Geochemical Assessment of Gypsum Scale Formation in the Hydrated Lime Neutralization Facility of the Daedeok Mine, South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
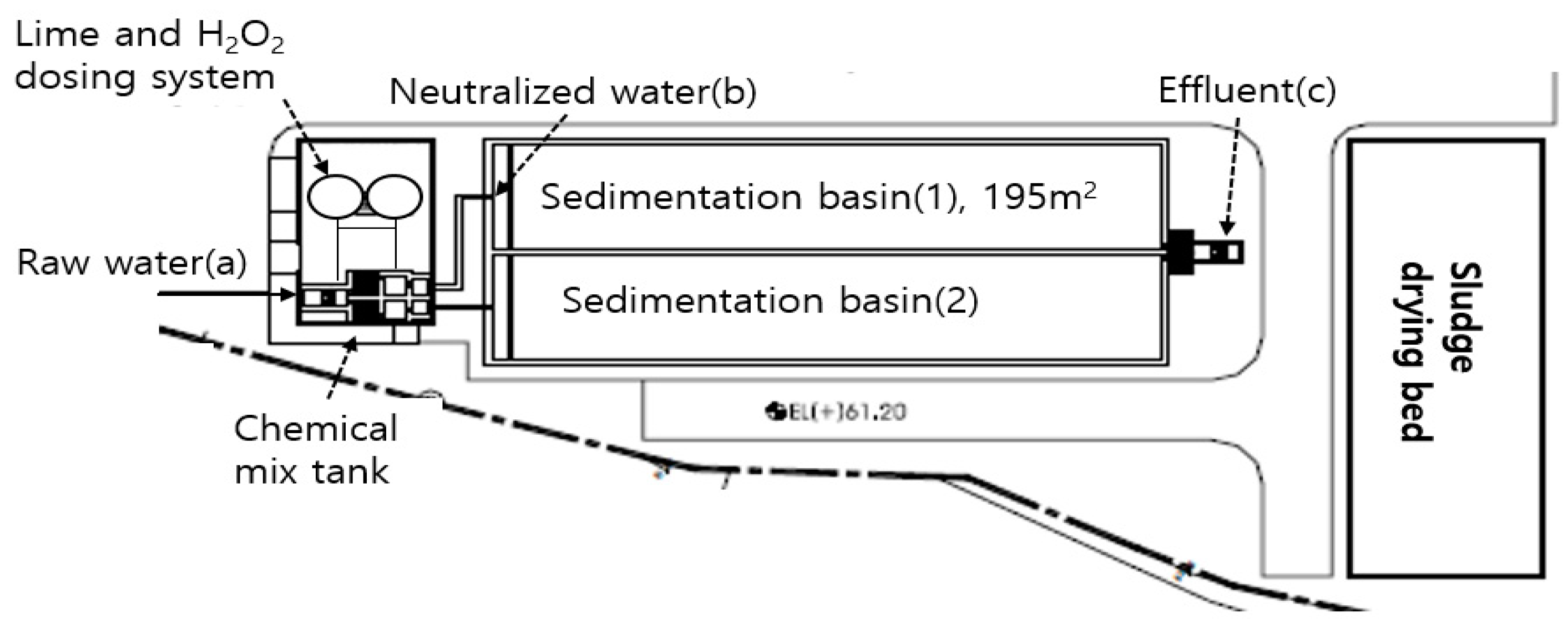
2.1. Onsite Survey and Neutralization Experiments
2.2. Geochemical Modeling and Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
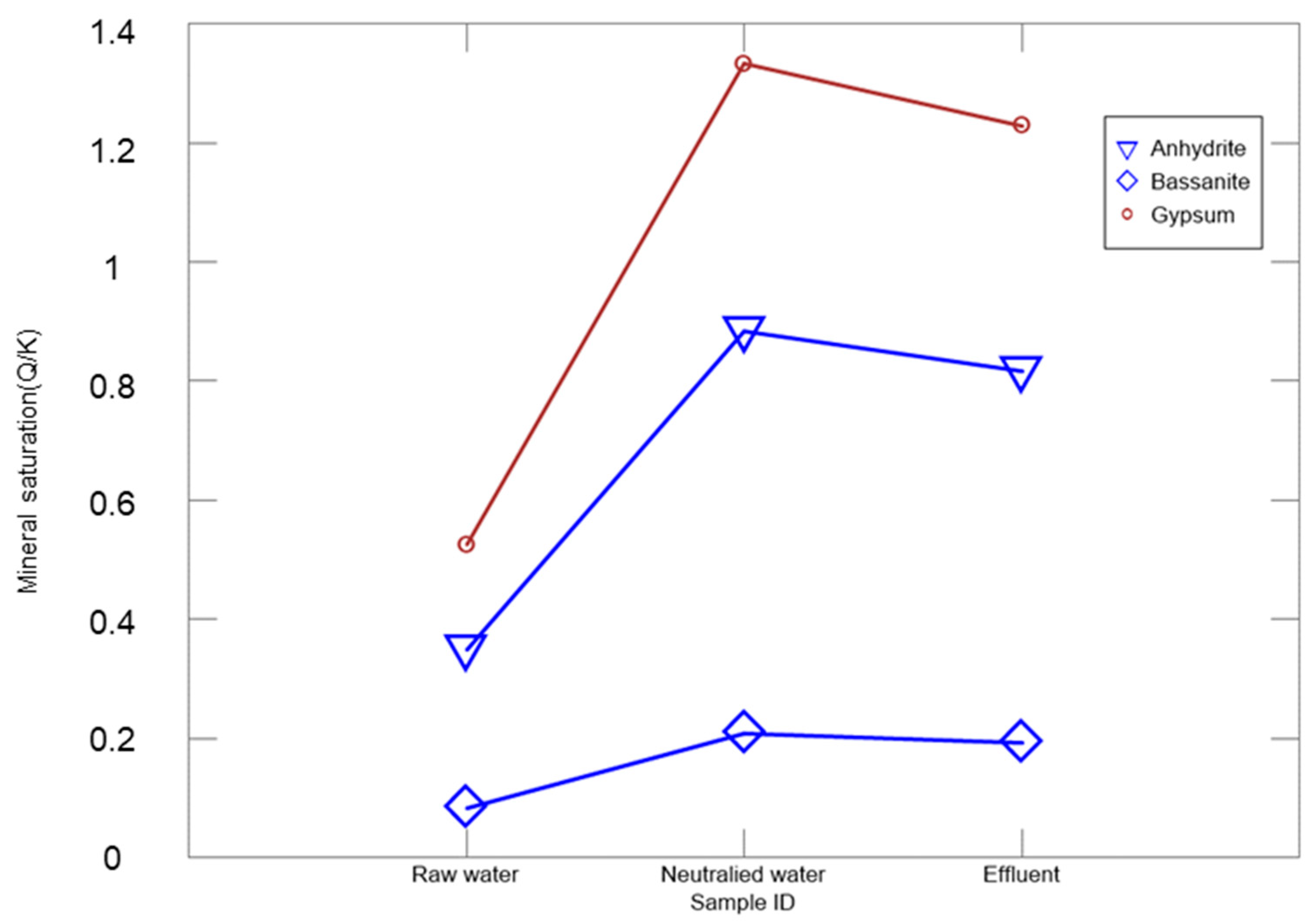
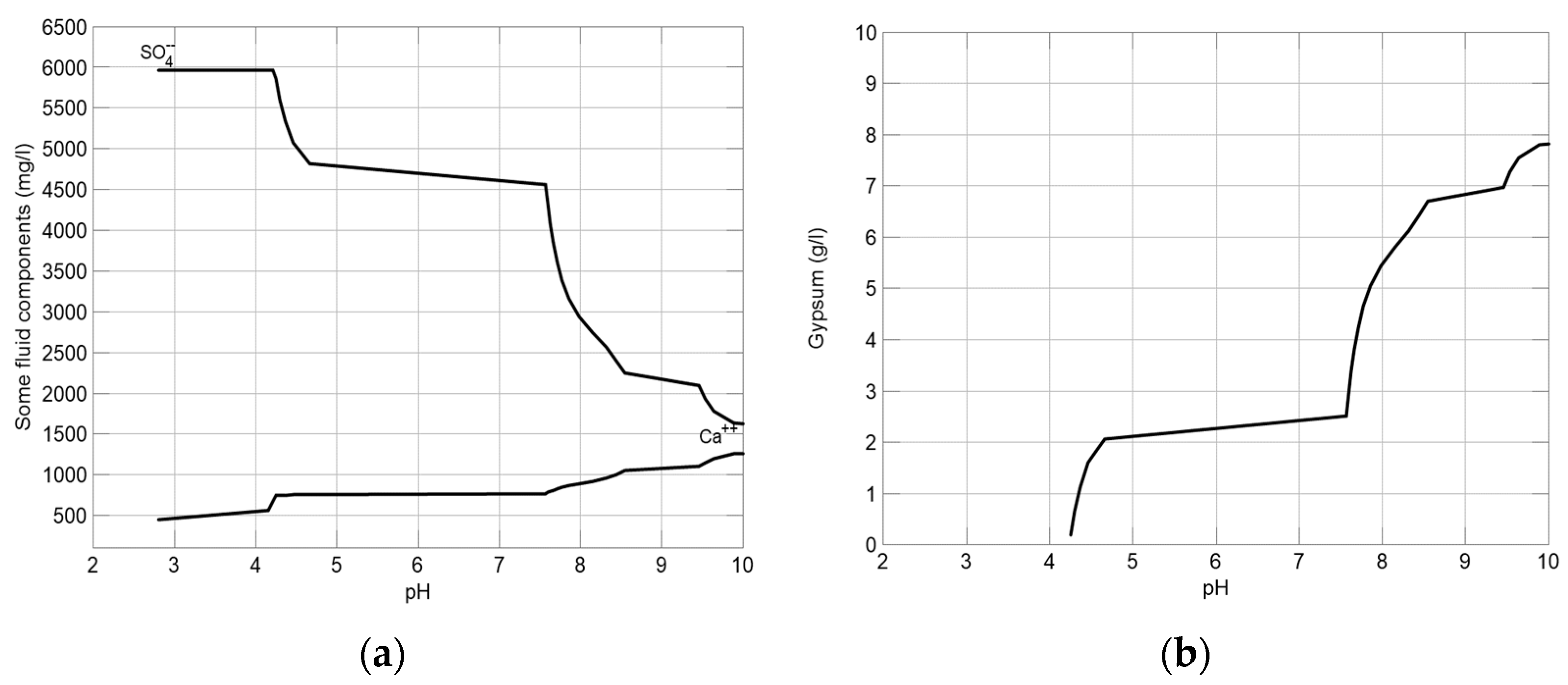
3.1. Prediction of Water Quality Changes and Mineral Production in the Lime Neutralization Facility
