A Comparative Study on the Effect of Flotation Reagents on Growth and Iron Oxidation Activities of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism and Culture Conditions
2.2. Flotation Reagents
2.3. Analytical Procedures
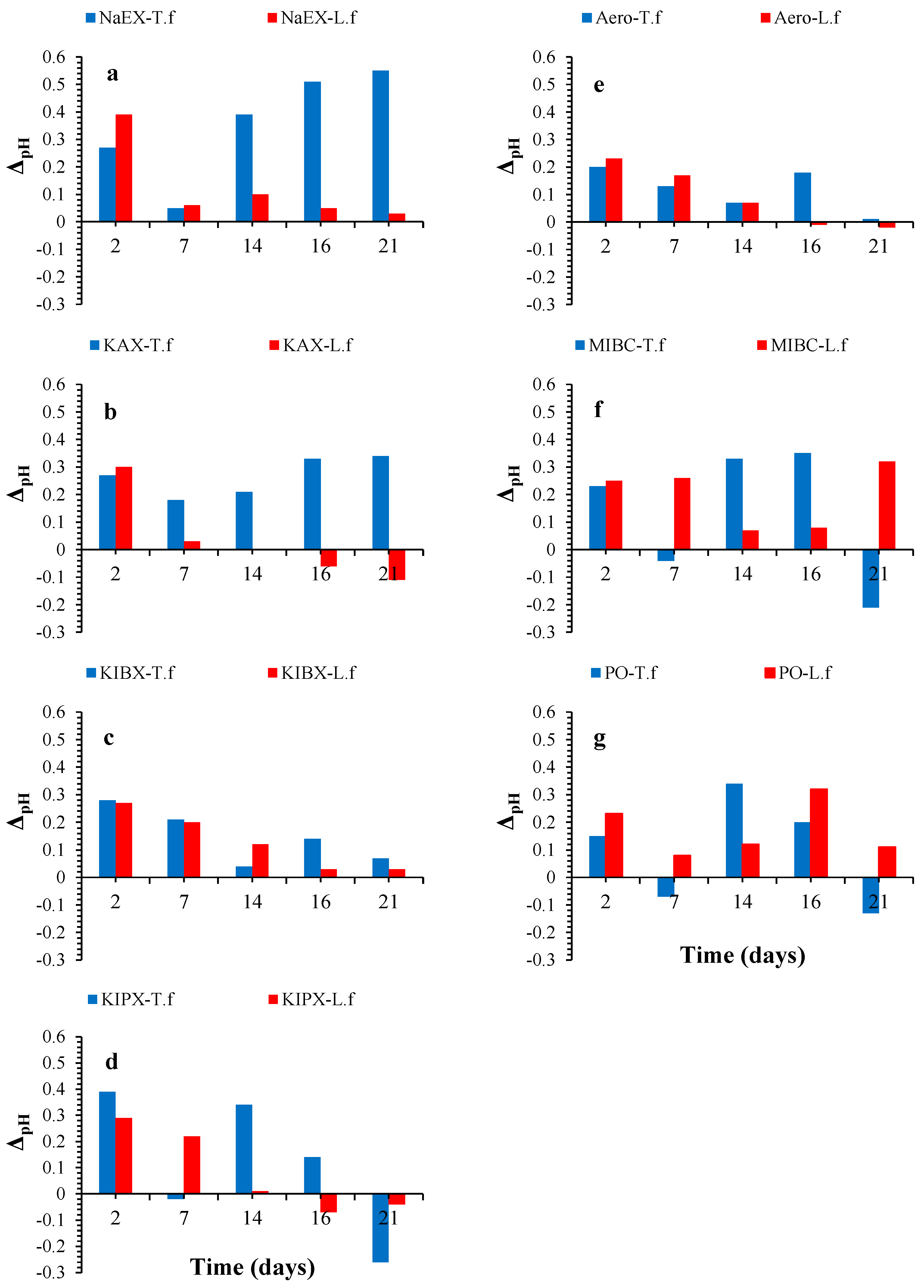
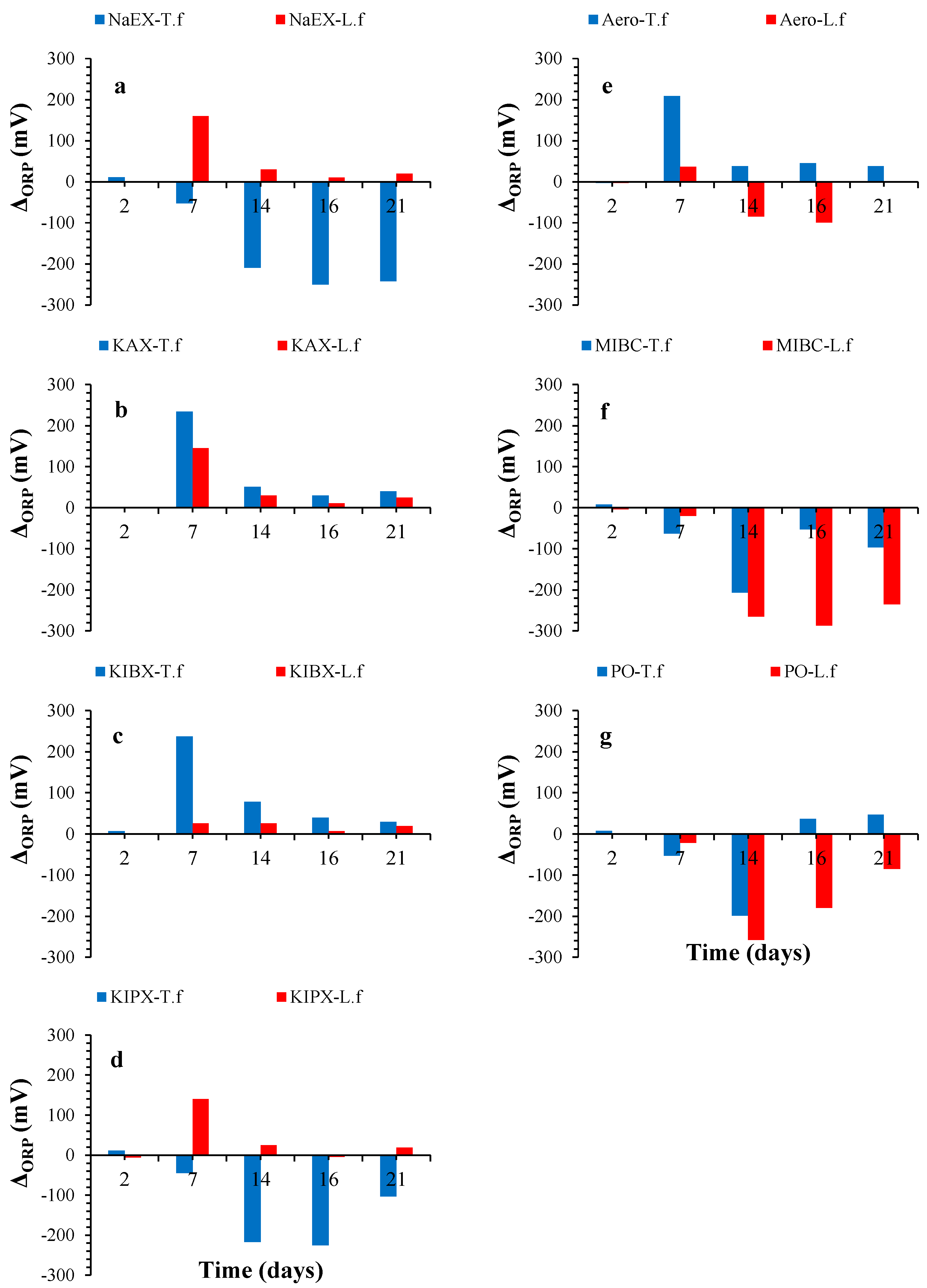
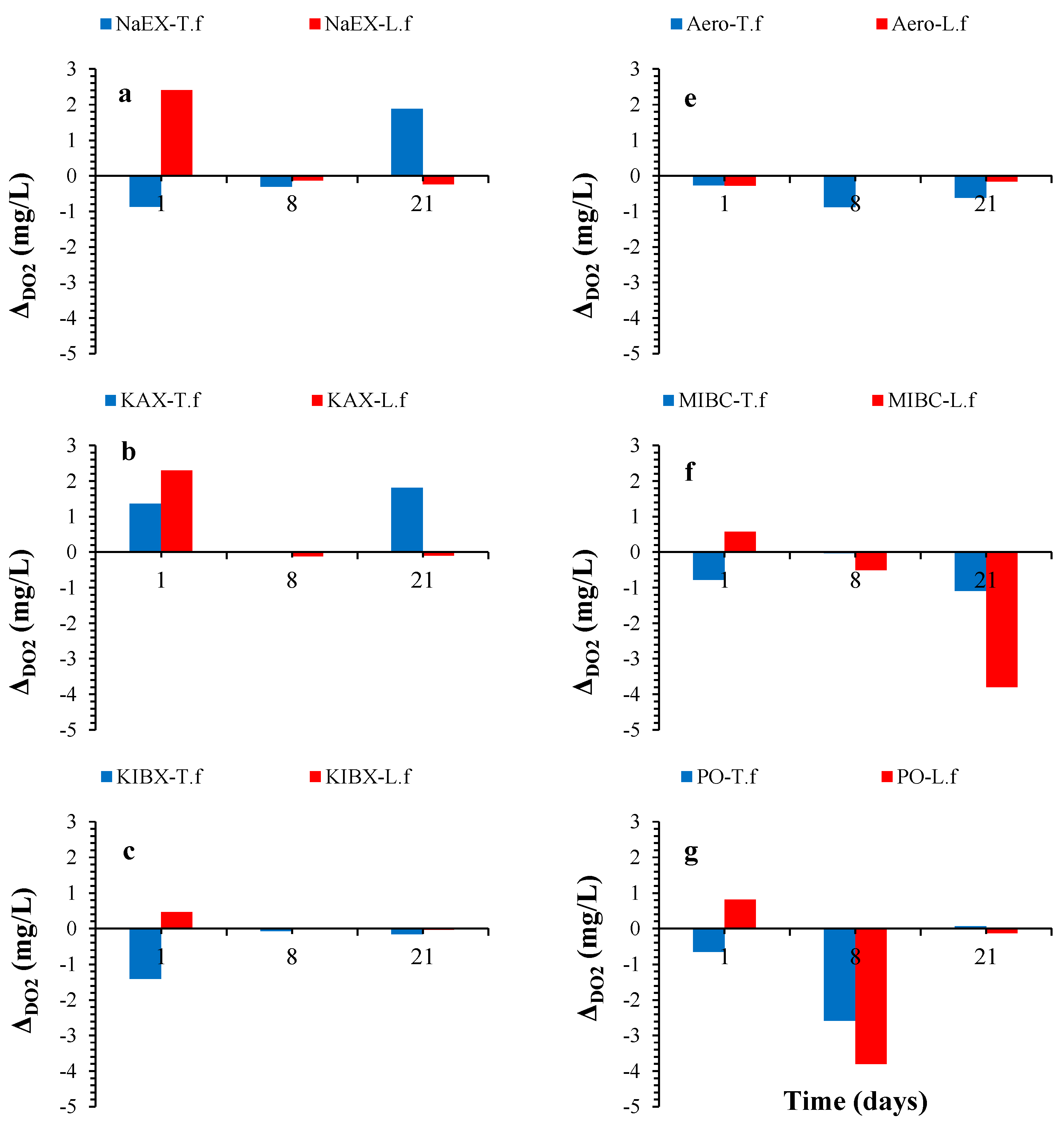
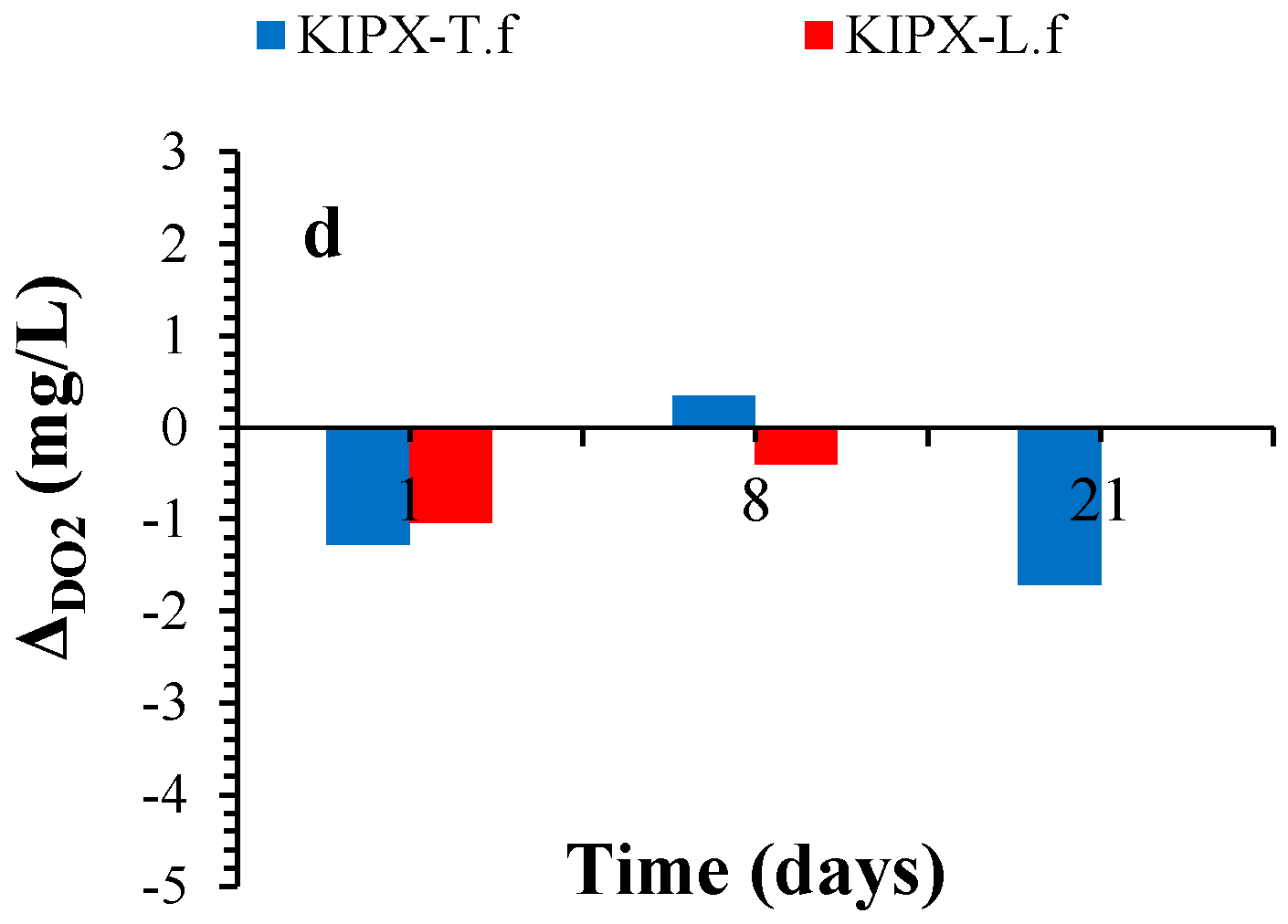
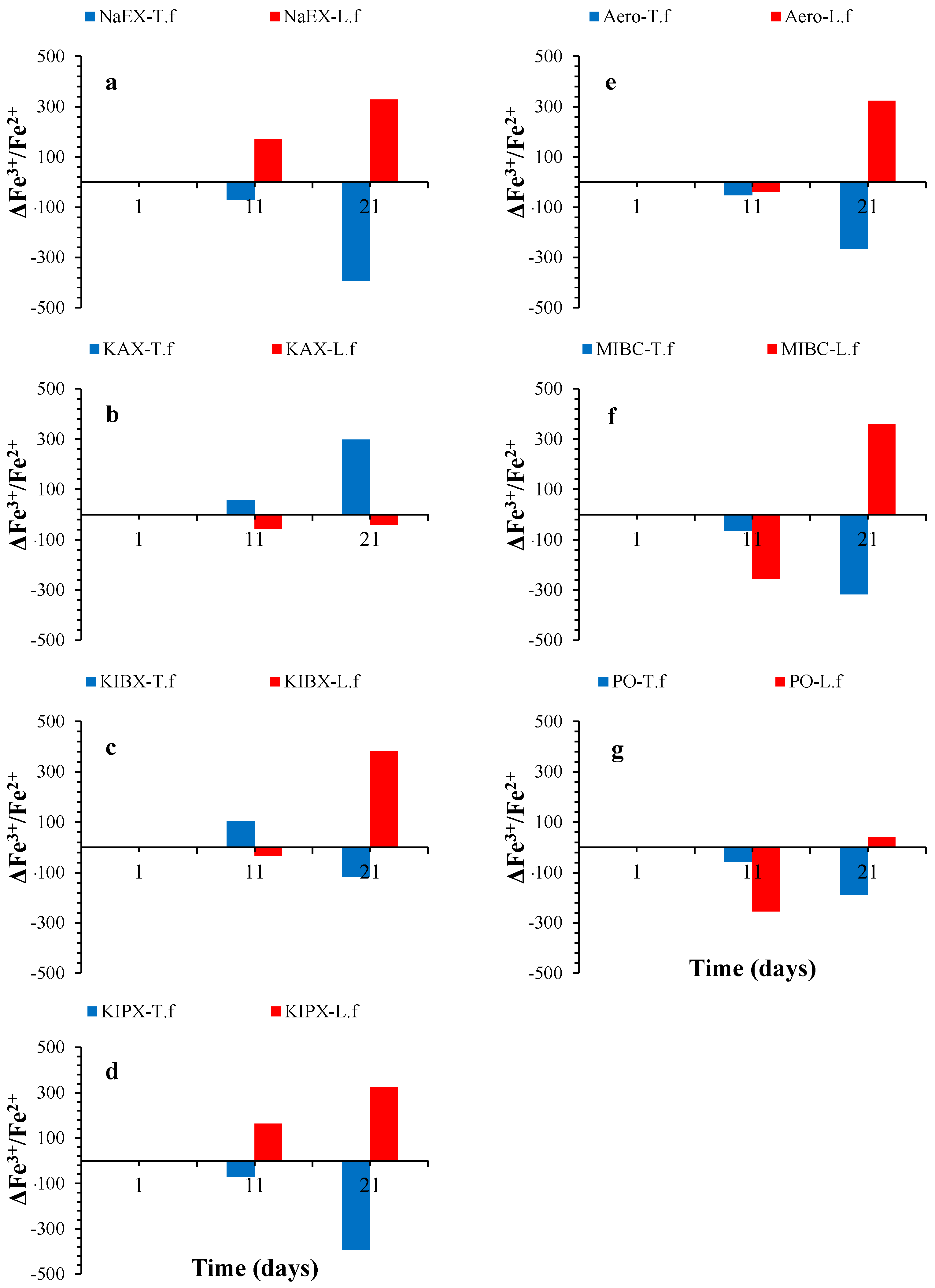
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Subsection
3.2. ORP Variations
3.3. DO2 Variation
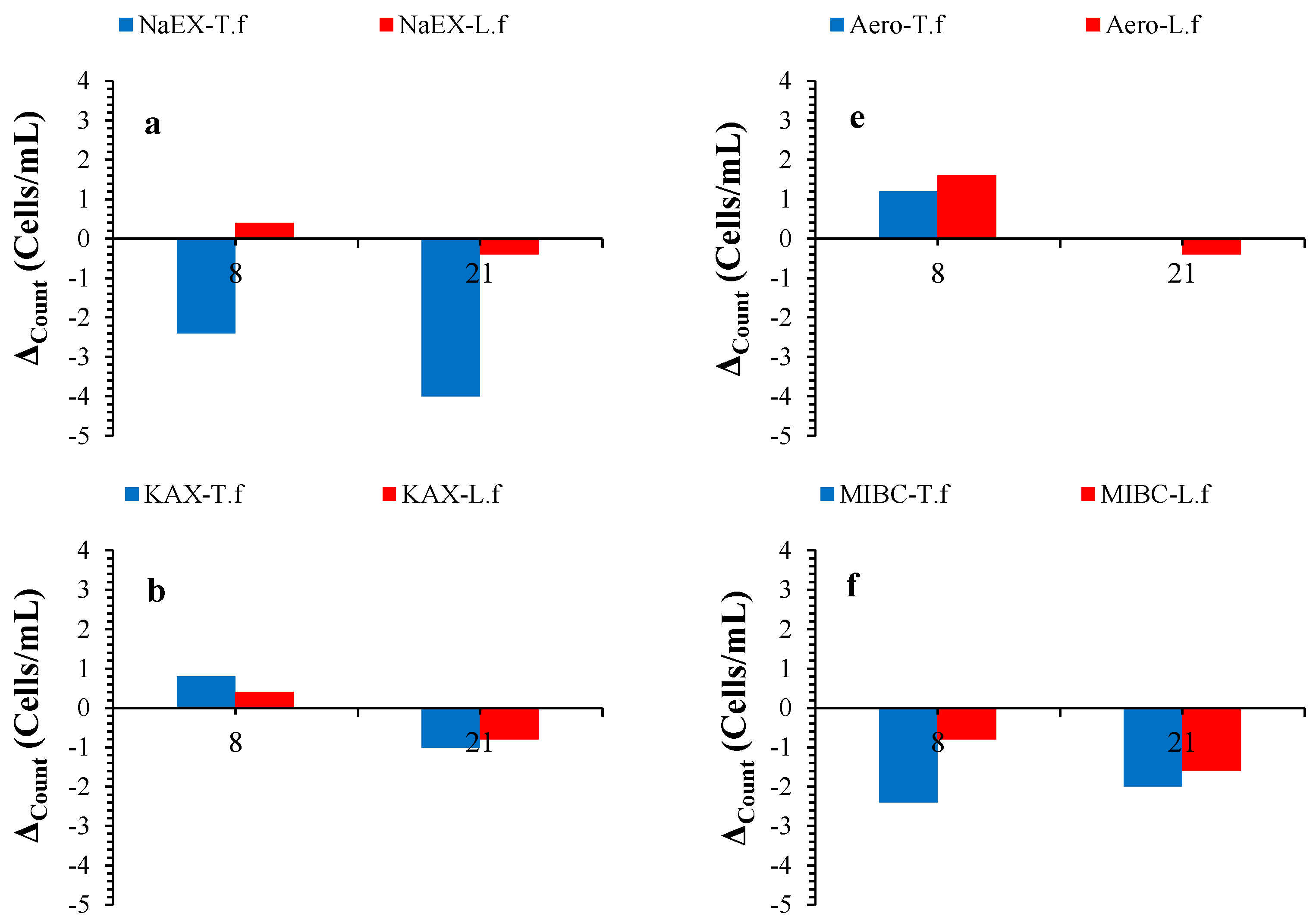
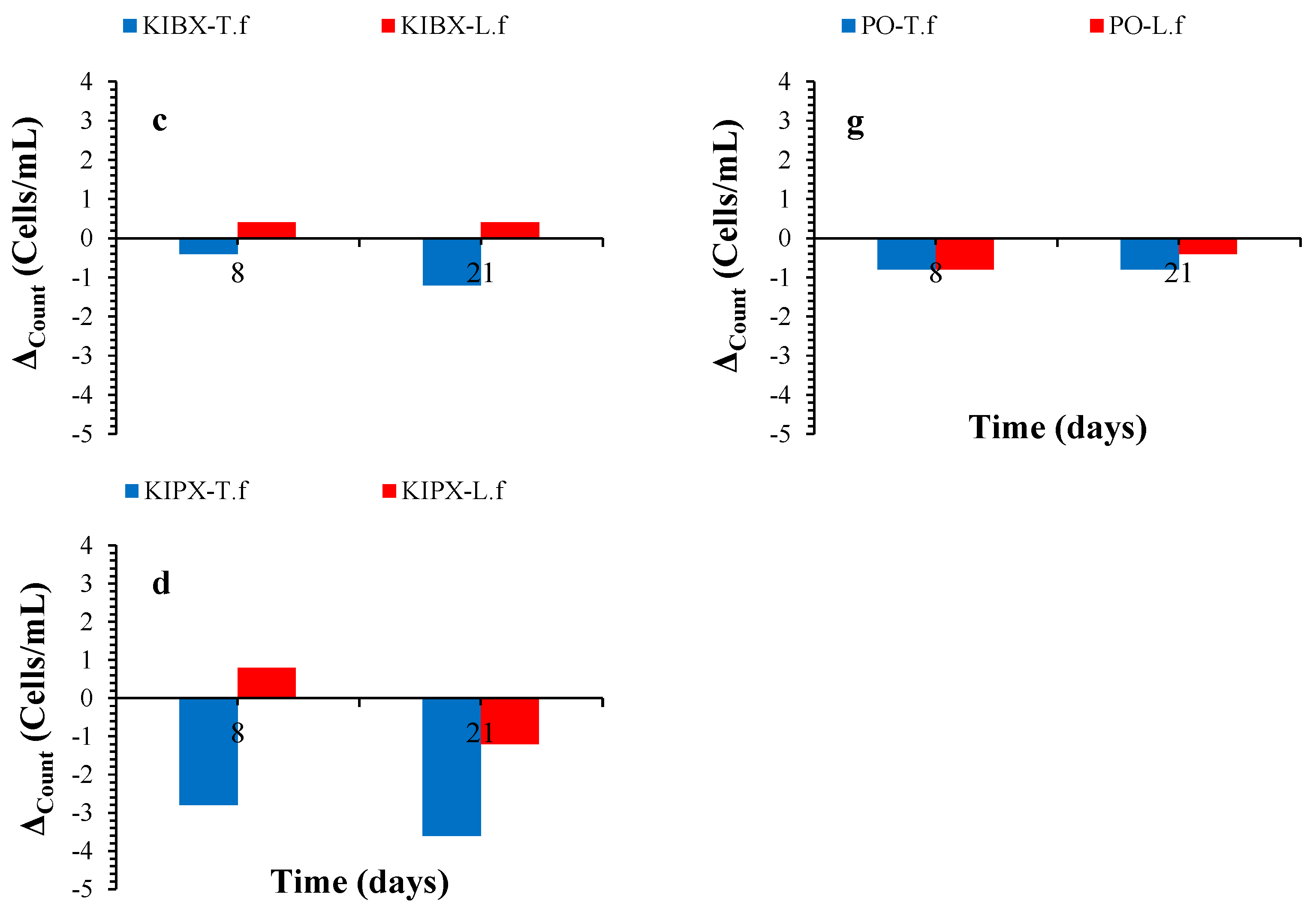
3.4. Microorganism Population
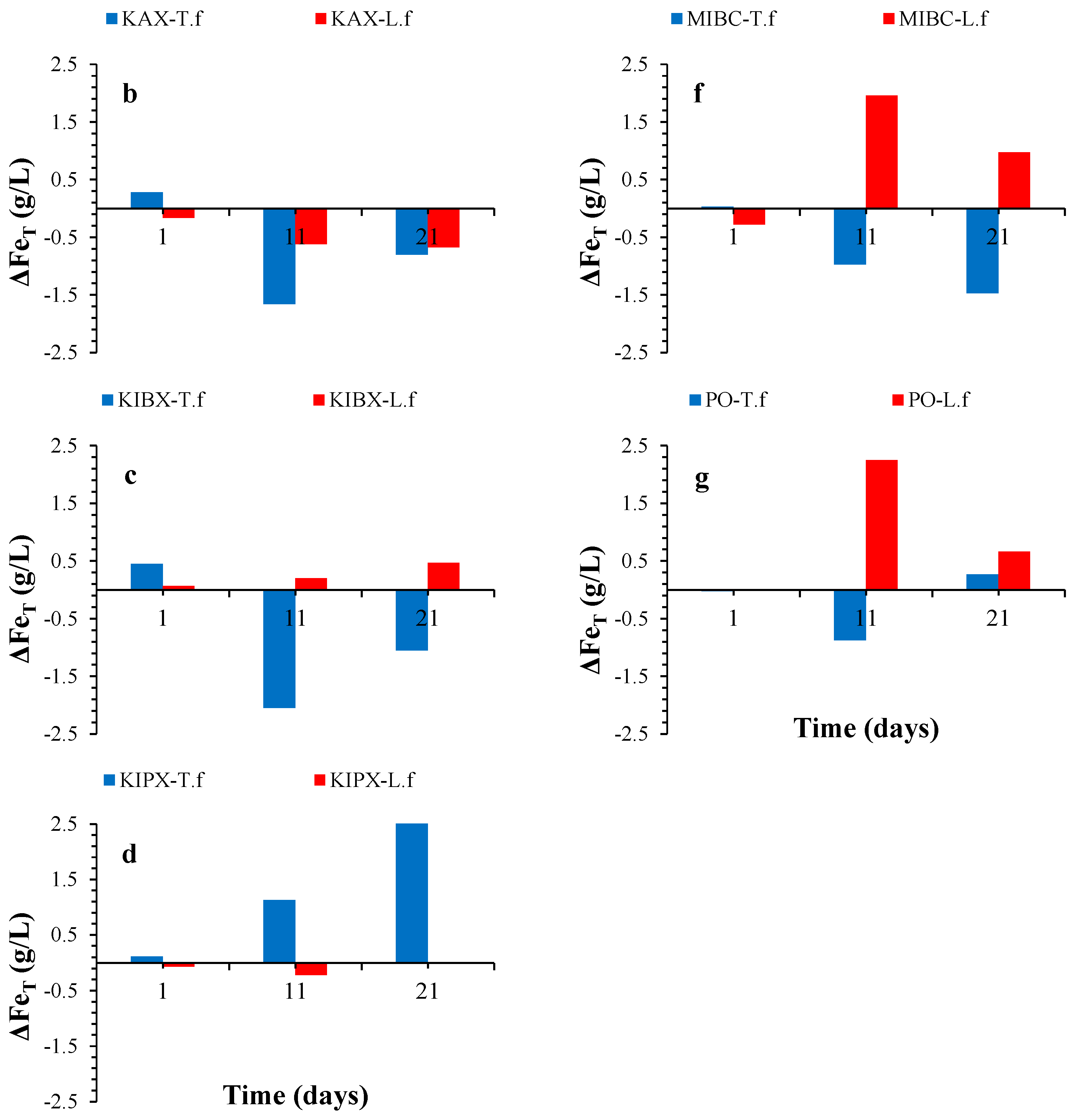
3.5. Fe Variation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dehghan, R.; Dianati, M. The effects of Pb-Zn flotation reagents on the bioleaching process by mesophilic bacteria. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 143, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, N.; Natarajan, K. Biological removal of some flotation collector reagents from aqueous solutions and mineral surfaces. Miner. Eng. 1998, 11, 717–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lin, H. Influences of flotation reagents