Gold Leaching from Printed Circuit Boards Using a Novel Synergistic Effect of Glycine and Thiosulfate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
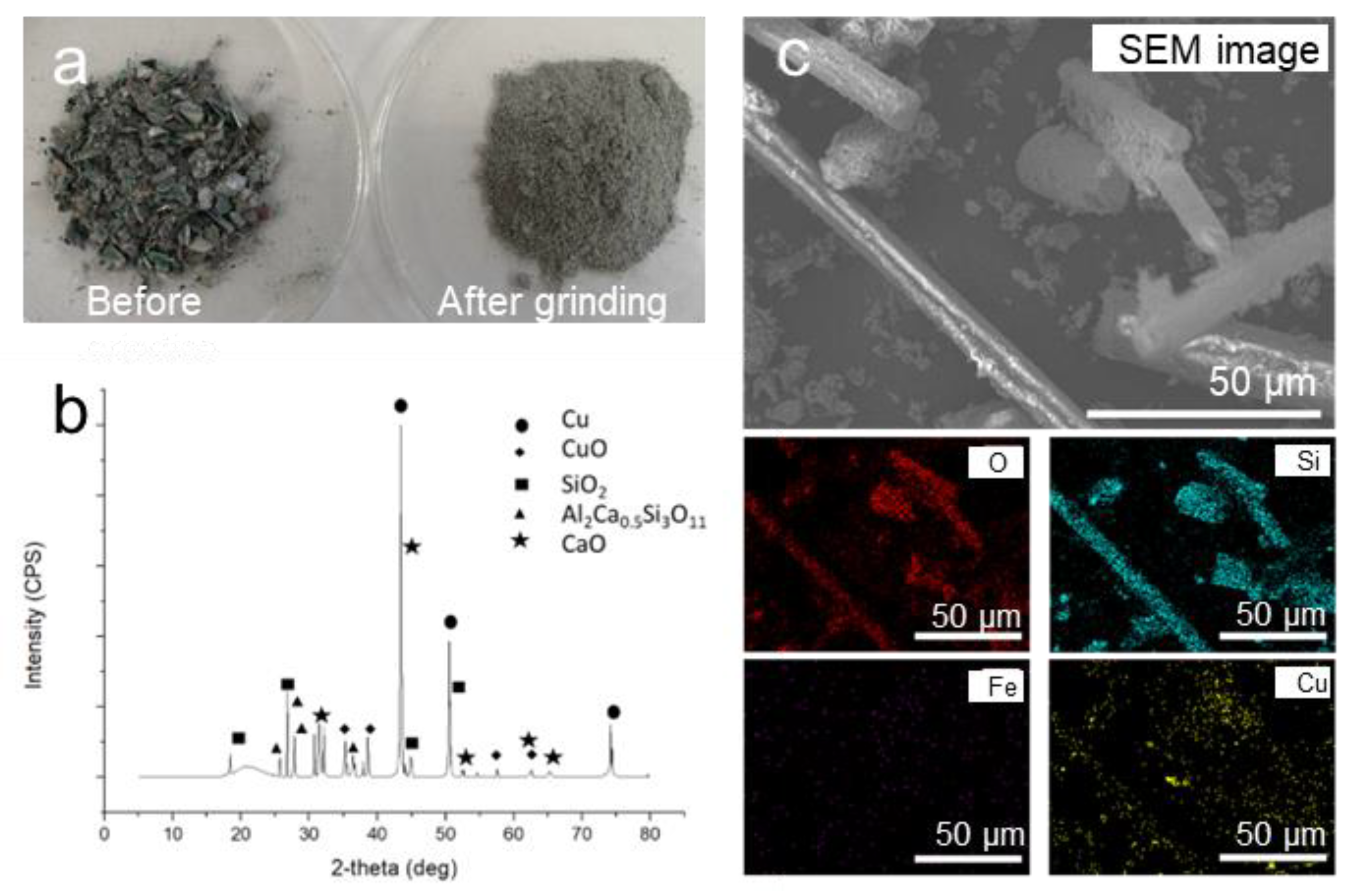
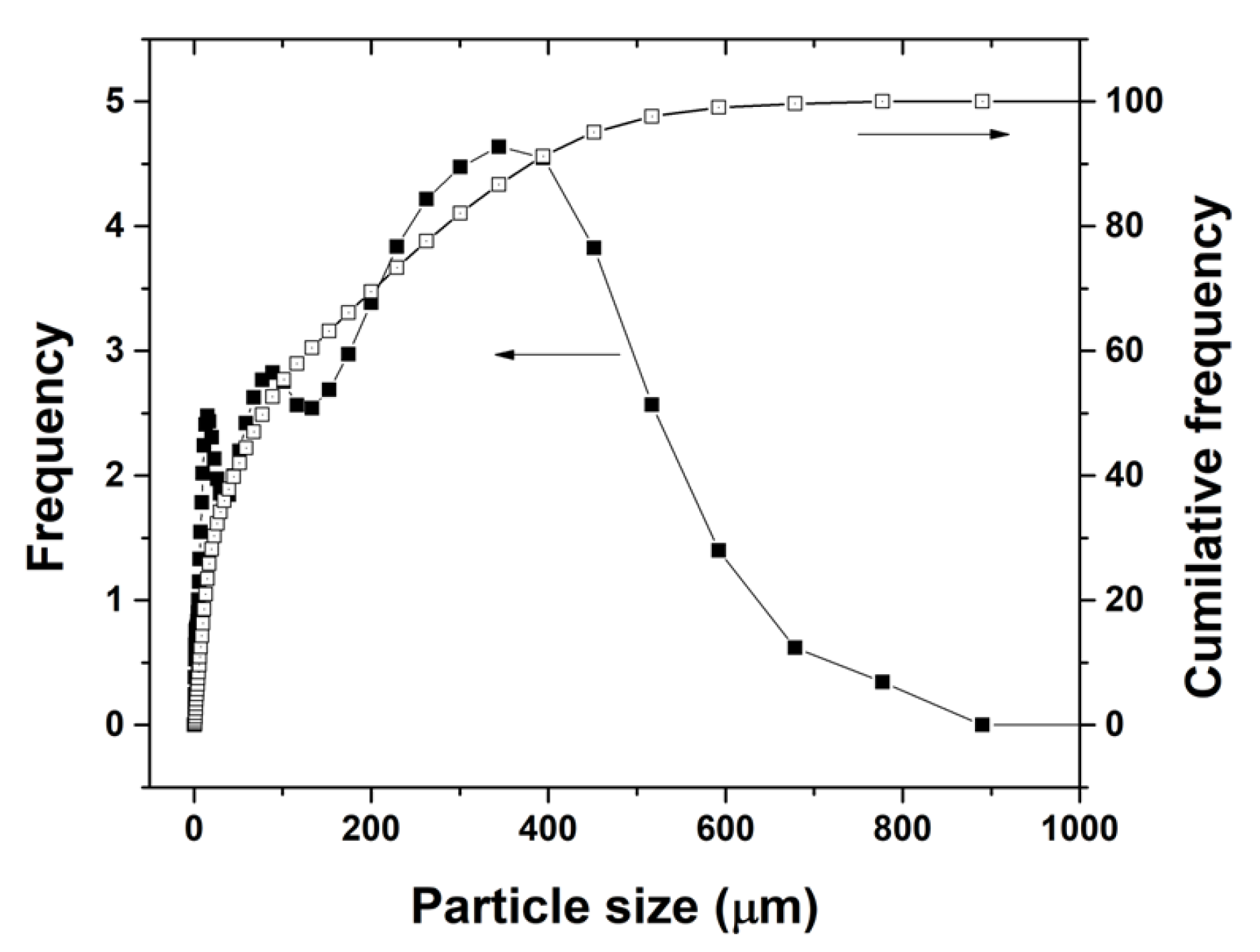
2.1. Characterisation of PCBs
2.2. Pre-Treatment of PCBs for Removal of Cu
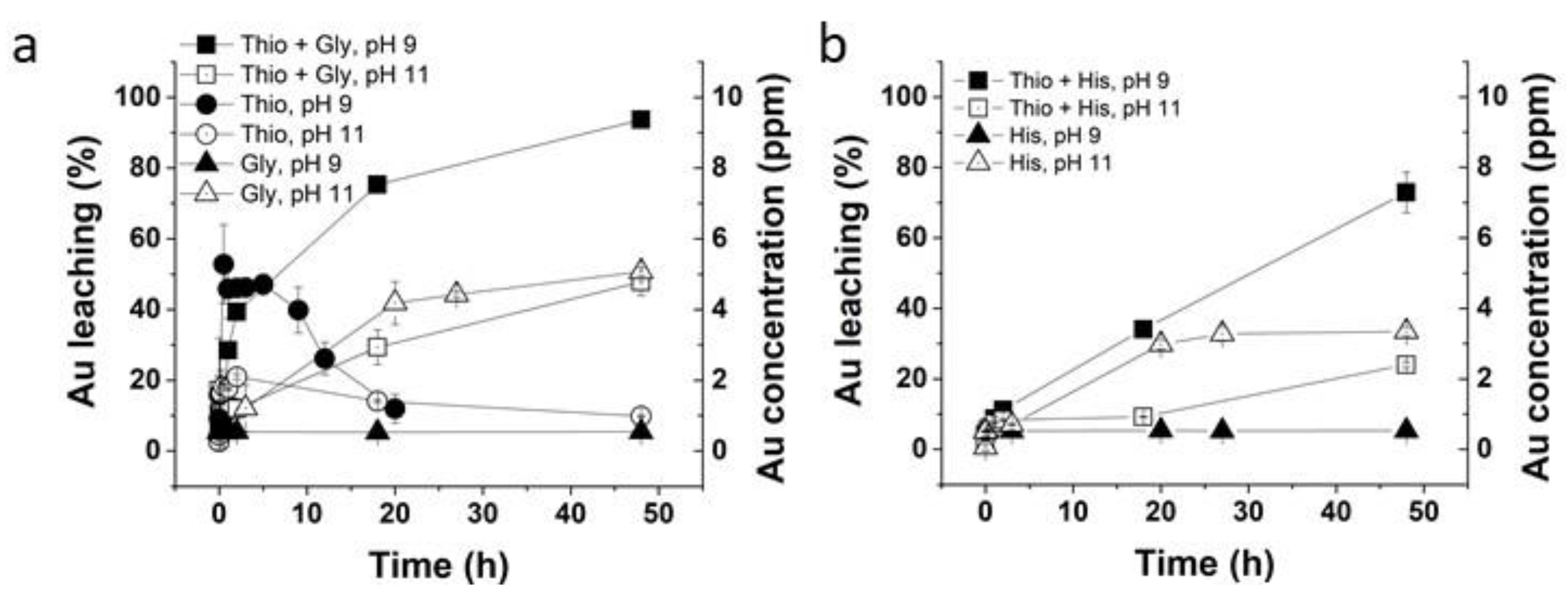
2.3. Glycine–Thiosulfate and Histidine–Thiosulfate Leaching Systems for Au Leaching
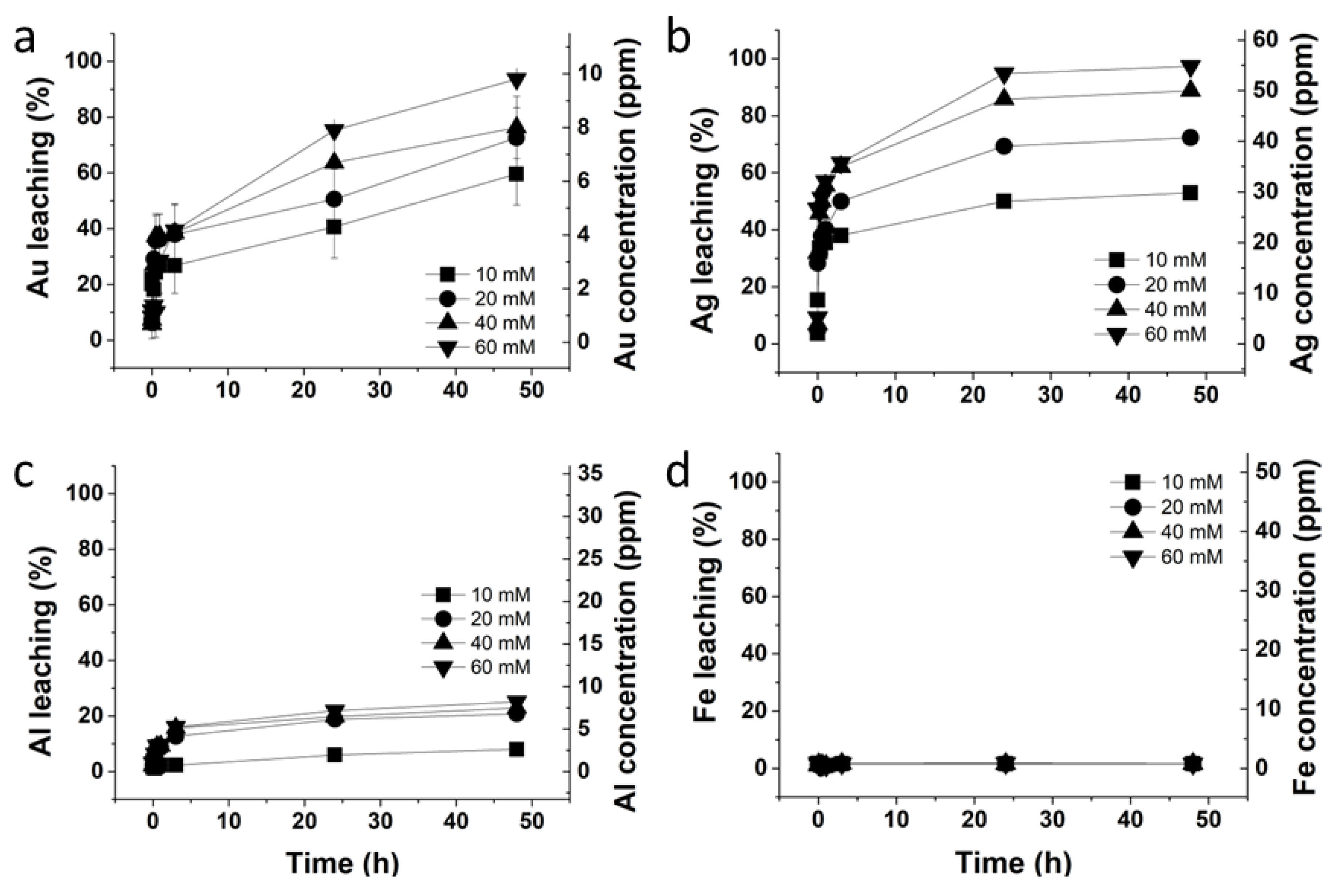
2.4. Investigation to Lower the Thiosulfate Concentration in the Glycine–Thiosulfate System
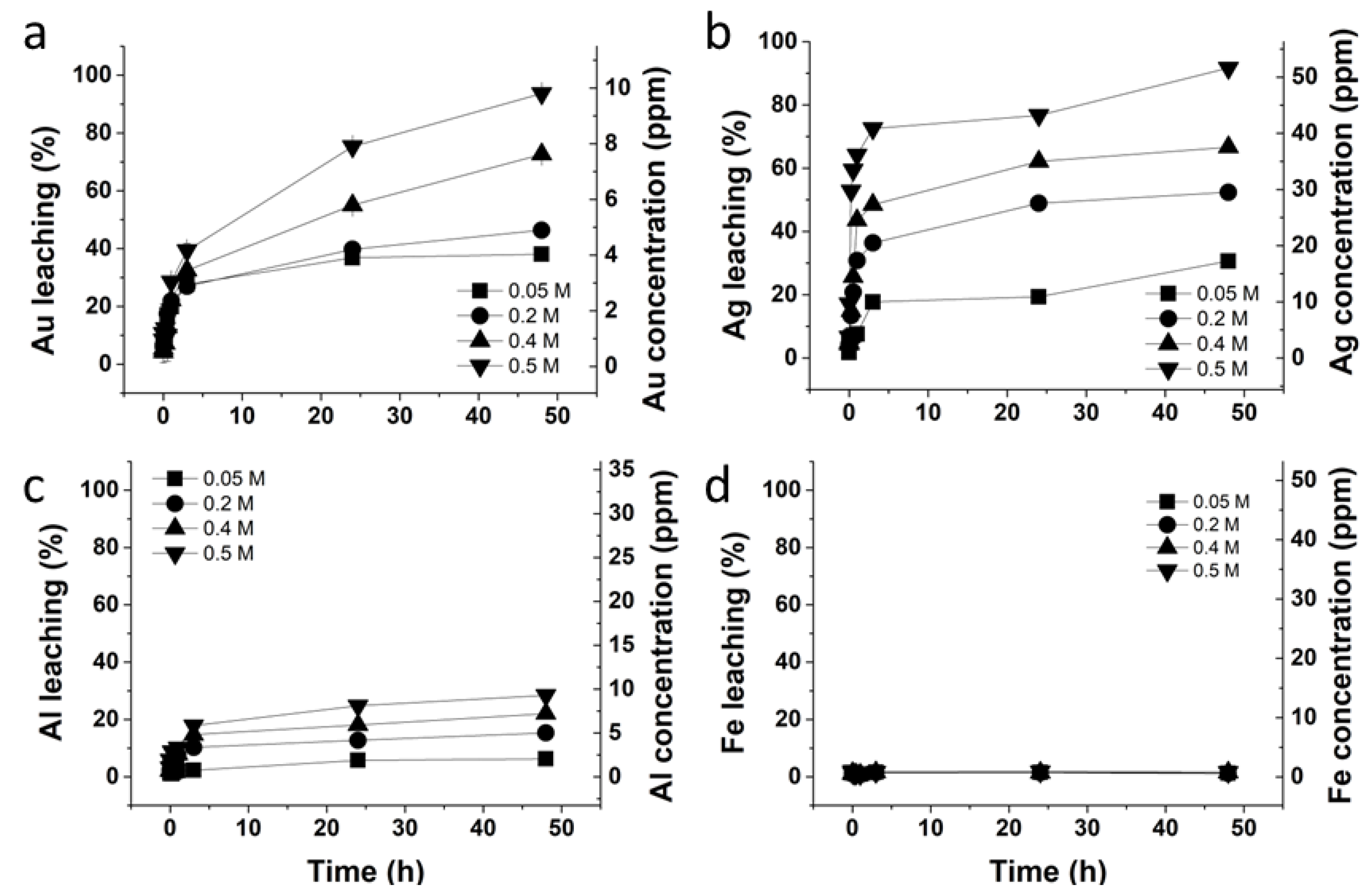
2.5. Investigation to Lower the Glycine Concentration in the Glycine–Thiosulfate System
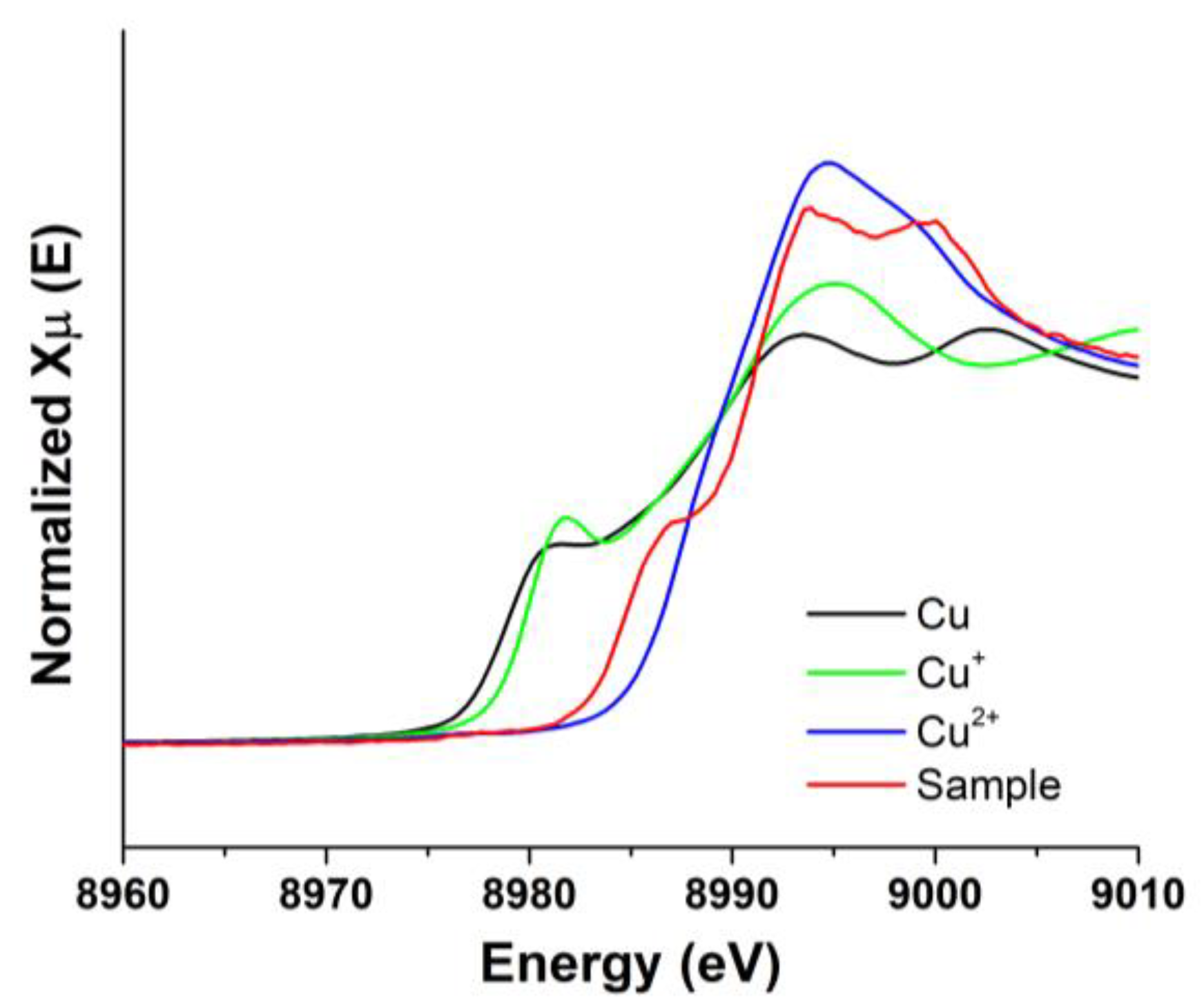
2.6. Investigation of the Presence of Cu+ during the Au Leaching
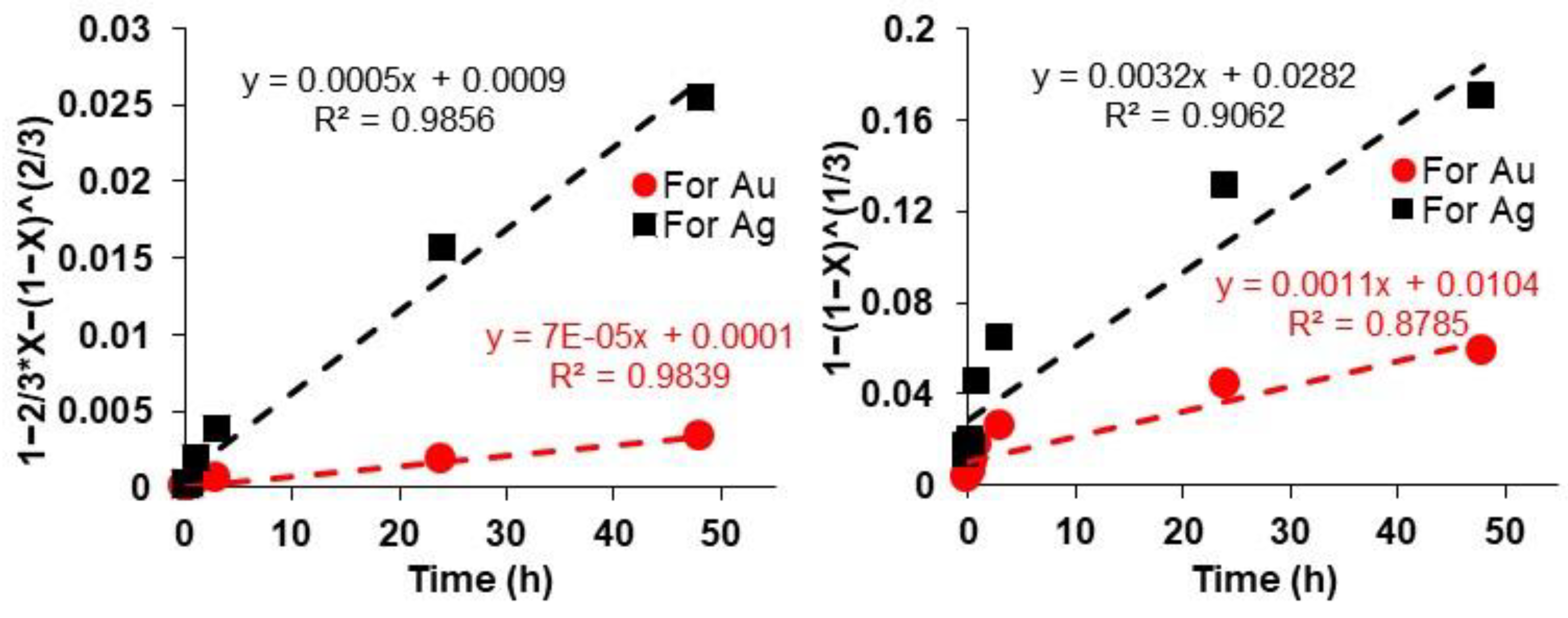
2.7. Kinetic Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterisation of PCBs
3.2. Glycine–Thiosulfate and Histidine–Thiosulfate Systems for Au Leaching
3.3. Investigation to Lower Thiosulfate Concentration in the Glycine–Thiosulfate System
3.4. Investigation to Lower Glycine Concentration in the Glycine–Thiosulfate System
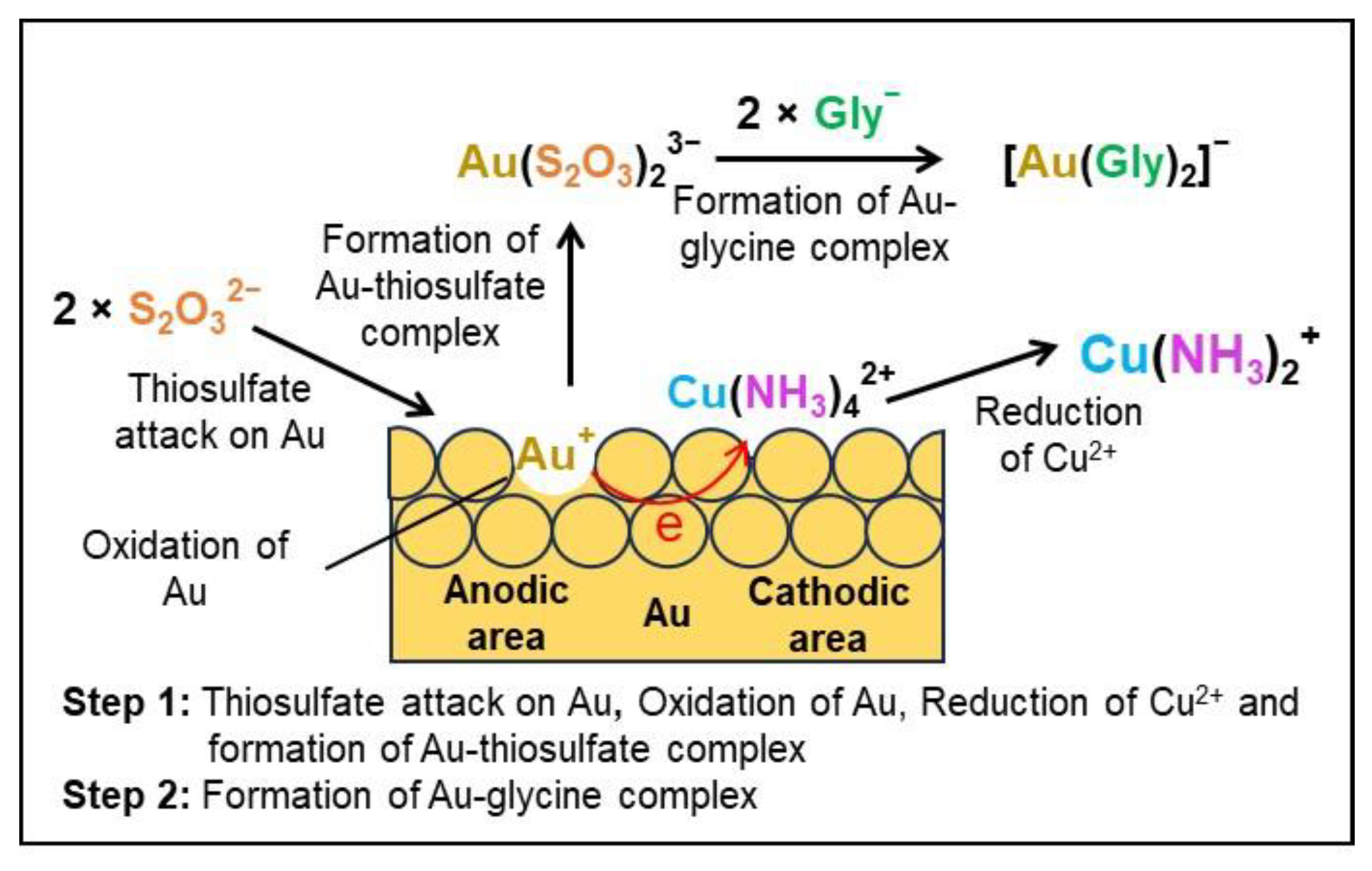
3.5. Formation of Cu+ during the Au Leaching
3.6. Kinetic Studies Related to Au and Ag Leaching
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havlik, T.; Orac, D.; Petranikova, M.; Miskufova, A. Hydrometallurgical Treatment of Used Printed Circuit Boards after Thermal Treatment. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, N.M.; Passadoro, M.; Ferella, F.; Pellei, G.; Vegliò, F. Recovery of Metals from Printed Circuit Boards by Gold-REC 1 Hydrometallurgical Process. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S. Recovery of Gold from Secondary Sources—A Review. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 115–116, 30–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altansukh, B.; Haga, K.; Huang, H.H.; Shibayama, A. Gold Recovery from Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Advanced Hydrometallurgical Processing. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, U.; Hocheng, H. Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Metals from Large Printed Circuit Board Pieces. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizki, I.N.; Tanaka, Y.; Okibe, N. Thiourea Bioleaching for Gold Recycling from E-Waste. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, H.; Chang, C.C.; Ekberg, C. Recovery of Precious Metals from Electronic Waste and Spent Catalysts: A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Lyu, X. A Review of Gold Extraction Using Alternatives to Cyanide: Focus on Current Status and Future Prospects of the Novel Eco-Friendly Synthetic Gold Lixiviants. Miner. Eng. 2022, 176, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Chen, J.N.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Review of Gold Leaching in Thiosulfate-Based Solutions. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 31, 3506–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Kong, W.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X. A Review of Thiosulfate Leaching of Gold: Focus on Thiosulfate Consumption and Gold Recovery from Pregnant Solution. Metals 2017, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahtiainen, R.; Lundström, M. Cyanide-Free Gold Leaching in Exceptionally Mild Chloride Solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, E.A.; Li, H.; Eksteen, J.J. An Alkaline Glycine-Based Leach Process of Base and Precious Metals from Powdered Waste Printed Circuit Boards. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2020, 11, 3897–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D. Advances in Gold Ore Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Safarzadeh, M.S.; Moats, M.S.; Miller, J.D.; Levier, K.M.; Dietrich, M.; Wan, R.Y. Thiocyanate Hydrometallurgy for the Recovery of Gold. Part I: Chemical and Thermodynamic Considerations. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 113–114, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yin, W.; Jiang, T.; Li, G. Thiosulfate Leaching of Au, Ag and Pd from a High Sn, Pb and Sb Bearing Decopperized Anode Slime. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampinen, M.; Laari, A.; Turunen, I. Ammoniacal Thiosulfate Leaching of Pressure Oxidized Sulfide Gold Concentrate with Low Reagent Consumption. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Thiosulphate Leaching of Gold in the Presence of Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC). Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Guo, X.Y.; Tian, Q.H.; Zhang, L. A Systematic Review of Gold Extraction: Fundamentals, Advancements, and Challenges toward Alternative Lixiviants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, P.L.; Jeffrey, M.I. Thiosulfate Leaching Kinetics of Gold in the Presence of Copper and Ammonia. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbruzzese, C.; Massidda, R.; Vegli, F.; Ubaldini, S. Thiosulphate Leaching for Gold Hydrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy 1995, 39, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, G. Role of Copper(II), Carbonate and Sulphite in Gold Leaching and Thiosulphate Degradation by Oxygenated Alkaline Non-Ammoniacal Solutions. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Oraby, E.; Eksteen, J. Amino Acids as Lixiviants for Metals Extraction from Natural and Secondary Resources with Emphasis on Glycine: A Literature Review. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 216, 106008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, E.A.; Eksteen, J.J. The Selective Leaching of Copper from a Gold-Copper Concentrate in Glycine Solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 150, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksteen, J.J.; Oraby, E.A. The Leaching and Adsorption of Gold Using Low Concentration Amino Acids and Hydrogen Peroxide: Effect of Catalytic Ions, Sulphide Minerals and Amino Acid Type. Miner. Eng. 2015, 70, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvar, M.; Shafaei Tonkaboni, Z.; Noaparast, M.; Badiei, A.R.; Amiri, A. Application of Amino Acids for Gold Leaching: Effective Parameters and the Role of Amino Acid Structure. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 391, 136123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, E.A.; Eksteen, J.J. The Leaching of Gold, Silver and Their Alloys in Alkaline Glycine-Peroxide Solutions and Their Adsorption on Carbon. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 152, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, J.; Rodelas, B.; Pozo, C.; Salmerón-López, V.; Martínez-Toledo, M.V.; Salmerón, V. Liberation of Amino Acids by Heterotrophic Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria. Amino Acids 2005, 28, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munive, G.T.; Encinas, M.A.; Salazar Campoy, M.M.; Álvarez, V.E.; Vazquez, V.M.; Choque, D.C. Leaching Gold and Silver with an Alternative System: Glycine and Thiosulfate from Mineral Tailings. JOM 2020, 72, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinkaya, P.; Wang, Z.; Korolev, I.; Hamuyuni, J.; Haapalainen, M.; Kolehmainen, E.; Yliniemi, K.; Lundström, M. Leaching and Recovery of Gold from Ore in Cyanide-Free Glycine Media. Miner. Eng. 2020, 158, 106610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, E.A.; Eksteen, J.J.; Karrech, A.; Attar, M. Gold Extraction from Paleochannel Ores Using an Aerated Alkaline Glycine Lixiviant for Consideration in Heap and In-Situ Leaching Applications. Miner. Eng. 2019, 138, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylmore, M.G. Thiosulfate as an Alternative Lixiviant to Cyanide for Gold Ores. In Gold Ore Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 485–523. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Pan, Y.; Liu, F.; Xu, Z. Thermodynamic Analysis of Gold Leaching by Copper-Glycine-Thiosulfate Solutions Using Eh-pH and Species Distribution Diagrams. Miner. Eng. 2022, 179, 107438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, E.A.; Eksteen, J.J.; O’Connor, G.M. Gold Leaching from Oxide Ores in Alkaline Glycine Solutions in the Presence of Permanganate. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 198, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, E.A.; Eksteen, J.J.; Tanda, B.C. Gold and Copper Leaching from Gold-Copper Ores and Concentrates Using a Synergistic Lixiviant Mixture of Glycine and Cyanide. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, K.; Kogani, Y.; Nazarian, F. Leaching of Complex Gold Ore Using a Cyanide-Glycine Solution. Miner. Eng. 2022, 180, 107475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, E.A.; Eksteen, J.J. Gold Leaching in Cyanide-Starved Copper Solutions in the Presence of Glycine. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L. Metallurgical Recovery of Metals from Electronic Waste: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Wang, H.; Liang, W.; Fu, J.; Yi, X. Liberation Characteristic and Physical Separation of Printed Circuit Board (PCB). Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Pan, Y.; Lu, M.; Yang, C. Liberation Characteristics after Cryogenic Modification and Air Table Separation of Discarded Printed Circuit Boards. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 311, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suponik, T.; Franke, D.M.; Nuckowski, P.M.; Matusiak, P.; Kowol, D.; Tora, B. Impact of Grinding of Printed Circuit Boards on the Efficiency of Metal Recovery by Means of Electrostatic Separation. Minerals 2021, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.; Hummler, K.; Sapp, B. Challenges in Thin Wafer Handling and Processing. In Proceedings of the ASMC 2013 SEMI Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing Conference, Saratoga Springs, NY, USA, 14–16 May 2013; pp. 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ippolito, N.M.; Belardi, G.; Innocenzi, V.; Medici, F.; Pietrelli, L.; Piga, L. Smart Determination of Gold Content in PCBs of Waste Mobile Phones by Coupling of XRF and AAS Techniques. Processes 2021, 9, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnamfard, A.; Salarirad, M.M.; Veglio, F. Process Development for Recovery of Copper and Precious Metals from Waste Printed Circuit Boards with Emphasize on Palladium and Gold Leaching and Precipitation. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birloaga, I.; De Michelis, I.; Ferella, F.; Buzatu, M.; Vegliò, F. Study on the Influence of Various Factors in the Hydrometallurgical Processing of Waste Printed Circuit Boards for Copper and Gold Recovery. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serga, V.; Zarkov, A.; Blumbergs, E.; Shishkin, A.; Baronins, J.; Elsts, E.; Pankratov, V. Leaching of Gold and Copper from Printed Circuit Boards under the Alternating Current Action in Hydrochloric Acid Electrolytes. Metals 2022, 12, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, E.A. Gold Leaching in Thiosulfate Solutions and Its Environmental Effects Compared with Cyanide. Ph.D. Thesis, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Fleming, C.A.; West-Sells, P.G.; Hackl, R.P. Method for Thiosulfate Leaching of Precious Metal-Containing Materials. US8597399B2, 3 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, V.H.; Lee, J.; Jeong, J.; Hai, H.T.; Jha, M.K. Thiosulfate Leaching of Gold from Waste Mobile Phones. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molleman, E.; Dreisinger, D. The Treatment of Copper-Gold Ores by Ammonium Thiosulfate Leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 66, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hethey, J.; Lai, J.; Loutet, S.; Martin, M.; Tang, V. Effects of Tricine, Glycine and Tris Buffers on Alkaline Phosphatase Activity. J. Exp. Microbiol. Immunol. (JEMI) 2022, 2, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.; Ito, M.; Tabelin, C.B.; Pongsumrankul, R.; Kitajima, N.; Park, l.; Hiroyoshi, N. Gold Recovery from Shredder Light Fraction of E-Waste Recycling Plant by Flotation-Ammonium Thiosulfate Leaching. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Ito, M.; Tabelin, C.B.; Pongsumrankul, R.; Tanaka, S.; Kitajima, N.; Saito, A.; Park, I.; Hiroyoshi, N. A Physical Separation Scheme to Improve Ammonium Thiosulfate Leaching of Gold by Separation of Base Metals in Crushed Mobile Phones. Miner. Eng. 2019, 138, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, M.A.; Clark, N.A.; Swain, J.E. Biological PH Buffers in IVF: Help or Hindrance to Success. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2011, 28, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanbo, C.; Guanglin, Q.; Guangsheng, L.; Xingfu, Z.; Congquan, Y.; Zhongbo, L.; Qiang, J.; Juntong, Z.; Chao, X.; Mingming, C.; et al. Experimental Study on Thiosulfate Leaching of Gold from a High Copper Gold Concentrate. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 271, 04001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The Role of Amino Acids in the Thiosulphate Leaching of Gold. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Wang, F.; Yan, C.; Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B.; Yuan, R.; Yao, J. Leaching Behavior of Metals from Iron Tailings under Varying PH and Low-Molecular-Weight Organic Acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, N.M.; Medici, F.; Pietrelli, L.; Piga, L. Effect of Acid Leaching Pre-Treatment on Gold Extraction from Printed Circuit Boards of Spent Mobile Phones. Materials 2021, 14, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylmore, M.G.; Muir, D.M. Thiosulfate Leaching of Gold—A Review. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 135–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter-Arakelyan, K. On Technological Expediency of Sodium Thiosulphate Usage for Gold Extraction from Raw Material. LZV VUZ Tsvetn. Metall. 1984, 5, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tauetsile, P.J.; Oraby, E.A.; Eksteen, J.J. Activated Carbon Adsorption of Gold from Cyanide-Starved Glycine Solutions Containing Copper. Part 2: Kinetics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kwon, O.; Yoo, K.; Alorro, R.D. Removal of Zn from Contaminated