The Geochemical Characteristics and Environmental Implications of the Paleocene–Eocene in the Jiangling Depression, Southwestern Jianghan Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
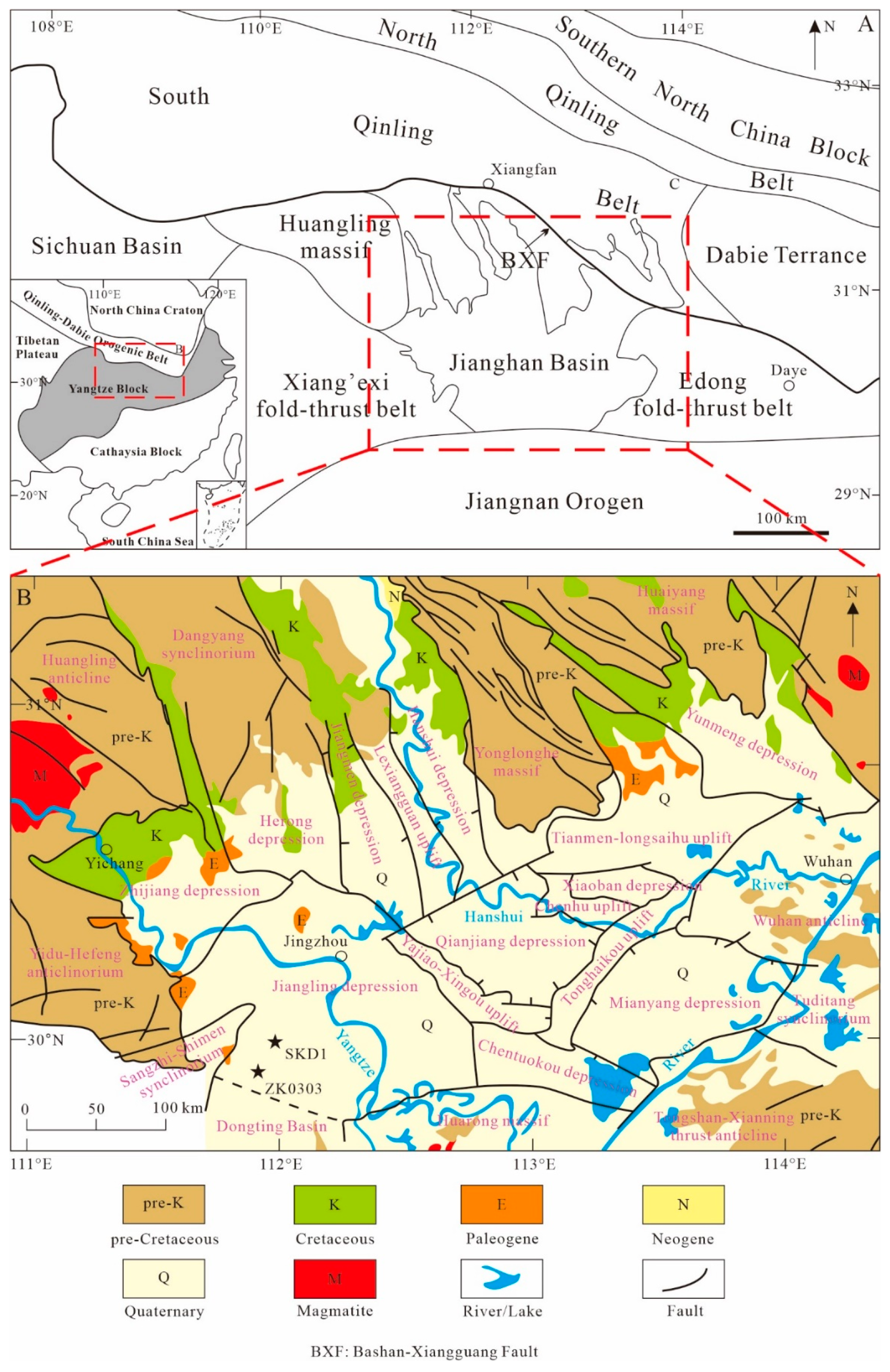
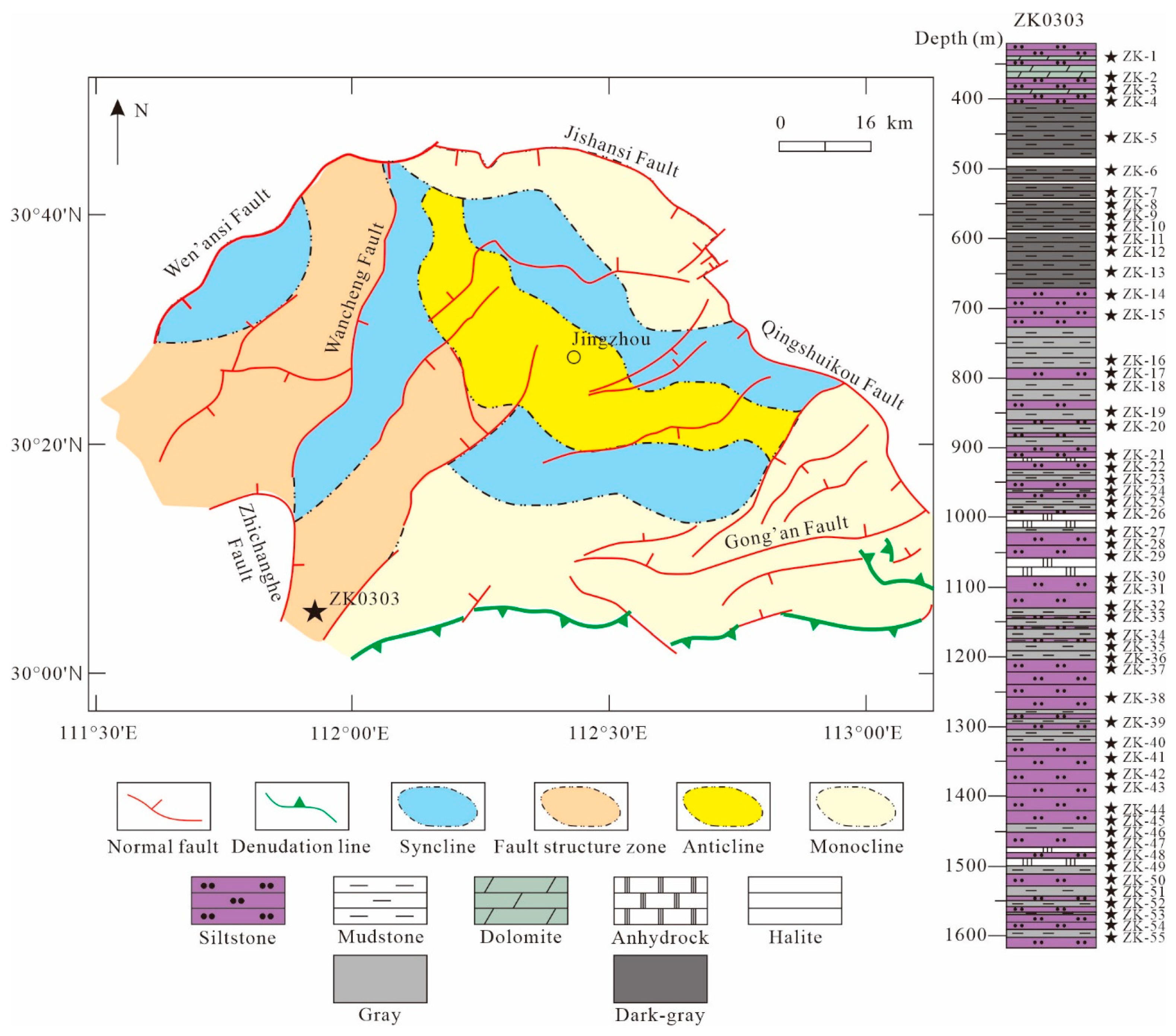
2. Geological Setting
3. Sampling and Methods
3.1. Analyses of Major and Trace Elements
3.2. Indicators of Paleoclimate and Paleoenvironment
4. Results
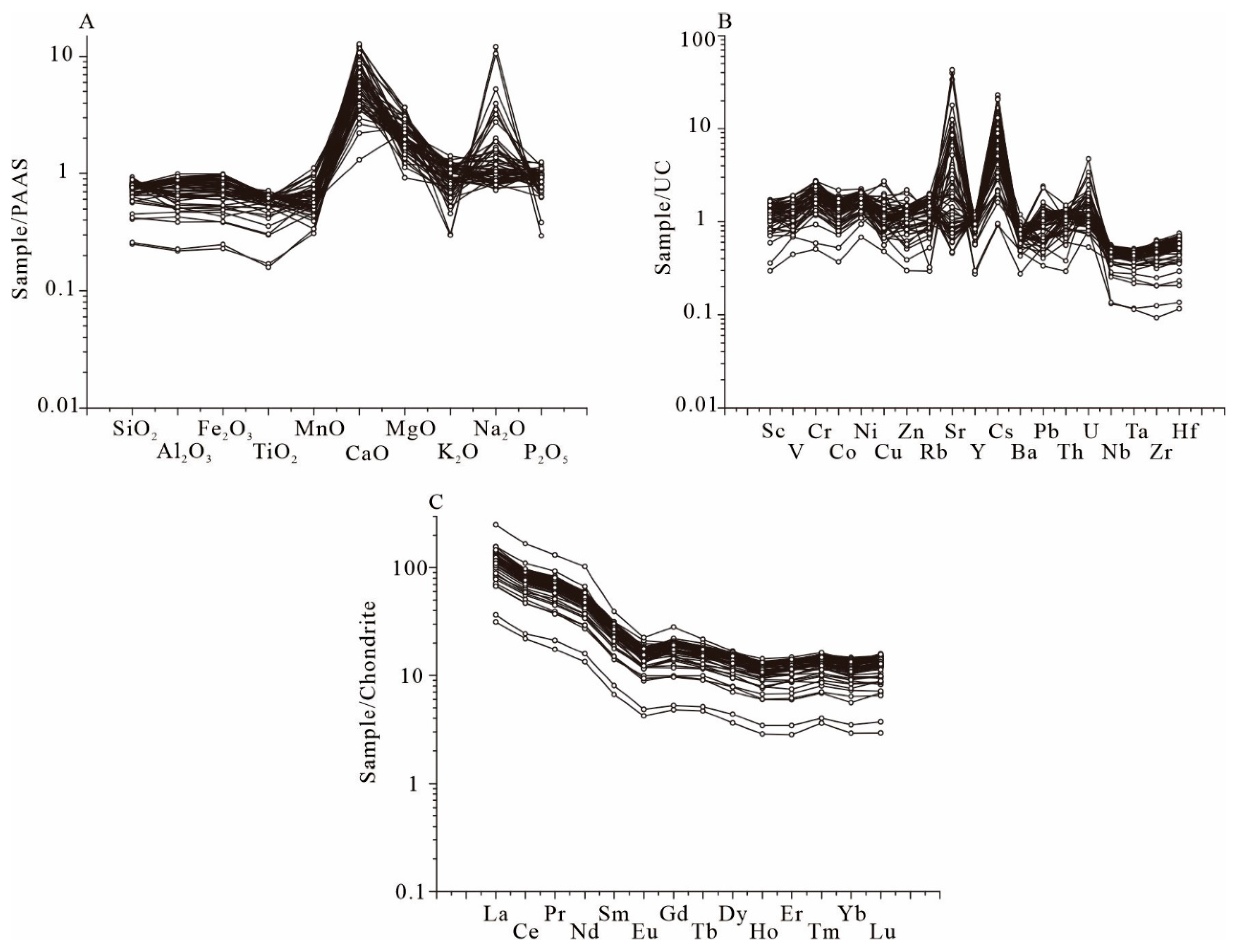
4.1. Major Elements Geochemistry
4.2. Trace and Rare Elements Geochemistry
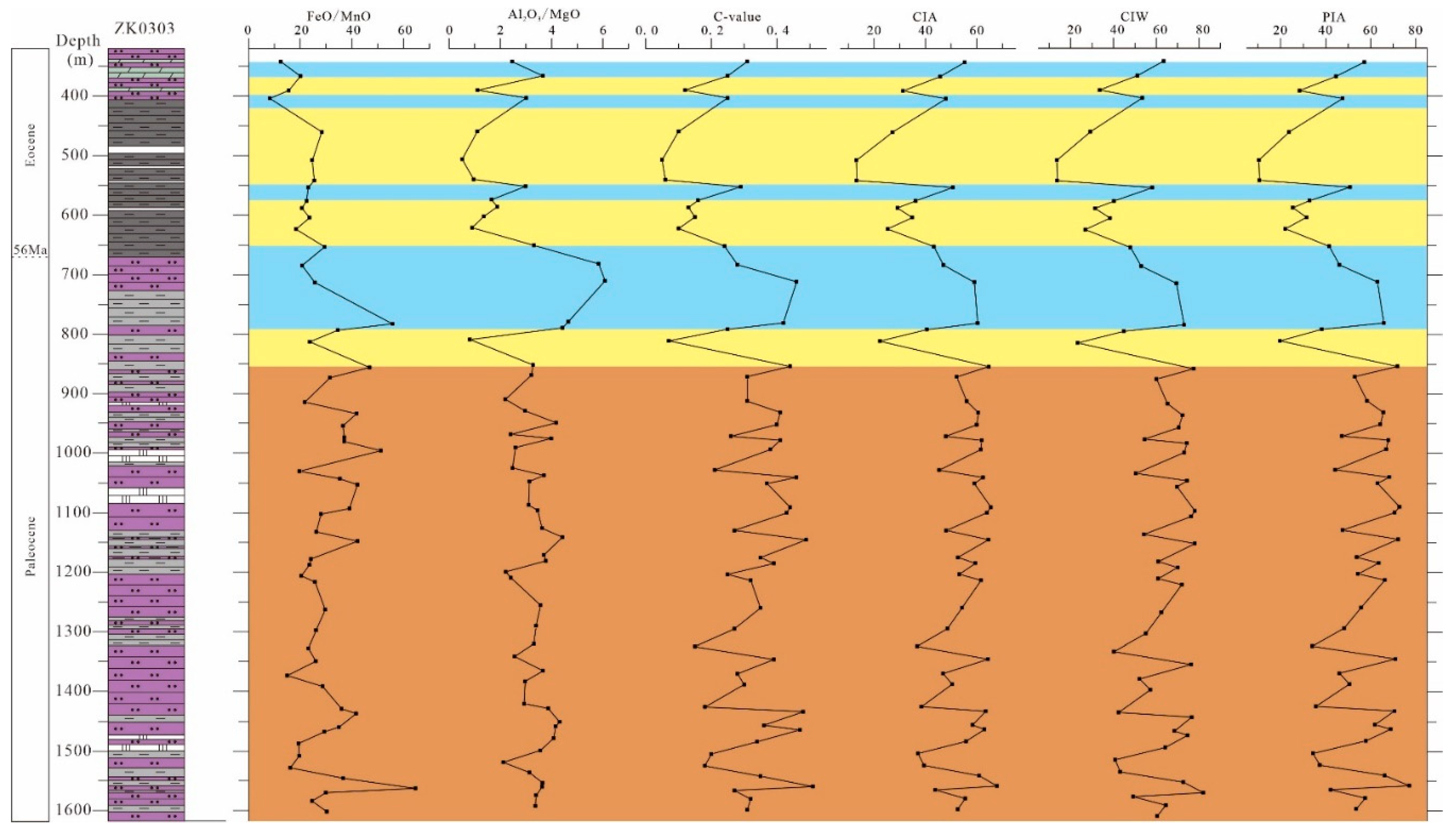
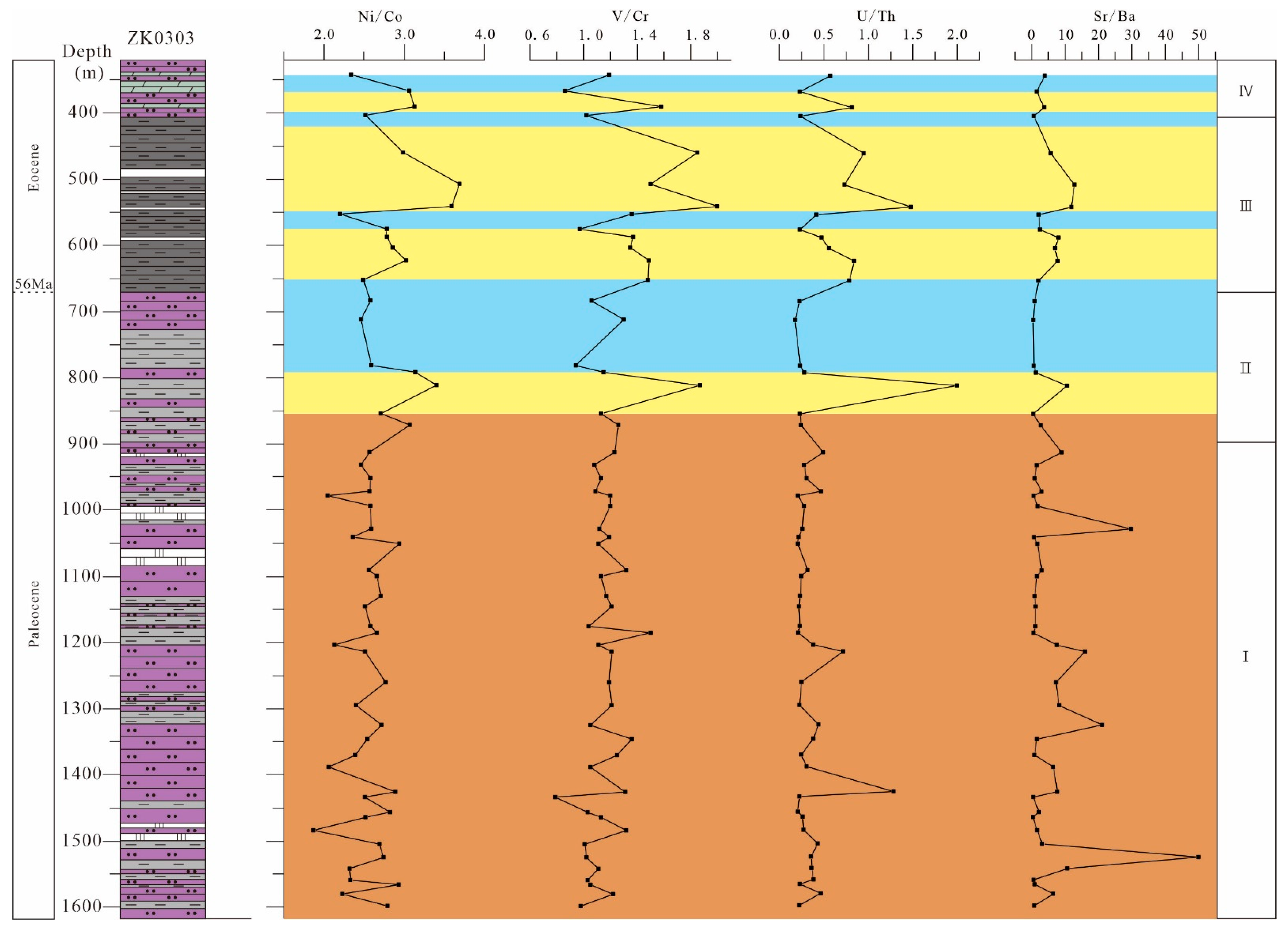
4.3. Change Trends of Element Ratios
5. Discussion
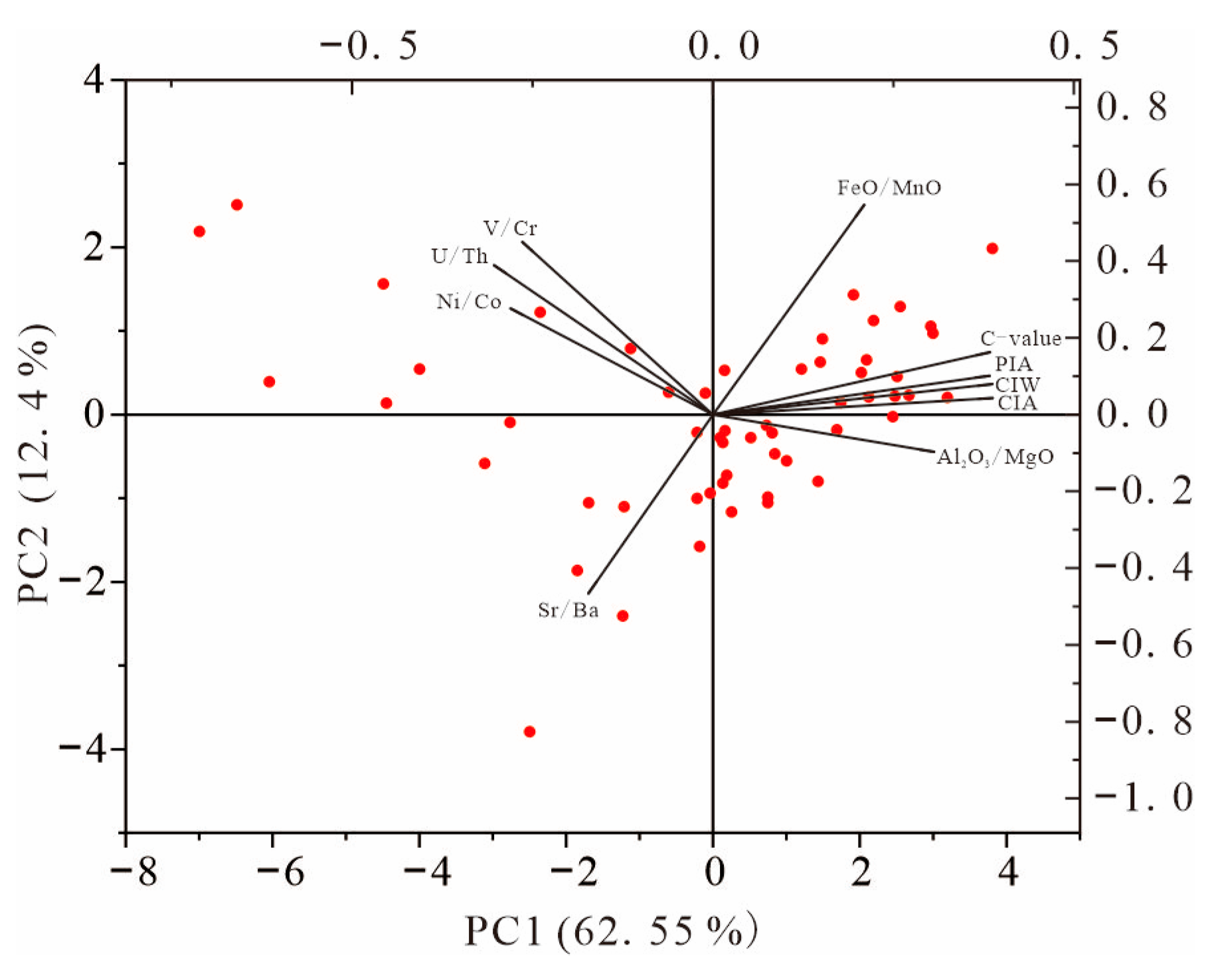
5.1. Paleoclimate and Paleoweathering
5.2. Redox Conditions
5.3. Paleosalinity
5.3.1. Playa Lake (Stage I)
5.3.2. Brackish Lake (Stage II)
5.3.3. Saline Lake (Stage III)
5.3.4. Brackish Playa-Lake (Stage IV)
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Jiangling depression experienced a semi-humid to semi-arid climate during the early–middle Paleocene. There was a rapid shift to a humid climate during the PETM, following a short period of intense dryness. In the Eocene, the climate was arid, but it experienced short periods of humidity. The trend of chemical weathering is similar to that of climate change. The instability of subtropical highs controlled by the planetary wind system, and hyperthermals (such as PETM) may be important factors in climate change.
- (2)
- The climate of the Jiangling depression underwent frequent fluctuations between humid and arid conditions during the Paleocene–Eocene. In the humid periods and alternations of aridity and humidity, the lake received external water, resulting in a weak stratification of the lake water, so sediments were formed under oxic conditions. In the arid phase, the lake became a still water environment, leading to reducing conditions for sedimentation.
- (3)
- Under the control of climatic conditions, the salinity of the lake changed greatly in the early–middle Paleocene. From the late Paleocene to the early Eocene, the overall salinity of the lake was low; in the Eocene, the salinity of the lake increased, but there were still several decreases.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, L.C.; Zhang, L.B. Carbon and oxygen isotopes characteristics of Paleocene saline lake facies carbonates in Jiangling depression and their environmental significance. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.L.; Yu, X.C.; Li, R.Q.; Yan, K.; You, C. Origin of lithium-potassium brines in the Jianghan Basin, South China: Constraints by water-rock reactions of Mesozoic-Cenozoic igneous rocks. Minerals 2021, 11, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L. Characteristics and formation of potash deposits in continental rift basins: A review. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 515–527. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.J.; Liu, C.L.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, L.C.; Liu, B.K.; Zhang, L.B. Paleocene mineral assemblage characteristics of Jianghan depression and their significance for potash formation. Miner. Depos. 2014, 33, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Fang, X.M.; Lv, F.L.; Wang, L.C.; Yan, M.D.; Zhang, H.; Ding, T. Plate tectonic control on the distribution and formation of the marine potash deposits. