Abstract
The processing of zinc ore using hydrometallurgical methods leads to the formation and accumulation of a by-product called jarosite, which contains concentrated precious metals. In this study, we propose the recovery of In and its separation from Cu, Zn, Fe, Pb, and Ag. This study also presents a proposal for a new technological procedure for jarosite treatment. First we roasted the jarosite, and then the calcine collected was leached in water. The leaching extraction values obtained for Cu, Zn, Fe, and In were 91.07%, 91.97%, 9.60%, and 100.0%, respectively. Following the leaching of the roasted material in water, Pb, Ag, and most of the Fe obtained remained in the solid residue. The leaching solution was treated further by a precipitation process using NaOH, where In and Fe were precipitated and consequently separated from Cu and Zn. The In (OH)3 and Fe(OH)3 precipitates were dissolved further in a diluted H2SO4 solution, and then the cementation of In with Al was performed. We used HCl acid to remove Al from the In, after which unwrought In was obtained.
1. Introduction
Increased ore-processing activity and the demand for metals worldwide have inevitably led to the depletion of high-grade ore resources. The new challenges faced by the industry, in terms of the economic and sustainable exploitation of complex low-content ore deposits, are the subject of research being conducted by many scientists to date [1,2].
In addition to zinc, zinc concentrates also contain several commercially important metals, one of which is indium. This metal does not occur in its own mineral deposit, but rather as a companion with zinc. During the hydrometallurgical production of zinc by roasting, leaching, and electrolytic extraction processes, indium is concentrated in the output sediments of so-called jarosite as a by-product [3,4]. Thus, the by-product creates a new resource and forms a reserve [5,6]. In Serbia, this by-product occurs throughout a large area of the country, the processing of which, in addition to Cu, Zn, Pb, Ag, and Au, can also produce indium, which favorably affects its overall economic value, since the price of these metals is relatively high [7,8].
Jarosite, as a newly formed mineral, is very stable and poorly soluble in diluted acid [9]. The accompanying zinc metal collected from jarosite is usually obtained using the Waelz pyrometallurgical process. The pyrometallurgical methods of processing the secondary raw materials and waste sludge produced by zinc hydrometallurgies are very efficient; however, they involve the use of expensive, high-capacity industrial plants in order to be economical. These processes release harmful gases that can have a serious impact on the environment. Some authors have shown in the literature that the application of pyrometallurgical processes, such as the Waelz and Ausmelt methods, expends a considerable amount of coal to provide the power required to attain a high operating temperature (1100–1300 °C) [10,11]. These methods are not economically viable in the industry; therefore, jarosite is usually deposited as a waste product.
Additionally, in a study conducted by a group of authors [12], the processes of treating Pb–Ag jarosite sludge using magnetic separation, flotation, and melting are presented. From the results, it can be concluded that none of the applied procedures produced satisfactory results because it was not possible to achieve metal selectivity.
There are several studies that present different procedures useful for the treatment of jarosite-rich raw materials. Some authors have shown the processes of acid and brine leaching for the extraction of Zn and Pb [13], whereas other authors successfully developed a mixing process using H2SO4, roasting, water leaching, and finally leaching with NaCl to obtain Zn and Pb [14]. In India and Italy, some researchers, at present, intend to produce construction and ceramic materials with jarosite [15,16,17,18]. This activity creates a risk of environmental pollution, and valuable elements can be lost in the process. The extraction of lead and silver using brine leaching and then Na2S precipitation to obtain the Pb–Ag concentrate is also one of the methods proposed by the authors [19]. The Jarogain hydrometallurgical process produces additional metals; however, it requires sulfide precipitation, dissolution in the NH4 solution, and hot H2SO4. Working in such an aggressive environment is unsafe and can lead to environmental damage.
Data from the literature show that liquid extraction enables the isolation and separation of almost all metals with high efficiency and selectivity [20]. Moreover, these data also show that using amino acids to conduct the extraction process requires a long time to establish an extraction equilibrium in the form of stable complexes, and the amino acids produced are toxic. They accumulate in the environment and are not readily biodegradable. The use of oxime and azomethine for the extraction of heavy metals, especially those present in multimetallic solutions, showed that the extraction was not complete.
Our study also incorporated the SX extraction process; however, since high selectivity and utilization parameters were not achieved, we did not conduct additional tests. In addition, extraction was used for an unlimited quantity of raw materials that can be exploited for many years. Since the extractants used in the research are very expensive, we decided to continue the research by adopting the classic hydrometallurgical treatment method. Since the jarosite used in the study was not formed naturally, but as a by-product during the production of Zn, its quantity was limited because the production of Zn was terminated. For such a limited quantity of the product, the extraction procedure using organic extractants was expensive, and the hydrometallurgical procedure we utilized presented good selectivity and relatively high utilization properties.
Indium is an important metal that is widely used in the fields of electronics, medicine and healthcare, photo-electronics, and computers. It is predominantly one of the most widely dispersed metals and is found mainly in sphalerite as an isomorphic impurity. For this reason, sphalerite is the most important source of indium, which is required for improving the national economy [21].
To successfully produce a very pure form of indium, such as that used in the semiconductor industry, the following raw-metal-refining processes were used: chemical, electrolytic refining, vacuum distillation, and zonal refining.
Chemical purification processes, in which indium is obtained with only 10−3%–10−4% impurities, include (a) melting under a layer of sodium hydroxide, where, at 320–350 °C, most of the remaining zinc, aluminum, lead, and tin obtained from indium are converted into sodium hydroxide slag; (b) melting under a layer of ammonium chloride and glycerin where, at 160–170 °C, impurities with affinities closer to chlorine than indium (zinc, cadmium, iron) are converted into chlorides; and (c) melting under a layer of potassium iodide and glycerin, where indium is purified from cadmium and thallium, which form very stable iodides [22].
Ordinary electrolytic refining processes using unwrought indium anodes are generally performed in weakly acid chloride solutions, which usually contain 40–60 g/L In and 30–80 g/L NaCl. Sheets of pure indium, aluminum, or titanium, on which indium is deposited, can serve as cathodes. This process can produce indium that does not contain more than 10−4% of any impurities [23].
Amalgam refining occurs in a three-part electrolyzer with a mercury bipolar electrode. The unwrought indium at the anode first becomes an electrolyte and then forms an amalgam on a mercury cathode. In the middle space, the amalgam is decomposed anodically and then indium is converted back into an electrolyte. These amalgamations and dissolutions are repeated until indium, cleansed of any impurities, finally settles on the platinum. This procedure produced a product containing 99.999% indium [24].
The vacuum-refining process conducted at 600–900 °C and 1.3 × 103 Pa pressure removes any evaporable impurities, such as zinc, cadmium, and mercury [25].
The zonal-refining process is usually used in the final stage of obtaining a high-purity form of indium. In this way, nickel, silver, and copper can be almost completely removed; however, this method is not suitable for the removal of lead, cadmium, and zinc [26].
This paper describes a hydrometallurgical method for processing jarosite Pb–Ag tailings waste. The present study presents the possibility of separating the metals and obtaining commercial, unwrought In. Jarosite + Pb–Ag sludge, obtained from the Elixir Zorka factory in Šabac, Serbia, is the residue produced by hot-acid leaching. The product is obtained by using traditional refining technology to obtain zinc, where, in addition to Pb–Ag precipitates, jarosite is also obtained. The jarosite + Pb–Ag sludge obtained from the factory, presented in Figure 1, was the residue produced by the hot-acid leaching process. It was obtained according to the traditional refining method used to obtain zinc, where, in addition to Pb–Ag precipitates, jarosite was also obtained.

Figure 1.
View of jarosite waste tailings at the Elixir Zorka Šabac factory.
2. Materials and Methods
The sample of jarosite tailings waste used in this study was a by-product collected from the Elixir Zorka Šabac factory. The sample was homogenized, dried, and re-homogenized, followed by exposure to granulometric, mineralogical, SEM-EDS, and chemical analyses.
