Sulfur Isotope Fractionation as an Indicator of Biogeochemical Processes in an AMD Passive Bioremediation System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
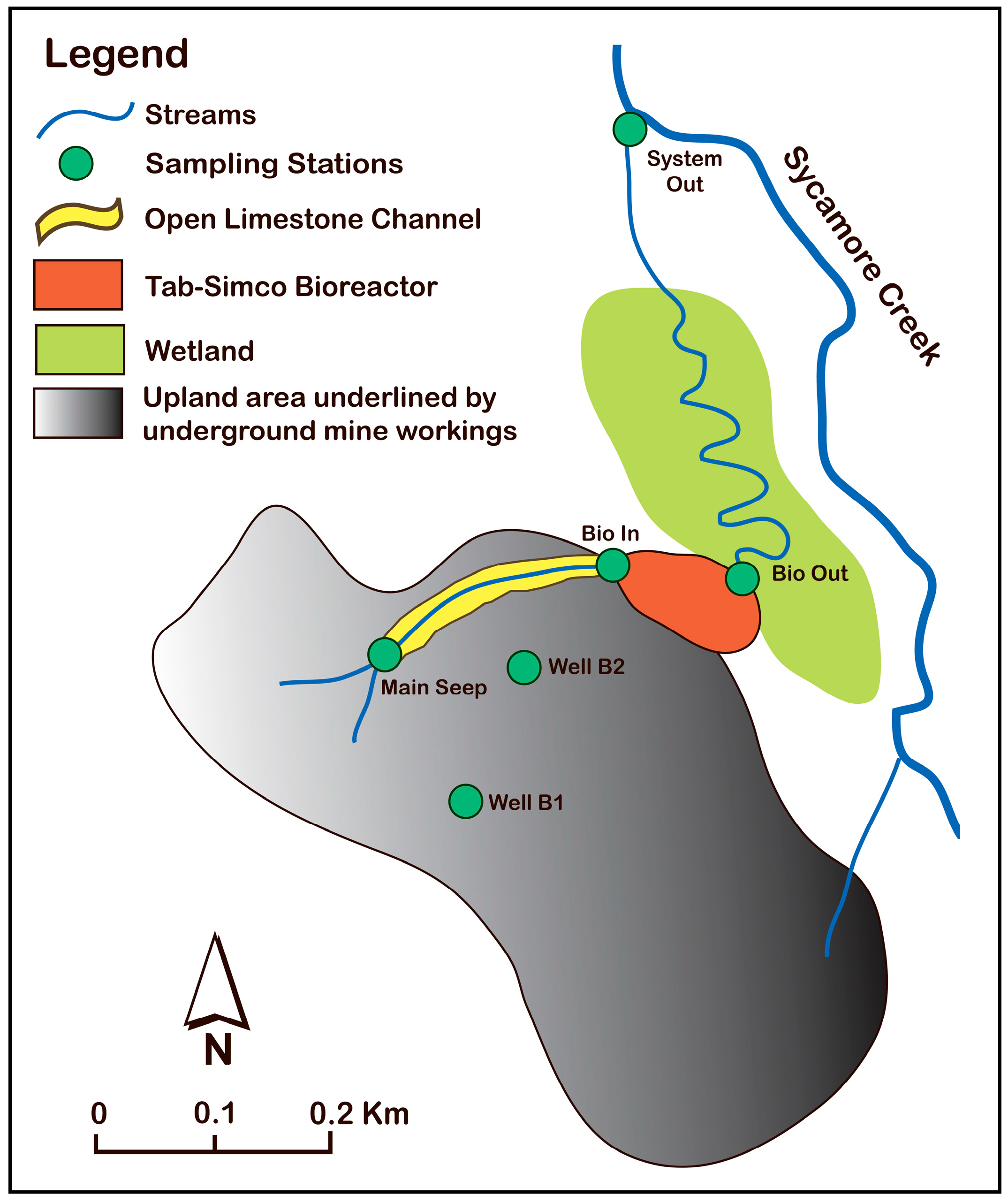
2.1. Description of the Tab-Simco Site
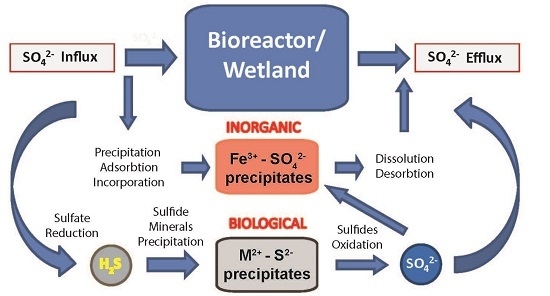
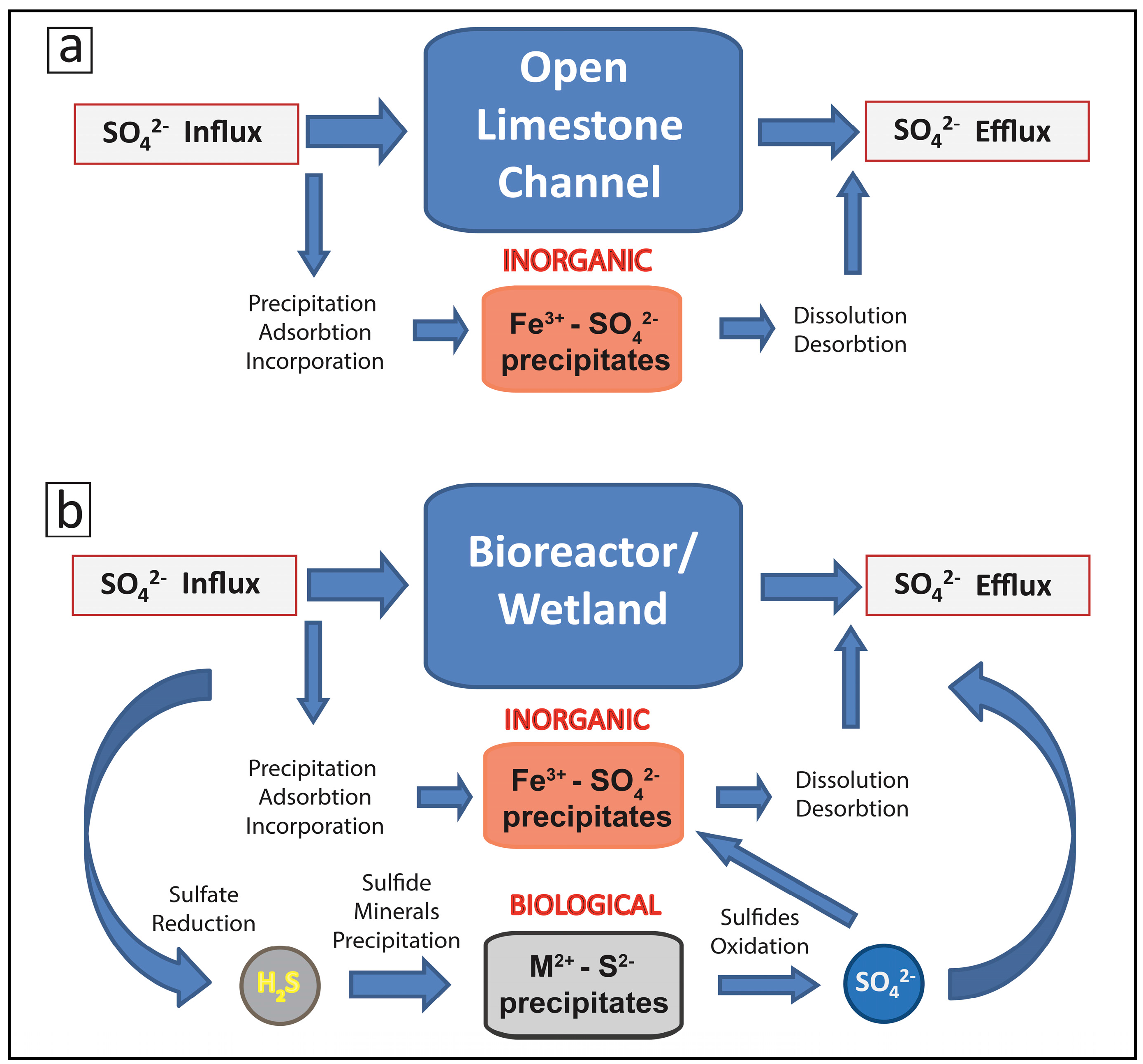
2.2. Biogeochemical Sulfur Cycling in the Tab-Simco PBS
2.3. Sulfur Isotope Systematics in the Tab-Simco PBS
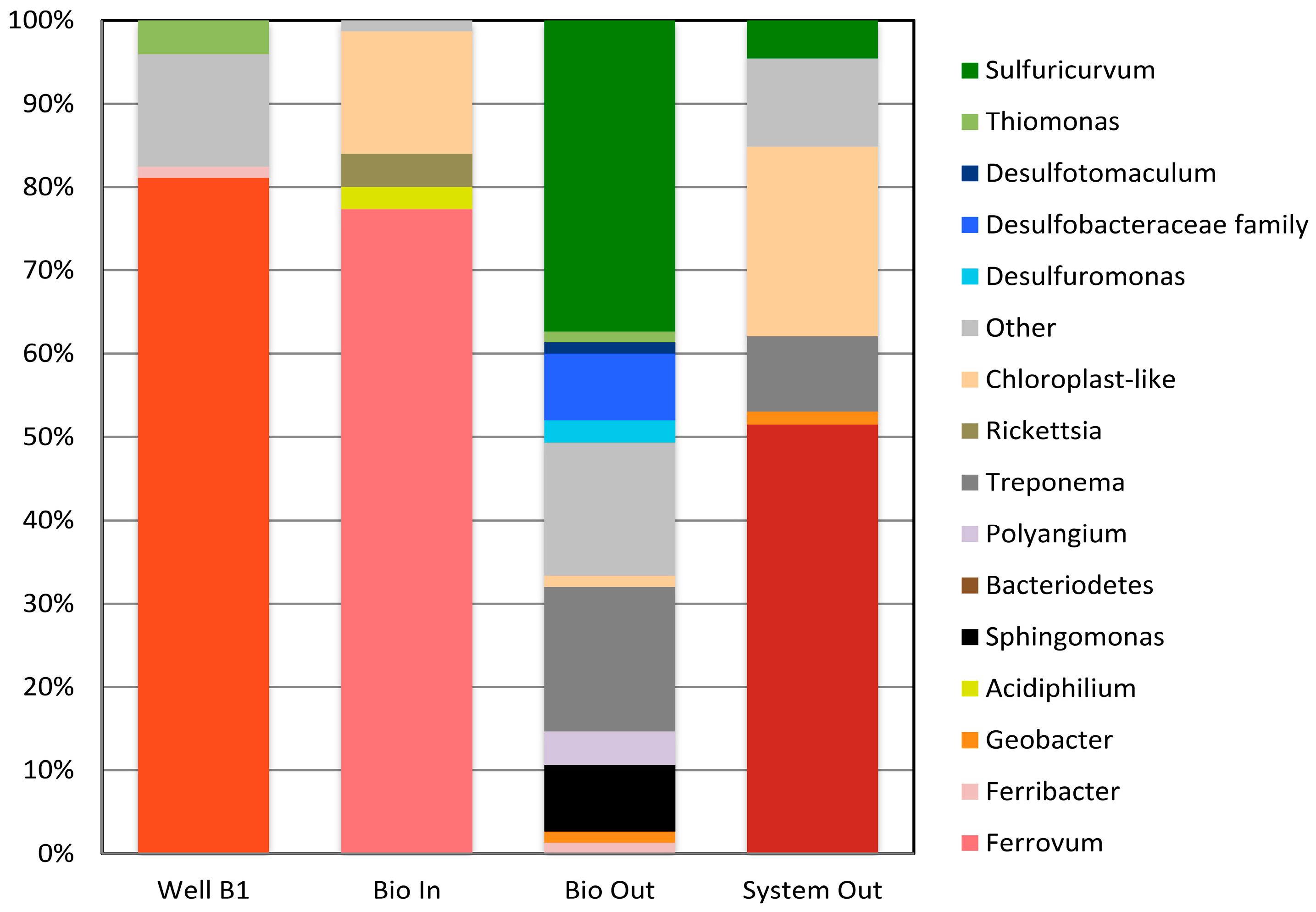
2.4. Microbial Communities in the Tab-Simco PBS
