Hybrid Model for Optimisation of Waste Dump Design and Site Selection in Open Pit Mining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hybrid Model Development
2.1. Methods
- Random selection (Monte Carlo simulation)—to simulate the geometry of potential solutions,
- Genetic algorithm—to optimise solutions,
- Multi-criteria decision making—AHP method—for defining variable values,
- Heuristic method—for expert interpretation and finalisation of solutions
2.1.1. The Monte Carlo Method
- Generation of a static model (process functions),
- Defining input parameters using probability distribution functions,
- Generation of random variables from the set of distribution of input parameters,
- Analysis of the obtained results.
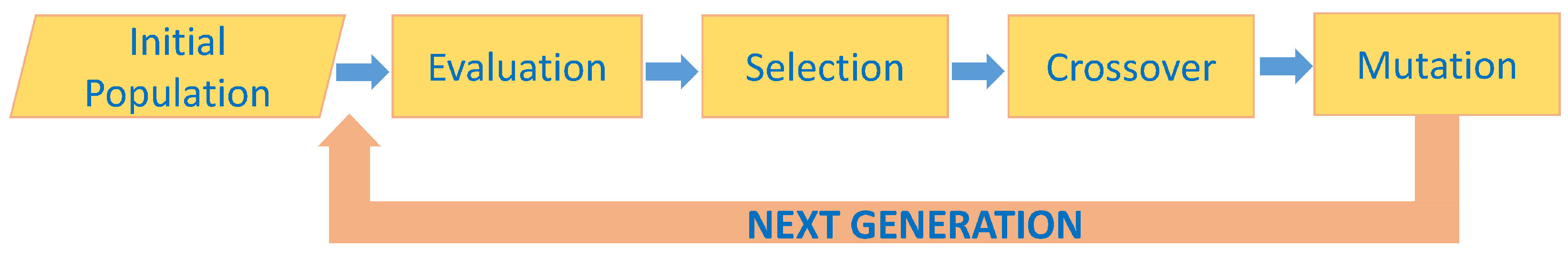
2.1.2. Genetic Algorithm
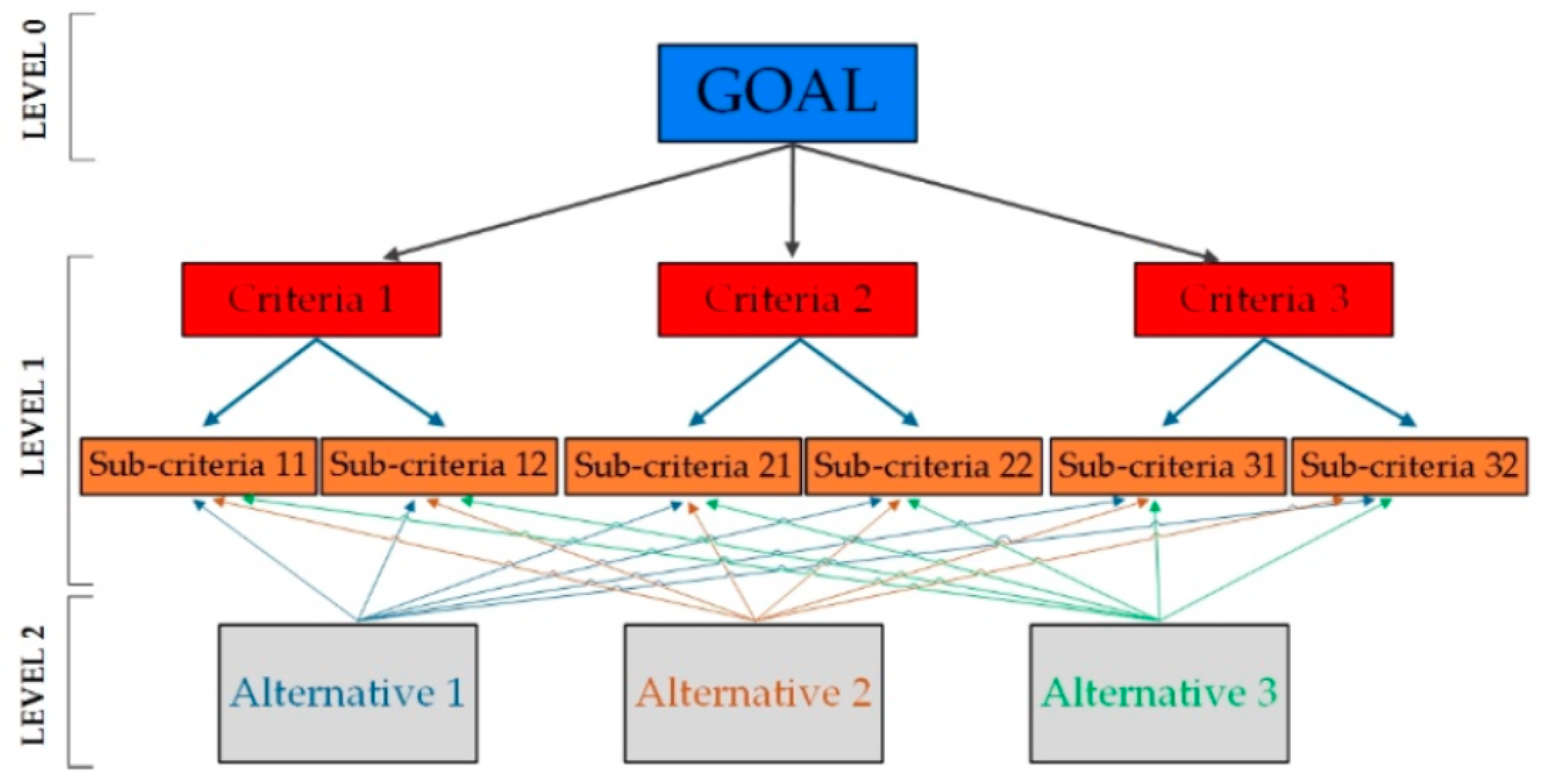
2.1.3. Analytic Hierarchy Process
- Define the unstructured problem and clearly state the objectives and outcomes.
- Decompose the complex problem into a hierarchical structure with decision elements (criteria, detailed criteria and alternatives).
- Pairwise comparisons—assess the relative importance of criteria and alternatives using pairwise comparisons (using a scale that reflects their relative preference or importance).
- Derive priority weights—based on pairwise comparisons; the AHP calculates priority weights for each element in the hierarchy (these weights quantify the relative importance of each element in achieving the goal).
- Consistency check—evaluates the consistency of the pairwise comparisons to ensure their reliability.
- Aggregation and ranking—combine the priority weights to obtain a comprehensive ranking of the alternatives.
