Abstract
This study provides a comprehensive characterization of the low-to-intermediate sulfidation (LS-to-IS) epithermal Molai Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) ore (Vigla-Mesovouni orebody) in Laconia, Greece, and provides insights on how such data may be employed in beneficiation flow-sheet design. Detailed mineralogical, chemical, textural, and physicochemical characterization defines a systematic transition from early refractory Ge-rich to late-stage refractory Ag-rich mineralization, including sulfides and fahlores. Germanium, although present in all sphalerite varieties (Sp-I, Sp-II, and Sp-III), is predominantly enriched in early sphalerite (Sp-I, up to 1891.60 ppm). Interestingly, Ge is also enriched in early Py-I pyrite, with content reaching up to 383 ppm. Silver is mainly concentrated in late-stage tetrahedrite Ttr-II (up to 3.60%), galena (Ga-II), and, to a lesser extent, late sphalerite (Sp-III). Liberation studies reveal effective liberation of Py-I and Sp-I, major Ge carriers, in the coarser fractions (+0.150 mm) and near complete liberation of all ore phases below 0.036 mm. Combined beneficiation via Wilfley pre-concentration and differential flotation produced up to ~35% Pb and ~65% Zn at >85% recovery for the smallest fractions (−0.036 mm). Ore characterization revealed that secondary circuits may be developed to further enhance the economic value of Molai ore (Ge from Py-I, and Ag±[Sb,As] from Ttr-II and Ag-bearing sulfosalts), which are dismissed as wastes in Pb and Zn flotation circuits. The results of our study establish a robust foundation for the design of tailored, multi-stage metallurgical flow-sheets aimed at maximizing the economic value of the Molai epithermal resource.
1. Introduction
Contemporary advances in analyzing techniques, including both detection limits and spatial resolution, have led to significant changes in the way the scientific community approaches hypogene sulfide ores, their corresponding classification (refer to [1,2,3,4,5]), and commodities (see [6,7,8]). At the same time, contemporary developments in ore processing and metallurgy have also redefined base and precious metal deposits worldwide in terms of the metals produced [9,10,11]. Considering the contemporary need for critical raw materials (CRMs), the vast majority of exploited or under exploitation sulfide deposits around the world are being re-assessed, especially regarding their critical and strategic metal content [8,12]. For instance, germanium (Ge) is one of the thirty critical raw materials (CRMs) defined by the European Union (2020) due to its strategic importance in high-tech applications [13] (accessed on 14 July 2025). Germanium plays a key role in the photonic, semiconductor, and photovoltaic industries, in which its unique optical and photoelectronic properties make it essential for advanced technologies. The mineralogical and hence metallurgical properties of Ge-enriched ores are critical in determining the ultimate achievable performance in any plausible mining and processing operations.
Under this scope, the Molai sulfide deposit, located in Laconia, Southeastern Peloponnese, although primarily described as a Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide (Kuroko-type) ore (see [14,15]), has recently been redefined as a Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) epithermal ore deposit evolving from early low-sulfidation to late intermediate sulfidation state [16] (Figure 1). At the same time, it was originally considered as a Pb-Zn±Ag resource, yet it is now been proven to be enriched in Ge, with a JORC resource of 15 Mt, corresponding to ~1.1 Mt Zn, 0.26 Mt Pb, ~19 Moz Ag, and ~1.05 kt Ge, predominantly recovered as a by-product [17] (accessed on 16 July 2025). The Molai Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) deposit is classified as medium-class for silver and ranks amongst the top 20 undeveloped zinc deposits worldwide, based on tonnage, grade, and a combined metal content of 9.96% Zn Eq [16]. Preliminary bulk flotation tests performed in the early 1980s reported 96% zinc, 92% lead, and 91% silver recoveries, respectively [15,18], whereas hydrometallurgical processing (chlorination) has also been proposed, yet has not been tested to this day [19].
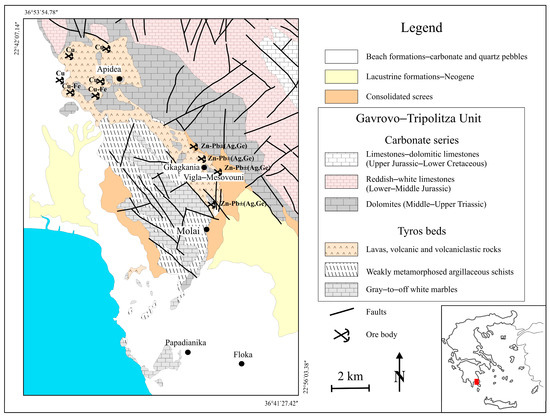
Figure 1.
Simplified geological map of the Molai Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) epithermal ore, with the locations of the major ore bodies (with modifications after [16]).
Besides traditional ore characterization based on ore mineralogy, mineral chemistry, and geochemistry, ore physical and mechanical characterization provide valuable insights into the ore types being mined, enabling the identification of optimal methods to maximize the final value, especially when considering CRMs that are usually found at trace content levels (below 1000 ppm) [11,20,21,22,23]. Understanding of ore’s physical, mechanical, and chemical characteristics empowers mining operations to implement energy-efficient processes, enhance recovery rates, increase production output and economic value, reduce operational costs, and meet international quality and environmental standards [24,25].
This study employs a comprehensive workflow that includes optical, electron (SEM), and cathodoluminescence (CL) microscopy; X-ray diffraction (XRD); X-ray fluorescence (XRF); porosimetry (BET); and Raman spectroscopy, with the objective of defining the physicochemical and mechanical characteristics of Molai epithermal ore. Additionally, electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) and in situ LA-ICP-MS analysis are utilized to establish the trace element geochemical properties of the various ore phases of the Molai deposit. In the second stage, the results of the ore characterization are used to evaluate the pre-concentration of the low-grade Molai ore and are also compared with the results of the flotation circuits examined, the latter focused on the major commodities Pb and Zn. The objective of the present study is to address the importance of a process-oriented ore characterization study and how such characterizations may be employed in the development of processing circuits for the redefined Molai epithermal system. Moreover, the broader study has important implications for constraining the geochemical controls on Ge and Ag enrichment in epithermal deposits and for assessing the potential to increase Ge recovery as a by-product.
2. Molai Deposit Geology
The Molai Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) low-to-intermediate sulfidation (LS-to-IS) epithermal deposit is hosted in the upper Permian-to-middle Triassic “volcanosedimentary” sequence of “Tyros Beds” (for details on the regional and deposit geology, refer to [16,26,27,28,29,30]).
The sulfide ore is epigenetic, replacing the host lithologies, and comprises nine major stratabound orebodies (e.g., Vigla, Mesovouni, Gkagkania, Finiki, and Elia), ranging in thickness from a few cm to ~15 m [15]. The orebodies extend over a total strike length of ~7 km along a broadly N-S direction, dipping 60° eastwards and follow NW- and NE-trending faults. The orebodies are predominantly hosted in pyroclastics (~60–65 vol.%), which alternate with andesitic flows, volcanic breccias and volcaniclastics, and tuffaceous sedimentary rocks (Figure 1). Lapilli tuffs represent the second main host of the Molai ores, particularly when they are rich in volcanic glass clasts and intensely altered, i.e., silicified and sericitized (refer to [16] and references therein).
