In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization
Abstract
1. Introduction
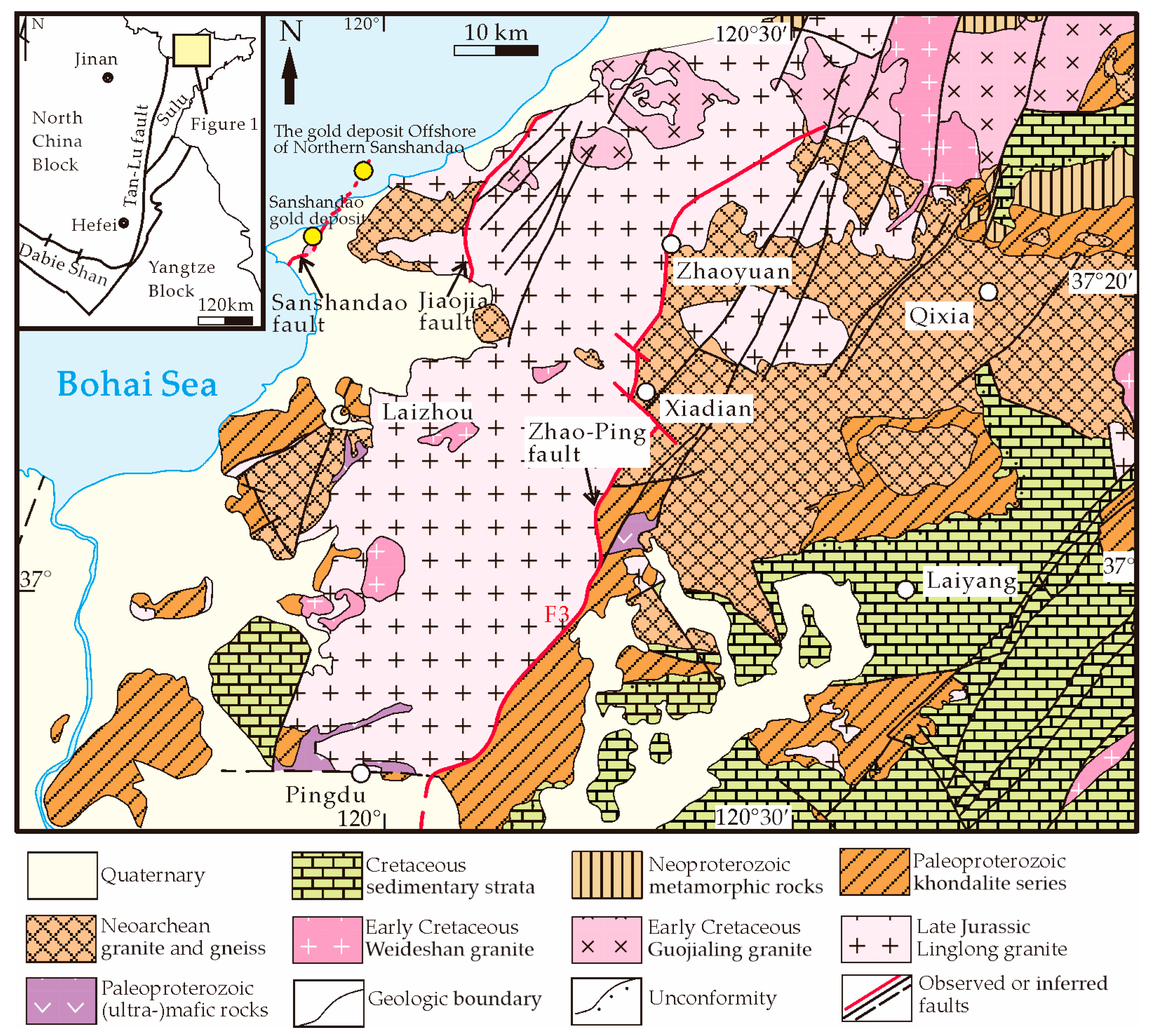
2. Regional Geological Background
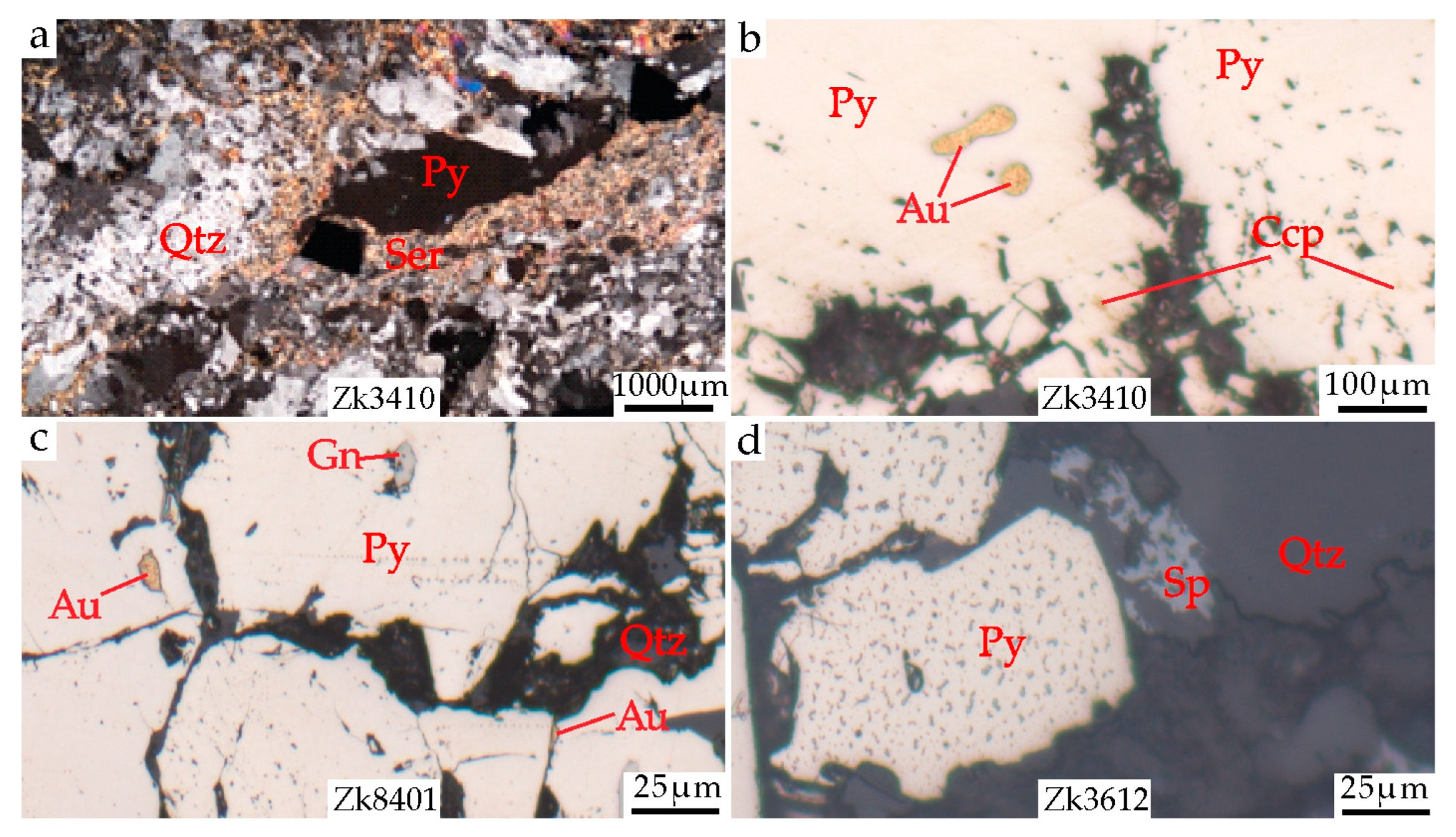
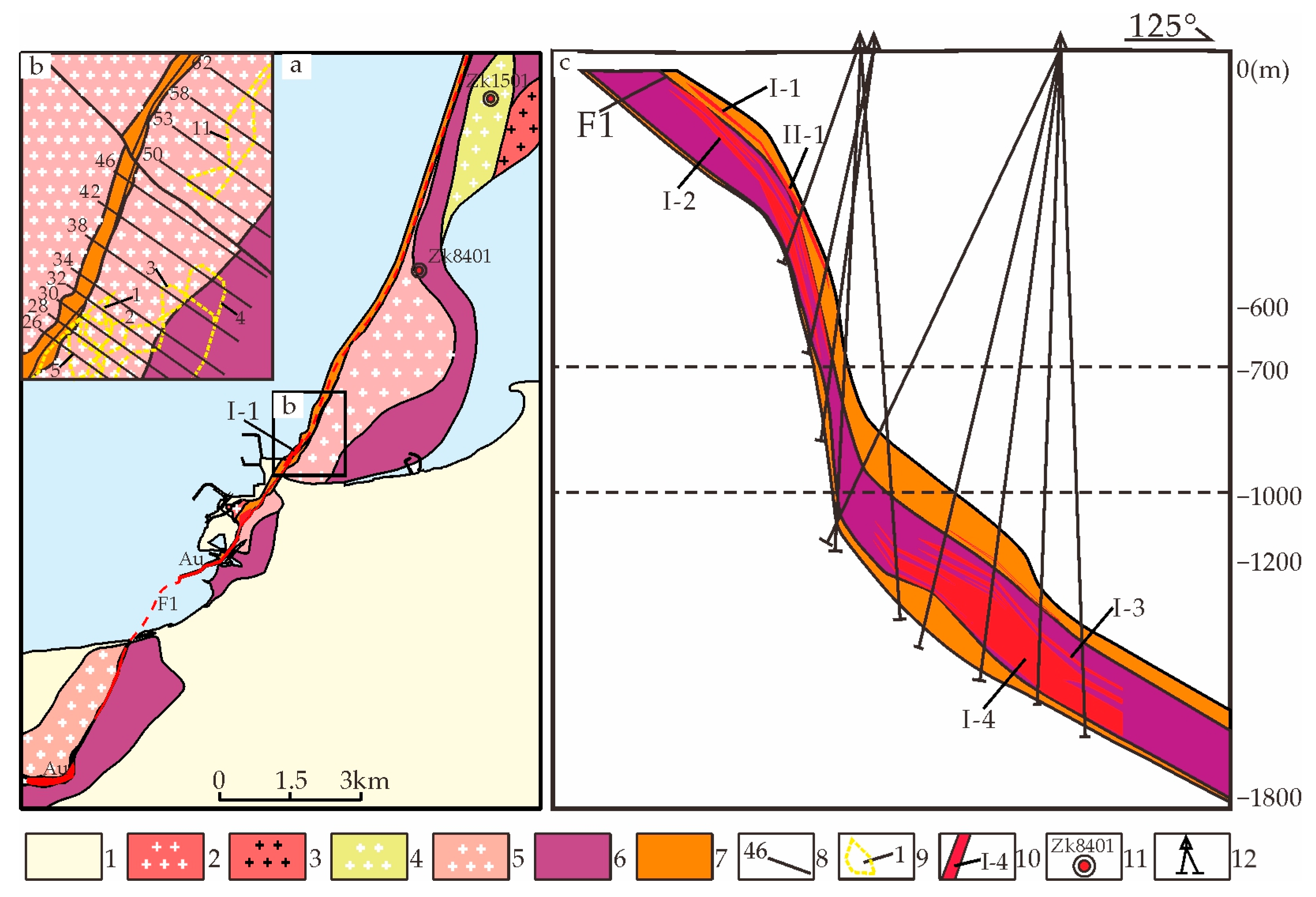
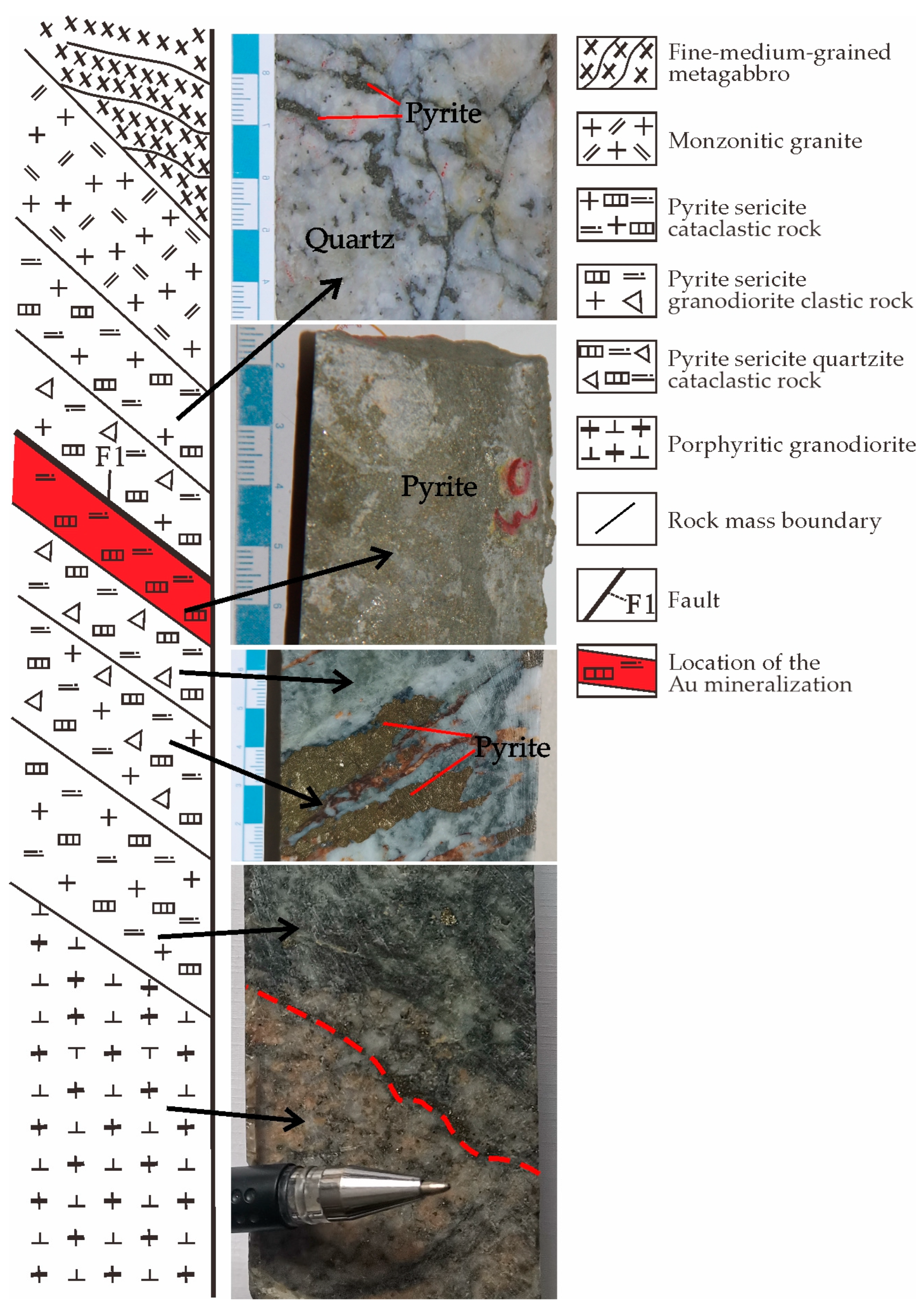
3. Ore Deposit Geology
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
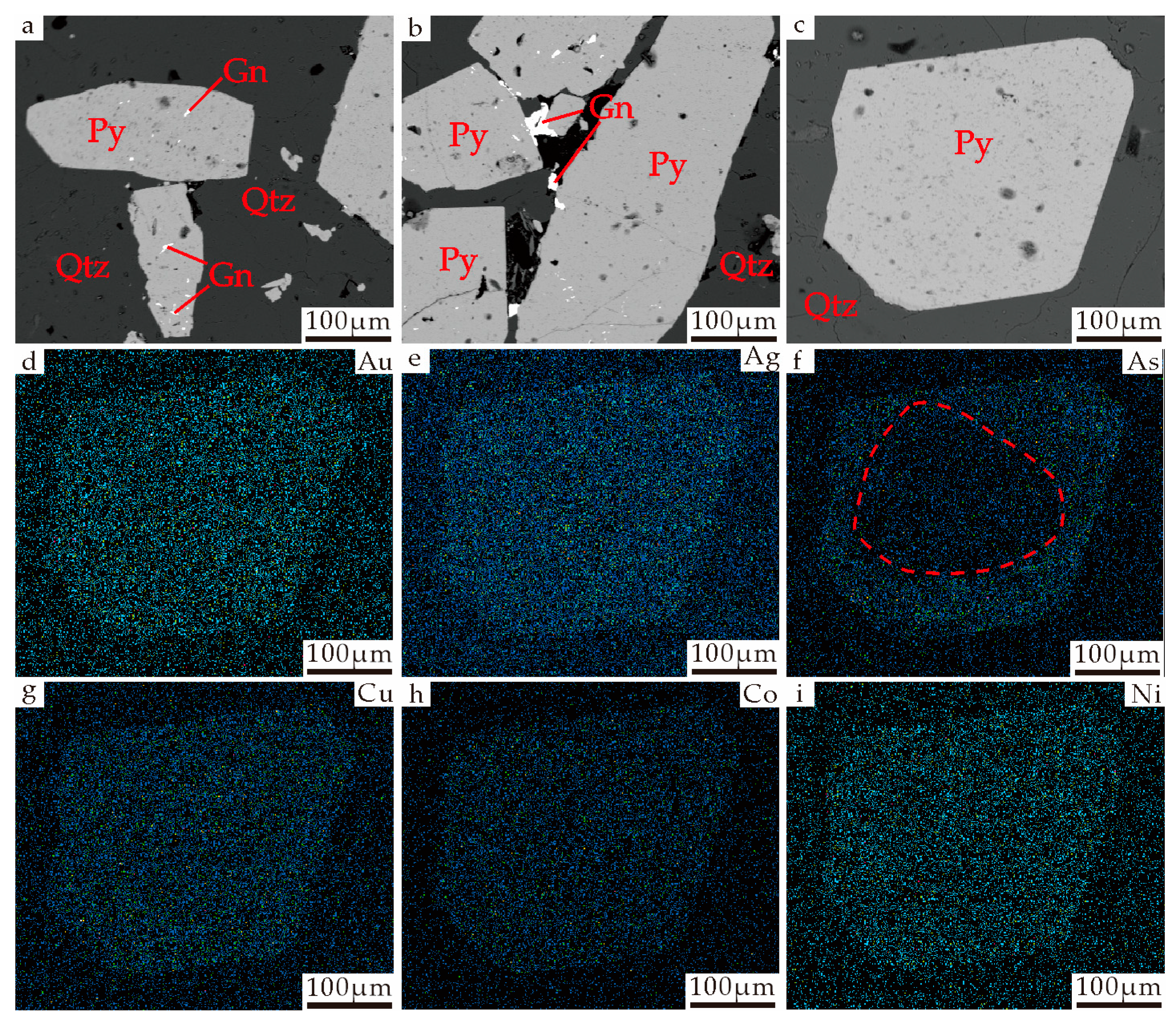
4.1. Backscattered Electron (BSE) Imaging and Wavelength Dispersive Elemental Maps
4.2. In-Situ Trace Element Analysis of Pyrite Using LA-ICP-MS
4.3. In-Situ S Isotope Analysis of Pyrite Using LA-MC-ICP-MS
4.4. Rb–Sr Dating
5. Results
5.1. Wavelength Dispersive Elemental Maps
5.2. In-Situ Trace Element Compositions
5.3. In-Situ Sulfur Isotopic Compositions
5.4. Rb–Sr Age
6. Discussion
6.1. Trace Element Distribution Characteristics of Pyrite
6.2. Occurrence of Gold
6.3. Metallogenic Age
6.4. Sources of Ore-Forming Material
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.J.; Luo, Z.K.; Liu, X.Y.; Xu, W.D.; Luo, H. Geodynamic setting for formation of large-superlarge gold deposits and Mesozoic granites in Jiaodong area. Miner. Depos. 2005, 24, 361–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Yang, L.Q.; Ge, L.S.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B.F.; Zhou, Y.F.; Jiang, S.Q. Research advances in the Mesozoic tectonic regimes during the formation of Jiaodong ore cluster area. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2006, 16, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.F. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Res. 2016, 36, 219–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.R.; Santosh, M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: Records from the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 376–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Santosh, M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique? Geosci. Front. 2014, 5, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.C.; Ding, Z.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Song, Y.X.; Bo, J.W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Li, S.Y.; Li, J.J.; Li, R.X. Geology and mineralization of the Sanshandao supergiant gold deposit (1200 t) in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A review. China Geol. 2021, 4, 686–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.F.; Goldfarb, R.J. Gold Deposits of the Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern China; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.C.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, P.J.; Yang, L.Q.; Liu, D.H.; Ding, Z.J.; Song, Y.X. Discover and tectonic-magmatic background of superlarge gold deposit in offshore of northern Sanshandao, Shandong peninsula. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 365–383. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.H.; Lv, G.X.; Zhang, P.J.; Ding, Z.