Hydrothermal Fluids and Diagenesis of Mississippian Carbonates: Implications for Regional Mineralization in Western Kansas, U.S.A
Abstract
1. Introduction
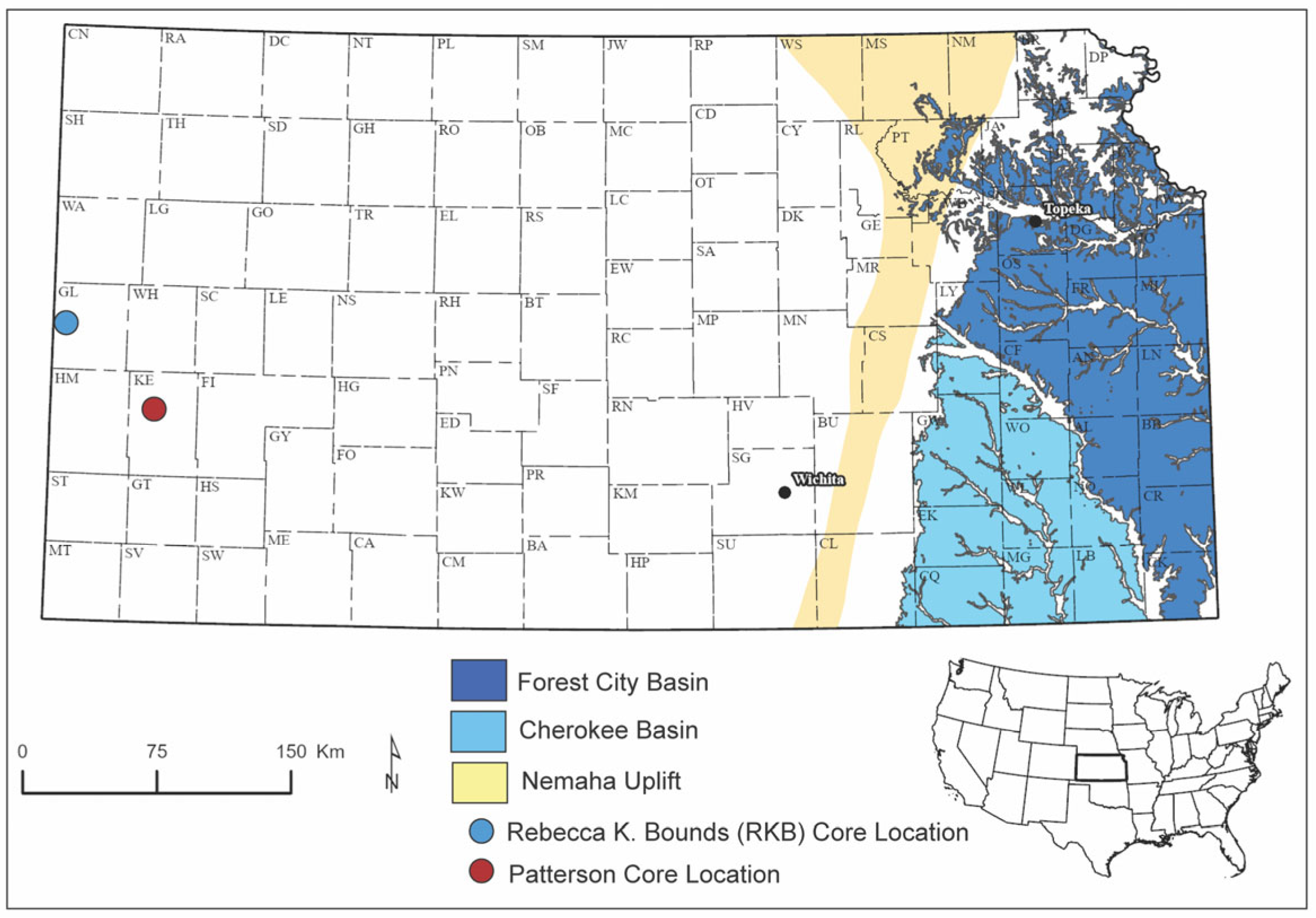
2. Geological Setting
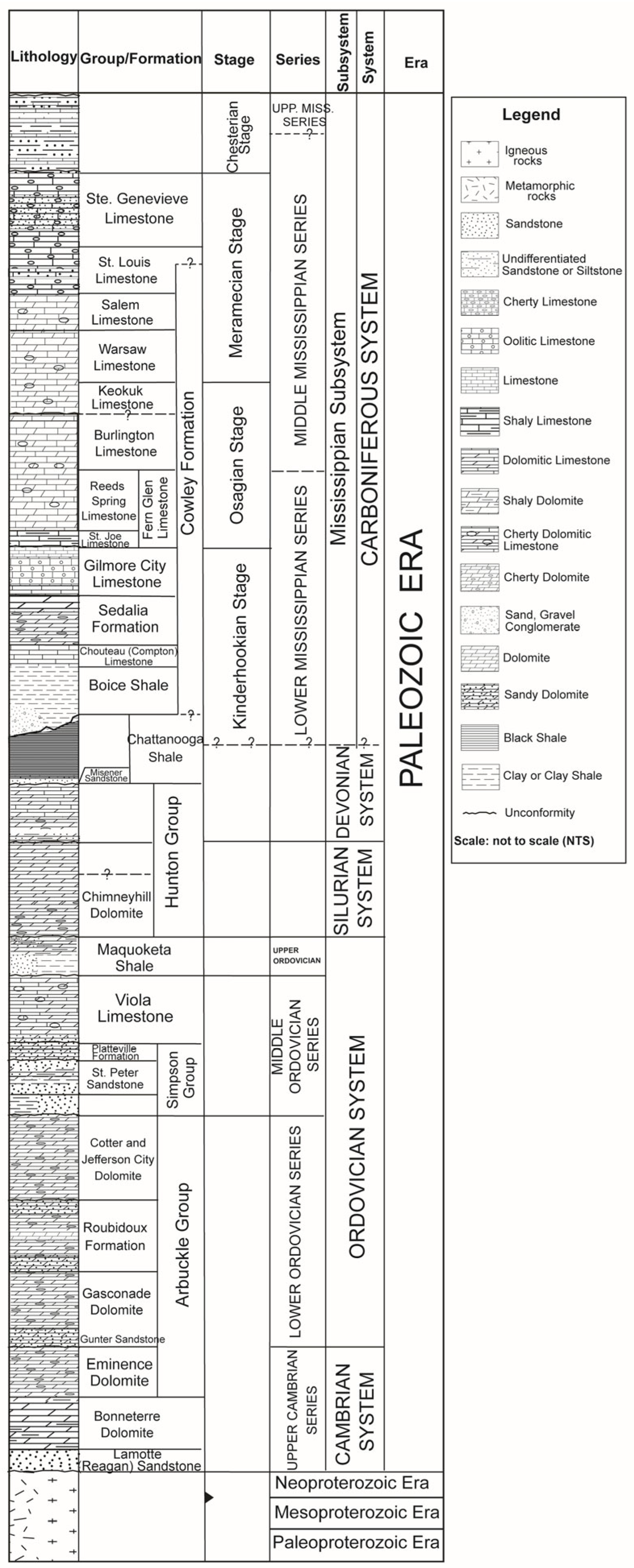
2.1. Stratigraphy
2.2. Structure
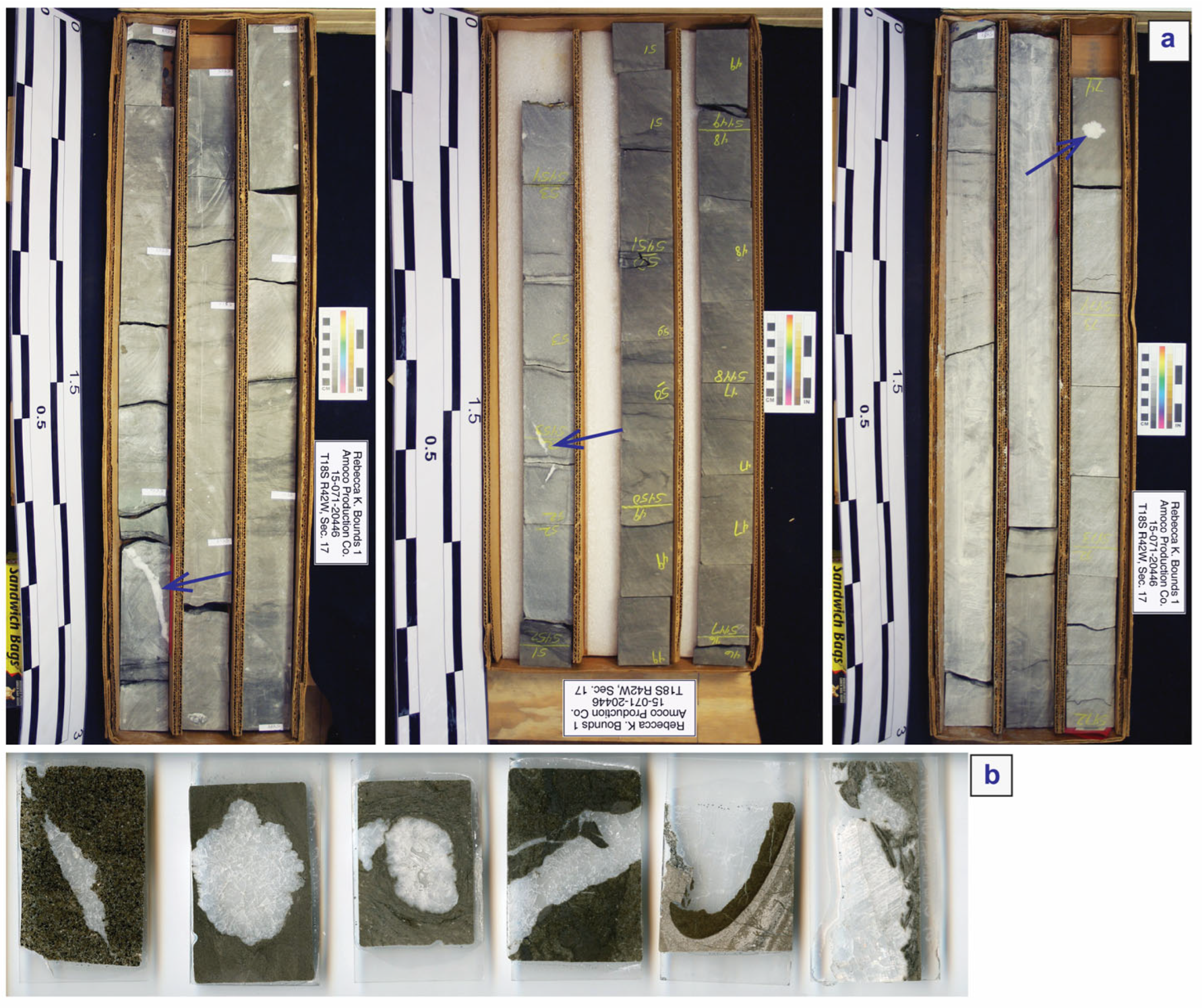
3. Methods
4. Results
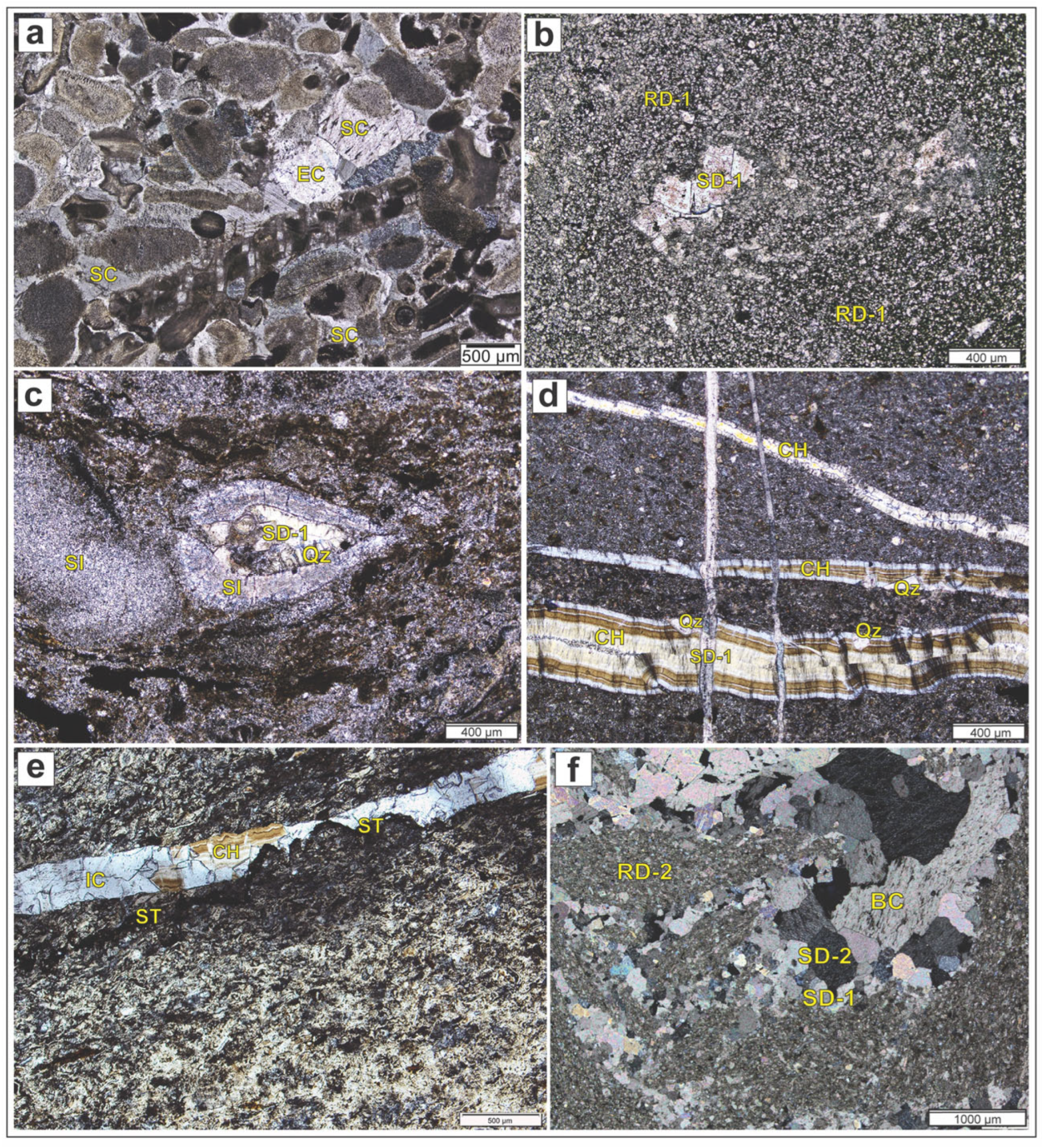
4.1. Petrography
4.2. Fluid Inclusions
4.3. Isotope Geochemistry
5. Discussion
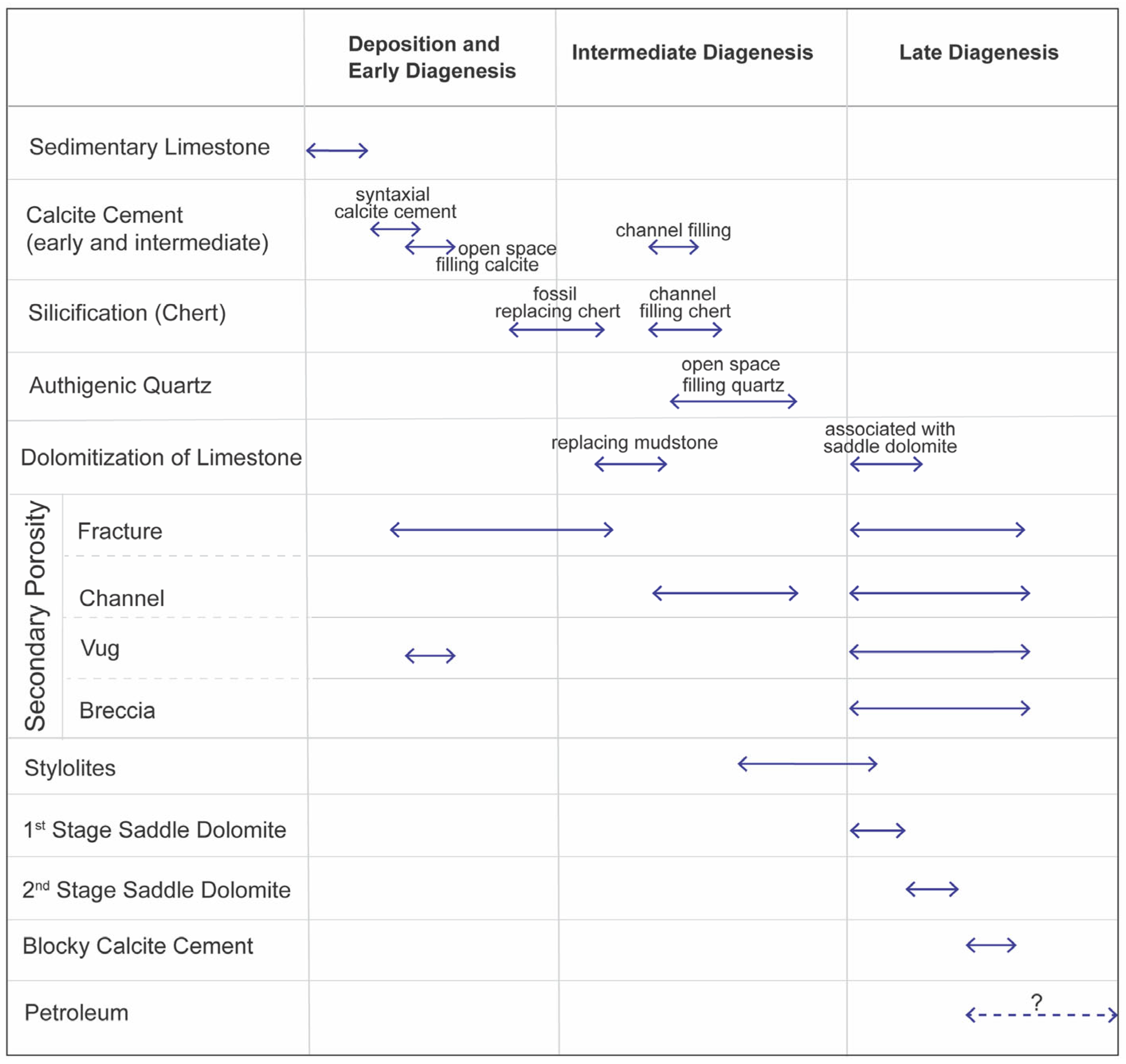
5.1. Paragenesis in the Mississippian of Western Kansas
5.2. Composition of Late Diagenetic Fluids
5.3. Fluid Sources and Timing
5.4. Implications for MVT-Style Mineralization in Western Kansas
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammadi, S.; Hollenbach, A.; Goldstein, R.; Moller, A. Timing of hydrothermal fluid flow events in Kansas and Tri-State Mineral District. In Midcontinent Carbonate Research Virtual Symposium Extended Abstracts; Ortega-Ariza, D., Bode-Omoleye, I., Hasiuk, F.J., Mohammadi, S., Franseen, E.K., Eds.; Technical Series 24; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2021; pp. 34–36. Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/Bulletins/TS24/TechnicalSeries24-MidcontinentCarbResearch.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Mohammadi, S.; Hollenbach, A.M.; Goldstein, R.H.; Möller, A.; Burberry, C.M. Controls on timing of hydrothermal fluid flow in south-central Kansas, north-central Oklahoma, and the Tri-State Mineral District. Midcont. Geosci. 2022, 3, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.L.C. Sphalerite mineralization in deep lying dolomites of Upper Arbuckle age, west central Kansas. Econ. Geol. 1962, 57, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveney, R.M., Jr.; Goebel, E.D. New fluid inclusion homogenization temperatures for sphalerite from minor occurrences in the midcontinent area. In International Conference on Mississippi Valley-type Lead Zinc Deposits: Proceedings Volume; Kisvarsanyi, G., Grant, S.K., Pratt, W.P., Koenig, J.W., Eds.; University of Missouri-Rolla: Rolla, MO, USA, 1983; pp. 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Shelton, K.L.; Bauer, R.M.; Gregg, J.M. Fluid inclusion studies of regionally extensive epigenetic dolomites, Bonneterre Dolomite (Cambrian), southeast Missouri: Evidence of multiple fluids during dolomitization and lead-zinc mineralization. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1992, 104, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.M.; Shelton, K.L. Mississippi Valley-type mineralization and ore deposits in the Cambrian-Ordovician Great American Carbonate Bank. In The Great American Carbonate Bank: The Geology and Economic Resources of the Cambrian-Ordovician Sauk Megasequence of Laurentia; Derby, J.R., Fritz, R.D., Longacre, S.A., Morgan, W.A., Sternach, C.A., Eds.; Memoir 98; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2012; pp. 