Dehydration and Rehydration of Carbonated Fluor- and Hydroxylapatite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Sample Analysis and Characterization
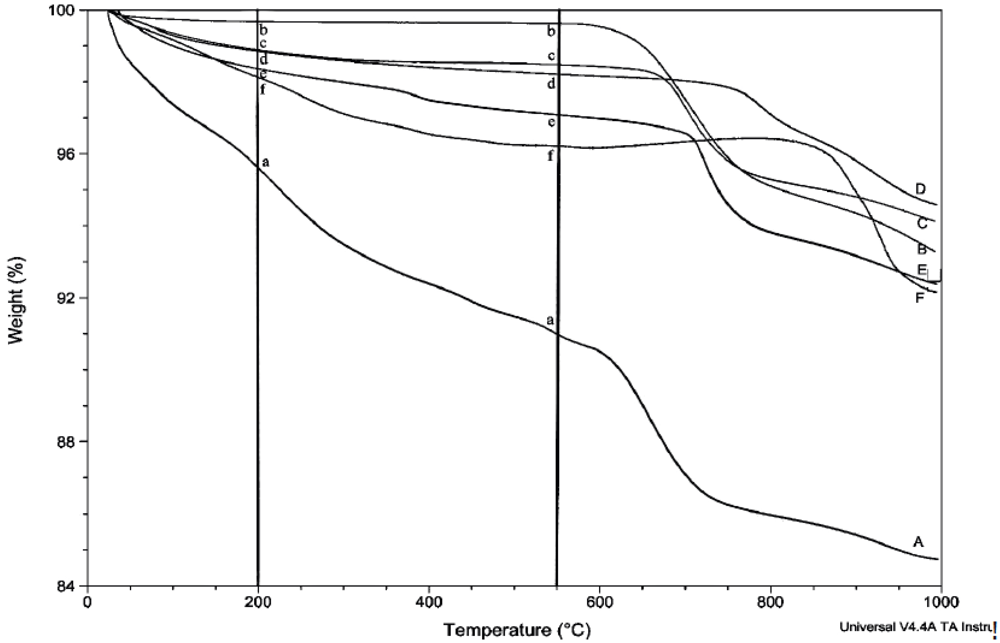
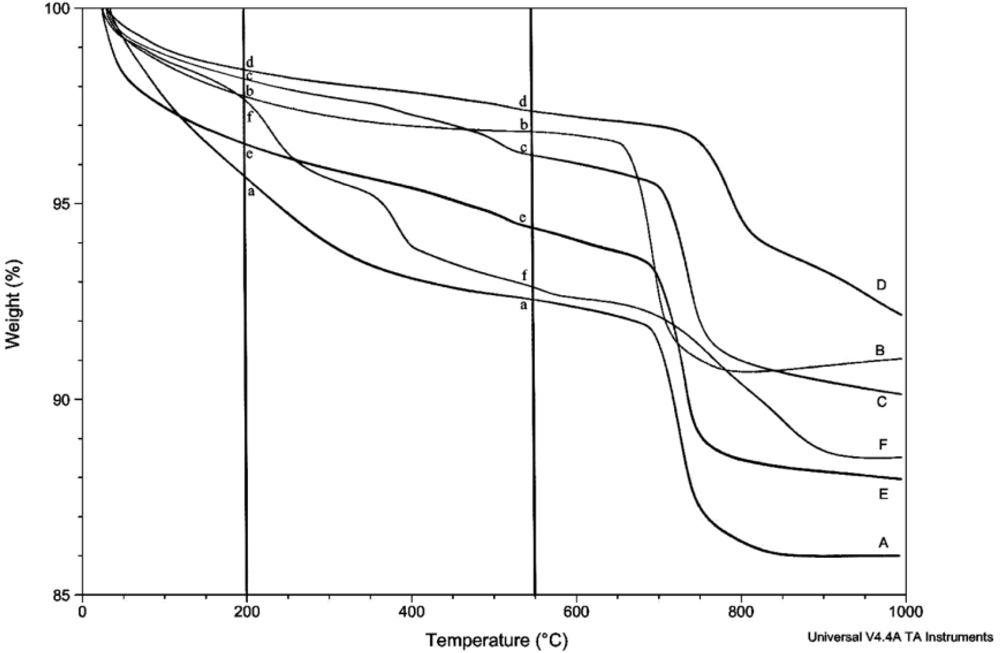
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.4. Rehydration Experiments
3. Results
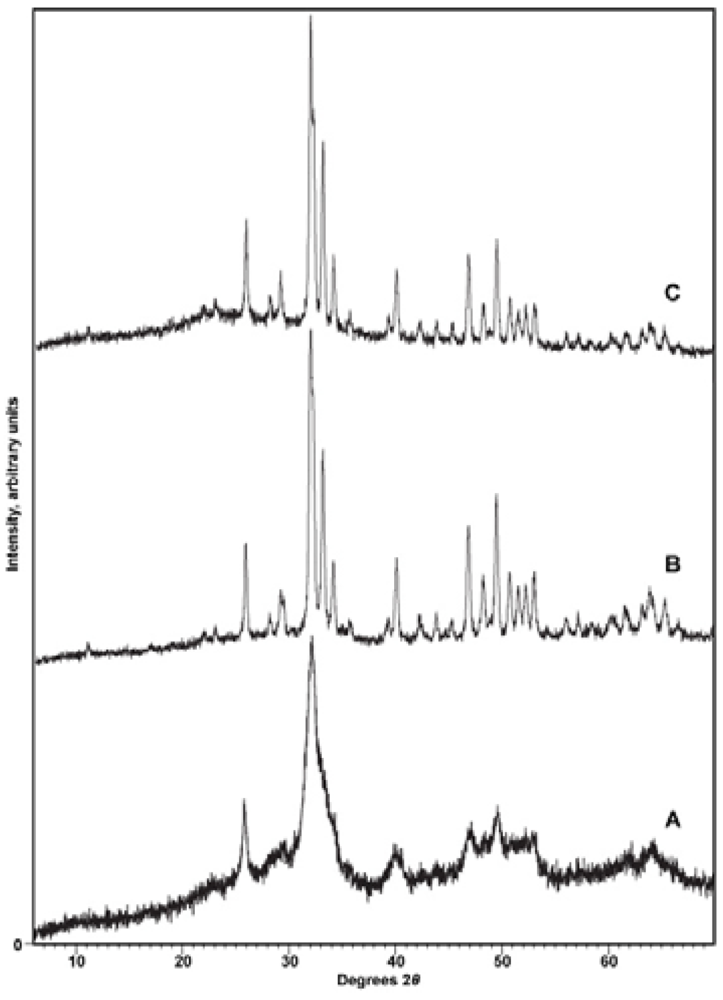
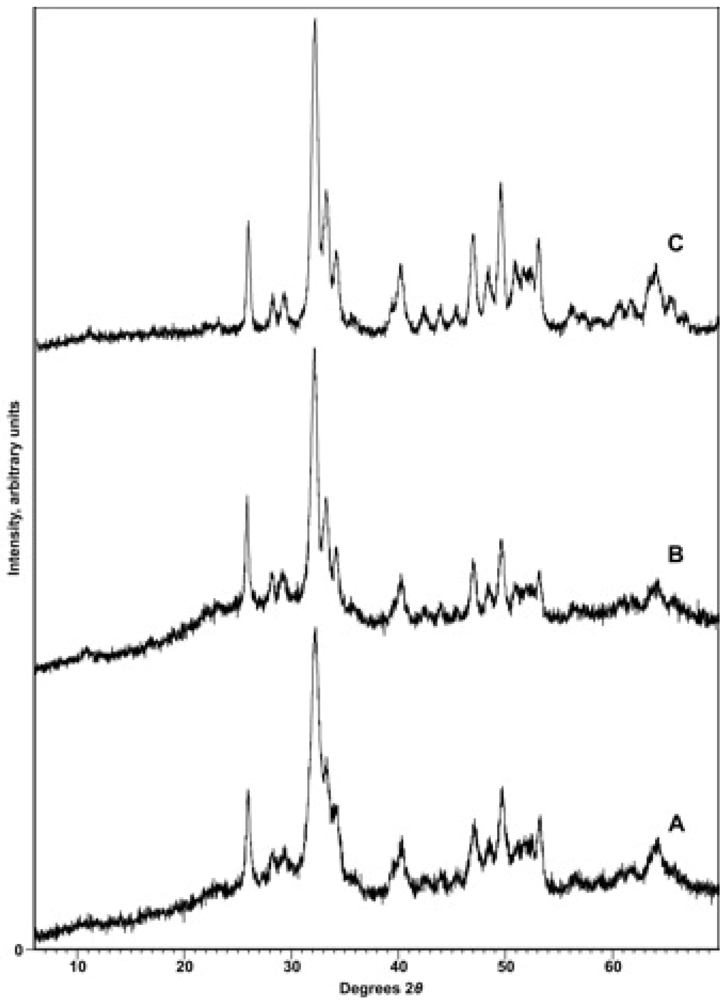
3.1. Characterization of Compounds
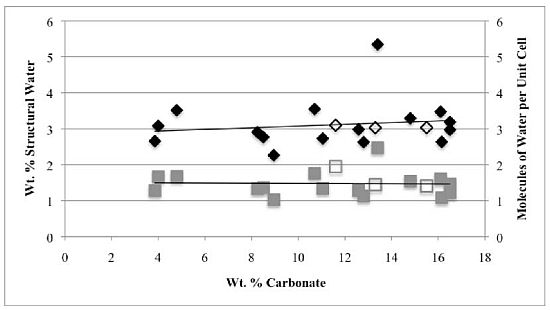
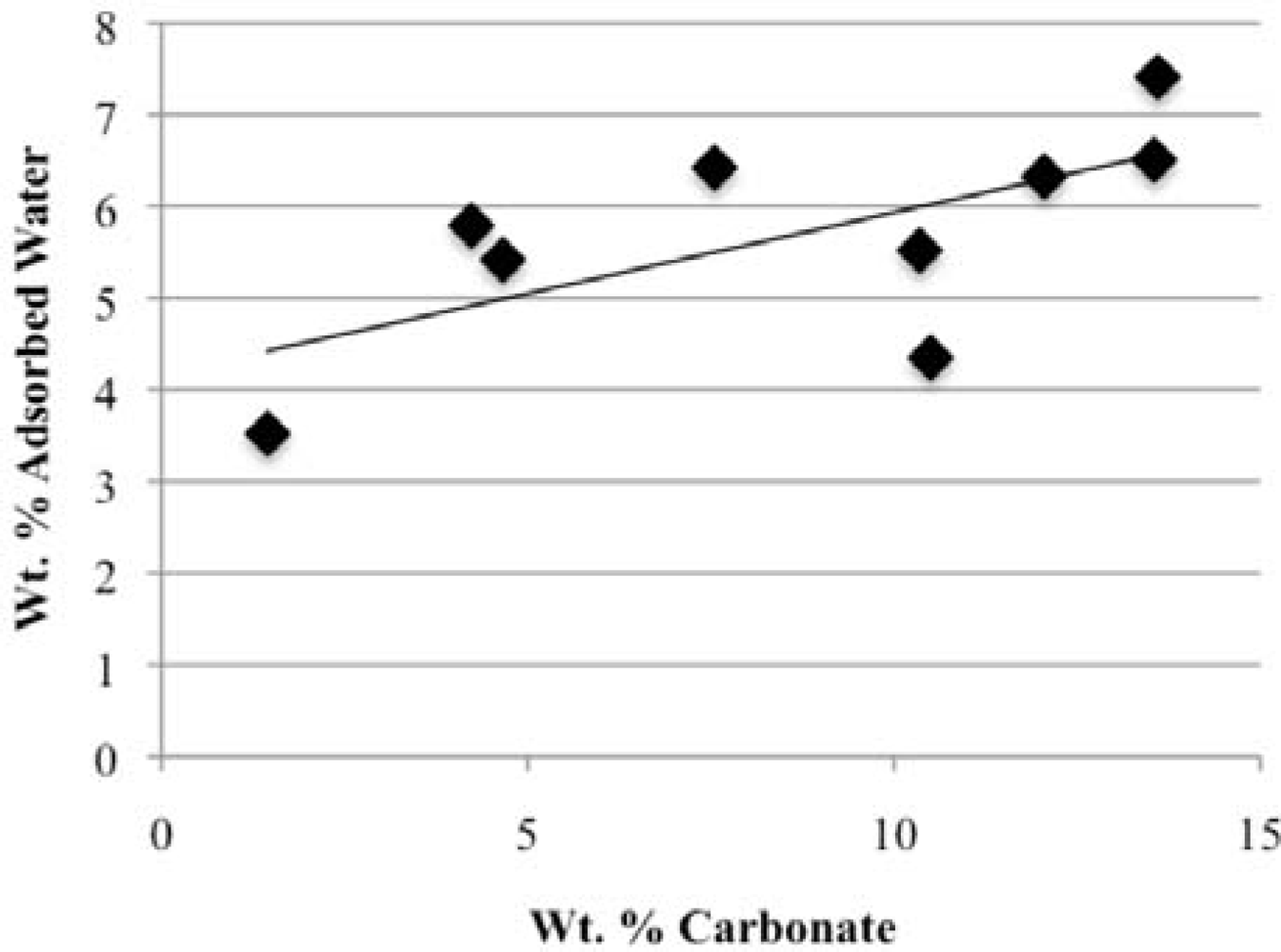
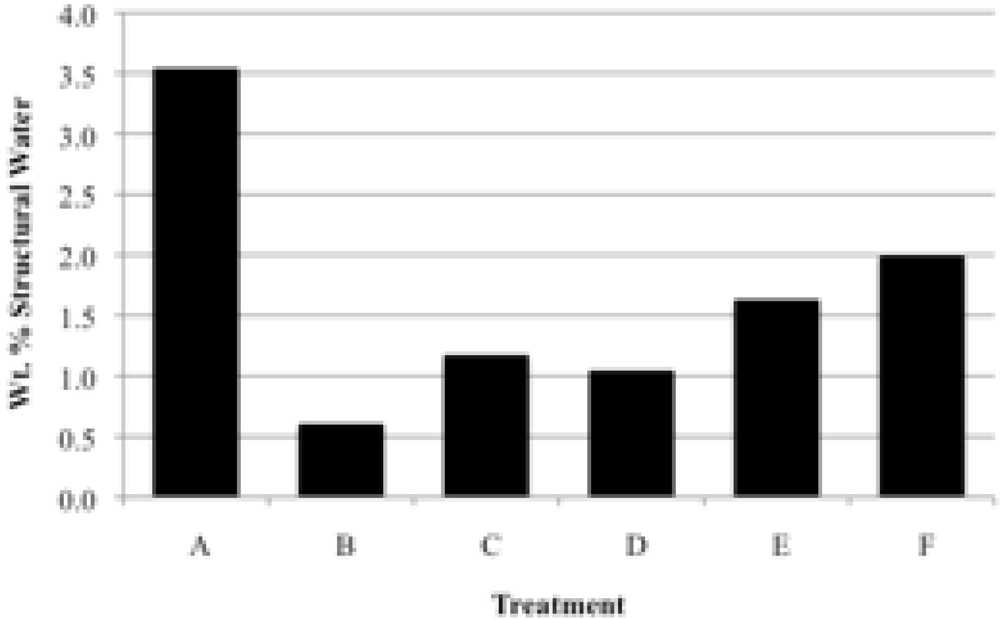
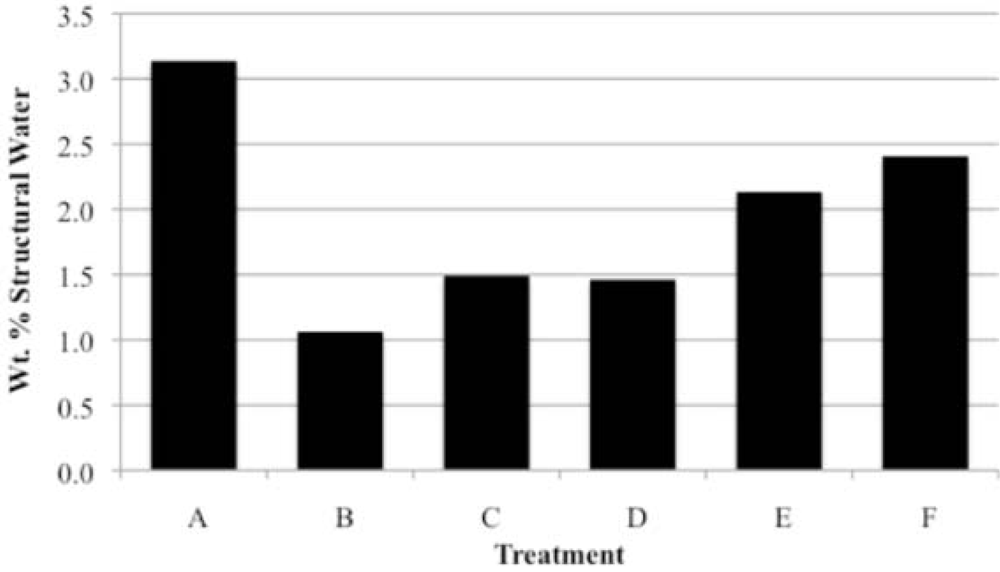
3.2. Structural Water

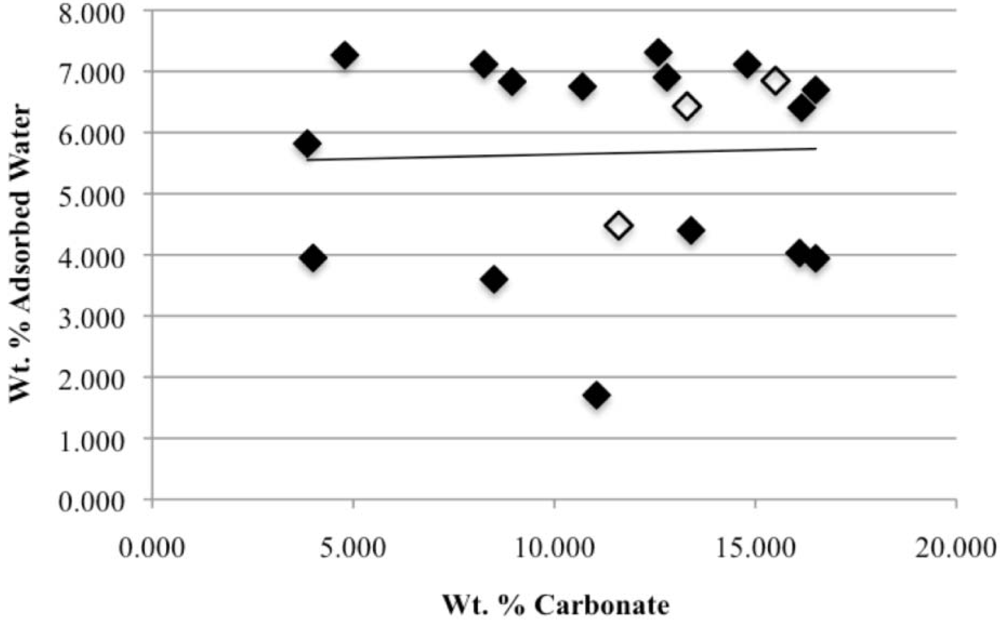
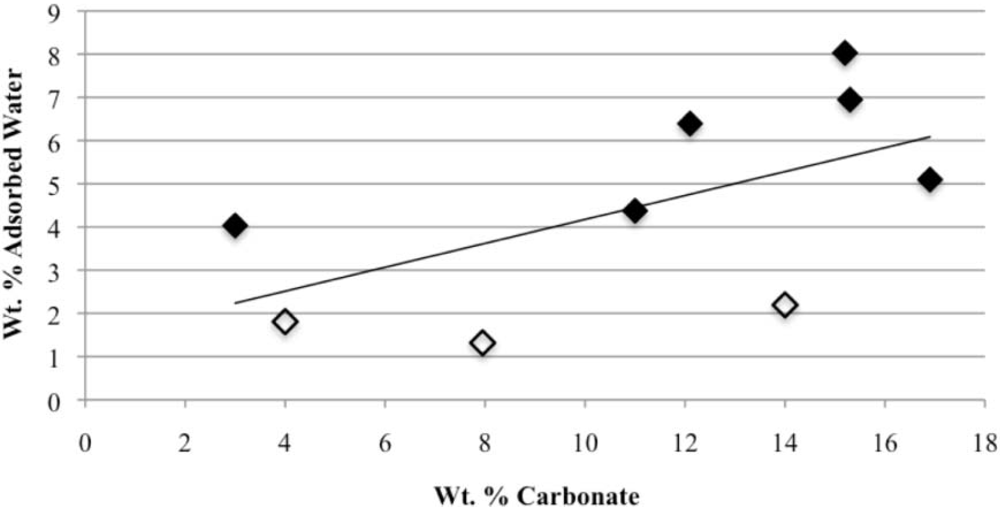
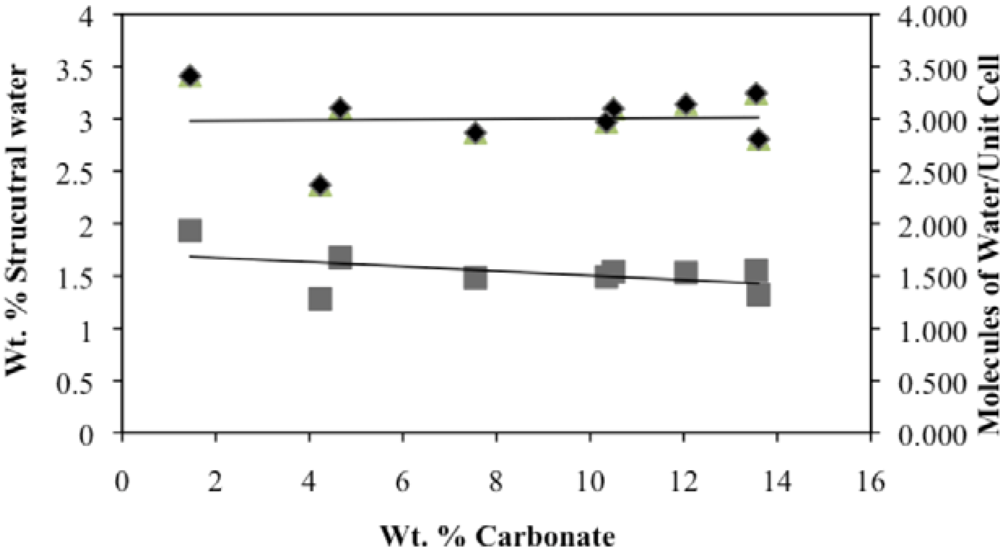
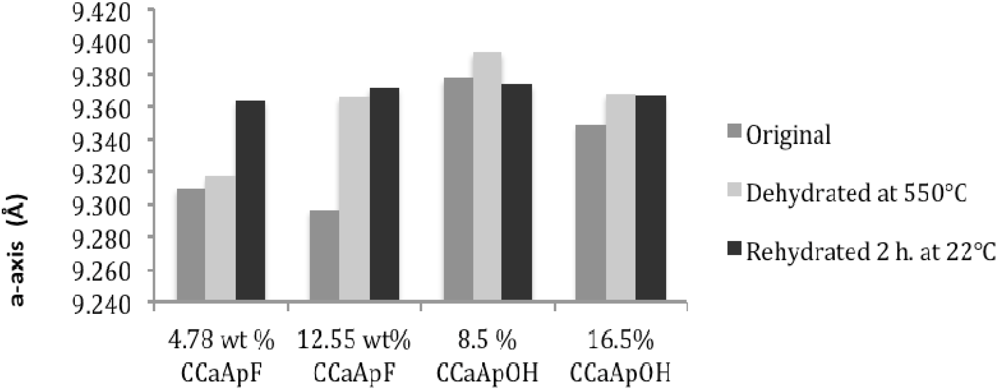
3.3. Rehydration
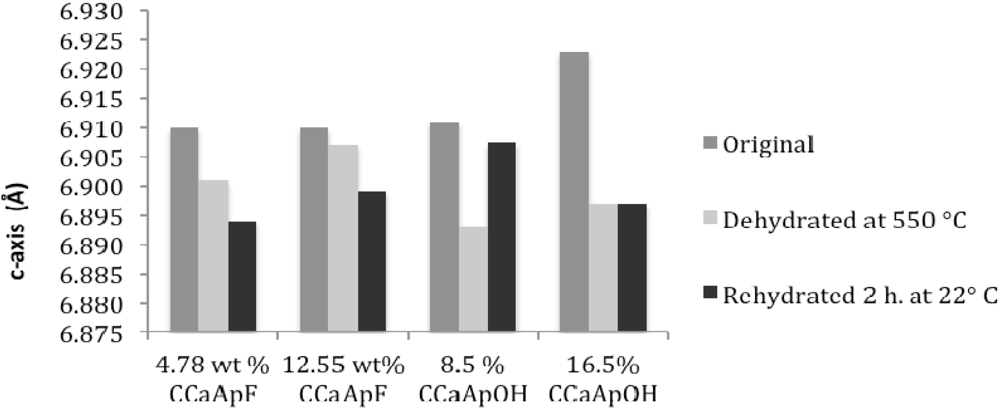
4. Discussion
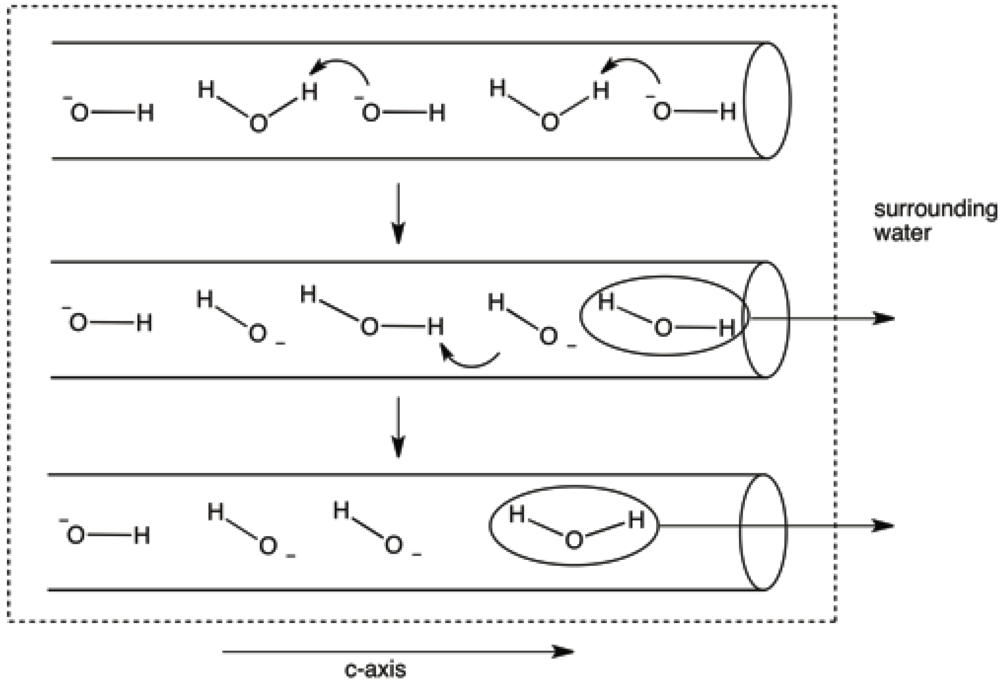
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- McConnell, D. The crystal structure of bone. Clin. Orthop. 1962, 23, 253–268. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, D. Crystal chemistry of bone mineral: Hydrated carbonate apatites. Am. Mineral. 1970, 55, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, D.R. The nature of alkali carbonate apatites. Am. Miner. 1964, 49, 363–376. [Google Scholar]