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Lin, D.W.; Lv, C.X.; Wang, Z.Y. A study of 3D ore-controlling of the tectonic altered rocks of the Sanshandao fault in Jiaodong Peninsular and the discovery of an offshore super-large gold deposit in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 162–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.W.; Shen, J.F.; Li, G.W.; Wang, L.M.; Sun, N.Y.; Liu, H.D.; Chi, L.; Zhang, H.F.; Du, B.S. Characteristics of Cell Parameters and Thermoelectricity of the Pyrite in the Sanshandao North Offshore Gold Deposit, Shandong Province, China. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2020, 39, 1205–1214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.W.; Liu, W.Q.; Deng, H.J.; Shen, J.F.; Zhao, G.C. Hydrothermal Alteration Characteristics and Migration Rules of Trace Elements in the North Sanshandao Sea Gold Deposit, Shandong, China. Northwestern Geol. 2023, 56, 245–253. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Mao, M.Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.P.; Yu, X.W.; Wang, L.G.; Zhang, G.L. The Genesis of the Haiyu Gold deposit in the northern part of Sanshandao gold metallogenic belt in the eastern Shandong: Constraints from geological characteristics and fluid inclusion study. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2023, 43, 521–532. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.X.; Li, S.R.; Shen, J.F.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.T.; Zeng, Y.J. Characteristics and prospecting significance of thermoluminescence patterns and cell parameters of quartz from the undersea gold deposit off northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 305–319. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, L.X.; Ma, S.M.; Tang, S.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhou, W.W. Application of the multi-attribute anomaly model for prospecting potential at depth: A case study of the Haiyu Au deposit in the Jiaodong Gold Province, China. J. Geochem. Explor. J. Assoc. Explor. Geochem. 2019, 207, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P. Geochemical Mechanism of Gold Accumulation in Offshore of Northern Sanshandao Gold Deposit in the Jiaodong Gold Province, Eastern China. Ph.D Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, T.; Liu, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.D. Hydrothermal alteration of the xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong, China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2016, 32, 2433–2450. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.C. Origins of Ore-Forming Materials and the Metallogenic Model of Gold Deposits in the Jiaoxibei Area. Ph.D Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.J. Study on Metallogenic Regularity of Mesozoic Precious and Non-Ferrous Deposits in Jiaodong Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.S.