Location Prediction Study of Fluorite Ore in Shallow Cover Area: Evidence from Integrated Geophysical Surveys
Abstract
1. Introduction
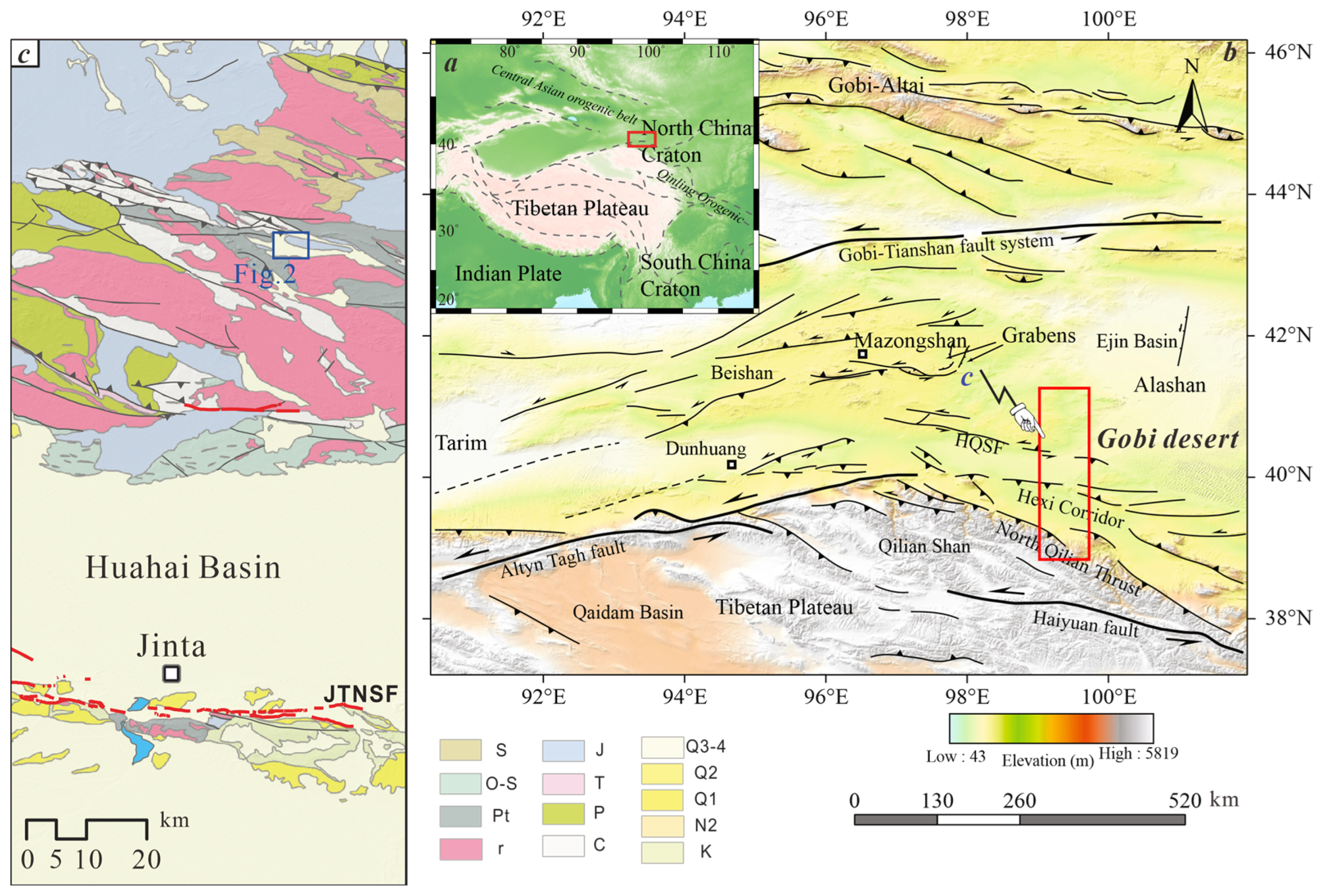
2. Regional Geological and Geophysical Characteristics
2.1. Regional Geology
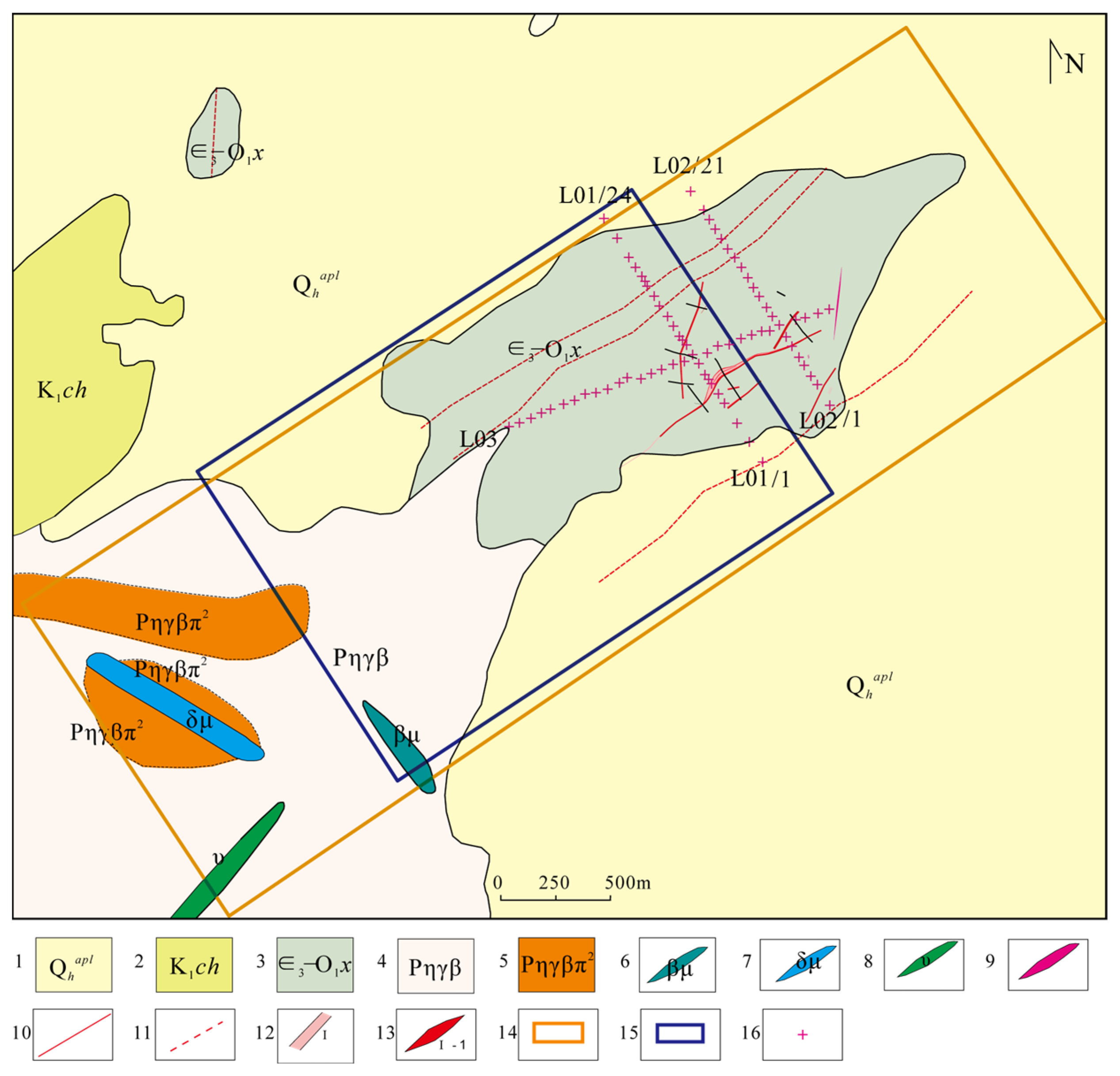
2.2. Deposit Geology
2.3. Geophysical Characteristics of the Deposit
3. Integrated Geophysical Exploration and Processing
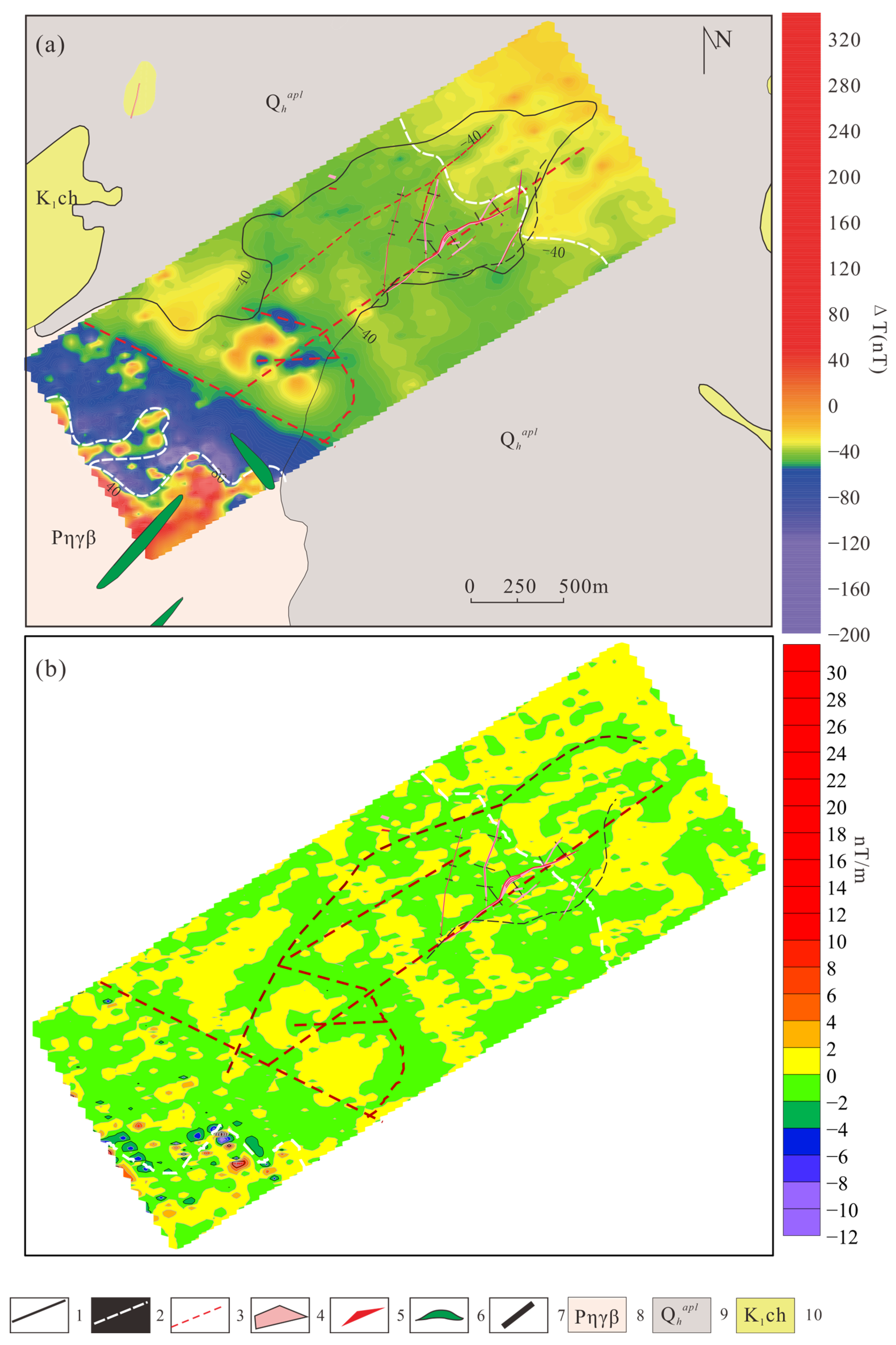
3.1. Ground Magnetic Method (GM)
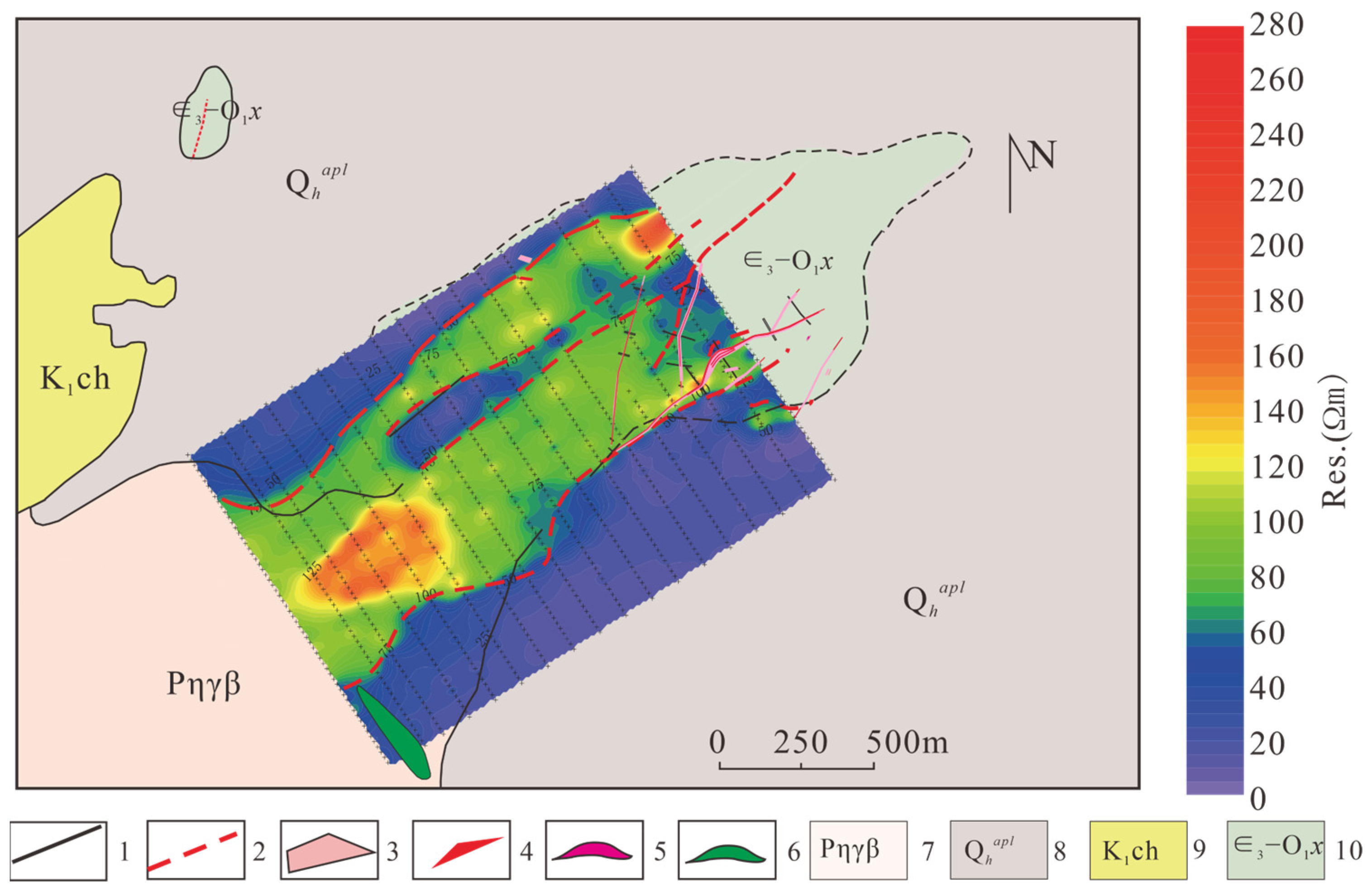
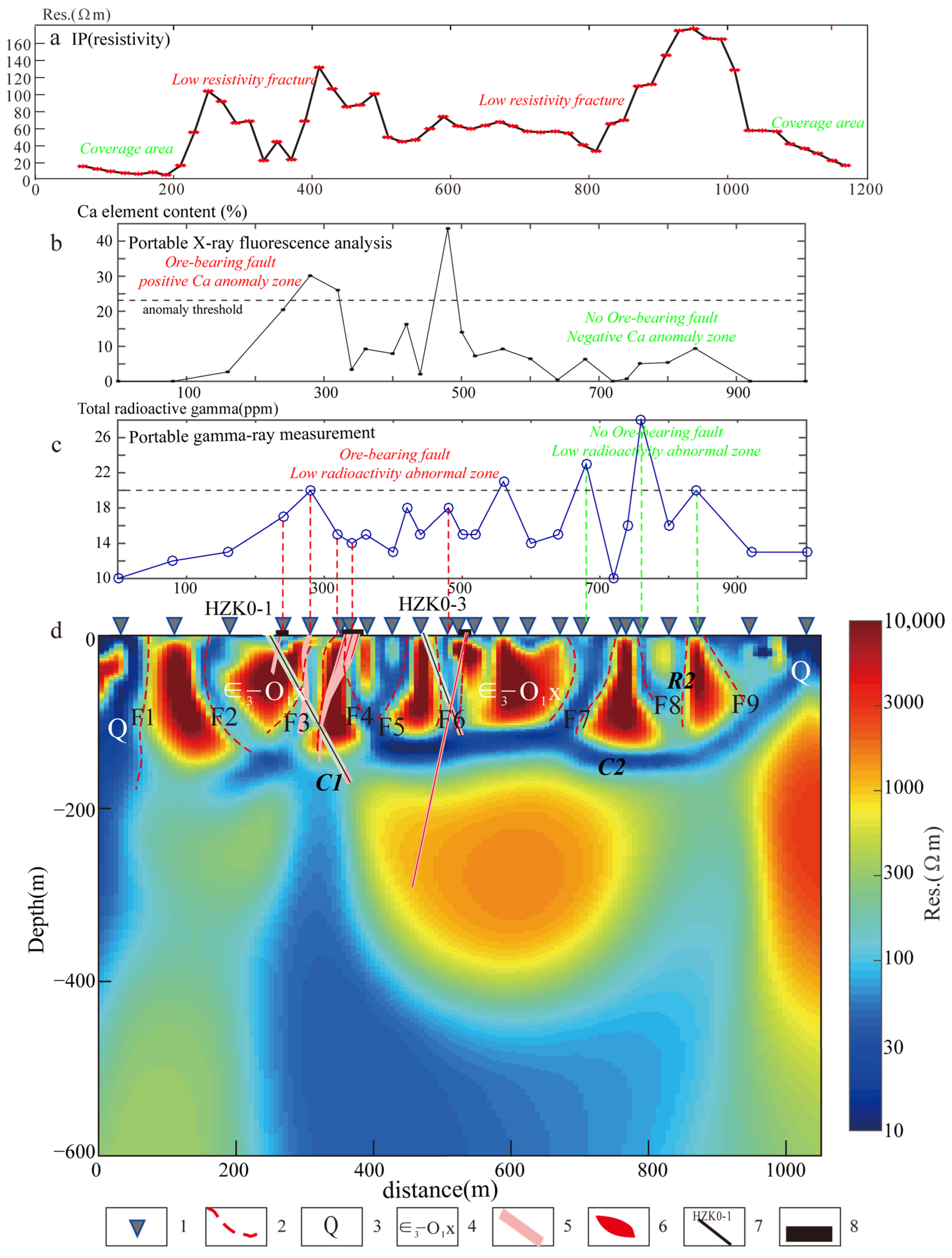
3.2. Induced Polarization Method
3.3. Ore-Bearing Potential Detection Technology of Fluorite Ore in Shallow Covering Area
3.4. Audio Magnetotelluric Sounding
3.4.1. Data Acquisition and Processing
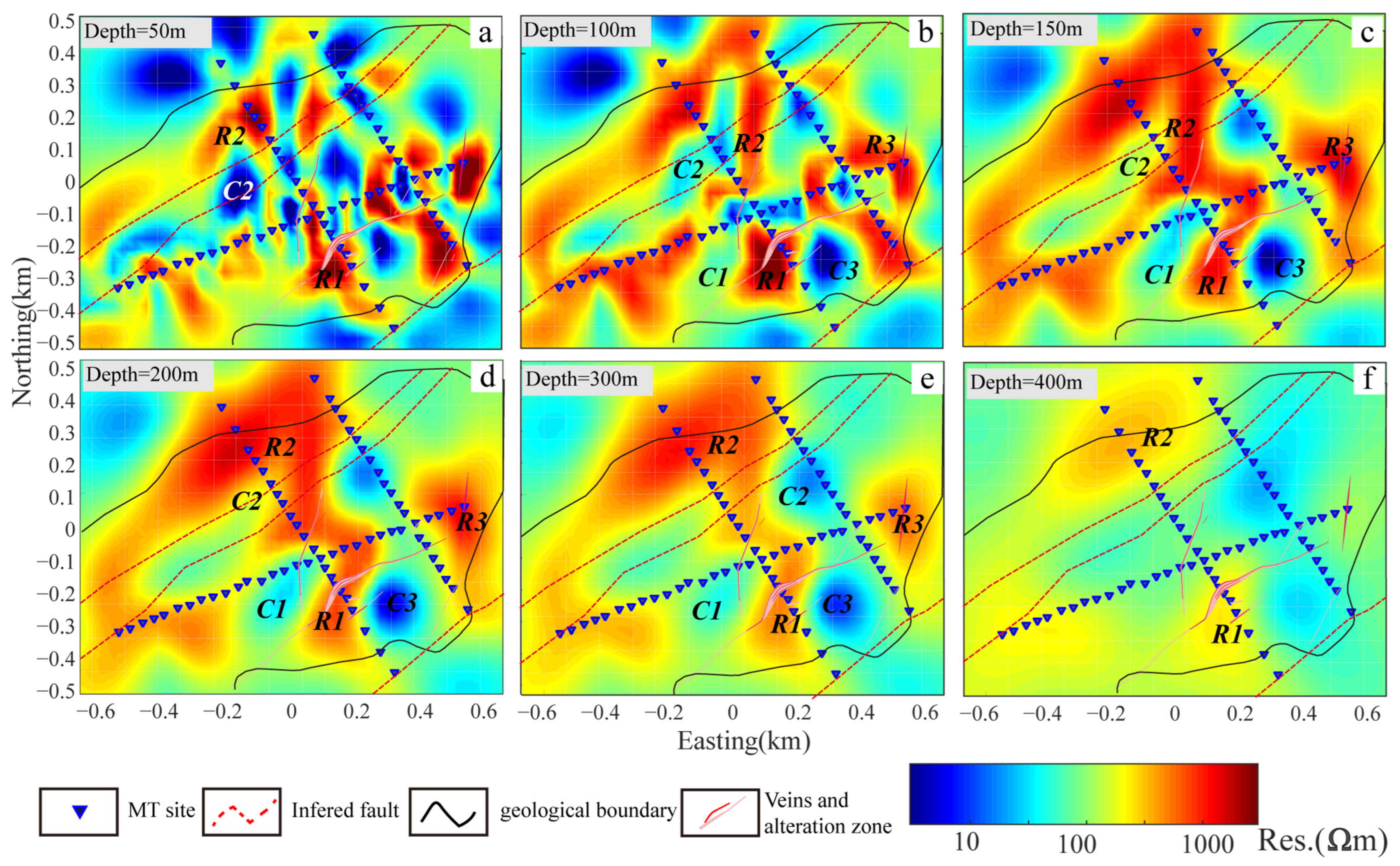
3.4.2. Two-Dimensional Inversion and Results
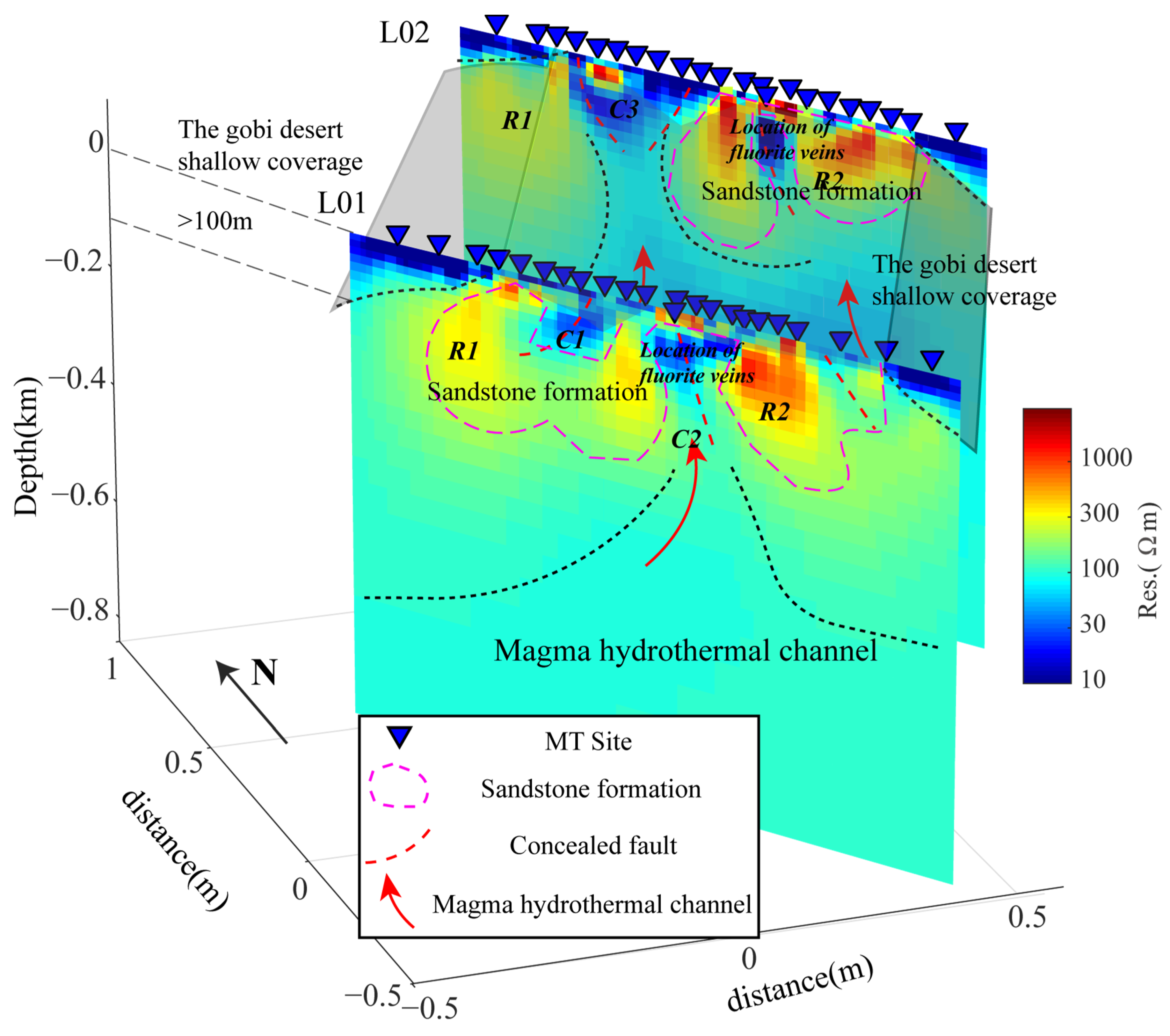
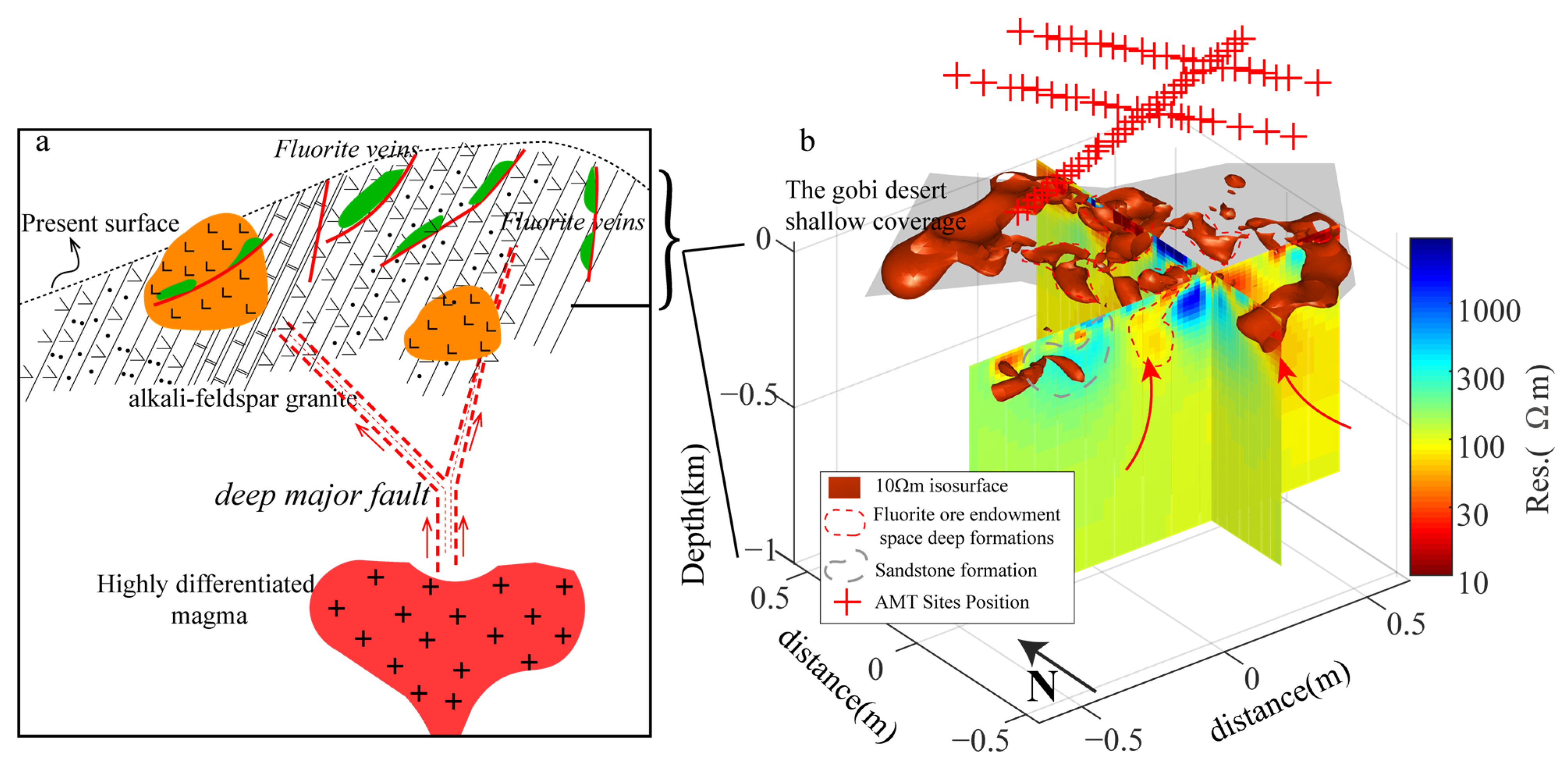
3.4.3. Three-Dimensional Inversion and Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Constraints of Integrated Geophysical Exploration Results on Hidden Fluorite Deposits
4.2. Method System of Shallow Coverage Area Positioning Prediction Technology
4.3. Formation Mechanism of Mineral Deposits
5. Conclusions
- Summarized the phased fluorite deposit positioning and prediction technology process in the shallow-covered areas of the Gobi Desert. Initially, GM and IP surveys were utilized to identify potential concealed ore-bearing fault structures, representing possible structures that control hydrothermal solution movement. Subsequently, PGR and PXRF were employed to constrain anomalies associated with potential mineralization within spatial occurrences of fluorite deposits. Finally, combining deep-seated information provided by electromagnetic detection with drilling and trenching verification led to discovering multiple concealed fluorite deposits, providing valuable references for positioning and predicting fluorite deposits in shallow-covered areas.
- The resistivity model constrained by the audio Magnetotelluric method, especially 3D inversion, was used to constrain the deep subsurface structures of known mineralized faults. The fluorite ore bodies of Huashitoushan are mainly located at the junction regions of high-resistivity sandstone formation and relatively high-conductivity fault/fissure alteration zones.