on bioleaching of chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Miner. Eng. 2012, 32, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yao, J.; Wang, F.; Yuan, Z.; Bararunyeretse, P.; Zhao, Y. Effect of three typical sulfide mineral flotation collectors on soil microbial activity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7425–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okibe, N.; Johnson, D.B. Toxicity of flotation reagents to moderately thermophilic bioleaching microorganisms. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dew, D.W.; Lawson, E.N.; Broadhurst, J.L. The biox® process for biooxidation of gold-bearing ores or concentrates. In Biomining; Rawlings, D.E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997; pp. 45–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tuovinen, O.H. Inhibition of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans by mineral flotation reagents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1978, 5, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, A.; Blázquez, M.; González, F.; Muñoz, J. New information on the sphalerite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 71, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Deveci, H.; Akcil, A.; Alp, I. Bioleaching of complex zinc sulphides using mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria: Comparative importance of pH and iron. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 73, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, B.; Quiroz, L.; Vargas, T. Effect of flotation and solvent extraction reagents on the bioleaching of a copper concentrate with Sulfolobus metallicus. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 71, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, D.; Silver, M. Ore leaching by bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1980, 34, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, C.L. Microbiological mining. Sci. Am. 1982, 247, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.P.; Wood, A.P. Reclassification of some species of Thiobacillus to the newly designated genera Acidithiobacillus gen. Nov., halothiobacillus gen. Nov. and thermithiobacillus gen. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temple, K.L.; Colmer, A.R. The autotrophic oxidation of iron by a new bacterium: Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J. Bacteriol. 