Comparison of Three Key Marine Shale Reservoirs in the Southeastern Margin of the Sichuan Basin, SW China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
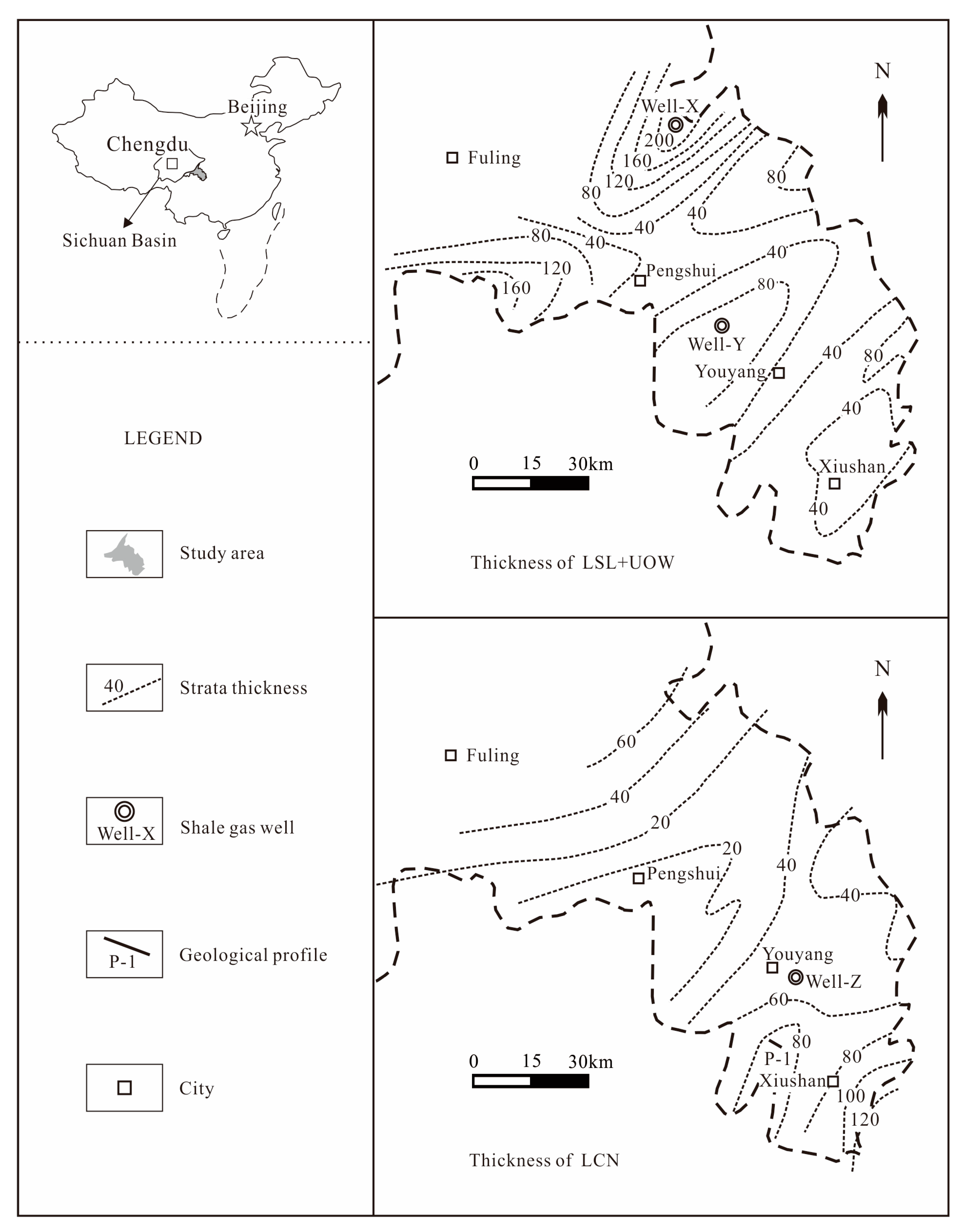
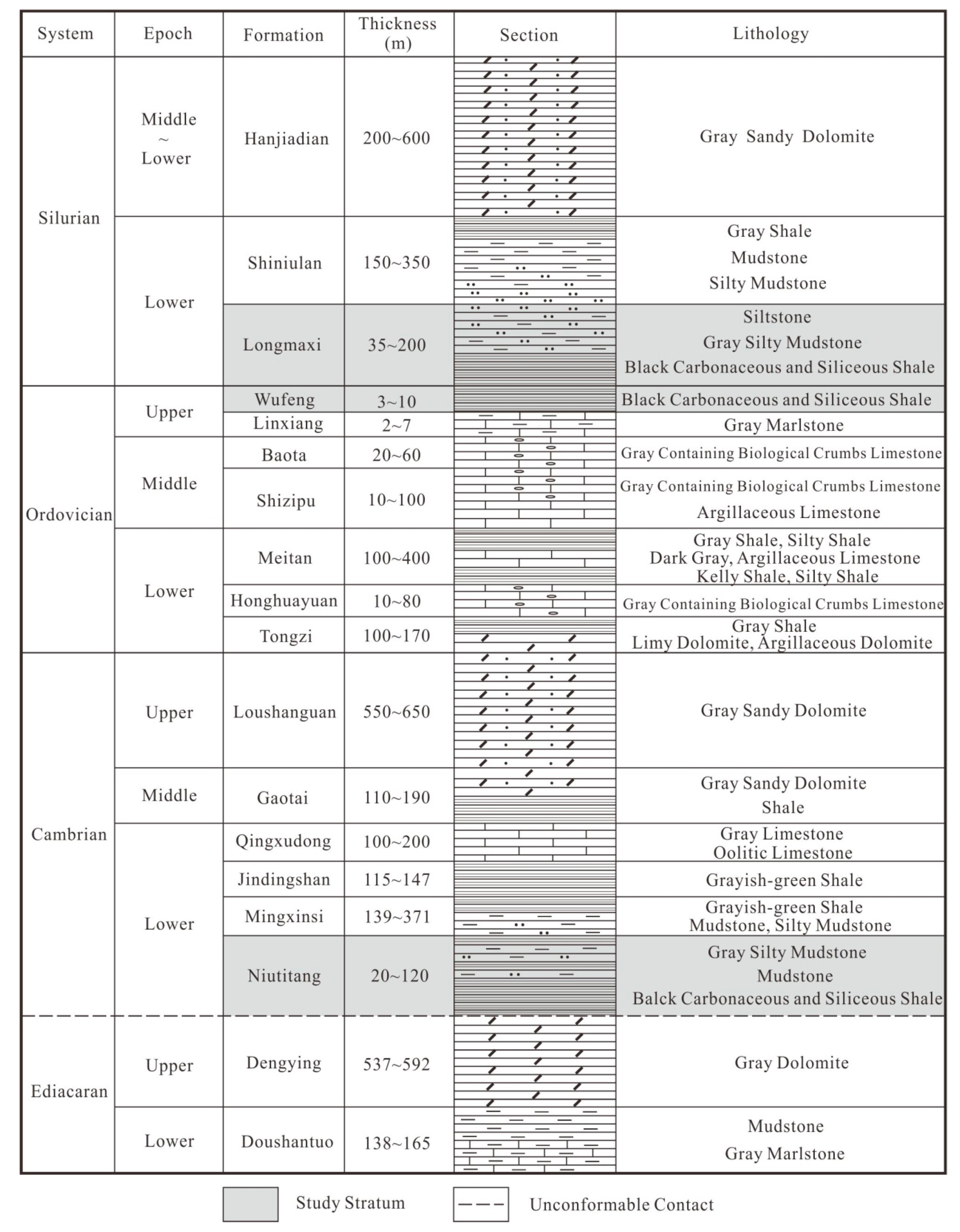
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
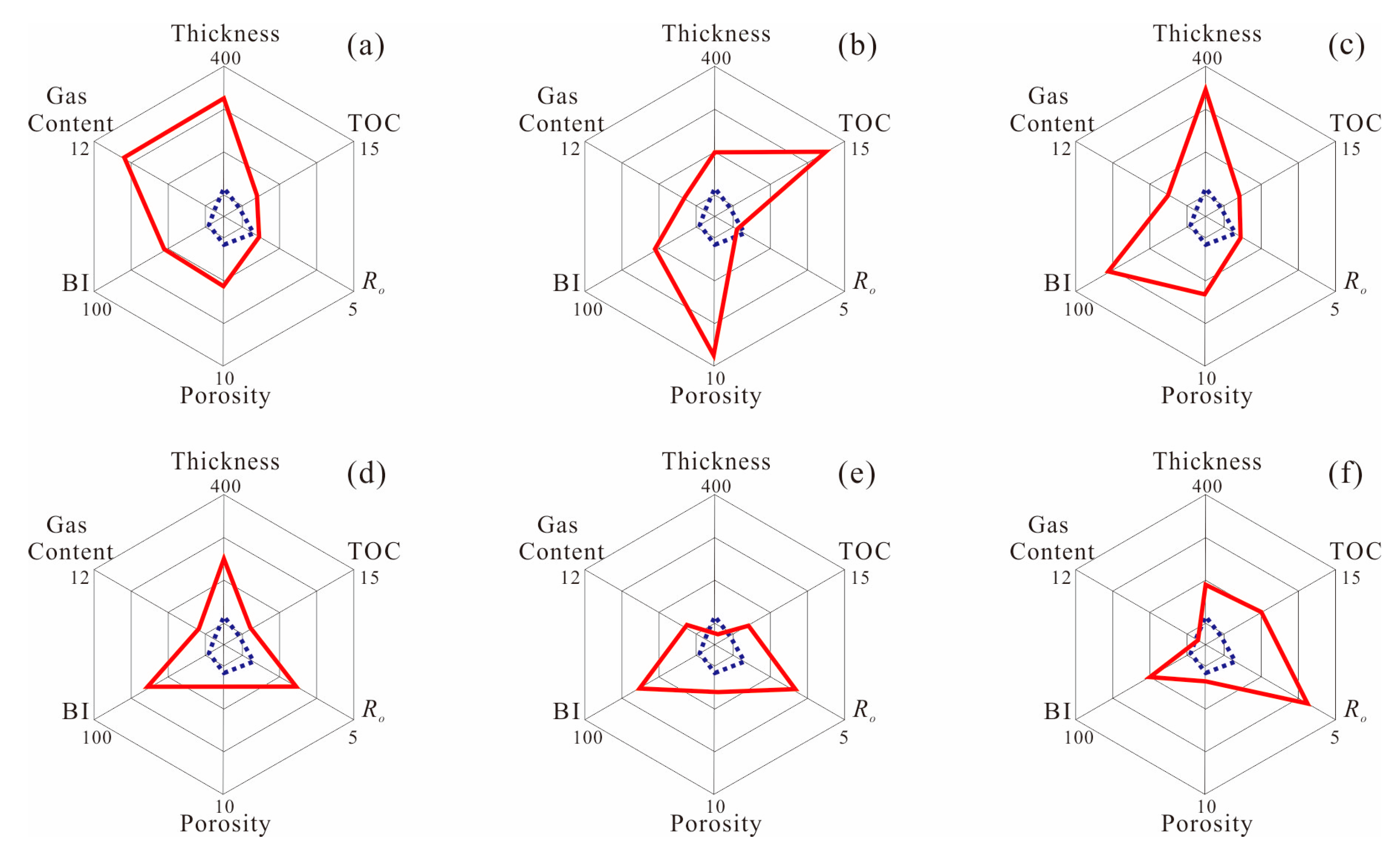
4. Results and Discussion
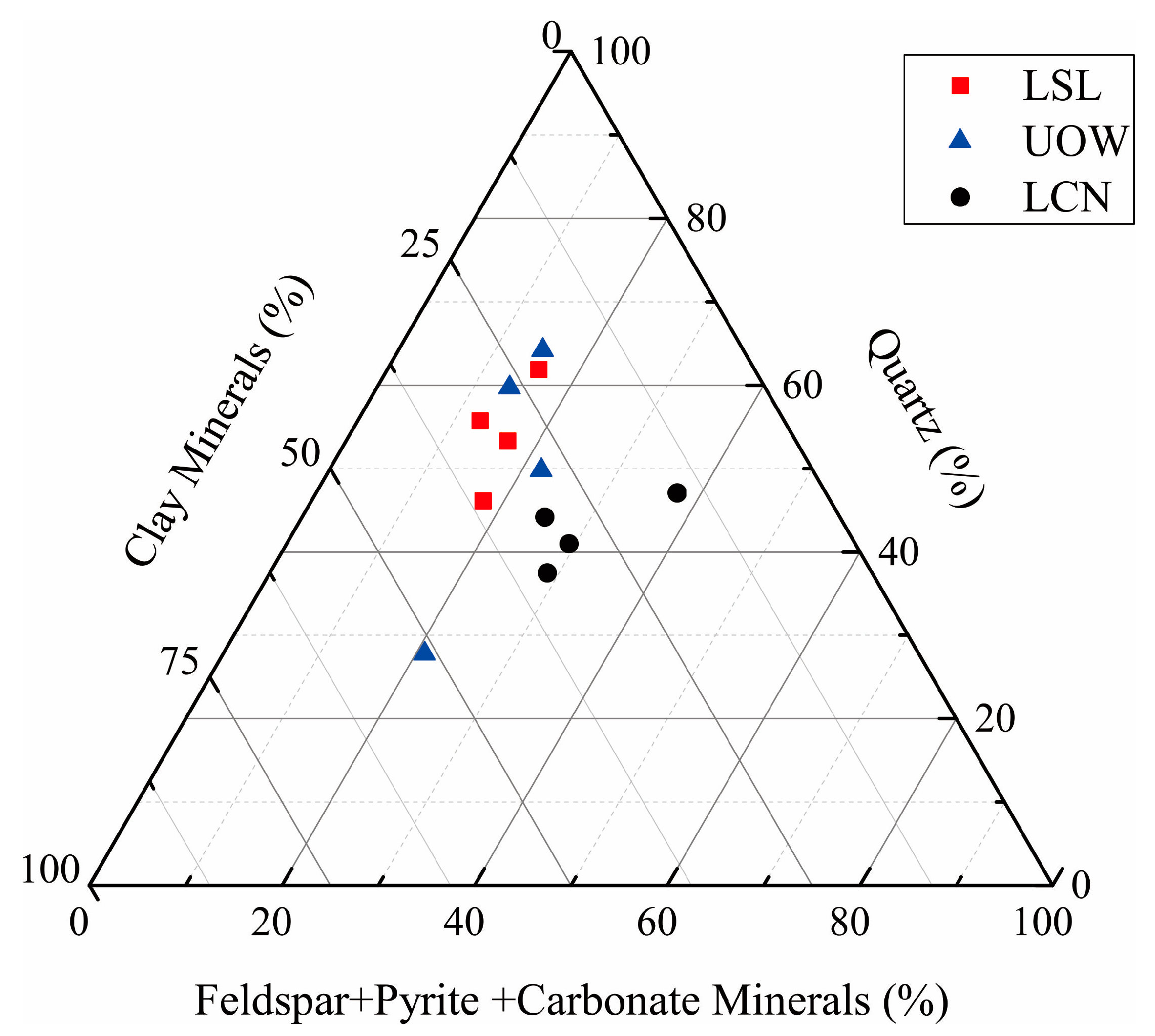
4.1. Lithology and Mineralogy
4.2. Petro-Physical Properties of Shale Gas Reservoirs
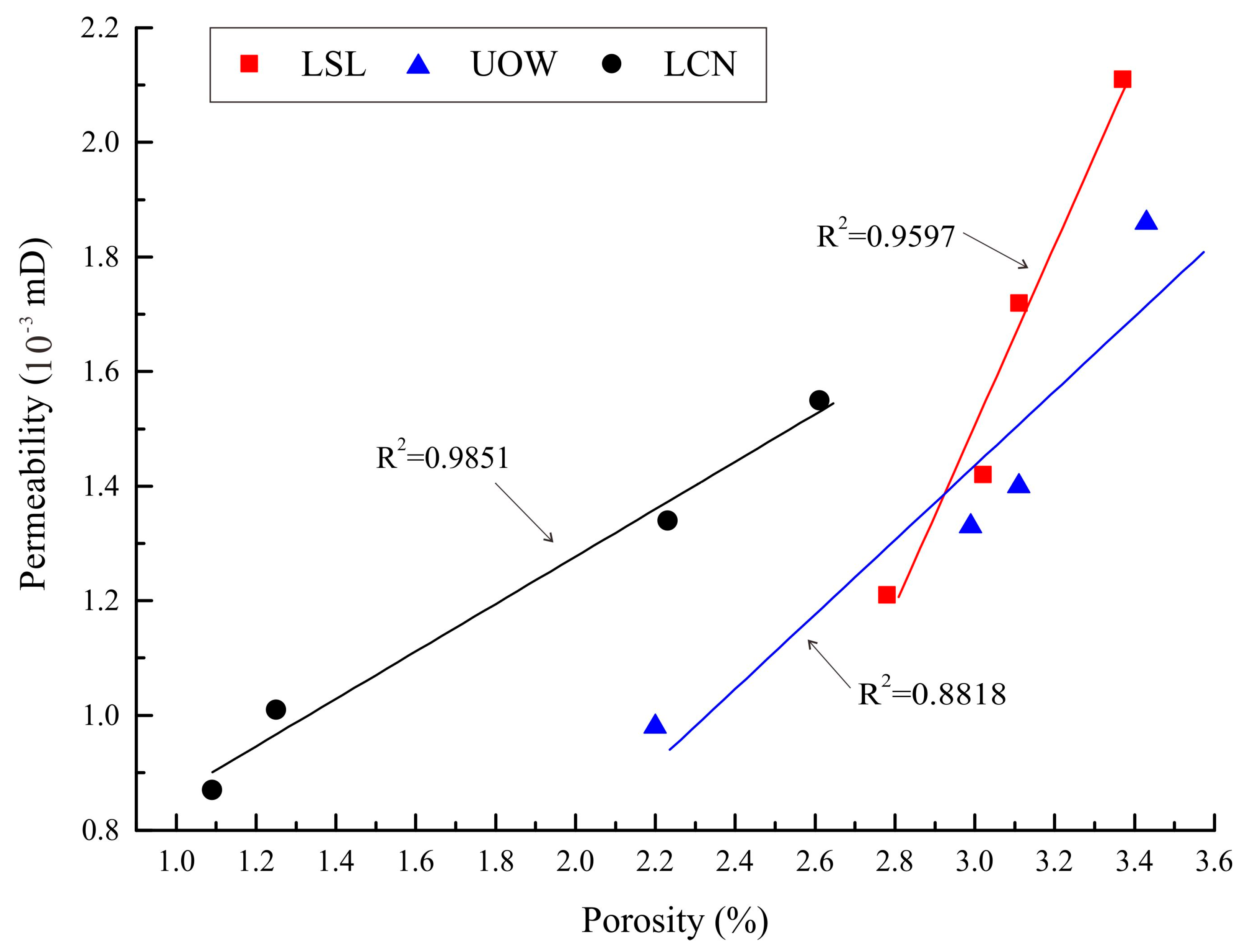
4.2.1. Porosity and Permeability
4.2.2. FE-SEM Observation
4.2.3. Pore Size Distribution (PSD)
4.3. TOC Content and Thermal Maturity
4.4. Gas-Bearing Properties
4.4.1. In Situ Gas Content and Methane Adsorption Capacity
4.4.2. Gas Molecular Composition
4.5. Gas Production Potential
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarvie, D.M.; Hill, R.J.; Ruble, T.E.; Pollastro, R.M. Unconventional shale-gas system: The Mississippian Barnett shale on north-center Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment. AAPG Bull. 2007, 91, 475–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosha, A.; Warnera, N.; Jacksona, R.; Darraha, T. The effects of shale gas exploration and hydraulic fracturing on the quality of water resources in the United States. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 7, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA. 2016. Available online: http://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=27512 (accessed on 15 August 2016).
- Xin, G.; Cole, D.R.; Rother, G.; Mildner, D.F.R.; Brantley, S.L. Pores in Marcellus shale: A neutron scattering and FIB-SEM study. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.X.; Dong, D.Z.; Ni, Y.Y.; Wu, W.; Gong, D.Y.; Huang, S. Geochemical characteristics of marine and terrestrial shale gas in China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 76, 444–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Nie, H.K.; Jiang, S.L. Favorable geological conditions for Paleozoic shale gas accumulation in China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 868, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.G.; Yang, Y.H. The current situation of shale gas in Sichuan, China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 653–664. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Tang, X.L.; Cai, D.S.; Xue, G.; He, Z.L.; Long, S.X.; Peng, Y.M.; Gao, B.; Xu, Z.Y.; Dahdah, N. Comparison of marine, transitional, and lacustrine shales: A case study from the Sichuan Basin in China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 150, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Guo, L.; Liang, C. Lithofacies and sedimentary characteristics of the Silurian Longmaxi shale in the Southeastern Sichuan Basin, China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2013, 2, 238–251. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yao, Y.B.; Elsworth, D.; Pan, Z.J.; Sun, X.X.; Ao, W.H. Sedimentary characteristics of the lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in the southeast margin of Sichuan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 36, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.X.; Zou, C.N.; Liao, S.M.; Dong, D.Z.; Ni, Y.Y.; Huang, J.L.; Wu, W.; Gong, D.Y.; Huang, S.P.; Hu, G.Y. Geochemistry of the extremely high thermal maturity Longmaxi shale gas, Southern Sichuan Basin. Org. Geochem. 2014, 74, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.D.; Yu, B.S.; Hu, Q.H.; Chen, S.; Xia, W.; Ye, R.C. Nanoscale pore characteristics of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang formation shale: A case study from well Yuke #1 in the southeast of Chongqing, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 154, 16–29. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, H.Y.; Pan, Z.J.