Iron Extraction from South African Ilmenite Concentrate Leaching by Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) in the Presence of Reductant (Metallic Fe) and Additive (MgSO4)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
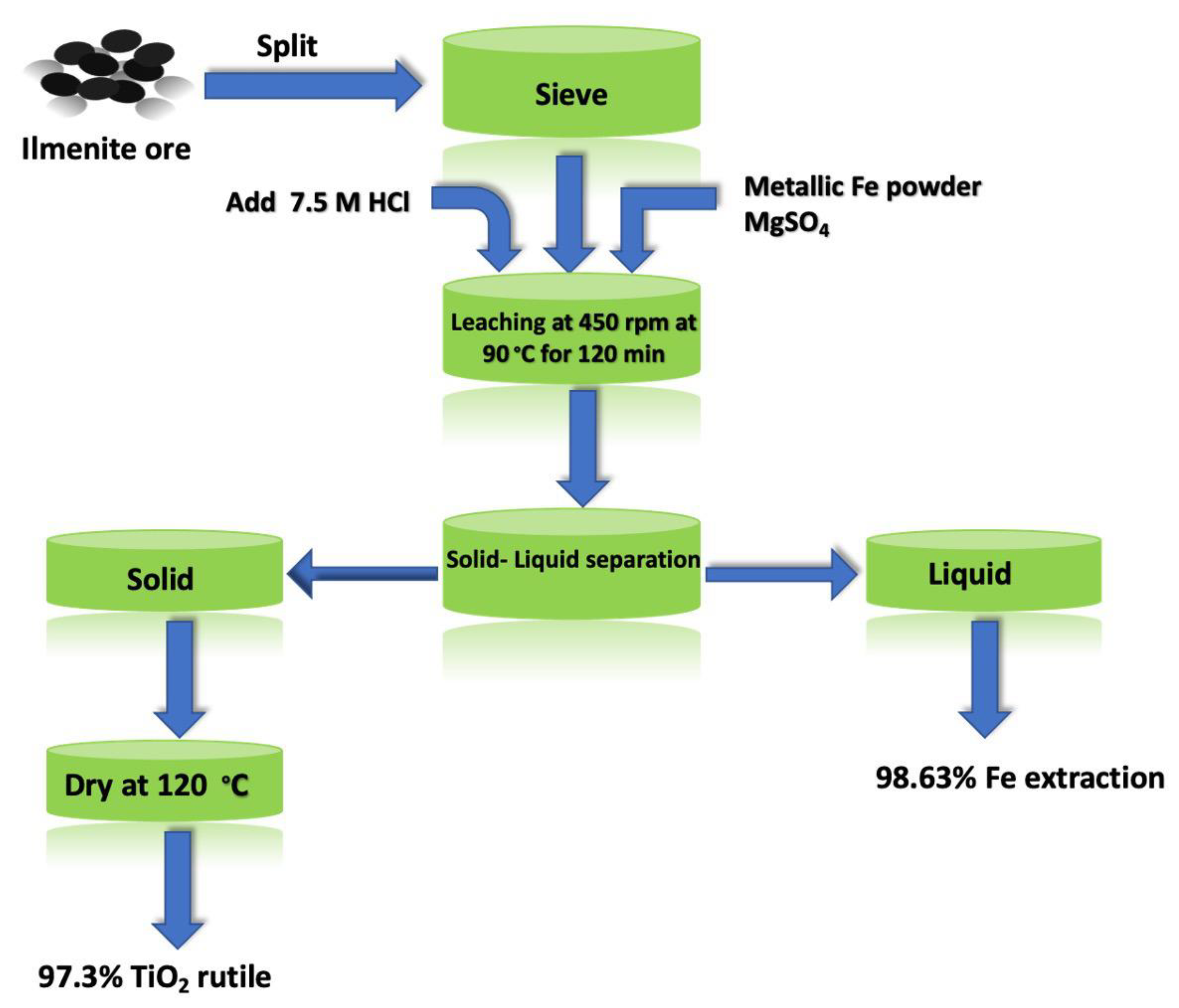
2.3. Leaching Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
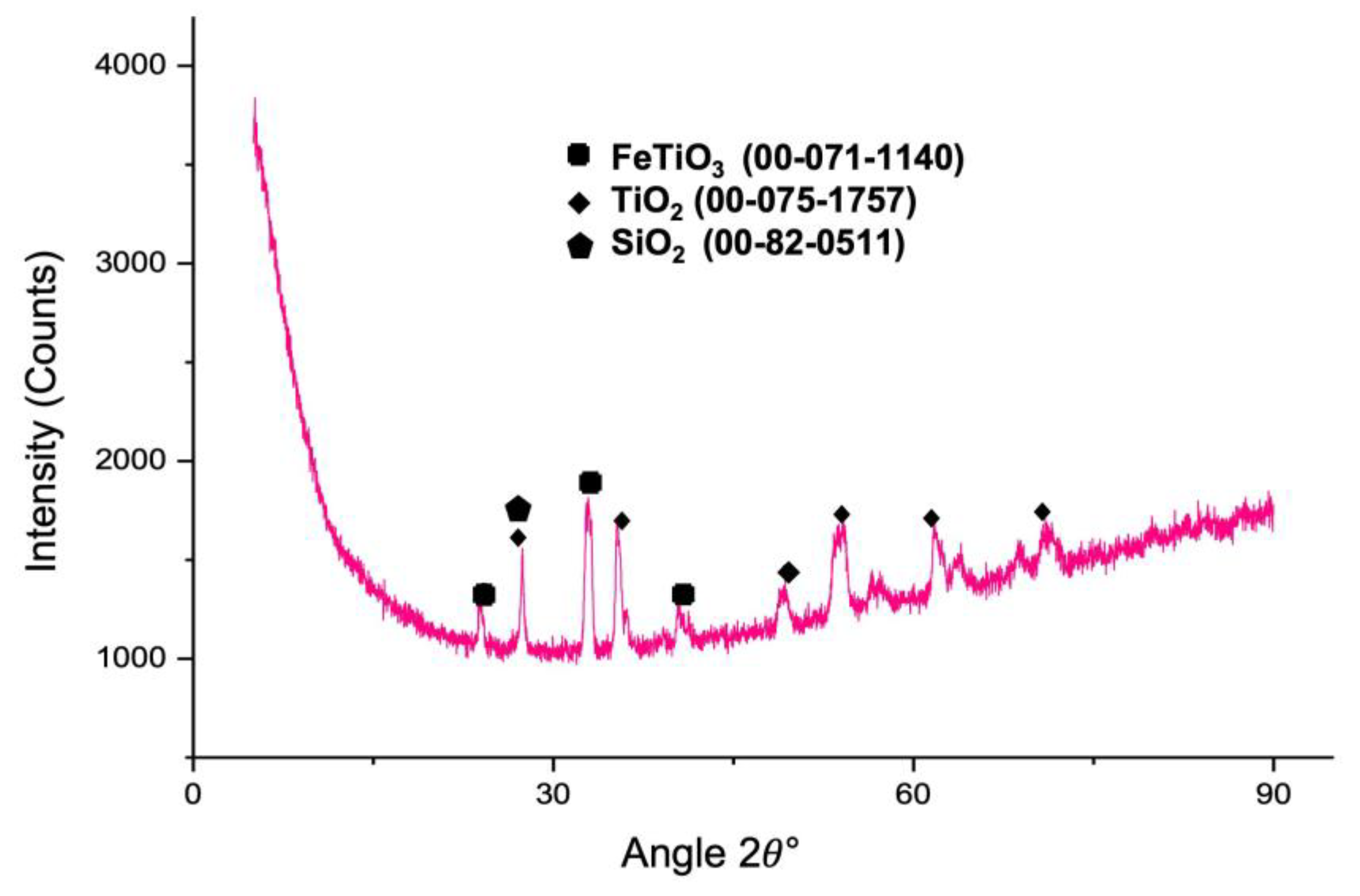
3.1. Mineralogical Analysis
3.2. The Effect of Particle Size Distribution
3.3. Influence of HCl Acid Concentration
3.4. Effect of Temperature
3.5. Effect of Agitation Speed
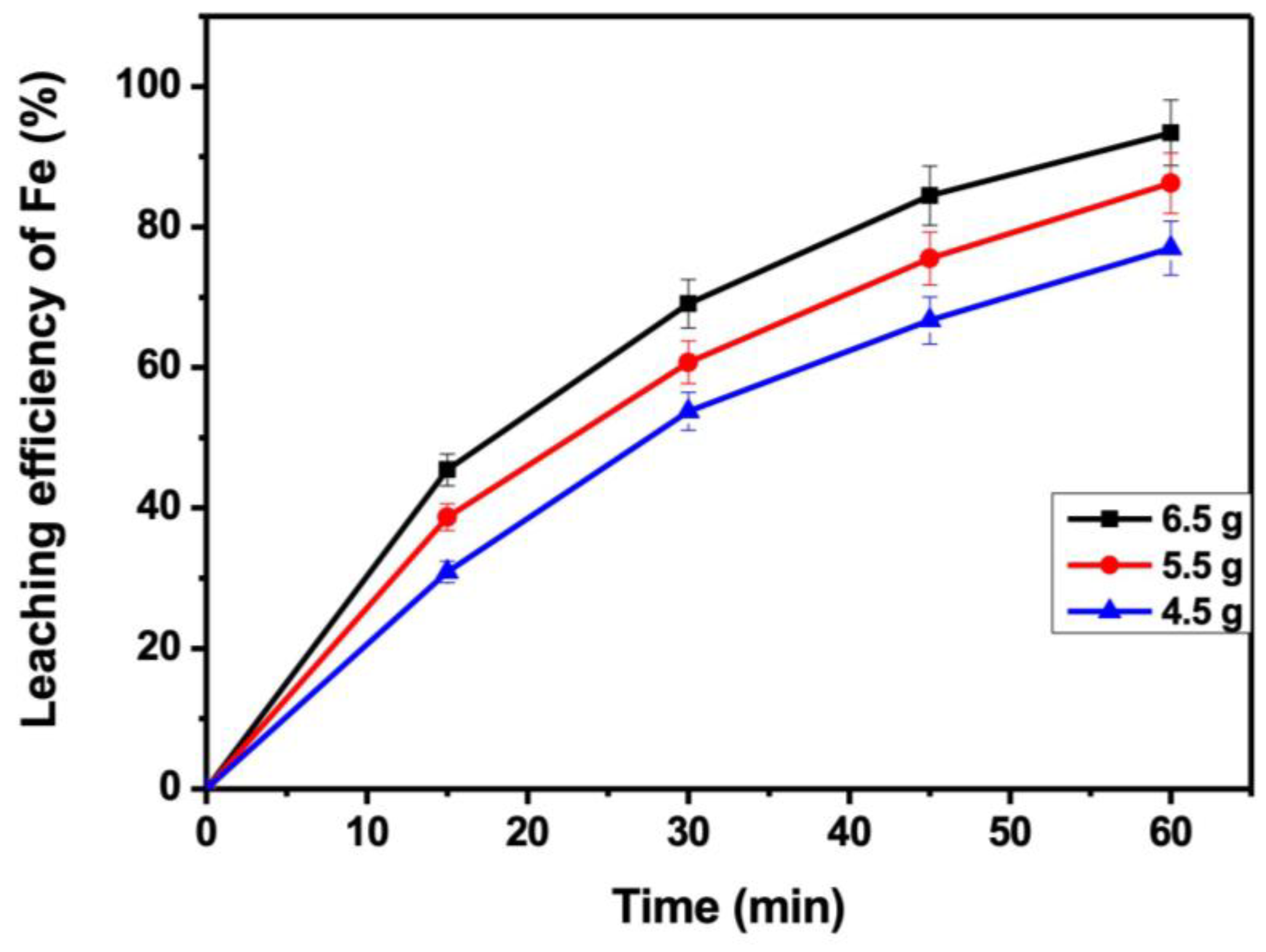
3.6. Effect of Solid–Liquid Ratio
3.7. Effect of Metallic Fe Powder Addition
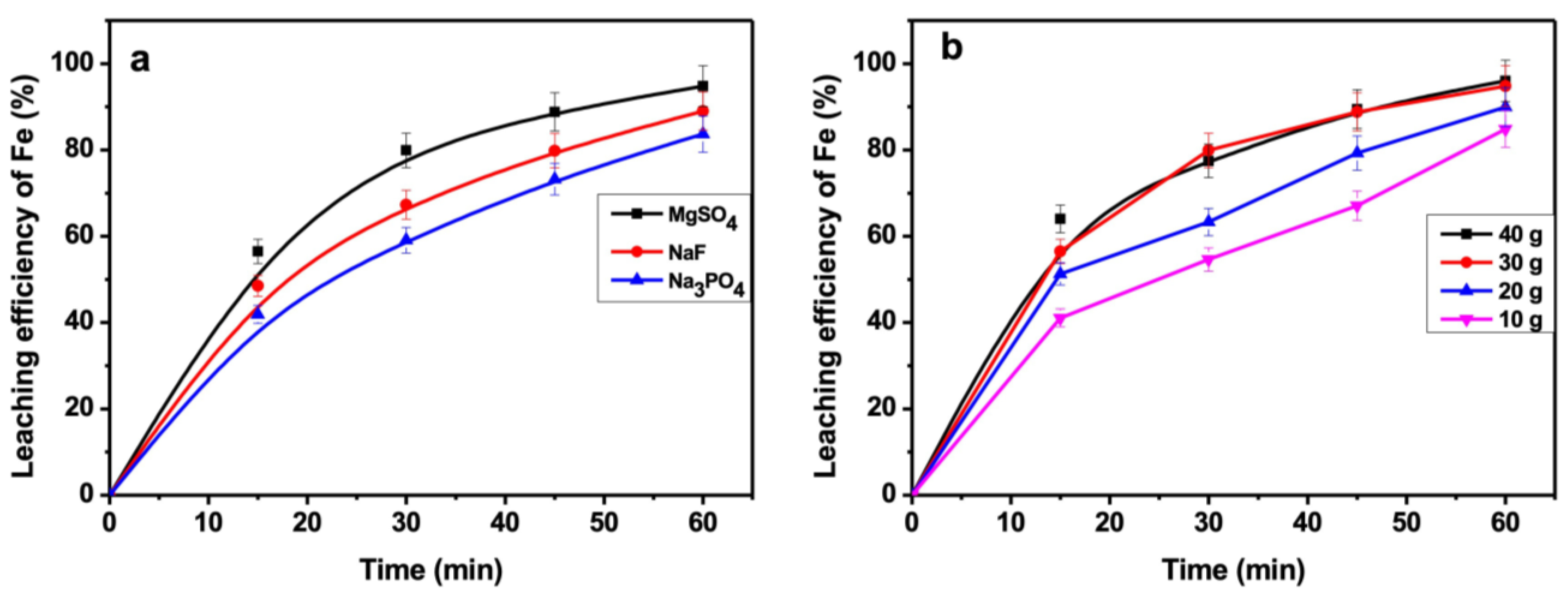
3.8. Effect of Additives
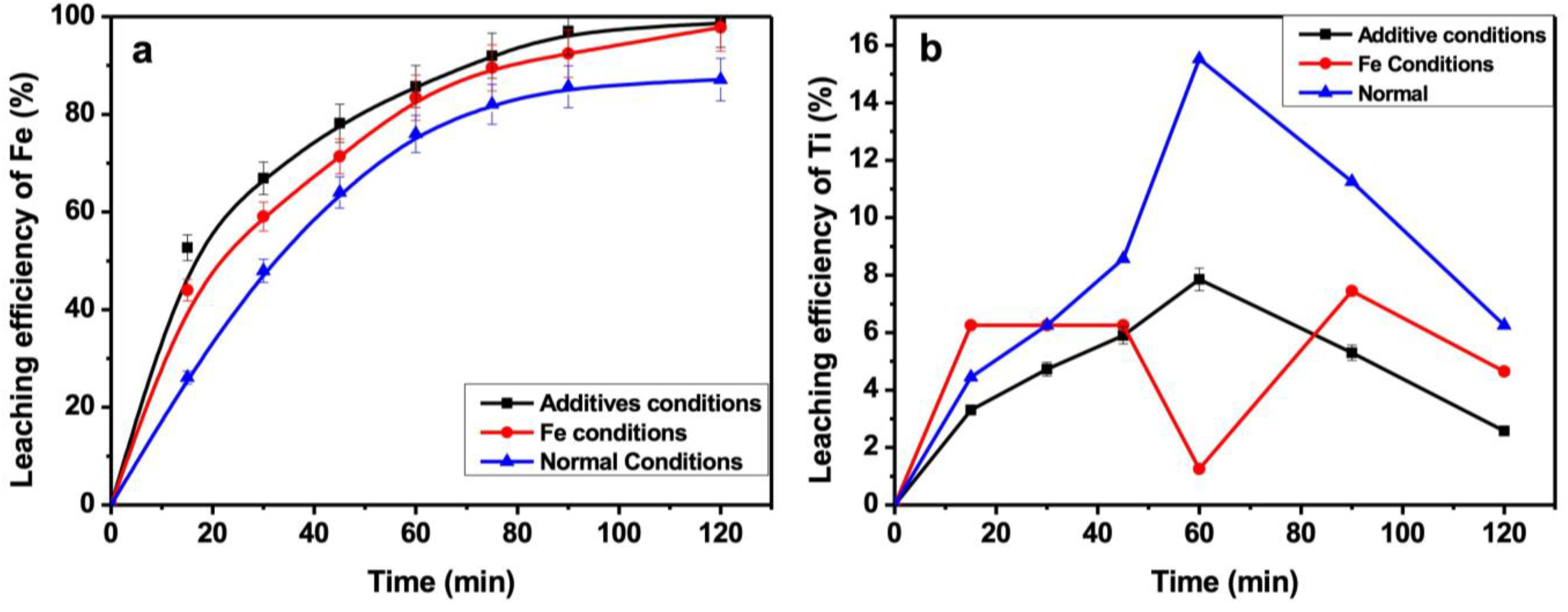
3.9. Effect of Retention Time
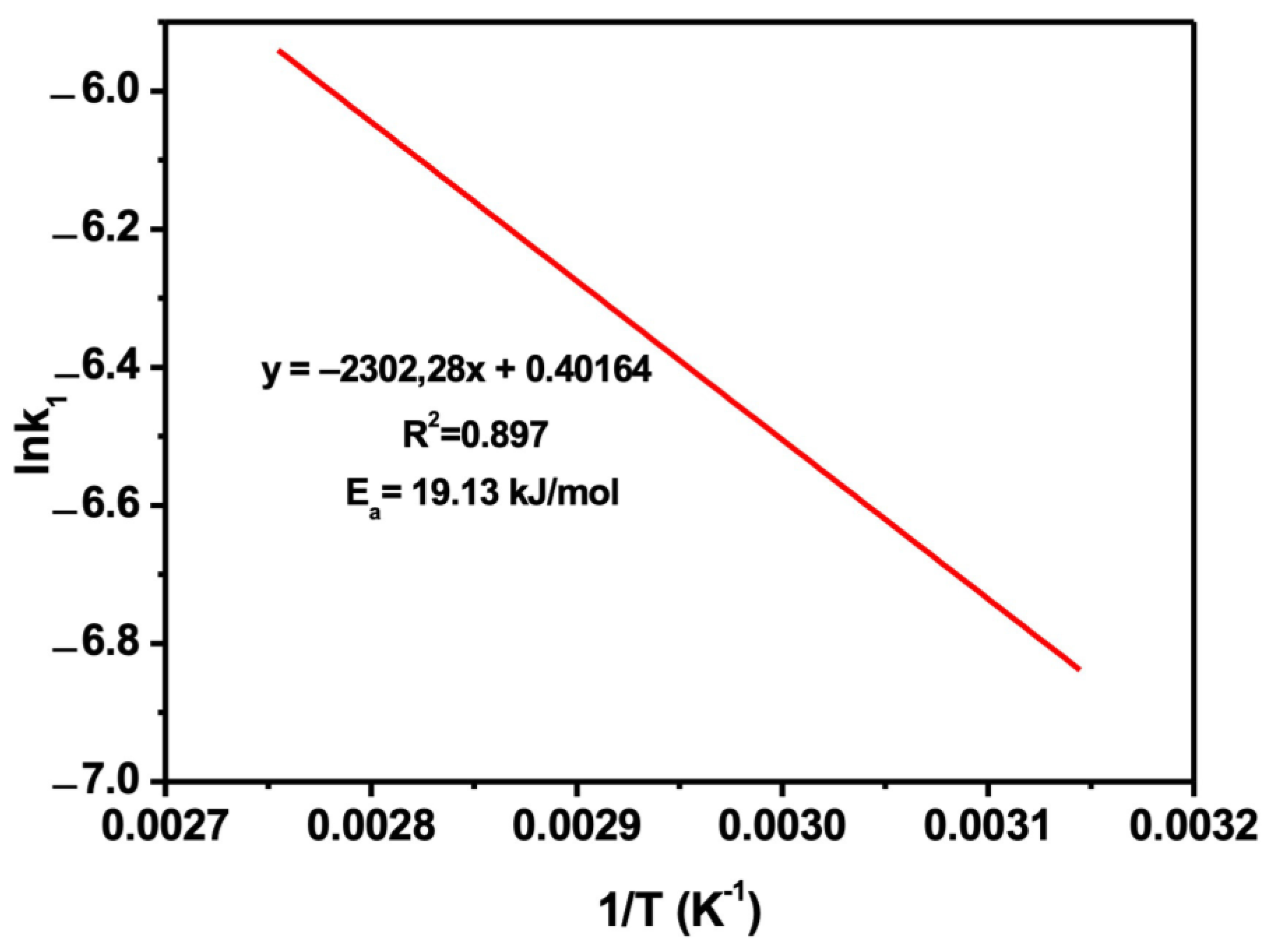
3.10. Leaching Kinetics
3.11. Characterization of the Leach Residue
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juergen, H.; Braun, A.; Baidins, R.; Marganski, E. TiO2 Pigment Technology: A Review. Prog. Org. Coat. 1992, 20, 109–110. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Sutton, N.B.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Langenhoff, A.A.M. Corrigendum to “Degradation of Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater Using Immobilized TiO2 Photocatalysis under Simulated Solar Irradiation” [Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 182 (2016) 132–141]. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 189, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.C.; Sharma, A.; Devan, R.S.; Shirage, P.M. Role of Different Counter Electrodes on Performance of TiO2 Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell (DSSC) Fabricated with Dye Extracted from Hibiscus Sabdariffa as Sensitizer. Opt. Mater. 2022, 124, 112066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Paik, U. TiO2 as an Active or Supplemental Material for Lithium Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S. The Dissolution of Iron in the Hydrochloric Acid Leach of Titania Slag Obtained from Plasma Melt Separation of Metalized Ilmenite. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 2190–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambiliyagodage, C.; Wijesekera, R.; Bakker, M.G. Leaching of Ilmenite to Produce Titanium Based Materials: A Review. Discov. Mater. 2021, 1, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahien, M.G.; Khedr, M.M.H.; Maurice, A.E.; Farghali, A.A.; Ali, R.A.M. Synthesis of High Purity Rutile Nanoparticles from Medium-Grade Egyptian Natural Ilmenite. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, A.M.; Farghaly, M.; Fathy, W.M.; Ahmed, M.M. Leaching and Kinetics Studies on Processing of Abu-Ghalaga Ilmenite Ore. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.H.H.; Afifi, A.A.I.; Ibrahim, I.A. Reductive Leaching of Ilmenite Ore in Hydrochloric Acid for Preparation of Synthetic Rutile. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 73, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, I.; MacRae, C.; Silvester, E.; Susini, J. Behaviour of Impurity Elements during the Weathering of Ilmenite. Mineral. Mag. 2005, 69, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Matsuura, H.; Tsukihashi, F. Reduction Extraction Kinetics of Titania and Iron from an Ilmenite by H2–Ar Gas Mixtures. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhgar, B.N.; Pazouki, M.; Ranjbar, M.; Hosseinnia, A.; Salarian, R. Application of Taguchi Method for Optimization of Synthetic Rutile Nano Powder Preparation from Ilmenite Concentrate. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhique, A.J.; Focke, W.W.; Madivate, C. Titania Recovery from Low-Grade Titanoferrous Minerals. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeri, M.Y.; Kipouros, G.J. Processing Titanium and Lithium for Reduced-Cost Application. JOM 1997, 49, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, C.Y. A Literature Review of Titanium Metallurgical Processes. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, T.; Chu, J.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Y. Decomposition of Ilmenite by Concentrated KOH Solution under Atmospheric Pressure. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 81, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.S. A Critical Evaluation of Processes to Produce Primary Titanium. