Extreme Element Enrichment by the Interaction of Supercritical Fluids from the Mantle with Crustal Rocks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sample Materials and Methodology
2.1. Sample Materials
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Raman Spectroscopy
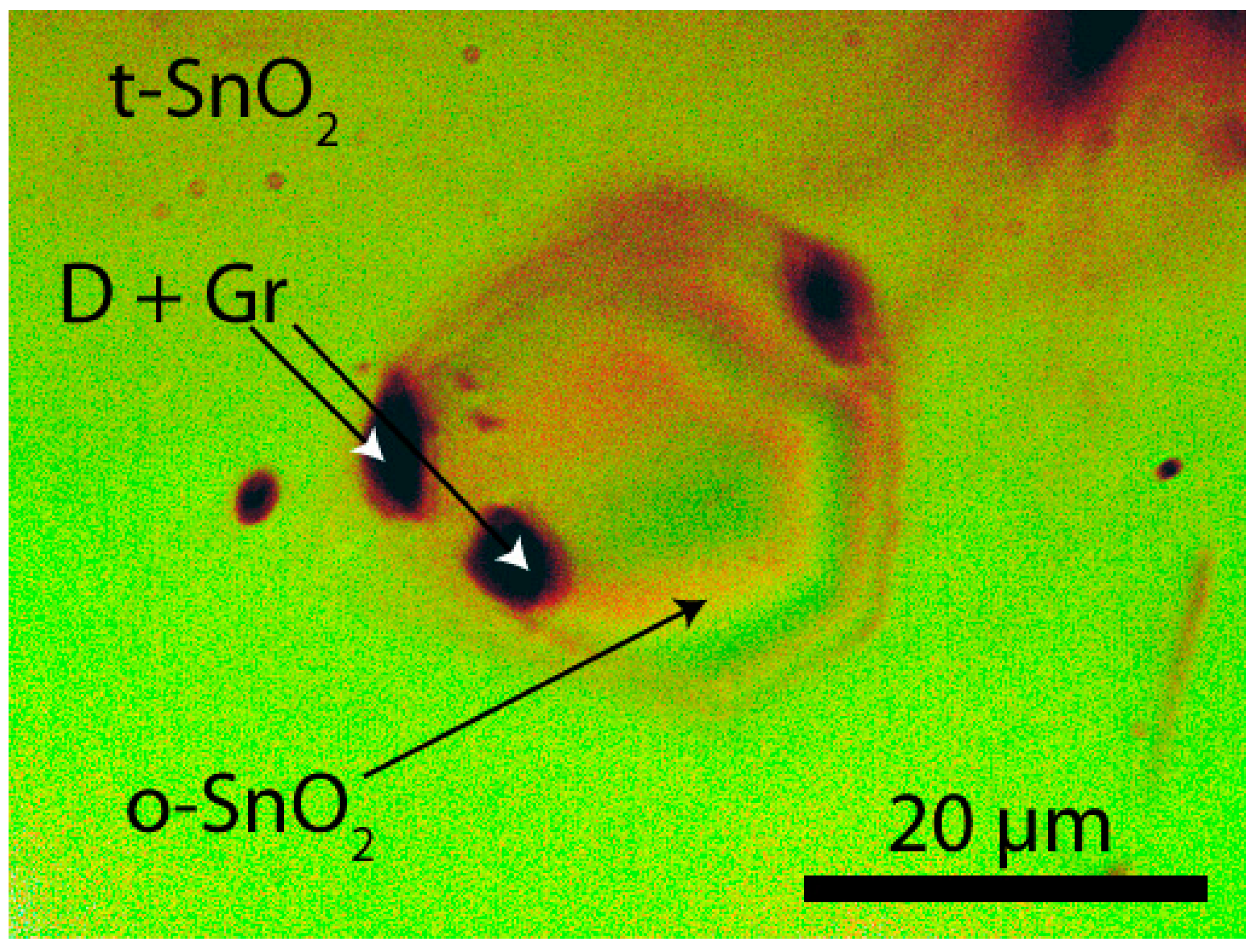
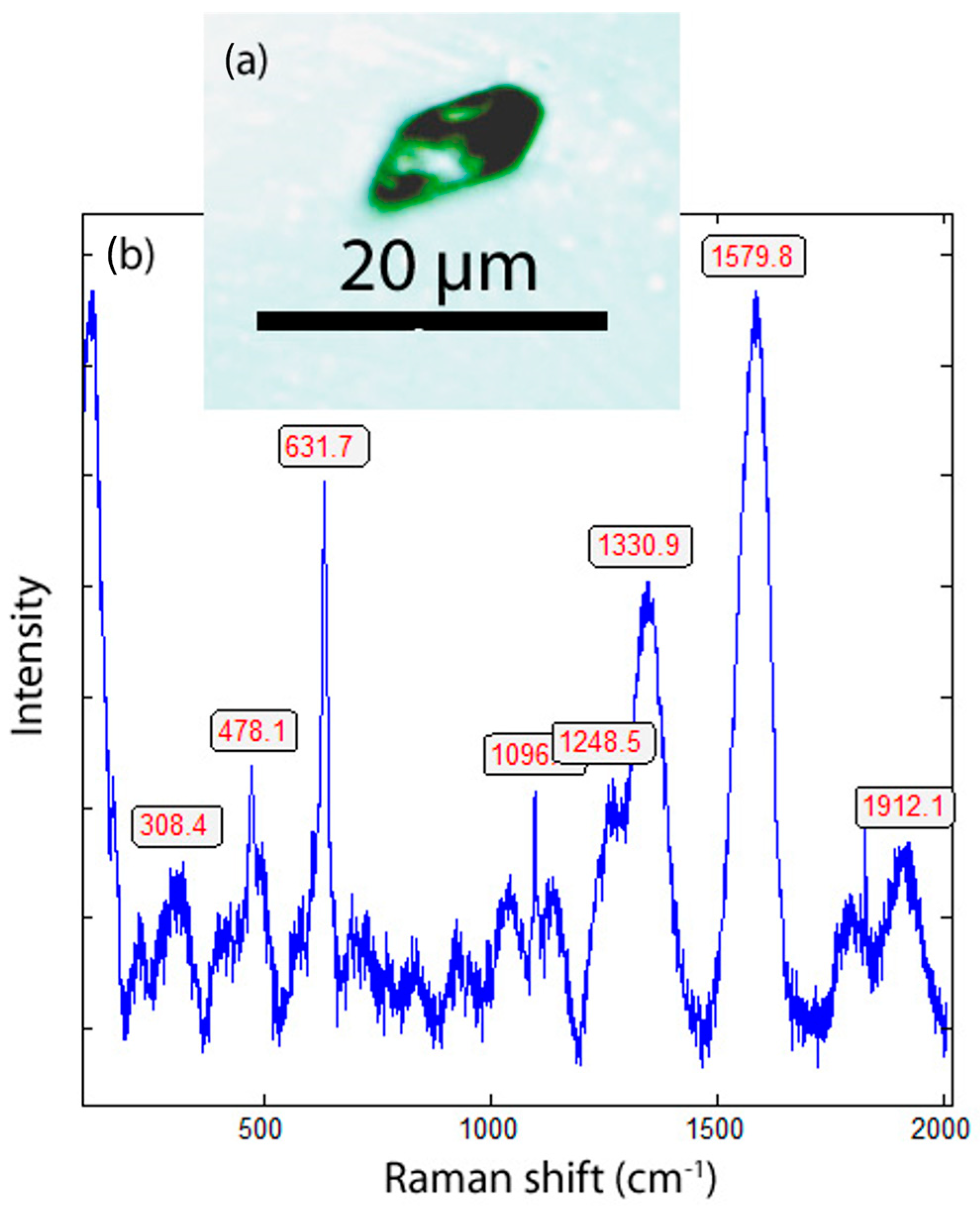
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, R. Determination of water contents of granite melt inclusions by confocal laser Ramanan microprobe spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Davidson, P. Laser Raman spectroscopic measurements of water in unexposed glass inclusions. Am. Mineral. 2006, 91, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.-M.; Koch-Müller, M.; Reichart, P.; Rhede, D.; Thomas, R.; Wirth, R.; Matsyuk, S. IR calibration for water determination in olivine, r-GeO2, and SiO2 polymorphs. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2009, 36, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R. Determination of the H3BO3 concentration in fluid and melt inclusions in granite pegmatites by laser Raman microprobe spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Webster, J.D.; Davidson, R. Be-daughter minerals in fluid and melt inclusions: Implications for the enrichment of Be in granite-pegmatite systems. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2011, 161, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Davidson, P.; Appel, K. The enhanced element enrichment in the supercritical states of granite-pegmatite systems. Acta Geochim. 2019, 38, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Davidson, P.; Rericha, A.; Voznyak, D.K. Water-rich melt inclusions as “frozen” samples of the supercritical state in granites and pegmatites reveal extreme element enrichment resulting under non-equilibrium conditions. Mineral. J. 2022, 44, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Rericha, A. Meaning of supercritical fluids in pegmatite formation and critical-element redistribution. Geol. Earth Mar. Sci. 2024, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rösler, J.H.; Lange, H. Geochemische Tabellen; VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie: Leipzig, Germany, 1975; 675p. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, H.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, X.; Mao, Z.; Wang, J. Supercritical fluids at subduction zones: Evidence, formation conditions, and physicochemical properties. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 167, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, X. Structures and transport properties of supercritical SiO2-H2O and NaAlSi3O8-H2O fluids. Am. Mineral. 2023, 108, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenetsky, M.B.; Sobolev, A.V.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Maas, R.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Thomas, R.; Pokhilenko, N.P.; Sobolev, N.V. Kimberlite melts rich in alkali chlorides and carbonates: A potent metasomatic agent in the mantle. Geology 2004, 32, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, F.; Wirth, R.; Marsyuk, S.; Schreiber, A.; Thomas, R. Nyerereite and nahcolite inclusions in diamond: Evidence for lower-mantle carbonatitic magmas. Mineral. Mag. 2009, 73, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolmatov, D.; Brazhkin, V.V.; Trachenko, K. Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H. Introduction to advances in the study of supercritical geofluids. Science China. Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 2391–2394. [Google Scholar]