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, F.J. Controls on matrix permeability of shale samples from Longmaxi and Niutitang formations, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 33, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, S.; Hu, Q.H.; Hu, D.F.; Zhang, S.W.; Yi, J.Z. Pore characterization and methane sorption capacity of over-mature organic-rich Wufeng and Longmaxi shales in the Southeast Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Pan, Z.J.; Zhong, N.N.; Connell, L.D.; Down, D.I.; Lin, W.L.; Zhang, L. Experimental study of anisotropic gas permeability and its relationship with fracture structure of Longmaxi shales, Sichuan Basin, China. Fuel 2016, 180, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Jiang, Z.X.; Han, M.; Wu, M.H.; Lin, W. The lithofacies and reservoir characteristics of the Upper Ordovician and Lower Silurian black shale in the Southern Sichuan Basin and its periphery, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 75, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Pan, L.; Zhang, T.W.; Xiao, X.M.; Meng, Z.P.; Huang, B. Pore characterization of organic-rich Lower Cambrian shales in Qiannan Depression of Guizhou Province, Southwestern China. J. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 62, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, S.H.; Liu, H.Q.; He, S.L.; Mo, S.Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, R.H.; Huang, X.; Tian, J.; Lv, X.C.; Wu, D.X.; et al. Shale reservoir characteristics and exploration potential in the target: A case study in the Longmaxi formation from the Southern Sichuan Basin of China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 31, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsch, R.J.; Mai, H.; Sun, Z.; Gorter, J.D. The Sichuan Basin, southwest China—A Late Proterozoic (Sinian) petroleum province. Precambrian Res. 1991, 54, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wang, Z.M.; Krupnick, A.; Liu, X.L. Stimulating shale gas development in China: A comparison with the US experience. Energy Policy 2014, 75, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, Y.C.