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaker, E.M.; Goldstein, R.H.; Franseen, E.K.; Wantney, W.L. What controls porosity in cherty fine-grained carbonate reservoir rocks? Impact of stratigraphy, unconformities, structural setting and hydrothermal fluid flow: Mississippian, SE Kansas. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2015, 406, 179–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.A. Diagenesis of the Arbuckle Group in Northeastern and North-Central Oklahoma, USA. Master’s Thesis, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/2280578097?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true&sourcetype=Dissertations%20&%20Theses (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Goldstein, R.H.; King, D.B.; Watney, W.L.; Pugliano, T.M. Drivers and history of late fluid flow: Impact on midcontinent reservoir rocks. In Mississippian Reservoirs of the Mid-Continent, U.S.A.; Grammer, G.M., Gregg, J.M., Puckette, J.O., Jaiswal, P., Pranter, M., Mazzullo, S.J., Goldstein, R.H., Eds.; Memoir 122; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2019; pp. 417–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Gregg, J.M.; Shelton, K.L.; Appold, M.S.; Puckette, J.O. Influence of late diagenetic fluids on Mississippian carbonate rocks on the Cherokee—Ozark Platform, NE Oklahoma, NW Arkansas, SW Missouri, and SE Kansas. In Mississippian Reservoirs of the Mid-Continent, U.S.A.; Grammer, G.M., Gregg, J.M., Puckette, J.O., Jaiswal, P., Pranter, M., Mazzullo, S.J., Goldstein, R.H., Eds.; Memoir 122; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2019; pp. 325–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Ewald, T.; Gregg, J.M.; Shelton, K.L. Diagenetic history of Mississippian carbonate rocks in the Nemaha Ridge area, north-central Oklahoma, USA. In Mississippian Reservoirs of the Mid-Continent, U.S.A.; Grammer, G.M., Gregg, J.M., Puckette, J.O., Jaiswal, P., Pranter, M., Mazzullo, S.J., Goldstein, R.H., Eds.; Memoir 122; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2019; pp. 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, B.J.; Bailey, P.A.; Gregg, J.M. Carbonate diagenesis of the Arbuckle Group north central Oklahoma to southeastern Missouri. Shale Shak. 2018, 71, 10–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbach, A.M.; Mohammadi, S.; Goldstein, R.H.; Möller, A. Hydrothermal fluid flow and burial history in the STACK play of north-central Oklahoma. In Midcontinent Carbonate Research Virtual Symposium Extended Abstracts; Ortega-Ariza, D., Bode-Omoleye, I., Hasiuk, F.J., Mohammadi, S., Franseen, E.K., Eds.; Technical Series 24; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2021; pp. 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Machel, H.G.; Lonnee, J. Hydrothermal dolomite—A product of poor definition and imagination. Sediment. Geol. 2002, 152, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.S.; Newell, D.K. The Mississippian Limestone Play in Kansas: Oil and Gas in a Complex Geologic Setting. Kansas Geological Survey Public Information Circular 33. 2013, pp. 1–6. Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/PIC/pic33.html (accessed on 10 March 2018).