- Unlike the traditional geophysical detection of metal–sulfide deposits in shallow coverage areas, the physical properties of the ore body and the surrounding rocks are significantly different, and the prediction of fluorite ore positioning needs to be constrained by the combination of two phases of spatial detection of endowment and metallogenetic potential, as well as by a combination of various technological methods.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Summaries, M.C. Mineral Commodity Summaries; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2021; p. 200.
- Camprubí, A.; González-Partida, E.; Richard, A.; Boiron, M.-C.; González-Ruiz, L.E.; Aguilar-Ramírez, C.F.; Fuentes-Guzmán, E.; González-Ruiz, D.; Legouix, C. MVT-like fluorite deposits and oligocene magmatic-hydrothermal fluorite–Be–U–Mo–P–V overprints in northern Coahuila, Mexico. Minerals 2019, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castorina, F.; Masi, U.; Gorello, I. Rare earth element and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence for the origin of fluorite from the Silius vein deposit (southeastern Sardinia, Italy). J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 215, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Dinani, H.; Aftabi, A. Vertical lithogeochemical halos and zoning vectors at Goushfil Zn–Pb deposit, Irankuh district, southwestern Isfahan, Iran: Implications for concealed ore exploration and genetic models. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 1004–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.K.; Bedrosian, P.A.; Anderson, E.D.; Kelley, K.D.; Lang, J. Integrated geophysical imaging of a concealed mineral deposit: A case study of the world-class Pebble porphyry deposit in southwestern Alaska. Geophysics 2013, 78, B317–B328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Pei, Q.; Fang, Y.; Cao, H.; Zou, H.; Yin, S. Exploration of concealed fluorite deposit in shallow overburden areas: A case study in Elimutai, Inner Mongolia, China. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Pei, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Ware, B.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Yu, H. Application of field-portable geophysical and geochemical methods for tracing the Mesozoic-Cenozoic vein-type fluorite deposits in shallow overburden areas: A case from the Wuliji’Oboo deposit, Inner Mongolia, NE China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 142, 104685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schamper, C.; Rejiba, F.; Guérin, R. 1D single-site and laterally constrained inversion of multifrequency and multicomponent ground-based electromagnetic induction data—Application to the investigation of a near-surface clayey overburden. Geophysics 2012, 77, WB19–WB35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, R.; Lin, T.; Wang, W. Application