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.Q.; Guo, T.L.; Luo, C.; Xing, F.C. Sequence stratigraphy and its application in marine shale gas exploration: A case study of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi formation in the Jiaoshiba shale gas field and its adjacent area in Southeast Sichuan Basin, SW China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.M.; Yong, Z.Q.; Zhu, J.P.; Xin-Min, Y.E.; Hao, W.; Shuang, Z. Features of Wufeng formation and Longmaxi formation shale in Nanchuan, southeast of Sichuan, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. 2013, 40, 696–702. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, R.C.; Ambrose, R.J.; Akkutlu, I.Y. Shale gas-in-place calculations Part II—Multicomponent gas adsorption. In Proceedings of the SPE Unconventional Gas Conference, Woodlands, TX, USA, 14–16 June 2011; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, G.R.L.; Bustin, R.M. Lower Cretaceous gas shales in northeastern British Columbia, Part I: Geological controls on methane sorption capacity. Bull. Can. Pet. Geol. 2008, 56, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, H. Dispersed solid bitumens as an indicator for migration and maturity in prospecting for oil and gas. Erdöl Kohle Erdgas Petrochem. 1985, 38, 365–392. [Google Scholar]
- Rickman, R.; Mullen, M.J.; Petre, J.E.; Grieser, W.V.; Kundert, D. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett shale. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, CO, USA, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, F. Screening criteria for shale-gas systems. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 2009, 59, 779–793. [Google Scholar]