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Yu, X.C.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, L.C.; Xu, H.M.; Li, J.; Wang, C.L. A tentative discussion on regional metallogenic background and mineralization mechanism of subterranean brines rich in potassium and lithium in south China block. Miner. Depos. 2016, 35, 1119–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.J.; Wang, P.X. How old is the Asian monsoon system? Palaeobotanical records from China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 222, 181–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.T.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Z.S.; Peng, S.Z.; Xiao, G.Q.; Ge, J.Y.; Hao, Q.Z.; Qiao, Y.S.; Liang, M.Y.; Liu, J.F.; et al. A major reorganization of Asian climate by the early Miocene. Clim. Past 2008, 4, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, J.; Pagani, M.; Sloan, L.; Thomas, E.; Billups, K. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present. Science 2001, 292, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, F.A.; Wing, S.L. The Paleocene-Eocene thermal maximum: A perturbation of carbon cycle, climate, and biosphere with implications for the future. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2011, 39, 489–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennett, J.P.; Stott, L.D. Abrupt deep-sea warming, palaeoceanographic changes and benthic extinctions at the end of the palaeocene. Nature 1991, 353, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, M.; Pedentchouk, N.; Huber, M.; Sluijs, A.; Schoutern, S.; Brinkhuis, H.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Dickens, G.R.; Expedition 302 Scientists. Arctic hydrology during global warming at the Palaeocene/Eocene thermal maximum. Nature 2006, 442, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Kump, L.R.; Ridgwell, A.J.; Charles, A.J.; Junium, C.K.; Diefendorf, A.F.; Freeman, K.H.; Urban, N.M.; Harding, I.C. Slow release of fossil carbon during the Palaeocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhu, M.; Dong, X.; Tang, Z.; Peng, P.; Ding, Z.L. Structure of the carbon isotope excursion in a high-resolution lacustrine Paleocene-Eocene thermal maximum record from Central China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 408, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Ding, Z.L.; Tang, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.L. Early Eocene carbon isotope excursions: Evidence from the terrestrial coal seam in the Fushun Basin, Northeast China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3559–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.H.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Yan, K.; Luo, Z. Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum lacustrine sediments in deep drill core SKD1 in the Jianghan Basin: A record of enhanced precipitation in central China. Glob. Planet. Change 2021, 205, 103620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.L.; Wu, F.L.; Fang, X.M. A transient south subtropical forest ecosystem in central China driven by rapid global warming during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum. Gondwana Res. 2022, 101, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Ding, Z.L.; Sun, J.M.; Yang, S.L.; Ni, X.J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; He, W. Freshwater ecosystem collapse and mass mortalities at the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal maximum. Glob. Planet. Change 2023, 227, 104175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.N.