Bi-Ag-Sulfosalts and Sulfoarsenides in the Ruwai Zn-Pb-Ag Skarn Deposit, Central Borneo, Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
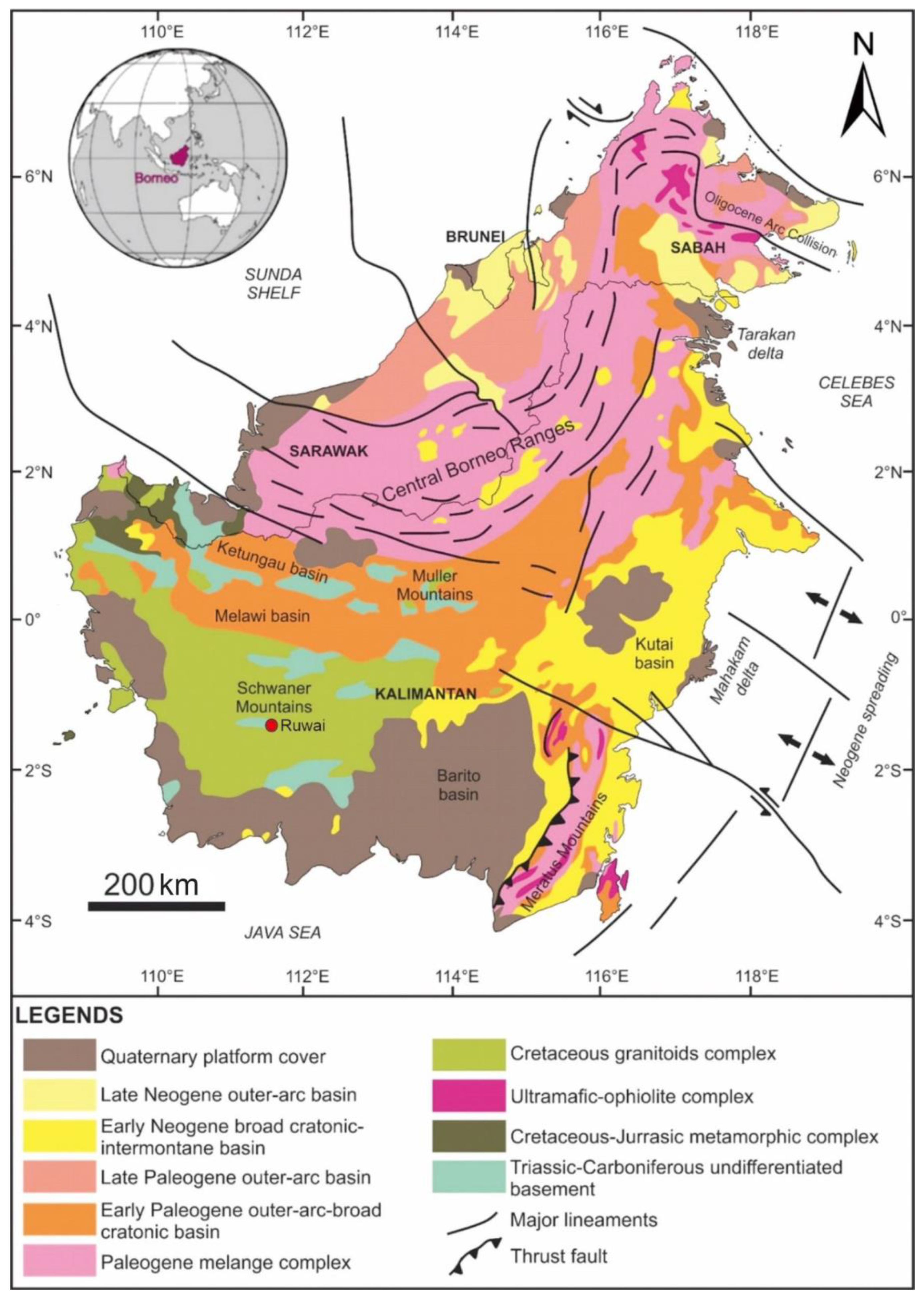