- Grathoff, G.H.; Peltz, M.; Enzmann, F.; Kaufhold, S. Porosity and permeability determination of organic-rich Posidonia shales based on 3-D analyses by FIB-SEM microscopy. Solid Earth Discuss. 2016, 7, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.J.K.; Bustin, R.M. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Wirth, R.; Schreiber, A.; Schulz, H.M.; Horsfield, B. Formation of nanoporous pyrobitumen residues during maturation of the Barnett Shale (Fort Worth Basin). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 103, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.Q.; Jiang, P.X.; Xu, R.N.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.W. Comparison of marine, transitional, and lacustrine shales: A case study from the Sichuan Basin in China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 29, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Leng, J.G.; Li, P.; Li, F. Characteristics and its main enrichment controlling factors of shale gas of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang formation in northeastern Guizhou Province. J. Palaeogeogr. 2016, 18, 605–614, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Xiao, X.M.J. Gas content of organic-rich shales with very high maturities. J. China Coal Soc. 2013, 38, 737–741. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sondergeld, C.H.; Newsham, K.E.; Comisky, J.T.; Rice, M.C.; Rai, C.S. Petrophysical considerations in evaluating and producing shale gas resources. In Proceedings of the SPE Unconventional Gas Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 23–25 February 2010; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.Q.; Xu, M.; Shan, J.N.; Yuan, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, S.B. Quantifying the denudations of major tectonic events in Sichuan Basin: Constrained by the paleothermal records. Geol. China 2009, 36, 1268–1277. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Tang, D.Z.; Xu, H.; Yang, F.; Zhou, C.W.; Li, S. The analysis for thermal evolution history of high–over mature source rock from Cambrian to Silurian in Upper- Middle Yangtze Region. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 1126–1133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.Y.; Ding, W.L.; Gong, D.J.; Leng, J.G.; Wang, X.H.; Yin, S.; Sun, Y.X. Gas preservation conditions of marine shale in Northern Guizhou area: A case study of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang formation in the Cen’gong block, Guizhou Province. Oil Gas Geol. 2016, 37, 45–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhang, R.Q.; Feng, J.F.; He, Z.L. Fluid alteration mechanism of dolomite reservoirs in Dengying formation, south China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2015, 36, 1188–1198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, E.; Akkutlu, I.Y. Multi-component gas transport and adsorption effects during CO2 injection and enhanced shale gas recovery. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 123, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, M.; Koperna, G.; Petrusak, R.; Oudinot, A. Enhanced Gas Recovery and CO2 Storage in Gas Shale: A Summary Review of its Status and Potential. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 5849–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.; Jarvie, D.; Bowker, K.; Pollastro, R. Mississippian Barnett Shale, Fort Worth Basin, north-central Texas: Gas-shale play with multi-trillion cubic foot potential. Precambrian Res. 2005, 89, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ning, Z.F.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, H.W.; Krooss, B.M. Investigations on the methane sorption capacity of marine shales from Sichuan Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 146, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Tang, S.H.; Pan, Z.J. Evaluation of the shale gas potential of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi formation in Northwest Hunan Province, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 79, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.B. Fractured shale-gas systems. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 1921–1938. [Google Scholar]