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2009, 109, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Habashi, F.; Kamaleddine, F.; Bourricaudy, E. A New Process to Upgrade Ilmenite to Synthetic Rutile. Metall 2015, 69, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara, T.; de Araújo, R.V.V. Hydrochloric Acid Leaching of a Pre-Reduced Brazilian Ilmenite Concentrate in an Autoclave. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 56, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, N.Y.; Hessien, M.M.; Shaltout, A.A. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterizations of Ti Substituted Mn-Ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 529, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demopoulos, G.P.; Li, Z.; Becze, L.; Moldoveanu, G.; Cheng, T.C.; Harris, B. New Technologies for HCl Regeneration in Chloride Hydrometallurgy. World Metall. 2008, 61, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- De, A.K.; Khopkar, S.M.; Chalmers, R.A. Solvent Extraction of Metals; Ven Nostrand, Reinhold Co.: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M. Chemistry of Solvent Extraction; Kyoritsu Shuppan: Tokyo, Japan, 1977; pp. 2–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sasikumar, C.; Rao, D.S.; Srikanth, S.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K.; Mehrotra, S.P. Dissolution Studies of Mechanically Activated Manavalakurichi Ilmenite with HCl and H2SO4. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 88, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, T.S. Acid Leaching of Ilmenite into Synthetic Rutile. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1974, 13, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Chen, Q.Y.; Hu, H.P.; Yin, Z.L.; Chen, Y. TiO2 Nanoparticles Prepared by Hydrochloric Acid Leaching of Mechanically Activated and Carbothermic Reduced Ilmenite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2012, 22, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Hu, H.; Chen, Q.; Tan, J. Effects of Mechanical Activation on the HCl Leaching Behavior of Plagioclase, Ilmenite and Their Mixtures. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 99, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.; Metson, J. Acid Attack on New Zealand Ilmenite. I: The Mechanism of Dissolution. II: The Structure and Composition of the Solid. N.Z.J. Sci. 1982, 25, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Sasikumar, C.; Rao, D.S.; Srikanth, S.; Ravikumar, B.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K.; Mehrotra, S.P. Effect of Mechanical Activation on the Kinetics of Sulfuric Acid Leaching of Beach Sand Ilmenite from Orissa, India. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 75, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkáčová, K.; Baláž, P. Reactivity of Mechanically Activated Chalcopyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1996, 44, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welham, N.J. Enhanced Dissolution of Tantalite/Columbite Following Milling. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2001, 61, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.K.; Pranolo, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, C.Y. Leaching of Ilmenite Ores by Acidic Chloride Solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 133, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gireesh, V.S.; Vinod, V.P.; Nair, S.K.; Ninan, G. Effect of Sulphate Ions on Leaching of Ilmenite with Hydrochloric Acid. J. Acad. Ind. Res. 2013, 2, 402–404. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, M.A.; Biswas, R.K.; Ali, M.R.; Hasan, A.K.M. Leaching of Non-Treated Ilmenite by HCl-CH3OH-H2O Mixture and Its Kinetics. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2006, 13, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, A.; Putnis, A. Processes of Oxidation and HCl-Leaching of Tellnes Ilmenite. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakokovhu, M.; Ramakokovhu, M.M.; Olubambi, P.A.; Mbaya, R.K.K.; Mojisola, T.; Teffo, M.L. Mineralogical and Leaching Characteristics of Altered Ilmenite Beach Placer Sands. Minerals 2020, 10, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojisola, T.; Ramakokovhu, M.M.; Raethel, J.; Olubambi, P.A.; Matizamhuka, W.R. In-Situ Synthesis and Characterization of Fe–TiC Based Cermet