The deposit is predominantly fine-to-very fine-grained, and four major ore textures are identified [16] (ESM-S1 Figures S1–S4): (i) bedded, massive-to-semi-massive ore, consisting primarily of sphalerite, galena, and chalcopyrite, with subordinate pyrite, tetrahedrite, and trace amounts of arsenopyrite; (ii) clastic, massive-to-semi-massive ore, in which sphalerite and galena are hosted within fine-grained volcaniclastic rocks, cementing the clasts; (iii) sulfide breccias, composed of chalcopyrite, sphalerite, galena, milky quartz, calcite, and minor pyrite, hosted within tuffs and ashes; and (iv) vein-type ore, crosscutting all aforementioned textures, occurring mainly as veinlets and, to a lesser extent, stockworks, characterized by predominant galena intergrown with clear quartz and minor chlorite and epidote.
The deposit is characterized by complex mineralogy and a polymetallic geochemistry. Detailed mineralogical and textural investigation revealed ore deposition in three major ore-forming stages (Figure 2): early stage I with predominant pyrite (Py-I), sphalerite (Sp-I), chalcopyrite, and arsenopyrite; intermediate stage II with predominant sphalerite (varieties Sp-II and Sp-III), galena (Gn-I), tetrahedrite (Ttr-I), and pyrite (Py-II); and late stage III with galena (Gn-II), tetrahedrite (Ttr-II), and Ag-bearing sulfosalts (pyrargirite and stephanite). Genetically, the first two stages correspond to the epigenetic stratabound ore, while late stage III is associated with the vein-type galena-rich ore that crosscuts former stages I and II. Radiogenic Pb data verify the contemporaneous formation of all three ore stages (unpublished data), depicting a hydrothermal system gradually evolving to shallower levels. Further details on the deposit geology are provided by [16].
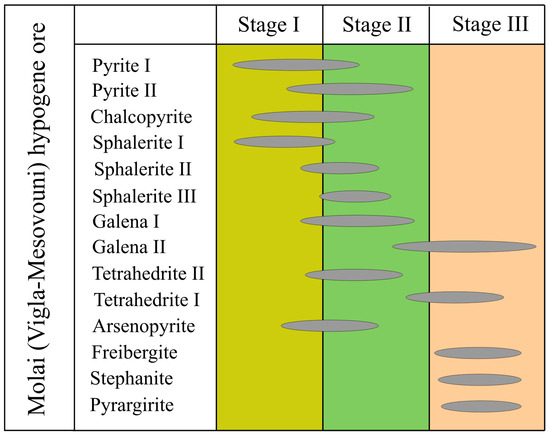
Figure 2.
Paragenetic sequence of the hypogene Molai (Vigla-Mesovouni) Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) sulfide ore.
3. Methodology and Analytical Techniques
The methodology employed in this study involves the following steps (Figure 3-flowchart):
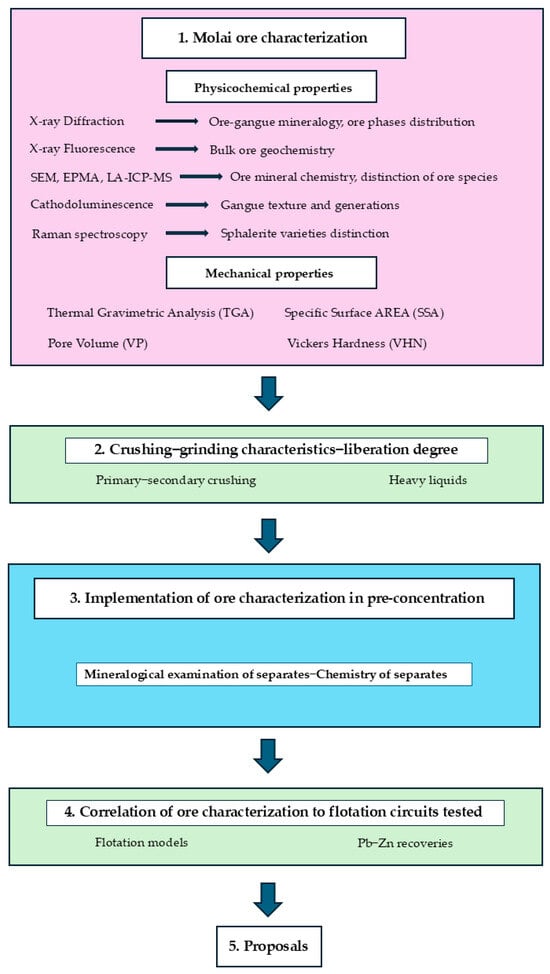
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the methodology and steps employed in this study.
- Examination of the physicochemical and mechanical characteristics of the low-grade and fine-grained Molai sulfide ore (details in ESM-S1, ESM-S2);
- Examination of the crushing and grinding characteristics and liberation degree of the ore;
- Correlation of ore characterization with the Pb-Zn flotation circuits tested.
To examine Molai ore’s physicochemical characterization, the applied methodologies involved X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS), cathodoluminescence (CL), and thermal–gravimetric analysis (TGA). Additionally, the specific surface area (SSA), the pore volume (VP), and the pore size distribution of pyrite and sphalerite were determined, and the Vickers Hardness (VHN) test was employed to evaluate their mechanical properties. For details on the samples used in this study, refer to [16], whereas details on the analytical methods and conditions may be found in Electronic Supplementary Material-1 (ESM-S1).
The liberation, pre-concentration, and flotation circuit testing involved a ~240 kg coarse-to-medium-grained mixed sample from the Vigla-Mesovouni ore body provided by the E.A.G.M.E.—Hellenic Authority for Geological and Mining Research (mixed sample from various drill cores). Initially, larger fragments were manually broken with a hammer to facilitate feeding into the jaw crusher. After crushing, the material was homogenized and cross-sampled to produce 8 subsamples of ~30 kg each. One subsample was further processed to produce working samples of ~1.5 kg, and a representative fraction was extracted using a Jones riffle splitter for mineralogical and lithogeochemical analysis. For details on the pre-concentration workflow and the flotation tests performed, refer to Electronic Supplementary Material-3 (ESM-S3) and [31].
4. Results
4.1. Mineralogy and Geochemistry of the Bulk Sample
Semi-quantitative X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) techniques were applied to determine the mineralogical and geochemical features of the bulk sample used for the pre-concentration examination and the flotation circuits tested. The semi-quantitative XRD analysis revealed that quartz is the predominant gangue phase, comprising ~43.5 vol.%, followed by lower contents of calcite, epidote, orthoclase, albite, and chlorite (Table 1). Hypogene sulfide ore (undifferentiated; 2.3 ± 1.3% of total sample) comprises sphalerite (66.5 ± 3.7%), pyrite (19.5 ± 4.3%), galena (9.5 ± 2.4%), magnetite (2.3 ± 0.2%), and chalcopyrite (2.2 ± 0.4%) with a Ge-enriched ore/Gangue ratio of 4.85 ± 2.48% (Table 1). The raw feed contained average metal contents of 1.12% Pb, 6.34% Zn, 0.06% Cu, 40 ppm Cd, and 35 ppm Ag (Table 2).

Table 1.
Semi-quantitative phase composition of the bulk and ore samples, statistical analysis, VHN and E statistics for Py-I and Sp-I (N = 28), microporosity, and crystallite size results of Py-I and Sp-I from the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody (specific surface area (SSA) and pore volume and size).

Table 2.
Whole-rock geochemistry of the Vigla-Mesovouni bulk ore (analyses 1 to 3) and the average geochemical analysis of the mixed sulfide ore sample used for the pre-concentration and flotation tests (results in wt%).