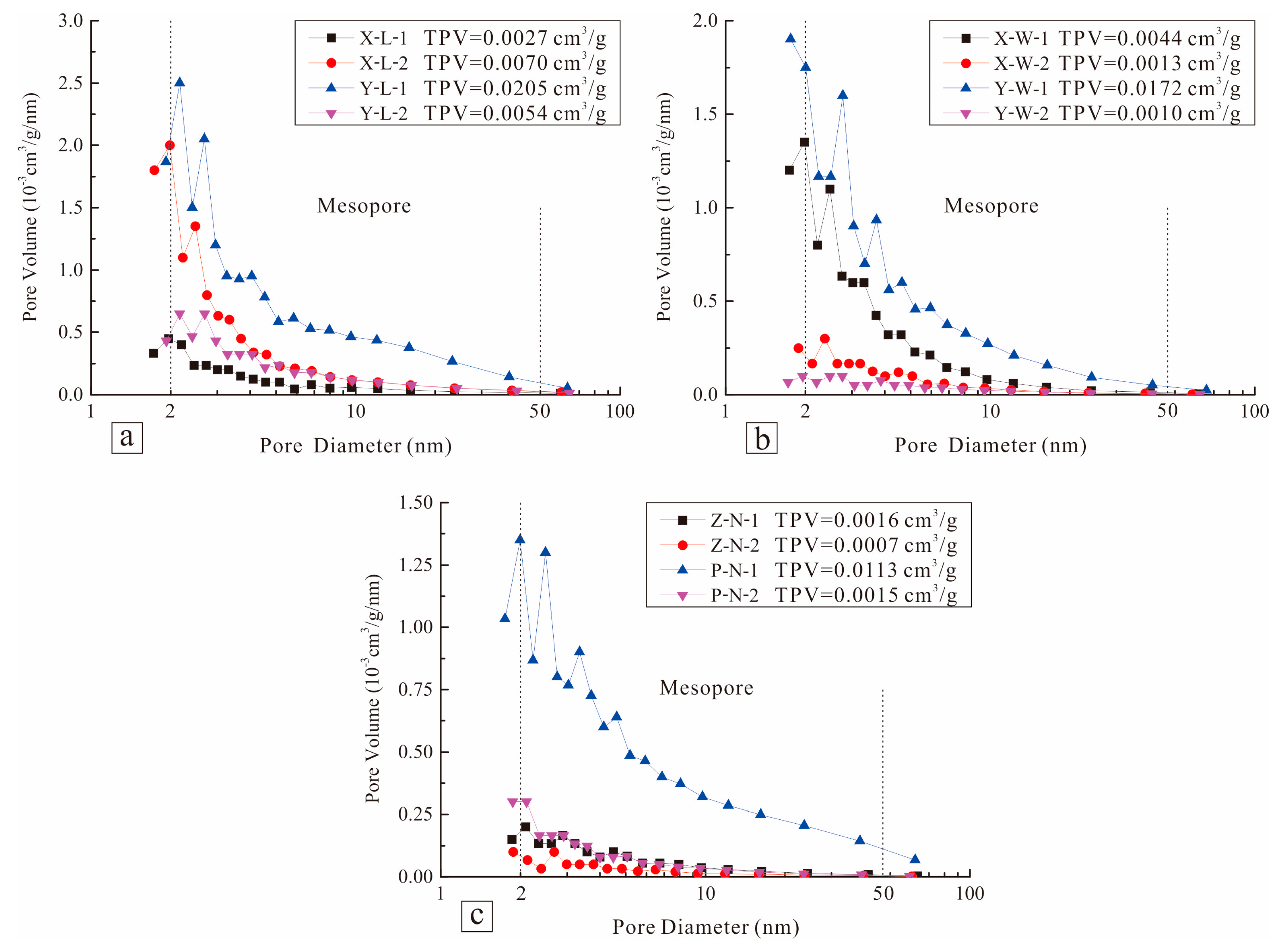
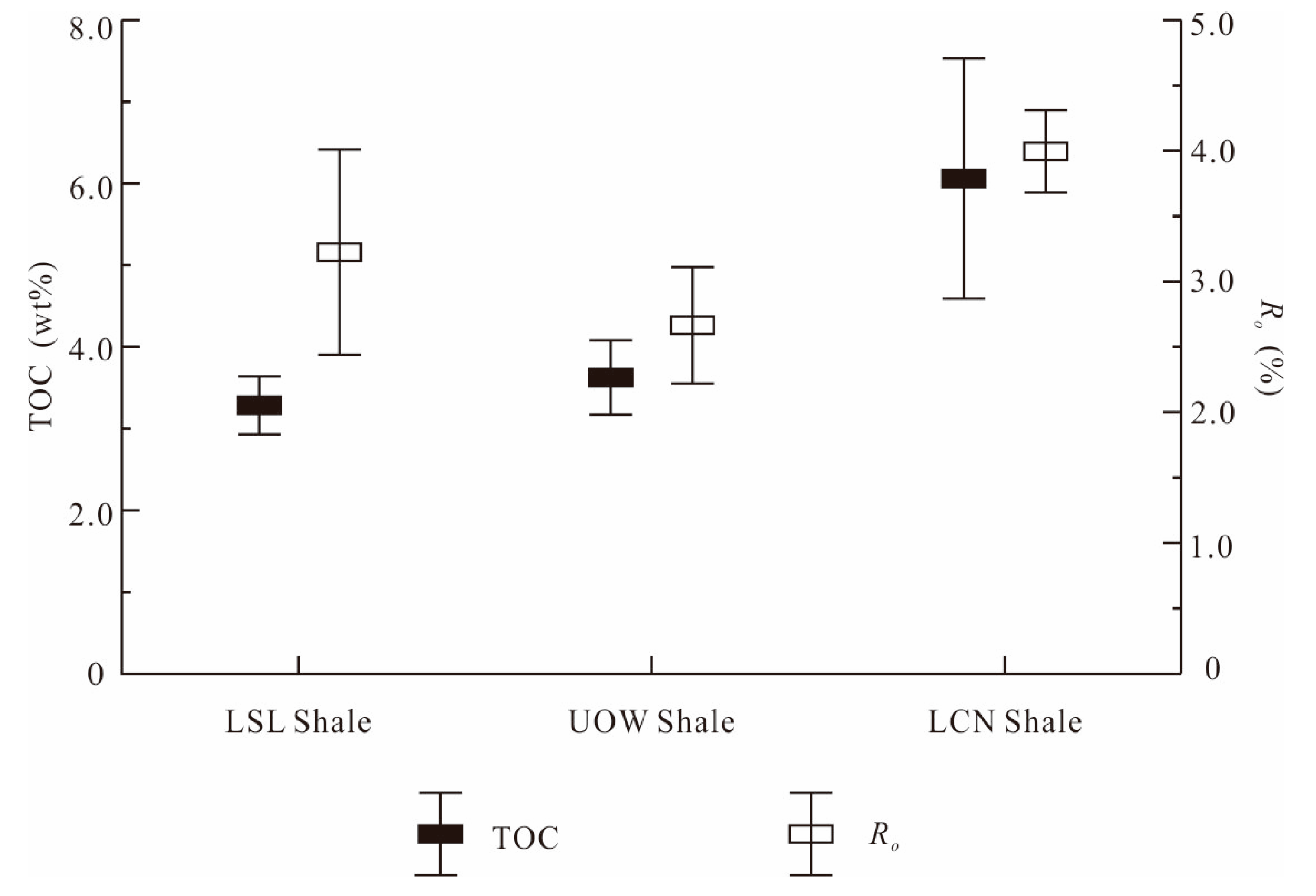
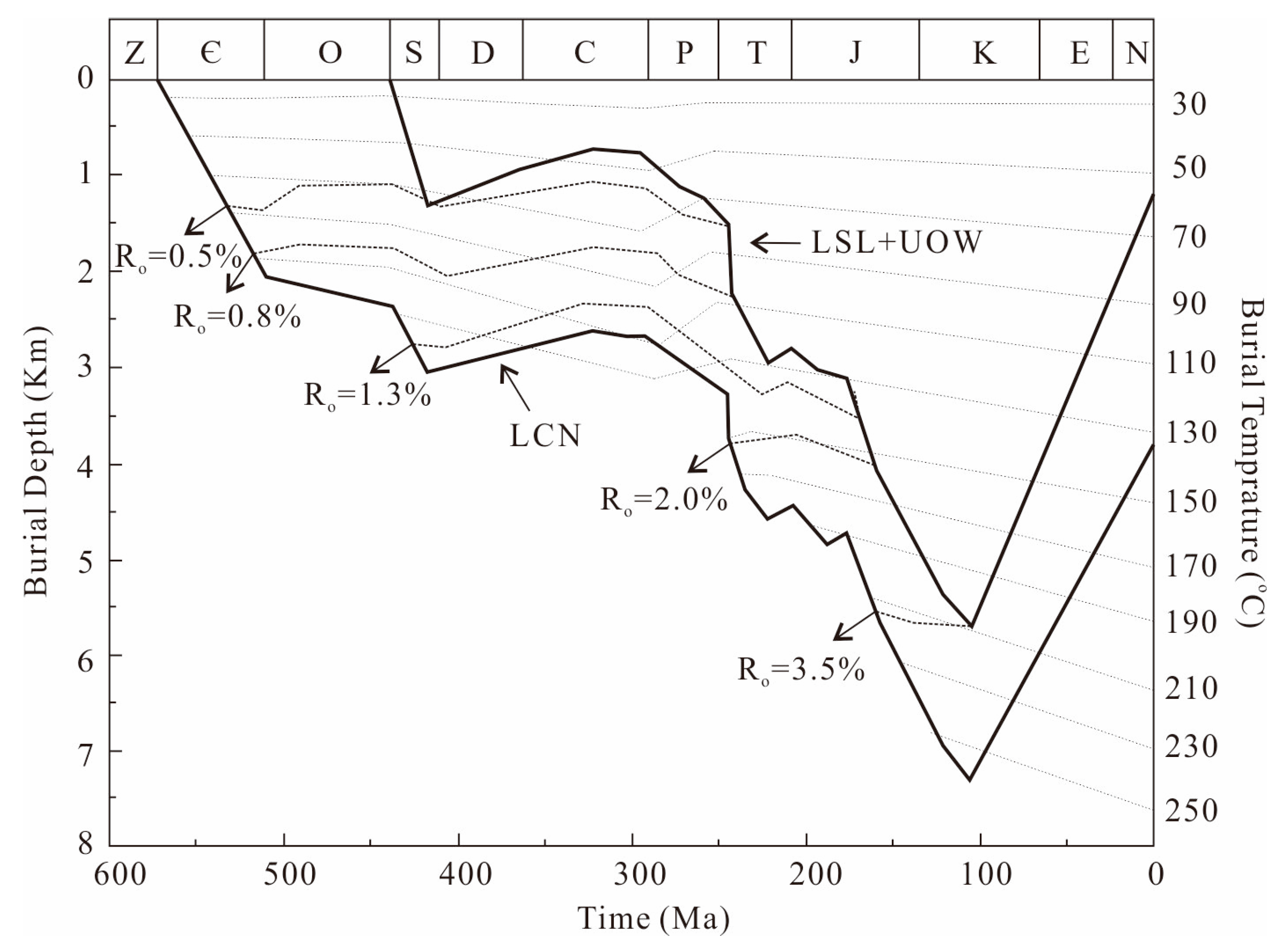

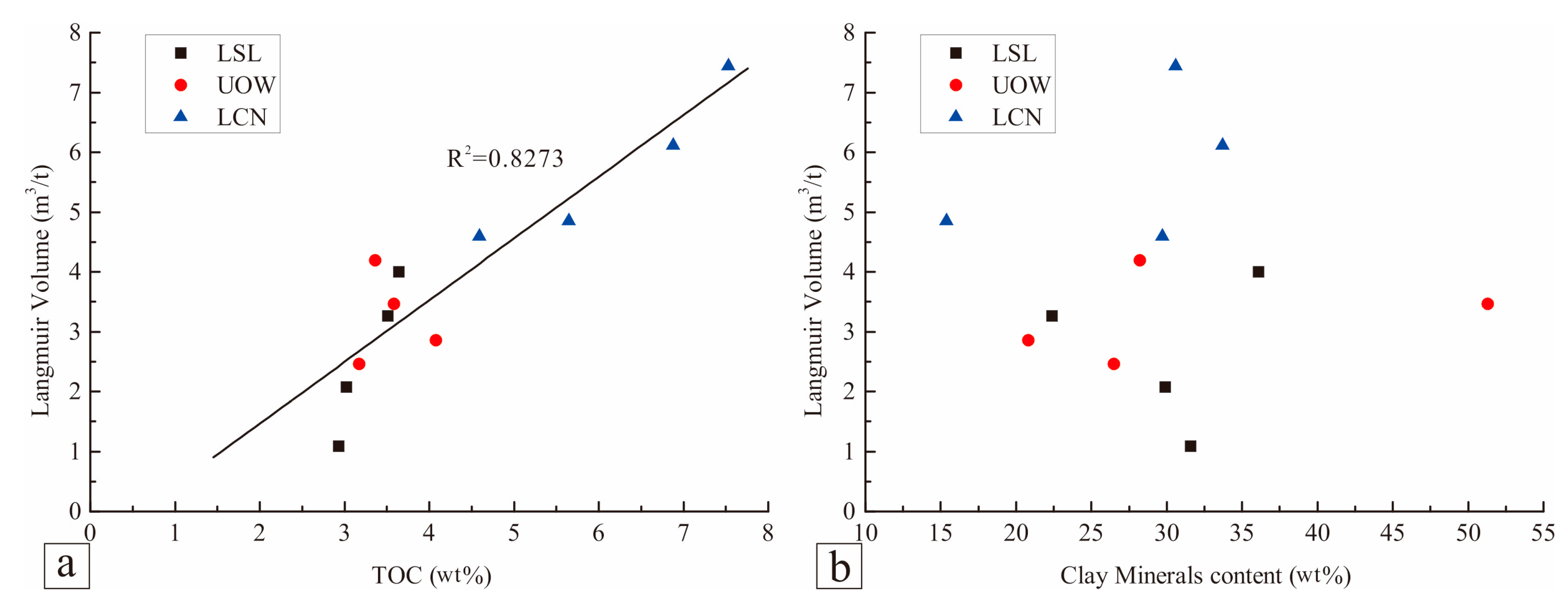
| Sample ID | Sampling Point | Strata | TOC (%) | Ro (%) | Porosity (%) | Permeability (10−3 mD) | BI (%) | Mineral Composition (wt %) | VL (m3/t) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | F | C | Py | Cly | |||||||||
| X-L-1 | Well-X | LSL | 2.93 | 3.12 | 2.78 | 1.21 | 61.5 | 55.7 | 7.2 | 3.2 | 2.3 | 31.6 | 1.090 |
| X-L-2 | Well-X | LSL | 3.51 | 4.01 | 3.02 | 1.42 | 71.0 | 61.9 | 8.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 22.4 | 3.263 |
| Y-L-1 | Well-Y | LSL | 3.02 | 2.44 | 3.37 | 2.11 | 58.8 | 53.3 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 1.6 | 29.9 | 2.077 |
| Y-L-2 | Well-Y | LSL | 3.64 | 2.83 | 3.11 | 1.72 | 52.1 | 46.1 | 8.1 | 6.3 | 3.4 | 36.1 | 3.999 |
| X-W-1 | Well-X | OUW | 3.58 | 2.75 | 2.99 | 1.33 | 32.2 | 27.8 | 10.9 | 7.2 | 2.8 | 51.3 | 3.464 |
| X-W-2 | Well-X | OUW | 3.17 | 2.97 | 3.43 | 1.86 | 67.0 | 59.7 | 7.9 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 26.5 | 2.457 |
| Y-W-1 | Well-Y | OUW | 4.08 | 3.11 | 3.11 | 1.40 | 72.6 | 64.2 | 7.4 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 20.8 | 2.855 |
| Y-W-2 | Well-Y | OUW | 3.36 | 2.22 | 2.20 | 0.98 | 54.7 | 49.8 | 5.2 | 13.1 | 3.7 | 28.2 | 4.198 |
| Z-N-1 | Well-Z | LCN | 5.65 | 3.68 | 2.61 | 1.55 | 56.7 | 47.1 | 13.3 | 20.5 | 3.7 | 15.4 | 4.846 |
| Z-N-2 | Well-Z | LCN | 7.53 | 4.27 | 1.25 | 1.01 | 54.0 | 44.2 | 11.5 | 7.1 | 6.6 | 30.6 | 7.441 |
| P-N-1 | P-1 | LCN | 4.59 | 3.91 | 2.23 | 1.34 | 46.1 | 41.0 | 7.9 | 18.3 | 3.1 | 29.7 | 4.590 |
| P-N-2 | P-1 | LCN | 6.88 | 4.31 | 1.09 | 0.87 | 45.1 | 37.5 | 12.3 | 11.9 | 4.6 | 33.7 | 6.106 |