- Hagni, R.D.; Grawe, O.R. Mineral paragenesis in the Tri-state district Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma. Econ. Geol. 1964, 59, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Burberry, C.M.; Möller, A.; Goldstein, R.H. Data Analyses for Patterson KGS Core in Kearny County, Kansas, and Tectonic Activity Data of the Midcontinent. Kansas Geological Survey Open-File Report 2024-44. 2024. 20p. Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/OFR/2024/OFR2024-44.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Walters, R.F. Buried Precambrian hills in northeastern Barton County, central Kansas. AAPG Bull. 1946, 30, 660–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriam, D.F. The Geologic History of Kansas; Kansas Geological Survey Bulletin 162; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, V.B. Subsurface Ordovician-Cambrian Rocks in Kansas. Kansas Geological Survey, Subsurface Geology Series 2. 1975. 18p. Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/Bulletins/Sub2/ (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Franseen, E.K.; Byrnes, A.P.; Cansler, J.R.; Steinhauff, D.M.; Carr, T.R.; Dubois, M.K. Geologic Controls on Variable Character of Arbuckle Reservoirs in Kansas—An Emerging Picture. Kansas Geological Survey Open-file Report 2003-59. 2003. 30p. Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/PRS/publication/2003/ofr2003-59/Arbuckle2003_59OFR.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2004).
- Lee, W. Stratigraphy and Structural Development of the Forest City Basin in Kansas; Kansas Geological Survey Bulletin 121; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1956; pp. 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, E.D. Ordovician System in Kansas. In Stratigraphic Succession in Kansas; Zeller, D.E., Ed.; Kansas Geological Survey Bulletin 189; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1968; pp. 39–53. Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/Bulletins/189/05_ordo.html (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Zeller, D.E. Classification of Rocks in Kansas, Revised by Kansas Geological Survey Stratigraphic Nomenclature Committee. In The Stratigraphic Succession in Kansas. Kansas Geological Survey Bulletin 189 [1968]; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2008; Volume 81, chart, Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/General/Strat/Chart/gifs/ks_strat_chart_nov_2018.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Hall, T. Siluro-Devonian strata in central Kansas. AAPG Bull. 1946, 30, 1221–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutschick, R.C.; Sandberg, C.A. Mississippian continental margins of the conterminous United States. In The Shelfbreak; Stanley, D.J., Moore, G.T., Eds.; SEPM: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1983; Volume 33, pp. 