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Yang, S.G.; Xu, H.M.; Hu, H.B.; Yu, X.C.; Liu, J.L. Paleotemperatures of Early Eocene in the Jiangling depression: Evidence from fluid inclusions in thenardite. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.N.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Yang, S.G.; Xu, H.M.; Yu, X.C.; Hu, H.B. A research on early Eocene homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions in halite and its paleoclimatic significance in Jiangling depression. Miner. Depos. 2016, 35, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.R.; Crook, K.A. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1986, 92, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M.; Hemming, S.R.; Taylor, S.R.; Eriksson, K.A. Early Proterozoic crustal evolution: Geochemical and Nd-Pb isotopic evidence from metasedimentary rocks, southwestern North America. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1153–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzel, A.; März, C.; Vogt, C.; Brumsack, H.J. Geochemical environment of Cenomanian-Turonian black shale deposition at Wunstorf (northern Germany). Cretac. Res. 2011, 32, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.G.; Zhang, C.C.; Huang, N.; Teng, L.; Li, C.H.; Shao, W.; Zeng, M. Geological significance of rare earth elements in marine shale of the upper Permian Dalong Formation in the lower Yangtze region, south China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullers, R.L. The controls on the major and trace element variation of shales, siltstones, and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age from uplifted continental blocks in Colorado to platform sediment in Kansas, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 4955–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xia, B.; Lin, G.; Cui, X.J.; Hu, X.Q.; Yan, P.; Zhang, F.Q. Geochemistry of the sedimentary rocks from the Nanxiong Basin, south China and implications for provenance, paleoenvironment and paleoclimate at the K/T boundary. Sediment. Geol. 2007, 197, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Wang, J.; Fu, X.G.; Zhan, W.Z.; Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Yu, F.; Song, C.Y.; Zeng, S.Q. Geochemistry of the upper Triassic black mudstones in the Qiangtang Basin, Tibet: Implications for paleoenvironment, provenance, and tectonic setting. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 160, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanas, H.A.; Assal, E.M. Provenance, tectonic setting and source area-paleoweathering of sandstones of the Bahariya Formation in the Bahariya Oasis, Egypt: An implication to paleoclimate and paleogeography of the southern Neo-Tethys region during early Cenomanian. Sediment. Geol. 2021, 413, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, F.; Gong, L.; Hu, J.L.; Ma, Z.R.