Filling Characteristics of Radiolarian Siliceous Shell Cavities at Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale in Sichuan Basin, Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
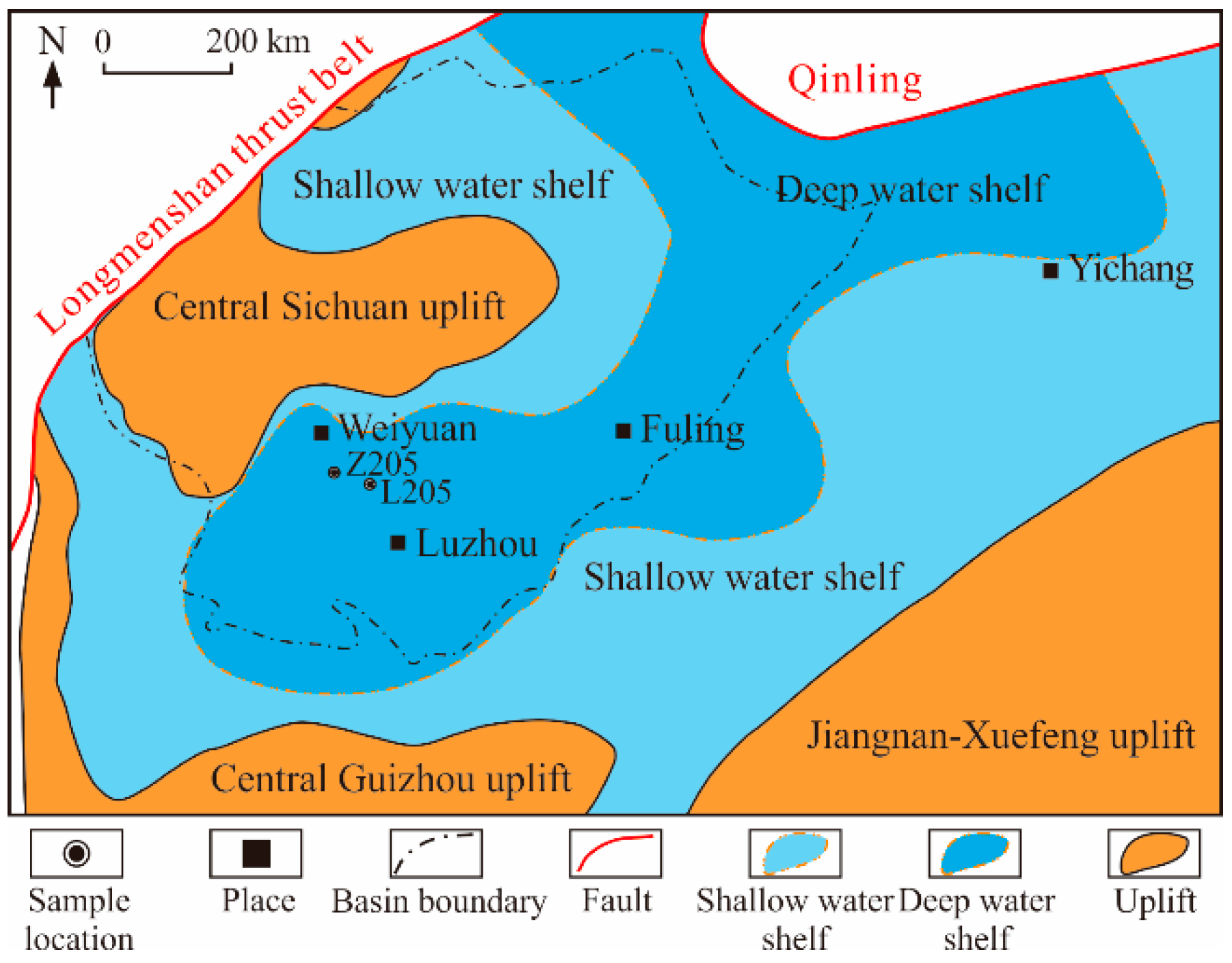
2. Geological Setting
3. Methods
4. Results
4.1. Characteristics of Radiolarian Siliceous Shells
4.2. Characteristics of Radiolarian Siliceous Shell Cavities
5. Discussion
5.1. Filling Sequences
5.2. Filling Development Period
5.3. Calcite Development Process
5.4. Pyrite Development Process
5.5. Organic–Silicon Complex Development Process
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Both complete and uncompleted radiolarian siliceous shells were abundant in Wufeng-Longmaxi radiolarian siliceous shale laminae in Sichuan Basin, which was filled with calcite, pyrite and organic–silicon complex.
