Leaching Platinum Group Metals from Simulated Spent Auto-Catalyst Material Using Ozone and Hydrochloric Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PGM Extraction
3.2. Extraction Kinetics
3.3. Satistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| PGM | SS: | df: | MS: | : | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 25.108 | 2 | 12.6 | 0.525 | 0.656 | 0.974 |
| Pd | 0.334 | 2 | 0.167 | 0.0368 | 0.965 | 0.971 |
| Rh | 18.2 | 2 | 9.12 | 47.9 | 0.0204 | 0.958 |
References
- Kašpar, J.; Fornasiero, P.; Hickey, N. Automotive catalytic converters: Current status and some perspectives. Catal. Today 2003, 77, 419–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kočí, P. Automotive Emission Control Catalysts. Catalysts 2016, 6, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.E.; Haque, N.; Northey, S.A.; Giddey, S. Platinum Group Metals: A Review of Resources, Production and Usage with a Focus on Catalysts. Resources 2021, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez De Aberasturi, D.; Pinedo, R.; Ruiz De Larramendi, I.; Ruiz De Larramendi, J.I.; Rojo, T. Recovery by hydrometallurgical extraction of the platinum-group metals from car catalytic converters. Min. Eng. 2011, 24, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.B.; Lee, J.-C.; Suh, Y.; Lee, J. A review on the recycling processes of spent auto-catalysts: Towards the development of sustainable metallurgy. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilli, M.L.; Slobozeanu, A.E.; Larosa, C.; Paneva, D.; Yakoumis, I.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z. Platinum Group Metals: Green Recovery from Spent Auto-Catalysts and Reuse in New Catalysts—A Review. Crystals 2023, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoumis, I.; Panou, M.; Moschovi, A.M.; Panias, D. Recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts: A review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 3, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L. Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagelüken, C. Recycling of Electronic Scrap at Umicore Precious Metals Refining. Acta Metall. Slovaca 2006, 12, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hagelüken, C. Improving metal returns and eco-efficiency in electronics recycling—A holistic approach for interface optimisation between pre-processing and integrated metals smelting and refining. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Electronics & the Environment, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–11 May 2006; IEEE: Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2006; pp. 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, H.; Chang, C.; Ekberg, C. Recovery of precious metals from electronic waste and spent catalysts: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriek, R.J. Leaching of Selected PGMs: A Thermodynamic and Electrochemical Study Employing Less Aggressive Lixiviants. Master’s Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, B. Recovery of platinum group metals from spent catalysts: A review. Int. J. Miner. Process 2015, 145, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. (Ed.) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 90th ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Habashi, F. Textbook of Hydrometallurgy, 2nd ed.; Métallurgie Extractive Québec: Québec, QC, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk, C.; Libra, J.A.; Saupe, A. Ozonation of Water and Wastewater; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, S.C. Degradation and Biodegradability Enhancement of Nitrobenzene and 2,4-Dichlorophenol by Means of Advanced Oxidation Processes Based on Ozone. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2002. Available online: https://diposit.ub.edu/dspace/bitstream/2445/35396/1/TOL167A.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Viñals, J.; Juan, E.; Ruiz, M.; Ferrando, E.; Cruells, M.; Roca, A.; Casado, J. Leaching of gold and palladium with aqueous ozone in dilute chloride media. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 81, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, A. Ozone technology of German industrial enterprises. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1999, 21, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornalczyk, A.; Saternus, M. Removal of Platinum Group Metals from the Used Auto Catalytic Converter. Metallurgija 2009, 48, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.; Lapidus, G.T. Platinum, palladium and gold leaching from magnetite ore, with concentrated chloride solutions and ozone. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 166, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogwase, B.M.S. An Electrochemical Study of the Oxidation of Platinum Employing Ozone as Oxidant and Chloride as Complexing Agent. Master’s Thesis, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2012. Available online: https://dspace.nwu.ac.za/handle/10394/9790 (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Trinh, H.B.; Lee, J.C.; Srivastava, R.R.; Kim, S.; Ilyas, S. Eco-threat Minimization in HCl Leaching of PGMs from Spent Automobile Catalysts by Formic Acid Prereduction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7302–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shen, S.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lv, B.; Wang, F. Effect of O2, H2 and CO pretreatments on leaching Rh from spent auto-catalysts with acidic sodium chlorate solution. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 144–145, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, E.; Kim, M.; Kim, B.-S.; Kumar, V. Leaching of platinum group metals (PGMs) from spent automotive catalyst using electro-generated chlorine in HCl solution. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, M.A. Optimizing a Method for Leaching PGMs from Simulated Spent Auto-Catalyst Material Using Ozone & Hydrochloric Acid. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Saguru, C.; Ndlovu, S.; Moropeng, D. A review of recent studies into hydrometallurgical methods for recovering PGMs from used catalytic converters. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 182, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, N.V.; Belousov, O.V.; Borisov, R.V.; Akimenko, A.A. Autoclave Dissolution of Platinum Metals in Hydrochloric Acid Oxidizing Media. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2021, 62, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
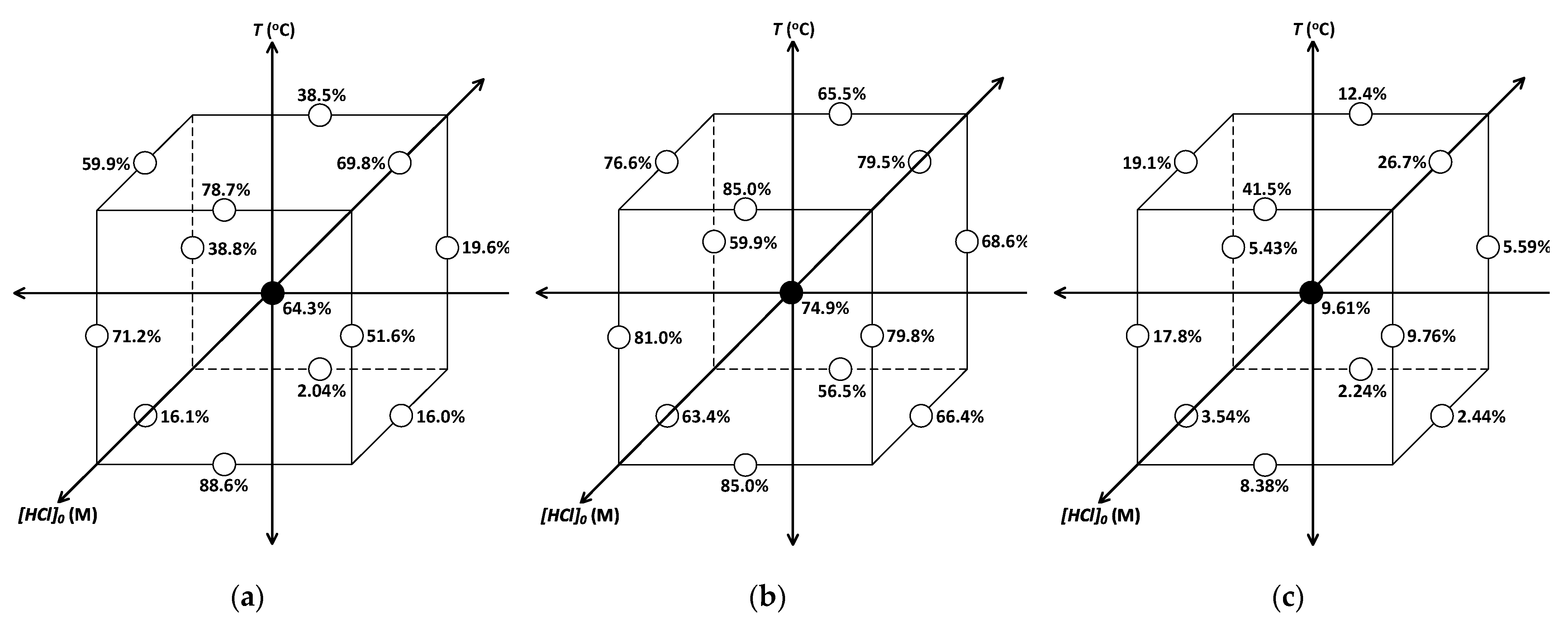



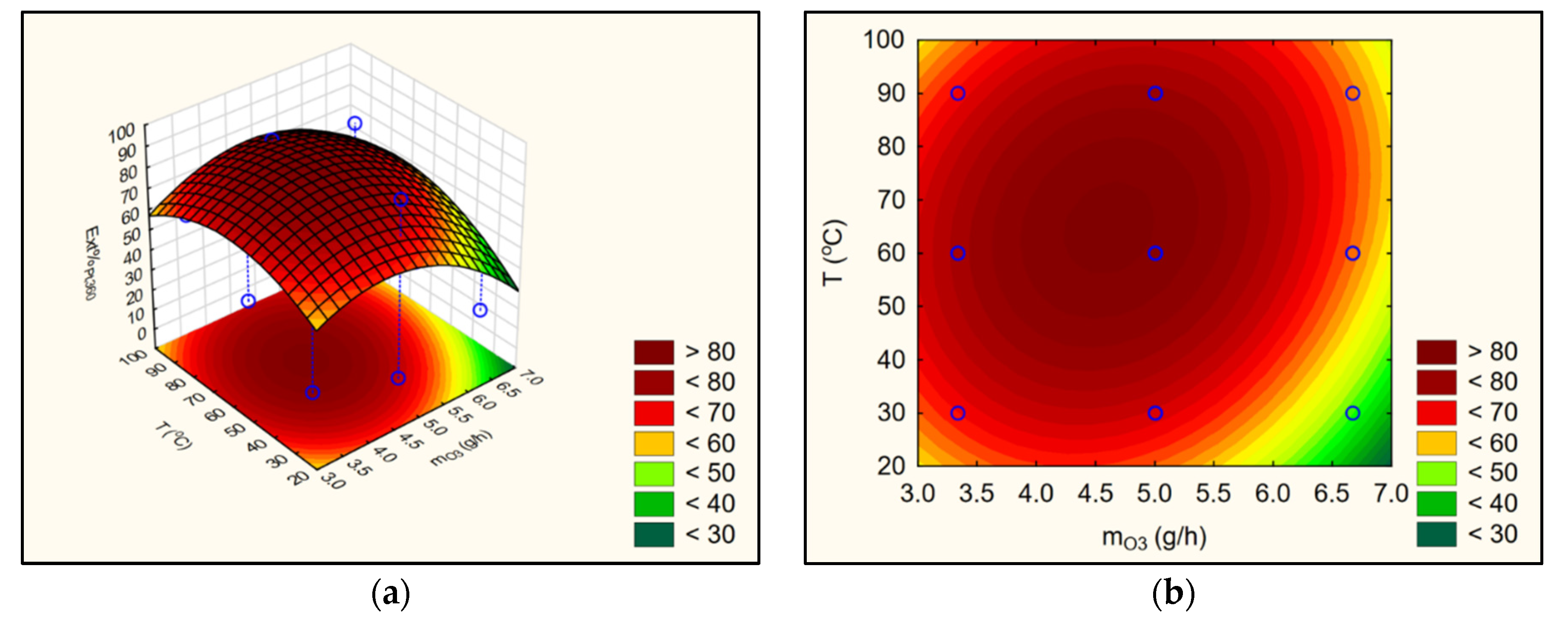