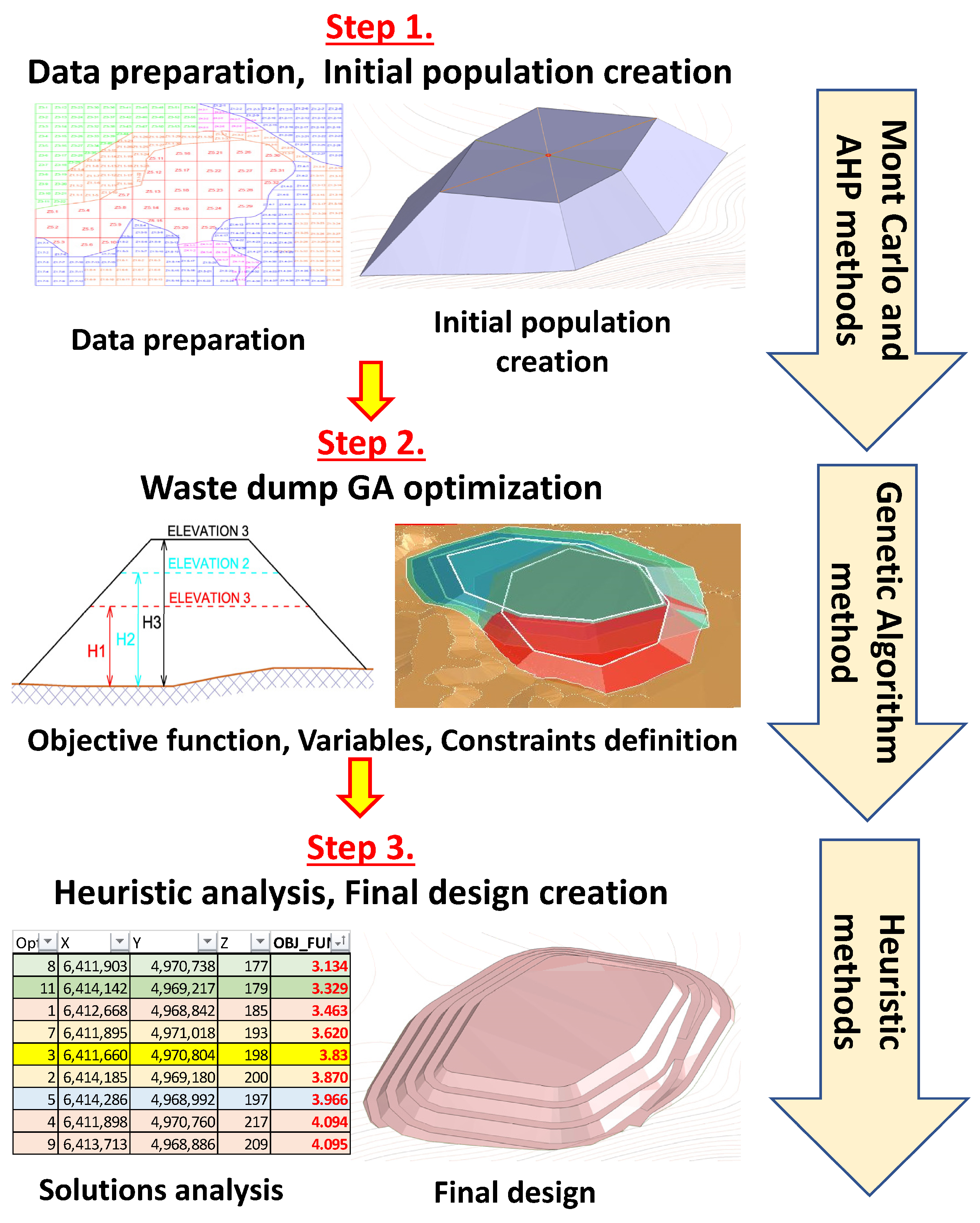
2.2. Model Algorithm
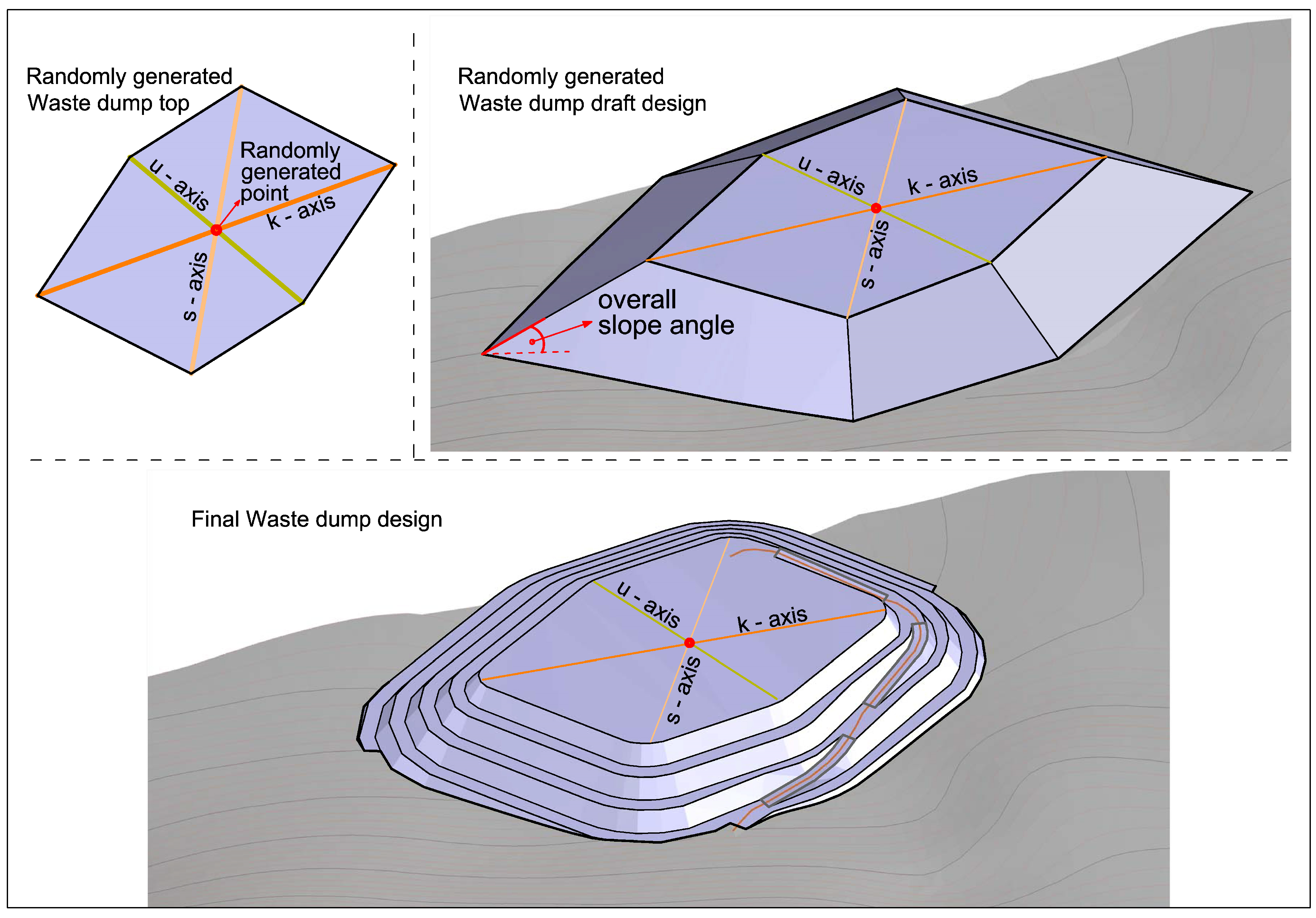
2.2.1. Step 1—Data Preparation and Initial Population Creation
- Waste dump capacity,
- Overall slope angle of the waste dump,
- Basic geometry (shape) and elevation of waste dump top area,
- Definition of terrain zones to be analysed using the model and zone evaluation.