Produced from Enhanced Carbothermally Reduced Ilmenite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 78, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepka, M.; Lawniczak-Jablonska, K.; Jablonski, M.; Wolska, A.; Minikayev, R.; Paszkowicz, W.; Przepiera, A.; Spolnik, Z.; Grieken, R. Van Combined XRD, EPMA and X-Ray Absorption Study of Mineral Ilmenite Used in Pigments Production. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 401, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, A.A.; Awwad, N.S.; Aly, H.F. Kinetics of Acid Leaching of Ilmenite Decomposed by KOH. Part 2. Leaching by H2SO4 and C2H2O4. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, R.G.; Kruger, D.; Rajashekar, R. The Digestion of New Zealand Ilmenite by Hydrochloric Acid. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 163, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilakazi, A.Q. Hydrometallurgical Beneficiation of Ilmenite. Master’s Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, M.; Gazquez, J.; Bolivar, J.P. Isolation and Characterization of the Mineral Phases in Ilmenite Ore: Optimization of the TiO2 Pigment Process Abstract. J. Waste Recycl. 2017, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hugo, V.E. A Study of Titanium-Bearing Oxides in Heavy Mineral Deposits along the East Coast of South Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Natal, Durban, South Africa, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Olanipekun, E. A Kinetic Study of the Leaching of a Nogerian Ilmenite Ore by Hydrocloric Acid. Hydrometallurgy 1999, 53, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.A.; Swaroopa, S.; Ghosh, M.K.; Adekola, F.A. Mineralogical Characterization and Leaching Behavior of Nigerian Ilmenite Ore. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2013, 23, 2743–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabit, N.A. Chemical and Electrochemical Leaching Studies of Synthetic and Natural Ilmenite in Hydrochloric Acid Solutions. Ph.D. Thesis, Murdoch University, Perth, Australia, 2017; pp. 1–303. [Google Scholar]