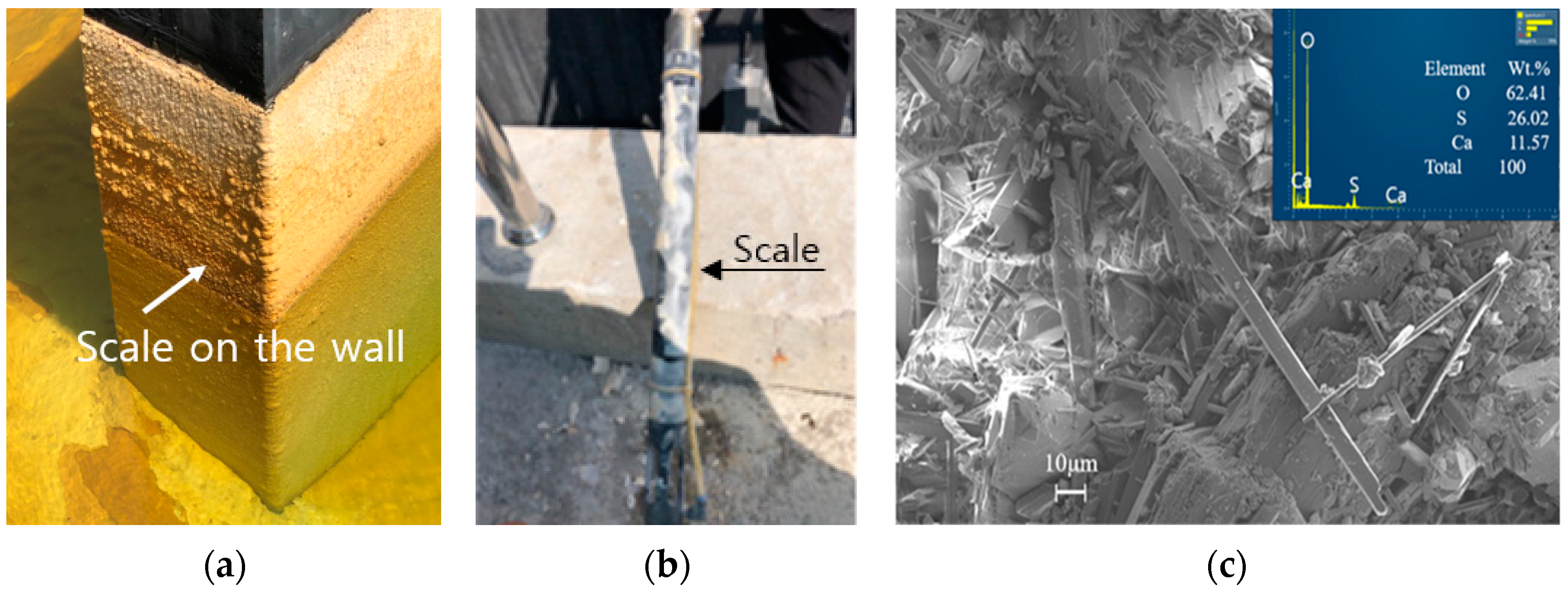
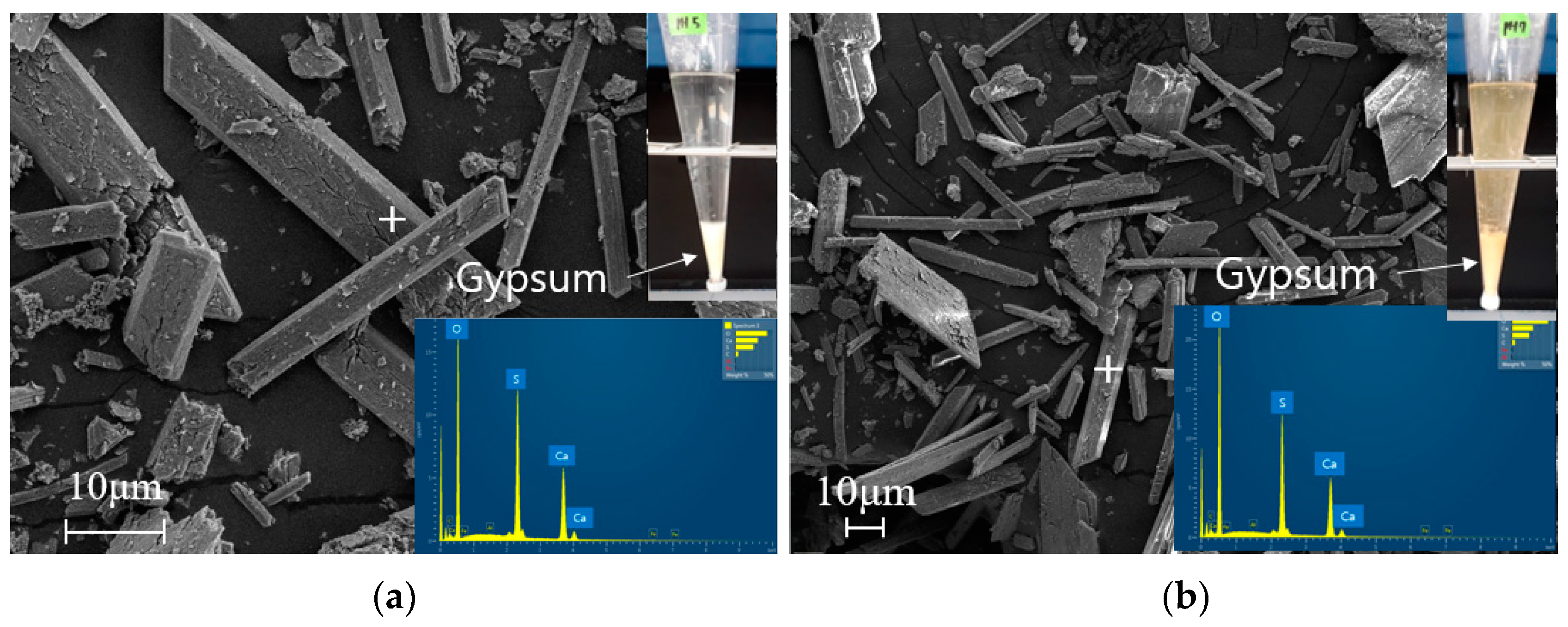
3.2. Identification of Scale Minerals within the Lime Neutralization Facility
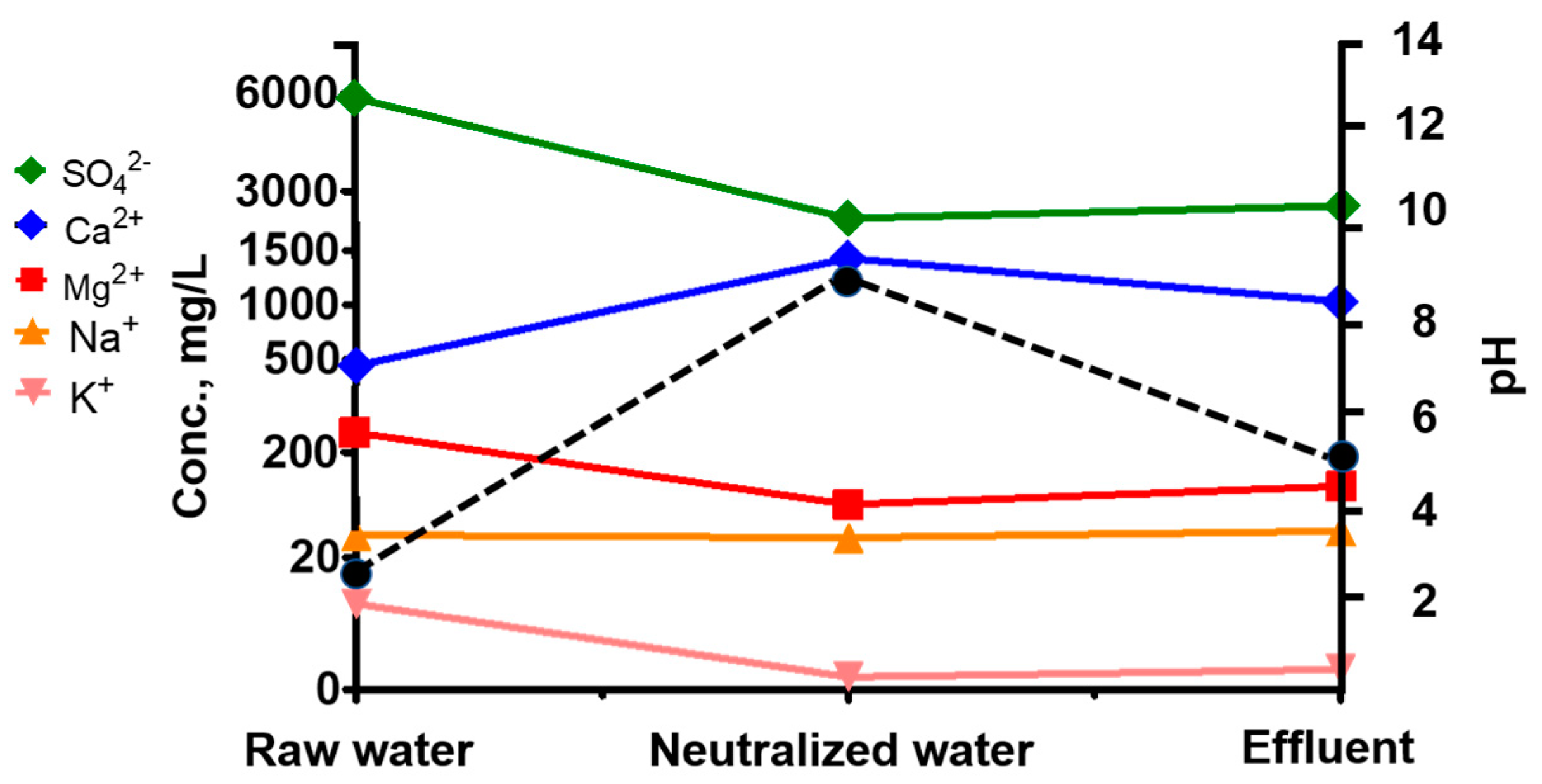
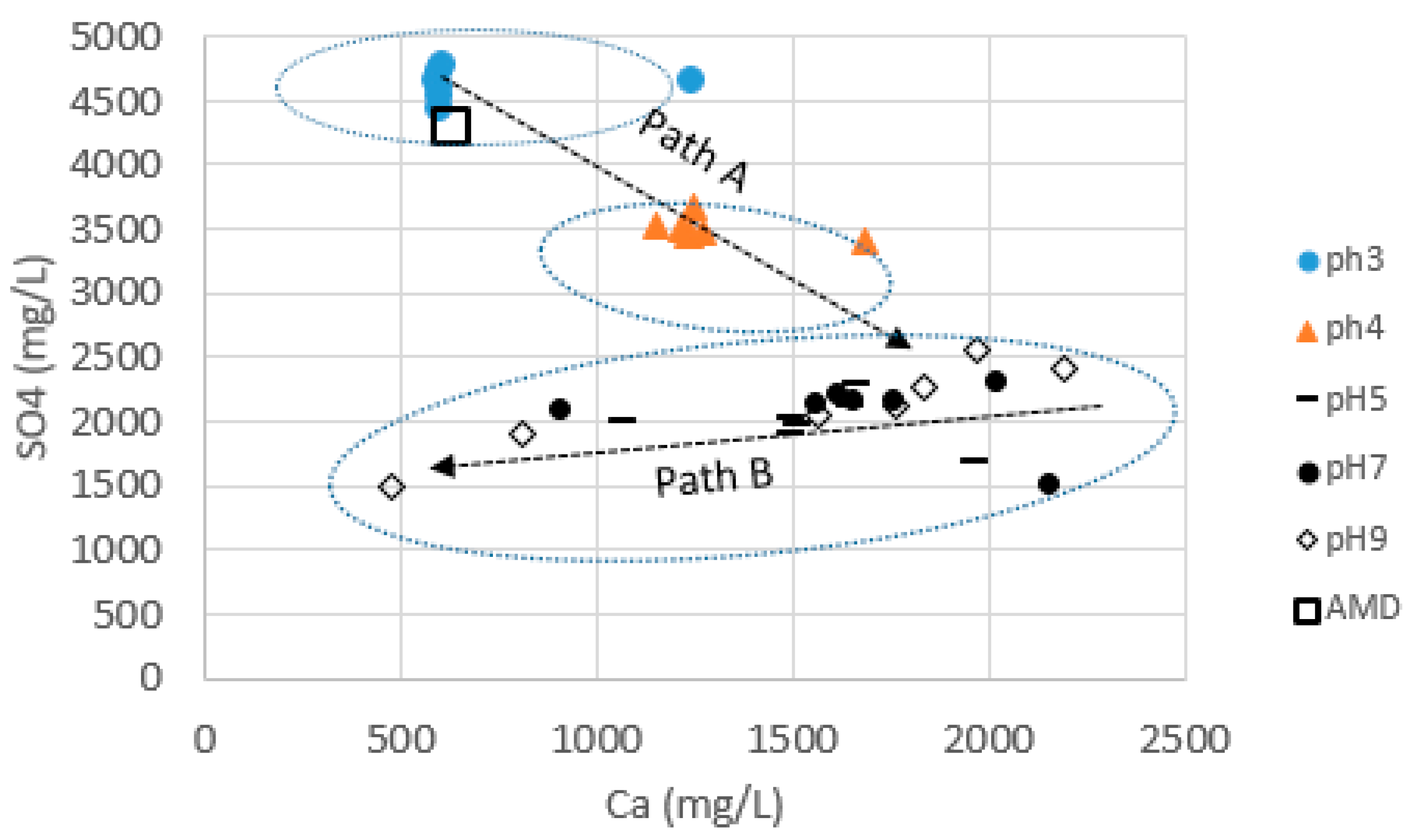
3.3. Changes in Ca/SO4 Concentrations and Gypsum Production during Simulation and Neutralization Experiments
3.4. Amount of Gypsum Produced in Neutralization Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younger, P.L.; Banwart, S.A.; Hedin, R.S. Mine water: Hydrology, pollution, remediation. Kluwer Acad. Publ. 2002, 1, 1–442. [Google Scholar]
- Aube, B.; Zinck, J. Lime treatment of acid mine drainage in Canada. In Proceedings of the Brazil-Canada Seminar on Mine Rehabilitation, Florianópolis, Brazil, 1–3 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Aube, B.; Lee, D. The high density sludge (HDS) process and sulphate control. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage (ICARD) & IMWA Annual Conference, Santiago, Chile, 21–24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.J.; Kim, J.; Tazaki, K. Mineralogical characterization of microbial ferrihydrite and schwertmannite, and non-biogenic Al-sulfate precipitates from acid mine drainage in the Donghae mine area, Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2002, 42, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Madzivire, G.; Tekere, M. Reclamation of water and the synthesis of gypsum and limestone from acid mine drainage treatment process using a combination of pre-treated magnesite nanosheets, lime, and CO2 bubbling. Water Resour. Ind. 2018, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Li, X.; Seno, K.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailings recycling. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazel, M.; Chesters, S.; Gibson, G. Controlling calcium sulphate scale formation in acid mine waters. In Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 15–17 August 2019; 2019; 124, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tolonen, E.T.; Sarpola, A.; Hu, T.; Ramo, J.; Lassi, U. Acid mine drainage treatment using by-products from quicklime manufacturing as neutralization chemicals. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madzivire, G.; Petrik, L.F.; Gitari, W.M.; Ojumu, T.V.; Balfour, G. Application of coal fly ash to circumneutral mine waters for the removal of sulphates as gypsum and ettringite. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USPDEP. PA DEP-BAMR Active Mine Drainage Treatment Facilities. 2019. Available online: http://files.dep.state.pa.us/Mining/Abandoned%20Mine%20Reclamation/AbandonedMinePortalFiles/AMDSetAsideProgram/BAMR_Current_Active_AMD_Treatment_Plants_02-21-2019.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- International Network for Acid Prevention (INAP). Treatment of Sulphate in Mine Effluents; Lorax Environmental: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2003; Available online: https://www.inap.com.au/wp-content/uploads/Treatment_of_Sulphate_in_Mine_Effluents_-_Lorax_Report.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2022).