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Zong, K.Q.; Chen, H.H.; Hu, S.H. “Wave” Signal-Smoothing and Mercury-Removing Device for Laser Ablation Quadrupole and Multiple Collector ICPMS Analysis: Application to Lead Isotope Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, S.; Gunther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.G.; Chen, H.H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.L.; Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, M.; Zong, K.Q.; Gao, S.; Hu, S.H. In situ sulfur isotopes (δ34S and δ33S) analyses in sulfides and elemental sulfur using high sensitivity cones combined with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation MC-ICP-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 911, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.C.; Liu, Y.S. Iso-Compass: New freeware software for isotopic data reduction of LA-MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.P. The Mesozoic Gold Polymetallic Regional Metallogeny in Qipengfu Ore Concentration Area, Jiaodong Peninsula. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.G.; Liu, H.B.; Li, G.Z.; Xiao, Z.B.; Tu, J.R.; Li, H.M. The Application of Ion Exchange Resins in Sr-Nd Isotopic Assay of Geological Samples. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 2584–2592. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barker, S.L.; Hickey, K.A.; Cline, J.S.; Dipple, G.M.; Kilburn, M.R.; Vaughan, J.R.; Longo, A.A. Uncloaking invisible gold: Use of nanoSIMS to evaluate gold, trace elements, and sulfur isotopes in pyrite from Carlin-type gold deposits. Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.L.; Cook, N.J.; Utsunomiya, S.; Kogagwa, M.; Green, L.; Gilbert, S.; Wade, B. Gold-telluride nanoparticles revealed in arsenic-free pyrite. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.L.; Cook, N.J.; Pring, A.; Brugger, J.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Shimizu, M. ‘Invisible gold’ in bismuth chalcogenides. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1970–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Meria, D.; Silcock, D.; Wade, B. Arsenopyrite-Pyrite Association in an Orogenic Gold Ore: Tracing Mineralization History from Textures and Trace Elements. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Mao, J.W. Textural control on gold distribution in As-free pyrite from the Dongping, Huangtuliang, and Hougou gold deposits, North China Craton (Hebei Province, China). Chem. Geol. 2009, 264, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, T.; Long, D.G.F.; Kamber, B.S.; Whitehouse, M.J. In Situ Trace Element and Sulfur Isotope Analysis of Pyrite in a Paleoproterozoic Gold Placer Deposit, Pardo and Clement Townships, Ontario, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2011, 106, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Li, X.H.; Zuo, Y.B.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Hu, F.F.; Feng, K. In-situ LA-(MC)-ICPMS and (Nano) SIMS trace elements and sulfur isotope analyses on sulfides and application to confine metallogenic process of ore deposit. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 3479–3496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Zhao, G.; Hong, J.X.; Liu, J.J.; Zhai, D.G. In situ LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of pyrite and its application in study of Au deposit. Miner. Depos. 2022, 41, 1182–1199. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.L.; Zeng, Q.D.; Sun, G.T.; Duan, X.X.; Bonnetti, C.; Biegler, T.; Long, D.G.F.; Kamber, B. Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) elemental mapping and its applications in ore geology. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 1964–1978. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koglin, N.; Frimmel, H.E.; Lawrie Minter, W.E.; Brätz, H. Trace-element characteristics of different pyrite types in Mesoarchaean to Palaeoproterozoic placer deposits. Miner. Depos. 2010, 45, 259–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bralia, A.; Sabatini, G.; Troja, F. A revaluation of the Co/Ni ratio in pyrite as geochemical tool in ore genesis problems. Miner. Depos. 1979, 14, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Palenik, C.S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Ewing, R.C. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.W.; Zhao, X.F.; Xiong, L.; Zhu, Z.X. In-situ trace element analysis characteristics of pyrite in Sanshandao Gold Deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula: Implications for ore genesis. Adv. Earth Sci. 2019, 34, 399–413. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deditius, A.P.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Walshe, J.; Ewing, R.C. The coupled geochemistry of Au and As in pyrite from hydrothermal ore deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 140, 644–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, S.F.; White, N.C.; John, D.A. Geological Characteristics of Epithermal Precious and Base Metal Deposits. In One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 485–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Zhao, X.F.; Lin, Z.W.; Zhao, S.R. In Situ Trace Elements and Sulfur Isotope Analysis of Pyrite from Jinchiling Gold Deposit in the Jiaodong Region: Implications for Ore Genesis. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 945–959. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.G.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, J.H.; Miao, L.C. Large-scale cluster of gold deposits in east Shandong: Anorogenic metallogenes. Earth Sci. Front. 2004, 11, 85–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Qiu, K.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Goldfarb, R.; Yang, L.Q.; Zi, J.W.; Geng, J.Z.; Ma, Y. In Situ Dating of Hydrothermal Monazite and Implications for the Geodynamic Controls on Ore Formation in the Jiaodong Gold Province, Eastern China. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.F.; Jiang, P.; Fan, H.R.; Zuo, Y.B.; Yang, Y.H. Tectonic transition from a compressional to extensional metallogenic environment at similar to 120 Ma revealed in the Hushan gold deposit, Jiaodong, North China Craton. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 160, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Weinberg, R.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Groves, D.I.; Sai, S.X.; Matchan, E.; Phillips, D.; Kohn, B.P.; Miggins, D.P.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mesozoic Orogenic Gold Mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A Focused Event at 120 +/− 2 Ma During Cooling of Pregold Granite Intrusions. Econ Geol. 2020, 115, 415–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.F.; Fan, H.R.; Santosh, M.; Hu, F.F.; Wilde, S.A.; Lan, T.G.; Lu, L.N.; Liu, Y.S. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton. Lithos 2012, 146, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.G.; Qiu, Y.M.; McNaughton, N.J.; Groves, D.I.; Luo, Z.K.; Huang, J.Z.; Liu, Y.K. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids. Ore Geol. Rev. 1998, 13, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.F.; Fan, H.R.; Jiang, X.H.; Yang, K.F. Fluid inclusions in different depths at Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Implication for ore genesis. Geofluids 2013, 13, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Yu, X.W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.G.; Wang, Q.Y.; Guo, R.P. 40Ar/39Ar Age and Its Significance of Sericite in Pyrite Sericite in Sanshandao Gold Deposit in Northwest of Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2020, 36, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cawood, P.A.; Wilde, S.A.; Liu, R.; Song, H.; Li, W.; Snee, L.W. Geology and timing of mineralization at the Cangshang gold deposit, north-western Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Miner. Depos. 2003, 38, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of Sulfur and Carbon Isotopes in Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussidon, M.; Albarède, F.; Sheppard, S.M.F. Sulphur isotope variations in the mantle from ion microprobe analyses of micro-sulphide inclusions. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1989, 92, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Routledge: London, UK, 1993; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9781315845548/using-geochemical-data-hugh-rollinson (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Wen, B.J.; Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Liu, X.; Yang, K.F.; Sun, Z.F.; Sun, Z.F. Fluid evolution and ore genesis of the giant Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and H-O-S-He-Ar isotopic compositions. J. Geochem. Explor. J. Assoc. Explor. Geochem. 2016, 171, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z. Characteristics of the Ore-Forming Fluid and Thermodynamic Simulation of Water-Rock Interaction at the Sanshandao Gold Deposit, Shandong Province, China. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.X.; Fan, H.R.; Li, J.W.; Meng, Q.R.; Li, S.R.; Zeng, Q.D. Decratonic gold deposits. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, C.M.; Bagas, L.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Lu, Y.J. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Miner. Depos. 2015, 50, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zhu, F.S.; Gong, R.T. Tectonic isotope geochemistry—Further study on sulphur isotope of Jiaodong Gold Concentration Area. Gold 2002, 23, 1–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.Y. Sulfur isotope studies of the metallogenic series of gold deposits in Jiaodong area. Miner. Depos. 1994, 13, 75–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Q.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L.N.; Song, M.C.; Zheng, X.L. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2447–2467. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Song, M.C.; Liang, J.L.; Jiang, M.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Ding, Z.J.; Su, F. Source of ore-forming fluids of the Jiaojia deeplyseated gold deposit: Evidences from trace elements and sulfur-helium-argon isotopes of pyrite. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 36, 297–313. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; An, M.Y.; Song, M.C.; Wang, M.Y.; Ding, Z.J.; Bao, Z.Y.; Wang, S.S. Sulfur isotopic composition and its source of Jiaodong gold deposit. Geol. Bull. China 2022, 41, 993–1009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Fan, H.R.; Groves, D.I.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y.C. Geochronological and sulfur isotopic evidence for the genesis of the post-magmatic, deeply sourced, and anomalously gold-rich Daliuhang orogenic deposit, Jiaodong, China. Miner. Depos. 2020, 55, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yang, L.Q.; Groves, D.I.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, K.F.; Wang, Q.F. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, eastern China. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.L.; Jiang, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ling, H.F. S-Pb isotope geochemistry and Rb-Sr geochronology of the Penglai gold field in the eastern Shangdong province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 2525–2533. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J.; Pirajno, F.; Lai, Y.; Li, C. Metallogenic time and tectonic setting of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2004, 20, 907–922. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, M.; Caridroit, M.; Charvet, J. The Late Jurassic oblique collisional orogen of SW Japan: New structural data and synthesis. Tectonics 1986, 5, 1089–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L. Sr and O isotopic characteristics of porphyries in the Qinling molybdenum deposit belt and their implication To genetic mechanism and type. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2001, 43, 82–94. [Google Scholar]

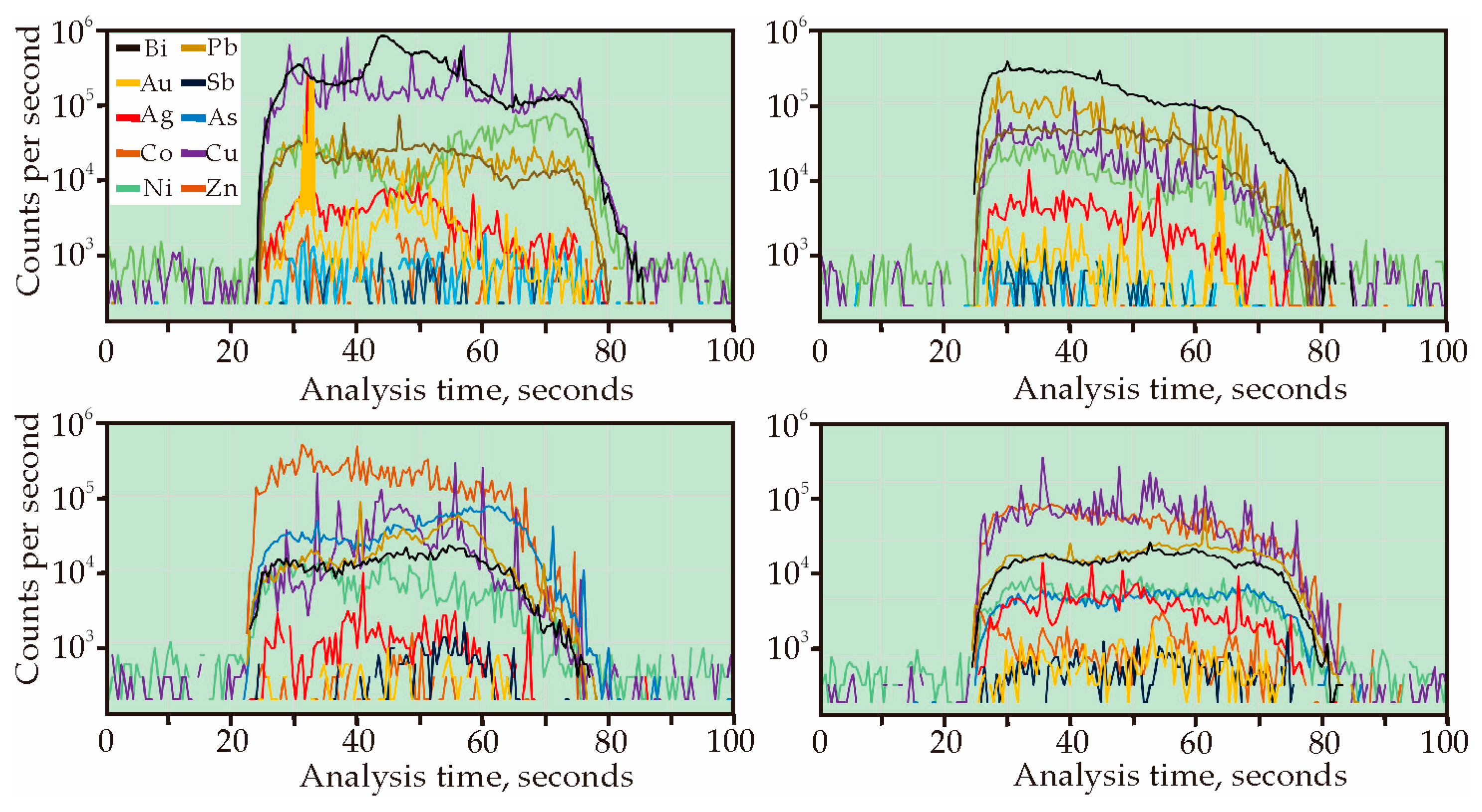