- Deysel, K. Leucoxene Study: A Mineral Liberation Analysis (MLA) Investigation. In Proceedings of the the 6th International Heavy Minerals Conference ‘Back to Basics’, Hluhluwe, South Africa, 9–14 September 2007; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J.S. A Kinetic Study of the Dissolution of Allard Lake Ilmenite in Hydrochloric Acid; The University of Utah: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1975; ISBN 9798660719035. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, H.N. Hydrochloric Acid Leaching of Ilmenite. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Extractive Metallurgy, Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Melborne, Australia, 12–14 November 1984; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Li, J.-J.; Wang, L.-L.; Wang, Z.-J.; Wang, J.-C. Implementing Continuous Freeze-Casting by Separated Control of Thermal Gradient and Solidification Rate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 133, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, J.P.; Vegter, N.M.; Pistorius, P.C. Kinetics of Ilmenite Dissolution in Hydrochloric Acid. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 65, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.-Y.; Muir, D.M. Dissolution of Metal Ferrites and Iron Oxides by HCl under Oxidising and Reducing Conditions. Hydrometallurgy 1988, 21, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.F.; Sinha, H.N.; Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization. Treatment of Ilmenite. U.S. Patent US3922164A, 25 November 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Dubenko, A.; Nikolenko, M.; Kostyniuk, A.; Likozar, B. Sulfuric Acid Leaching of Altered Ilmenite Using Thermal, Mechanical and Chemical Activation. Minerals 2020, 10, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 047125424X. [Google Scholar]
- Crundwell, F.K. The Dissolution and Leaching of Minerals: Mechanisms, Myths and Misunderstandings. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 139, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabit, N.A.; Senanayake, G. Characterization and Leaching Kinetics of Ilmenite in Hydrochloric Acid Solution for Titanium Dioxide Production. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1082, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