- (2)
- Fillings in radiolarian siliceous shell cavities were developed in the following order: calcite, pyrite, organic–silicon complex. Calcite was developed during sedimentation of radiolarian siliceous shells, after that pyrite and organic–silicon complex successively filled dissolved pores associated with calcite.
- (3)
- Calcite was derived from microbial activities producing calcium carbonate at the seawater surface. The radiolarian siliceous shell cavity promotes sulfate reducing bacterial growth or dissolved hydrogen sulfide reducing Fe3+ into Fe2+, contributing positively to pyrite development. The organic–silicon complex was produced by the metabolism of microorganisms.
- (4)
- Complete radiolarian siliceous shells could withstand overburden pressure, where honeycomb-like organic pores were developed in organic–silicon complex. However, uncompleted radiolarian siliceous shells had weak compressive strength and, as a result, organic pores were poorly developed in organic–silicon complex.
- (5)
- The only approach to figure out organic pore carriers and investigate sequences and development processes of minerals and organic matter is to select weakly compacted radiolarian siliceous shale laminae to carry out micro- and ultra-micropetrological observation and geochemical testing on weakly compacted radiolarian siliceous shale laminae.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turgeon, S.; Brumsack, H.J. Anoxic vs dysoxic events reflected in sediment geochemistry during the Cenomanian-Turonian Boundary Event(Cretaceous)in the Umbria-Marche Basin of central Italy. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.J.; Bustin, R.M. Sediment geochemistry of the Lower Jurassic Gordon dale Member, northeastern British Columbia. Bull. Can. Pet. Geol. 2006, 54, 337–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.J.; Bustin, R.M. Investigating the use of sedimentary geochemical proxies for paleo environment interpretation of thermally mature organic-rich strata: Examples from the Devonian-Mississippian shales, Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin. Chem. Geol. 2009, 260, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.D.; Shen, J.; Feng, Q.L. Applications of radiolarian for productivity and hydrocarbon-source rocks. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2012, 37, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zou, C.; Dong, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, Z. Biogenic silica of organic-rich shale in Sichuan basin and its significance for shale gas. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2014, 50, 476–486. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Cai, Y. Evidences of biogenic silica of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation shale in Jiaoshiba area and its geological significance. J. China Univ. Pet. Ed. Nat. Sci. 2017, 41, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, T.T.; Deng, M.; Song, Z.G.; Liu, G.X.; Huang, Y.R.; Hursthouse, A.S. Study on the effect of pyrite on the accumulation of shale oil and gas. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2018, 29, 404–414. [Google Scholar]
- Milliken, K.L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Ni, Y. Mineral diagenetic control of expulsion efficiency in organic-rich mudrocks, Bakken Formation (Devonian-Mississippian), Williston Basin, North Dakota, USA. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 127, 104869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longfei, L.U.; Jianzhong, Q.I.; Baojian, S.H.; Weixin, L.; Qingzhen, Z. Biogenic origin and hydrocarbon significance of siliceous shale from the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Fuling area, southeastern Sichuan Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2016, 38, 460–465. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Qin, J.; Shen, B.; Tenger. The origin of biogenic silica in siliceous shale from Wufeng-Longmaxi formation in the Middle and Upper Yangtze region and its relationship with shale gas enrichment. Earth Sci. Front. 2018, 25, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Longman, M.W.; Drake, W.R.; Milliken, K.L.; Olson, T.M. A Comparison of Silica Diagenesis in the Devonian Woodford Shale (Central Basin Platform, West Texas) and Cretaceous Mowry Shale (Powder River Basin, Wyoming); GeoScienceWorld: Tysons Corner, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 49–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, W.; Li, X.; Xiaowei, Z.; Pingping, L.; Junmin, Y. Occurrence characteristics, genesis and petroleum geological significance of micro-nano silica-organic matter aggregate in radiolarian siliceous shell cavity: A case study of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formationin Sichuan Basin, SW China. J. China Univ. Petrol. 