- Sengers, J.L. How Fluids Unmix: Discoveries by the School of Van der Waals and Kameringh Onnes; Koninklikjke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; 302p. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R. 13C-rich diamond in a pegmatite from Rønne, Bornholm Island: Proof for the interaction between mantle and crust. Geol. Earth Mar. Sci. 2024, 6, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.; Grew, E. Coesite inclusions in prismatine from Waldheim, Germany: New constraints on the pressure-temperature evolution of the Saxony Granulite Complex. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Mineralogical Conference in Cracow, Cracow, Poland, 29 August–2 September 2021. Book of Abstracts: 391. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R. Ergebnisse der Thermobarometrischen Untersuchungen an Flüssigkeitseinschlüssen in Mineralen der Postmagmatischen Zinn-Wolfram-Mineralisation des Erzgebirges; Freiberger Forschungshefte C370; Bergakademie Freiberg: Freiberg, Germany, 1982; 85p. [Google Scholar]
- Schröcke, H. Zur Paragenese erzgebirgischer Zinnlagerstätten. Neues Jahrb. Mineral. Abh. 1954, 87, 33–109. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, L.; Kuschka, E.; Seifert, T. Lagerstätten des Erzgebirges; Enke: Stuttgart, Germany, 2000; 300p. [Google Scholar]
- Kotlánová, M.K.; Dolniček, Z.; René, M.; Prochaska, W.; Ulmanová, J.; Kapusta, J.; Maček, V.; Kropác, K. Fluid evolution of greisen from Krupka Sn-W ore district, Bohemian Massif (Czech Republic). Minerals 2024, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Davidson, P.; Rericha, A.; Recknagel, U. Water-rich coesite in prismatine-granulite from Waldheim/Saxony. Veröffentlichungen Naturkunde Mus. Chemnitz 2022, 45, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.; Davidson, P.; Rericha, A.; Recknagel, U. Mineral inclusions in a crustal granite: Evidence for a novel transcrustal transport mechanism. Geosciences 2023, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Klemm, W. Microthermometric study of silicate melt inclusions in Variscan granites from SE Germany: Volatile contents and entrapment conditions. J. Petrol. 1997, 38, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütze, H.; Stiehl, G.; Wetzel, K.; Beuge, P.; Haberlandt, R.; Gerstenberger, H.; Tischendorf, G.; Wand, U.; Mühle, K.; Rösler, H.