Analytical Determinations
The solution acidity was measured using a combined pH electrode produced in Germany. Zinc, copper, and iron present in the solution were measured by absorption spectrometry (PerkinElmer 403, USA). The concentration of indium in the solution was determined by using an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES; Spectro Arcos model) manufactured in Germany. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed on a Rigaku MiniFlex 600 instrument produced in Japan with a D/teX Ultra 250 high-speed detector and an X-ray tube with a copper anode. The recording conditions were the following: angle range: 3°–90°, step: 0.02°, and recording rate: 10°/min. The X-ray tube’s voltage was 40 kV and the current was 15 mA. Mineral identification was performed using PDXL 2 Version 2.4.2.0 software, and the diffractograms we obtained were compared to the data obtained from the ICDD database (PDF-2 Release 2015 RDB). The detection limit for the XRD analysis was approximately 1%. The elemental analyzer LECO CHN 628, produced in the USA, was used to determine the presence of N2, C, and H2 in the jarosite sample. Thermogravimetric analysis was performed using an SDT Q600 V20.9 Build 20 instrument (Milford, MA, USA), with the temperature ranging from 25 to 700 °C. TGA analysis was performed in a stream of nitrogen with a flow rate of 100 mL/min and heating value of 10 °C/min using a ceramic pot. Particle size distribution measurement of the jarosite sample was performed using an optical laser particle size analyzer (MASTERSIZER 2000, Hydro2000MU) produced in the United Kingdom, which could determine grain sizes ranging from 20 nanometers to 100 microns. For the analysis of the samples, a scanning electron microscope (JSM IT 300 LV (JEOL, Japan)) was used, which can function in both low- and high-vacuum conditions, achieving high image resolutions with magnifications of up to 300,000× by using a tungsten filament as an electron source (cathode). The microscope was equipped with a detector for the secondary electrons (SEDs) and backscattered electrons (BEDs), and with a modern energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Grain Size Distribution of the Jarosite Sample
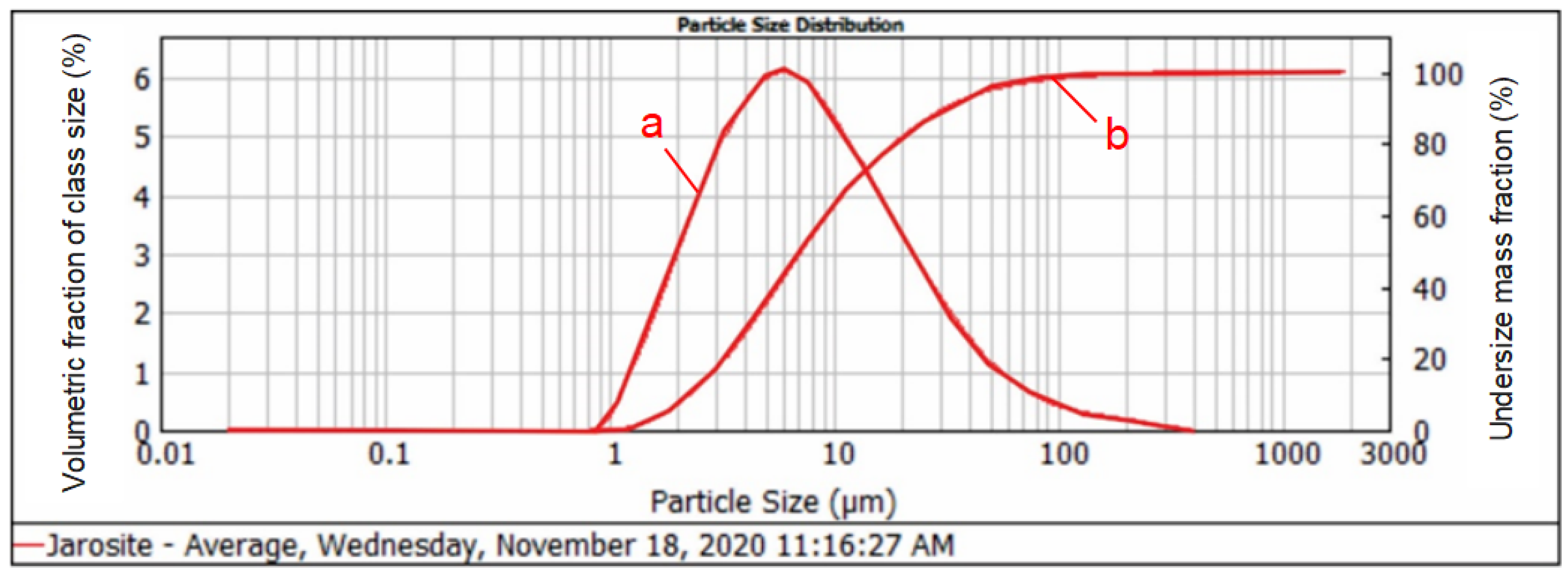
The particle size distribution measurement of the jarosite sample was performed on an optical laser particle size analyzer. The sample was measured three times and the average value of the three measurements was used as the final result. The particle size distribution of the jarosite sample is presented in Figure 2.
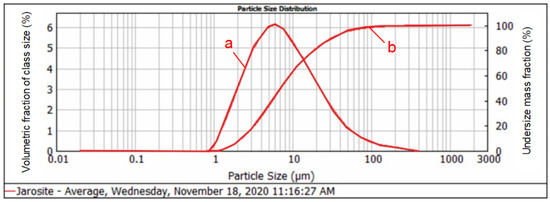
Figure 2.
Graphical presentation of the identified size classes and particle size distribution of the jarosite sample: (a) incremental (direct) curve values that correspond to the left axis; (b) undersize distribution curve values that correspond to the right axis.
It can be observed from the graph that the size class of 31.467 µm is represented by 90%, the size class of 7.258 µm is represented by 30%, and the size class of 2.307 µm is represented by 10%.
It can also be observed in Figure 2 that a fine jarosite size was obtained as an intermediate during the production of zinc. This fine size of jarosite does not need to be exposed to additional crushing or pulverizing for further treatment.
3.2. Mineralogical Composition of the Jarosite Sample
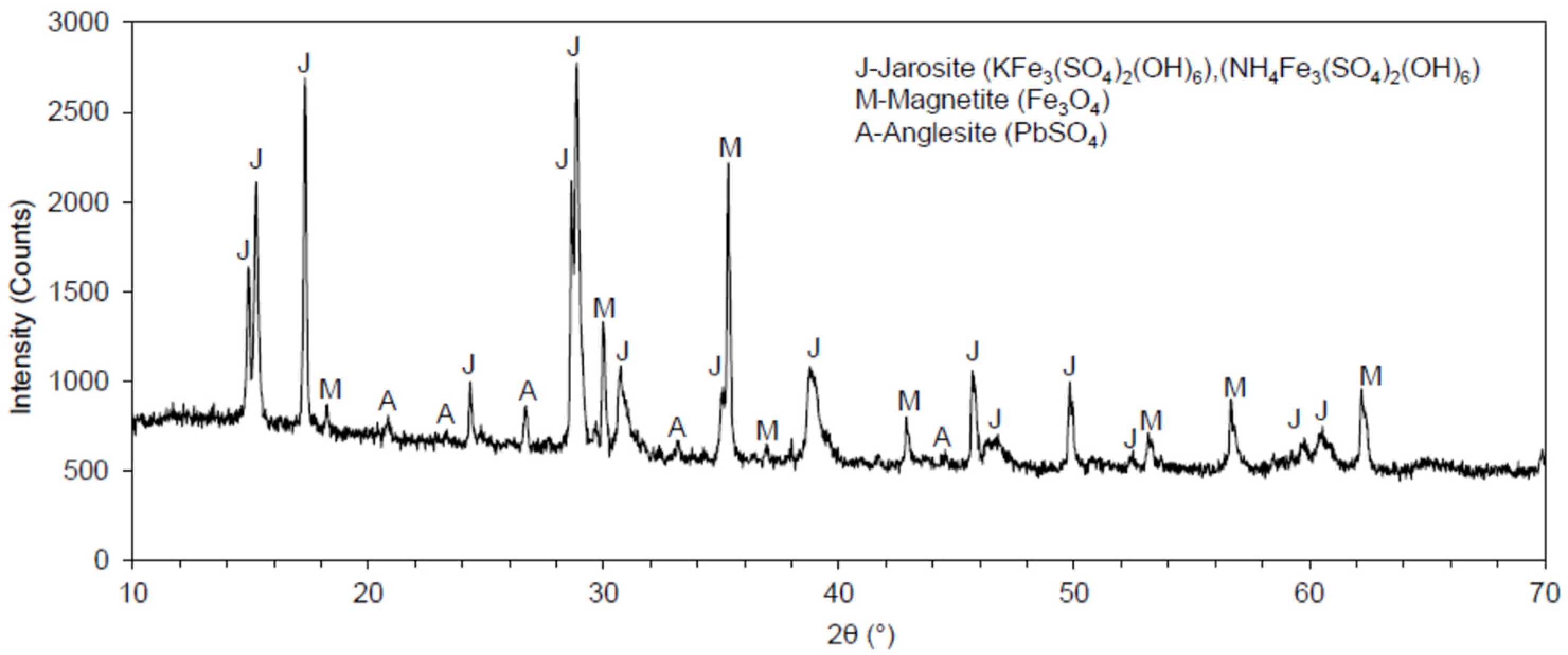
The XRD pattern obtained for the jarosite sample is presented in Figure 3. The XRD of the pulverized samples was performed prior to and following the roasting process of the jarosite.