4.2. Chemical Characterization
Three different populations of sphalerite are distinguished based on their XFeS molar fraction and Fe/S and Zn/S atomic ratios (Table 3; Figure 4; ESM-S2 Table S3; ESM-S2 Figure S3a). They correspond to sphalerite varieties Sp-I, Sp-II, and Sp-III from Vigla and Gkagkania orebodies reported by Kevrekidis et al. [16] (for details on the structure of sphalerite, refer to [33,34]). The LA-ICP-MS analysis (in ppm) revealed that Sp-I is enriched in Ge and As, while Sp-II is rich in Cu, Pb, and Sb (Table 3; Figure 4C). Sphalerite-III, in contrast, is enriched in Cd, Ag, and Ga (Table 3). The Raman spectroscopy results of the sphalerite varieties for Molai ore show three distinct spectra bands at ~350, ~300, and ~330 cm−1, detected in all sphalerite populations (Sp-I, Sp-II, and Sp-III). These bands are characteristic of Zn-S (~350 cm−1) and Fe-S (~330 and ~300 cm−1) bond vibrations in cubic-structured sphalerite (ESM-S1 Figure S12).

Table 3.
LA-ICP-MS trace element composition (in ppm) of Sp-I, Sp-II, and Sp-III from the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody (samples MO10 and 18).
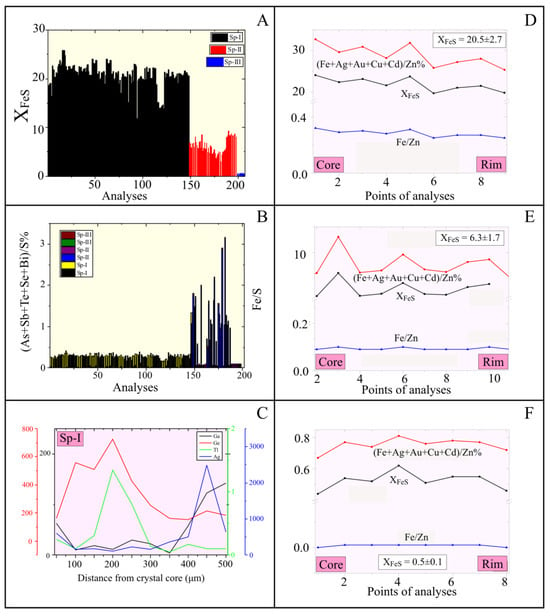
Figure 4.
(A) Discriminant histogram of the different sphalerite populations based on their XFeS molar ratios; (B) discriminant histogram of the different sphalerite populations based on their (As + Sb + Te + Se + Bi)/S% and Fe/S ratios; (C) micro-traverse profiles of selected elements (core-to-rim) of Sp-I from the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody, Molai ore deposit (LA-ICP-MS data); (D–F) micro-traverse profiles (core-to-rim) of XFeS = 20.5 ± 2.7 (Sp-I), XFeS = 6.3 ± 1.7 (Sp-II), and XFeS = 0.5 ± 0.1 (Sp-III) sphalerites, including Fe/Zn, (Fe + Ag + Au + Cu + Cd)/Zn%, and XFeS molar ratios (Vigla-Mesovouni Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) orebodies, Molai ore deposit).
Kevrekidis et al. [16] distinguished two pyrite populations, i.e., early Py-I and later Py-II, based on textural features, and the EPMA- and LA-ICP-MS-derived ore mineral chemistry further supports this discrimination (Table 4; Figure 5A,B; ESM-S2, Table S1; ESM-S2 Figure S1) (for details on the structure of pyrite, refer to [35,36]). Pyrite-I contains high concentrations of Cu, As, Au, and Ge, while Py-II is characterized by the presence of Mn and Ga (Table 4).

Table 4.
LA-ICP-MS trace element composition of Py-I and Py-II (in ppm) from the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody (samples MO10 and 18).
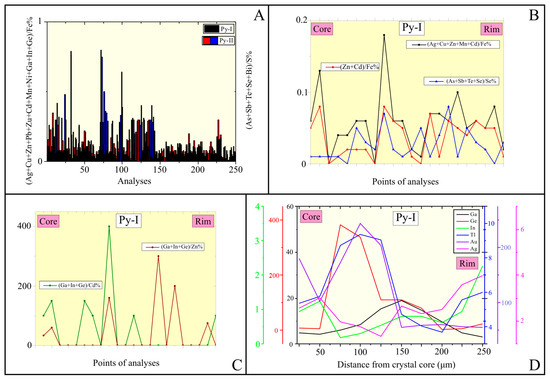
Figure 5.
(A) Discriminant histogram of the different pyrite populations based on their (Ag + Cu + Zn + Pb + Au + Cd + Mn + Ni + Ga + In + Ge)/Fe%, and (As + Sb + Te + Se + Bi)/S% ratios; (B) micro-traverse profiles (core-to-rim) of Py-I (Ag + Cu + Zn + Cd + Mn)/Fe%, (Zn + Cd)/Fe%, and (As + Sb + Te + Se)/S% ratios from the Vigla-Mesovouni Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) orebodies, Molai ore deposit; (C) micro-traverse profiles (core-to-rim) of Py-I of the (Ga + In + Ge)/Cd%, and (Ga + In + Ge)/Zn% ratios from the Vigla-Mesovouni Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) orebodies, Molai ore deposit; (D) micro-traverse profiles of selected elements (core-to-rim) of Py-I from the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody, Molai ore deposit (LA-ICP-MS data).
The traversed LA-ICP-MS results (cores-to-rims) reveal notable compositional micro-zoning in both Sp-I and Py-I crystals. Sp-I cores are enriched in Ge (~730 ppm) and Tl (~1.5 ppm), while their rims show increased Ag (~2500 ppm) and Ga (~140 ppm) content (Figure 4C). Similarly, Py-I cores are enriched in Ge (~380 ppm), Au (~240 ppm), and Tl (~10 ppm), with rims exhibiting higher Ag (~4 ppm) and In (~2 ppm) content (Figure 5C,D). Ga displays intermediate enrichment (~200 ppm) in transitional segments.
The EPMA results also revealed two distinct galena populations based on mineral chemistry, namely, Ga-I and Ga-II (Figure 6A; ESM-S2 Table S2). Early Ga-I is genetically associated with stage II [16] and is enriched in Zn, Cu, Fe, Ga, and Ge, whereas Ga-II is rich in Ag (up to ~2.55%), Sn, Se, and Bi (for details on the structure of galena, refer to [37,38]).
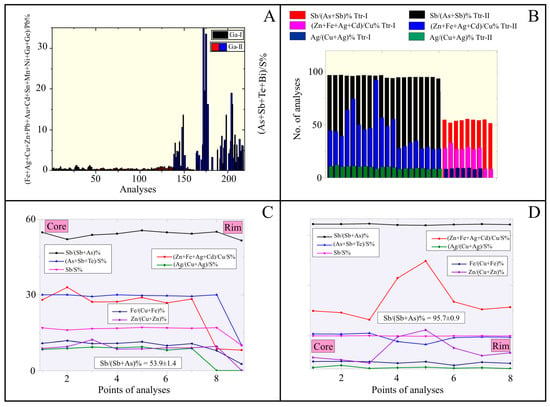
Figure 6.