- Liang, H.C.; Tamburini, J.; Johns, F. Designing a mine water treatment facility to remove sulfate. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage (ICARD) & IMWA Annual Conference, Santiago, Chile, 21–24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen, P.; Kyllönen, H.; Kaartinen, T.; Mäkinen, J.; Heikkinen, J.; Miettinen, V. Sulphate removal from mine water with chemical, biological and membrane technologies. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 2017, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.W.; Sibrell, P.L.; Wildeman, T.R. Comparison of sludge characteristics between lime and limestone/lime treatment of acid mine drainage. In Proceedings of the 24th National meetings of the American Society of Mining and Reclamation (ASMR), Gillette, WY, USA, 2–6 June 2007; 1, pp. 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.-W.; Lim, G.-J.; Cheong, Y.-W.; Yoo, K. Treatment efficiency of acid mine drainage by the Ho-Nam Coal Mine passive treatment system. Geosystem Eng. 2012, 15, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Kim, S.; Ko, J. The status of the passive treatment systems for acid mine drainage in South Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2008, 55, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparon, M.; Smedley, A.; Jong, T.; Costagliola, P.; Benvenuti, M. Acid Mine Drainage at Mount Morgan, Queensland (Australia): Experimental Simulation and Geochemical Modelling of Buffering Reactions. In Water in Mining Environments; IMWA Symposium: Cagliari, Italy, 2007; pp. 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, R.M.; Perilli, T.A.G.; Ladeira, A.C.Q. Oxidative precipitation of manganese from acid mine drainage by potassium permanganate. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camden-Smith, B.; Johnson, R.H.; Camden-Smith, P.; Tutu, H. Geochemical modelling of water quality and solutes transport from mining environments. Res. Pract. Water Qual. 2015, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vriens, B.; Plante, B.; Seigneur, N.; Jamieson, H. Mine waste rock: Insights for sustainable hydrogeochemical management. Minerals 2020, 10, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniruzzaman, M.; Karlsson, T.; Kauppila, P.M. Modelling tools for the prediction of drainage quality from mine wastes. Geol. Surv. Finl. Bull. 2018, 408, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Geldenhuys, P.; Maree, A.J.; Beer, J.P.; Hlabela, M. An integrated limestone/lime process for partial sulphate removal. J. South Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2003, 103, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Gominšek, T.; Lubej, A.; Pohar, C. Continuous precipitation of calcium sulfate dihydrate from waste sulfuric acid and lime. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine Reclamation Corp (MIRECO). Development of enhanced process to improve physico-chemical treatment efficiency of mine drainage. Res. Rep. 2020, 36, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Le Gouellec, Y.; Elimelech, M. Calcium sulfate (gypsum) scaling in nanofiltration of agricultural drainage water. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 205, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitari, W.; Petrik, L.; Etchebers, O.; Key, D.; Okujeni, C. Utilization of fly ash for treatment of coal mines wastewater: Solubility controls on major inorganic contaminants. Fuel 2008, 87, 2450–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madzivire, G.; Gitari, W.M.; Vadapalli, V.R.K.; Ojumu, T.V.; Petrik, L.F. Fate of sulphate removed during the treatment of circumneutral mine water and acid mine drainage with coal fly ash: Modelling and experimental approach. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheong, Y.-W.; Cho, D.-W.; Yim, G.-J.; Park, H.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Geochemical Assessment of Gypsum Scale Formation in the Hydrated Lime Neutralization Facility of the Daedeok Mine, South Korea. Minerals 2022, 12, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050574
Cheong Y-W, Cho D-W, Yim G-J, Park H-S, Kim S-J, Lee J-H. Geochemical Assessment of Gypsum Scale Formation in the Hydrated Lime Neutralization Facility of the Daedeok Mine, South Korea. Minerals. 2022; 12(5):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050574
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheong, Young-Wook, Dong-Wan Cho, Gil-Jae Yim, Hyeon-Sung Park, Sun-Joon Kim, and Joon-Hak Lee. 2022. "Geochemical Assessment of Gypsum Scale Formation in the Hydrated Lime Neutralization Facility of the Daedeok Mine, South Korea" Minerals 12, no. 5: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050574
APA StyleCheong, Y.-W., Cho, D.-W., Yim, G.-J., Park, H.-S., Kim, S.-J., & Lee, J.-H. (2022). Geochemical Assessment of Gypsum Scale Formation in the Hydrated Lime Neutralization Facility of the Daedeok Mine, South Korea. Minerals, 12(5), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050574