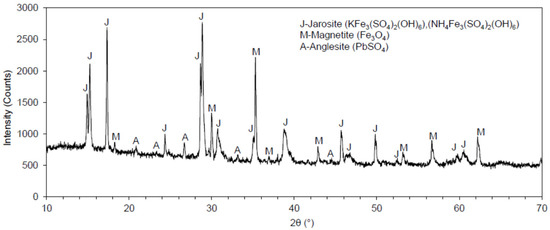
Figure 3.
Diffractogram of the jarosite tailings waste sample.
The diffractogram produced by the XRD analysis of the jarosite tailings waste sample is presented in Figure 2. The following minerals were identified in the sample: (a) jarosite, in the form of (KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6) and/or (NH4Fe3(SO4)2(OH)6); (b) magnetite (Fe3O4); and (c) anglesite (PbSO4). Jarosite and magnetite were the most prevalent minerals in the sample, while anglesite was less abundant. For the analyzed sample of jarosite, the peaks of potassium jarosite and ammonium jarosite matched each other because their angles also matched one another; therefore, these minerals presented the same crystal structures.
3.3. SEM-EDS Analysis
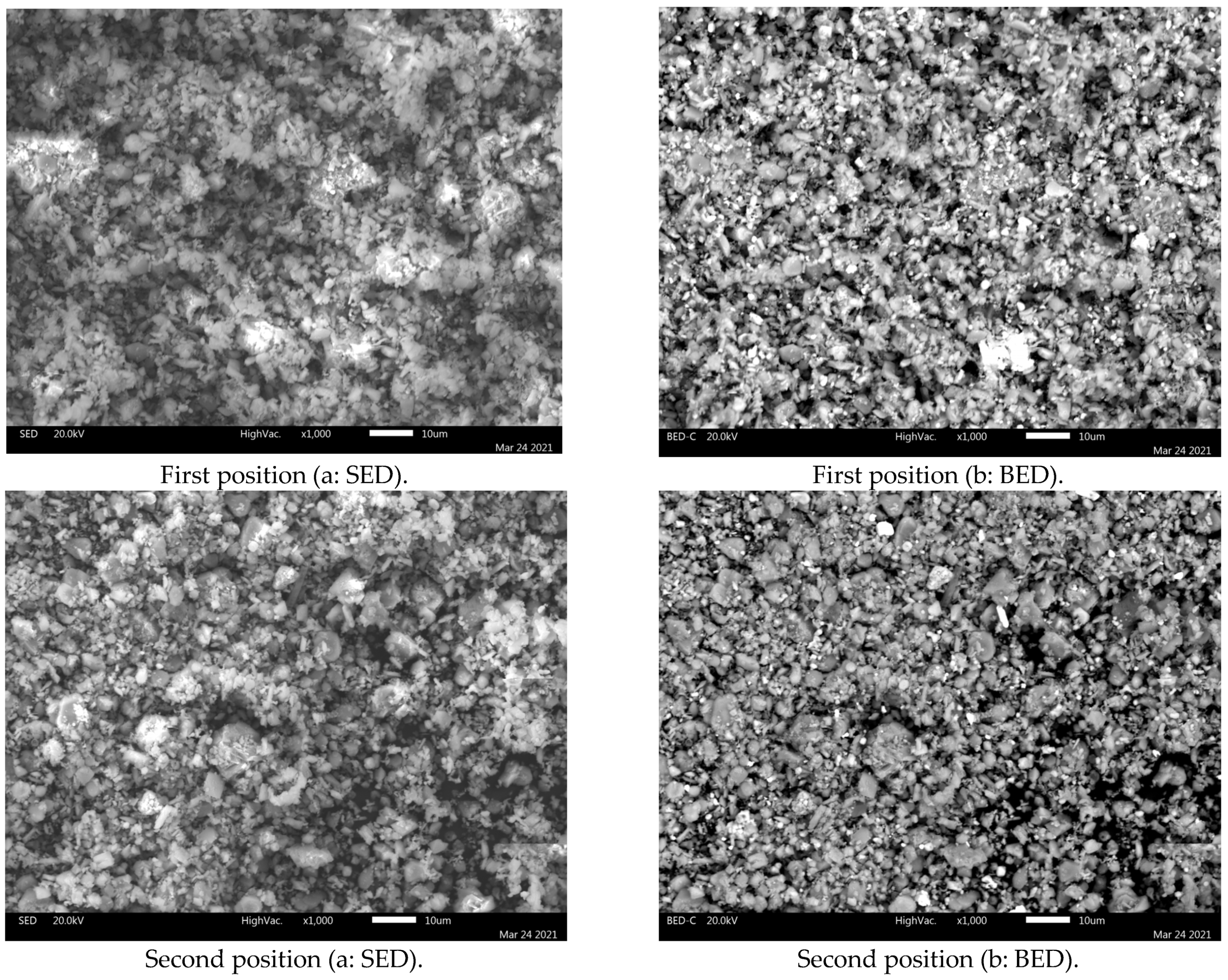
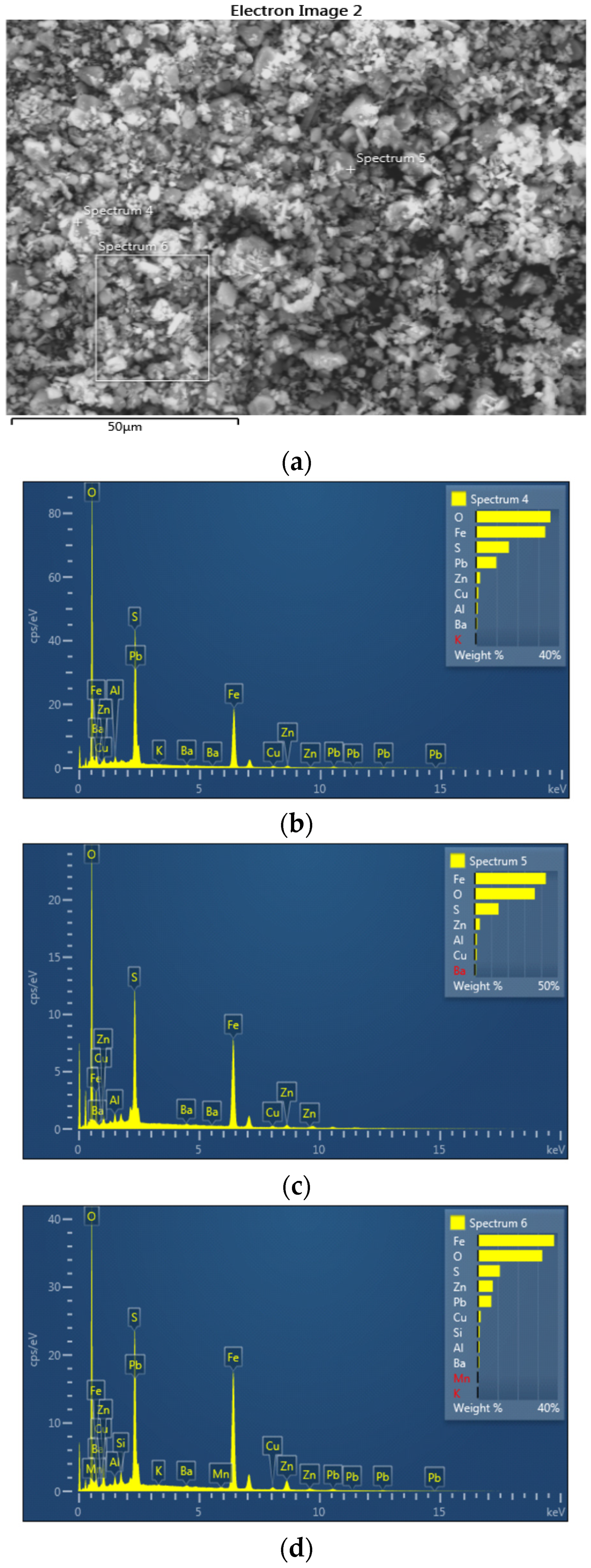
SEM-EDS analysis was performed on the jarosite sample. Figure 4 presents the SEM images (a: SED image; b: BED) of the jarosite sample recorded at 1000× magnification at two different positions.