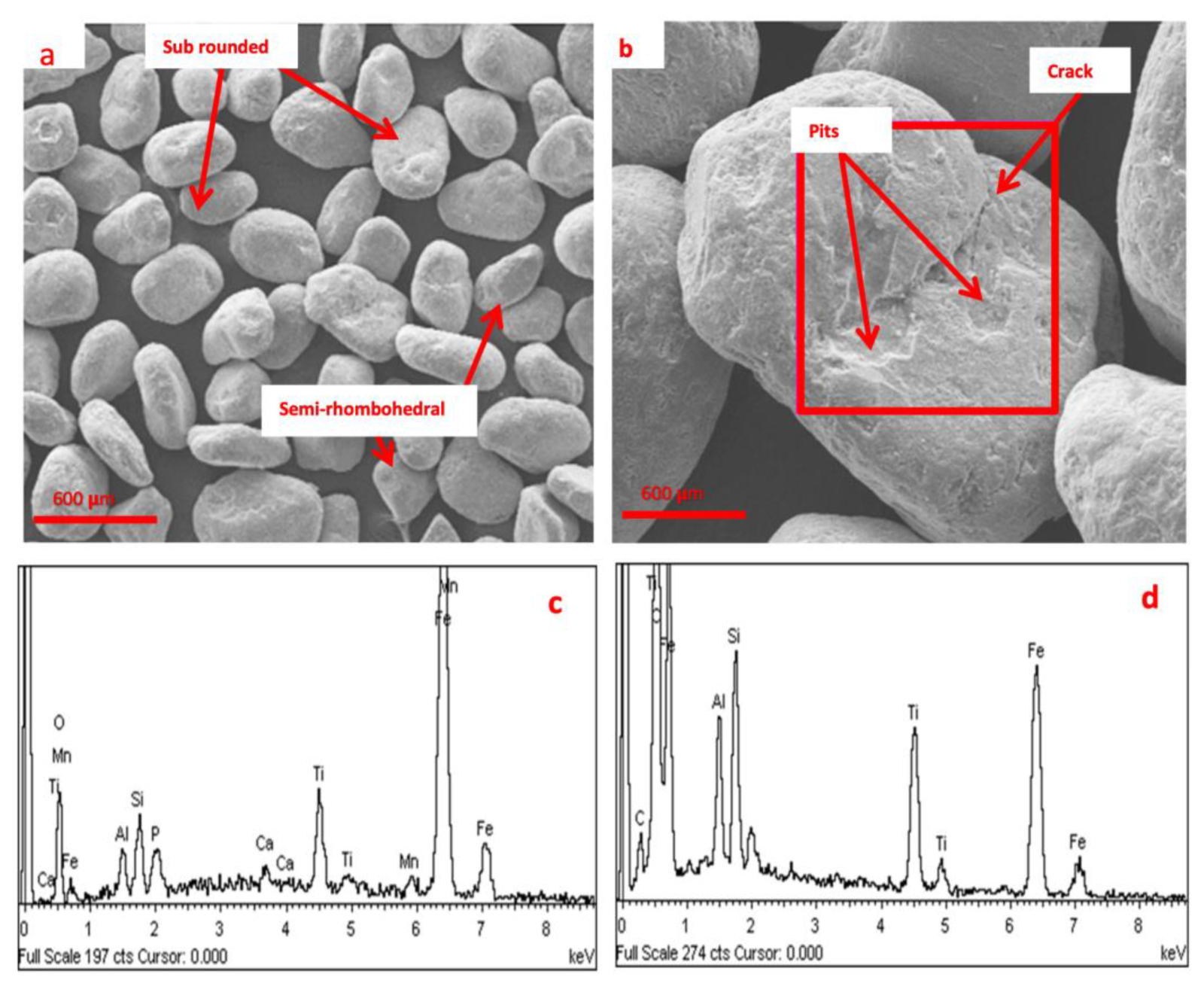
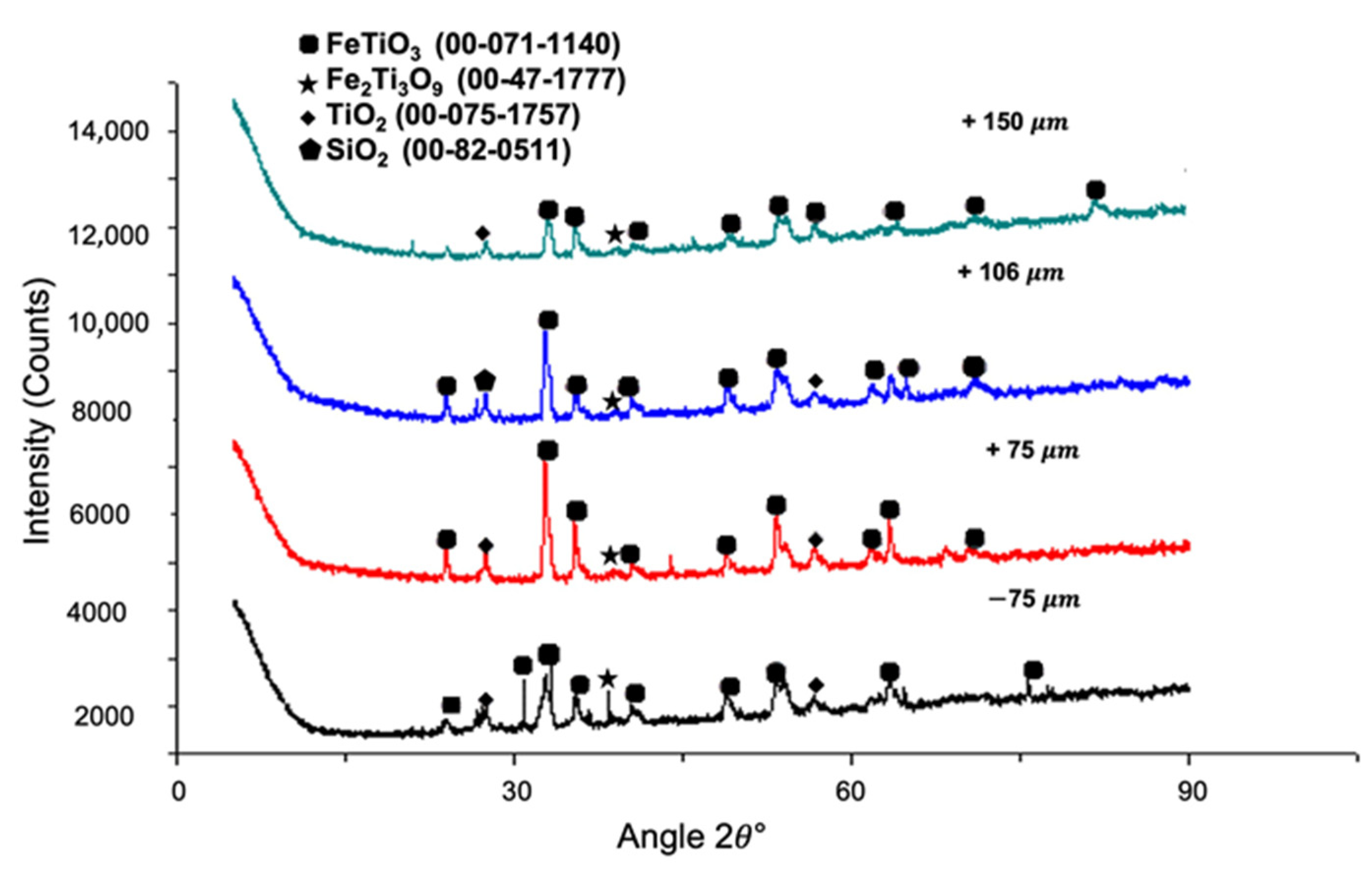

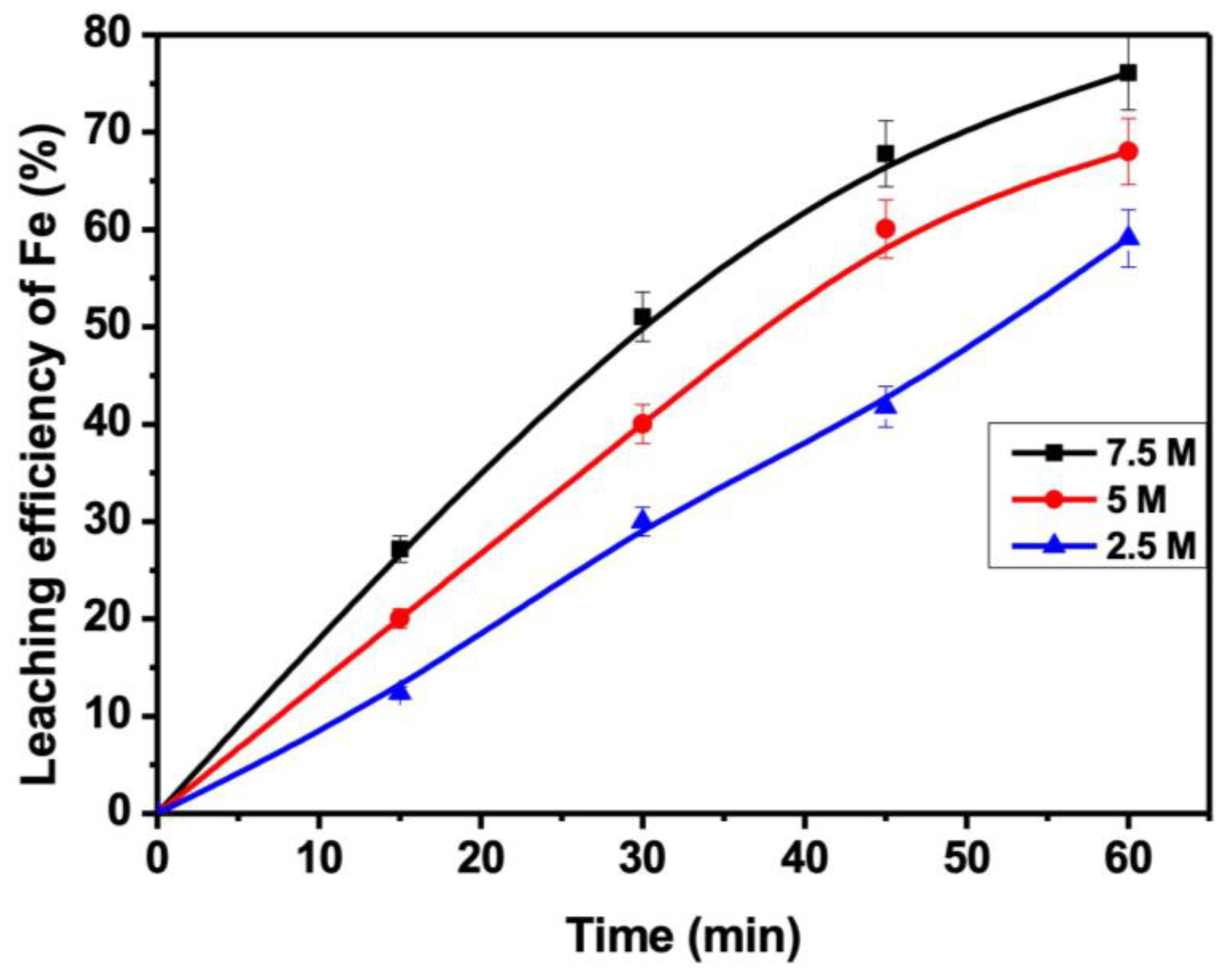
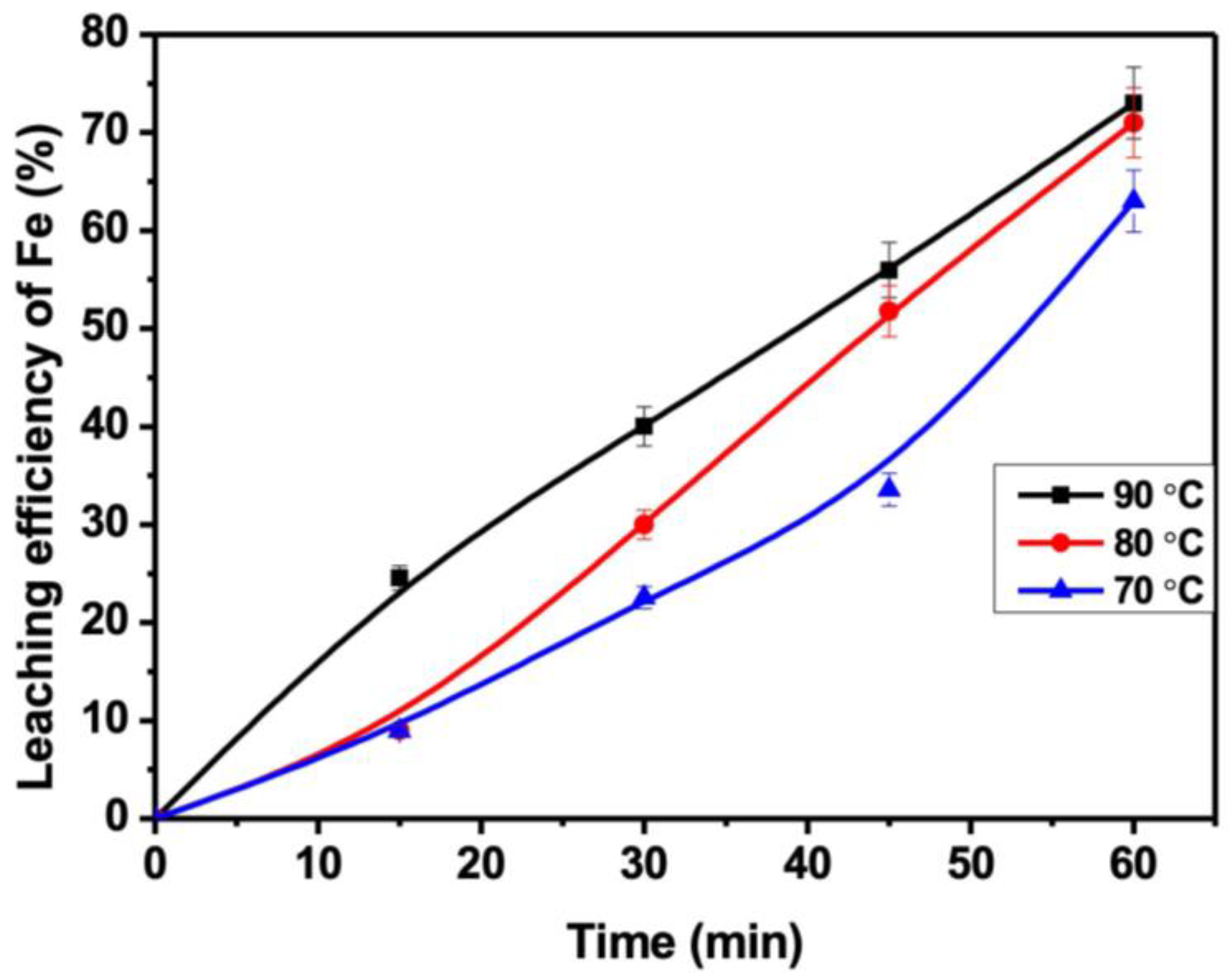


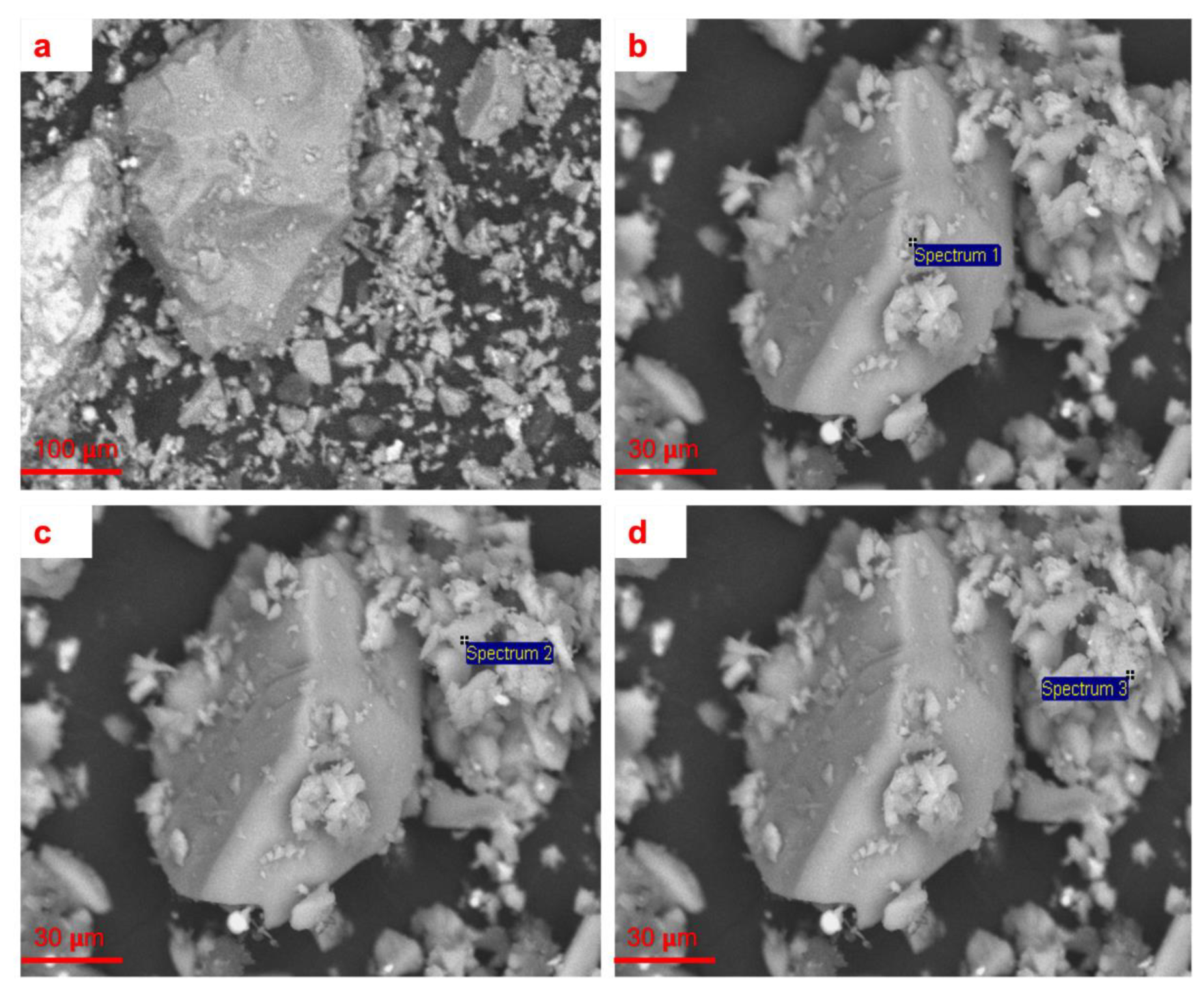
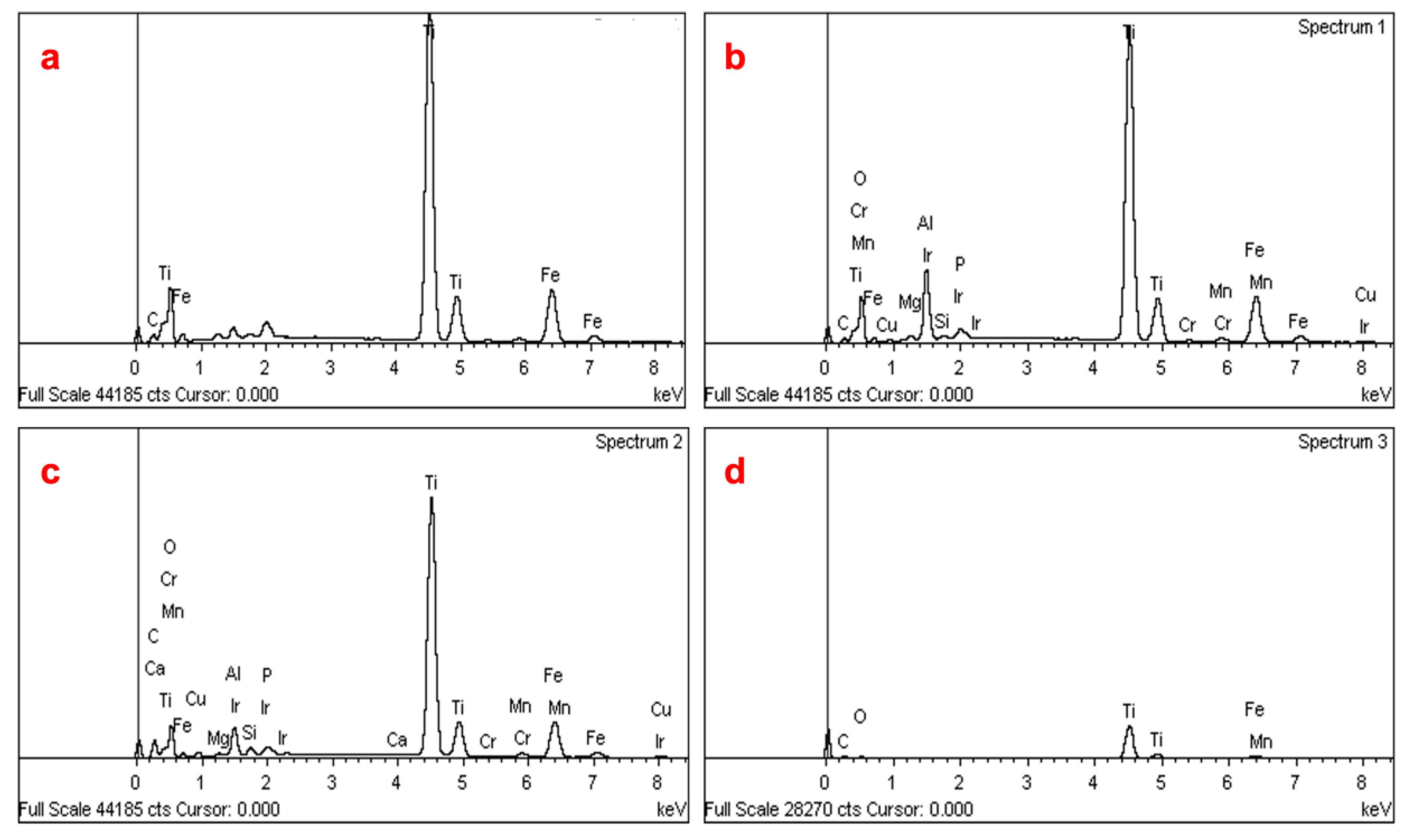
| Leaching Experiment | Material | Temperature (°C) | Concentration (M) | Additives (30 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition 1 | 70 g ilmenite HCl | 70 | 2.5 | |
| 80 | 5 | |||
| 90 | 7.5 | |||
| Condition 2 | 70 g ilmenite HCl | 90 | 7.5 | Fe metallic powder MgSO4 Na3PO4 NaF |
| Compounds | Percentage (wt.%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ilmenite | −75 µm | +75 µm | +106 µm | +150 µm | |
| Fe2O3 TiO2 | 48.23 42.93 | 46.49 41.47 | 48.10 43.55 | 48.39 43.34 | 47.20 39.99 |
| SiO2 | 2.94 | 4.63 | 2.49 | 2.51 | 5.61 |
| Al2O3 | 1.71 | 2.17 | 1.63 | 1.65 | 2.21 |
| MnO | 1.11 | 1.04 | 0.99 | 1.06 | 1.36 |
| MgO | 0.80 | 1.08 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.90 |
| V2O5 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.33 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.40 |
| ZrO2 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.09 |
| CaO | 0.13 | 0.43 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.24 |
| Na2O | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.29 |
| Nb2O5 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.59 |
| P2O5 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.43 |
| Co3O4 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| K2O | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| ZnO | 0.14 | 0,07 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| Gd2O3 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| LOI | 0.43 | 0.84 | 0.9 | 0.95 | 0.14 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Elements | Concentration 10 mL HNO3 30 mL HCl | Concentration 20 mL HNO3 60 mL HCl |
|---|---|---|
| wt% | wt% | |
| Al | 9.1 | 6.4 |
| Co | 12.7 | 2.3 |
| Cu | 4.5 | 1.2 |
| Fe | 53.3 | 79.9 |
| Ni | 12.3 | 7.1 |
| S | 4.9 | 1.6 |
| Si | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| * Zn | 0.6 | - |
| * Th | - | 0.1 |