1951, 62, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, D.; Tributsch, H.; Hansford, G. Reasons why ‘Leptospirillum’-like species rather than Thiobacillus ferrooxidans are the dominant iron-oxidizing bacteria in many commercial processes for the biooxidation of pyrite and related ores. Microbiology 1999, 145, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, S.R. Selection of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans SRPCBL and development for enhanced ferric regeneration in stirred tank and airlift column reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7803–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, L.J.; Rice, N.M. The adaptation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for the treatment of nickel–iron sulphide concentrates. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M.P.; Lundgren, D.G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium ferrobacillus ferrooxidans: I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J. Bacteriol. 1959, 77, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.L.; Leão, V.A.; Gomes, O.; Lambert, F.; Bastin, D.; Gaydardzhiev, S. Copper extraction from coarsely ground printed circuit boards using moderate thermophilic bacteria in a rotating-drum reactor. Waste Manag. 2015, 41, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.L.; Lopes, K.C.; Leôncio, H.C.; Silva, L.A.; Leão, V.A. Bioleaching of fluoride-bearing secondary copper sulphides: Column experiments with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, T.C.; Sicupira, L.C.; Rodrigues, I.C.; Silva, L.A.; Leão, V.A. The effects of fluoride and aluminum ions on ferrous-iron oxidation and copper sulfide bioleaching with Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 62, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, I.; Cooke, S. Dissociation constant of xanthic acid as determined by spectrophotometric method. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1321–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomianowski, A.; Leja, J. Spectrophotometric study of xanthate and dixanthogen solutions. Can. J. Chem. 1963, 41, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Woodcock, J. Decomposition of alkyl dixanthogens in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1983, 10, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhakka, J.; Tuovinen, O.H. Effect of organic compounds on the microbiological leaching of a complex sulphide ore