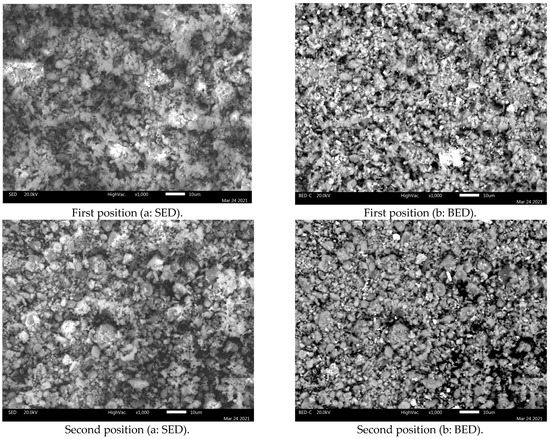
Figure 4.
SEM (a: SED; b: BED) images of the jarosite sample recorded at 1000× magnification at two different positions.
Clearly visible in the SEM images is that most particles range between approx. 1 and 10 µm in size, with a few exceeding 10 µm. The results of the SEM analysis are in good agreement with the laser diffraction grain size analysis results, when considering the difference between the volume fraction (obtained using the laser-diffraction method) and numerical frequency (observable when using SEM).
The BED images, acquired in the compositional mode, present a distinct domination by a single mineral phase: jarosite (observe EDS spectra in Figure 5 and Figure 6). However, numerous bright particles can be observed in these images corresponding to magnetite and anglesite, the two phases also identified by XRD analysis. Moreover, a few dark particles are evident in the images, corresponding to silicate residuum.
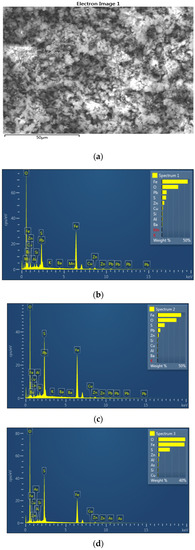
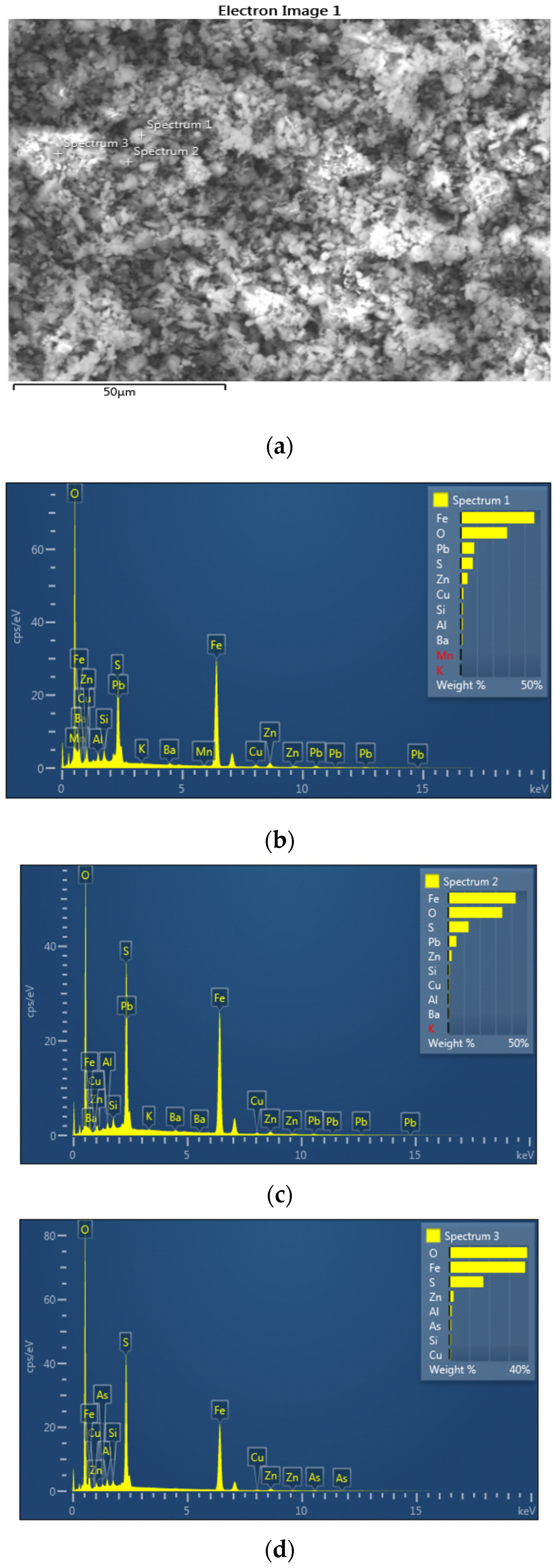
Figure 5.
EDS image (a) with EDS spectra (b–d) of the jarosite sample recorded at 1000× magnification; first position.
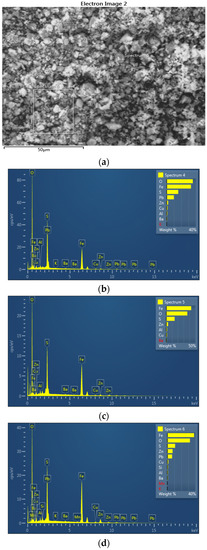
Figure 6.
EDS image (a) with EDS spectra (b–d) of the jarosite sample recorded at 1000× magnification; second position.
Jarosite occurs in generally irregular, tabular, and pseudo-cubic crystals, unevenly fractured and frequently rounded. The presence of well-developed hexagonal crystals, revealing its true hexagonal scalenohedral symmetry, is quite rare.
Based on the SEM EDS analysis of the jarosite sample, it can be observed in Table 1 that the jarosite sample contains 33.35% to 45.97% iron, 0.65% to 1.48% copper, 5.11% to 9.85% lead, and 2.04% to 7.44% zinc, in the form of oxides and sulfates. Indium and silver were not detected when using the EDS method of analysis because their content in the sample was less than the detection limit.
3.4. Chemical Analyses
The chemical analysis of jarosite is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Element content values (wt% dry basis) for the jarosite sample.
3.5. Jarosite Roasting
Previous research has shown that the leaching of jarosite in 15% H2SO4 under the conditions of 90 °C, 6 h, and S:L = 1:10 produces the best leaching results for Cu, Zn, and In, namely, 93.76%, 91.64%, and 97.59%, respectively [27]. However, in addition to this high leaching capacity of the metals of interest, the leaching of Fe over 80% also occurs. Studies have also shown that the precipitation of Fe with NaOH produces a large mass of precipitates. When this occurs, a significant amount of Cu and Zn is occluded and, together with Fe, settles in the precipitate as an irreversible loss. For this reason, the jarosite sample was subjected to roasting processes.