- Biltz, M.M.; Pellegrino, E.D. The hydroxyl content of calcified tissue mineral. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1971, 36, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- LeGeros, R.Z.; Bonel, G.; Legros, R. Types of “H2O” in human enamel and in precipitated apatites. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1978, 26, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, T.I.; Frank-Kamenetaskaya, O.V.; Kol’tsov, A.B.; Ugolkov, V.L. Crystal structure of calcium-deficient carbonated hydroxyapatite. Thermal decomposition. J. Solid State Chem. 2001, 160, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.M.; Elliott, J.C.; Dowker, S.E.P.; Smith, R.I. Rietveld structure refinement of precipitated carbonate apatite using neutron diffraction data. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, E.E.; Awonusi, A.; Morris, M.D.; Kohn, D.H.; Tecklenburg, M.M.J.; Beck, L.W. Three structural roles for water in bone observed by solid-state NMR. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 3722–3731. [Google Scholar]
- Yesinowski, J.; Eckert, H. Hydrogen environments in calcium phosphates: Proton MAS NMR at high spinning speeds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 6274–6282. [Google Scholar]
- Sfihi, H.; Rey, C. 1-D and 2-D double heteronuclear magnetic resonance study of the local structure of type b carbonate fluoroapatite. In Magnetic Resonance in Colloid and Interface Science, Nato ASI Series II; Fraissard, J., Lapina, B., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 409–422. [Google Scholar]
