng. 2015, 81, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.F.; Feng, J.; Yang, H.F.; Yang, T.W. Degradation of n-butyl xanthate by vacuum UV-ozone (VUV/O3) in comparison with ozone and VUV photolysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Gong, W.Q.; Mei, G.J.; Zhou, Q.; Bai, C.P.; Xu, N. Primary biodegradation of sulfide mineral flotation collectors. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, D.M.; Yoshida, M.I.; Takahashi, J.A.; Carvalho, C.F.; Stapelfeldt, F. Biodegradation studies on fatty amines used for reverse flotation of iron ore. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2010, 64, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Shafaei, S.Z.A.; Abdollahi, H.; Gharabaghi, M.; Chelgani, S.C. A comparative study on the effect of flotation reagents on growth and iron oxidation activities of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Minerals 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahiroglu, A.; Tarlan-Yel, E.; Sevimli, M.F. Treatment of combined acid mine drainage (AMD)-flotation circuit effluents from copper mine via Fenton’s process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvester, E.; Truccolo, D.; Hao, F.P. Kinetics and mechanism of the oxidation of ethyl xanthate and ethyl thiocarbonate by hydrogen peroxide. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2002, 2, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Xiong, P.; Zhan, W.; Xiong, L. Degradation of ethylthionocarbamate by pyrite-activated persulfate. Miner. Eng. 2018, 12, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Ouyang, L.L. Photocatalytic photodegradation of xanthate over Zn1-xMnxO under visible light irradiation. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 479, L4–L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, G.C.; Cayo, C.H.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Bernardes, A.M. Sodium isopropyl xanthate degradation by advanced oxidation processes. Miner. Eng. 2013, 45, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.C.; Wen, S.M.; Zhao, W.J.; Liu, J.; Liu, D. Effect of pH on surface characteristics and flotation of sulfidized cerussite. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2016, 52, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, C.E.; Kelebek, S. Sensitivity of pentlandite flotation in complex sulfide ores towards pH control by lime versus soda ash: Effect on ore type. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 127, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehelin, J.; Hoigné, J. Decomposition of ozone in water: Rate of initiation by hydroxide ions and hydrogen peroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1982, 16, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yershov, B.G.; Morozov, P.A.; Gordeev, A.V.; Seliverstov, A.F. Kinetic regularities of ozone decomposition in water. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2009, 31, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Ng, H.Y. Degradation of C.I. Reactive Red 2 (RR2) using ozone-based systems: Comparisons of decolorization efficiency and power consumption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Canonica, S.; von Gunten, U. Efficiency and energy requirements for the transformation of organic micropollutants by ozone, O3/H2O2 and UV/H2O2. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3811–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, R.M.; Ata, S.; Jameson, G.J. Study of froth behaviour in a controlled plant environment‒Part 2: Effect of collector and frother concentration. Miner. Eng. 2015, 81, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.H.; Chen, L.; Li, W.Q.; Ren, H.Q.; Li, K.; Wu, B.; Hu, H.D.; Xu, K. Insight into the characteristics, removal, and toxicity of effluent organic matter from a pharmaceutical wastewater treatment plant during catalytic ozonation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.Y.; Chu, L.B.; Wang, J.L. Advanced treatment of petrochemical wastewater by combined ozonation and biological aerated filter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9673–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Nagaraj, D.R.; Farinato, R.; Somasundaran, P. Study of xanthate decomposition in aqueous solutions. Miner. Eng. 2016, 93, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Hu, Y.H.; Peng, H.; Cao, X.F. Degradation of ethyl xanthate in flotation residues by hydrogen peroxide. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.F.; Chen, G.Q.; Ye, M.Y.; Sun, S.Y.; Ma, H.T.; Lin, W.X. Oxidation of potassium n-butyl xanthate with ozone: Products and pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Heredia, J.; Torregrosa, J.; Dominguez, J.R.; Peres, J.A. Kinetics of the reaction between ozone and phenolic acids present in agro-industrial wastewaters. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, F.J.; Garcia-Araya, J.F.; Alvarez, P.M. pH sequential ozonation of domestic and wine-distillery wastewaters. Water Res. 2001, 35, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiasn, N.; Hans, F.; Clemens, V.S. Ozonation of wastewater: Rate of ozone consumption and hydroxyl radical yield. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 15, 5990–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoigné, J.; Bader, H. Rate constants of reactions of ozone with organic and inorganic compounds in water-I Non-dissociating organic compounds. Water Res. 1983, 17, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoigné, J.; Bader, H. Rate constants of reactions of ozone with organic and inorganic compounds in water-II Dissociating organic compounds. Water Res. 1983, 17, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Lin, H.; Huo, H.X.; Dong, Y.B.; Xue, Q.Y.; Cao, L.X. Continuous removal of ore floatation reagents by an anaerobic–aerobic biological filter. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, K.A.; Sabari Prakasan, M.R. Biodegradation of sodium isopropyl xanthate by Paenibacillus polymyxa and Pseudomonas putida. Miner. Metall. Process. 2013, 30, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.F.; Chen, X.Q.; Yan, M.; Tang, T.Z.; Li, S.Y. Processing of aniline aerofloat wastewater with SBR system and its biodegradation mechanism. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 14, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar]