of Multiple Geophysical Methods to Prospect Concealed Ores Beneath Quaternary Cover: A Case Study from a Copper-Polymetallic Deposit. In Technology and Application of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, ICEEG, Beijing, China, 26–29 June 2016; Di, Q., Xue, G., Xia, J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, G.; Zhang, L.; Hou, D.; Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, X. Integrated geological and geophysical investigations for the discovery of deeply buried gold–polymetallic deposits in China. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Gelius, L.-J.; Sakyi, P.; Zhou, N.; Chen, W.; Su, B.; Li, H.; Zhong, H.; Su, Y. Discovery of a hidden BIF deposit in Anhui province, China by integrated geological and geophysical investigations. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Jia, S.; Wang, E. Combined magnetic, transient electromagnetic, and magnetotelluric methods to detect a BIF-type concealed iron ore body: A case study in gongchangling iron ore concentration area, southern liaoning province, China. Minerals 2020, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Yan, J.; Chen, H.; Meng, G.; Yu, H.; Fan, L.; Luo, L.; Tao, X. 3D inversion of audio-magnetotelluric data for mineral exploration: A case study of Layikeleke buried porphyry copper deposit, Xinjiang, China. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 17, 576–588. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.; Lv, Q.; Yan, J.; Deng, Z.; Qi, G.; Xue, R. The research and application of explorational technology of “Penetrating” to geology and mineral investigation in overburden area. Acta Geosci. Sin 2019, 40, 637–650. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Meng, G.; Lv, Q.; Deng, Z.; Qi, G.; Tang, H.; Zhao, J.; Xue, R.; Wang, X. Prediction and location of concealed deposits in desertgobi coverage areas using integrated geophysics: An example of the Layikeleke copper polymetallic deposit in Xinjiang, Northwest China. Chin. J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 4117–4133. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; Tang, L. Integrated Exploration Model for Concealed Ore Deposit: A Case Study from Shuitou Fluorite Deposit, Inner Mongolia, North China. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 32, 370–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zou, H.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, Z.; Gao, F. Comprehensive exploration method for fluorite deposits in grasslands covered area: A case study of the Saiboluogoumen fluorite deposit in Linxi, Inner Mongolia. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2014, 41, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Li, M.; Santosh, M.; Zheng, D.; Cao, H.; Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Z. Fault-controlled carbonate-hosted barite-fluorite mineral systems: The Shuanghe deposit, Yangtze Block, South China. Gondwana Res. 2022, 101, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Teng, C.; Yang, X.; Huang, F.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H. Geochronology, geochemistry, and tectonic implications of early Neoproterozoic granitic rocks from the eastern Beishan Orogenic Belt, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Precambrian Res. 2021, 352, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, B.; Xue, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W. Geology and genesis of the Cihai mafic intrusions in Beishan Terrane, Xinjiang, Northwest China: Implication for iron mineralization and tectonic setting. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 121, 103573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Wei, W.; Yu, Y.; Lv, X. Geology, geochronology, mineral chemistry and geochemistry of the Hongnieshan mafic–ultramafic complex in the Beishan area, southern Central Asian orogenic Belt, NW China: Implications for petrogenesis and regional Ni mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Jiang, A. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of the Xiaohongshan vanadium-titanium magnetite deposit, Ejin Banner, Beishan, Inner Mongolia, and its geological implications. Geol. Bull. China 2015, 34, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, J.; Lei, R.; Chen, B.; Muhtar, M.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Cai, Y.; Wu, C. Zircon genesis and geochronology for the Zhangbaoshan super-large rubidium deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Implication to magmatic-hydrothermal evolution and mineralization processes. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 682720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhao, G.; Tan, W. The Metallogenic Rule of Mesozoic Hypogene Deposits in the Eastern Tianshan-Beishan Area. Northwest Geol. 2022, 55, 280–299. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, M.; Lu, K.; Si, X.; Dai, S.; Lu, M.; Xue, Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, D.; Xie, G. Geological structural features and copper-gold prospecting direction of the northern Hutoushan in the eastern section of the Beishan Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia. Miner. Explor. 