Sediment by FeCl3 in HCl Solution. Metals 2015, 5, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Eom, Y.; Yoo, K.; Jha, M.K. Leaching of Copper from Waste-Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) in Sulfate Medium Using Cupric Ion and Oxygen. Metals 2021, 11, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Hernández-Ávila, J.; Cerecedo-Sáenz, E.; Arenas-Flores, A.; Veloz-Rodríguez, M.A.; Toro, N.; Gutiérrez-Amador, M.D.P.; Acevedo-Sandoval, O.A. Leaching of Copper Contained in Waste Printed Circuit Boards, Using the Thiosulfate—Oxygen System: A Kinetic Approach. Materials 2022, 15, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phann, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Okibe, N. Utilization of Amino Acid for Selective Leaching of Critical Metals from Spent Hydrodesulfurization Catalyst. Front Chem 2022, 10, 1011518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Method | Metal (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Al | Fe | Ag | Au | |
| ICP-OES | 8.10 | 3.69 | 1.49 | 0.28 | 0.026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godigamuwa, K.; Okibe, N. Gold Leaching from Printed Circuit Boards Using a Novel Synergistic Effect of Glycine and Thiosulfate. Minerals 2023, 13, 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101270
Godigamuwa K, Okibe N. Gold Leaching from Printed Circuit Boards Using a Novel Synergistic Effect of Glycine and Thiosulfate. Minerals. 2023; 13(10):1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101270
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodigamuwa, Kasun, and Naoko Okibe. 2023. "Gold Leaching from Printed Circuit Boards Using a Novel Synergistic Effect of Glycine and Thiosulfate" Minerals 13, no. 10: 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101270
APA StyleGodigamuwa, K., & Okibe, N. (2023). Gold Leaching from Printed Circuit Boards Using a Novel Synergistic Effect of Glycine and Thiosulfate. Minerals, 13(10), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101270