- López Valdivieso, A.; Sánchez López, A.A.; Ojeda Escamilla, C.; Fuerstenau, M.C. Flotation and depression control of arsenopyrite through pH and pulp redox potential using xanthate as the collector. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 81, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, N.I. Dixanthogen Formation in Flotation. J. Min. Sci. 2012, 48, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalti, M.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopic study of the kinetics of adsorption of ethyl xanthate on pyrite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 143, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava-Alonso, F.; Pecina-Treviño, T.; Pérez-Garibay, R.; Uribe-Salas, A. Pulp potential control in flotation: The effect of hydrogen peroxide addition on the extent of xanthate oxidation. Can. Metall. Q. 2002, 41, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Liu, W.G.; Duan, H.; Liu, W.B. Degradation mechanism study of amine collectors in Fenton process by quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 54, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, F.; Salhi, E.; Koester, O.; Kaiser, H.P.; Egli, T.; von Gunten, U. Mechanistic and kinetic evaluation of organic disinfection by-product and assimilable organic carbon (AOC) formation during the ozonation of drinking water. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2275–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramseier, M.K.; von Gunten, U. Mechanisms of phenol ozonation‒kinetics of formation of primary and secondary reaction products. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2009, 31, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.T.; Englehardt, J.D. Peroxone mineralization of chemical oxygen demand for direct potable water reuse: Kinetics and process control. Water Res. 2015, 73, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.P.; Liang, Y.Y.; Chang, C.N.; Chao, A.C. Differentiating ozone direct and indirect reactions on decomposition of humic substances. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, E.M.; Bertola, N.C.; Zaritzky, N.E. Monitoring the ozonation of phenol solutions at constant pH by different methods. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 9799–9809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, B.Y.; Nigmatullin, R.; Puma, G.L. Ozonation kinetics of cork-processing water in a bubble column reactor. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2473–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, J.R.; Bircger, K.G.; Tumas, W.; Tolman, C.A. Figure-of-merit for the technical development and application of advanced oxidation technologies for both electric- and solar-derived systems. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeldt, E.J.; Linden, K.G.; Canonica, S.; von Gunten, U. Comparison of the efficiency of OH radical formation during ozonation and the advanced oxidation processes O3/H2O2 and UV/H2O2. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3695–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goslan, E.H.; Gurses, F.; Banks, J.; Parsons, S.A. An investigation into reservoir NOM reduction by UV photolysis and advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Collector Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Structure | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| potassium ethyl xanthate | C2H4OCS2K | 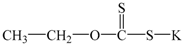 | EX |
| sodium diethyl dithiocarbamate | (C2H5)2NCSSNa |  | SN-9 |
| O-isopropyl-N-ethyl thionocarbamate | (CH3)2CHOCSNHC2H5 | 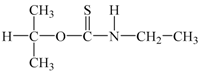 | Z-200 |
| dianilino dithiophoshoric acid | (C6H5NH)2PSSH | 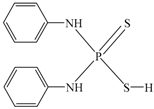 | DDA |
| Collector | Kinetic Equation | kcollector (min−1) | t1/2 (min) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EX | Ct = C0·e−0.0579t | 0.0579 | 11.97 | 0.9903 |
| SN-9 | Ct = C0·e−0.0687t | 0.0687 | 10.09 | 0.9918 |
| Z-200 | Ct = C0·e−0.0194t | 0.0194 | 35.69 | 0.9835 |
| DDA | Ct = C0·e−0.0164t | 0.0164 | 42.27 | 0.9967 |
| Collector | Removal Ratio of Collector (%) | Removal of COD | Mineralization Ratio (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal Ratio of COD (%) | kCOD (min−1) | R2 | Carbon | Sulfur | ||
| EX | 99.98 (90 min) | 60.04 (90 min) | 0.0111 | 0.9843 | 18.42 (90 min) | 11.95 (90 min) |
| SN-9 | 99.87 (90 min) | 43.47 (90 min) | 0.00694 | 0.9838 | 17.84 (90 min) | 21.21 (90 min) |
| Z-200 | 87.38 (90 min) | 13.67 (90 min) | 0.00188 | 0.9858 | 8.31 (90 min) | 12.54 (90 min) |
| 98.37(120 min) | 14.97 (120 min) | 11.82 (120 min) | 20.92 (120 min) | |||
| DDA | 79.71 (90 min) | 53.25 (90 min) | 0.00779 | 0.9888 | 16.35 (90 min) | 7.89 (90 min) |
| 90.91(180 min) | 61.11 (180 min) | 26.05 (180 min) | 21.98 (180 min) | |||
| Collector | EX | SN-9 | Z-200 | DDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE/O (kWh/(m3·order)) | 0.45 | 0.33 | 3.18 | 6.06 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, P.; Lin, X.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Peng, H. Degradation of Thiol Collectors Using Ozone at a Low Dosage: Kinetics, Mineralization, Ozone Utilization, and Changes of Biodegradability and Water Quality Parameters. Minerals 2018, 8, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110477
Fu P, Lin X, Li G, Chen Z, Peng H. Degradation of Thiol Collectors Using Ozone at a Low Dosage: Kinetics, Mineralization, Ozone Utilization, and Changes of Biodegradability and Water Quality Parameters. Minerals. 2018; 8(11):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110477
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Pingfeng, Xiaofeng Lin, Gen Li, Zihao Chen, and Hua Peng. 2018. "Degradation of Thiol Collectors Using Ozone at a Low Dosage: Kinetics, Mineralization, Ozone Utilization, and Changes of Biodegradability and Water Quality Parameters" Minerals 8, no. 11: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110477
APA StyleFu, P., Lin, X., Li, G., Chen, Z., & Peng, H. (2018). Degradation of Thiol Collectors Using Ozone at a Low Dosage: Kinetics, Mineralization, Ozone Utilization, and Changes of Biodegradability and Water Quality Parameters. Minerals, 8(11), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110477