2020, 11, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Q.; Zhang, S.; Hayashi, K.I.; Wang, L.; Cao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Song, K.; Chao, W. Nature and genesis of the Xiaobeigou fluorite deposit, Inner Mongolia, northeast China: Evidence from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes. Resour. Geol. 2019, 69, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Shang, P.; Han, Z.; Wang, C.; Jiao, S.; Wang, G.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yan, X. Comprehensive Information Prospecting Method for Fluorite Deposits in Shaowu Area, Northern Fujian Province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2022, 43, 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Chen, X.; Shang, P.; Yu, X.; Han, Z.; Wei, F.; Liu, Z. Application of the prospecting method of geophysical and geochemical integrated information in the exploration of fluorite deposits. Geol. Surv. China 2019, 6, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, S.; Zou, H.; Cao, H.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Z. The application of the field gamma ray spectrometry to the prospecting for fluorite deposits in LinXi area of Inner Monggolia. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 37, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; Chen, A.; Gao, F.; Tang, L.; Deng, M. The radioactive elements content of natural fluorite and its influence. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 38, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Shang, P.; Gao, Y.; Jiao, S.; Yao, C.; Zou, H.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zheng, H. Fluorite deposits in China: Geological features, metallogenic regularity, and research progress. China Geol. 2020, 3, 473–489. [Google Scholar]
- Orešković, J.; Milošević, A.; Kolar, S.; Borojević Šoštarić, S. The Žune Ba-F epithermal deposit: Geophysical characterization and exploration perspective. Geol. Croat. 2023, 76, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Kwan, K.; Groves, D.I. Geophysical implications for the exploration of concealed orogenic gold deposits: A case study in the Sandy Lake and Favourable Lake Archean greenstone belts, Superior Province, Ontario, Canada. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 128, 103892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hronsky, J.M.; Groves, D.I. Science of targeting: Definition, strategies, targeting and performance measurement. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2008, 55, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adagunodo, T.; Sunmonu, L.; Adeniji, A. An overview of magnetic method in mineral exploration. J. Glob. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 3, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Wang, M.; Shang, P.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y. Application of high-accuracy ground magnetic survey to the exploration of fluorite deposits. J. Geol. 2019, 3, 428–433. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Biswas, A.; Baranwal, V. Very low-frequency electromagnetic method: A shallow subsurface investigation technique for geophysical applications. In Recent Trends in Modelling of Environmental Contaminants; Sengupta, D., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 119–141. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zou, H.; Wang, G.; Cao, H.; Li, H. The application of VLF and AMT to the exploration of fluorite deposit. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 37, 800–803. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y. Geological characteristics, types and development and utilization value of Shuitou fluorite deposit in Linxi, Inner Mongolia. Geol. China 2023, 50, 795–805. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Hao, Q.; Chu, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, X. Application of very low frequency electromagnetic method to positioning of concealed metal deposits: An example of copper polymetallic ore occurrences in the southwest greater Hinggan mountains. Geol. Explor. 2017, 53, 528–532. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, B.; Cao, H.; Pei, Q.; Yang, B.; Wu, Z.; Xu, T.; Han, S. Exploration of fluorite deposit by the combination of VLF-EM and EH4 on shallow-covered area. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2016, 36, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Li, Z.; Sang, J.; Zhao, L.; Tie, W. Radioactive characteristics and prospecting significance of fluorite deposits in Southern Song County of Western Henan Province. Miner. Explor. 2024, 15, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Li, F. Review of in situ X-ray fluorescence analysis technology in China. X-ray Spectrom. 2020, 49, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, B.; Wei, L.; Li, H.; Meng, F.; Dong, F. Application of the integrated electrical method to exploration in the Zhaishang gold deposit, West Qinling. Geol. Explor. 