Chromium Immobilization as Cr-Spinel by Regulation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) Concentrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Precipitation Experiments
2.2. Methods for Sample Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fe(II) Contributions to the Formation and Stability of Cr-Spinel
3.2. The Roles of Fe(III) and Cr(III) in Cr-Spinel Formation
3.3. Cr-Spinel Formation from Different Mixing Orders of Fe(II), Fe(III), and Cr(III) Precipitates
3.4. Remediation Strategies of Cr-Contaminated Sites through Cr-Spinel Precipitation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von, R.; Liu, D. Chromium and hexavalent chromium. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1993, 13, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Singh, N.; Verma, M. Hexavalent-chromium-induced oxidative stress and the protective role of antioxidants against cellular toxicity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, V.; Callao, M.P. Chromium determination and speciation since 2000. Trac-Trend. Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhu, L. Photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) over different TiO2 photocatalysts and the effects of dissolved organic species. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, L.B.; Mourad, W.E.; Rophael, M.W. Photocatalytic reduction of environmental pollutant Cr(VI) over some semiconductors under UV/visible light illumination. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 1998, 17, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianzhong, Z.; Mei, S.; Juan, L. Reductive immobilization of hexavalent chromium in contaminated soil and groundwater systems: A review. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, L.; Gueye, M.T.; Petrucci, E. Hexavalent chromium reduction in contaminated soil: A comparison between ferrous sulphate and nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 281, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J. Effects of abiotic mineral transformation of FeS on the dynamic immobilization of Cr(VI) in oxic aquatic environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, M.; Tumen, F. Chromium removal from aqueous solution by the ferrite process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 109, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Chen, Y.; Su, B. Oxygen-fugacity evolution of magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposits in East Kunlun: Insights from Cr-spinel composition. Am. Mineral. 