2021, 45, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Guo, W.; Liang, P.; Yu, J. Characteristics, formation mechanism and influence on physical properties of carbonate minerals in shale reservoir of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2022, 33, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Chen, M.H.; Xiang, R. Progress and prospect in research on living radiolaria ecoloy: A basic study of paleoenvironmental and paleoeanographic reconstructions. Adv. Earth Sci. 2006, 21, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.L.; Chen, M.H.; Hu, W.F.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, R. Vertical distribution of living radiolarians and its environmental implication. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2013, 32, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, M.H.; Suzuki, N.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Cheng, X.W.; Zhang, Q. The higher level classification of modern radiolarians and their ecological significance. Acta Micropalaeontol. Sin. 2020, 37, 82–98. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hu, B.; Chang, H.; Cheng, X.; Xiang, R. Radiolarian distribution in surface sediments of the Philippine Sea and adjacent areas and its response to environment. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2021, 41, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z. A new method for the production of radiolarian skeleton specimens. Ocean. Limnol. 1964, 6, 309–310. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Feng, Q. Treatment and separation methods of radiolarians in limestone. Acta Micropalaeontol. Sin. 2012, 29, 416–419. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Feng, Q.; Cao, W.; Zhang, L.; Ye, Y.; Gu, S. Radiolarian fauna from the Chiungchussuan Shuijingtuo Formation (Cambrian Series 2) in Western Hubei Province, South China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 49, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, A.; Tada, R. Silica diagenesis of Neogene diatomaceous and volcaniclastic sediments in northern Japan. Sedimentology 1981, 28, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschet, C. On the origin of cherts. Facies 1984, 10, 257–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, J.; Shao, X. Detecting detrital carbonate in shale successions-Relevance for evaluation of depositional setting and sequence stratigraphic interpretation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 130, 105130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M. Scanning-electron-microscope petrographic Evidence for distinguishing organic-matter pores associated with depositional organic matter versus migrated organic matter in mudrocks. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. J. 2014, 3, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, X.; Huang, W.; Ma, W.-X. Basic characteristics of shale and continuous-discontinuous transition gas reservoirs in SichuanBasin, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2009, 36, 578–592. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.S.; Jinxi, Z.Y.; Lei, J. Sichuan Basin: A superimposed sedimentary basin mainly controlled by its peripheric tectonics. Chin. J. Geol. 2018, 53, 308–326. [Google Scholar]
- Guowei, H.D.; Renqi, Z.L.; Zhu, W. Formation and evolution of multi-cycle superposed Sichuan Basin, China. Chin. J. Geol. 2011, 46, 589–606. [Google Scholar]
- Zhili, L.U.; Jianhui, H.A.; Chao, L.U.; Qihou, L.U.; Keyou, H. The discovery, characteristics and prospects of commercial oil and gas layers/reservoirs in Sichuan Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2013, 34, 504–514. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, K.K.; Liang, W.; Ge, X.Y.; Chen, X.W. Relationship between sedimentary facies and shale gas geological conditions of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas. J. Palaeogeogr. 2016, 18, 457–472. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. Main factors controlling the sedimentation of high-quality shale in Wufeng–Longmaxi Fm, Upper Yangtze region. Nat. Gas Ind. 2017, 37, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; He, Z.; Liu, G.; Du, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, G. Genetic mechanism of high-quality shale gas reservoirs in the Wufeng–Longmaxi Fms in the Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2020, 40, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Zhou, T.; Guo, W.; Liang, P.; Cheng, F. Quantitative paleogeographic mapping and sedimentary microfacies division in a deep-water marine shale shel: Case study of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale, southern Sichuan Basin, China. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Xuewen, S.; Yiqing, Z.; Jia, L.; Yi, L.; Liang, H.; Liang, X.; Yanyou, L.; Yao, C.; Jiayu, J. Sedimentary evolution and organic matter enrichment of Katian-Aeronian deep-water shale in Luzhou area, southern Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 43, 469–482. [Google Scholar]