2020, 56, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Sun, B.; Ye, G.; Hao, Z.; Xue, D.; Deng, A. Comprehensive geophysical study of Zhaishang Gold deposit, West Qinling. Geol. Rev. 2022, 68, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitiya, R.; Lu, M.; Chen, R.; Nong, G.; Chen, S.; Yao, H.; Shen, R.; Jiang, E. Audio Magnetotellurics Study of the Geoelectric Structure across the Zhugongtang Giant Lead–Zinc Deposit, NW Guizhou Province, China. Minerals 2022, 12, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D. Robust multiple-station magnetotelluric data processing. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 130, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W.; Mackie, R.L. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion. Geophysics 2001, 66, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, X. Refined techniques for data processing and two-dimensional inversion in magnetotelluric II: Which data polarization mode should be used in 2D inversion. Chin. J. Geophys. 2010, 53, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Fang, H.; Qiu, G.; Huang, J. The deep electrical structure across Anqing-Guichi ore concentration area. Geol. China 2019, 46, 795–806. [Google Scholar]
- Egbert, G.D.; Kelbert, A. Computational recipes for electromagnetic inverse problems. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 189, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelbert, A.; Meqbel, N.; Egbert, G.D.; Tandon, K. ModEM: A modular system for inversion of electromagnetic geophysical data. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, X.; Unsworth, M.; Cui, T.; Sun, X.; Han, B. Comparison of 2D and 3D inversion results: A case study of an MT profile. In Proceedings of the 24th EM Induction Workshop, Helsingør, Denmark, 12–19 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Rani, A.; Mahajan, R.K. 226Ra, 232Th and 40K analysis in soil samples from some areas of Punjab and Himachal Pradesh, India using gamma ray spectrometry. Radiat. Meas. 2005, 39, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yao, C.; Deng, Z.; Ren, Z.; Li, C. Application of Induced Polarization Method in Mineral Resource Exploration. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Bai, D.; Cheng, H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, A.; Sun, J.; Zhao, H. Application of the time—Domain IP method to the exploration of concealed fluorite deposits:A case study of the Tielu fluorite deposit in Fangcheng County, Henan Province. Geol. Explor. 2022, 58, 369–380. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shang, P.; Xiong, X.; Yang, H.-Y.; Tang, Y. Metallogenic regularities of fluorite deposits in China. Geol. China 2015, 42, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Rock Types | Samples | Magnetic Susceptibility SI (10−6) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Average | ||