2.2.2. Step 2—Waste Dump Optimisation—Objective Function, Constraints and Variables
- Costs related to the value of the land on which the waste dump is built and
- Haulage costs.
- waste dump capacity (volume),
- waste dump elevation,
- waste dump position in XY plane.
2.2.3. Step 3—Heuristic Analysis of Optimization Results and Final Waste Dump Design
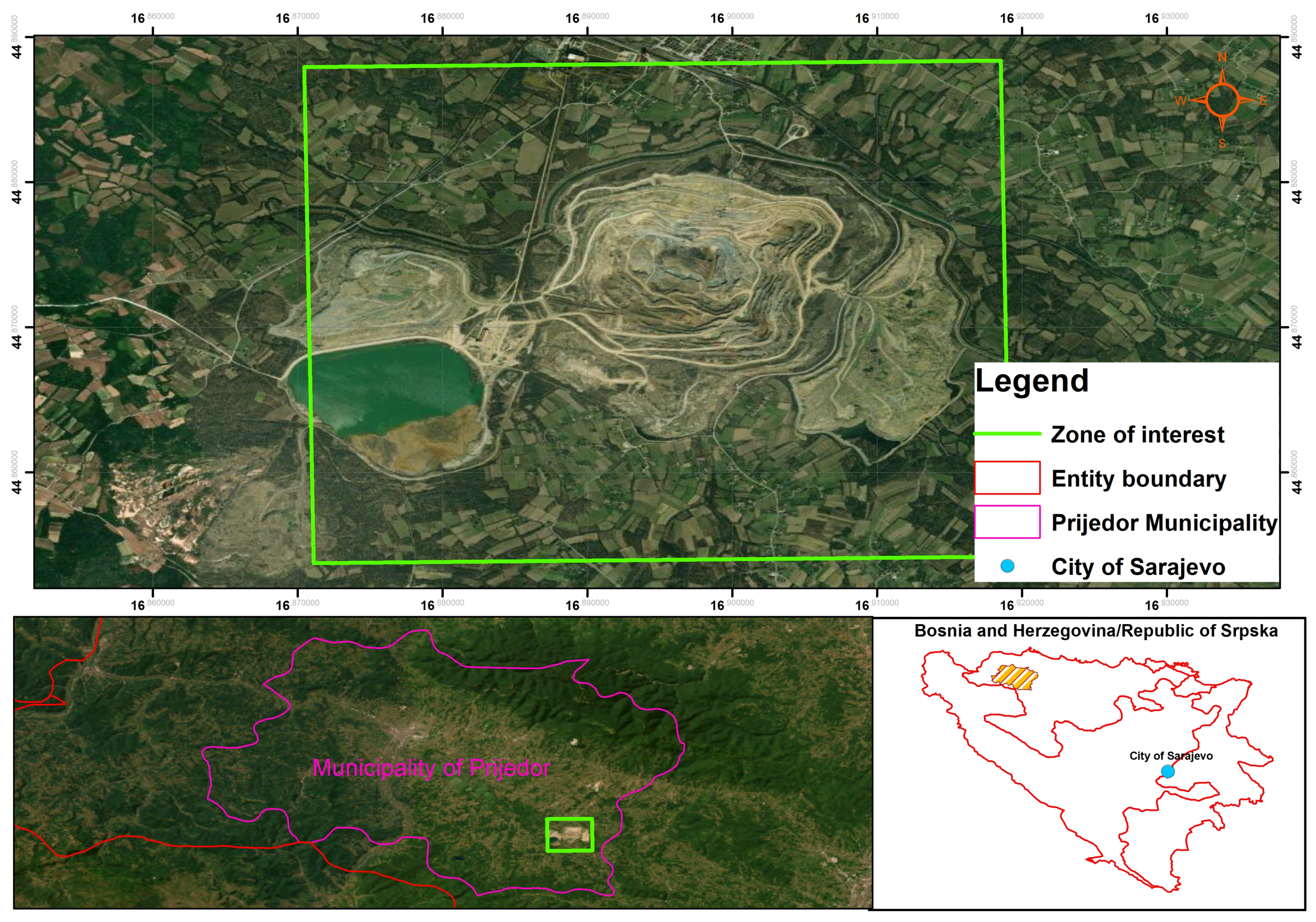
3. Case Study
Buvac Waste Dump Optimization
4. Analysis and Results
- Bench height is 10 m, Bench angle is 33°, Safety bench width is 40 m,
- Ramp gradient is 8%, Ramp width is 25 m.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dincer, T. Application pit optimization algorithms beyond open pit limits. In Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Mining Congress and Exhibition of Turkey: IMCET 2001, Ankara, Turkey, 19–22 June 2001; pp. 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- Scoble, M.; Klein, B.; Dunbar, W.S. Mining waste: Transforming mining system for waste management. Int. J. Surf. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2003, 17, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarie, S.; Gamache, M. Overview of solution strategies used in truck dispatching systems for open pit mines. Int. J. Surf. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2002, 16, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, B.; Kumral, M. A system-wide approach to minimize the operational cost of bench production in open-cast mining operations. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, Y.; Bonates, E. Truck and shovel dispatching rules assessment using simulation. Min. Sci. Technol. 1987, 5, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subtil, R.F.; Silva, D.M.; Alves, J.C. A practical approach to truck dispatch for open pit mines. In Proceedings of the 35th APCOM Symposium, Wollongong, Australia, 24–30 September 2011; pp. 765–778. [Google Scholar]
- Tabelin, C.B.; Dallas, J.A.; Casanova, S.; Pelech, T.M.; Bournival, G.; Saydam, S.; Canbulat, I. Towards a low-carbon society: A review of lithium resource availability, challenges and innovations in mining, extraction and recycling, and future perspectives. Miner. Eng. 2021, 163, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phengsaart, T.; Srichonphaisan, P.; Kertbundit, C.; Soonthornwiphat, N.; Sinthugoot, S.; Phumkokrux, N.; Juntarasakul, O.; Maneeintr, K.; Numprasanthai, A.; Park, I.; et al. Conventional and recent advances in gravity separation technologies for coal cleaning: A systematic and critical review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julapong, P.; Numprasanthai, A.; Tangwattananukul, L.; Juntarasakul, O.; Srichonphaisarn, P.; Aikawa, K.; Park, I.; Ito, M.; Tabelin, C.B.; Phengsaart, T. Rare Earth Elements Recovery from Primary and Secondary Resources Using Flotation: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelin, C.B.; Park, I.; Phengsaart, T.; Jeon, S.; Villacorte-Tabelin, M.; Alonzo, D.; Yoo, K.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. Copper and critical metals production from porphyry ores and E-wastes: A review of resource availability, processing/recycling challenges, socio-environmental aspects, and sustainability issues. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 170, 105610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumral, M.; Dimitrakopoulos, R. Selection of waste dump sites using a tabu search algorithm. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2008, 108, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hustrulid, W.A.; Kuchta, M.; Martin, R.K. Open Pit Mine Planning and Design, Two Volume Set & CD-ROM Pack, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Topal, E.; Williams, D. Waste rock dumping optimization using mixed integer programming (MIP). Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2013, 27, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, G.M. The Sustainability of Mining in Australia: Key Production Trends and Environmental Implications for the Future; Research Report No. RR5; Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University and Mineral Policy Institute: Melbourne, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Northey, S.; Mohr, S.; Mudd, G.M.; Weng, Z.; Giurco, D. Modelling future copper ore grade decline based on a detailed assessment of copper resources and mining. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, G.; Mudd, G.; Valero, A.; Valero, A. Decreasing Ore Grades in Global Metallic Mining: A Theoretical Issue or a Global Reality? Resources 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, G.; Palacios, J.L.; Valero, A. The influence of ore grade decline on energy consumption and GhG emissions: The case of gold. Environ. Dev. 2022, 41, 100683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Topal, E.; Williams, D.J. Optimisation of waste rock placement using mixed integer programming. Min. Tech. 2014, 123, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Topal, E.; Ramazan, S. Optimising the long-term mine waste management and truck schedule in a large-scale open pit mine. Min. Technol. 2016, 125, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Li, Y.; Topal, E.; Williams, D.J. A new tool for optimisation of mine waste management in potential acid forming conditions. In Proceedings of the Tailings and Mine Waste Management for the 21st Century, Sydney, Australia, 27–28 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hajarian, A.; Osanloo, M. A New Developed Model to Determine Waste Dump Site Selection in Open Pit Mines: An Approach to Minimize Haul Road Construction Cost. Int. J. Eng. IJE 2020, 33, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahba, S.; Arjmandi, R.; Monavari, M.; Ghodusi, J. Application of multi-attribute decision-making methods in SWOT analysis of mine waste management (case study: Sirjan’s Golgohar iron mine, Iran). Resour. Policy 2017, 51, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanloo, M.; Ataei, M. Factors affecting the selection of site for arrangement of pit rock-dumps. J. Min. Sci. 2003, 39, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmat, A.; Osanloo, M.; Shirazi, A.M. New approach for selection of waste dump sites in open pit mines. Min. Tech. 2008, 117, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani-Chamzini, A.; Ahmadi, Z.; Oraee, K.; Basiri, M.H. Waste Dump Site Selection by Using Fuzzy VIKOR. In Proceedings of the 5th Conference of Applied Geology and the Environment, Eslamshahr, Iran, 7 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mensah, F. Integrating Global Positioning Systems and Geographic Information Systems in Mine Waste disposal: The Case of Goldfields Ghana Limited. Master’s Thesis, University of Mines and Technology, Tarkwa, Ghana, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Suleman, H.A.; Baffoe, P.E. Selecting suitable sites for mine waste dumps using GIS techniques at Goldfields, Damang Mine. Ghana Min. J. 2017, 17, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Bao, J.J.; Liu, Y.J. Discussion on the safety distance between the bottom of the inner dump and the stope. Surf. Coal Min. Technol. 2003, 2, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, D.; Kainthola, A.; Gupte, S.S.; Singh, T.N. A finite element approach of stability analysis of internal dump slope in Wardha valley coal field, India, Maharashtra. Am. J. Min. Metall. 2013, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cheskidov, V.I.; Norri, V.K. Stripping with direct dumping in Kuzbass open pit mines: The current state and prospects. J. Min. Sci. 2016, 52, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, D.; Banković, M.; Rupar, V.; Milisavljević, V.; Cvjetić, A.; Kržanović, D. Waste Dump Design Optimization, Case Study Open Pit Drmno. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium Mining and Environmental Protection, MEP 17, Vrdnik, Serbia, 21–24 June 2017; pp. 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, Y.A.; Kumral, M. A landfill based approach to surface mine design. J. Cent. South Univ. 2018, 25, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, D. Research on Inpit Dumping Height during Tracing Mining Period between Two Adjacent Surface Coal Mines. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3450584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaykov, D.; Koprev, I. Rationalising The Location And Design Of The Waste Dump In The Case Of Open-Pit Mining. Sustain. Extr. Process. Raw Mater. 2020, 1, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.J.; Scott, P.; Johnston, D.; Lee, G. Rock Dump Design to Limit Potential Acid Drainage. In Proceedings of the First International Seminar on the Management of Rock Dumps, Stockpiles and Heap Leach Pads, Perth, Western Australia, 5–6 March 2008; Australian Centre for Geomechanics (ACG). pp. 207–217. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, C.A.; Ercelebi, S.; Onsel, I.E.; Ozkan, M. Open pit mine waste dump area design based on stability principles. In Proceedings of the 24th International Mining Congress and Exhibition of Turkey, IMCET’15, Antalya, Turkey, 14–17 April 2015; pp. 570–578. [Google Scholar]