(A) Discriminant histogram of the different galena populations based on their (Fe + Ag + Cu + Zn + Pb + Au + Cd + Sn + Mn + Ni + Ga + Ge)/Pb% and (As + Sb + Te + Se + Bi)/S% ratios; (B) discriminant histogram of Ttr-I and Ttr-II based on their Sb/(As + Sb)%, (Zn + Fe + Ag + Cd)/Cu% and Ag/(Cu + Ag)% ratios; (C,D) micro-traverse profiles (core-to-rim) of Sb/(Sb + As)% = 53.9 ± 1.4 (Ttr-I) and Sb/(Sb + As)% = 95.7 ± 0.9 (Ttr-II) tetrahedrites, including Sb/(Sb + As)%, (Zn + Fe + Ag + Cd)/Cu%, (As + Sb + Te + Se + Bi)/S%, Sb/S, Ag/(Cu + Ag)%, Fe/(Cu + Fe)%, and Zn/(Cu + Zn)% ratios from the Vigla-Mesovouni Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) orebodies, Molai ore deposit.
Additionally, two distinct populations of tetrahedrite were distinguished based on their Sb/(Sb + As)% and (Zn + Fe + Ag + Cd)/Cu% ratios (Figure 6B; ESM-S2 Table S4) (for details on the structure of tetrahedrite, refer to [39]). Early Ttr-I corresponds to tetrahedrite–tennantite solid solutions and is genetically related to stage II [16] (Figure 5C), while Ttr-II (Figure 6D) corresponds to nearly pure tetrahedrite and is associated with the late stage III [16]. The Ttr-II population is the primary silver carrier, containing up to ~3.6% Ag (ESM-S2 Table S4).
4.3. Physical and Mechanical Characterization of Ore Phases
The X-ray diffraction peaks observed index cubic-structured Py-I (JCPDS card No. 42-1340, space group Pa3) and Sp-I (JCPDS card No. 77-2100, space group F43m) [40,41]. Py-I and Sp-I are euhedral, with well-developed {111} faces, forming cubes to pyritohedra, and tabular crystals of striated surfaces due to {111} twinning, growing along the (110) direction (ESM-S1 Figures S7 and S8). The crystallite sizes are 64.3 ± 8.2 μm for Py-I and 75.1 ± 4.1 μm for Sp-I, consistent with SEM imaging (ESM-S1 Figure S9).
The Vickers Hardness Number (VHN) for Sp-I-rich ore samples (>80%) ranges from 207.5 to 226.5, with an average of 216.8 ± 6.3. In contrast, Py-I-rich samples exhibit significantly higher hardness values, ranging from 1501.0 to 1545.6, with an average of 1525.0 ± 12.3 (Table 1). The corresponding Young’s modulus (E) for Py-I falls between 136.7 and 140.9 GPa, with an average value of 138.9 ± 1.14 GPa. For Sp-I, E ranges from 70.4 to 77.5 GPa, with an average of 73.9 ± 2.3 GPa (ESM-S1 Figure S10).
The Py-I and Sp-I separates exhibit typical type IV isotherms (ESM-S1 Figure S11). For Py-I, the adsorption isotherms rise at a constant rate up to ~0.4 P/P0, followed by an exponential rise after this point. The opposite behavior is observed for Sp-I, with a constant rate up to ~0.4 P/P0, followed by a lower rate after this point. Moreover, Sp-I and Py-I develop pore diameters of ~1.89 nm and ~1.73 nm, respectively (ESM-S1 Figure S11).
The thermogravimetry analysis (TGA) profile of Py-I shows a minor loss of water (surface moisture) and H2S up to ~510 °C. Between ~510° and ~580 °C and ~650° and ~820 °C, a sharp mass decrease of ~1.1% is observed, ascribed to partial endothermic desulfurization to pyrrhotite. Py-I is thermally stable up to ~510 °C and then decomposes to pyrrhotite (ESM-S1 Figure S13). Sp-I and Sp-III exhibit minimal mass loss up to T ~320° and ~500 °C, respectively. However, Sp-I undergoes a sharp mass loss of ~20% between ~420 °C and ~635 °C, which is associated with partial decomposition of its iron content (XFeS = 20.5 ± 2.7 [16]) to pyrrhotite and its oxidation to SO2 [42]. In contrast, Sp-III (XFeS = 0.6 ± 0.1) experienced a small mass loss of ~2% between T ~600° and~770°, attributed to its exothermic oxidation to SO2 [42].
4.4. Crushing, Grinding, Liberation Degree, and Ore Pre-Concentration
The results of primary and secondary crushing (ESM-S3 Tables S2 and S3) revealed that the bulk ore is easily crushed. Stereoscopic investigation, heavy liquid, and area measurement (ESM-S3, Tables S4–S6) reveal gradual gangue liberation from the +0.5 mm fraction, which increases significantly with decreasing fraction size. At the same time, liberation of useful minerals is effective only at fractions below 0.250 mm, reaching nearly 100% at very fine fractions (−0.036 mm). The geochemical analyses of the secondary crushing fractions showed fluctuations in the distribution of Pb and Zn in the various fractions, with a slight increase in the smallest fractions (ESM-S3 Table S3).
Examination of the liberation degree [43] in the primary raw feed was also performed using polished blocks under the optical microscope at the size fractions −0.82 + 0.45 mm, −0.45 + 0.25 mm, −0.25 + 0.15 mm, −0.15 + 0.071 mm, −0.071 + 0.036 mm, and −0.036 mm (Figure 5). The investigation revealed successful liberation of the Molai sulfide ore phases in the finer fractions below 0.150 mm. Pyrite (Py-I) is the most effectively separated ore phase of the Molai ore. Its liberation is present even in the coarser fraction (−0.82 + 0.45 mm), found as isolated free fragments, with similar behavior in the finer fractions (Figure 7A,C–E). Sphalerite-I is effectively liberated from the −0.45 mm fraction, yet with a high percentage of crystals rich in pyrite and/or tetrahedrite inclusions, and shows complete liberation at the −0.150 mm fraction (Figure 7A–D). Sphalerite-II and III are effectively liberated in the −0.071 mm fraction, as well as galena (Figure 7D–F). Finally, in all fractions examined, abundant interlocking fragments comprise either mixed ore phases or mixed ore phases with gangue (Figure 7A–D).
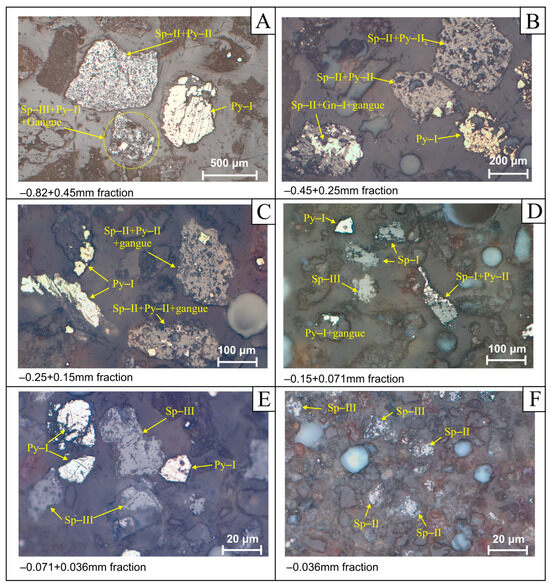
Figure 7.
Reflected light optical microscopy photomicrographs of the grinding fractions after the liberation examination of the Molai ore. (A) 0.82–0.45 mm fraction: liberated Py-I grains, fragments of Sp-II + Py-II inclusions, and mixed sulfide-gangue clasts (Sp-III + Py-II + gangue); (B) 0.45–0.25 mm fraction: Py-I + gangue, Sp-II + Gn + gangue, and mixed Sp-II + Py-II clasts; (C) 0.25–0.15 mm fraction: liberated Py-I, mixed Sp-II + Py-II + gangue fragments; (D) 0.15–0.071 mm fraction: liberated Py-I, Sp-I and Sp-III fragments, and mixed Py-I + gangue and Sp-I + Py-II fragments; (E) 0.071–0.036 mm fraction: liberated Py-I and Sp-III grains; (F) −0.036 mm fraction: liberated Sp-II and Sp-III grains. Py: pyrite, Gn: galena, Sp: sphalerite (abbreviations after [32]).