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.Y.; Xiao, Y.X. Paleoenvironmental, paleoclimatic, and tectonic implications of the Yanghugou Formation in the western margin of the Ordos Basin, China: Evidence from palynology and elemental geochemical characteristics. Minerals 2024, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilder, S.A.; Keller, G.R.; Luo, M.; Goodell, P.C. Timing and spatial distribution of rifting in China. Tectonophysics 1991, 197, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Q.; Shu, L.S.; Deng, P.; Wang, B.; Zu, F.P. The sedimentary features of the Jurassic-Tertiary terrestrial strata in southeast China. J. Stratigr. 2003, 27, 224–263. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, X.H.; Fang, X.M.; Kaufman, A.J.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Zan, J.B.; Yang, Y.B.; Wang, C.L.; Xu, H.M.; Schulte, R.F.; et al. Sedimentological and mineralogical records from drill core SKD1 in the Jianghan Basin, Central China, and their implications for late Cretaceous-early Eocene climate change. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 182, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Raza, A.; Min, K.; Kohn, B.P.; Reiners, P.W.; Ketcham, R.A.; Wang, J.; Gleadow, A.J.W. Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic thermotectonic evolution along a transect from the north China craton through the Qinling orogen into the Yangtze craton, central China. Tectonics 2006, 25, TC6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.B.; Donelick, R.A.; O’Sullivan, P.B.; Jonckheere, R.; Yang, Z.; She, Z.B.; Miu, X.L.; Ge, X. Provenance and hinterland exhumation from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb and fission-track double dating of Cretaceous sediments in the Jianghan Basin, Yangtze block, central China. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 281, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, S.; Xue, H.; Zhang, P.; Wu, S. The formation environment and developmental models of argillaceous dolomite in the Xingouzui Formation, the Jianghan Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 67, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Mei, L.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Luo, J.; Min, C.Z.; Lu, S.L.; Li, M.H.; Guo, L.B. Multiple provenance of rift sediments in the composite basin-mountain system: Constraints from detrital Zircon U-Pb geochronology and heavy minerals of the early Eocene Jianghan Basin, Central China. Sediment. Geol. 2017, 349, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Yan, K.; Yu, X.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, D.H.; Shen, L.J.; Li, R.Q.; You, C. 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Volcanic Rocks in the Jiangling Basin, China. Minerals 2022, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.W. Discussion on the regional structural features of Jianghan Basin since the indosinian movement. J. Geomech. 1996, 2, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.H.; Li, Z.X.; Li, W.X.; Su, L.; Yang, J.H. Detrital provenance evolution of the Ediacaran-Silurian Nanhua foreland basin, South China. Gondwana Res. 2015, 28, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, X. Late Paleoproterozoic sedimentary and mafic rocks in the Hekou area, SW China: Implication for the reconstruction of the Yangtze Block in Columbia. Precambrian Res. 2013, 231, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.S.; Faure, M.; Wang, B.; Zhou, X.M.; Song, B. Late Palaeozoic-Early Mesozoic geological features of South China: Response to the Indosinian collision events in Southeast Asia. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2008, 340, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cui, X.J.; Liu, F.T. Cenozoic rifting and volcanism in eastern China: A mantle dynamic link to the Indo-Asian collision? Tectonophysics 2004, 393, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhu, P.M.; Kusky, T.M.; Gu, Y.; Peng, S.B.; Yuan, Y.F.; Fu, J.M. Has the Yangtze craton lost its root? A comparison between the North China and Yangtze cratons. Tectonophysics 2015, 655, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Q.; Chen, K.Q.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Zhan, H.J. Constituent evolution and exploration potential in Jianghan depression. Nat. Gas Ind. 2003, 23, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.C.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, C.L.; Xu, H.M. Provenance of rift sediments in a composite basin-mountain system: Constraints from petrography, whole-rock geochemistry, and detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Paleocene Shashi Formation, southwestern Jianghan Basin, central China. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 107, 2741–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Mischke, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Yu, X.C. Reconstruction of early Paleogene landscapes and climate in the Jianghan Basin, central China: Evidence from evaporates and palynology. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2022, 601, 111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.H.; Liu, D.; Deng, Y.L.; Tang, J.X.; Wang, X.H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Cui, Z.W.; Feng, Y.X.; Yin, Q.; Xie, F.W.; et al. Detrital zircon geochronology and geochemistry of Jurassic sandstones in the Xiongcun district, southern Lhasa subterrane, Tibet, China: Implications for provenance and tectonic setting. Geol. Mag. 2018, 156, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhou, D.S. Application of microelements analysis in identifying sedimentary environment-taking Qianjiang Formation in the Jianghan Basin as an example. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2007, 29, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.F.; Sun, L.X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Li, Y.F.; Ma, H.L.; Lu, C.; Yang, C.; Guo, G.W. Geochemical characteristics of the Jurassic Yan’an and Zhiluo Formations in the northern margin of Ordos Basin and their paleoenvironmental implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 3454–3472. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.L.; Jiang, Y.; Kang, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, S.C.; Sun, G.Q. Analysis of paleoclimate and source of the upper section, lower Ganchaigou Formation, Lenghu No. 7 region, north Qaidam Basin. Acta Sediment. Sin. 2021, 39, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, C.D. The aqueous geochemistry of metals in the weathering environment: Strengths and weaknesses in our understanding of speciation and process. Geol. Mag. 2018, 67, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worash, G. Geochemistry provenance and tectonic setting of the Adigrat sandstone northern Ethiopia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2002, 35, 185–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.H.; Wang, H.J.; Liao, J.D.; Liu, C.M. Distribution characteristics and applications of trace elements in Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Explor. Dev. 2007, 30, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Hu, K.; Bian, L.Z.; Wang, L.G.; Zhang, Y. Trace and rare earth elements geochemistry of Jurassic mudstones in the northern Qaidam basin, northwest China. Chem. Erde-Geochem. 