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Geochemical Analyses
3.2. Stable Isotope Measurements
4. Results and Discussion
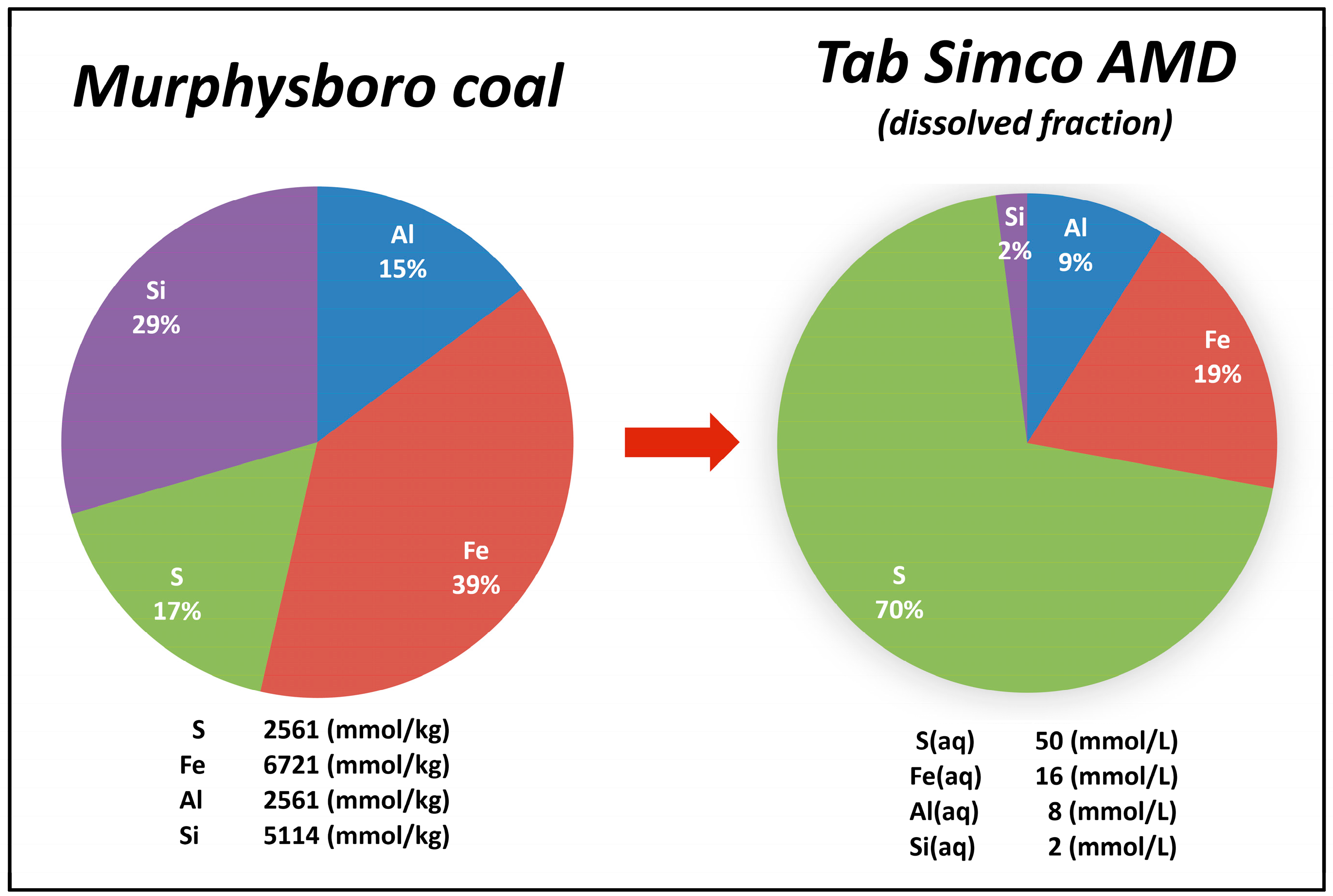
4.1. Coal Composition and Sulfur Compounds in Coal and Coal Mining Waste
4.2. AMD Drainage Characteristics
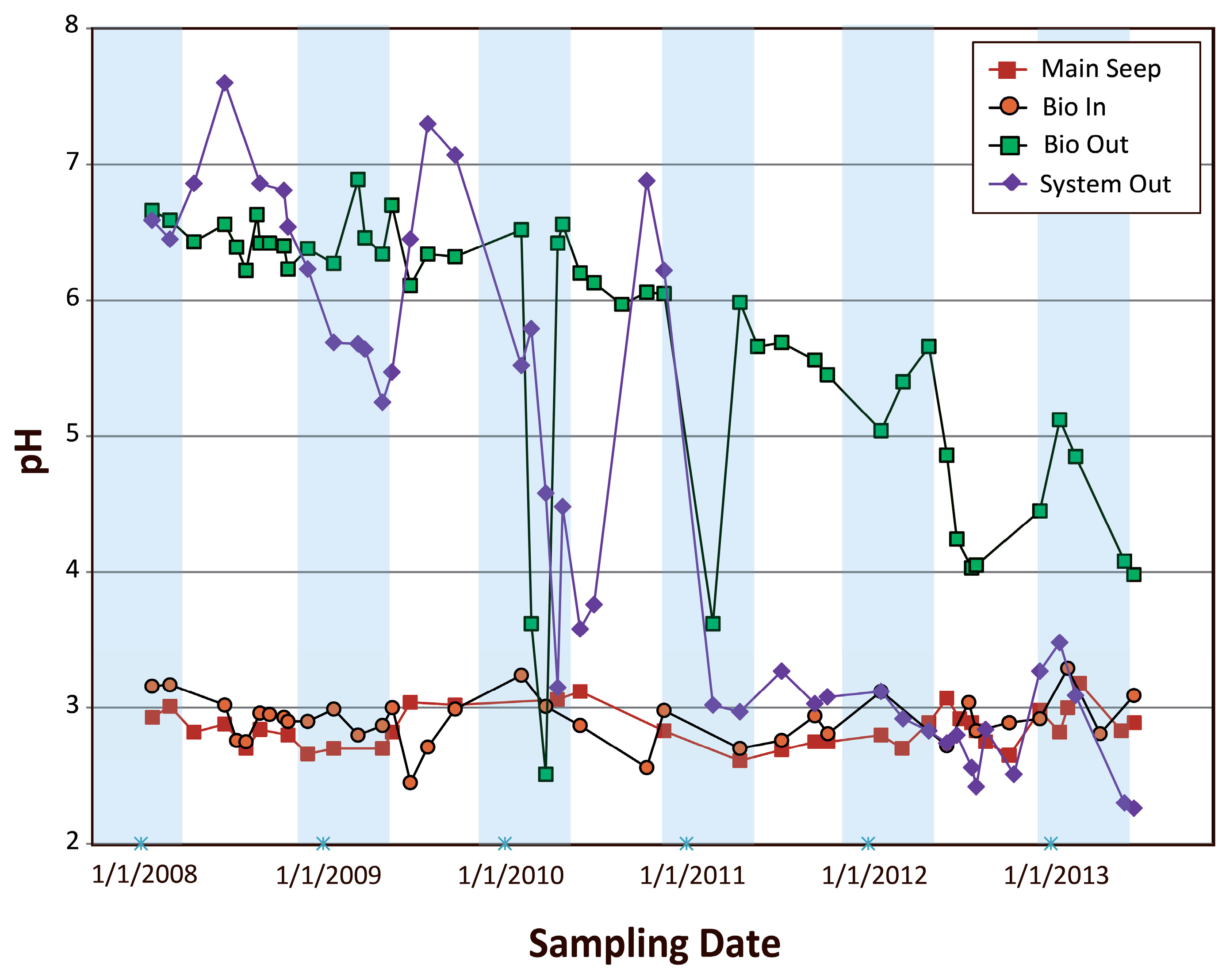
4.2.1. Examination of pH Variations
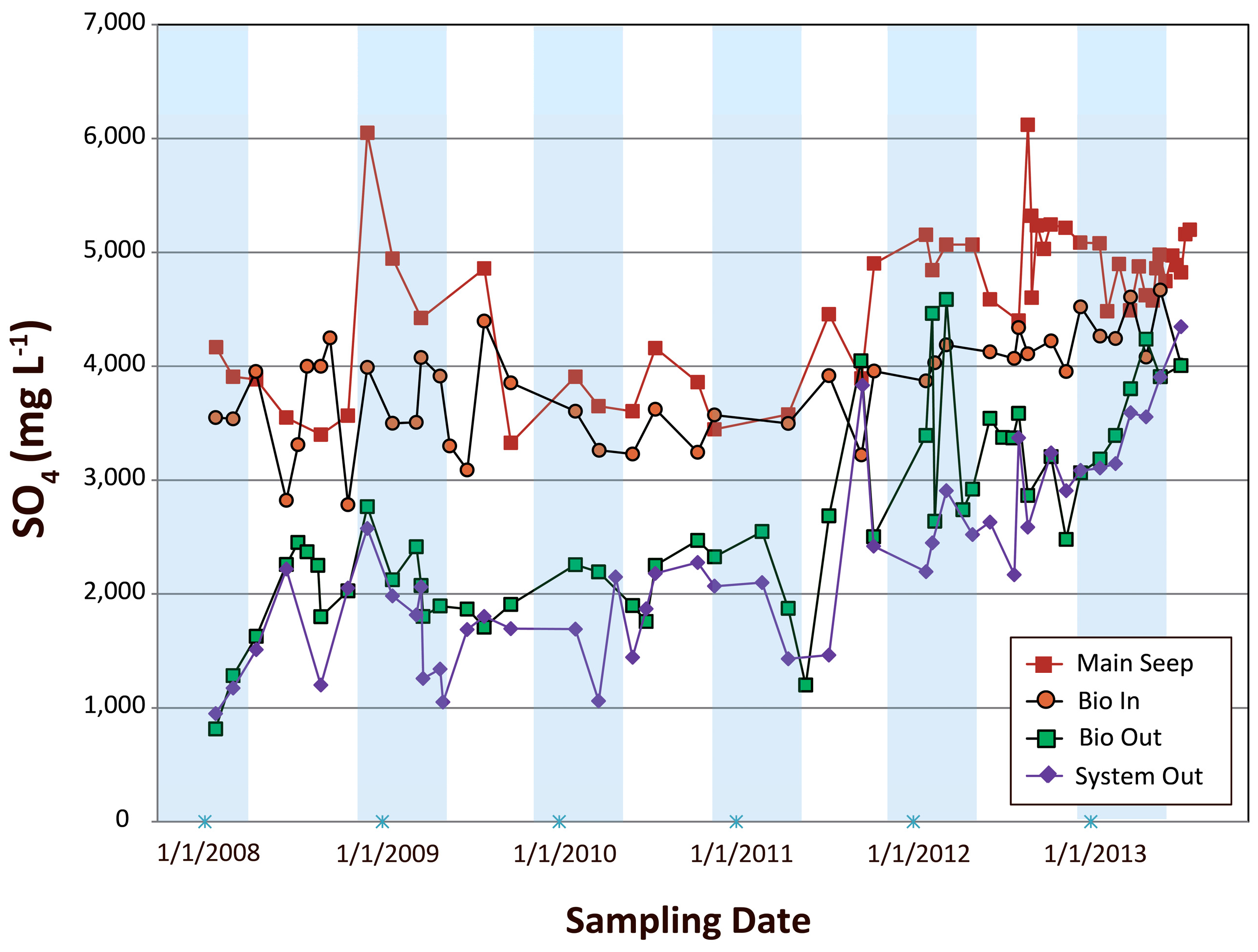
4.2.2. Examination of SO42− Concentration Variations
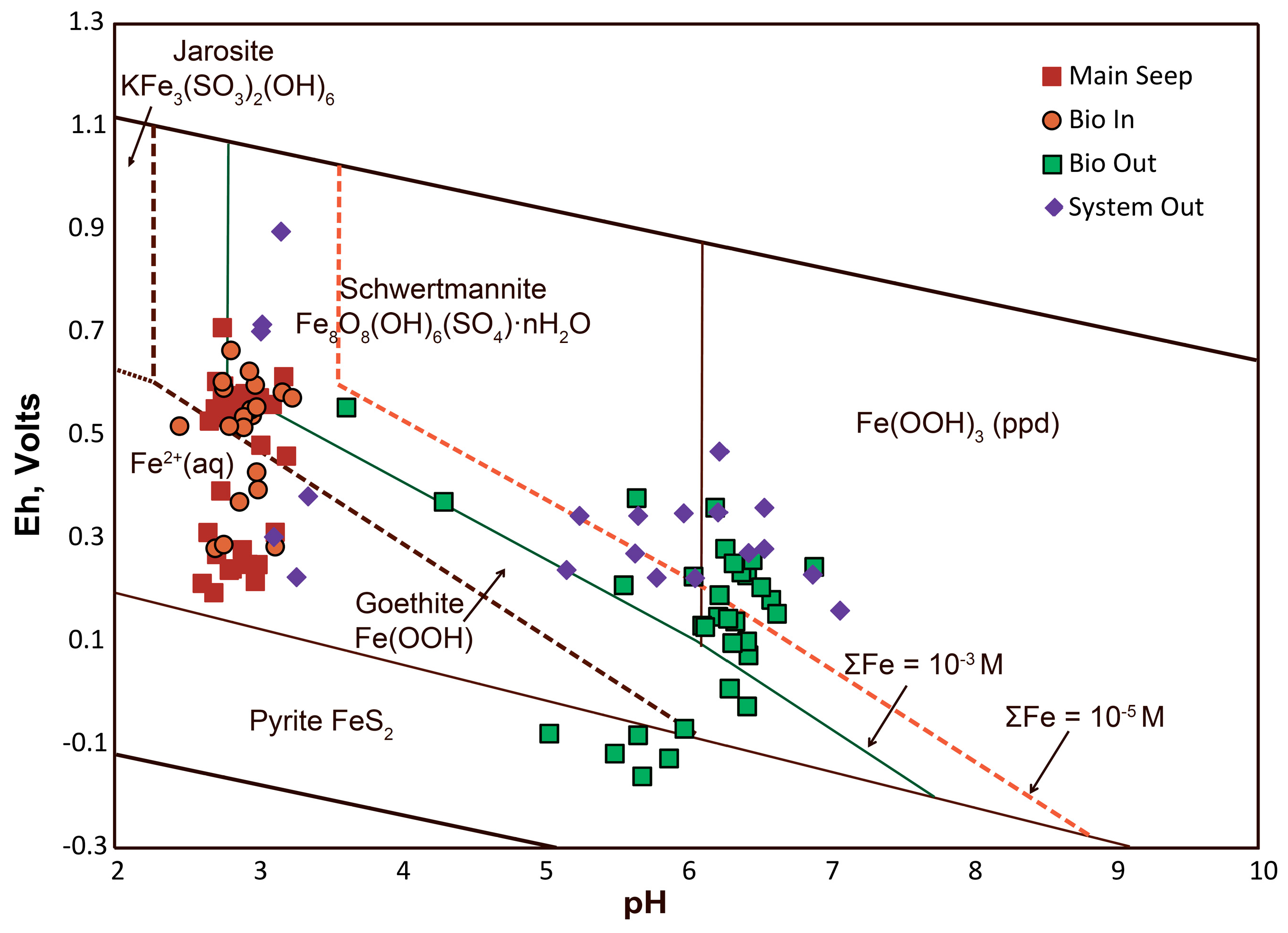
4.2.3. Examination of Eh-pH Diagram