material. World J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1987, 3, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loon, H.Y.; Madgwick, J. The effect of xanthate floatation reagents on bacterial leaching of chalcopyrite by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biotechnol. Lett. 1995, 17, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Forsling, W. The degradation kinetics of ethyl-xanthate as a function of pH in aqueous solution. Miner. Eng. 1997, 10, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, G.M.; Li, X.; Xu, W.H.; Fan, T. Effect of solids concentration on removal of heavy metals from mine tailings via bioleaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.G.; Xia, J.L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Peng, A.A.; Nie, Z.Y.; Qiu, G.Z. Comparative study on effects of tween-80 and sodium isobutyl-xanthate on growth and sulfur-oxidizing activities of Acidithiobacillus allbertensis by-05. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, D.E. Characteristics and adaptability of iron-and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms used for the recovery of metals from minerals and their concentrates. Microb. Cell Fact. 2005, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norris, P. Iron and mineral oxidation with Leptospirillum-like bacteria. In Recent Progress in Biohydrometallurgy; Rossi, G., Torma, A.E., Eds.; Associazione Mineraria Sarda: Iglesias, Italy, 1983; pp. 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Sand, W.; Rohde, K.; Sobotke, B.; Zenneck, C. Evaluation of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans for leaching. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hojjati, H.; Penev, K.; Pupkevich, V.R.; Karamanev, D.G. Modeling, simulation, and optimization of hybrid Fe(II)/Fe(III) redox flow fuel cell system. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, M.; Heijnen, J. Gas–liquid mass transfer phenomena in bio-oxidation experiments of sulphide minerals: A critical review of literature data. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 48, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, H.; Akcil, A.; Alp, I. Parameters for control and optimization of bioleaching of sulfide minerals. In Proceedings of the Materials Science and Technology Symposium: Process Control and Optimization in Ferrous and Non Ferrous Industry, Chicago, IL, USA, 9–12 November 2003; pp. 77–90.