- Kaflak-Hachulska, A.; Samoson, A.; Kolodziejski, W. 1H MAS and 1H CP/MAS NMR study of human bone mineral. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2003, 73, 476–486. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmas, J.; Kolodziejski, W. Concentration of hydroxyl groups in dental apatites: A solid-state 1H MAS NMR study using inverse 31P-1H cross-polarization. Chem. Commun. 2007, 4390–4392. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, G.; Wu, Y.; Ackerman, J.L. Detection of hydroxyl ions in bone mineral by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Science 2003, 300, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Sandström, D.E.; Jarlbring, M.; Antzutkin, O.N.; Forsling, W. A spectroscopic study of calcium surface sites and adsorbed iron species at aqueous fluorapatite by means of 1H and 31P MAS NMR. Langmuir 2006, 22, 11060–11064. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, H.E.; McCubbin, F.M.; Smirnov, A.; Phillips, B.L. Solid-state NMR and IR spectroscopic investigation of the role of structural water and F in carbonate-rich fluorapatite. Am. Mineral. 2009, 94, 507–516. [Google Scholar]
- Yoder, C.H.; Pasteris, J.D.; Worcester, K.N.; Schermerhorn, D.V. Structural water in carbonated hydroxylapatite and fluorapatite: Confirmation by solid state 2H NMR. Calcif. Tis. Int. 2011, 90, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- LeGeros, R.Z.; Trautz, O.R.; Klein, E.; LeGeros, J.P. Two types of carbonate substitution in the apatite structure. Experientia 1969, 25, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Elliot, J.C. Structure and chemistry of the apatites and other calcium orthophosphates. In Studies in Inorganic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, J.C. Calcium phosphate biominerals. In Phosphates-geochemical, Geobiological, and Materials Importance; Kohn, M.J., Rakovan, J., Hughes, J.M., Eds.; Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2002; Volume 48, pp. 427–453. [Google Scholar]
- Penel, G.; Leroy, G.; Rey, C.; Bres, E. MicroRaman spectral study of the PO4 and CO3 vibrational modes in synthetic and biological apatites. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1998, 63, 475–481. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Fleet, M.E. Compositions of the apatite-group minerals: Substitution mechanisms and controlling factors. In Phosphates-Geochemical, Geobiological, and Materials Importance; Kohn, M.J., Rakovan, J., Hughes, J.M., Eds.; Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2002; Volume 48, pp. 13–49. [Google Scholar]