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franseen, E.K. Mississippian (Osagean) shallow-water, mid-latitude siliceous sponge spicule and heterozoan carbonate facies: An example from Kansas with implications for regional controls and distribution of potential reservoir facies. Curr. Res. Earth Sci. Kans. Geol. Surv. Bull. 2006, 252 Pt 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, H.R.; De Keyser, T.L. Paleogeography of the Late Early Mississippian (Tournaisian 3) in the central and southwestern United States. In Paleozoic Paleogeography of the West-Central United States; Fouch, T.D., Megathan, E.R., Eds.; Symposium 1; SEPM Rocky Mountain Section: Denver, CO, USA, 1980; pp. 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Van Schmus, W.R.; Hinze, W.J. The midcontinent rift system. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1985, 13, 345–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, D.L. Basement tectonic configuration in Kansas. Kans. Geol. Surv. Bull. 1995, 237, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, P.; Blair, K.P. Subsurface structural maps over the Central North American rift system (CNARS), central Kansas, with discussion. Kgsbulletin 1986, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolton, G.L.; Finn, T.M. Petroleum Geology of Nemaha Uplift, Central Midcontinent; US Geological Survey, Open-file-Report 88-450D; Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1989; 39p. [Google Scholar]
- Gay, S.P. The Nemaha Trend—A system of compressional thrust-fold, strike-slip structural features in Kansas and Oklahoma, Part 2. Shale Shak. 2003, 54, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Baars, D.L.; Stevenson, G.M. Subtle stratigraphic traps in Paleozoic rocks of Paradox Basin. In The Deliberate Search for the Subtle Trap; Halbouty, M.T., Ed.; Memoir 32; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1982; pp. 131–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, R.E.; Puckett, R.E., Jr.; Keller, G.R.; Brueseke, M.E.; Bulen, C.L.; Mertzman, S.A.; Finegan, S.A.; McCleery, D.A. Intraplate magmatism related to opening of the southern Iapetus Ocean: Cambrian Wichita igneous province in the Southern Oklahoma rift zone. Lithos 2013, 174, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turko, M.; Mitra, S. Structural geometry and evolution of the Carter-Knox structure, Anadarko Basin, Oklahoma. AAPG Bull. 2021, 105, 1993–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turko, M.; Mitra, S. Macroscopic structural styles in the southeastern Anadarko Basin, southern Oklahoma. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 125, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, N.F.; van Wijk, J.W.; Leary, R.; Axen, G.J. Late Paleozoic evolution of the Anadarko Basin: Implications for Laurentian tectonics and the assembly of Pangea. Tectonics 2022, 41, e2021TC007197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, D.A. Stratigraphy of lower Pennsylvanian rocks in northeastern Hugoton Embayment. In South-Central Kansas: Guidebook, 24th Field Conference in Cooperation with the Kansas Geological Survey; Kansas Geological Society: Wichita, KS, USA, 1959; pp. 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, R.D.; Mitchell, J.R. The Anadarko “Super” Basin: 10 key characteristics to understand its productivity. AAPG Bull. 2021, 105, 1199–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, A.B.; Yonkee, A. The Laramide orogeny: Current understanding of the structural style, timing, and spatial distribution of the classic foreland thick-skinned tectonic system. In Laurentia: Turning Points in the Evolution of a Continent; Whitmeyer, S.J., Williams, M.L., Kellett, D.A., Tikoff, B., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2023; pp. 707–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Ortega-Ariza, D.; Khameiss, B. Preliminary data on the diagenesis of Mississippian (Osagian) strata: A study of the Rebecca K. Bounds core, Greeley County, Kansas. Kansas Geological Survey Open-File Report 2024-15. 2024, pp. 1–12. Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/OFR/2024/OFR2024-15.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Dunham, R.J. Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture. In Classification of Carbonate Rocks; Ham, W.E., Ed.; Memoir 1; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1962; pp. 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, D.F.; Gregg, J.M. Classification of dolomite rock textures. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1987, 57, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquette, P.W.; Pray, L.C. Geologic nomenclature and classification of porosity in sedimentary carbonates. AAPG Bull. 1970, 54, 207–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.H.; Reynolds, T.J. Systematics of Fluid Inclusions in Diagenetic Minerals; SEPM: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1994; Short Course 31; Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20220402030508id_/http://foldtudomany.elte.hu/fluid/fluid%20inclusions.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Bodnar, R.J. Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H20-NaCl solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.R.; Clayton, R.N.; Mayeda, T.K. Oxygen isotope fractionation in divalent metal carbonates. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 5547–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, I.; O’Neil, J.R. Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1977, 440-KK. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0440kk/report.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Buxton, T.M.; Sibley, D.F. Pressure solution features in shallow buried limestone. J. Sediment. Res. 1981, 51, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedder, E. Fluid Inclusions: Mineralogical Society of America Reviews in Mineralogy; Mineralogical Society of America (MSA): Chantilly, VA, USA, 1984; Volume 12, 644p. [Google Scholar]