2. Geological Background
3. Methods
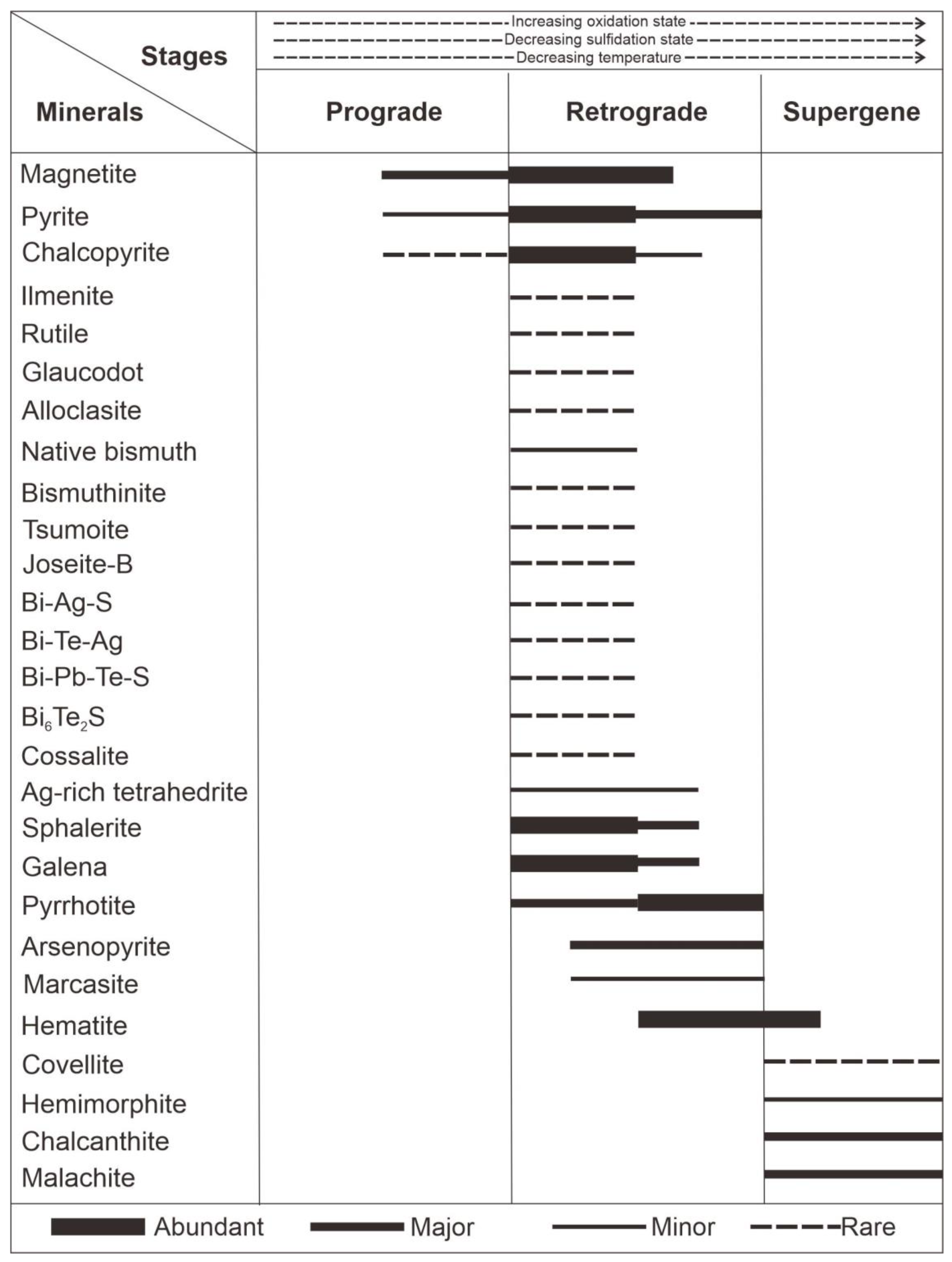
4. Results
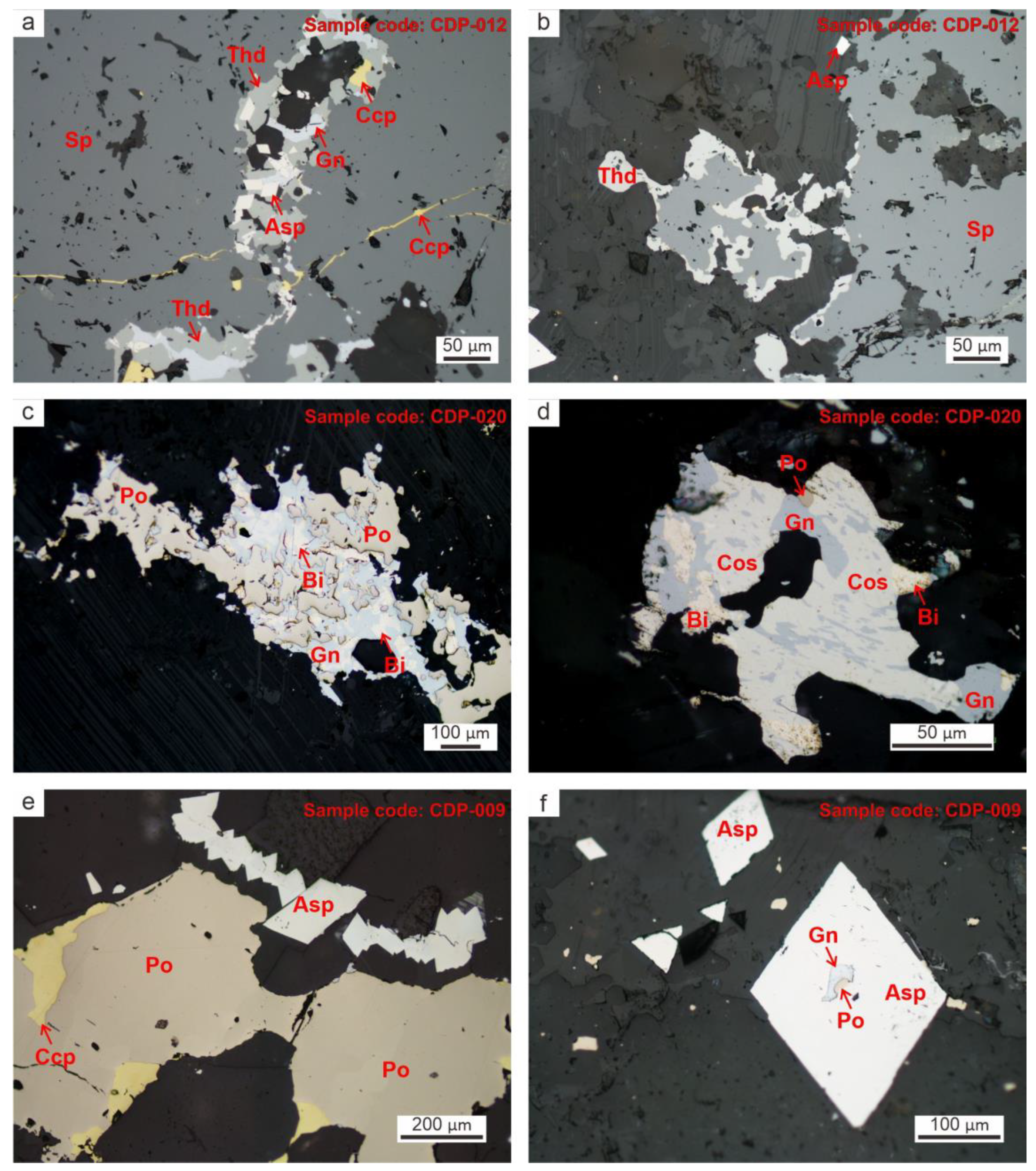
4.1. Mode of Occurrences of Bi-Ag-Co Minerals
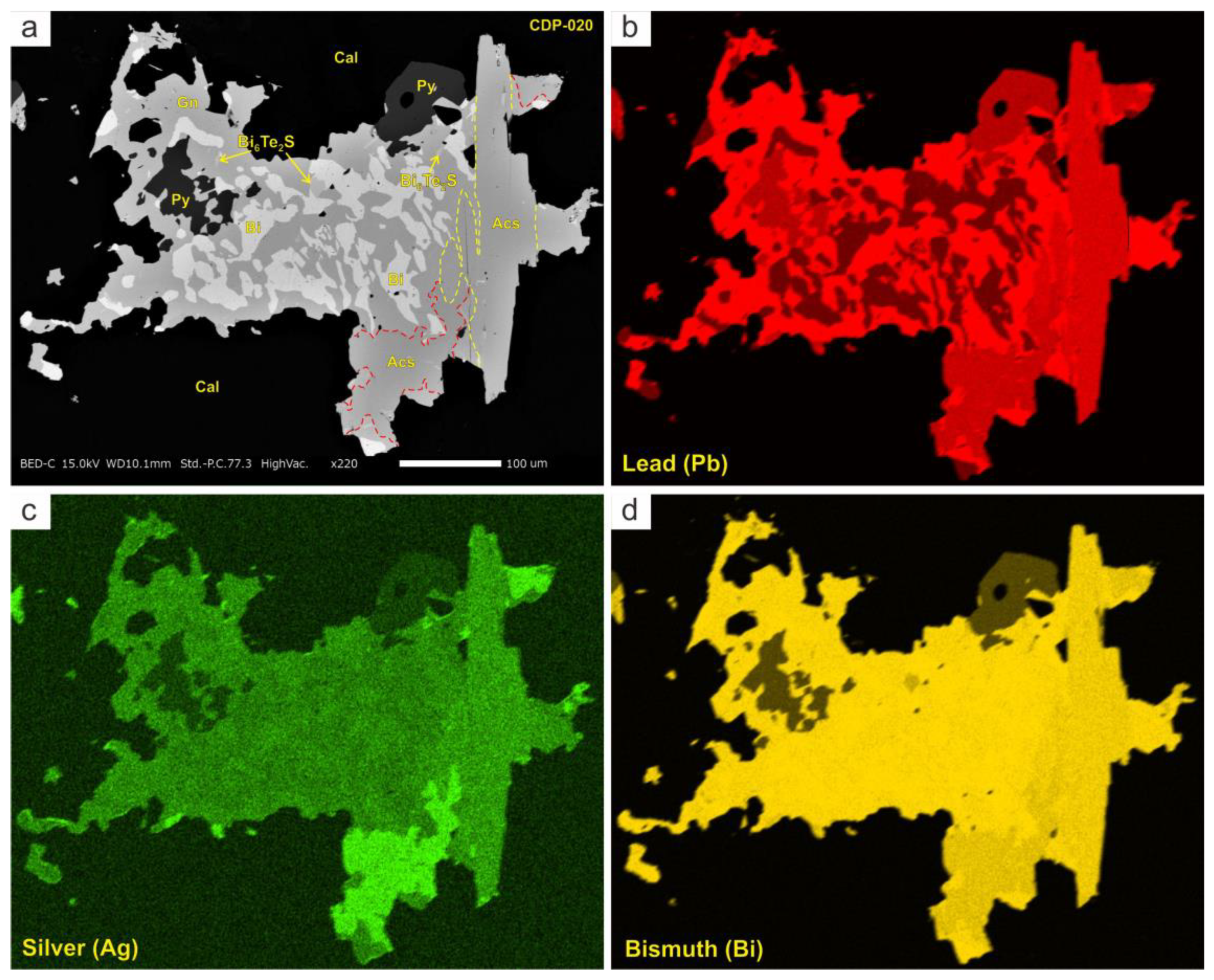
4.2. Mineral Chemistry
4.2.1. Ag-Sulfosalt
4.2.2. Bi-Sulfosalts
4.2.3. Sulfoarsenides
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- The most common Bi-Ag-bearing minerals identified in the Ruwai skarn deposit are native Bi, Ag-rich tetrahedrite, cossalite, joseite-B, tsumoite, and bismuthinite, whereas the most common sulfoarsenides are arsenopyrite and glaucodot.