4.3. Sulfur Isotope Patterns in the Tab-Simco PBS
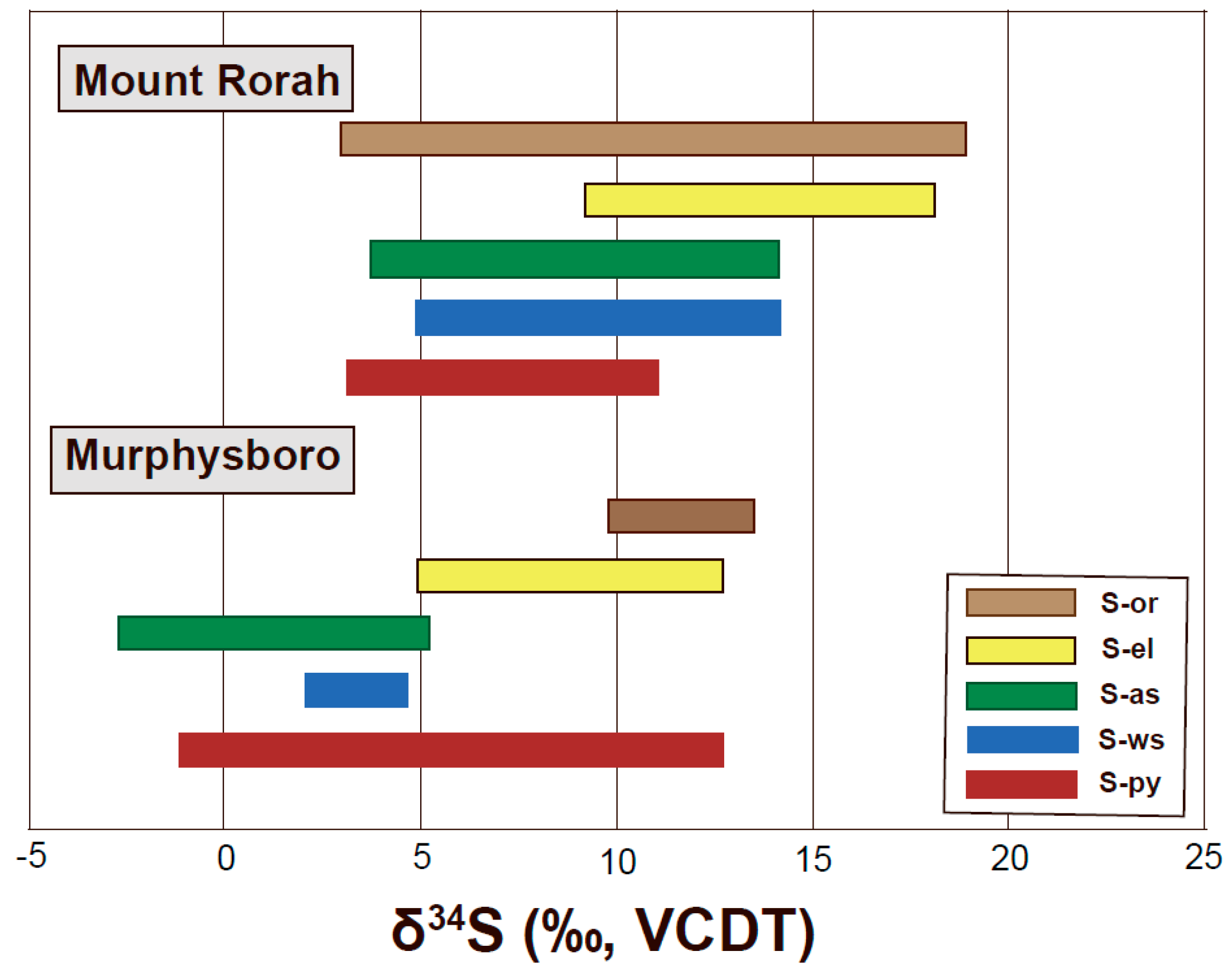
4.3.1. Sulfur Isotope Composition of Murphysboro and Mt. Rorah Coals
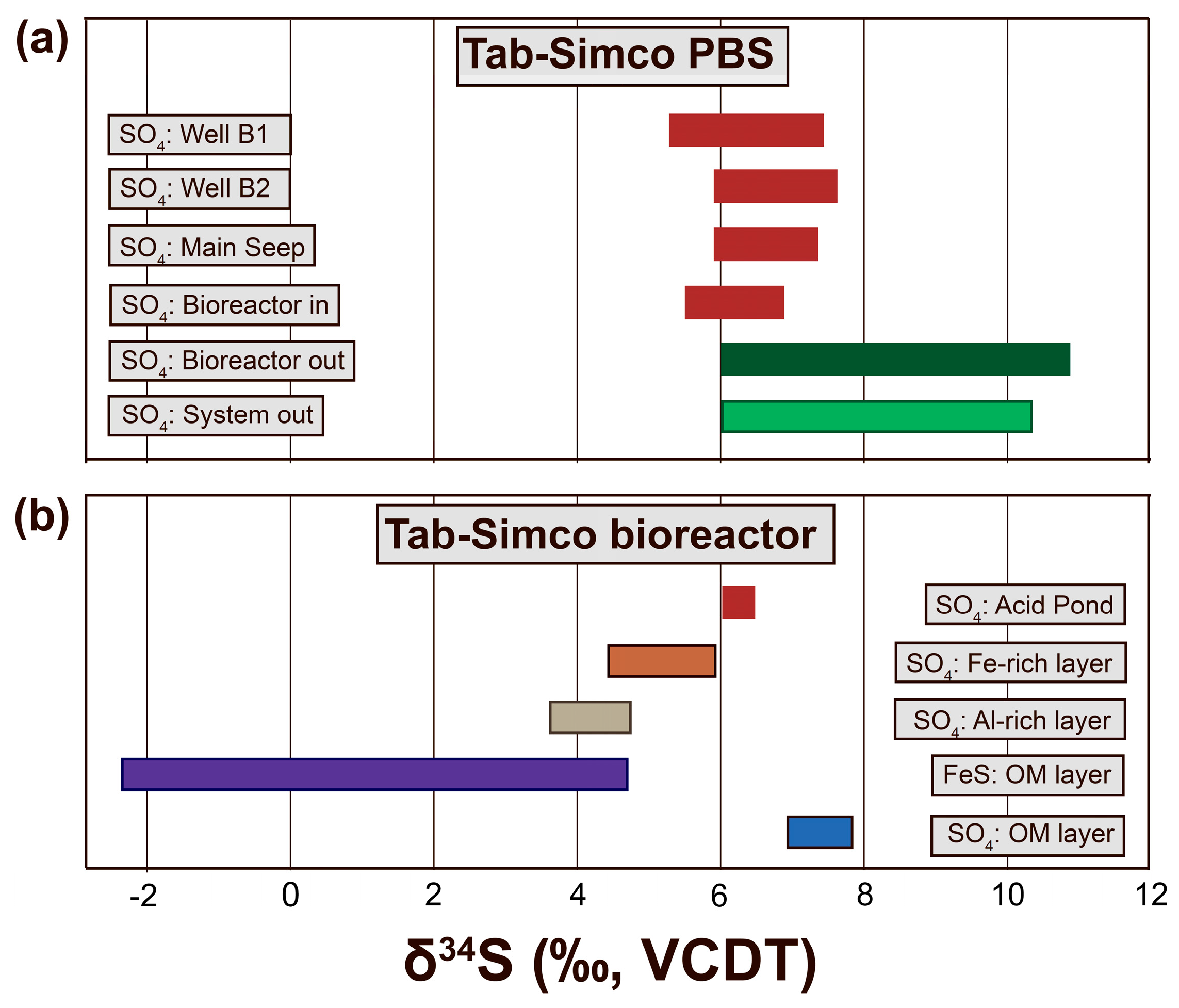
4.3.2. Sulfur Isotope Composition of Dissolve Sulfate in AMD
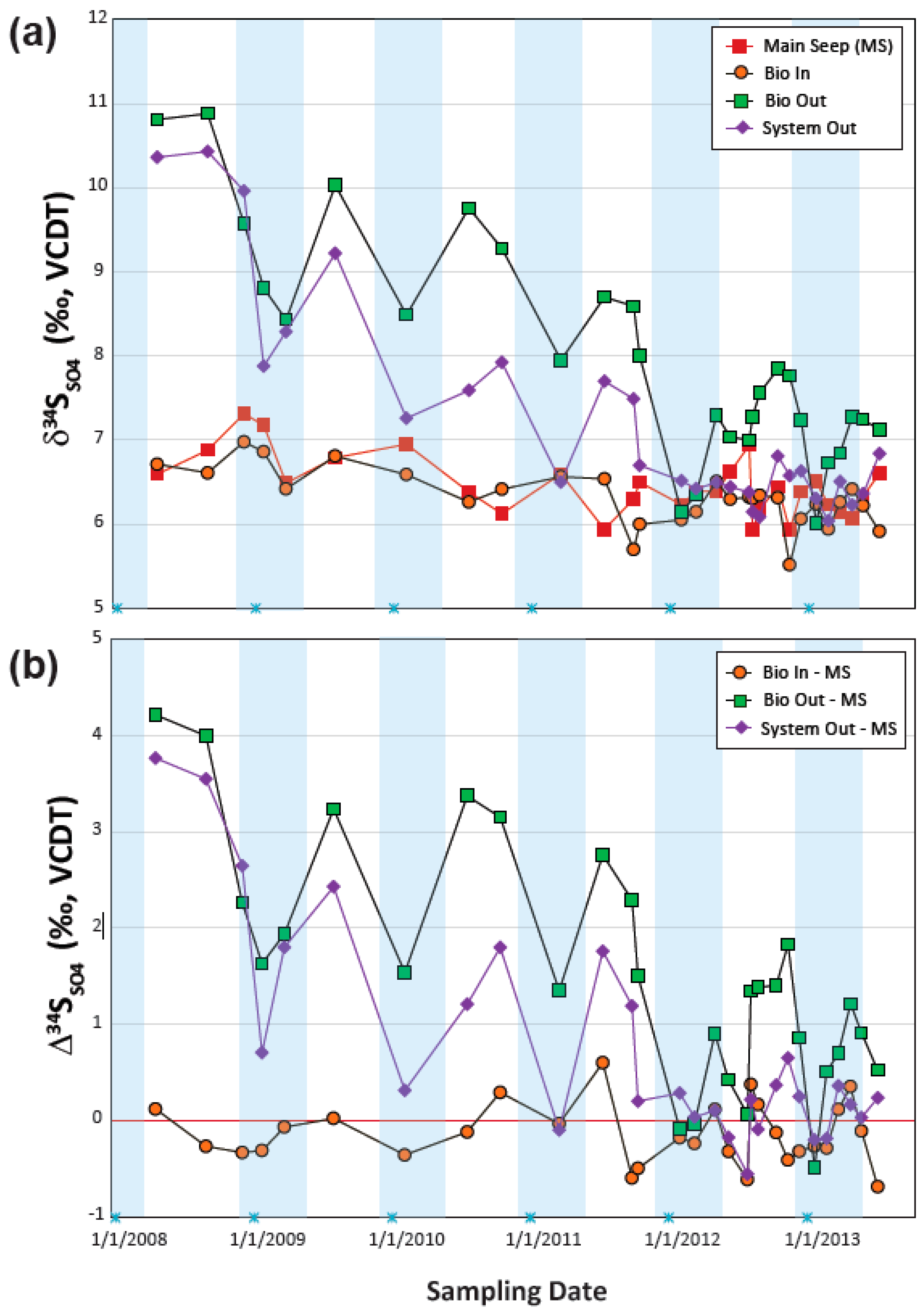
4.3.3. Sulfur Isotope Temporal Trends
4.3.4. Using Sulfur Isotopes to Fingerprint BSR Processes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cravotta, C.A. Dissolved metals and associated