- Puell Ortiz, J. Methodology for a dump design optimization in large-scale open pit mines. Cogent Eng. 2017, 4, 1387955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Ulam, S. The Monte Carlo Method. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1949, 44, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.L. Metropolis, Monte Carlo and the MANIAC. Los Alamos Sci. 1986, 14, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Vujić, S.; Ivić, A. Mathematical Methods in Mining and Geology; Faculty of Mining and Geology, University of Belgrade: Beograd, Serbia, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović, D. Open Pit Mine Optimization and Planning with Stochastic Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Mining and Geology, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvageau, M.; Kumral, M. Cash flow at risk valuation of mining project using Monte Carlo simulations with stochastic processes calibrated on historical data. Eng. Econ. 2018, 63, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Jian, Z.; Jianglan, L. Mining Investment Risk Analysis Based on Monte Carlo Simulation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Management of e-Commerce and e-Government, Wuhan, China, 5–6 November 2011; pp. 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacz, M.; Kryzia, D.; Kryzia, K. Assessment of sustainable development of hard coal mining industry in Poland with use of bootstrap sampling and copula-based Monte Carlo simulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; The University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, Michigan, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt, R. Stan Ulam, John von Neumann, and the Monte Carlo method. Los Alamos Sci. Spec. Issue 1987, 15, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanković, R.; Lilić, N.; Obradović, I. Prediction of air pollution by coupling neural networks and genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the Informatics, Ecology and Management in Surface Mining of Mineral Resources, Aranđelovac, Serbia, 3 June 1997; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, P.C.; Huang, W.H.; Ting, C.J. Dynamic diversity control in genetic algorithm for mining unsearched solution space in TSP problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Karaboga, D. Intelligent Optimisation Techniques: Genetic Algorithms, Tabu Search, Simulated Annealing and Neural Networks; Springer: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Khodaiari, A.A.; Jafari, A.J.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. Production scheduling of open-pit mines using genetic algorithm: A case study. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2020, 15, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, R.; Pourrahimian, Y. A systematic review of artificial intelligence and data-driven approaches in strategic open-pit mine planning. Resour. Policy 2022, 77, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Cao, M.; Wang, C.; Yu, N.; Qing, H. Research On Mining Maximum Subsidence Prediction Based On Genetic Algorithm Combined with Xgboost Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.R.; Shahabi, R.S. Cutoff grade optimization in open pit mines using genetic algorithm. Resour. Policy 2018, 55, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paithankar, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Goodfellow, R. Open-pit mining complex optimization under uncertainty with integrated cut-off grade based destination policies. Resour. Policy 2021, 70, 101875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Singh, J.; Kumral, M.; Ramirez Ruiseco, J. Exploring Deep Learning for Dig-Limit Optimization in Open-Pit Mines. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 2085–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banković, M.; Stevanović, D.; Pešić, M.; Tomašević, A.; Kolonja, L.J. Improving efficiency of thermal power plants through mine coal quality planning and control. Therm. Sci. 2018, 22, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T. The Analytical Hierarchy Process; Mc-Graw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Pessoa, I.C.; Trojan, F.; Oliveira, G.A.; Setti, D. The statistical sampling about levels of utilization of multi-criteria methods to solve problems in POM. In Proceedings of the POMS 26th Annual Conference-Production and Operations Management Society, Wasington, DC, USA, 8–11 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic, I.; Djenadic, S.; Ignjatovic, D.; Jovancic, P.; Subaranovic, T.; Ristovic, I. Multi-Criteria Approach for Selecting Optimal Dozer Type in Open-Cast Coal Mining. Energies 2019, 12, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T. Decision-making with the AHP: Why is the principal eigenvector necessary. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 145, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.I.; Chen, W.C.; Chang, C.J. A fuzzy AHP and BSC approach for evaluating performance of IT department in manufacturing industry in Taiwan. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 34, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petković, D.; Radovanović, M. Primena genetskog algoritma za optimizaciju obradnih procesa na primeru struganja. IMK-14-Istraživanje I Razvoj 2011, 17, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Matlab, MathWorks, Additional Information. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Excel, Microsoft, Additional Information. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/excel (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Geovia Surpac, Dessault Systemes, Additional Information. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/products-services/geovia/products/surpac/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).

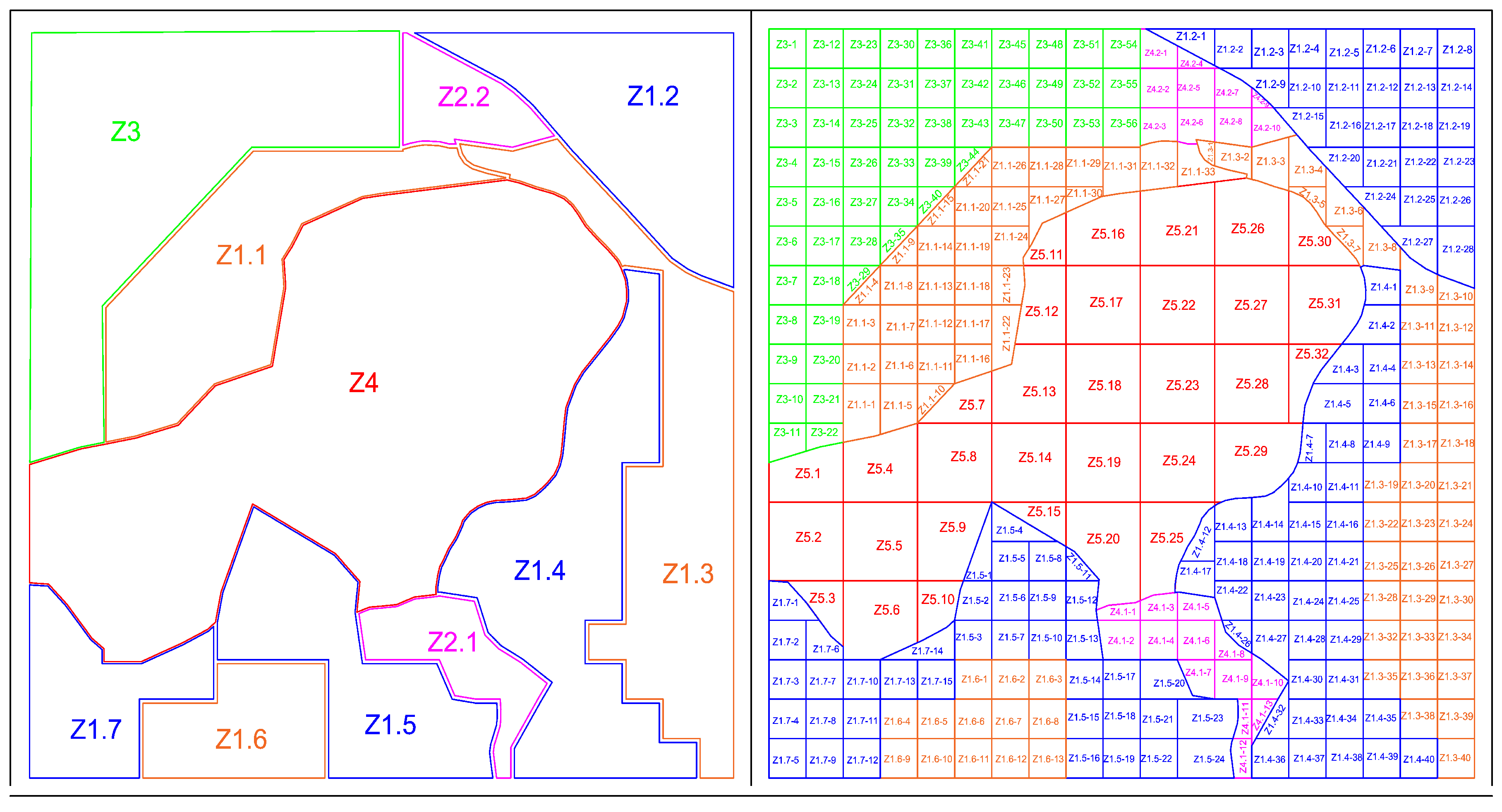
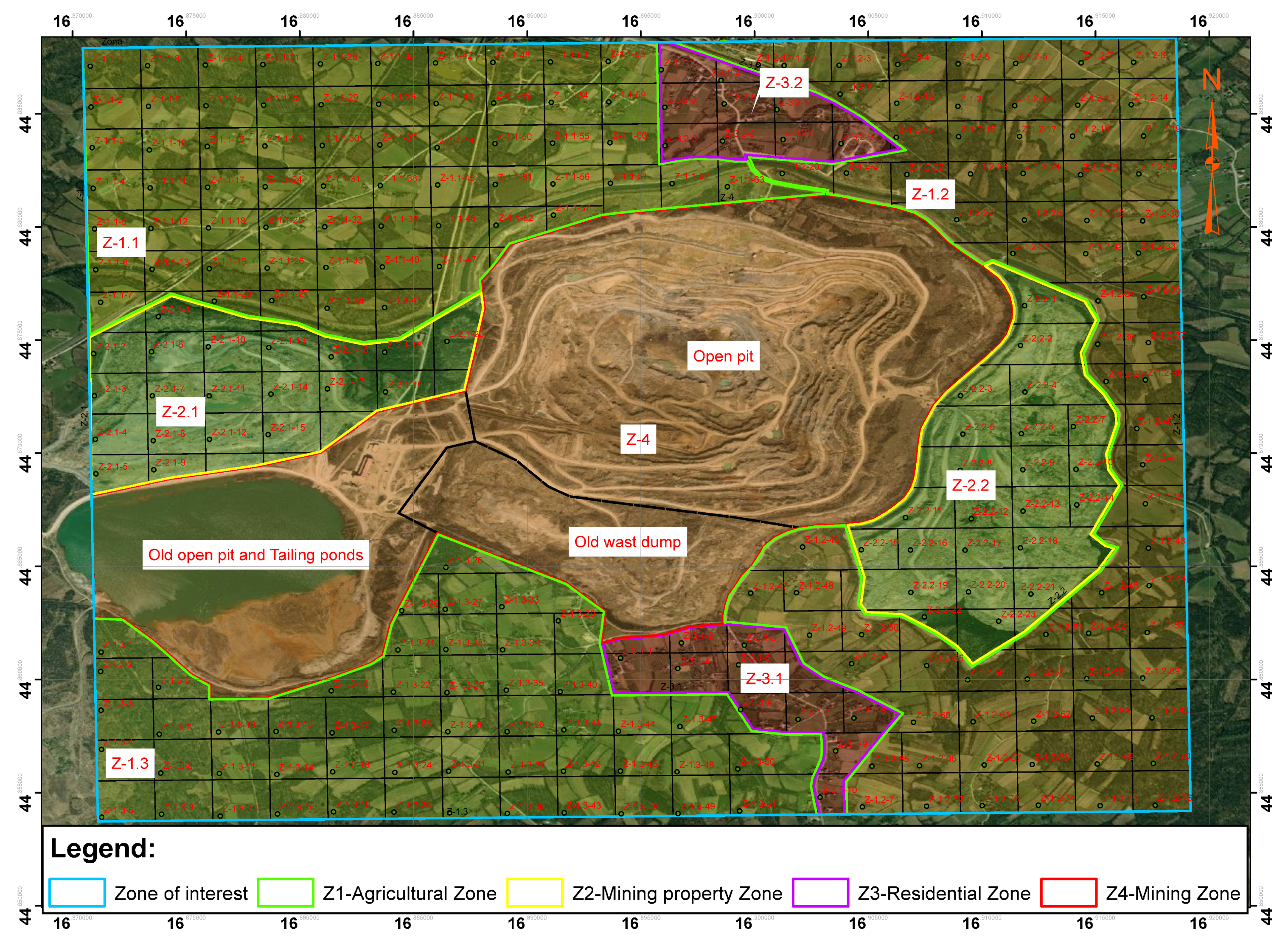
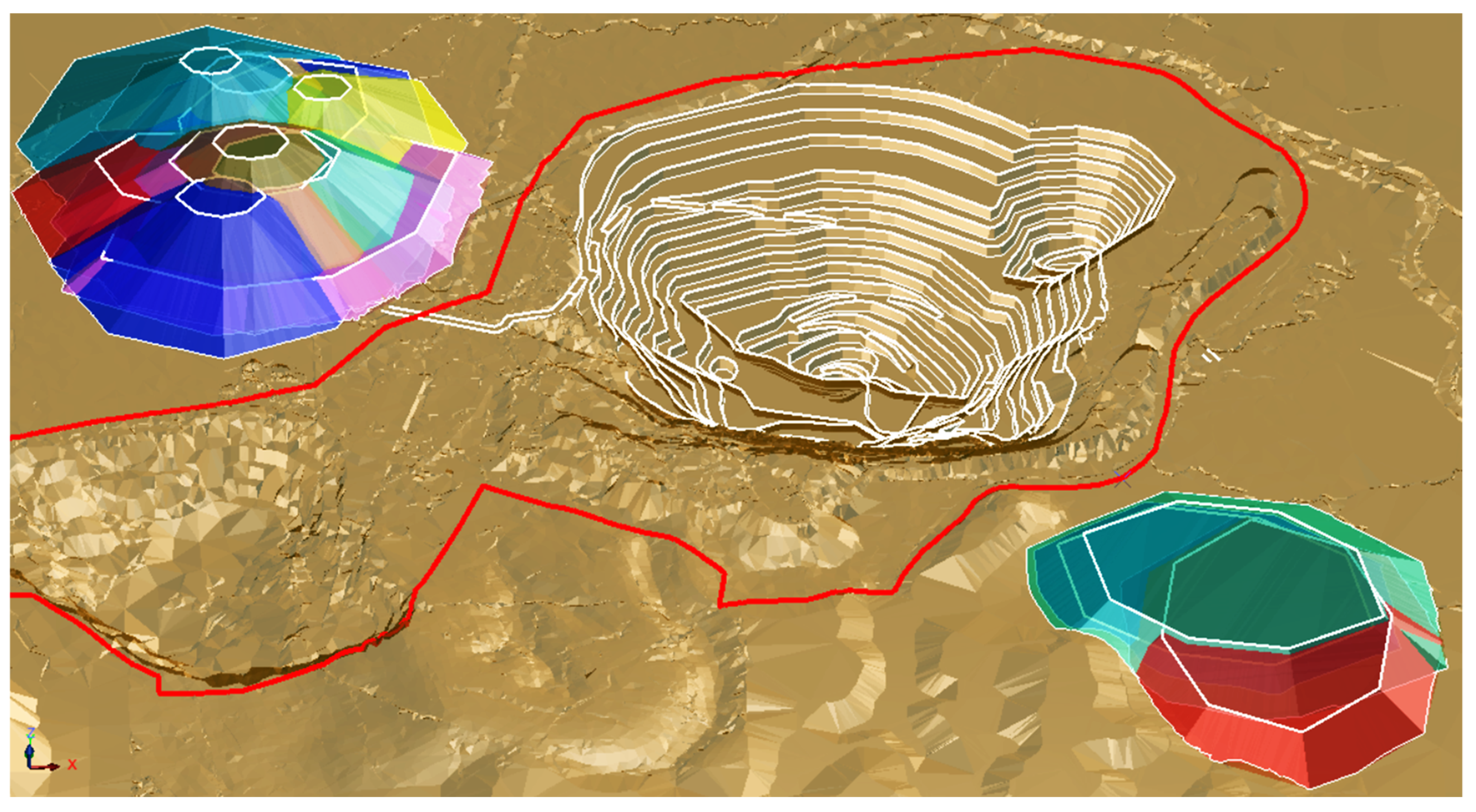
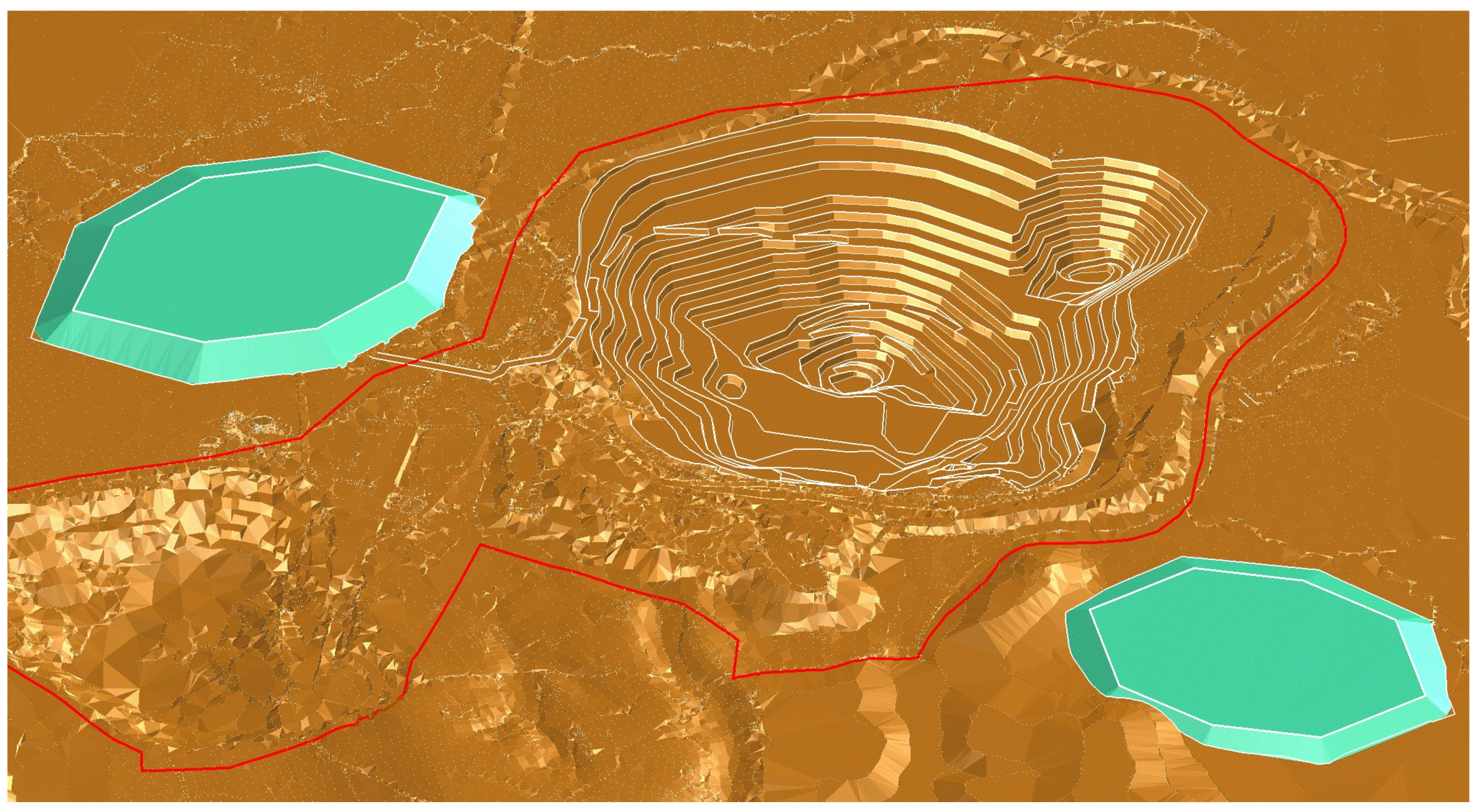
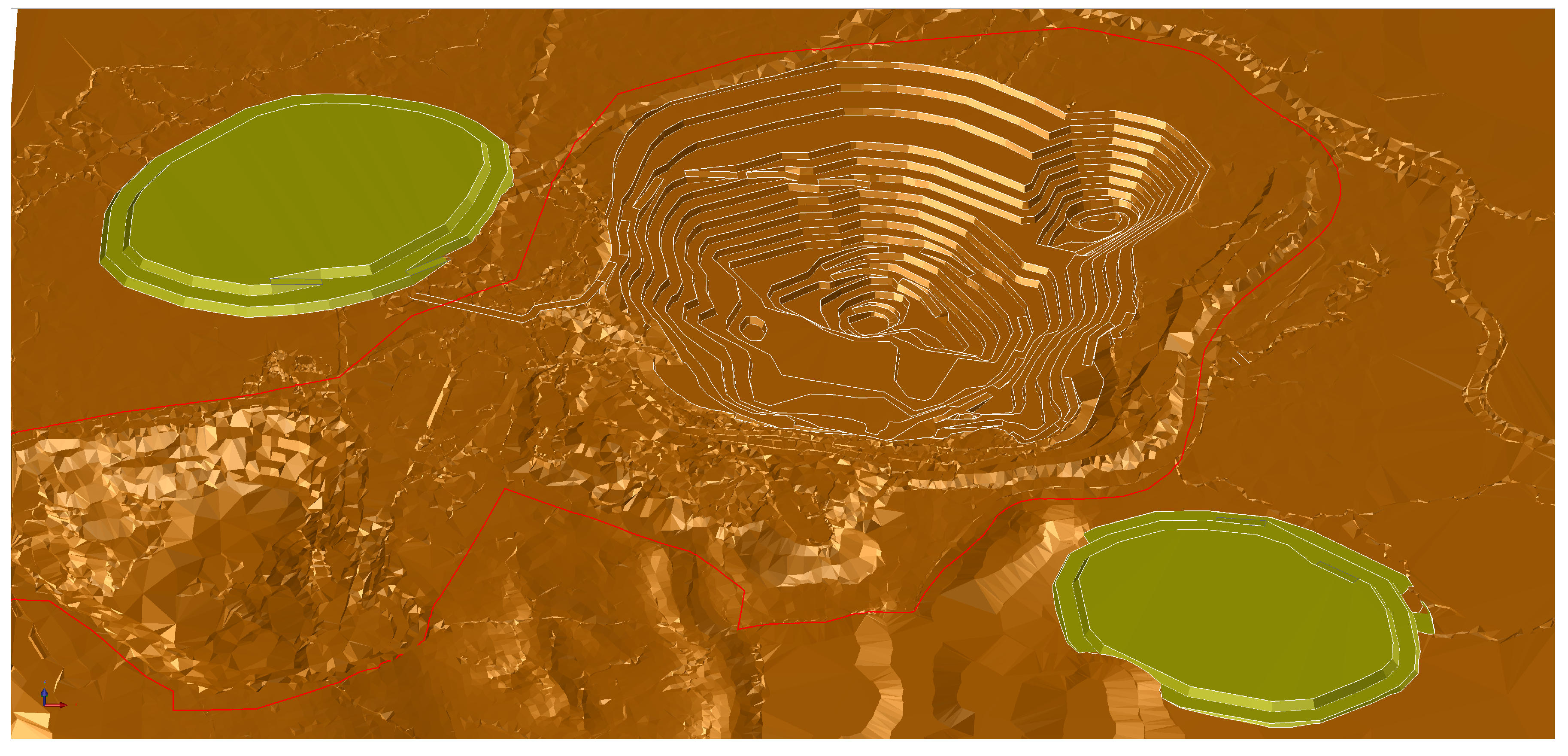
| Factor | Coefficient | Rang | Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potential open pit expansion | 0.657 | 1 | K1 |
| Potential administrative obstacles | 0.105 | 3 | K2 |
| Increased environmental impact | 0.238 | 2 | K3 |
| Model Operational Mod | Volume Range (m3) | Number of Initial Population Members | Number of Optimisations | Generations Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mod 2 | 6 × 106–22 × 106 | 2250 | 15 | 5 |