| Sample ID | Strata | Gas Content (m3/t) | Main Molecular Component (vol %) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2H6 | C3H8 | CO2 | N2 | H2 | |||
| X-L-1 | LSL | 0.95 | 97.39 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 0.78 | 1.31 | 0.03 |
| X-L-2 | LSL | 1.86 | 97.11 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 1.87 | - |
| Y-L-1 | LSL | 1.97 | 94.55 | 0.51 | - | 1.78 | 3.08 | 0.01 |
| Y-L-2 | LSL | 2.49 | 96.01 | 1.23 | 0.02 | 0.44 | 2.27 | - |
| X-W-1 | OUW | 1.41 | 95.55 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 1.16 | 2.84 | - |
| X-W-2 | OUW | 1.59 | 97.26 | 0.70 | - | 0.04 | 1.90 | 0.07 |
| Y-W-1 | OUW | 2.66 | 96.27 | 0.57 | - | 1.05 | 2.07 | - |
| Y-W-2 | OUW | 3.17 | 96.32 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 1.04 | 1.81 | 0.15 |
| Z-N-1 | LCN | 0.49 | 23.17 | 0.08 | - | 16.41 | 56.18 | 2.38 |
| Z-N-2 | LCN | 1.32 | 16.27 | 0.02 | - | 22.80 | 58.48 | 1.08 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, D.; Pan, Z.; Cai, Y. Comparison of Three Key Marine Shale Reservoirs in the Southeastern Margin of the Sichuan Basin, SW China. Minerals 2017, 7, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7100179
Liu J, Yao Y, Liu D, Pan Z, Cai Y. Comparison of Three Key Marine Shale Reservoirs in the Southeastern Margin of the Sichuan Basin, SW China. Minerals. 2017; 7(10):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7100179
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jun, Yanbin Yao, Dameng Liu, Zhejun Pan, and Yidong Cai. 2017. "Comparison of Three Key Marine Shale Reservoirs in the Southeastern Margin of the Sichuan Basin, SW China" Minerals 7, no. 10: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7100179
APA StyleLiu, J., Yao, Y., Liu, D., Pan, Z., & Cai, Y. (2017). Comparison of Three Key Marine Shale Reservoirs in the Southeastern Margin of the Sichuan Basin, SW China. Minerals, 7(10), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7100179