constituents in abandoned coal-mine discharges, Pennsylvania, USA. Part 1: Constituent concentrations and correlations. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 166–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Eshleman, K.N.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; Hendryx, M.S.; Lemly, A.D.; Likens, G.E.; Loucks, O.L.; Powers, M.E.; et al. Mountain Mining Consequences. Science 2010, 327, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Lindberg, T.T.; Merola, B.R.; Ruhl, L.; Warner, N.R.; White, A.; Dwyer, G.S.; Di Giulio, R.T. Isotopic imprints of mountaintop mining contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10041–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson-Edwards, K. Tackling mine wastes. Science 2016, 352, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behum, P.T.; Lefticariu, L.; Bender, K.S.; Segid, Y.T.; Burns, A.S.; Pugh, C.W. Remediation of coal-mine drainage by a sulfate-reducing bioreactor: A case study from the Illinois coal basin, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, S162–S166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefticariu, L.; Sutton, S.R.; Bender, K.S.; Lefticariu, M.; Pentrak, M.; Stucki, J.W. Impacts of detrital nano-and micro-scale particles (dNP) on contaminant dynamics in a coal mine AMD treatment system. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. Health Effects from Exposure to High Levels of Sulfate in Drinking Water Study; EPA 815-R-99-001; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; Volume 4607.