- Ritter, M.E.; Goldstein, R.H. Diagenetic controls on porosity preservation in lowstand oolitic and crinoidal carbonates, Mississippian, Kansas and Missouri, USA. In Linking Diagenesis to Sequence Stratigraphy; Morad, S., Ketzer, M., de Ros, L.F., Eds.; Special Publication 45; International Association of Sedimentologists: London, UK, 2012; pp. 379–406. [Google Scholar]
- Mii, H.; Grossman, E.L.; Yancey, T.E. Carboniferous isotope stratigraphies of North America: Implications for Carboniferous paleoceanography and Mississippian glaciation. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1999, 111, 960–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.P.; Longman, M.W.; Lloyd, R.M. Spiculitic Chert Reservoir in Glick Field, South-Central Kansas; The Mountain Geologist: Denver, CO, USA, 1995; Volume 32, pp. 1–22. Available online: https://archives.datapages.com/data/rmag/mg/1995/rogers.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Colleary, W.M.; Dolly, E.D.; Longman, M.W.; Mullarkey, J.C. Hydrocarbon Production from Low Resistivity Chert and Carbonate Reservoirs in the Mississippian of Kansas: American Association of Petroleum Geologists; Rocky Mountain Section Meeting, Program Book and Expanded Abstracts Volume; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1997; pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, S.L.; Mullarkey, J.C.; Longman, M.W.; Colleary, W.M.; Rogers, J.P. Mississippian “chat” reservoirs, South Kansas: Low-Resistivity pay in a complex chert reservoir. AAPG Bull. 1998, 82, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watney, W.L.; Guy, W.J.; Byrnes, A.P. Characterization of the Mississippian chat in south-central Kansas. AAPG Bull. 2001, 85, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.C.; Schot, E.H. Stylolites: Their nature and origin. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1968, 38, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, B.M.; Mathis, R.L. On the formation and occurrence of saddle dolomite. J. Sediment. Res. 1980, 50, 1149–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.M.; Sibley, D.F. Epigenetic dolomitization and the origin of xenotopic dolomite texture. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1984, 54, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, B.D.; Goldstein, R.H. History of hydrothermal fluid flow in the midcontinent, USA: The relationship between inverted thermal structure, unconformities and porosity distribution. In Reservoir Quality of Clastic and Carbonate Rocks: Analysis, Modelling and Prediction; Armitage, P.J., Butcher, A.R., Churchill, J.M., Csoma, A.E., Hollis, C., Lander, R.H., Omma, J.E., Worden, R.H., Eds.; Special Publication 435; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2018; pp. 283–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garven, G.; Ge, S.; Person, M.A.; Sverjensky, D.A. Genesis of stratabound ore deposits in the Midcontinent basins of North America. 