- Rosseeva, E.V.; Buder, J.; Simon, P.; Schwarz, U.; Frank-Kamenetskaya, O.V.; Kneip, R. Synthesis, characterization, and morphogenesis of carbonated fluorapatite-gelatine nanocomposites: A complex biomimetic approach toward the mineralization of hard tissues. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6003–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, D.W.; Young, R.A. Thermal decomposition of human tooth enamel. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1980, 31, 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Füredi-Milhofer, H.; Hlady, V.; Baker, F.S.; Beebe, R.A.; Wikholm, N.W. Temperature-programmed dehydration of hydroxyapatite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1979, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Casga, J.; Garcia-Garcia, R.; Arellano-Jimenez, M.J.; Sanchez-Pastenes, E.; Tiznado-Orozco, G.E.; Gill-Chavarria, I.M.; Gomez-Casga, G. Structural and thermal behaviour of human tooth and three synthetic hydroxyapaties from 20 to 600 °C. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, A.A.; Fox, J.L.; Young, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Hsu, J.; Higuchi, W.I.; Chhettry, A.; Zhuang, H.; Otsuka, M. Relationships among carbonated apatite solubility, crystallite size, and microstrain parameters. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1999, 64, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termine, J.D.; Eanes, E.D.; Greenfield, D.J.; Nylen, M.U.; Harper, R.A. Hydrazine-deproteinated bone mineral: Physical and chemical properties. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1973, 12, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, C.; Combes, C.; Drouet, C.; Sfihi, H.; Barroug, A. Physico-chemical properties of nanocrystalline apatites: Implications for biominerals and biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wilson, R.M.; Elliott, J.C.; Dowker, S.E.P.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.M. Rietveld refinements and spectroscopic studies of the structure of Ca-deficient apatite. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Termine, J.D.; Lundy, D.R. Hydroxide and carbonate in rat bone mineral and its synthetic analogues. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1973, 13, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, C. Apatite chanel and zeolite-like properties. In Hydroxyapatite and Related Materials; Brown, P.W., Constanz, B., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, C.; Miquel, J.L.; Facchini, L.; Legrand, A.P.; Glimcher, M.J. Hydroxyl groups in bone mineral. Bone 1995, 16, 583–586. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Klocke, A.; Zhang, M.; Bismayer, U. Thermal behavior of dental enamel and geologic apatite: An infrared spectroscopic study. Am. Mineral. 2003, 88, 1866–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Pasteris, J.D.; Wopenka, B.; Freeman, J.J.; Rogers, K.; Valsami-Jones, E.; van der Houwen, J.A.M.; Silva, M.J. Lack of OH in nanocrystalline apatite as a function of degree of atomic order: Implications for bone and biomaterials. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Etok, S.E.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Wess, T.J.; Hiller, J.C.; Maxwell, C.A.; Rogers, K.D.; Manning, D.A.C.; White, M.L.; Lopez-Capel, E.; Collins, M.J.; et al. Structural and chemical changes of thermally treated bone apatite. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 9807–9816. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, L.; Grypas, M.D.; Rey, C.C.; Wu, Y.; Ackerman, J.L.; Glimcher, M.J. A comparison of the physical and chemical differences between cancellous and cortical bovine bone mineral at two ages. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2008, 83, 146–154. [Google Scholar]
- Joris, S.J.; Amberg, C.H. The nature of the deficiency in nonstoichiometric hydroxyapatite. II. Spectroscopic studies of calcium and strontium hydroxyapatite. J. Phys. Chem. 1971, 75, 3172–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maeyer, E.A.P.; Verbeeck, R.M.H.; Naessens, D.E. Stoichiometry of Na+- and CO32−-containing apatites obtained by hydrolysis of monetite. Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 5709–5714. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, E.E.; Awonusi, A.; Morris, M.D.; Kohn, D.H.; Tecklenburg, M.M.J. Three structural roles for water in bone observed by solid-state NMR. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 3722–3731. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoder, C.; Pasteris, J.; Worcester, K.; Schermerhorn, D.; Sternlieb, M.; Goldenberg, J.; Wilt, Z. Dehydration and Rehydration of Carbonated Fluor- and Hydroxylapatite. Minerals 2012, 2, 100-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/min2020100
Yoder C, Pasteris J, Worcester K, Schermerhorn D, Sternlieb M, Goldenberg J, Wilt Z. Dehydration and Rehydration of Carbonated Fluor- and Hydroxylapatite. Minerals. 2012; 2(2):100-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/min2020100
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoder, Claude, Jill Pasteris, Kimberly Worcester, Demetra Schermerhorn, Mitchell Sternlieb, Jennifer Goldenberg, and Zachary Wilt. 2012. "Dehydration and Rehydration of Carbonated Fluor- and Hydroxylapatite" Minerals 2, no. 2: 100-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/min2020100
APA StyleYoder, C., Pasteris, J., Worcester, K., Schermerhorn, D., Sternlieb, M., Goldenberg, J., & Wilt, Z. (2012). Dehydration and Rehydration of Carbonated Fluor- and Hydroxylapatite. Minerals, 2(2), 100-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/min2020100