3.5.1. Roasting Pb–Ag Jarosite Sludge
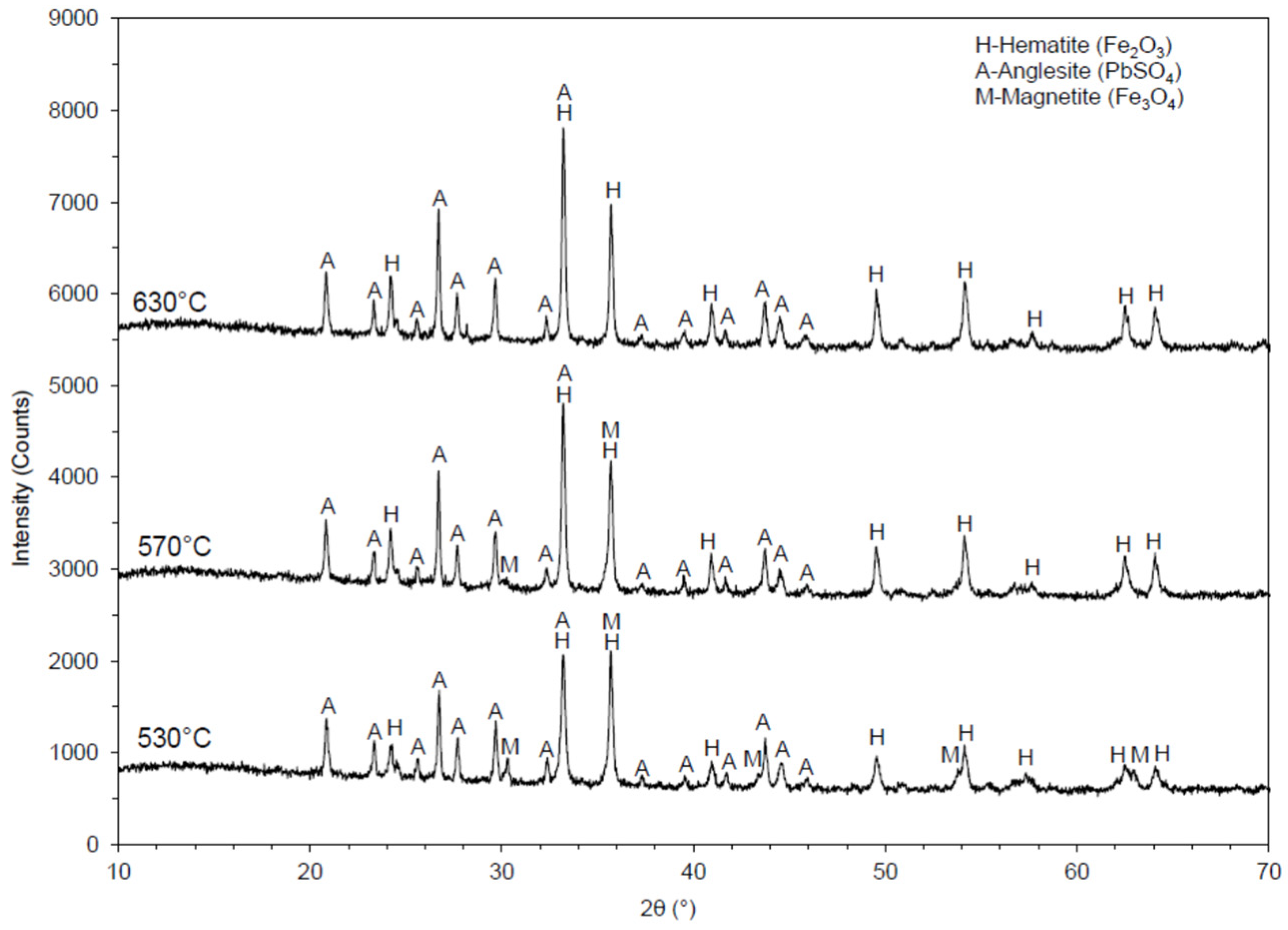
XRD analyses for each roasted sample were performed to determine the relevant decomposition effect. Diffractograms, obtained by the XRD analysis of a sample roasted at 530, 570, and 630 °C, are presented in Figure 7.
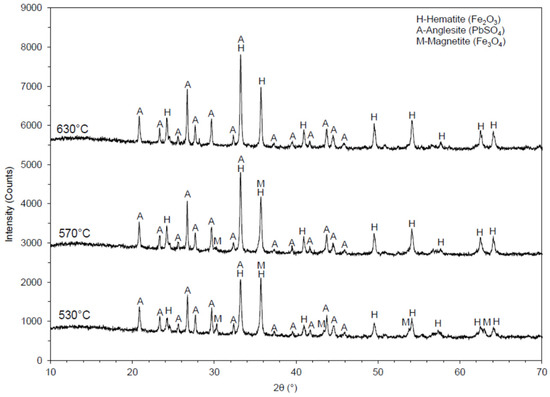
Figure 7.
Diffractogram of calcined jarosite samples at 530, 570, and 630 °C.
A diffractogram obtained from XRD analysis of the jarosite sample roasted at 570 °C is presented in Figure 6. In this sample, the following minerals were identified: hematite (Fe2O3), anglesite (PbSO4), and magnetite (Fe3O4). Hematite was the most common mineral identified in the sample, anglesite was less evident, while magnetite was the least evident. By comparison, the magnetite peak intensities presented in the diffractograms of the samples at 530 and 570 °C showed that the presence of magnetite in the jarosite sample roasted at 570 °C was less than in the sample roasted at 530 °C.
A diffractogram obtained from XRD analysis of a sample roasted at 530 °C is presented in Figure 6. In this sample, hematite (Fe2O3) and anglesite (PbSO4) were identified. Hematite was the more common mineral in the sample, while anglesite was less evident. The XRD analysis showed that, at 630 °C, iron was completely transformed into Fe2O3.
With increasing roasting temperature the sulfate decomposed, releasing SO2 that entered the atmosphere and thus reduced the acidity in the environment; therefore, the metal leaching activity was reduced (Table 3). According to the data, the sulfates of some metals, as well as sulfuric acid, decompose when exposed to the following temperatures [28]:

Table 3.
Conditions for the jarosite roasting and leaching process.
CuSO4 500–600 °C
ZnSO4 740 °C
Fe2 (SO4)3 480 °C
In2 (SO4)3 600 °C
H2SO4 338 °C
At temperatures higher than 480 °C, Fe2(SO4)3 decomposes and transforms into FeO, and by increasing the temperature to 630 °C, Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 completely transform into Fe2O3, which is insoluble in water and slightly soluble in a weak sulfuric acid solution. Here, the separation of iron from other metals can be achieved by leaching.
After the roasting stage, the material was leached in water. Table 3 displays the roasting and leaching conditions for the experiments we performed, presenting only those that provided the best recovery of metals.
It can be observed in Table 3 that the best leaching result for the metals is obtained after roasting the jarosite at a temperature of 530 °C under a roasting time of 4 h and leaching the roasted material in water, where 91.07%, 91.97%, and 100.00% of Cu, Zn, and In were leached separately. It can also be observed from the results that in experiment 1, following the roasting of jarosite at 530 °C and the leaching of the roasted material in water under the conditions of S:L = 1:5 and a leaching time 1 h, the measured pH of the solution after leaching was 2.25. Compared with the measured pH of the solutions obtained in experiments 2 (pH = 2.73) and 3 (pH = 4.79), it can be observed that in experiment 1, there was sufficient acid to perform the leaching process; in other words, the acid was not spent. The reason for the greater degree of In, Cu, and Zn leaching during the roasting process at low temperatures was that they remained in the form of sulfates that are easily leached in water, while the iron was transformed into hematite, which is virtually insoluble. Additionally, in experiment 1, in addition to the leaching of Cu, Zn, and In, the increased leaching activity of Fe was obtained in comparison to experiments 2 and 3; however, Fe leaching activity was relatively low compared to the direct leaching of the raw jarosite in sulfuric acid [27]. Since the jarosite sample was obtained as a by-product during the zinc production process by the conventional electrolytic refining process, it is well known from the literature that focuses on the structure of sulfate minerals. Extensive research on the leaching process in both acid and water, separately, has been conducted. By measuring pH after leaching, it was determined that there was no need to perform leaching in acid because the pH was lower than 1. For this reason, we decided to use water for the leaching process. Based on the previous experience gained through long-term research, it was decided that the S:L ratio should be 1:5, which is a reasonable ratio. The selected leaching time of 1 h was sufficient because sulfates are easily soluble in water.