| Solution Rang Number | Point Coordinates | Haul Distance Component (m) | Costs (mil EUR ) | Waste Dump Volume (106 m3) | Objective Function (EUR/m3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | Horiz. | Verti. | C1 | C2 | C3 | |||
| 1. | 6,411,903 | 4,970,738 | 177 | 1288 | 1740 | 13.82 | 28.02 | 0.19 | 13.05 | 3.13 |
| 2. | 6,414,142 | 4,969,217 | 179 | 1459 | 1786 | 10.21 | 18.75 | 0.14 | 8.12 | 3.33 |
| 3. | 6,411,895 | 4,971,018 | 193 | 1430 | 2053 | 13.68 | 29.46 | 0.14 | 11.96 | 3.62 |
| 4. | 6,412,230 | 4,971,409 | 192 | 1465 | 2048 | 21.05 | 44.15 | 0.20 | 17.97 | 3.64 |
| 5. | 6,411,660 | 4,970,804 | 198 | 1537 | 2158 | 12.23 | 25.76 | 0.14 | 9.95 | 3.83 |
| 6. | 6,414,185 | 4,969,180 | 200 | 1516 | 2207 | 24.22 | 52.90 | 0.18 | 20.48 | 3.87 |
| 7. | 6,414,286 | 4,968,992 | 197 | 1719 | 2150 | 24.70 | 46.32 | 0.20 | 17.96 | 3.97 |
| 8. | 6,411,898 | 4,970,760 | 217 | 1301 | 2537 | 16.43 | 48.06 | 0.15 | 15.79 | 4.09 |
| 9. | 6,411,834 | 4,971,128 | 209 | 1543 | 2374 | 10.63 | 24.53 | 0.11 | 8.61 | 4.10 |
| 10. | 6,412,016 | 4,971,044 | 216 | 1348 | 2520 | 9.36 | 26.26 | 0.12 | 8.68 | 4.12 |
| 11. | 6,411,836 | 4,970,765 | 216 | 1359 | 2524 | 20.39 | 56.78 | 0.16 | 18.75 | 4.12 |
| 12. | 6,411,942 | 4,970,816 | 220 | 1286 | 2598 | 19.81 | 60.04 | 0.16 | 19.26 | 4.15 |
| 13. | 6,411,761 | 4,970,614 | 220 | 1378 | 2606 | 14.70 | 41.73 | 0.12 | 13.34 | 4.24 |
| 14. | 6,411,836 | 4,970,765 | 236 | 1359 | 2912 | 21.73 | 69.84 | 0.17 | 19.98 | 4.59 |
| 15. | 6,411,745 | 4,971,070 | 238 | 1584 | 2963 | 25.19 | 70.69 | 0.18 | 19.88 | 4.83 |
| Compared Options | Option 1 (Solution—Rang Number 6) | Option 2 (Combination of Solutions with Rang Number 1 and 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solution with Rang Number 1 | Solution with Rang Number 2 | ||
| Top elevation | 200 m | 177 m | 179 m |
| Volume | 21.48 × 106 m3 | 13.05 | 8.12 |
| Volume sum = 13.41 + 8.74 = 21.2 × 106 m3 | |||
| Objective function | 3.87 | 3.13 | 3.33 |
| 3.21 (mean value weighted by volume) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doderovic, A.; Doderovic, S.-M.; Stepanovic, S.; Bankovic, M.; Stevanovic, D. Hybrid Model for Optimisation of Waste Dump Design and Site Selection in Open Pit Mining. Minerals 2023, 13, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13111401
Doderovic A, Doderovic S-M, Stepanovic S, Bankovic M, Stevanovic D. Hybrid Model for Optimisation of Waste Dump Design and Site Selection in Open Pit Mining. Minerals. 2023; 13(11):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13111401
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoderovic, Aleksandar, Svetozar-Milan Doderovic, Sasa Stepanovic, Mirjana Bankovic, and Dejan Stevanovic. 2023. "Hybrid Model for Optimisation of Waste Dump Design and Site Selection in Open Pit Mining" Minerals 13, no. 11: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13111401
APA StyleDoderovic, A., Doderovic, S.-M., Stepanovic, S., Bankovic, M., & Stevanovic, D. (2023). Hybrid Model for Optimisation of Waste Dump Design and Site Selection in Open Pit Mining. Minerals, 13(11), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13111401