- Bi-Ag sulfosalts documented in this study have relatively minor abundance, although they have non-negligible contributions to the high Ag-grade ore.
- The formation of Bi-Ag sulfosalt and sulfoarsenides in the Ruwai skarn deposit is associated with the retrograde stage under highly oxidized conditions and a relatively low sulfidation state.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Setijadji, L.D.; Kajino, S.; Imai, A.; Watanabe, K. Cenozoic island arc magmatism in Java Island (Sunda Arc, Indonesia): Clues on relationships between geodynamics of volcanic centers and ore mineralization. Resour. Geol. 2006, 56, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, T.M. Twenty Five More Years of Mineral Exploration in Indonesia (1993–2017), 1st ed.; Masyarakat Geologi Ekonomi Indonesia 10th Anniversary Special Publication; Masyarakat Geologi Ekonomi: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.; Shu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Li, X.; Jin, Z. Mineralogy, fluid inclusions, and S–Pb isotope geochemistry study of the Tuboh Pb–Zn–Ag polymetallic deposit, Lubuklinggau, Sumatra, Indonesia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 112, 103032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchin, S. Resource Estimation of the KPC Concession Area for PT Kapuas Prima Coal; Internal Report; Mining One Consultants, Melbourne: Melbourne, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Idrus, A.; Setijadji, L.D.; Tamba, F.; Anggara, F. Geology and characteristics of Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag skarn deposit at Ruwai, Lamandau Regency, Central Kalimantan. J. Appl. Geol. 2011, 3, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simbolon, D.; Diar, C.; Whitehouse, L. Metallogenic model of the Ruwai Fe-Zn-Pb-Ag skarn deposit, Central Borneo: Understanding the complexity from proximal to distal basemetal mineralization. In Proceedings of the Mgei Unlocking Concealed and Complex Deposits (UCCD 2019), Bogor, Indonesia, 24–26 September 2019; pp. 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Dana, C.D.P.; Simarmata, J.; Aditya, P.; Widyastanto, A. Hydrothermal alteration zoning and mineralization style in Southwest Gossan Block of Ruwai skarn Zn-Pb-Ag deposit, Lamandau, Central Borneo: An implication to ore genesis and exploration. In Proceedings of the Joint Convention Yogyakarta, HAGI–IAGI–IAFMI–IATMI, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 25–28 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R.; Nichols, G. Cenozoic sedimentation and tectonics in Borneo: Climatic influences on orogenesis. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2002, 191, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayson, J.N.R. PT. Tebolai Seng Perdana—Summary of Exploration Activities (Preliminary Report); PT. Tebolai Seng Perdana: Jakarta, Indonesia, 1997; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, D.; Kitto, P. Report on the Mineral Prospectivity of the Tebolai and Schwaner COW’s, Southwest Kalimantan, Indonesia; University of Tasmania: Tasmania, Australia, 1997; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Dana, C.D.P.; Agangi, A.; Takahashi, R.; Idrus, A.; Lai, C.K.; Nainggolan, N.A. Element mobility during formation of the Ruwai Zn-pB-Ag skarn deposit, Central Borneo, Indonesia. Resour. Geol. 2022, 72, e12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, D. Review of Exploration Data from the Ruwai Zinc-Lead-Silver Prospect, West Kalimantan, Indonesia; Internal Report; Prufrock Partners Ltd.: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Q.; Chang, Z.; Hammerli, J.; Lai, Y.; Huizenga, J.-M. Composition and evolution of fluids forming the Baiyinnuo’er skarn Zn-Pb deposit, northeastern China: Insights from laser ablation ICP-MS study of fluid inclusions. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 1441–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Chang, Z.; Mavrogenes, J. Fluid compositions reveal fluid nature, metal deposition mechanisms, and mineralization potential: An example at the Haobugao Zn-Pb skarn, China. Geology 2021, 49, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbethur, T.; Weiser, T.W. Gold-bismuth-telluride-sulphide assemblages at the Viceroy Mine, Harare-Bindura-Shamva greenstone belt, Zimbabwe. Mineral. Mag. 2008, 72, 953–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, T.; Walter, B.F.; Scharrer, M.; Lehmann, G.; Henze, K.; Heimgärtner, C.; Bach, W.; Markl, G. Quartz veins with associated Sb-Pb-Ag±Au mineralization in the Schwarzwald, SW Germany: A record of metamorphic cooling, tectonic rifting, and element remobilization processes in the Variscan belt. Miner. Depos. 2019, 54, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, M.; Akasaka, M.; Morifuku, Y. Ore and Skarn Mineralogy of the Yamato Mine, Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan, with Emphasis on Silver-, Bismuth-, Cobalt-, and Tin-bearing Sulfides. Resour. Geol. 2016, 66, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, X.; Fu, Y.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L. Mineralogy and mineral chemistry of Bi-minerals: Constraints on ore genesis of the Beiya giant porphyry-skarn gold deposit, southwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 79, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Shu, Q.; Meinert, L.D. Skarn deposits of China. Society of Economic Geologists, Special Publication. Spec. Publ. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2019, 22, 189–234. [Google Scholar]
- Ivashchenko, V.I. Rare-Metal (In, Bi, Te, Se, Be) Mineralization of Skarn Ores in the Pitkäranta Mining District, Ladoga Karelia, Russia. Minerals 2021, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, M.; Morishita, Y.; Imoto, Y.; Imaoka, T. Ore and skarn mineralogy of the Eboshi deposit of the Naganobori copper mine, Yamaguchi, Japan. J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci. 2021, 116, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimis, P.; Dalla Costa, L.; Guastoni, A. Cobaltite-rich mineralization in the iron skarn deposit of Traversella (Western Alps, Italy). Mineral. Mag. 2014, 78, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L. Bismuth tellurides and sulphosalts from the Larga hydrothermal system, Metaliferi Mts., Romania: Paragenesis and genetic significance. Mineral. Mag. 2004, 68, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooth, B.; Brugger, J.; Ciobanu, C.; Liu, W. Modeling of gold scavenging by bismuth melts coexisting with hydrothermal fluids. Geology 2008, 36, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooth, B.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Green, L.; O’Neill, B.; Brugger, J. Bi-melt formation and gold scavenging from hydrothermal fluids: An experimental study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 5423–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmar, U.; Scott, S.D. Phase relations involving arsenopyrite in the system Fe-As-S and their application. Can. Mineral. 1976, 14, 364–386. [Google Scholar]
- Voudouris, P.C.; Spry, P.G.; Mavrogonatos, C.; Sakellaris, G.-A.; Bristol, S.K.; Melfos, V.; Fornadel, A.P. Bismuthinite derivatives, lillianite homologues, and bismuth sulfotellurides as indicators of gold mineralization in the Stanos shear-zone related deposit, Chalkidiki, northern Greece. Can. Mineral. 2013, 51, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.L.Y.; Hoda, S.H. Phase relations in the system PbS-Cu2S-Bi2S3 and the stability of galenobismutite. Am. Mineral. 1977, 62, 346–350. [Google Scholar]