| Altered cataclastic rock | 10 | 1~5 | 3.34 |
| Fluorite veins | 15 | 0~5 | 1.06 |
| Granite | 10 | 36~179 | 81.3 |
| Quartz sandstone | 16 | 3~20 | 8.7 |
| Rock Types | Samples | ρ (Ω·m) | η (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | Average | Minimum | Maximum | Average | ||
| Quartz sandstone | 5 | 4722 | 9398 | 7037 | 0.895 | 2.276 | 1.74 |
| Quartz vein | 5 | 1978 | 10,712 | 5598 | 0.306 | 1.426 | 0.77 |
| Tectonic breccia | 5 | 5403.3 | 5403.3 | 5403.3 | 1.02 | 2.82 | 1.82 |
| Altered cataclastic rock | 5 | 6822.0 | 16,830.5 | 11,223.3 | 0.75 | 1.70 | 1.12 |
| quaternary | 20 | 3 | 52 | 18.72 | |||
| Lithology | Tc/10−6 | Deposit Location | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variation Interval | Mean Value | ||
| granite | 35.4~99.3 | 65.9 | Southern Songxian County, Henan Province, China |
| Rhyolite porphyry | 25.6~70.3 | 50.1 | |
| Altered granite | 40.6~95.1 | 62.3 | |
| Altered rhyolite | 21.0~72.3 | 48.9 | |
| Massive fluorite ore | 11.2~40.0 | 23.0 | |
| Cemented fluorite ore | 13.0~48.3 | 25.8 | |
| Banded fluorite ore | 14.2~45.5 | 27.3 | |
| Quartz–fluorite ore | 15.8~50.4 | 26.5 | |
| Fine vein fluorite ore | 14.1~73.4 | 37.6 | |
| sand slate | 9.4~25.0 | 15.9 | Linxi County, Inner Mongolia, China |
| fluorite ore | 4.5~8.9 | 6.3 | |
| limestone | 6.7~20.0 | 11.03 | Pengshui County, Chongqing, China |
| fluorite ore | 0.9~7.4 | 3.86 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, L.; Han, L.; Kai, Y.; Yongbao, G.; Weidong, T.; Chuan, Y. Location Prediction Study of Fluorite Ore in Shallow Cover Area: Evidence from Integrated Geophysical Surveys. Minerals 2024, 14, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080838
Cheng L, Han L, Kai Y, Yongbao G, Weidong T, Chuan Y. Location Prediction Study of Fluorite Ore in Shallow Cover Area: Evidence from Integrated Geophysical Surveys. Minerals. 2024; 14(8):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080838
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Liu, Li Han, Yang Kai, Gao Yongbao, Tang Weidong, and Yao Chuan. 2024. "Location Prediction Study of Fluorite Ore in Shallow Cover Area: Evidence from Integrated Geophysical Surveys" Minerals 14, no. 8: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080838
APA StyleCheng, L., Han, L., Kai, Y., Yongbao, G., Weidong, T., & Chuan, Y. (2024). Location Prediction Study of Fluorite Ore in Shallow Cover Area: Evidence from Integrated Geophysical Surveys. Minerals, 14(8), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080838