2012, 72, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnois, L. The CIW index: A new chemical index of weathering. Sediment. Geol. 1988, 55, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Van der Weijden, C.H.; Woittiez, J.R.W. Chemical processes affecting the mobility of major, minor and trace elements during weathering of granitic rocks. Chem. Geol. 1988, 68, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M.; Hemming, S.; McDaniel, D.K.; Hanson, G.N. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics. Spec. Pap.-Geol. Soc. Am. 1993, 284, 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Fedo, C.M.; Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosoils, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 1995, 23, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic-rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, R. A study on the regulation of the concentrations of some trace metals (Rb, Sr, Zn, Pb, Cu, V, Cr, Ni, Mn and Mo) in Saanich Inlet Sediments, British Columbia, Canada. Mar. Geol. 1988, 83, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, M.A.; Sageman, B.B. Marine black shales: Depositional mechanisms and environments of ancient deposits. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1994, 22, 499–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuri, Z.N.; Eder, V.G.; Zamirailova, A.G. Composition and formation environments of the Upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous black shale Bazhenov Formation (the central part of the West Siberian Basin). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2008, 25, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribovillard, N.; Algeo, T.J.; Lyons, T.; Riboulleau, A. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update. Chem. Geol. 2006, 232, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Manning, D.A.C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem. Geol. 1994, 111, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.T.; Liu, Z.J.; Bruch, A.A.; Liu, R.; Hu, F. Palaeoclimatic evolution during Eocene and its influence on oil shale mineralisation, Fushun Basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 45, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.L.; Liu, Z.J.; Bechtel, A.; Strobl, S.A.I.; Sun, P.C. Tectonic and climate control of oil shale deposition in the Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation (Songliao Basin, NE China). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 102, 1717–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.G.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.B.; Feng, X.L.; Wang, D.; Song, C.Y.; Zeng, S.Q. Elemental geochemistry of the early Jurassic black shales in the Qiangtang Basin, eastern Tethys: Constraints for palaeoenvironment conditions. Geol. J. 2016, 51, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1989, 21, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. J. Geol. 1985, 94, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Boynton, W.V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In Developments in Geochemistry; Henderson, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 63–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Vecchi, G.A.; Reichler, T. Expansion of Hadley cell under global warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L06805. [Google Scholar]