4.5. Flotation Circuits
Several flotation circuits with different characteristics and conditions were developed (refer to ESM-S3 for details) to assess the production potential of the major Molai ore commodities, Pb and Zn. Due to the very fine-grained character of the Molai ore, the flotation circuits tested were mainly focused on processing fine-grained feed (−0.036 mm), while the effect of pre-concentration in the flotation flow-sheet was also examined. The following flotation circuits were tested (for details, refer to ESM-S3 Figures S14–S21 and [31]):
- Mixed (bulk) flotation circuit on finely-ground material (~81% −0.036 mm), designed to separate the ore and obtain a bulk galena–sphalerite concentrate (Table 5; ESM-S3 Table S17).
 Table 5. Pb and Zn grades and recoveries of the various flotation tests employed in the study.
Table 5. Pb and Zn grades and recoveries of the various flotation tests employed in the study. - Direct differential flotation circuit on finely-ground material (~81% −0.036 mm), designed to provide separate PbS and ZnS concentrates. In this circuit, the pH was the critical factor, with galena floating best around pH = 9, while sphalerite performed best around pH = 11. Additionally, a cleaning stage was incorporated to enhance concentrate quality (Table 5; ESM-S3 Table S18). The Pb concentrate closely met commercial KS4 specifications, while the Zn concentrate exceeded KTs2 quality standards (ESM-S3 Table S1b).
- Combined bulk and differential (mixed) flotation circuit on finely-ground material (~81% −0.036 mm), with one cleaning stage and a scavenger flotation on tailings, designed to provide separate PbS and ZnS concentrates (Table 5; ESM-S3 Table S19). These combined circuits provided zinc concentrate grades exceeding KTs1 metallurgical quality standards (ESM-S3 Tables S1b and S19).
- Flotation circuit on coarse-grained material (~59% −0.036 mm), with a cleaning stage and an additional mixed concentrate from tailings cleaning. Moreover, a combined mixed and differential flotation circuit was also developed (Table 5; ESM-S3 Table S20).
- Flotation circuit on pre-concentrated material from the shaking table. Flotation tests were carried out on a pre-concentrated sample obtained from an initial separation process on the Wilfley shaking table, with the complex flotation circuits, including “middlings”, providing the best overall results (Table 5; ESM-S3 Table S22).
5. Discussion
5.1. Ore Characterization—Critical Metal Distribution
The Vigla-Mesovouni orebody of the Molai sulfide ore comprises an average Ge and Ag content in the bulk ore of approximately 95 and 35 ppm, respectively (Table 2), while the detailed mineralogical and mineral chemistry analyses revealed the refractory nature of both Ge and Ag. Sphalerite (all varieties) is typically the main host for Ge, with Sp-I showing the highest grades (up to 1892 ppm), followed by Sp-II (up to 579 ppm) and Sp-III (up to 657 ppm) (Table 3). Interestingly, stage I pyrite (Py-I) also shows significant Ge content (up to 383 ppm) (Table 4); see [21,22,44]. Raman spectroscopy also verifies the structural integration of Ge into the lattice of sphalerite (all varieties) (ESM 1 Figure S12). For Sp-I, the resonance band at ~340 cm−1 indicates the presence of Ge in its lattice [45], while similar patterns were observed at the Apex mine in Utah, USA [46], and the Lehong deposit in Yunnan, China [47]. In contrast, for Sp-II and Sp-III, this band shifts to ~330 cm−1 and either diminishes in intensity or disappears entirely due to the lower Ge content incorporated in their lattice. This is also verified by the geochemical analyses (Table 3). Additionally, in Sp-III, a resonance band at ~250 cm−1 is identified, possibly corresponding to the presence of In in its lattice [48], although the LA-ICP-MS results show very low In content in Sp-III (up to 1.1 ppm, Table 3). Our findings are critical for beneficiation circuit design, as Ge primarily transports into solution, mainly as Ge(OH)4−, under acidic to mildly alkaline conditions [49]. The compositional variations identified in the Molai ore clearly suggest that the ore-forming fluids were initially enriched in Ge, Au, and Tl, but as they evolved, they became richer in Ag and In.
Silver is mostly enriched in late-stage pure tetrahedrite (Ttr-II: ~3.6%), Sp-III (up to 3264 ppm), and galena (Ga-II: ~2.55%). LA-ICP-MS and electron microscopy reveal micro-scale chemical zoning, with Ge enriched in the cores of the major ore minerals and Ag in the rims (Figure 4C, Figure 5D and Figure 6), depicting a hydrothermal system evolving from early Ge-rich to late-stage Ag-rich fluids. This zoning has also been observed at the Kipushi deposit (DR Congo), where early-stage sphalerite hosts Ge and late-stage minerals carry Ag [50].
5.2. Correlation of Ore Characterization with Beneficiation
The geological and hydrothermal processes that contributed to the formation of the Molai (Vigla-Mesovouni) deposit resulted in the formation of a low-grade, fine-grained polymetallic ore with both complex geochemistry and a complex precious and critical metal distribution. These specific features clearly pose challenges during the development of ore-processing circuits. Early enrichment studies on the Molai sulfide ore examined the potential pre-concentration using heavy liquids and also supported grinding to <20 μm to produce marketable concentrates [15,18]. Major contributions of the flotation tests performed in the present study are the incorporation of shaking table pre-concentration and processing of the −0.036 mm fraction.
The pre-concentration was evaluated across different size fractions, and while coarse fractions (>0.5 mm) showed a minimal response, the −0.5 + 0.25 mm and −0.25 + 0.125 mm fractions yielded promising results, with gangue rejection of ~21% (ESM-S3 Tables S11–S16). The preliminary pre-concentration study revealed the effective liberation of major Ge carriers in the −0.071 mm fraction.
As stated earlier, the flotation circuits examined were focused on the major commodities, Pb and Zn (ESM-S3 Figures S14–S21). In general, among the flotation circuits tested, combined flotation systems integrating early pre-concentration via a shaking table outperform single-method approaches, especially for Zn. Moreover, circuits incorporating pH adjustments further enhance recoveries. Galena responds best at ~pH = 9, while sphalerite shows superior floatability at pH = 11. Both minerals perform poorly in acidic conditions due to their hydrophilic surfaces, emphasizing the need for alkaline environments during flotation.
Interestingly, the flotation circuit developed with coarse-grained feed (~59% −0.036 mm) produced the highest Zn grades, yet with lower recoveries. This circuit performed best due to the larger crystallite size of Sp-I, yet the low recovery is largely related to the ineffective liberation of Sp-II and Sp-III due to interlocking either with other sulfides and/or gangue. Improved results arise from the flotation circuits incorporating a pre-concentrated feed, as they provide ZnS concentrates with the highest recoveries and grades (Table 5). This is directly related to the ZnS textural, physical, and mechanical characteristics of sphalerite in the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody. Sphalerite-I is effectively liberated in the +0.071 mm fraction, as most of the pyrite and tetrahedrite inclusions are developed along cracks of Sp-I, and during grinding, they are separated from the mineral. Finer grinding further enhances the liberation of the finer-grained varieties Sp-II and Sp-III. These two varieties are tightly interconnected with other sulfides and gangue, forming aggregates in the coarse fractions (+0.150 mm). The Raman spectra of Sp-II and Sp-III differ markedly from that of Sp-I, showing significant changes in the spectral shapes relative to their XFeS molar ratios (ESM-S1 Figure S12). Based on the h1/h3 ratio [51,52], Sp-I has larger crystallite sizes (33.7 ± 0.8) relative to Sp-II and Sp-III (ESM-S1 Table S5). Moreover, Sp-I shows very limited interlocking with gangue in the −0.150 mm fraction, resulting in improved grades during pre-concentration.