1. The role of regional groundwater flow. Am. J. Sci. 1993, 293, 497–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveney, R.M., Jr.; Ragan, V.M.; Brannon, J.C. Temporal benchmarks for modeling Phanerozoic flow of basinal brines and hydrocarbons in the southern Midcontinent based on radiometrically dated calcite. Geology 2000, 28, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, B.T.; Mazzullo, S.J.; Wilhite, B.W. Sedimentology, biota, and diagenesis of ‘reefs’ in Lower Mississippian (Kinderhookian To Basal Osagean: Lower Carboniferous) strata in the St. Joe Group in the western Ozark Area. Shale Shak. 2013, 64, 194–227. [Google Scholar]
- Coveney, R.M., Jr.; Goebel, E.D.; Ragan, V.M. Pressures and temperatures from aqueous fluid inclusions in sphalerite from midcontinent country rocks. Econ. Geol. 1987, 82, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garven, G. Continental Scale Groundwater Flow and Geologic Processes: Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences; Annual Reviews: San Mateo, CA, USA, 1995; Volume 23, pp. 89–117. [Google Scholar]


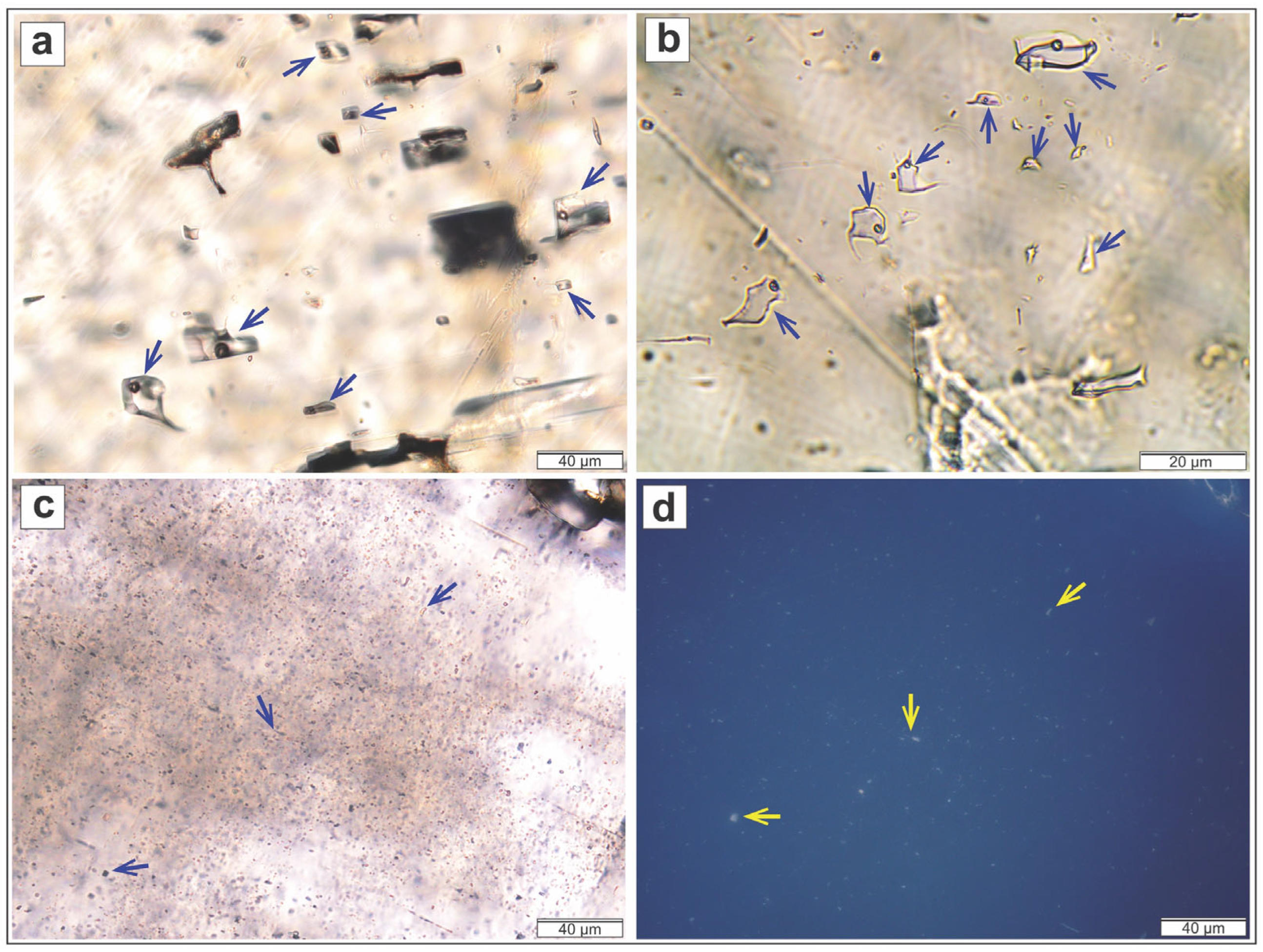
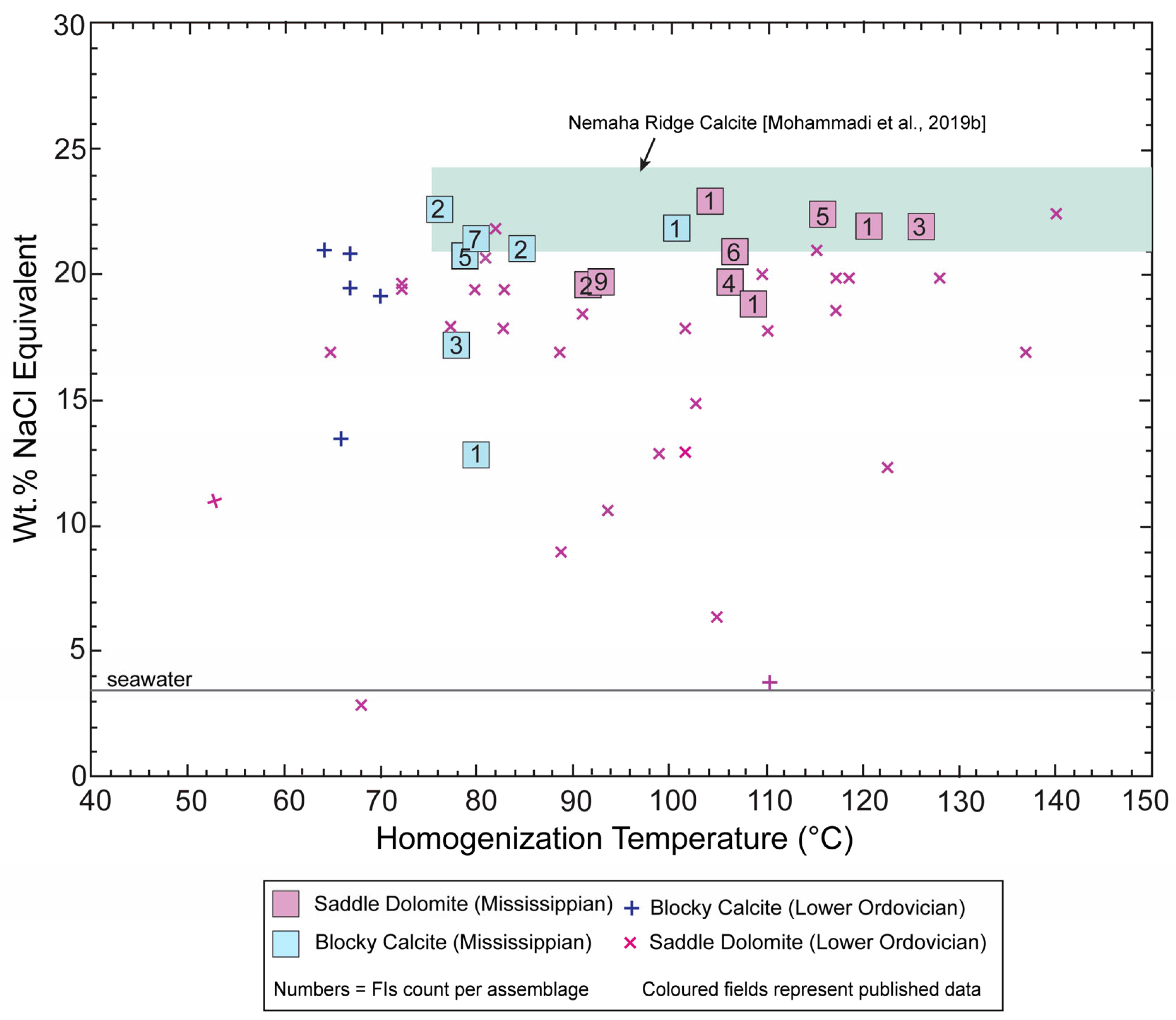
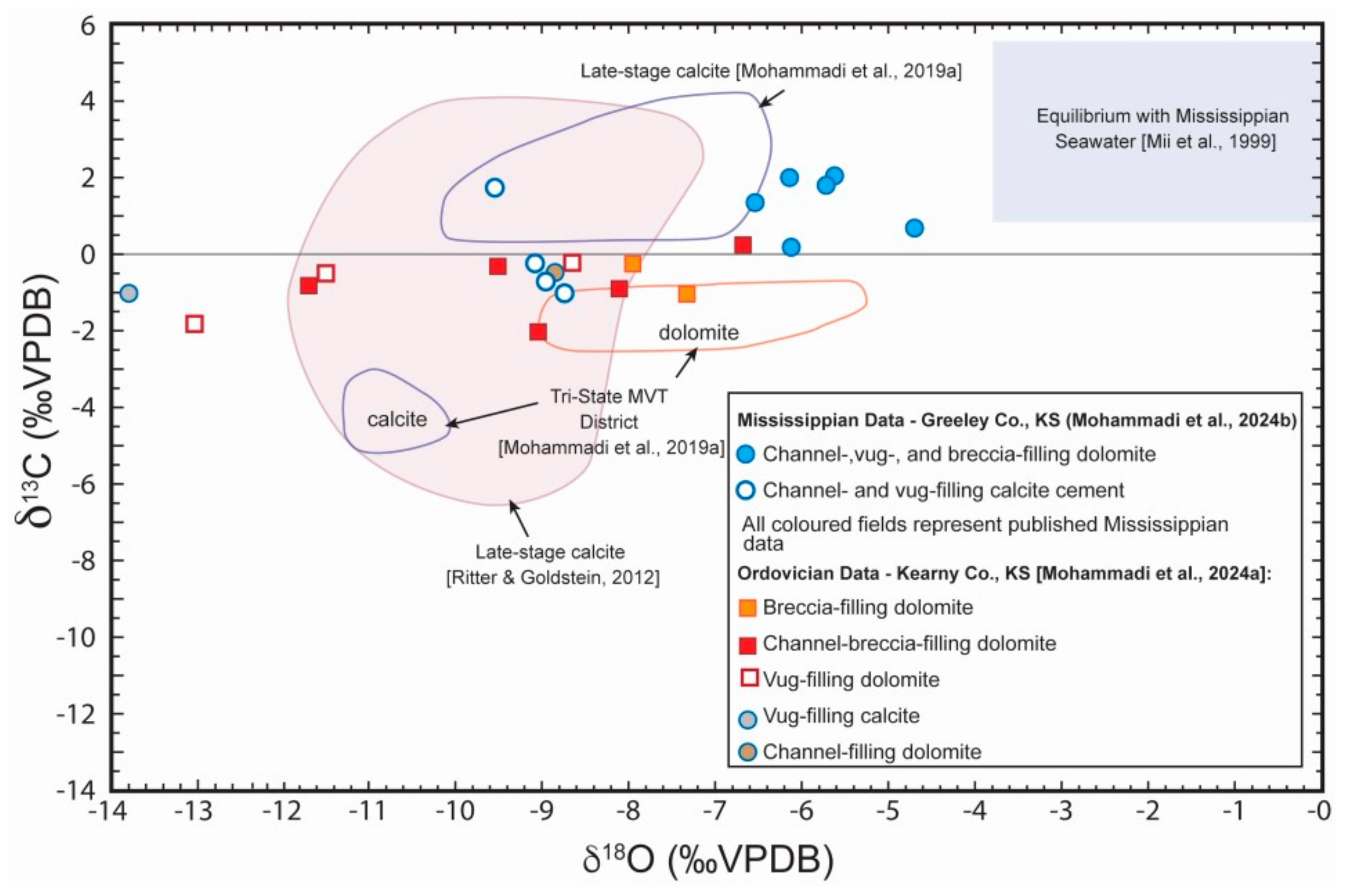
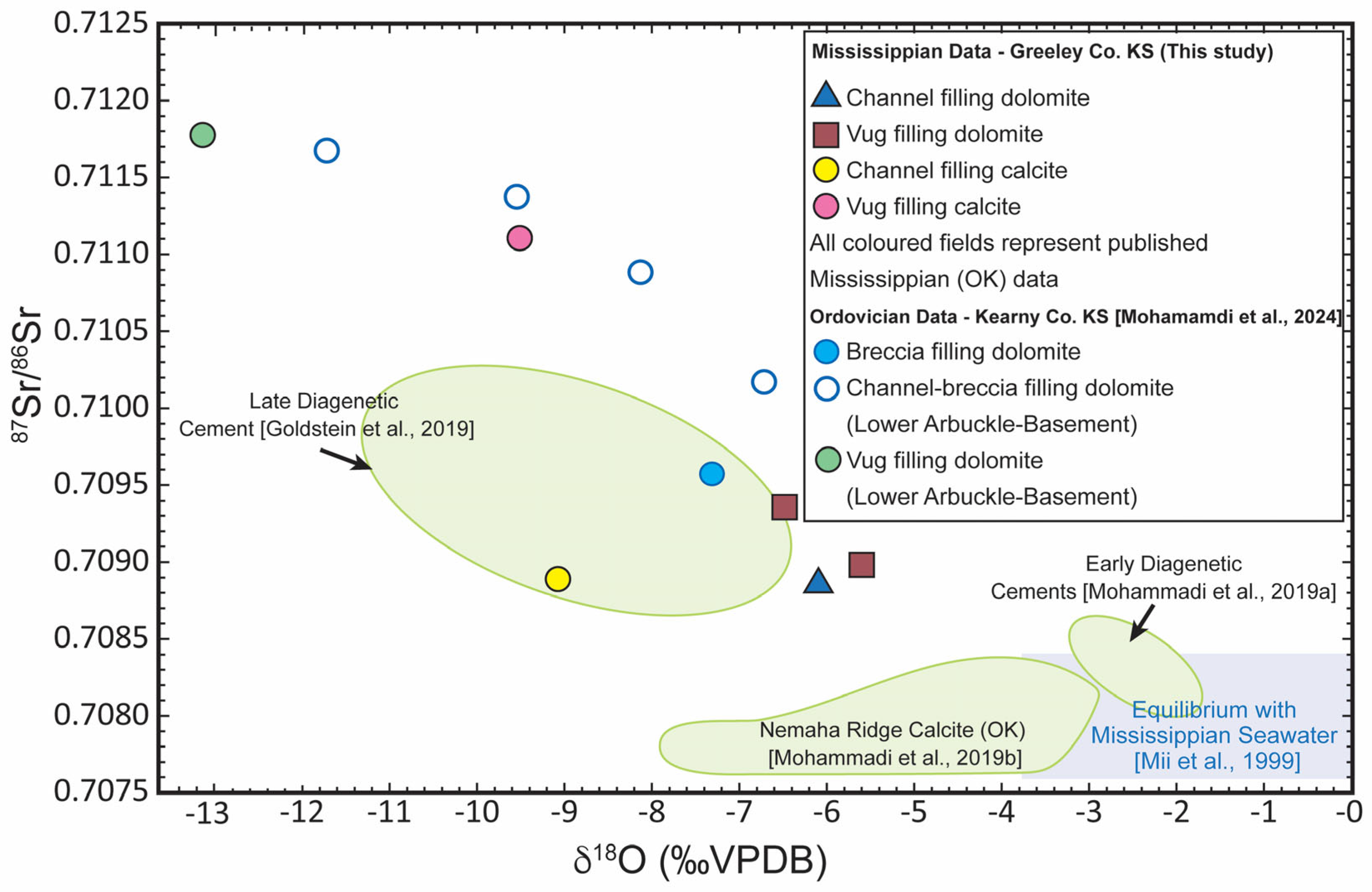
| Sample ID | Mineral | Assemblage | Th (°C) | NaCl Eq | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RKB-5453 | Dolomite | 1 | 106 | −16.5 | 19.8 | Primary |
| 106 | −16.5 | 19.8 | ||||
| 106 | −16.5 | 19.8 | ||||
| 106 | −16.5 | 19.8 | ||||
| 106 | −16.5 | 19.8 | ||||
| 2 | 93 | −15.2 | 18.8 | Primary | ||
| 93 | −15.2 | 18.8 | ||||
| 93 | −15.2 | 18.8 | ||||
| 93 | −15.2 | 18.8 | ||||
| 93 | −15.2 | 18.8 | ||||
| 93 | −15.2 | 18.8 | ||||
| 93 | −15.2 | 18.8 | ||||
| 3 | 92 | −15.2 | 18.8 | Primary | ||
| 92 | −15.2 | 18.8 | ||||
| 4 | 126 | −19.6 | 22.1 | |||
| 126 | −19.6 | 22.1 | ||||
| 126 | −19.6 | 22.1 | ||||
| - | 109 | −14.7 | 18.4 | Primary | ||
| RKB-5474.9 | Dolomite | 1 | 107 | −18 | 21.0 | Primary |
| 107 | −18 | 21.0 | ||||
| 107 | −18 | 21.0 | ||||
| - | 65 | - | Primary | |||
| - | 107 | −18 | 21.0 | Primary | ||
| - | 111 | −20 | 22.4 | Primary | ||
| - | 121 | −20 | 22.4 | Primary | ||
| RKB-5495 | Dolomite | 1 | 116 | −20 | 22.4 | Primary |
| 116 | −20 | 22.4 | ||||
| 116 | −20 | 22.4 | ||||
| 116 | −20 | 22.4 | ||||
| 116 | −20 | 22.4 | ||||
| - | 104 | −20.9 | 23.0 | Primary | ||
| 2 | 124 | - | Primary | |||
| 124 | - | |||||
| 3 | 104 | - | Primary | |||
| 104 | - | |||||
| - | - | −20.9 | 23.0 | Primary | ||
| RKB-5505.6 | Calcite | - | 79 | −18.2 | 21.1 | Primary |