2022, 107, 1968–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, H.; Jiao, J.; Xia, M. Origin of chromitites in the Songshugou peridotite massif, Qinling Orogen (Central China): Mineralogical and geochemical evidence. J. Earth Sci-China 2019, 30, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Ruifeng, Z.; Yichen, S. Status and prospect of in-situ remediation technologies applied in hexavalent chromium contaminated sites. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Yao, L.; Xiao, B. Mechanisms and influential factors of soil chromium long-term stability by an accelerated aging system after chemical stabilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, A.D.; Tare, V.; Bose, P. Extent of oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) under various conditions pertaining to natural environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Eljamal, O. Mini review on the application research of nanoscale zero valent iron in water treatment. Proc. Int. Exch. Innov. Conf. Eng. Sci. 2023, 9, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Mines, P.D. Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) synthesis in a Mg-aminoclay solution exhibits increased stability and reactivity for reductive decontamination. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2014, 147, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.M.; Lim, J.K. Complex interplay between colloidal stability, transport, chemical reactivity and magnetic separability of polyelectrolyte-functionalized nanoscale zero-valent iron particles (nZVI) toward their environmental engineering application. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 46, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookshaw, D.R.; Coker, V.S.; Lloyd, J.R. Redox interactions between Cr(VI) and Fe(II) in bioreduced biotite and chlorite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11337–11342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xue, Q.; Tang, J. New insights on Cr(VI) retention by ferrihydrite in the presence of Fe(II). Chemosphere 2019, 222, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Fu, F. Behaviors of structural Fe(II) of nontronite and aqueous Fe(II) on Cr(VI) removal in the presence of citrate. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjian, E.; Claisse, P.; Tyrer, M. Preliminary investigations into the use of secondary waste minerals as a novel cementitious landfill liner. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q. The regeneration of Fe-EDTA denitration solutions by nanoscale zero-valent iron. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yin, W.; Xu, M. Facile modification of activated carbon with highly dispersed nano-sized α-Fe2O3 for enhanced removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, S.