However, the flotation circuits developed show that Pb recoveries and grades are not significantly affected by pre-concentration, providing nearly similar products with or without the implementation of pre-concentration in the design (Table 5). Galena (all varieties) in the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody is mainly fine-grained and anhedral, creating complex interlocking with other sulfides and gangue. Moreover, its low hardness requires very fine grinding to increase the degree of liberation.
A major benefit of the ore characterization of the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody is the identification of pyrite (Py-I) as a major Ge carrier in the ore. In particular, Py-I shows Ge content up to 380 ppm and is an early-stage phase of the Molai ore. It forms euhedral crystals of size reaching up to 0.3 mm [16] (average crystallite size of 55–70 μm) and is characterized by increased hardness. These features enable effective Py-I liberation from the coarser fractions (+0.250 mm). Taking into consideration that Py (in general) is dismissed in the tailings in the flotation circuits tested, it is evident that there is strong potential for Ge recovery from Py-I as a by-product. Additionally, the removal of pyrite from the tailings of the circuits developed for Pb and Zn provides a sound barrier regarding the environmental impact of the Molai ore beneficiation. Targeted mineralogical studies and selective leaching of the resulting concentrates are recommended to evaluate and enhance this potential, offering an additional economic incentive in processing the Vigla-Mesovouni orebody. Based on these characteristics, a feasible beneficiation circuit for the production of pyrite concentrate is proposed that will provide added value to the Molai ore (ESM-S3 Figure S13).
Silver exhibits a dual distribution pattern in the Vigla-Mesovouni ore body, closely related to the ore texture and mineralogy. Silver is primarily incorporated in Ttr-II and, secondarily, as lattice-bound Ag in Ga-II. It is also found in the form of freibergite, as well as microinclusions of other Ag-bearing minerals such as stephanite and pyrargyrite within galena [15,16]. At first, these fine inclusions contribute to silver loss and increase the complexity of the beneficiation process. A possible route would include a later-stage recovery focusing on Ag-rich phases, including Ttr-II, Ga-II, and sulfosalts via selective flotation or pressure oxidation. Ag-bearing phases (besides galena) belong to the sulfosalt sub-group of the sulfide minerals group, and they are rich in Sb (±As), demanding careful environmental assessment during the design of the beneficiation circuit specialized for Ag recovery. As in the case of Py-I, such a circuit would not only provide additional economic value to the ore [Ag±(Sb,As)] but also reduce the content of toxic elements in the tailings.
Altogether, the comprehensive physicochemical, mechanical, mineralogical, and textural characterization of Molai ore supports a tailored, multi-stage beneficiation strategy focused primarily on Ge and secondarily on Ag, as Ge and Ag account for ~90% and ~58% of the concentrate’s total market value, respectively [15]. In this context, a proposed beneficiation circuit could involve early-stage treatment prioritizing on Ge-rich sphalerite (all varieties) and Py-I extraction through mechanical liberation and oxidative leaching, followed by high-temperature volatilization or chloride-based hydrometallurgy (as proposed by [19]).
Ongoing work is underway to define the mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of the produced concentrates and provide new insights on the design of beneficiation circuits for the Molai ore.
6. Conclusions
The detailed physicochemical and mechanical characterization of Molai (Vigla-Mesovouni) Zn-Pb±(Ag,Ge) ore reveals the following:
- The compositional variations identified in the Molai ore depict the evolution of the ore-forming fluids from early-stage and enriched in Ge (±Au, Tl) to later-stage and enriched in Ag and In.
- The distribution of precious and critical metals in the ore phases is complex, and no single phase incorporates each commodity. For instance, Ge is not only present in sphalerite (typical), but also in pyrite (atypical).
- Sphalerite (all varieties) and Py-I govern the distribution of the refractory Ge ore, while Ga-II and Ttr-II define the refractory Ag ore of the Vigla-Mesovouni low-grade sulfide ore. Despite accounting for ~90% and ~58% of concentrate value, respectively, Ge and Ag are hosted in lattice-bound forms, resulting in recovery losses and requiring advanced mineralogical targeting during processing.
- In addition to chemical characteristics, the physical properties of Sp-I and Py-I, such as crystallite size and hardness, play a key role in the design of ore processing routes.
The following points concern pre-concentration and beneficiation:
- Py-I and Sp-I, the major Ge-carriers, are easily liberated in the coarse fractions (+0.250 mm and +0.150 mm, respectively), exhibiting crystallite sizes in the range between 55 and 78 μm. The easy liberation of Py-I is directly related to its size and crystal shape in the primary ore, as well as its hardness, thus enhancing its liberation in the coarse fractions (+0.250 mm).
- Pre-concentration prior to flotation tests is essential for producing higher-grade material for feeding into the flotation circuit, particularly for Zn, as pre-concentration may discard ~21% of gangue, enhance downstream flotation performance, concentrate quality, and also reduce downstream processing costs.
- Regarding Pb and Zn, combined flotation circuits on finely ground and pre-concentrated material (−0.036 mm) may produce galena and sphalerite concentrates that meet industrial quality standards.
- Flotation circuits incorporating pH adjustments further enhance recoveries. Galena responds best to ~pH = 9, while sphalerite shows superior floatability at pH = 11.
- Taking into consideration that pyrite (all varieties) is dismissed in the tailings in the flotation circuits tested, it is evident that there is strong potential for Ge recovery from Py-I as a by-product.
- Another late-stage secondary plant should involve the recovery of Ag-rich phases, including Ttr-II, Ga-II, and sulfosalts via selective flotation or pressure oxidation.
- Besides increasing the economic potential of the Molai ore, these secondary flotation circuits also contribute to minimizing the environmental impact of Molai ore during beneficiation, as pyrite and sulfosalts are removed from the tailings.