The degree of metal leaching ξ (%) was calculated according to the following equation:
where ξ is the mass of the metal Meleac.sol (g) that was transferred into the solution by leaching.
∑Meleac.sol. = CMe (g/L) × V (L),
Mecalcine = CMecalcine (%) × mcalcine (g)/100%.
CMecalcine (%): metal concentration in calcine.
mcalcine (g): the mass of calcine for leaching.
Table 4 presents the metal content in the solution following the leaching of calcine, on the basis of which the metal leaching activity was calculated.

Table 4.
Metal concentrations in the leaching solution.
3.5.2. TGA Analyses of Jarosite Pb–Ag Sludge
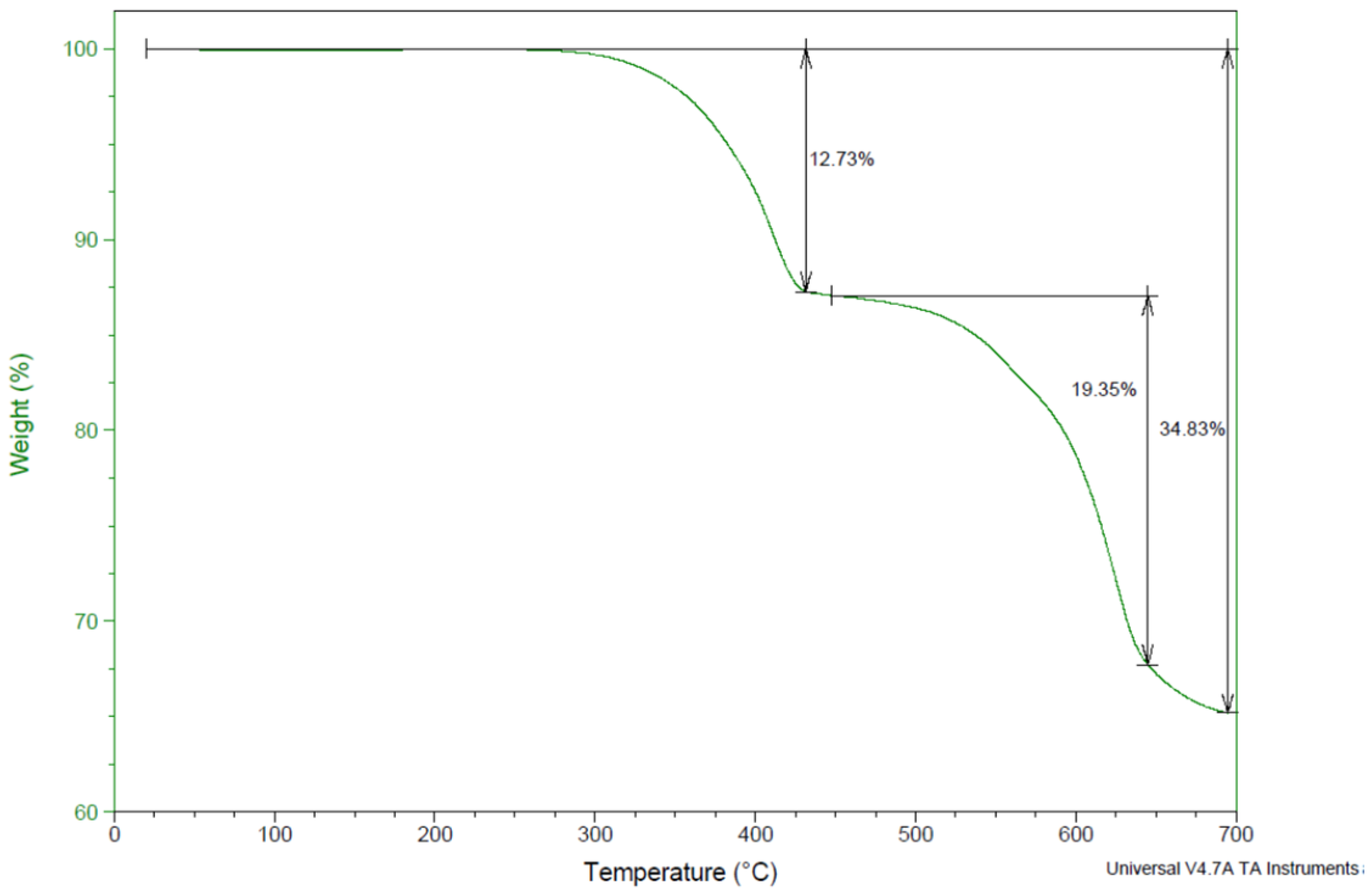
Figure 8 presents the thermogravimetric analysis of jarosite Pb–Ag sludge. The TGA curve shows that the sample is thermally stable up to 260 °C. In the temperature range 260–610 °C, a loss of mass in the sample was detected during two steps. It could be observed that a more significant mass loss from the sample started at 430 °C and was almost complete at a temperature of 610 °C, amounting to approximately 25%, and at higher temperatures it increased to 34.83%.
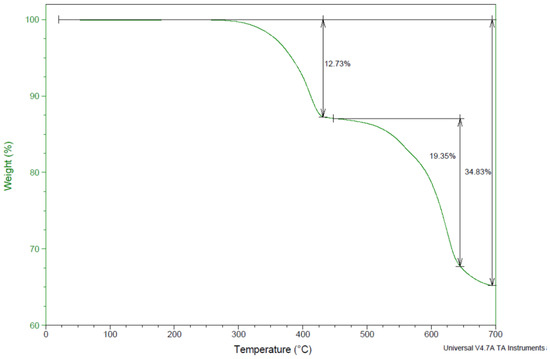
Figure 8.
TGA curve of jarosite Pb–Ag sludge.
The mechanisms of thermal decomposition and dissociation occur in four stages:
- Up to 120 °C (loss of absorbed water)
- 2.
- At 120–260 °C (dihydroxylation, loss of OH−)(M) present in jarosite can be NH4, K, Na, Pb.
- 3.
- At 260–389 °C (loss of ammonia and water)
This equation represents a loss of ammonia and water.
- 4.
- At 465–610 °C (loss SO2)
This equation represents the overall decomposition equation for iron sulfate.
This equation represents the loss of sulfur dioxide from iron sulfate.
At temperatures up to 120 °C for reaction 1, the moisture present in the sample evaporated, the mass loss was almost negligible, and it coincided with the TGA curve.
At 260–389 °C for reaction 3, the theoretical mass loss related to the loss of ammonia and water presented small deviations in relation to the TGA curve.
At 465–610 °C according to reaction 4, there were also certain deviations of the theoretical values from the results presented by the TGA curve.
Ammonium jarosite was stable up to 260 °C, after which there was a loss of structurally connected water, followed by a loss of ammonia and water at 389 °C and sulfur dioxide at temperatures higher than 465 °C.
Possible reactions during roasting include:
Destruction reactions of other sulfates, such as zinc and lead sulfates, occurred at temperatures of 740 °C and more than 1000 °C, respectively; therefore, they were not considered for this study because we were only interested in roasting at a temperature of 530 °C.
In the sample of ammonium jarosite, a subsequent analysis determined the contents of N2—1.315%, C—0.126%, and H2—1.670%, which confirmed the XRD analysis result that confirmed the presence of ammonium jarosite.
The total mass loss for up to 610 °C according to the TGA curve and the results obtained in the experiment during the drying of the ammonium jarosite sample was approximately 25%; however, there is a slight discrepancy in the theoretically calculated values we obtained based on the assumed reactions that occurred in the system during the drying process.
The loss of mass during roasting at temperatures higher than 610 °C was not important to us for these investigations because at higher temperatures, and as can be observed in reaction 4, there was a significant increase in the formation of SO2, which indicates a loss of sulfur that was required for the additional leaching of sulfate compounds in the water.
3.6. Leaching of the Roasted Jarosite Sample
After roasting the sample, leaching with water was performed. The best leaching result for the metals was obtained by jarosite roasting for 4 h at 530 °C and then the leaching of the roasted material with water. In experiment 1 (Table 1), a sulfate solution was obtained with a relatively low iron leaching value of 9.6% and high leaching values of Cu, Zn, and In, namely, 91.07%, 91.97%, and 100%, respectively; this is also one of the prerequisites for accepting the conditions in which the raw material of jarosite would be treated.