- Geurts, J.J.; Sarneel, J.M.; Willers, B.J.; Roelofs, J.G.; Verhoeven, J.T.; Lamers, L.P. Interacting effects of sulphate pollution, sulphide toxicity and eutrophication on vegetation development in fens: A mesocosm experiment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2072–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Mitchell, A. Impact of sulfate pollution on anaerobic biogeochemical cycles in a wetland sediment. Water Res. 2012, 46, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orem, W.; Fitz, H.C.; Krabbenhoft, D.; Tate, M.; Gilmour, C.; Shafer, M. Modeling sulfate transport and distribution and methylmercury production associated with Aquifer Storage and Recovery implementation in the Everglades Protection Area. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2014, 3, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willacker, J.J.; Eagles-Smith, C.A.; Ackerman, J.T. Mercury bioaccumulation in estuarine fishes: Novel insights from sulfur stable isotopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Hallberg, K.B. Acid mine drainage remediation options: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neculita, C.M.; Zagury, G.J.; Bussière, B. Passive treatment of acid mine drainage in bioreactors using sulfate-reducing bacteria. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, M.B.; Blowes, D.W.; Condon, P.D.; Ptacek, C.J. Organic carbon amendments for passive in situ treatment of mine drainage: Field experiments. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branam, T. Optimization of Bioreactor Cell Design for Treating Low-Flow Acid Mine Drainage in the Midwest: Model Development and Demonstration; Final Report OSM Cooperative Agreement Number: S06PC12060; Indiana Geological Survey: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Reeder, M.D.; Reeder, T.D.; Olyphant, G.A. Assessment of Two Field-Scale Sulfate Reducing Bioreactors Using Sulfur Isotopes; National Meeting of the American Society of Mining and Reclamation: Pittsburgh, PA, USA; Bridging Reclamation, Science and the Community: Madrid, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, A.S.; Pugh, C.W.; Segid, Y.T.; Behum, P.T.; Lefticariu, L.; Bender, K.S. Performance and microbial community dynamics of a sulfate-reducing bioreactor treating coal generated acid mine drainage. Biodegradation 2012, 23, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefticariu, L.; Walters, E.R.; Pugh, C.W.; Bender, K.S. Sulfate reducing bioreactor dependence on organic substrates for remediation of coal-generated acid mine drainage: Field experiments. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.E.; Wheeler, M.C.; Nordstrom, D.K. Isotope composition of sulfate in acid mine drainage as a measure of bacterial oxidation. Nature 1984, 308, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E. Biogeochemistry of sulfur isotopes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2001, 43, 607–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, D.; Rioux, J.P.; Roy, M. Geochemistry of iron and sulfur in the zone of microbial sulfate reduction in mine tailings. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 2, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praharaj, T.; Fortin, D. Indicators of microbial sulfate reduction in acidic sulfide-rich mine tailings. Geomicrobiol. J. 2004, 21, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druhan, J.L.; Steefel, C.I.; Conrad, M.E.; DePaolo, D.J. A large column analog experiment of stable isotope variations during reactive transport: I. A comprehensive model of sulfur cycling and δ34S fractionation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 124, 366–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefticariu, L.; Pratt, L.M.; Ripley, E.M. Mineralogic and sulfur isotopic effects accompanying oxidation of pyrite in millimolar solutions of hydrogen peroxide at temperatures from 4 to 150 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 4889–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefticariu, L.; Schimmelmann, A.; Pratt, L.M.; Ripley, E.M. Oxygen isotope partitioning during oxidation of pyrite by H2O2 and its dependence on temperature. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 5072–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.A. Characterization of an acid mine drainage site in Southern Illinois. In Proceedings of the 2002 National Meeting American Society of Mining and Reclamation, Lexington, KY, USA, 9–13 June 2002.
- Korose, C.P.; Elrick, S.D. Coal geology of Illinois. In 2010 Keystone Coal Industry Manual; Coal Age; Mining Media International: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 456–467. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, L.L. Addressing acid mine drainage from complex conditions at the Tab-Simco mine (Jackson County, Illinois). In Proceedings of the 30th Annual National Association Abandoned Mine Land Programs Conference, Durango, CO, USA, 26–29 October 2008.