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, L. Study on the passivation and stabilization mechanism of calcium-based magnetic biochar on Cr(VI) polluted soil and its effect on soil microbes. Acta Scie. Circumstantiae 2022, 42, 390–402. [Google Scholar]
- Stepniewska, Z.; Bucior, K.; Bennicelli, R.P. The effects of MnO2 on sorption and oxidation of Cr(III) by soils. Geoderma 2004, 122, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, M.L.; James, B.R.; Helz, G.R. Hydrogen peroxide effects on chromium oxidation state and solubility in four diverse, chromium-enriched soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4054–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Zheng, J. Different pathways for Cr(III) oxidation: Implications for Cr(VI) reoccurrence in reduced chromite ore processing residue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11971–11979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezonov, G.; Joseleau-Petit, D.; Ari, R. Escherichia coli physiology in Luria-Bertani broth. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8746–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefánsson, A. Iron(III) hydrolysis and solubility at 25 °C. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6117–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, H. Treatment mechanism of chromium-containing wastewater with carbonate minerals. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 5444–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chu, G.; Du, Y. The role of electron shuttle enhances Fe(III)-mediated reduction of Cr(VI) by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. World J. Microb. Biot. 2019, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookshaw, D.R.; Lloyd, J.R.; Vaughan, D.J. Effects of microbial Fe(III) reduction on the sorption of Cs and Sr on biotite and chlorite. Geomicrobiol. J. 2016, 33, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.; Lahav, O. The effect of pH on the kinetics of spontaneous Fe(II) oxidation by O2 in aqueous solution-basic principles and a simple heuristic description. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 2080–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, P.; ThomasArrigo, L.K.; Sawwa, D. Complexation by particulate organic matter alters iron redox behavior. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2024, 8, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, S.; Bøjesen, E.D.; Lock, N. Probing the validity of the spinel inversion model: A combined SPXRD, PDF, EXAFS and NMR study of ZnAl2O4. Dalton T. 2020, 49, 13449–13461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Alam, M.S.; Alessi, D.S. XAS characterization of nano-chromite particles precipitated on magnetite-biochar composites. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 175, 108544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyar, M.D.; Agresti, D.G.; Schaefer, M.W. Mössbauer spectroscopy of earth and planetary materials. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006, 34, 83–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurepin, V.A. Thermodynamics of cation distribution in simple spinels. Geokhimiya 1988, 5, 688–697. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Y. Enhanced reduction of Cr(VI) in UV/EKR system by organic acids: Focus on Cr(VI) desorption and Fe(III) catalysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 334, 126006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
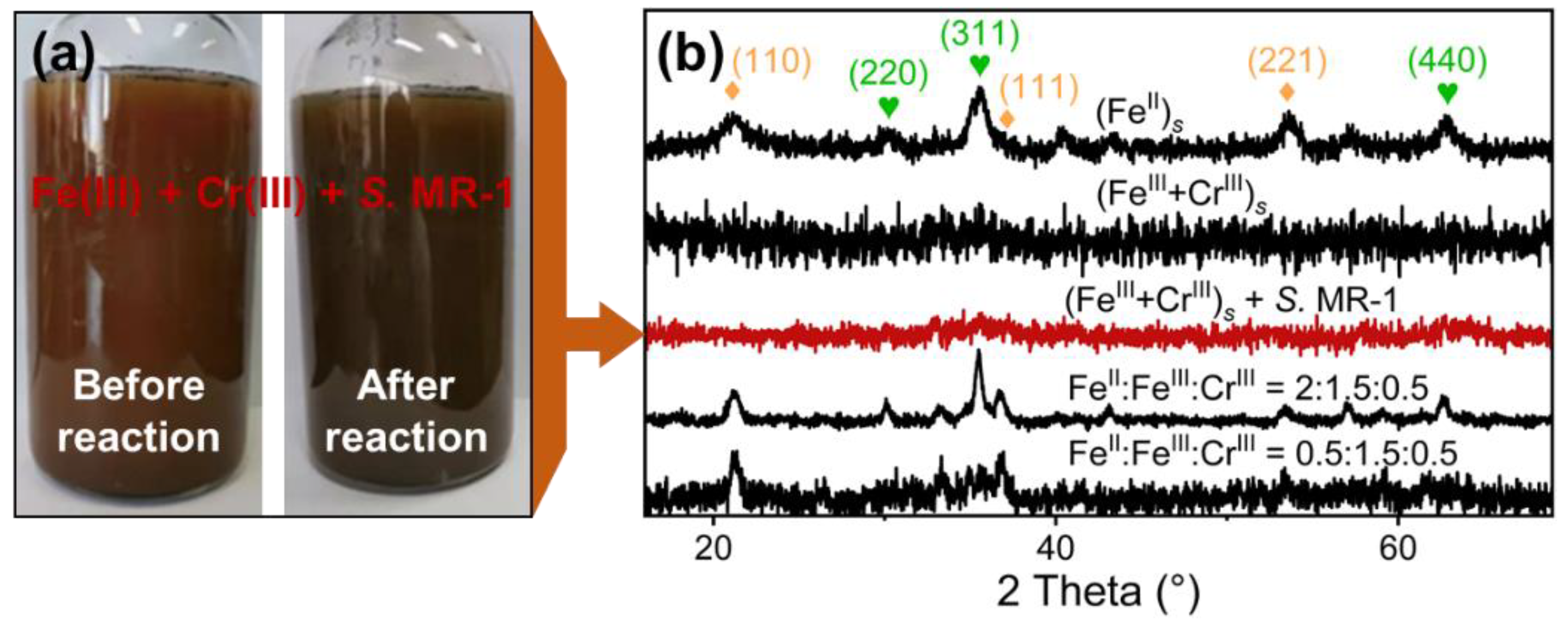
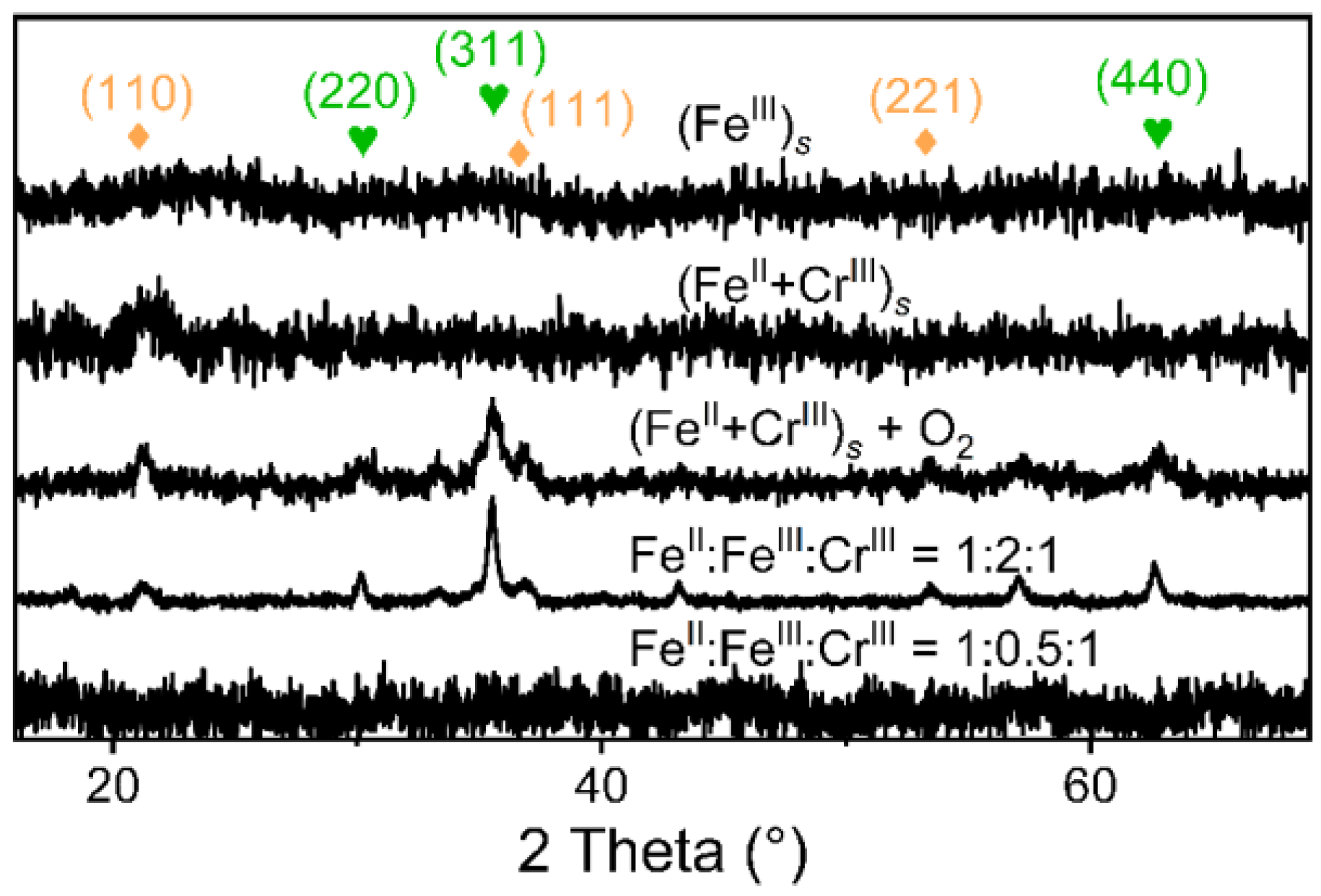
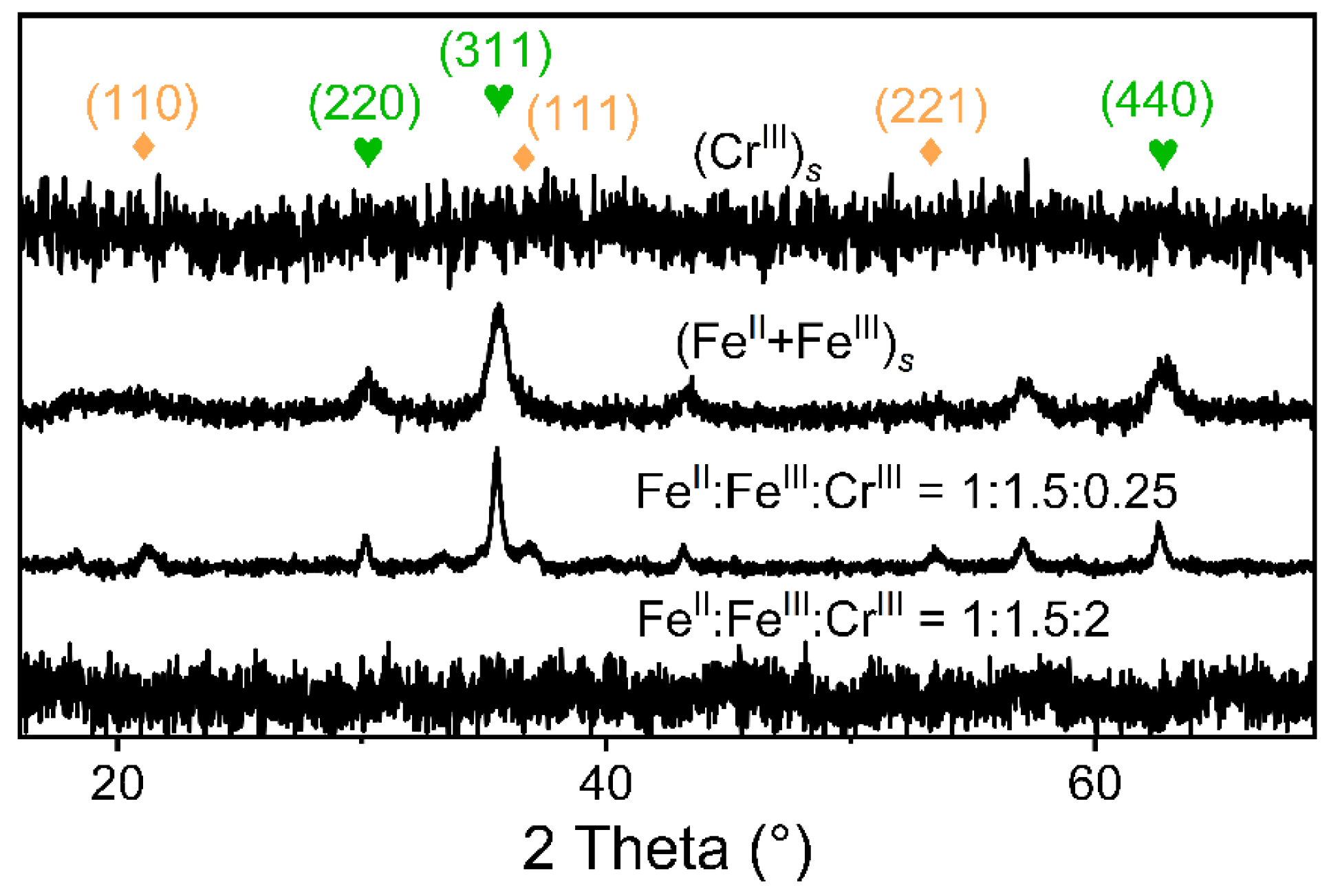
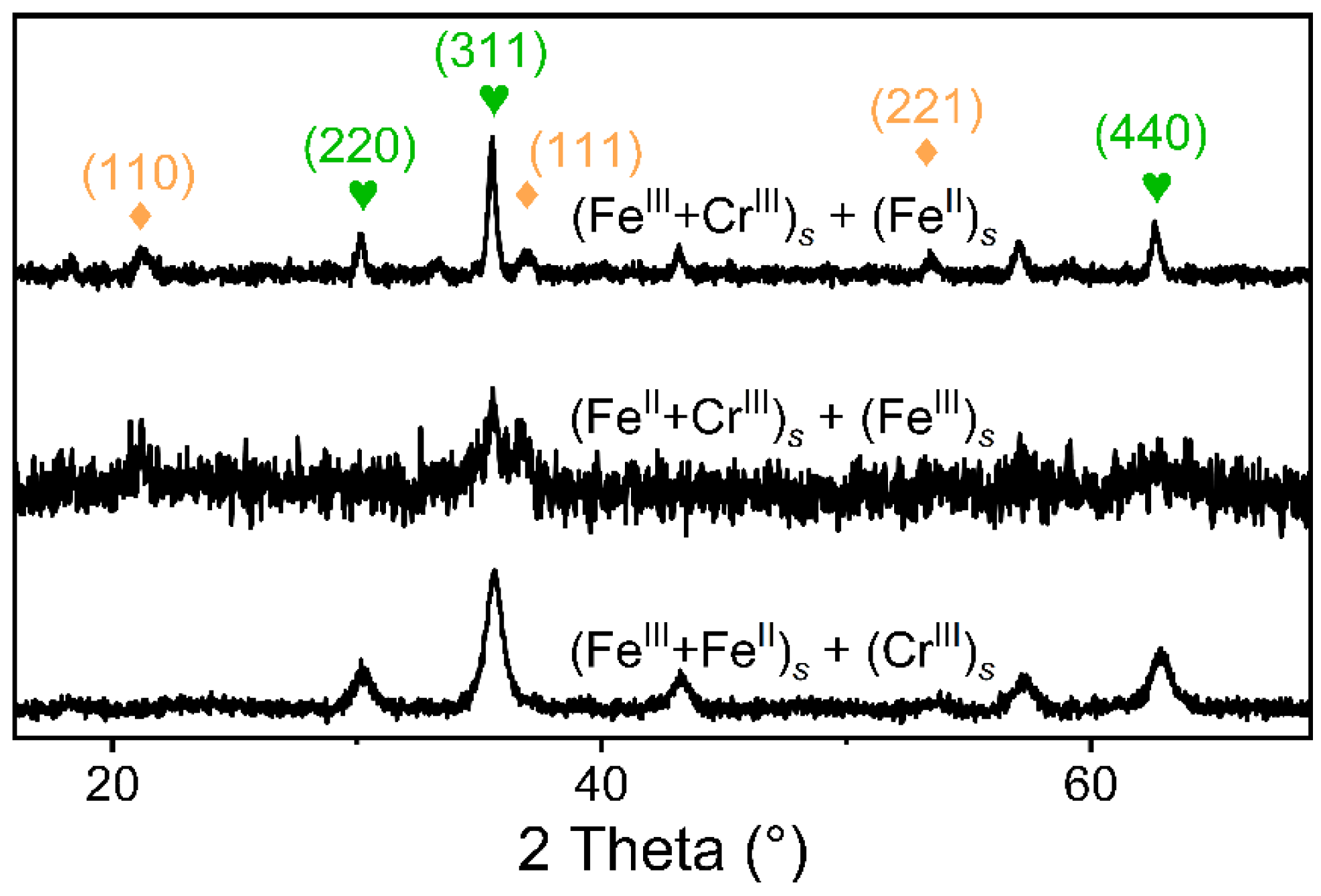
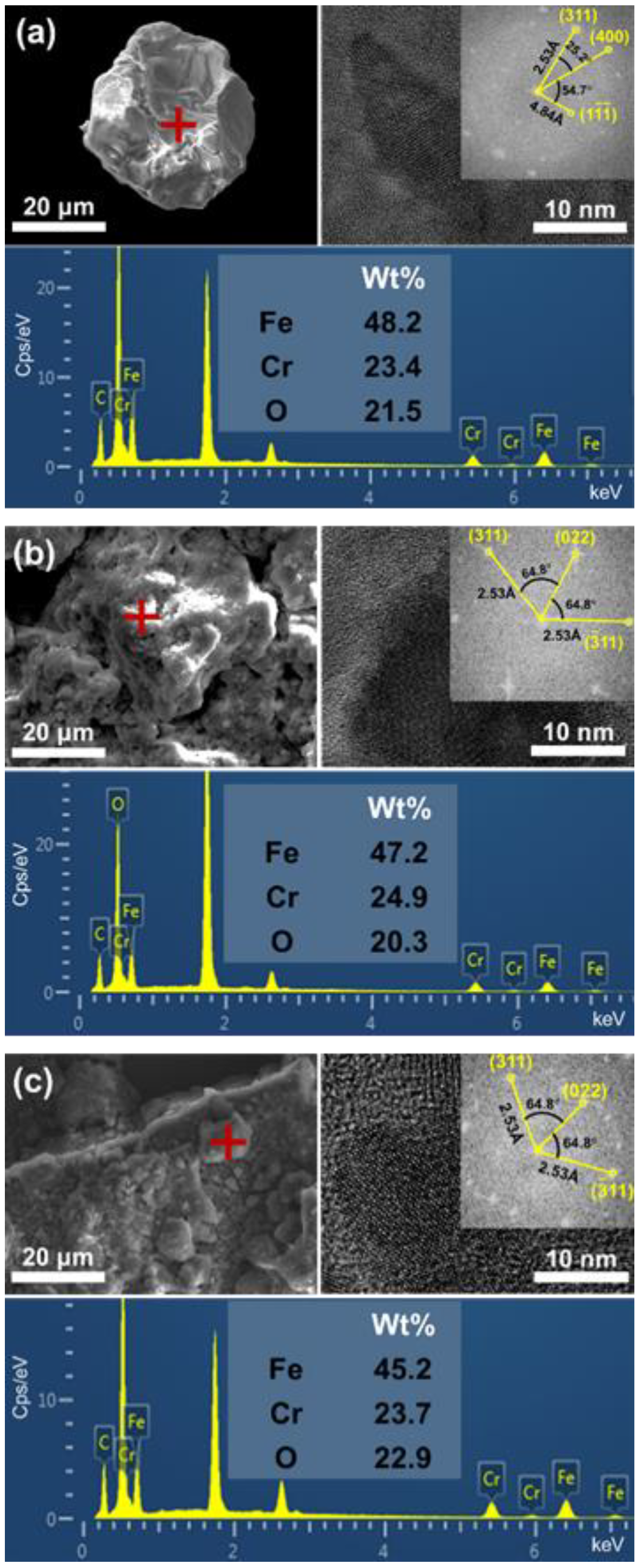
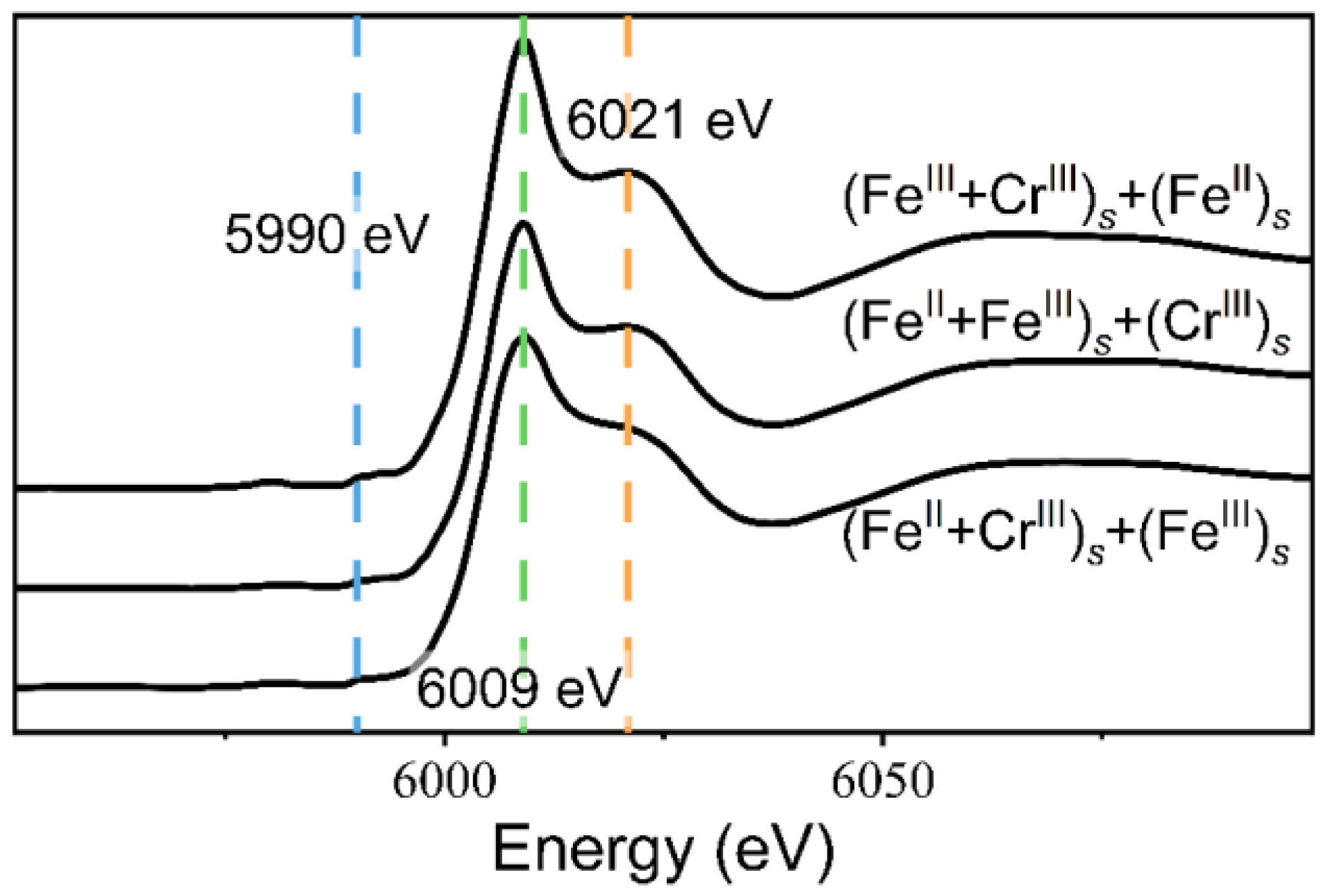
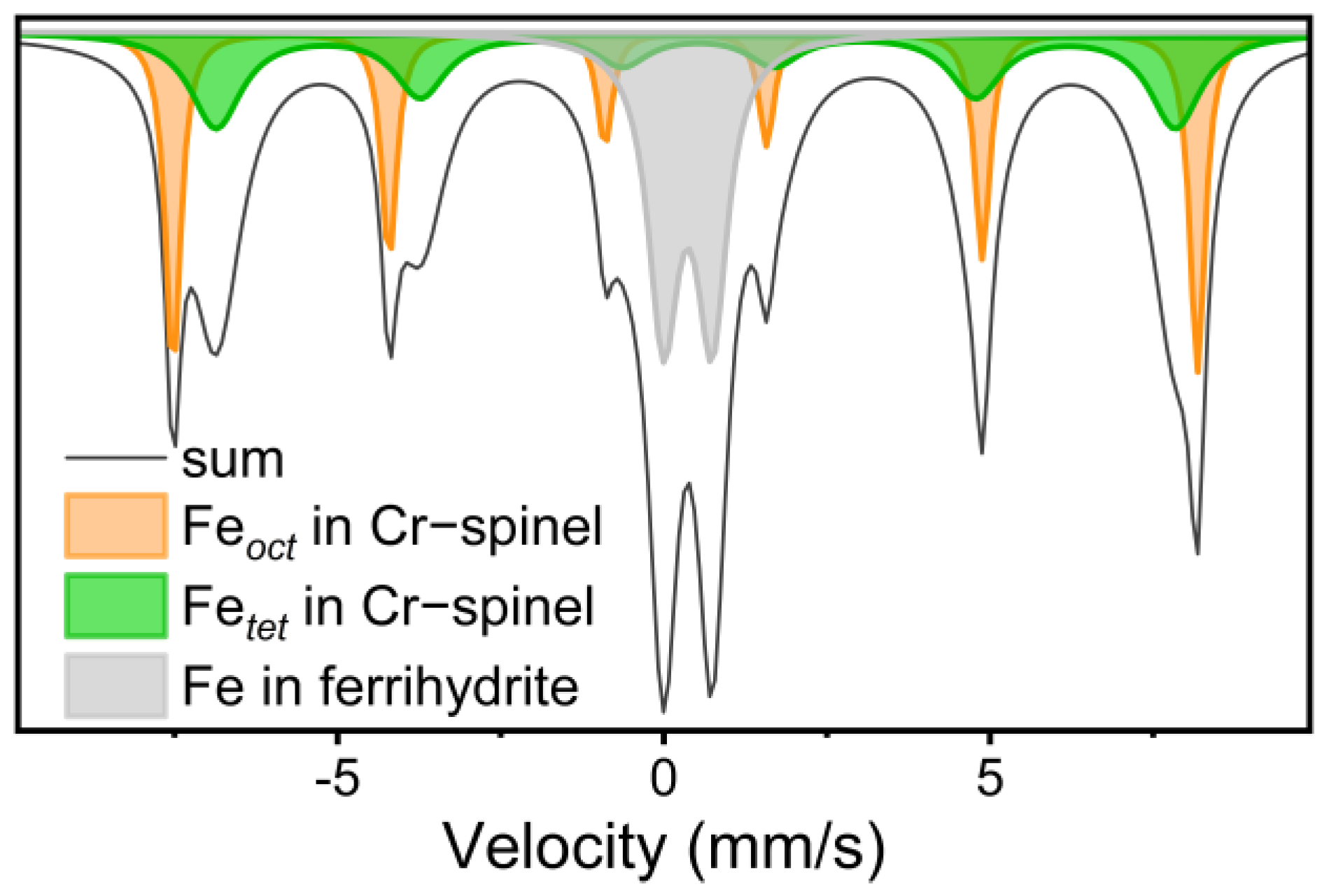
| Reaction Time (Day) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(II) (mg/L) | 0.0 | 78.5 | 100.5 | 135.0 | 152.0 | 174.0 | 198.5 | 223.0 |
| WL Peak | Post-WL Shoulder | WL/Post-WL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (FeIII + CrIII)s + (FeII)s | 2.045 | 1.438 | 1.422 |
| (FeII + FeIII)s + (CrIII)s | 1.663 | 1.192 | 1.395 |
| (FeII + CrIII)s + (FeIII)s | 1.599 | 1.181 | 1.354 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, T.; Li, Y.; Hou, B.; Du, Y.; Lu, A.; Li, Y. Chromium Immobilization as Cr-Spinel by Regulation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) Concentrations. Minerals 2024, 14, 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14101024
Hua T, Li Y, Hou B, Du Y, Lu A, Li Y. Chromium Immobilization as Cr-Spinel by Regulation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) Concentrations. Minerals. 2024; 14(10):1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14101024
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Tianci, Yanzhang Li, Bingxu Hou, Yimei Du, Anhuai Lu, and Yan Li. 2024. "Chromium Immobilization as Cr-Spinel by Regulation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) Concentrations" Minerals 14, no. 10: 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14101024
APA StyleHua, T., Li, Y., Hou, B., Du, Y., Lu, A., & Li, Y. (2024). Chromium Immobilization as Cr-Spinel by Regulation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) Concentrations. Minerals, 14(10), 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14101024