- Shu-gen, L.; Bin, D.; Yong, Z. Unique geological features of burial and superimposition of the Lower Paleozoic shale gas across the Sichuan Basin and its periphery. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, N.; Yang, Y.; Rui, X. Thermal maturity of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 953–971. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, B.; Wei, F.; Lu, L.; Pan, A. Marine shale gas exploration theory in southern China: Review and prospects. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Mou, C.; Ge, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Q.; Liang, W.; Chen, C. Study on clay minerals in the lower silurian Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin and its periphery. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2014, 25, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, B.; Liu, S.; Sun, W.; Ye, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, J. Lithofacies classification of shales of the Lower Paleozoic Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Sichuan Basin and its surrounding areas, China. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 96–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yu-Man, W.A.; Chu-Fang, W.A.; Da-Zhong, D.O. Lithofacies characterization of Longmaxi Formation of the Lower Silurian, southern Sichuan. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 119–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Nie, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R.; Du, W.; Wang, R. Quartz type and its control on shale gas enrichment and production: A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Sichuan Basin and its surrounding areas, China. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 3692–3704. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y. Research progress in Early diagenesis of biogenic silica. Geol. Rev. 2010, 56, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.F.; Wei, C.D.; Ning, W.K.; Xu, S.N.; Jiang, Y.S. Structure and adsorption properties of Nenjiang opal shale. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2010, 40, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Lu, L.; Liu, W.; Shen, B.; Yu, L.; Yang, Y. Pore network changes in opaline siliceous shale during diagenesis. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2017, 39, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Liu, W.; Yu, L.; Zhang, W.; Shen, B.; Teng, G. Early diagenesis characteristics of biogenic opal and its influence on porosity and pore network evolution of siliceous shale. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2020, 42, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Milliken, K.L.; Olson, T. Silica diagenesis, porosity evolution, and mechanical behavior in siliceous mudstones, Mowry Shale (Cretaceous),Rocky Mountains, U.S.A. J. Sediment. Res. 2017, 87, 366–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schicker, A.; Gier, S.; Schieber, J.; Krois, P. Diagenesis of the Malmian Mikulov Formation source rock, Vienna Basin: Focus on matrix and pores. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 129, 105082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, W. Study on the genesis of pyrite in the Longmaxi Formation shale in the Upper Yangtze Area. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.; Xian, Y.; Yuan, B.; Dai, X.; Cao, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Formation mechanism and formation environment of framboidal pyrite in Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation shale and its influence on shale reservoir in the southeastern Chongqing, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2020, 47, 514–521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Nie, H.; Tang, X.; DU, W.; Sun, C.; Chen, S. Pyrite type and its effect on shale gas accumulation: A case study of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin and its periphery. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2020, 42, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Grill, E.V.; Richards, F.A. Nutrient regeneration from phytoplankton decomposing in sea water. J. Mar. Res. 1964, 22, 51–69. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.C.; Huang, H.; Chen, F.Y.; Guo, Q.D. Carbonate factory and carbonate platform: Progress and prospects. J. Palaeogeogr. Chin. Ed. 2019, 21, 232–253. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, C.D. Diagenetic alteration in black shales. J. Geol. Soc. 1980, 137, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, J. Origin of carbonate minerals in organic matter-rich shale of Longmaxi formation in the Sichuan Basin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2019, 19, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, L.; Tao, Y.; Evans, C. Temporal and spatial distribution of whitings on Great Bahama Bank and a new lime budget. Geology 1997, 25, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chang, C.; Liu, C.; Zhong, D. Evolution of the Qinling Fold Belt and the movement of the north and south China blocks: The evidence of geology and paleomagnetism. Sci. Geol. Sin. 1990, 25, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, R. Planktonic foraminifera and deep sea carbonate dissolution. Offshore Oil 1982, 1, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Deep—sea carbonate compensation depth and lysocline. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 1987, 7, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Kemei, M.A. Carbonate compensation depth, saturation horizon and lysocline in the northeast region of South China Sea. Trop. Oceanol. 1988, 7, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S. Ocean drilling program and the development of paleoceanography. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 1994, 13, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P. Geological evolution of the ocean carbon cycle. Adv. Nat. Sci. 2006, 16, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Mou, C.; Wang, Q.; Ge, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, K.; Liang, W. Diagenesis of black shale in Longmaxi Formation, southern Sichuan Basin and its periphery. Acta Pet. Sin. 2015, 36, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J. Study of shale reservoir diagenesis of the Wufeng—Longmaxi Formations in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin. J. Miner. Pet. 2017, 37, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Machel, H.G. Bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings—Old and new insights. Sediment. Geol. 2001, 140, 143–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkin, R.T.; Barnes, H.L.; Brantlsy, S.L. The size distribution of framboidal pyrite in modern sediments: An indicator of redox conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 3897–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gong, Y. Pyrite Framboid: Indicator of Environments and Life. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2011, 36, 643–658. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, C. Morphologic and Isotopic Characteristics of Sedimentary Pyrite: A case study from deepwater facies, Ediacaran Lantian Formation in South China. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2020, 38, 138–149. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Zhou, W.; Deng, N.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X.; Yi, T.; Yang, P. Characteristics and geological significance of pyrites in Wufeng and Longmaxi Formation reservoir shale in Sichuan Basin, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2020, 47, 50–64. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lu, X.; Bian, L. Formation mechanism and geological significance of the pyrite framboids in the cyst of Tasmanites in the Dalong formatin cropped in the Kuangshanliang area, Northern Sichuan Province. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lu, X.; Bian, L. Formation of pyrite framboids in the chamber of foraminiferas and its geological significance: A case study of the foraminiferas fossils in the Qixia Formation in the Yanmenkou Area, Hubei Province. Geol. J. China Univ. 2009, 15, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.M.; Goering, J.J. Near-surface silica dissolution in the upwelling region off Northwest Africa. Deep Sea Res. 1977, 24, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.M.; Tréguer, P.; Brzezinski, M.A.; Leynaert, A.; Quéguiner, B. Production and dissolution of biogenic silica in the ocean: Revised global estimates, comparison with regional data and relationship to biogenic sedimentation. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 1995, 9, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, D.S.; Hurd, D.C.; Pankratz, H.S. Silica dissolution rates of decomposing phytoplankton assemblages at various temperatures. Am. J. Sci. 1978, 278, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamatani, A. Dissolution rates of silica from diatoms decomposing at various temperatures. Mar. Biol. 1982, 68, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolper, D.A.; Love, G.D.; Bates, S.; Lyons, T.W.; Young, E.; Sessions, A.L.; Grotzinger, J.P. Paleoecology and paleoceanography of the Athel silicilyte, Ediacaran-Cambrian boundary, Sultanate of Oman. Geobiology 2017, 15, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, J.I.; Keil, R.G.; Benner, R. What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Bioavailability of dissolved organic carbon linked with the regional carbon cycle in the East China Sea. Deep. Res. Part Ⅱ 2016, 124, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alldredge, A.L.; Cowles, T.J.; MacIntyre, S.; Rines, J.E.; Donaghay, P.L.; Greenlaw, C.F.; Holliday, D.V.; Dekshenieks, M.M.; Sullivan, J.M.; Zaneveld, J.R. Occurrence and mechanisms of formation of a dramatic thin layer of marine snow in a shallow Pacific fjord. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 233, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Shin, H.S.; Park, H. Characterization of humic substances present in landfill leachates with different landfill ages and its implications. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4023–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Bai, Z.; Li, Y.; Kong, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, C.; Yang, B.; Xu, F. Advances in environmental behaviors and effects of dissolved organic matter in aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2016, 46, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druffel, E.R.; Williams, P.M.; Bauer, J.E.; Ertel, J.R. Cycling of dissolved and particulate organic matter in the open ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1992, 97, 15639–15659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Cai, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, X. The diversity of organic matter in marine sediments and the suspiciousness of source parameters: A review. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Zeng, X.; Wei, H.; Song, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. From water body to sediments: Exploring the depositional processes of organic matter and their implications. J. Palaeogeogr. 2019, 21, 49–67. [Google Scholar]
- Tissot, B.; Durand, B.; Espitalié, J.; Combaz, A. Influence of nature and diagenesis of organic matter in formation of petroleum. AAPG Bull. 1974, 58, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Lewan, M.D. Hydrous pyrolysis. In Encyclopedia of Petroleum Geoscience; Sorkhabi, R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, R.G.; Ruppel, S.C. Mississippian Barnett Shale: Lithofacies and depositional setting of a deep-water shale-gas succession in the Fort Worth Basin, Texas. AAPG Bull. 2007, 91, 579–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Jarvie, D.M. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett shale. J. Sediment. Res. 2009, 79, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Hammes, U. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.M.; Loucks, R.G.; Ko, L.T. Scanning electron microscopic petrographic differentiation among different types of pores associated with organic matter mudrocks. GCAGS J. 2020, 9, 17–27. [Google Scholar]






| No. | Well | Depth/m | Fm. | Thickness/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H202-1 | Huang202 | 4079.03 | Longmaxi | 3.2 |
| L205-1 | Lu205 | 4031.23 | Longmaxi | 3.1 |
| L207-1 | Lu207 | 3461.58 | Wufeng | 1.0 |
| Z205-1 | Zi205 | 4103.37 | Wufeng | 4.8 |
| Z205-2 | Zi205 | 4103.96 | Wufeng | 1.8 |
| No. | Well | Depth/m | Sample Location | Results/Mass/% | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | FeO | MgO | MnO | Na2O | K2O | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | BaO | TiO2 | SrO | CO2 | Total | ||||
| H202-1 | Huang202 | 4079.03 | 1 | 55.645 | 0.301 | 0.148 | 0.079 | 0.018 | 0.024 | 0.014 | 0.019 | 0.015 | 0.002 | / | / | 43.721 | 99.986 |
| 2 | 55.601 | 0.241 | 0.057 | 0.356 | 0.008 | 0.012 | 0.031 | / | 0.014 | / | / | / | 43.687 | 100.007 | |||
| L205-1 | Lu205 | 4031.23 | 1 | 55.585 | 0.331 | 0.159 | 0.279 | / | / | / | / | 0.030 | / | 0.002 | / | 43.674 | 100.060 |
| 2 | 55.672 | 0.345 | 0.116 | 0.321 | 0.013 | / | / | 0.002 | 0.003 | / | / | / | 43.742 | 100.214 | |||
| L207-1 | Lu207 | 3461.58 | 1 | 55.929 | 0.040 | 0.021 | 0.019 | / | 0.017 | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.003 | / | / | / | 43.942 | 99.997 |
| 2 | 54.956 | 0.491 | 0.119 | 0.237 | 0.003 | 0.014 | 0.012 | / | 0.066 | / | 0.015 | / | 43.180 | 99.093 | |||
| Z205-1 | Zi205 | 4103.37 | 1 | 55.653 | 0.277 | 0.141 | 0.214 | / | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.039 | / | / | / | 43.727 | 100.089 |
| 2 | 55.435 | 0.416 | 0.102 | 0.067 | / | 0.005 | / | / | 0.024 | / | / | / | 43.556 | 99.605 | |||
| Z205-2 | Zi205 | 4103.96 | 1 | 55.872 | 0.080 | 0.013 | 0.028 | / | 0.008 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.041 | / | 0.005 | / | 43.899 | 99.969 |
| 2 | 55.814 | 0.143 | 0.127 | 0.079 | / | 0.078 | 0.010 | 0.009 | 0.026 | / | / | / | 43.854 | 100.141 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Liang, P.; Li, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Filling Characteristics of Radiolarian Siliceous Shell Cavities at Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale in Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Minerals 2022, 12, 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121545
Zhou X, Liang P, Li X, Guo W, Zhang X, Yu J. Filling Characteristics of Radiolarian Siliceous Shell Cavities at Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale in Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Minerals. 2022; 12(12):1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121545
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaofeng, Pingping Liang, Xizhe Li, Wei Guo, Xiaowei Zhang, and Jichen Yu. 2022. "Filling Characteristics of Radiolarian Siliceous Shell Cavities at Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale in Sichuan Basin, Southwest China" Minerals 12, no. 12: 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121545
APA StyleZhou, X., Liang, P., Li, X., Guo, W., Zhang, X., & Yu, J. (2022). Filling Characteristics of Radiolarian Siliceous Shell Cavities at Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale in Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Minerals, 12(12), 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121545