-J.; et al. Isotopen- und elementgeochemische sowie radiogeochronologische Aussagen zur Herkunft des Ehrenfriedersdorfer Granites.–Ableitung erster Modellvorstellungen. ZFI-Mitteilungen Leipz. 1983, 76, 232–254. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, K.; Veerapandy, V.; Fjellvag, H.; Vajeeston, P. First-principles exploration into the physical and chemical properties of certain newly identified SnO2 polymorphs. ACS Publ. 2022, 7, 10382–10393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werninghaus, T. MicroRaman Spectroscopy Investigations of Hard Coatings. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Chemnitz-Zwickau, Chemnitz, Germany, 1997; 163p. [Google Scholar]
- Brooker, M.H.; Hancock, G.; Rice, B.C.; Shapter, J. Raman frequency and intensity studies of liquid H2O, H218O and D2O. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1989, 20, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, S.R.; Kubo, A.; Duffy, T.S.; Prakapenka, V.B.; Shen, G. High-pressure phases in SnO2 to 117 GPa. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 014105-1–014105-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R. Rhomboedric cassiterite as inclusions in tetragonal cassiterite from Slavkovský les–North Bohemia (Czech Republic). Geol. Earth Mar. Sci. 2024, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R. Growth of SiC whiskers in beryl by a natural supercritical VLS process. Asp. Min. Miner. Sci. 2023, 11, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.; Leh, M. The formation of some quartz veins in the Lusatian Massif, E-Germany by supercritical fluids/melts bearing lonsdaleite and diamond and comparison with other similar formations in Middle-Saxonian and Thuringian/E-Germany. Geol. Earth Mar. Sci. 2024, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.; Davidson, P.; Rericha, A. Emerald from the Habachtal: New observations. Mineral. Petrol. 2020, 114, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
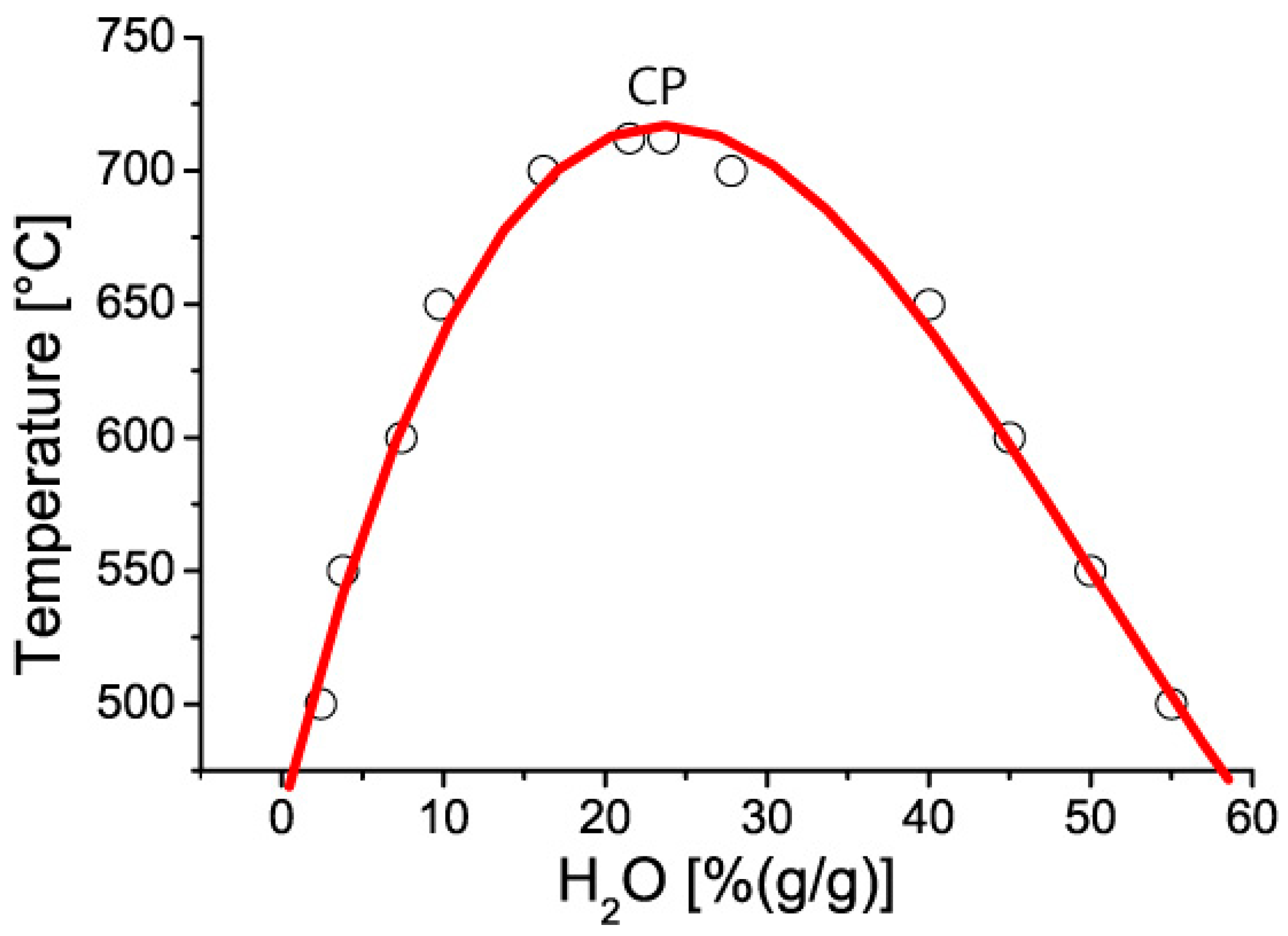
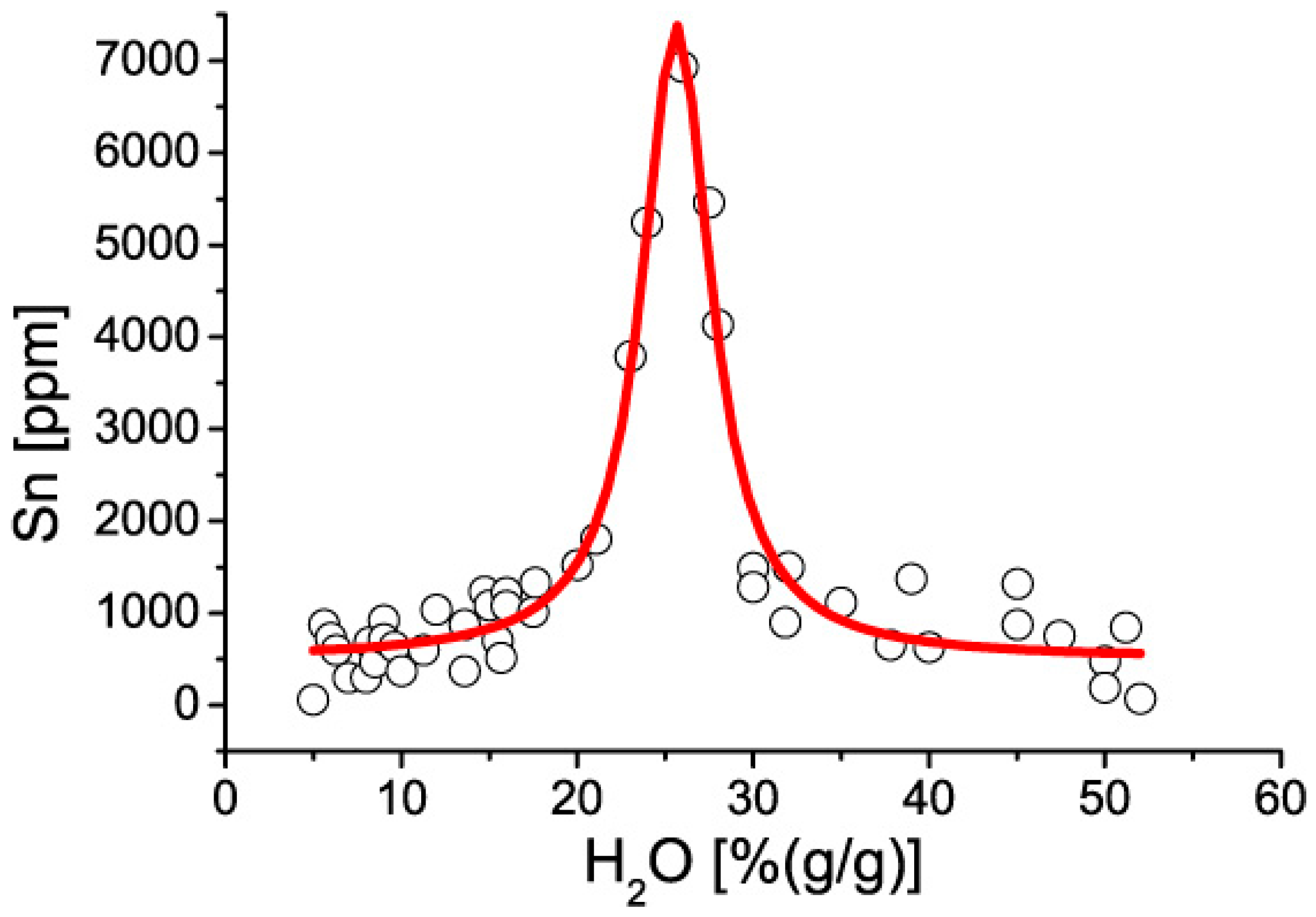
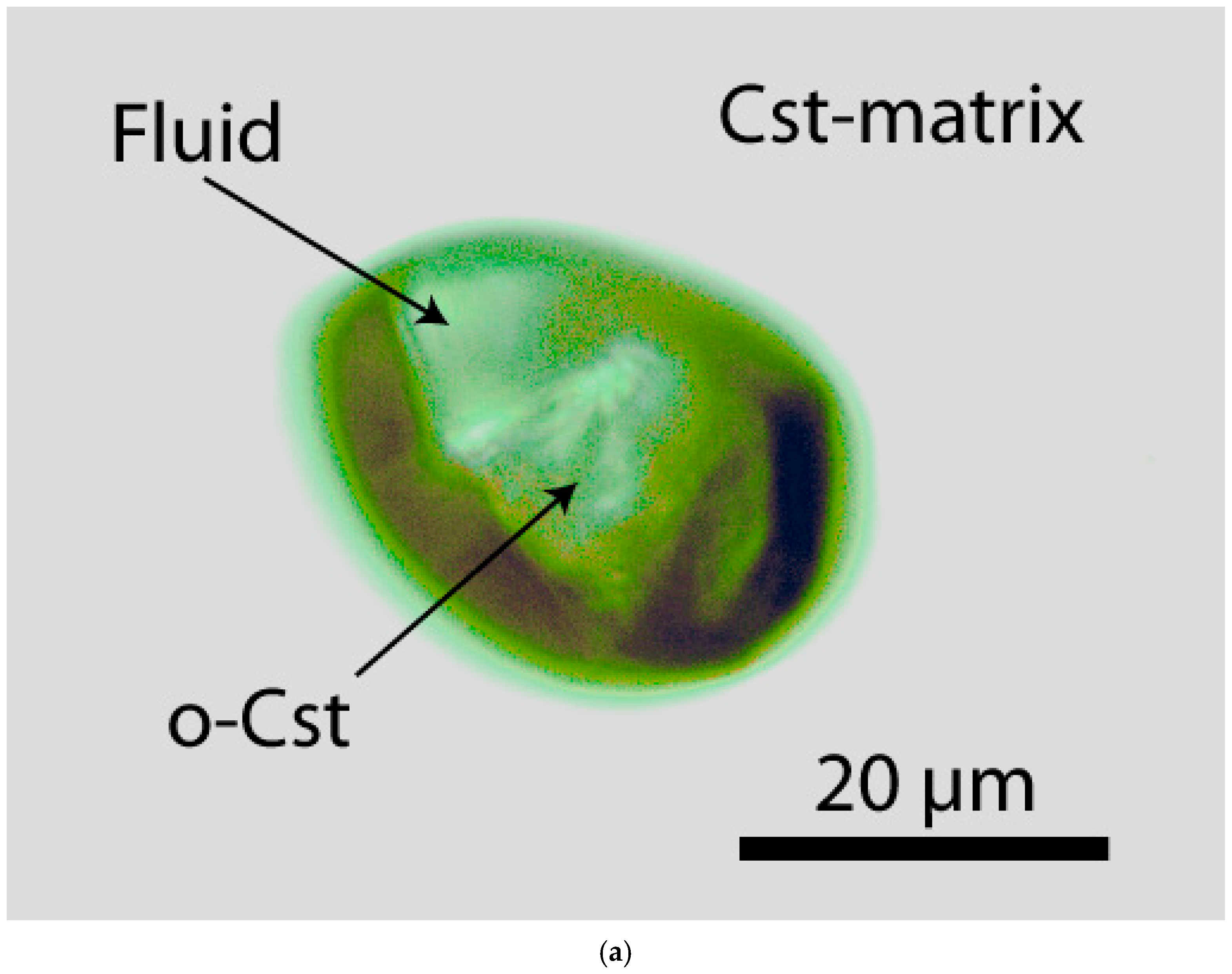
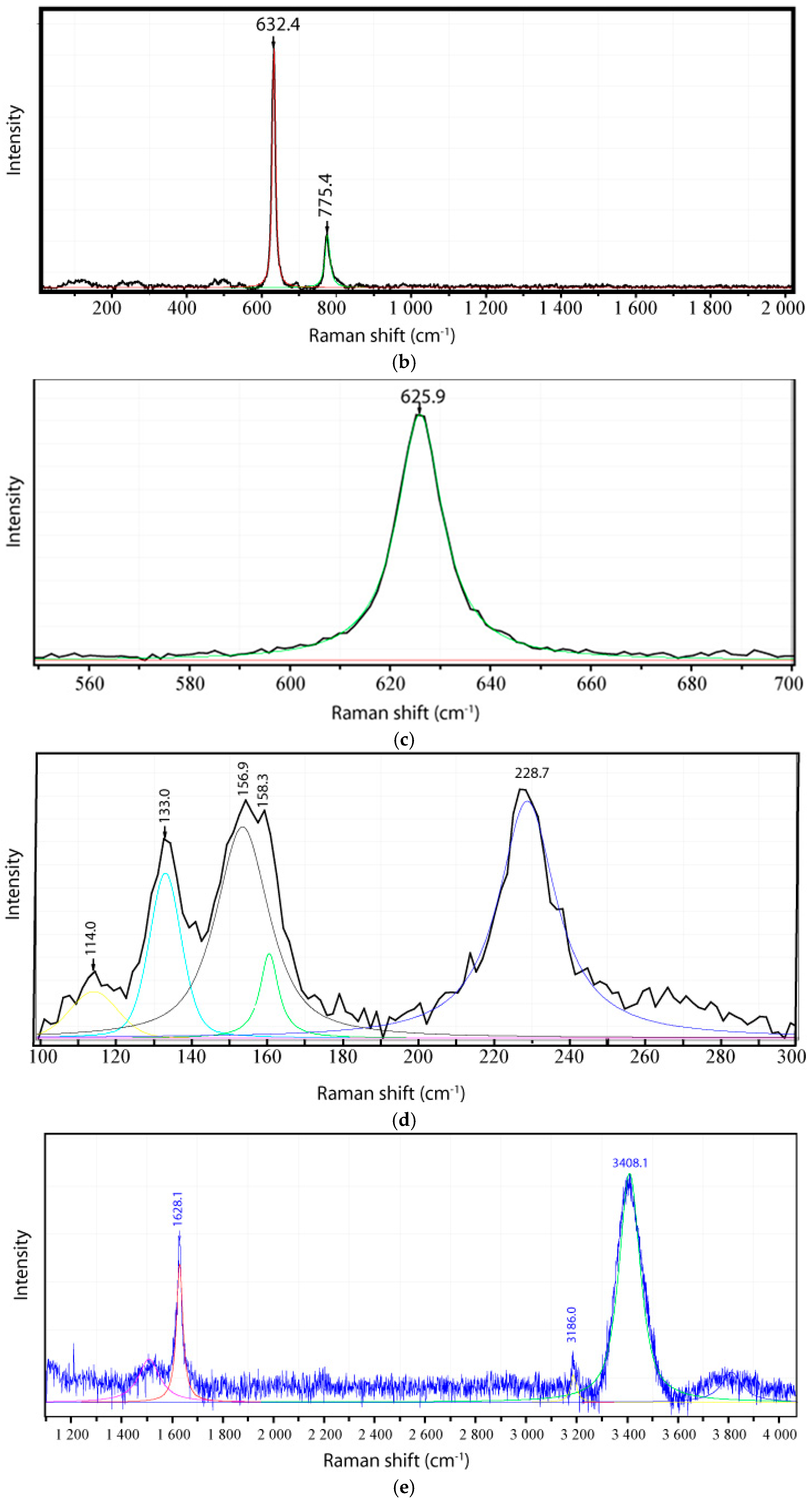

| Area | Center | Width | Offset | Height | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51,522 | 25.6% H2O | 4.77% H2O | 504 ppm Sn | 6882 ppm | 0.9455 |
| Orthorhombic Cassiterite (Pnma-I) as Inclusion in Cassiterite from Krupka | ||
|---|---|---|
| Raman Band | Raman Mode | Relative Intensity |
| 138.2 ± 2.2 | Ag | vs |
| 159.5 ± 2.6 | B1g | vs |
| 232.0 ± 2.4 | Ag | s |
| 474.0 ± 4.8 | B1g | w |
| 625.8 ± 2.0 | Ag | vs |
| 691.3 ± 0.6 | B1g | vw |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomas, R.; Rericha, A. Extreme Element Enrichment by the Interaction of Supercritical Fluids from the Mantle with Crustal Rocks. Minerals 2025, 15, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010033
Thomas R, Rericha A. Extreme Element Enrichment by the Interaction of Supercritical Fluids from the Mantle with Crustal Rocks. Minerals. 2025; 15(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomas, Rainer, and Adolf Rericha. 2025. "Extreme Element Enrichment by the Interaction of Supercritical Fluids from the Mantle with Crustal Rocks" Minerals 15, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010033
APA StyleThomas, R., & Rericha, A. (2025). Extreme Element Enrichment by the Interaction of Supercritical Fluids from the Mantle with Crustal Rocks. Minerals, 15(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010033