| Sample Serial Number | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Ag | Sb | Au | Pb | Bi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK8401-1 | 3.37 | - | 0.10 | 1.32 | 125 | 0.19 | - | 0.01 | 1.87 | 9.35 |
| ZK8401-2 | 5.22 | 0.06 | 2.24 | 1.04 | 68 | 0.42 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 8.40 | 10 |
| ZK8401-3 | 3.08 | 1.29 | 1.21 | 1.09 | 30 | 0.67 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 15 | 6.94 |
| ZK8401-4 | 134 | 42 | 2.14 | 0.66 | 25 | 0.41 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4.89 | 2.72 |
| ZK8401-5 | 130 | 38 | 5.16 | 1.26 | 22 | 2.58 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 77 | 43 |
| ZK8401-6 | 457 | 19 | 1.05 | 1.33 | 9 | 1.70 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 107 | 10 |
| ZK8401-7 | 7 | 0.37 | 0.24 | 1.36 | 35 | 0.07 | - | - | 1.45 | 4.93 |
| ZK8401-8 | 180 | 30 | 0.49 | 0.79 | 25 | 0.65 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 5.40 | 19 |
| ZK8401-9 | 89 | 58 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 12 | - | - | - | 0.65 | 2.02 |
| ZK8401-10 | 274 | 27 | 1.26 | 1.30 | 24 | 0.79 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 35 | 13.20 |
| ZK3612-1 | 20 | 1.50 | 31 | 4216 | 109 | 40 | 12 | 0.23 | 18,400 | 0.20 |
| ZK3612-2 | 47 | 24 | 23 | 2.90 | 8019 | 51 | 13 | 0.99 | 21,290 | 0.15 |
| ZK3612-3 | 24 | 25 | 11 | 1.50 | 7915 | 18 | 8.04 | 0.64 | 3750 | 0.03 |
| ZK3612-4 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 6.95 | 1.02 | 52 | 14 | 3.58 | 0.14 | 4386 | 0.02 |
| ZK3612-5 | 10 | 0.62 | 5.29 | 0.94 | 49 | 7.66 | 1.56 | 0.12 | 247 | - |
| ZK3612-6 | 0.23 | 0.55 | 0.19 | 1.49 | 0.70 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 7.86 | - |
| ZK3612-7 | 1.06 | 10 | 277 | 37 | 920 | 551 | 127 | 3.84 | 57,880 | 0.62 |
| ZK3612-8 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 13 | 0.94 | 166 | 33 | 7.13 | 0.15 | 9332 | 0.17 |
| ZK3612-9 | 0.06 | 3.02 | 59 | 1.83 | 4103 | 197 | 22 | 1.42 | 45,896 | 0.58 |
| ZK3612-10 | 0.25 | 0.87 | 88 | 15 | 468 | 6.12 | 1.97 | 0.25 | 492 | 0.05 |
| ZK3410-1 | 1.45 | 6.50 | 1.01 | 1.66 | 230 | 0.44 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 10 | 7.02 |
| ZK3410-2 | 3.76 | 4.51 | 0.55 | 1.24 | 136 | 0.40 | 0.12 | - | 3.87 | 6.52 |
| ZK3410-3 | 34 | 17 | 1.08 | 1.39 | 190 | 2.09 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 15 | 43 |
| ZK3410-4 | 4.65 | 5.60 | 0.56 | 1.14 | 87 | 0.08 | - | - | 2.04 | 1.81 |
| ZK3410-5 | 6.45 | 7.46 | 0.41 | 1.03 | 160 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 3.29 | 4.88 |
| ZK3410-6 | 23 | 13 | 3.53 | 0.55 | 438 | 3.94 | 2.31 | 0.37 | 18 | 10 |
| ZK3410-7 | 1.41 | 2.78 | 0.51 | 1.29 | 143 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 5.43 | 1.43 |
| ZK3410-8 | 27 | 9.20 | 20 | 1.32 | 270 | 5.55 | 4.07 | 0.17 | 100 | 30 |
| ZK3410-9 | 61 | 13 | 41 | 2.73 | 206 | 4.88 | 3.27 | 0.06 | 80 | 17 |
| ZK3410-10 | 2.43 | 2.03 | 3.37 | 1.17 | 574 | 2.79 | 2.36 | 0.07 | 23 | 4.17 |