3.7. Treatment of the Sulfate Solution
The sulfate solution containing Cu, Zn, Fe, and In was treated to separate the metals present. During the precipitation phase, the pH level was controlled and maintained at 4. By applying this pH, selectivity was achieved in terms of separating Cu and Zn from Fe and In. Fe and In were precipitated in the form of hydroxides. The precipitation of Cu and Zn occurred at a pH greater than 4.5; therefore, Cu and Zn remained in the solution. Copper and zinc were present in the solution in the form of easily soluble sulfate salts (zinc and copper sulfates). The treatment of the sulfate solution with NaOH produced indium hydroxide, In(OH)3, in the form of a precipitate. The solubility of In(OH)3 in the water was very low at (6 × 10−3 g/L) [29]. In addition to indium, iron was deposited as Fe(OH)3. Precipitation was carried out by using 1 M NaOH, where 94% Fe and 98% In were precipitated from the solution. In this way, Fe and In were separated in the form of precipitate enriched with indium, which contained Fe(OH)3 and In(OH)3.
The treatment of 100 g of the Pb–Ag jarosite sample by roasting, leaching, and precipitation processes produced approximately 3 g of dry precipitate, which means that In was concentrated 30 times, indicating that 0.9% In was present in the precipitate.
It is well known in the literature that the main sources in the world for obtaining In are intermediate and waste products from the processing of zinc, lead, tin, and other ores. In these raw materials, In is present in amounts as much as 0.001% [30]. It can certainly be concluded that the treated sample is far richer in indium than the usual raw materials from which it is exploited. The percentages of tested metals in the solution after leaching and precipitation processes are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Percentages of metals in the solution after leaching and precipitation.
It can be observed from Table 4 that Fe and In are almost absent from the solution following precipitation, thus indicating nearly complete precipitation. In this way, indium and iron were separated from the basic mass of copper and zinc, which remained in the solution.
The sulfate solution can be treated further to recover Cu and Zn, and a solid leaching residue can be treated further for the recovery of Pb, Ag, and Au.
3.8. Indium Recovery Procedure
The indium-enriched hydroxide precipitate was treated with diluted 50 g/L H2SO4 at room temperature to transfer it into the solution. The acid was carefully added and stirred until the hydroxide precipitate was completely dissolved. Following its dissolution, the chemical analysis showed the presence of trivalent iron in the solution. Since Fe3+ is detrimental in the cementation process, it must be transformed into Fe2+ by reduction [31]. For this reason, SO2 was used to reduce trivalent iron present in the solution to divalent iron. Following its reduction, the acidity of the solution increased and, as the cementation process occurred at pH = 2, it was necessary to adjust the pH. The pH was adjusted by the addition of 1 M NaOH solution. Indium obtained from the sulfate solution was treated by cementation, i.e., a process in which more electronegative metal is oxidized and transferred into the solution and a greater amount of electropositive metal is reduced and precipitated from the solution.
Zinc powder is commonly used for indium cementation [32]. Al powder was used in our experiments. The cementation of In with Al powder was performed at an elevated temperature (t = 70 °C). Cementation was performed at an elevated temperature to increase the efficiency and rate of the cementation process. After the completion of the cementation, which was determined by the analysis of the In content in the solution prior to and following cementation, the cement sludge obtained was filtered and rinsed with water. The filtrate, together with rinsing water, was neutralized further to pH = 7. The cementation of In with Al occurred according to the following reaction (10):
Cementation was performed with Al due to the very easy separation of Al from In. Following cementation, the dissolution of Al with saturated NaOH solution was performed, in which In was isolated as unwrought In. The unwrought In obtained was filtered and washed with water. The filtrate, together with the washing water, was neutralized further to pH = 7. The unwrought indium obtained was not pure; however, it produced the desired indium concentrate, a mixture of the cementation sludge of indium and other metals (cadmium and copper).
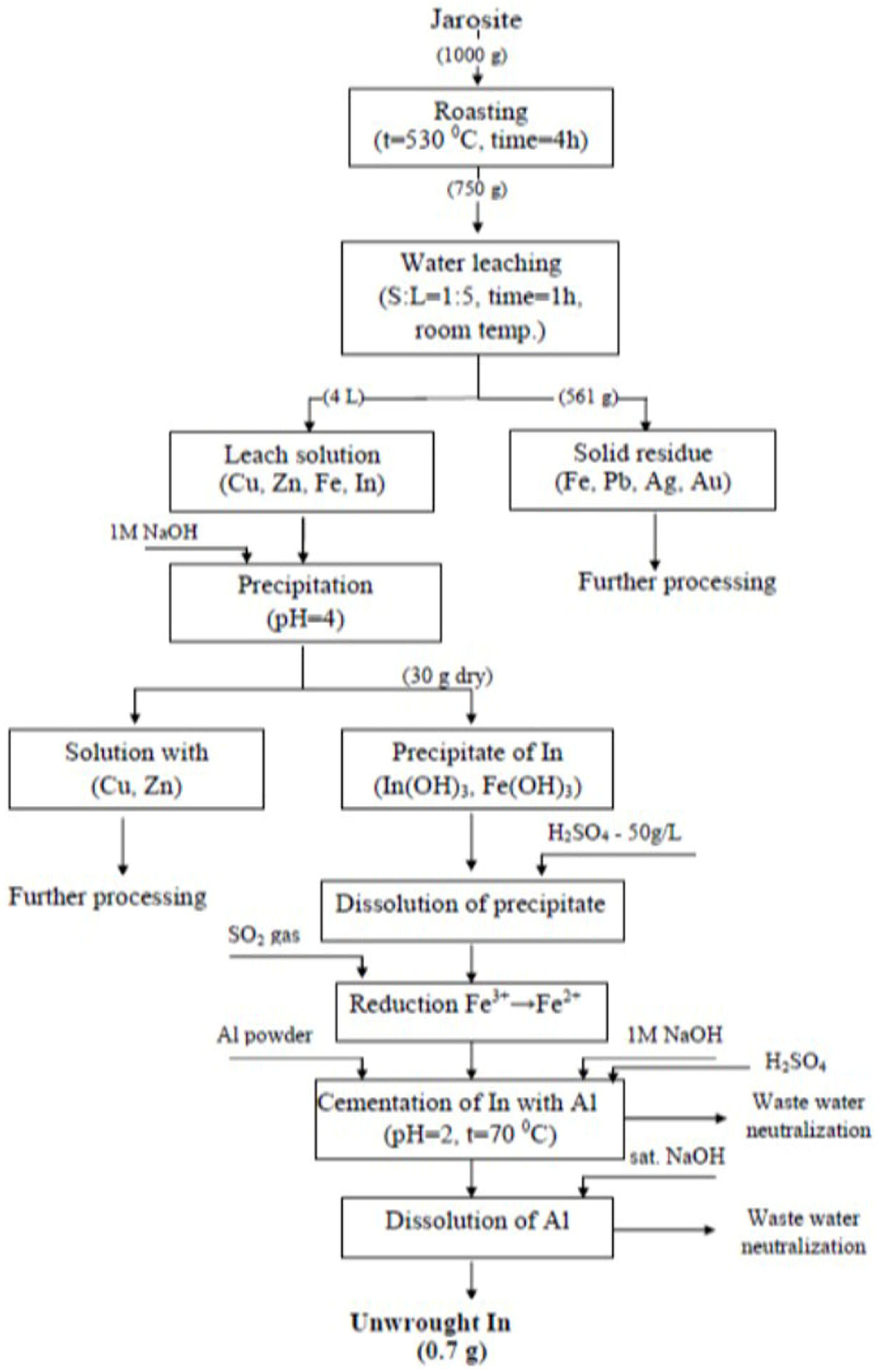
The unwrought indium contained 49.66% In, 12.62% Cu, 12.88% Fe, 9.40% As, 0.07% Ag, 0.86% Zn, and 14.5% Cd. The methodological approach for processing the jarosite tailings waste with the aim for recovering In is presented in Figure 9.