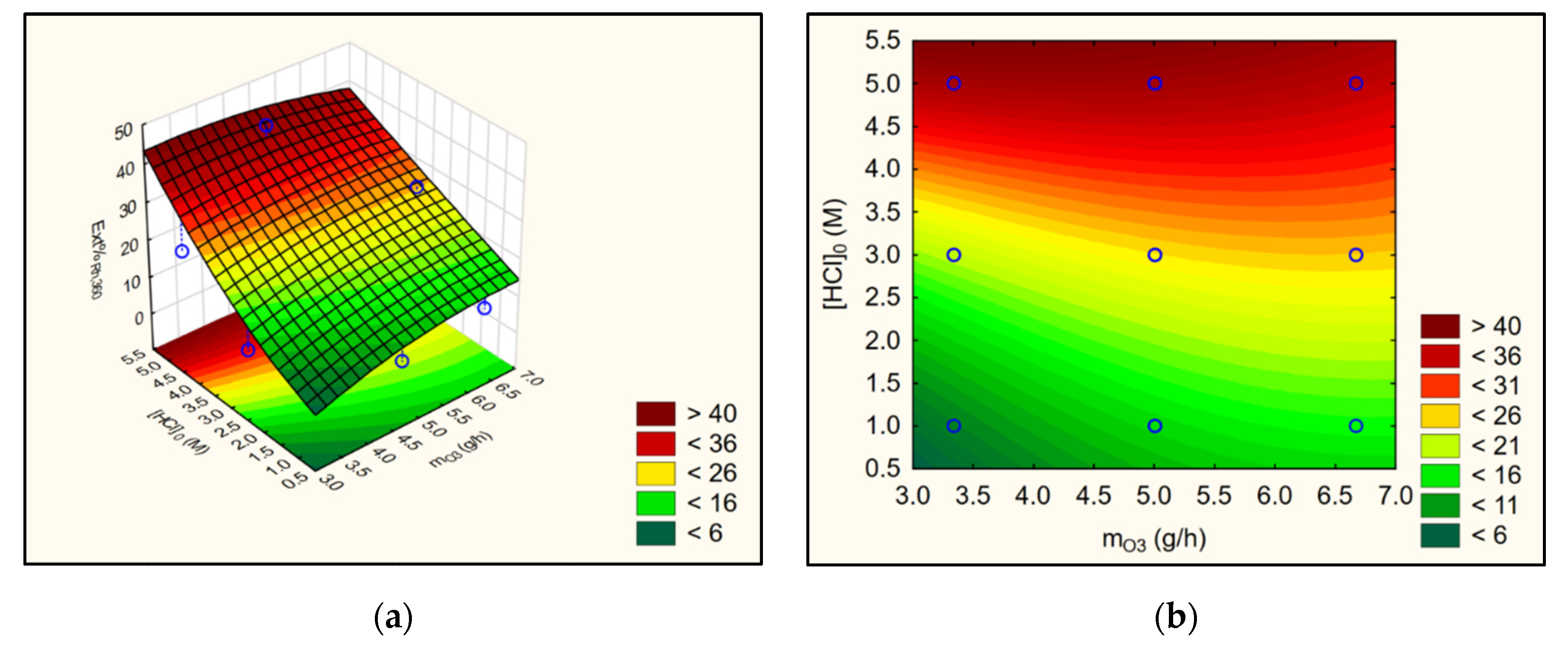
| Run Label: | PGM: | Ext: (%) | : (g/h) | : (M) | : (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimums | |||||
| 9 | Pt | 2.04 | 5.01 | 1.0 | 30 |
| Pd | 56.5 | ||||
| Rh | 2.24 | ||||
| Averages at centre point | |||||
| 13, 14, 15 | Pt | 64.3 | 5.01 | 3.0 | 60 |
| Pd | 74.9 | ||||
| Rh | 9.51 | ||||
| Maximums | |||||
| 10 | Pt | 88.6 | 5.01 | 5.0 | 30 |
| Pd | 85.0 | ||||
| Rh | 8.38 | ||||
| 12 | Pt | 78.7 | 5.01 | 5.0 | 90 |
| Pd | 85.0 | ||||
| Rh | 41.6 | ||||
| Run No.: | Impurity: | Ext: (%) | : (g/h) | : (M) | : (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimums: | |||||
| 10 | Si | 1.78 | 5.01 | 5.0 | 30 |
| Al | 5.08 | ||||
| Mg | 5.42 | ||||
| 9. | Si | 2.24 | 1.0 | ||
| Al | 1.40 | ||||
| Mg | 1.94 | ||||
| Averages at Centre-Point: | |||||
| 13 14 & 15 | Si | 2.65 | 5.01 | 3.0 | 60 |
| Al | 16.6 | ||||
| Mg | 17.0 | ||||
| Maximums: | |||||
| 11 | Si | 7.82 | 5.01 | 1.0 | 90 |
| Al | 39.7 | ||||
| Mg | 38.5 | ||||
| 12 | Si | 1.93 | 5.0 | ||
| Al | 66.6 | ||||
| Mg | 68.4 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knight, M.; van Wyk, P.; Akdogan, G.; Bradshaw, S. Leaching Platinum Group Metals from Simulated Spent Auto-Catalyst Material Using Ozone and Hydrochloric Acid. Minerals 2024, 14, 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14100998
Knight M, van Wyk P, Akdogan G, Bradshaw S. Leaching Platinum Group Metals from Simulated Spent Auto-Catalyst Material Using Ozone and Hydrochloric Acid. Minerals. 2024; 14(10):998. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14100998
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnight, Marcus, Petrie van Wyk, Guven Akdogan, and Steven Bradshaw. 2024. "Leaching Platinum Group Metals from Simulated Spent Auto-Catalyst Material Using Ozone and Hydrochloric Acid" Minerals 14, no. 10: 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14100998
APA StyleKnight, M., van Wyk, P., Akdogan, G., & Bradshaw, S. (2024). Leaching Platinum Group Metals from Simulated Spent Auto-Catalyst Material Using Ozone and Hydrochloric Acid. Minerals, 14(10), 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14100998