Collectively, our findings support the development of a customized, value-driven beneficiation flow-sheet for the Molai ore that enhances Ge and Ag resource utilization while minimizing environmental and operational costs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min15111152/s1, ESM-S1: Analytical techniques and ore physicochemical characteristics; ESM-S2: Ore mineral chemistry and characterization; ESM-S3: Beneficiation process. References [53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68] are found in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S.T., S.F.T. and E.S. (Elias Sammas).; methodology, S.S.T., S.F.T., E.S. (Elias Sammas), E.K. and S.K. (Sotirios Kokkalas); software, S.F.T., S.S.T., E.S. (Elias Sammas), C.M., K.K., K.P., P.N., I.K., J.P. and S.K. (Sotirios Kokkalas); validation, S.F.T., S.S.T., M.F., E.S. (Elias Sammas), E.K., D.Z., S.K. (Sotirios Kokkalas) and S.K. (Stavros Kalaitzidis); formal analysis, S.S.T., C.M. and K.K.; investigation, S.S.T., S.F.T., E.S. (Elias Sammas), E.S. (Ekaterini Spiliopoulou) and P.V.; resources, S.S.T., E.K. and E.S. (Elias Sammas); data curation, S.S.T., S.F.T., P.V., C.V., D.Z., S.K., S.K. (Stavros Kalaitzidis), D.Z. and I.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.T. and S.F.T.; writing—review and editing, S.S.T. and S.F.T.; visualization, S.F.T., S.S.T., E.S. (Elias Sammas) and E.S. (Ekaterini Spiliopoulou); supervision, S.S.T. and S.F.T.; project administration, S.S.T., S.F.T. and E.S. (Elias Sammas). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Hellenic Authority for Geological and Mining Research (EAGME) branch in Peloponnese for providing access to the cores and samples for logging and sampling. This paper is dedicated to the memory of our late colleague Karen St. Seymour, who passed away recently.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cox, D.P.; Singer, D.A. Mineral Deposit Models. In U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1693; U.S. Geological Survey: Preston, VA, USA, 1986; 379p. [Google Scholar]
- John, D.A.; Vikre, P.G.; du Bray, E.A.; Blakely, R.J.; Fey, D.L.; Rockwell, B.W.; Mauk, J.L.; Anderson, E.D.; Graybeal, F.T. Descriptive models for epithermal gold-silver deposits. In U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report, 2010–5070–Q; U.S. Geological Survey: Preston, VA, USA, 2018; 247p. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Ding, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yand, J.; Xu, Y. Element enrichment characteristics: Insights from element geochemistry of sphalerite in Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit, Sichuan, Southwest China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 186, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnavi, A.S.; McFarlane, C.R.M.; Lentz, D.R.; Walker, J.A. Assessment of pyrite composition by LA-ICP-MS techniques from massive sulfide of the Bathurst Mining Camp, Canada: From textural and chemical evolution to its application as a vectoring tool for the exploration of VMS deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 656–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winderbaum, L.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Cook, N.J.; Paul, M.; Metcalfe, A.; Gilbert, S. Multivariate Analysis of an LA-ICP-MS Trace Element Dataset for Pyrite. Math. Geosci. 2012, 44, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, R.A.; Mosier, D.L. Deposit type and associated commodities. In Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model; Shanks, W.C.P., III, Thurston, R., Eds.; U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010–5070–C; U.S. Geological Survey: Preston, VA, USA, 2012; Chapter 2; pp. 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.-M.; Huang, X.-W.; Hu, R.; Beaudoin, G.; Zhou, M.-F.; Meng, S. Deposit type discrimination based on trace elements in sphalerite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 165, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Groves, D.I.; Santosh, M.; Yang, C.-X. Critical metals: Their mineral systems and exploration. Geosystems Geoenvironment 2025, 4, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; Ciobanu, C.L.; George, L.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Wade, B.; Ehrig, K. Trace Element Analysis of Minerals in Magmatic-Hydrothermal Ores by Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: Approaches and Opportunities. Minerals 2016, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P.; Shen, J.F.; Li, S.R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.X. In—Situ LA-ICP-MS Trace Elements Analysis of Pyrite and the Physicochemical Conditions of Telluride Formation at the Baiyun Gold Deposit, North East China: Implications for Gold Distribution and Deposition. Minerals 2019, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiu, G.; Ghorbani, Y.; Jansson, N.; Wanhainen, C.; Bolin, N.-J. Ore mineral characteristics as rate-limiting factors in sphalerite flotation: Comparison of the mineral chemistry (iron and manganese content), grain size, and liberation. Miner. Eng. 2022, 185, 107705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, K.M. Verplanck and Hitzman: Rare earth and critical elements in ore deposits. Miner. Depos. 2017, 52, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RIMS—Raw Materials Information System. Available online: https://rmis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/rmp/Germanium (RMIS Dashboard) (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Skarpelis, N. Metallogeny of Massive Sulfides and Petrology of the External Metamorphic Belt of the Hellenides (SE Peloponnesus). Ph.D. Thesis, National Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 1982. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Grossou-Valta, M.; Adam, K.; Constantinides, D.C.; Prevosteau, J.M.; Dimou, E. Mineralogy of and potential beneficiation process for the Molai complex sulfide orebody, Greece. In Sulfide Deposits-Their Origin and Processing; Gray, P.M.J., Bowyer, G.L., Castle, J.F., Vaughan, D.J., Warner, N.A., Eds.; Institution of Mining and Metallurgy: London, UK, 1990; pp. 119–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kevrekidis, E.; Triantafyllidis, S.S.; Tombros, S.F.; Kokkalas, S.; Papavasiliou, J.; Kappis, K.; Papageorgiou, K.; Koukouvelas, I.; Fitros, M.; Zouzias, D.; et al. Revisiting the concealed Zn-Pb±(Ag, Ge) VMS-style ore deposit, Molai, Southeastern Peloponnese, Greece. Minerals 2024, 14, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockfire Resources. Available online: https://www.rockfireresources.com/projects/molaoi/ (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Grossou-Valta, M.; Mpasios, D.; Charalampidis, P.; Konstantinidou-Vartholomaiou, E. Discussion on the possible treatment of Molai mixed sulphide ore after experimental investigation of typical samples. In Metallurgical Research No. 37; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1984; E1292; 90p, (In Greek with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Adam, K.; Dimitriadis, D.; Papadimitriou, D.; Stefanakis, M. Applications of hydrometallurgy in processing mixed sulfide concentrates and ores. In Technical Chamber of Greece, Report 892; Scientific Department of Mining and Metallurgical Engineering: Reno, NV, USA, 1986; 86p. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Kelvin, M.; Whiteman, E.; Petrus, J.; Leybourne, M.; Nkuma, V. Application of LA-ICP-MS to process mineralogy: Gallium and germanium recovery at Kipushi Copper-Zinc deposit. Miner. Eng. 2022, 176, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, Z.; Sun, H.; Aka, D.; Koua, K.; Lyu, C. LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of sphalerite and pyrite from the Beishan Pb-Zn ore district, South China: Implications for ore genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 150, 105128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.J.; Ulrich, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Trace element compositions of sulfides from Pb-Zn deposits in the Northeast Yunnan and northwest Guizhou Provinces, SW China: Insights from LA-ICP-MS analyses of sphalerite and pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 141, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Hu, R.; Gao, J.; Leng, C.; Gao, W.; Gong, H. Trace and minor elements in sulfides from the Lengshuikeng Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, South China: A LA-ICP-MS study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 141, 104663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, W. Ore characterization, process mineralogy and lab automation a roadmap for future mining. Miner. Eng. 2014, 60, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, A.R.; Dehaine, Q.; Menzies, A.H.; Michaux, S.P. Characterization of Ore Properties for Geometallurgy. Elements 2023, 19, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebault, F.; Triboulet, C. Alpine metamorphism and de- formation in Phyllites Nappes (External Hellenides, Southern Peloponnesus, Greece): Geodynamic implications. J. Geol. 1984, 92, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheuz, P.; Krenn, K.; Fritz, H.; Kurz, W. Tectonometamorphic evolution of blueschist-facies rocks in the Phyllite-Quartzite Unit of the External Hellenides (Mani, Greece). Austrian J. Earth Sci. 2015, 108, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.H.F. Sedimentary evidence from the south Mediterranean region (Sicily, Crete, Peloponnese, Evia) used to test alternative models for the regional tectonic setting of Tethys during Late Palaeozoic–Early Mesozoic time. In Tectonic Development of the Eastern Mediterranean Region; Robertson, A.H.F., Mountrakis, D., Eds.; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2006; Spec Publ 260; pp. 91–154. [Google Scholar]