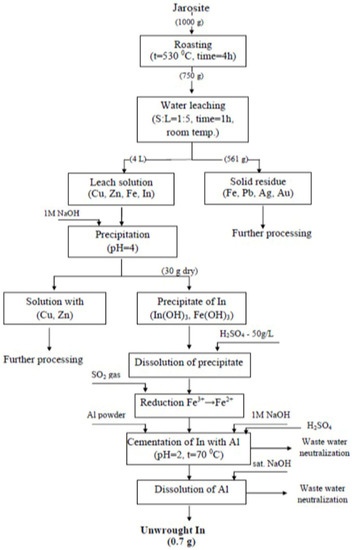
Figure 9.
Methodological approach for processing jarosite tailings waste.
4. Conclusions
Indium in jarosite tailings waste was recovered through the following main stages of treatment:
- Jarosite roasting to convert iron sulfate into insoluble hematite;
- Leaching in water in order to leach In;
- The precipitation of In from the leaching solution, 1 M NaOH;
- The dissolution of precipitate with dilute sulfuric acid and the cementation of In from solution with Al;
- The dissolution of Al with saturated NaOH, in which In was isolated as unwrought In.
This study showed that the combination of roasting and leaching provided a promising process for obtaining unwrought In. By using methods such as chemical processes, electrolytic refining, vacuum distillation, and zonal refining, it was possible to refine raw indium into high-purity indium. By treating the jarosite sample, a technological procedure for obtaining In, Cu, Zn, Pb, Ag, and Au was developed and presented in the technological schema. In this study (part I), we presented a procedure for obtaining raw In; in part II, a procedure for obtaining commercial products based on other metals was presented. Compared to the research conducted by many authors, our proposed technological process was not only efficient, but can be both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Future research should aim to valorize all useful metals from waste to commercial products.
Author Contributions
Investigation, Writing—original draft, Data curation, Visualization, Writing—review and editing, M.J. and V.C., Conceptualization, Methodology, Ž.K., Resources, Validation, Funding acquisition, L.A., Supervision, S.M., Investigation, Data, D.B., Review, I.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank Elixir Zorka, Serbia, for providing the sample and for their financial support in obtaining a solution to manage this waste; contract number 1061/19.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia, Grant No. 451-03-47/2023-01/200052 and 451-03-47/2023-01/200135. The authors wish to thank Nikoli Vukoviću, the Institute of Technology of Nuclear and Other Mineral Raw Materials, and Emini Požega and Suzani Dragulović from the Mining and Metallurgy Institute Bor for their assistance while preparing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Reyes, A.I.; Patiño, F.; Flores, U.M.; Pandiyan, T.; Cruz, R.; Gutiérrez, J.E.; Reyes, M.; Flores, H.V. Dissolution rates of jarosite-type compounds in H2SO4 medium: A kinetic analysis and its importance on the recovery of metal values from hydrometallurgical wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conić, V.; Rajčić Vujasinović, M.; Trujić, V.; Cvetkovski, V. Copper, Zinc, and Iron Bioleaching from a Polymetallic Sulphide Concentrate. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 3688–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-X.; Lv, J.F.; Liu, W.; Qin, W.-Q.; Wen, S.-M. An innovative technology for recovery of zinc, lead and silver from zinc leaching residue. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2016, 52, 943–954. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Jiang, B. Study on recovery of lead, zinc, iron from jarosite residues and simultaneous sulfur fixation by direct reduction. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 54, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Rashchi, F.; Dashti, A.; Arabpour-Yazdi, M.; Abdizadeh, H. Anglesite flotation: A study for lead recovery from zinc leach residue. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutandula, M.S.; Maloba, B. Recovery of cobalt and copper through reprocessing of tailings from flotation of oxidized ores. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojević, D.; Filipović-Petrović, L. Doprinos integrisanoj valorizaciji metala u hidrometalurgiji cinka. Zaštita Mater. 2014, 55, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sinadinović, D.; Kamberović, Ž.; Šutić, A. Leaching Kinetics of lead from Lead(II) Sulphate in Aqueous Calcium and Magnesium Chloride Solution. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 47, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerolli-Mustafa, M.; Ćurković, L.; Fajković, H.; Rončević, S. Ecological Risk Assessment of Jarosite Waste Disposal. Croat. Chem. Acta 2015, 88, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creedy, S.; Glinin, A.; Matusewics, R.; Hughes, S.; Reuter, M. Outotec Ausmelt Technology for Treating Zinc Residues. World Metall.-Erzmetall 2013, 66, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, S.; Reuter, M.A.; Baxter, R.; Kaye, A.; Hughes, S.; Reuter, M.A.; Baxter, R.; Kaye, A. Ausmelt Technology for Lead and Zinc Processing. Lead Zinc 2008, 2008, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kamberović, Ž.; Gajić, N.; Korać, M.; Jevtić, S.; Sokić, M.; Stojanović, J. Technologically Sustainable Route for Metals Valorization from Jarosite-PbAg Sludge. Minerals 2021, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, A.; en Sunkar, A.S.; Topkaya, Y.A. Zinc and lead extraction from Cinkur leach residues hydrometallurgical method. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Turan, M.D.; Altundoğan, H.S.; Tümen, F. Recovery of zinc and lead from zinc plant residue. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 75, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, P.; Saxena, M.; Asolekar, S.R. Hazardous jarosite use in developing nonhazardous product for engineering application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, P.; Saxena, M.; Asolekar, S.R. Recycling hazardous jarosite waste using coal combustion residues. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 1342–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelino, M. Recycling of zinc-hydrometallurgy wastes in glass and glass ceramic materials. Waste Manag. 2000, 20, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisciella, P.; Crisucci, S.; Karamanov, A. Chemical durability of glasses obtained by vitrification of industrial wastes. Waste Manag. 2001, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Seyrankaya, A.; Cöcen, I. Extraction of Lead and Silver from Zinc Leach Residue by Brine Leaching. In Proceedings of the XIIth International Mineral Processing Symposium, Cappadocia Nevsehir, Turkey, 6–8 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yudaev, P.; Chistyakov, E. Chelating Extractants for Metals. Metals 2022, 12, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.E.; Watson, J.L.; Peter, J. Zinc Production-a Survey of Existing Smelters and Refineries. Lead-Zinc 2000, 2000, 205–225. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Wang, G.; Fan, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Pan, J.; Wang, R. Preparation of high purity indium by chemical purification: Focus on removal of Cd, Pb, Sn and removal mechanism. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 200, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitbayeva, B.; Argimbayeva, A.; Rakhymbay, G.; Avchukir, K.; Tassibekov, K.; Nauryzbayev, M. Refining of Rough Indium by Method of Reactionary Electrolysis. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences REE-2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 23–25 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zelem, J. Application of Amalgam Metallurgy to the Extraction of Indium, Bachelors Theses and Reports, 1928–1970, Summer 6-4-1954, Montana Tech Library, Digital Commons @ Montana Tech. Available online: https://digitalcommons.mtech.edu/bach_theses (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Li, D.-S.; Dai, Y.-N.; Yang, B.; Liu, D.-C. Purification of indium by vacuum distillation and its analysis. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfantazi, A.M.; Moskalyk, R.R. Processing of indium: A review. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conić, V.; Božić, D.; Dragulović, S.; Avramović, L.J.; Jonović, R.; Bugarin, M. Research on acid leaching of Cu, Zn and In from Jarosite waste. In Proceedings of the XIV International Mineral Processing and Recycling Conference, Belgrade, Serbia, 12–14 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, R.; Wills, A.; Kloprogge, J.; Martens, W. Thermal decomposition of ammonium jarosite (NH4)Fe3(SO4)2(OH)6. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 84, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Richeys, R.; Baird, J. Chemical Equilibrium and Critical Phenomena: Solubility of Indium Oxide in Isobutyric Acid Water Near the Consolute Point. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 54, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokanc, M.; Eggert, R.; Redlinger, M. The Availability of Indium: The Present, Medium Term, and Long Term; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2015; pp. 1–79. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy16osti/62409.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Kangas, P.; Lundström, M.; Orko, I.; Koukkari, P. The Jarogain Process for Metals Recovery from Jarosite and Electric Arc Furnace Dust; VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd.: Espoo, Finland, 2017; ISBN 978-951-38-8596-0. ISSN 2242-1211. [Google Scholar]
- Rocchetti, L.; Amato, A.; Beolchini, F. Recovery of indium from liquid crystal displays. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 116, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).