| Sample Serial Number | Mineral | δ34SCDT (‰) | Sample Serial Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZK8401-1 | Pyrite | 11.9 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-2 | Pyrite | 12.6 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-3 | Pyrite | 12.6 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-4 | Pyrite | 12.1 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-5 | Pyrite | 12.0 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-6 | Pyrite | 11.6 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-7 | Pyrite | 12.4 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-8 | Pyrite | 11.4 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-9 | Pyrite | 12.1 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-10 | Pyrite | 11.6 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-11 | Pyrite | 10.5 | 963.5 m |
| ZK3612-1 | Pyrite | 11.1 | 1537.0 m |
| ZK3612-2 | Pyrite | 12.0 | 1537.0 m |
| ZK3612-3 | Pyrite | 11.3 | 1537.0 m |
| ZK3612-4 | Pyrite | 12.9 | 1537.0 m |
| ZK3410-1 | Pyrite | 10.0 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-2 | Pyrite | 10.3 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-3 | Pyrite | 10.6 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-4 | Pyrite | 11.9 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-5 | Pyrite | 11.4 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-6 | Pyrite | 10.8 | 1613.0 m |
| ZK3410-7 | Pyrite | 10.6 | 1613.0 m |
| ZK3410-8 | Pyrite | 13.0 | 1613.0 m |
| ZK3410-9 | Pyrite | 12.8 | 1613.0 m |
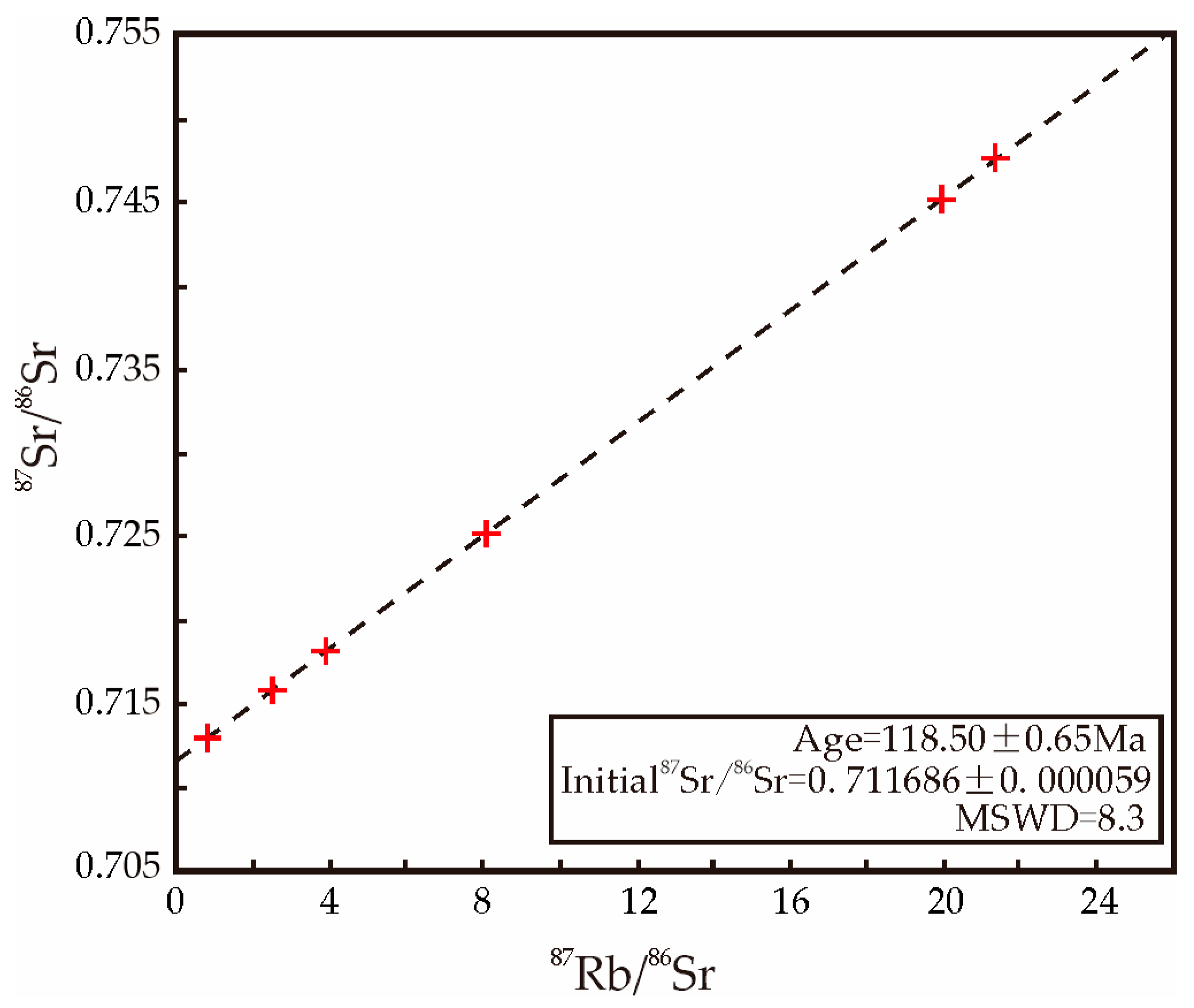
| Sample Serial Number | Ore Type | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | StdErr (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK3410-2 | Pyrite | 2.466515 | 0.715794 | 0.000012 |
| ZK3410-5 | Pyrite | 3.847805 | 0.718191 | 0.000022 |
| ZK3410-7 | Pyrite | 21.364224 | 0.747714 | 0.000019 |
| ZK3410-9 | Pyrite | 19.944731 | 0.745217 | 0.000017 |
| ZK3410-11 | Pyrite | 8.088107 | 0.725319 | 0.000015 |
| ZK3410-12 | Pyrite | 0.797712 | 0.713049 | 0.000024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Ren, T.; Sun, B. In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization. Minerals 2024, 14, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050456
Tian J, Wang J, Tian T, Wang L, Wang Y, Yu X, Zhang W, Ren T, Sun B. In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization. Minerals. 2024; 14(5):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050456
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jiepeng, Jinhui Wang, Tongliang Tian, Ligong Wang, Yingpeng Wang, Xiaowei Yu, Wen Zhang, Tianlong Ren, and Bin Sun. 2024. "In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization" Minerals 14, no. 5: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050456
APA StyleTian, J., Wang, J., Tian, T., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Yu, X., Zhang, W., Ren, T., & Sun, B. (2024). In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization. Minerals, 14(5), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050456