- Bigham, J.M.; Nordstrom, D.K. Iron and aluminum hydroxysulfates from acid sulfate waters. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2000, 40, 351–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.L.; Tomei, F.A. Characteristics and activities of sulfate-reducing bacteria. In Sulfate Reducing Bacteria; Barton, L.L., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Koschorreck, M. Microbial sulphate reduction at a low pH. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 64, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B. Geomicrobiology of extremely acidic subsurface environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 81, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balci, N.; Shanks, W.C., III; Mayer, B.; Mandernack, K.W. Oxygen and sulfur isotope systematics of sulfate produced by bacterial and abiotic oxidation of pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 3796–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druschel, G.K.; Baker, B.J.; Gihring, T.M.; Banfield, J.F. Acid mine drainage biogeochemistry at Iron Mountain, California. Geochem. Trans. 2004, 5, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Andrea, I.; Sanz, J.L.; Bijmans, M.F.; Stams, A.J. Sulfate reduction at low pH to remediate acid mine drainage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 269, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senko, J.M.; Zhang, G.X.; McDonough, J.T.; Bruns, M.A.; Burgos, W.D. Metal reduction at low pH by a Desulfosporosinus species: Implications for the biological treatment of acidic mine drainage. Geomicrobiol. J. 2009, 26, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, J.M.; Williams, M.W.; Stover, B.; Wireman, M. Characterization of acid mine drainage using a combination of hydrometric, chemical and isotopic analyses, Mary Murphy Mine, Colorado. Environ. Geochem. Health 2002, 24, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.; Piva, A.; Fortin, D. Enrichment of sulfate-reducing bacteria and resulting mineral formation in media mimicking pore water metal ion concentrations and pH conditions of acidic pit lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabisch, M.; Beulig, F.; Akob, D.M.; Küsel, K. Surprising abundance of Gallionella-related iron oxidizers in creek sediments at pH 4.4 or at high heavy metal concentrations. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, K.B.; Coupland, K.; Kimura, S.; Johnson, D.B. Macroscopic streamer growths in acidic, metal-rich mine waters in North Wales consist of novel and remarkably simple bacterial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.S.; Han, Y.J.; Chen, L.X.; Liu, J.; Hu, M.; Li, S.J.; Kuang, J.L.; Chain, P.S.; Huang, L.N.; Shu, W.S. Ecological roles of dominant and rare prokaryotes in acid mine drainage revealed by metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1280–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, C.M.; Haanela, A.; Johnson, D.B. Microorganisms in subterranean acidic waters within Europe’s deepest metal mine. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruneel, O.; Personné, J.C.; Casiot, C.; Leblanc, M.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Mahler, B.J.; Le Flèche, A.; Grimont, P.A. Mediation of arsenic oxidation by Thiomonas sp. in acid-mine drainage (Carnoulès, France). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, Y.; Watanabe, K. Sulfuricurvum kujiense gen. nov., sp nov., a facultatively anaerobic, chemolithoautotrophic, sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from an underground crude-oil storage cavity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 2297–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühling, M.; Poehlein, A.; Stuhr, A.; Voitel, M.; Daniel, R.; Schlömann, M. Reconstruction of the metabolic potential of acidophilic Sideroxydans strains from the metagenome of a microaerophilic enrichment culture of acidophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria from a pilot plant for the treatment of acid mine drainage reveals metabolic versatility and adaptation to life at low pH. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2082. [Google Scholar]
- Calkins, W.H. The chemical forms of sulfur in coal: A review. Fuel 1994, 73, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.L. Sulfur in coals: A review of geochemistry and origins. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 100, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. An Evaluation of the Sequential Extraction Method for Quantifying Sulfur Fractions in Coals from the Illinois Basin. Master’s. Thesis, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lefticariu, L. Integrated Study of Mercury and Other Trace Elements Distribution in Illinois Coal; Final Report; Illinois Clean Coal Institute: Carterville, IL, USA, 2009; 44p. [Google Scholar]
- Hardisty, D.S.; Olyphant, G.A.; Bell, J.B.; Johnson, A.P.; Pratt, L.M. Acidophilic sulfur disproportionation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 113, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchak, J.; Skousen, J.; McDonald, L.M. Longevity of acid discharges from underground mines located above the regional water table. West Virginia Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station, Morgantown, WV. Sci. Contrib. 2003, 2849, 656–668. [Google Scholar]
- Majzlan, J.; Navrotsky, A.; Schwertmann, U. Thermodynamics of iron oxides: Part III. Enthalpies of formation and stability of ferrihydrite (~Fe(OH)3), schwertmannite (~FeO(OH)3/4(SO4)1/8), and ɛ-Fe2O3. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraballo, M.A.; Rimstidt, J.D.; Macías, F.; Nieto, J.M.; Hochella, M.F. Metastability, nanocrystallinity and pseudo-solid solution effects on the understanding of schwertmannite solubility. Chem. Geol. 2013, 360, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigham, J.M.; Schwertmann, U.; Traina, S.J.; Winland, R.L.; Wolf, M. Schwertmannite and the chemical modeling of iron in acid sulfate waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, F.T.; Shieh, Y.N. The distribution and isotopic composition of sulfur in coals from the Illinois Basin. Econ. Geol. 1979, 74, 1445–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elswick, E.R.; Hower, J.C.; Carmo, A.M.; Sun, T.; Mardon, S.M. Sulfur and carbon isotope geochemistry of coal and derived coal combustion by-products: An example from an Eastern Kentucky mine and power plant. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.T.; Farquhar, J.; Canfield, D.E. Sulfur isotope insights into microbial sulfate reduction: When microbes meet models. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 3929–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.; Heyer, A.; Canfield, D.E.; Hoek, J.; Habicht, K.S. Temperature effect on the sulfur isotope fractionation during sulfate reduction by two strains of the hyperthermophilic Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2998–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiriţa, P.; Schlegel, M.L. Reaction of FeS with Fe(III)-bearing acidic solutions. Chem. Geol. 2012, 334, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Suflita, J.M.; McKinley, J.P.; Krumholz, L.R. Impact of clay minerals on sulfate reducing activity in aquifers. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 47, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, M.S.; Ono, S.; Donovan, K.; Templer, S.P.; Bosak, T. Effect of electron donors on the fractionation of sulfur isotopes by a marine Desulfovibrio sp. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 4244–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, M.S.; Bosak, T.; Ono, S. Large sulfur isotope fractionation does not require disproportionation. Science 2011, 333, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leavitt, W.D.; Halevy, I.; Bradley, A.S.; Johnston, D.T. Influence of sulfate reduction rates on the Phanerozoic sulfur isotope record. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11244–11249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lefticariu, L.; Behum, P.T.; Bender, K.S.; Lefticariu, M. Sulfur Isotope Fractionation as an Indicator of Biogeochemical Processes in an AMD Passive Bioremediation System. Minerals 2017, 7, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7030041
Lefticariu L, Behum PT, Bender KS, Lefticariu M. Sulfur Isotope Fractionation as an Indicator of Biogeochemical Processes in an AMD Passive Bioremediation System. Minerals. 2017; 7(3):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleLefticariu, Liliana, Paul T. Behum, Kelly S. Bender, and Mihai Lefticariu. 2017. "Sulfur Isotope Fractionation as an Indicator of Biogeochemical Processes in an AMD Passive Bioremediation System" Minerals 7, no. 3: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7030041
APA StyleLefticariu, L., Behum, P. T., Bender, K. S., & Lefticariu, M. (2017). Sulfur Isotope Fractionation as an Indicator of Biogeochemical Processes in an AMD Passive Bioremediation System. Minerals, 7(3), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7030041