- Zulauf, G.; Dörr, W.; Xypolias, P.; Gerdes, A.; Kowakczyk, G.; Linckens, J. Triassic evolution of the western Neotethys: Constraints from microfabrics and U–Pb detrital zircon ages of the Plattenkalk Unit (External Hellenides, Greece). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 108, 2493–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe-Piper, G.; Piper, D.J.W. The Igneous Rocks of Greece: The Anatomy of an Orogen; Gebrüder Borntraeger: Stuttgart, Germany, 2002; 573p. [Google Scholar]
- Sammas, E. Contribution in the enrichment of the mixed sulfide ore from Molai. Ph.D. Thesis, Section of Metallurgy and Materials Technology, School of Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, Athens, Greece, 2018; 239p. (In Greek with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Whitney, D.L.; Evans, B.W. Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. Am. Mineral. 2010, 95, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Sugaki, A. Phase relations in the Cu-Fe-Zn-S system between 500° and 300 °C under hydrothermal conditions. Econ. Geol. 1985, 80, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Ahmed, A.Q. Structural, electronic, and optical properties of sphalerite ZnS compound calculated using density functional theory (DFT). Chalcogenide Lett. 2022, 19, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabri, L.J. New data on phase relations in the Cu-Fe-S System. Econ. Geol. 1973, 68, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrouvel, C.; Eon, J. Understanding the Surfaces and Crystal Growth of Pyrite FeS2. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20171140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullerud, G. The lead-sulfur system. Am. J. Sci. 1969, 267, 233–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renock, D.; Becker, U. A first principles study of coupled substitution in galena. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 42, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagioni, C.; George, L.L.; Cook, N.J.; Makovicky, E.; Moëlo, Y.; Pasero, M.; Sejkora, J.; Stanley, C.J.; Welch, M.D.; Bosi, F. The tetrahedrite group: Nomenclature and classification. Am. Mineral. 2020, 105, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Gu, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Shu, Z.; Dick, J.; Lu, A. Mineralogical characteristics and photocatalytic properties of natural sphalerite from China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 89, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Kaur, M.; Thakur, A.; Kumar, A. Recent Progress on Pyrite FeS2 Nanomaterials for Energy and Environment Applications: Synthesis, Properties and Future Prospects. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 899–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Földvári, M. Handbook of Thermogravimetric System of Minerals and Its Use in Geological Practice; Geological Institute of Hungary: Budapest, Hungary, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, B.A.; Napier-Munn, T. Mineral Processing Technology. An Introduction to the Practical Aspects of Ore Treatment and Mineral, 7th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mondillo, N.; Arfè, G.; Herrington, R.; Boni, M.; Wilkinson, C.; Mormone, A. Germanium enrichment in supergene settings: Evidence from the Cristal nonsulfide Zn prospect, Bongará district, northern Peru. Miner. Depos. 2018, 53, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Yamaguchi, M. Resonant Raman scattering in GeS2. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 227–230, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, J.; Mosser-Ruck, R.; Caumon, M.C.; Rouer, O.; Andre-Mayer, A.S.; Cauzid, J.; Peiffert, C. Trace element distribution (Cu, Ga, Ge, Cd, and Fe) in sphalerite from the Tennessee MVT deposits, USA, by combined EMPA, LA-ICP-MS, Raman spectroscopy, and crystallography. Can. Mineral. 2016, 54, 1261–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ye, L.; Hu, Y.; Danyushevskiy, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, Z. Distribution and occurrence of Ge and related trace elements in sphalerite from the Lehong carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit, northeastern Yunnan, China: Insights from SEM and LA-ICP-MS studies. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasevska, H.; Kitts, C.; Ancora, C.; Ruani, G. Optimized In2S3 thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 637943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, M.S. A Review on Germanium Resources and its Extraction by Hydrometallurgical Method. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 406–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijlen, W.; Banks, D.A.; Muchez, P.; Stensgard, B.M.; Yardley, B.W.D. The Nature of Mineralizing Fluids of the Kipushi Zn-Cu Deposit, Katanga, Democratic Repubic of Congo: Quantitative Fluid Inclusion Analysis using Laser Ablation ICP-MS and Bulk Crush-Leach Methods. Econ. Geol. 2008, 103, 1459–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchii, G.E.; Gorbaty, Y.E. Raman spectra and unit cell parameters of sphalerite solid solutions (FexZn1−xS). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzatu, T.; Popescu, G.; Birloaga, I.; Săceanu, S. Study concerning the recovery of zinc and manganese from spent batteries by hydrometallurgical processes. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.M.; Reynolds, R.C., Jr. X-Ray Diffraction and Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; 378p. [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead, J.D.; Hellstrom, J.; Hergt, J.M.; Greig, A.; Maas, R. Isotopic and Elemental Imaging of Geological Materials by Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Geostand. Geoanalytical Res. 2007, 31, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.; Hellstrom, J.; Paul, B.; Woodhead, J.; Hergt, J. Iolite: Freeware for the visualization and processing of mass spectrometric data. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, C.J.; Dubé-Loubert, H.; Pagé, P.; Barnes, S.J.; Roy, M.; Savard, D.; Cave, B.; Arguin, J.P.; Mansur, E.T. Applications of trace element chemistry of pyrite and chalcopyrite in glacial sediments to mineral exploration targeting: Example from the Churchill Province, northern Quebec, Canada. J. Geoch Expl. 2018, 196, 105–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, D.; Griffin, W.L.; Pearson, N.J.; Powell, W.; Wieland, P.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Trace element partitioning in mixed-habit diamonds. Chem. Geol. 2013, 355, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, N.L. IMA-CNMNC approved mineral symbols. Miner. Mag. 2021, 85, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cases, J.M. Finely Disseminated Complex Sulphide Ores. In Complex Sulphide Ores; Jones, M.J., Ed.; Transactions IMM: London, UK, 1980; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- Bérubé, M.A.; Marchand, J.C. Evolution of the mineral liberation characteristics of an iron ore undergoing grinding. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1984, 13, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glembotskii, V.A.; Klassen, V.I.; Plaksin, I.N. Flotation; Rabinovich, H.S., Ed.; Hammond, R.E., Translator; Primary Sources: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Marabini, A.; Barbaro, M. Chelating reagents for flotation of sulphide minerals. In Sulphide Deposits—Their Origin and Processing; Transactions IMM: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel, S.A. Flotation Frothers, Their Action, Composition Properties and Structure. In Proceedings of the “Recent Developments in Mineral Dressing Symposium”, London, UK, 23–25 September 1953; Institution of Mining and Metallurgy (IMM): Carlton South, Australia, 1953; p. 211. [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud, M.; Partyka, S.; Cases, J.M. Ethylxanthate adsorption onto galena and sphalerite. Coll. Surf. 1989, 37, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabini, A.; Cozza, C. Determination of lead ethylxanthate on mineral surface by IR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta 1983, 388, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Girczys, J.; Laskowski, J.S. Mechanism of Flotation of Unactivated Sphalerite with Xanthates. Trans. IMM 1972, 81, C118. [Google Scholar]
- Marabini, A.M.; Rinelli, G. Flotation of lead-zinc ores. In Proceedings of the Advances in Mineral Processing, Processing Symposium Honoring N. Arbiter, New Orleans, LA, USA, 3–5 March 1986; pp. 269–288. [Google Scholar]
- Bulatovic, S.M. Flotation of Sulfide Ores. In Handbook of Flotation Reagents Chemistry, Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780080471372. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).