| Ti | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Other impurities | 1.7 | 0.9 |
| Time (min) | 350 rpm Actual Recovery | 450 rpm Actual Recovery | 550 rpm Actual Recovery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe % | Ti % | Fe % | Ti % | Fe % | Ti % | |
| 15 | 40.04 | 2.45 | 50.61 | 4.40 | 52.03 | 3.45 |
| 30 | 58.14 | 3.08 | 78.35 | 4.68 | 81.65 | 4.80 |
| 45 | 70.11 | 2.23 | 89.45 | 2.80 | 90.61 | 5.33 |
| 60 | 81.99 | 2.45 | 92.32 | 2.40 | 92.49 | 8.35 |
| Chemical Composition | wt.% |
|---|---|
| TiO2 | 91.4 |
| FeTiO3 | 4.37 |
| SiO2 | 2.23 |
| Al2O3 | 0.09 |
| CaO | 0.01 |
| MnO2 | 0.03 |
| MgO | 0.06 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.01 |
| V2O5 | 0.13 |
| LOI | 1.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daba, K.; Ramakokovhu, M.M.; Mojisola, T.; Shongwe, M.B.; Ntholeng, N. Iron Extraction from South African Ilmenite Concentrate Leaching by Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) in the Presence of Reductant (Metallic Fe) and Additive (MgSO4). Minerals 2022, 12, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101336
Daba K, Ramakokovhu MM, Mojisola T, Shongwe MB, Ntholeng N. Iron Extraction from South African Ilmenite Concentrate Leaching by Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) in the Presence of Reductant (Metallic Fe) and Additive (MgSO4). Minerals. 2022; 12(10):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101336
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaba, Khetho, Munyadziwa Mercy Ramakokovhu, Tajudeen Mojisola, Mxolisi Brendon Shongwe, and Nthabiseng Ntholeng. 2022. "Iron Extraction from South African Ilmenite Concentrate Leaching by Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) in the Presence of Reductant (Metallic Fe) and Additive (MgSO4)" Minerals 12, no. 10: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101336
APA StyleDaba, K., Ramakokovhu, M. M., Mojisola, T., Shongwe, M. B., & Ntholeng, N. (2022). Iron Extraction from South African Ilmenite Concentrate Leaching by Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) in the Presence of Reductant (Metallic Fe) and Additive (MgSO4). Minerals, 12(10), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101336