| - | 67 | −20 | 22.4 | Primary | ||
| - | 76 | −20 | 22.4 | Primary | ||
| - | 85 | −18.2 | 21.1 | Primary | ||
| - | 85 | −18.9 | 21.6 | Primary | ||
| - | 79 | −18.2 | 21.1 | Primary | ||
| - | 79 | −23.6 | 24.7 | Primary | ||
| 1 | 79 | −18.2 | 21.1 | Primary | ||
| 79 | −18.2 | 21.1 | ||||
| 79 | −18.2 | 21.1 | ||||
| 79 | −18.2 | 21.1 | ||||
| 79 | −20 | 22.4 | ||||
| RKB-5525 | Calcite | 1 | 78 | −13.5 | 17.3 | Primary |
| 78 | −13.5 | 17.3 | ||||
| 78 | −13.5 | 17.3 | ||||
| 2 | 78 | - | Primary | |||
| 78 | - | |||||
| 78 | - | |||||
| 78 | - | |||||
| - | 76 | - | Primary | |||
| - | 80 | −9.3 | 13.2 | Primary | ||
| - | 101 | −19.8 | 22.2 | Primary |
| Sample ID | Mineral and Open Space Type | δ13C‰ VPDB | δ18O‰ VPDB | δ18O‰ VSMOW | δ18O‰ Water VSMOW * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RKB-5453 | channel-filling saddle dolomite | 2.08 | −6.14 | 24.58 | 2.58 to 6.08 |
| RKB-5458.5 | channel-filling saddle dolomite | 1.98 | −5.67 | 25.06 | |
| RKB-5474.9 | vug-filling saddle dolomite | 1.90 | −5.64 | 25.10 | 1.4 to 6.1 |
| RKB-5495 | vug-filling saddle dolomite | 1.46 | −6.50 | 24.21 | 3.71 to 5.71 |
| RKB-5505.6 | channel-filling calcite | −0.25 | −9.08 | 21.55 | 0.05 to 2.55 |
| RKB-5525 | vug-filling calcite | 1.79 | −9.44 | 21.18 | 1.18 to 4.18 |
| RKB-5533.4 a | channel-filling saddle dolomite | 0.15 | −6.14 | 24.58 | |
| RKB-5533.4 b | channel-filling calcite | −0.96 | −8.86 | 21.78 | |
| RKB-5533.6 a | channel-filling saddle dolomite | 0.57 | −4.66 | 26.11 | |
| RKB-5533.6 b | channel-filling calcite | −1.01 | −8.69 | 21.95 |
| Sample ID | Mineral and Open Space Type | 87Sr/86Sr (Exp Corr) * |
|---|---|---|
| RKB-5453 | Channel-filling saddle dolomite | 0.7088812 |
| RKB-5474.9 | Vug-filling saddle dolomite | 0.7090068 |
| RKB-5495 | Vug-filling saddle dolomite | 0.7094432 |
| RKB-5505.6 | Channel-filling calcite | 0.7089503 |
| RKB-5525 | Vug-filling calcite | 0.7111501 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammadi, S. Hydrothermal Fluids and Diagenesis of Mississippian Carbonates: Implications for Regional Mineralization in Western Kansas, U.S.A. Minerals 2025, 15, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101076
Mohammadi S. Hydrothermal Fluids and Diagenesis of Mississippian Carbonates: Implications for Regional Mineralization in Western Kansas, U.S.A. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101076
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammadi, Sahar. 2025. "Hydrothermal Fluids and Diagenesis of Mississippian Carbonates: Implications for Regional Mineralization in Western Kansas, U.S.A" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101076
APA StyleMohammadi, S. (2025). Hydrothermal Fluids and Diagenesis of Mississippian Carbonates: Implications for Regional Mineralization in Western Kansas, U.S.A. Minerals, 15(10), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101076