- Buzatu, A.; Damian, G.; Dill, H.G.; Buzgar, N.; Apopei, A.I. Mineralogy and geochemistry of sulfosalts from Baia Sprie ore deposit (Romania)—New bismuth minerals occurrence. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumino, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Nagashima, M. Cuprobismutite group minerals (cuprobismutite, hodrušhite, kupčíkite and padĕraite), other Bi–sulfosalts and Bi–tellurides from the Obari mine, Yamagata Prefecture, Japan. J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci. 2014, 109, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, L.D. Skarn and skarn deposits. Geosci. Can. 1992, 19, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, L.D.; Dipple, G.M.; Nicolescu, S. World Skarn Deposits; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 299–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.D. Synthesen und Analysen in den Dreiecksdiagrammen FeAsS-CoAsS-NiAsS und FeS2-CoS2-NiS2, N. Jb. Miner. Abh. 1965, 103, 205–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammon, J.B. Some observations on minerals in the system CoAsS-FeAsS. Norsk. Geol. Tidsskr. 1966, 46, 405–426. [Google Scholar]
- Fanlo, I.; Subías, I.; Gervilla, F.; Paniagua, A.; García, B. The composition of Co–Ni–Fe sulfarsenides, diarsenides and triarsenides from the San Juan de Plan deposit, Central Pyrenees, Spain. Can. Mineral. 2004, 42, 1221–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| No | Mineral | Number of Analysis | Ideal Formula | Bi (wt.%) | Ag (wt.%) | Pb (wt.%) | Te (wt.%) | S (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Native bismuth | 8 | Bi0.96Cu0.01Mn0.03 | 96.64–97.83 | 0.01–0.02 | bdl | 0.02–0.05 | 0.01–0.02 |
| 2 | Ag-rich cossalite | 9 | (Pb0.65Ag0.32Cu0.03)2.2Bi1.9S4.9 | 44.25–48.00 | 6.20–7.00 | 26.25–28.81 | 0.03–0.04 | 15.80–16.31 |
| 3 | Ag-poor cossalite | 6 | 41.97–42.74 | 2.31–2.52 | 36.10–36.76 | bdl | 15.72–16.02 | |
| 4 | UM2008-43-S:BiTe | 4 | Bi5.7Te2.23S1.1 | 73.50–74.50 | bdl | bdl | 19.60–20.37 | 2.65–2.85 |
| 5 | Bismuthinite | 1 | Bi2S3 | 79.5 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 18.83 |
| 6 | Tsumoite | 2 | BiTe | 65.9–66.5 | n.d. | n.d. | 33.5–34.1 | n.d. |
| 7 | Joseite-B | 3 | Bi4Te2S | 76.3–76.8 | n.d. | n.d | 20.1–20.9 | 2.7–2.8 |
| 8 | Bismuth-silver sulfide | 2 | Bi-Ag-S | 45.2–45.3 | 16.5–16.8 | n.d | n.d. | 35.3–35.8 |
| 9 | Bismuth-silver telluride | 1 | Bi-Ag-Te | 79.0 | 2.6 | n.d. | 18.4 | n.d. |
| 10 | Bismuth-lead-telluro-sulfide | 3 | Bi-Pb-Te-S | 45.4–67.1 | n.d. | 5.2–36.2 | 11.4–26.6 | 7.0–12.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dana, C.D.P.; Agangi, A.; Idrus, A.; Lai, C.-K.; Simbolon, D.R. Bi-Ag-Sulfosalts and Sulfoarsenides in the Ruwai Zn-Pb-Ag Skarn Deposit, Central Borneo, Indonesia. Minerals 2022, 12, 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121564
Dana CDP, Agangi A, Idrus A, Lai C-K, Simbolon DR. Bi-Ag-Sulfosalts and Sulfoarsenides in the Ruwai Zn-Pb-Ag Skarn Deposit, Central Borneo, Indonesia. Minerals. 2022; 12(12):1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121564
Chicago/Turabian StyleDana, Cendi D. P., Andrea Agangi, Arifudin Idrus, Chun-Kit Lai, and Doly R. Simbolon. 2022. "Bi-Ag-Sulfosalts and Sulfoarsenides in the Ruwai Zn-Pb-Ag Skarn Deposit, Central Borneo, Indonesia" Minerals 12, no. 12: 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121564
APA StyleDana, C. D. P., Agangi, A., Idrus, A., Lai, C.-K., & Simbolon, D. R. (2022). Bi-Ag-Sulfosalts and Sulfoarsenides in the Ruwai Zn-Pb-Ag Skarn Deposit, Central Borneo, Indonesia. Minerals, 12(12), 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121564