- Johanson, C.M.; Fu, Q. Hadley cell widening: Model simulations versus observation. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2713–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Tada, R.; Jiang, X.; Suganuma, Y.; Imsamut, S.; Charusiri, P.; Ichinnorov, N.; Khand, Y. Drastic shrinking of the Hadley circulation during the mid-Cretaceous Supergreenhouse. Clim. Past 2012, 8, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Bera, M.K.; Ghosh, R.; Bera, S.; Filley, T.; Pande, K.; Rathore, S.S.; Rai, J.; Sarkar, A. Do the large carbon isotopic excursions in terrestrial organic matter across Paleocene-Eocene boundary in India indicate intensification of tropical precipitation? Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 387, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, H.A.; Lauretano, V.; Yperen, A.V.; Hopman, T.; Zachos, J.C.; Lourens, L.J.; Gingerich, P.D.; Bowen, G.J. Carbon isotope excursions in paleosol carbonate marking five early Eocene hyperthermals in the Bighorn Basin, Wyoming. Clim. Past 2015, 11, 1857–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier, K.L.; Kirchner, J.W.; Finkel, R.C. Weak influences of climate and mineral supply rates on chemical erosion rates: Measurements along two altitudinal transects in the Idaho Batholith. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, F02026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluth, G.S.; Kump, L.R. Lithologic and climatic controls of river chemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 2341–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, R.; Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Allegre, C.J. The global control of silicate weathering rates and the coupling with physical erosion: New insights from rivers of the Canadian Shield. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 196, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.; Brantley, S.; Richter, D.B.; Blum, A.; Dixon, J.; White, A.F. Strong climate and tectonic control on plagioclase weathering in granitic terrain. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 301, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, F. Chemical weathering of crystalline rocks in contrasting climatic conditions using geochemical proxies: An review. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 556, 109873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, N.D.; Retallack, G.J.; Tanaka, S. Geochemical climofunctions from North American Soils and Application to Paleosols across the Eocene-Oligocene Boundary in Oregon. J. Geol. 2002, 110, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korasidis, V.A.; Wing, S.L.; Nelson, D.M.; Baczynski, A.A. Reworked pollen reduces apparent floral change during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum. Geology 2022, 50, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Gao, Q.Q.; Liu, C.; Jin, Z.X.; Lu, L.Z. Paleomagnetic characteristics of eogene system and its basal boundary on northwest margin of Jianghan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 1992, 13, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kiehl, J.T.; Shields, C.A.; Snyder, M.A.; Zachos, J.C.; Rothstein, M. Greenhouse- and orbital-forced climate extremes during the early Eocene. Phil. Trans. R Soc. A 2018, 376, 20170085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Xu, S.; Hao, F.; Poulton, S.W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Guo, T.X.; Lu, Y.B.; Bai, N. Arid climate disturbance and the development of salinized lacustrine oil shale in the Middle Jurassic Dameigou Formation, Qaidam Basin, northwestern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 577, 110533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M.; Laroche, L.; Dürr, H.H.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Global variability of daily total suspended solids and their fluxes in rivers. Glob. Planet. Change 2003, 39, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, Y.; Cohen, H.; Laronne, J.B.; Reid, I. Suspended sediment load, bed load, and dissolved load yields from a semiarid drainage basin: A 15-year study. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W08408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvert, C.; Gratiot, N.; Evrard, O.; Navratil, O.; Némery, J.; Prat, C.; Esteves, M. Drivers of erosion and suspended sediment transport in three headwater catchments of the Mexican Central Highlands. Geomorphology 2010, 123, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart, F.; Pérez-Gallego, N.; Latron, J.; Catari, G.; Martínez-Carreras, N.; Nord, N. Short- and long- term studies of sediment dynamics in a small humid mountain Mediterranean basin with badlands. Geomorphology 2013, 196, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, M.K.; Bilotta, G.S.; Woockman, R.R.; Schwartz, J.S. Suspended sediment regimes in contrasting reference-condition freshwater ecosystems: Implications for water quality guidelines and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Blanco, M.L.; Taboada-Castro, M.M.; Taboada-Castro, M.T. An overview of patterns and dynamics of suspended sediment transport in an agroforest headwater system in humid climate: Results from a long-term monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, K.; Wang, C.; Chen, R.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Liu, L. The Geochemical Characteristics and Environmental Implications of the Paleocene–Eocene in the Jiangling Depression, Southwestern Jianghan Basin. Minerals 2024, 14, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030234
Yan K, Wang C, Chen R, Wang J, Li R, Liu L. The Geochemical Characteristics and Environmental Implications of the Paleocene–Eocene in the Jiangling Depression, Southwestern Jianghan Basin. Minerals. 2024; 14(3):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030234
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Kai, Chunlian Wang, Renyi Chen, Jiuyi Wang, Ruiqin Li, and Lihong Liu. 2024. "The Geochemical Characteristics and Environmental Implications of the Paleocene–Eocene in the Jiangling Depression, Southwestern Jianghan Basin" Minerals 14, no. 3: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030234
APA StyleYan, K., Wang, C., Chen, R., Wang, J., Li, R., & Liu, L. (2024). The Geochemical Characteristics and Environmental Implications of the Paleocene–Eocene in the Jiangling Depression, Southwestern Jianghan Basin. Minerals, 14(3), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030234