- Hulme, M.; Stranks, D. Induction and the regulation of production of cellulase by fungi. Nature 1970, 226, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torma, A.E.; Gabra, G.; Guay, R.; Silver, M. Effects of surface active agents on the oxidation of chalcopyrite by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 1976, 1, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopson, M.; Sundkvist, J.E.; Lindström, E.B. Toxicity of metal extraction and flotation chemicals to Sulfolobus metallicus and chalcopyrite bioleaching. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 81, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, R.; Friedrich, A.; Koops, H.P.; Pommerening-Röser, A.; Rohde, K.; Zenneck, C.; Sand, W. Physiological characteristics of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and physicochemical factors influence microbial metal leaching. Geomicrobiol. J. 1992, 10, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, F.; Ojumu, T. Investigation of ferrous-iron biooxidation kinetics by Leptospirillum ferriphilum in a novel packed-column bioreactor: Effects of temperature and jarosite accumulation. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 141, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Jing, L.; An, C.; Zhong, D.; Qian, L.; Qin, W.; Qiu, G.; Gu, G. Interaction mechanism of Cu2+, Fe3+ ions and extracellular polymeric substances during bioleaching chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ACTT2370. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curutchet, G.; Pogliani, C.; Donati, E.; Tedesco, P. Effect of iron (III) and its hydrolysis products (jarosites) on Thiobacillus ferrooxidans growth and on bacterial leaching. Biotechnol. Lett. 1992, 14, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, C.; Rawlings, D. Theory, microbes and industrial processes. In Biomining; Rawlings, D.E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, P.R.; Barr, D.W.; Hinson, D. Iron and mineral oxidation by acidophilic bacteria: Affinities for iron and attachment to pyrite. In Biohydrometallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium; Norris, P.R., Kelly, D.P., Eds.; Antony Rowe Ltd.: Chippenham, UK, 1987; pp. 43–59. [Google Scholar]
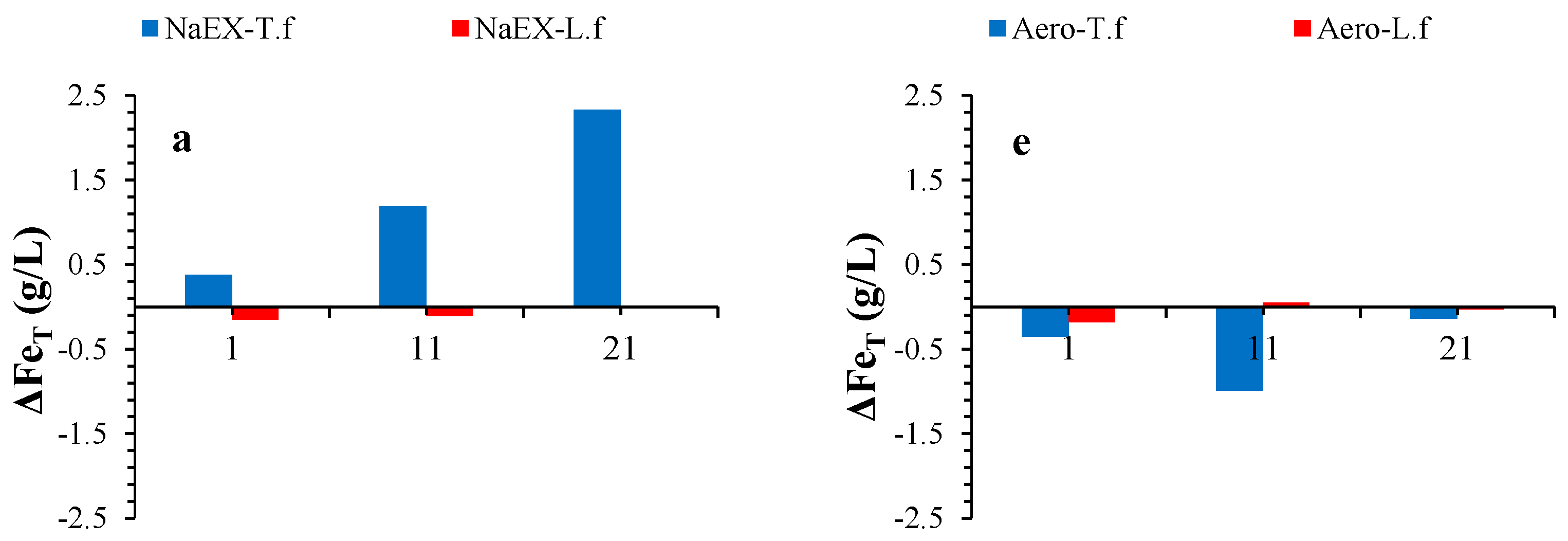
| Parameters | Collectors | Frothers |
|---|---|---|
| pH | NaEX > KIBX > KAX > Aero > KIPX | MIBC > PO |
| ORP | KIPX> Aero > NaEX > KIBX > KAX | MIBC > PO |
| DO2 | KIPX > Aero > KIBX > NaEX > KAX | MIBC ≥ PO |
| Count | KIPX > NaEX > KAX > KIBX > Aero | MIBC > PO |
| KAX > KIPX > KIBX > Aero > NaEX | MIBC ≥ PO | |
| Aero > KIPX > NaEX ≥ KAX > KIBX | MIBC ≥ PO |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jafari, M.; Shafaei, S.Z.A.; Abdollahi, H.; Gharabaghi, M.; Chehreh Chelgani, S. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Flotation Reagents on Growth and Iron Oxidation Activities of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Minerals 2017, 7, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7010002
Jafari M, Shafaei SZA, Abdollahi H, Gharabaghi M, Chehreh Chelgani S. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Flotation Reagents on Growth and Iron Oxidation Activities of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Minerals. 2017; 7(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleJafari, Mohammad, Said Zia Aldin Shafaei, Hadi Abdollahi, Mahdi Gharabaghi, and Saeed Chehreh Chelgani. 2017. "A Comparative Study on the Effect of Flotation Reagents on Growth and Iron Oxidation Activities of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans" Minerals 7, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7010002
APA StyleJafari, M., Shafaei, S. Z. A., Abdollahi, H., Gharabaghi, M., & Chehreh Chelgani, S. (2017). A Comparative Study on the Effect of Flotation Reagents on Growth and Iron Oxidation Activities of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Minerals, 7(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7010002







