Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Classification of Pb–Zn Deposit Types Using LA–ICP–MS Data of Sphalerite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Preparation and Packages
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Library and Package Preparation
3. Description of ML Methods and Pb–Zn Deposits
3.1. Description of ML Methods
3.2. Description of Deposits and Samples
4. Results
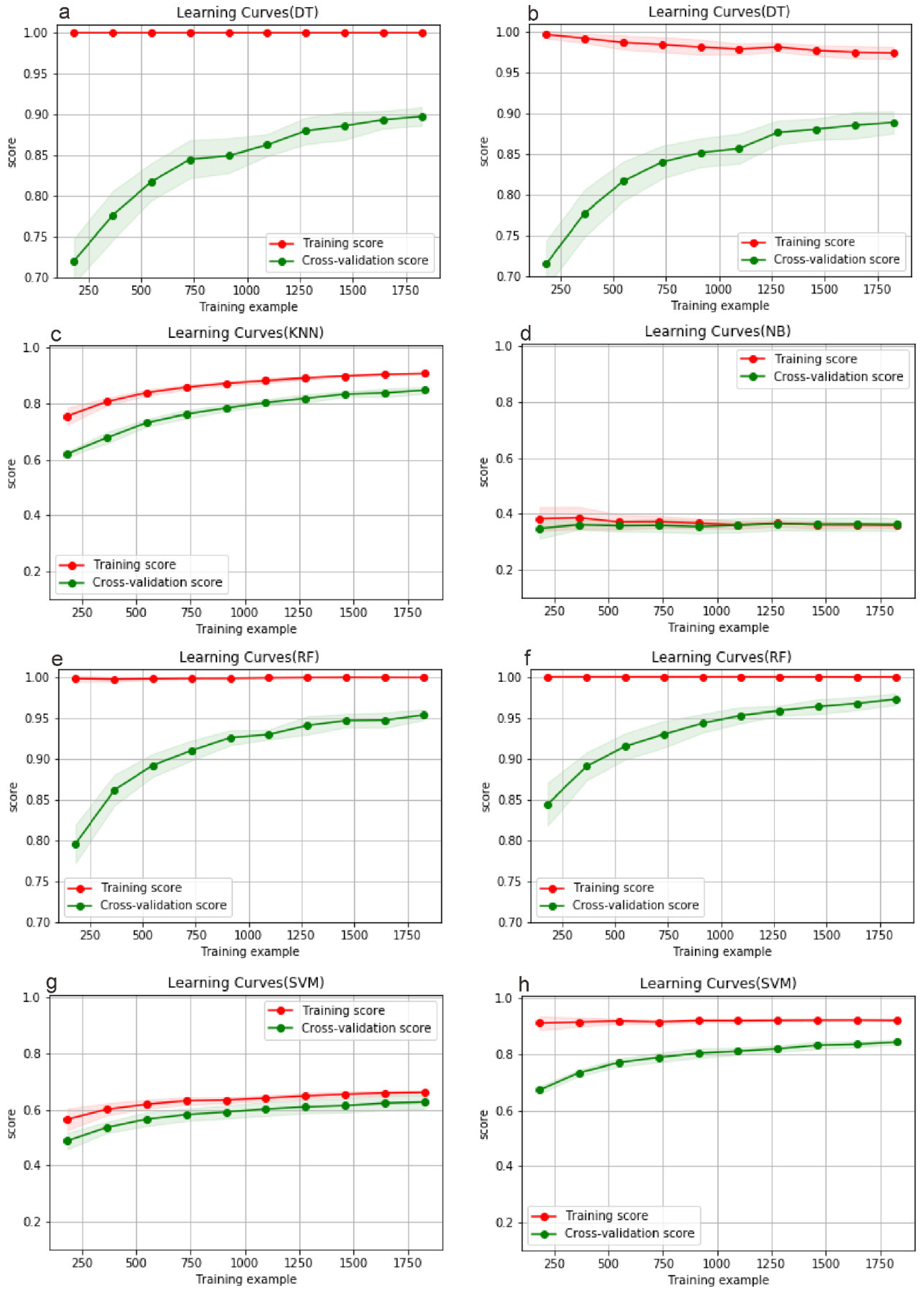
4.1. Learning Curves
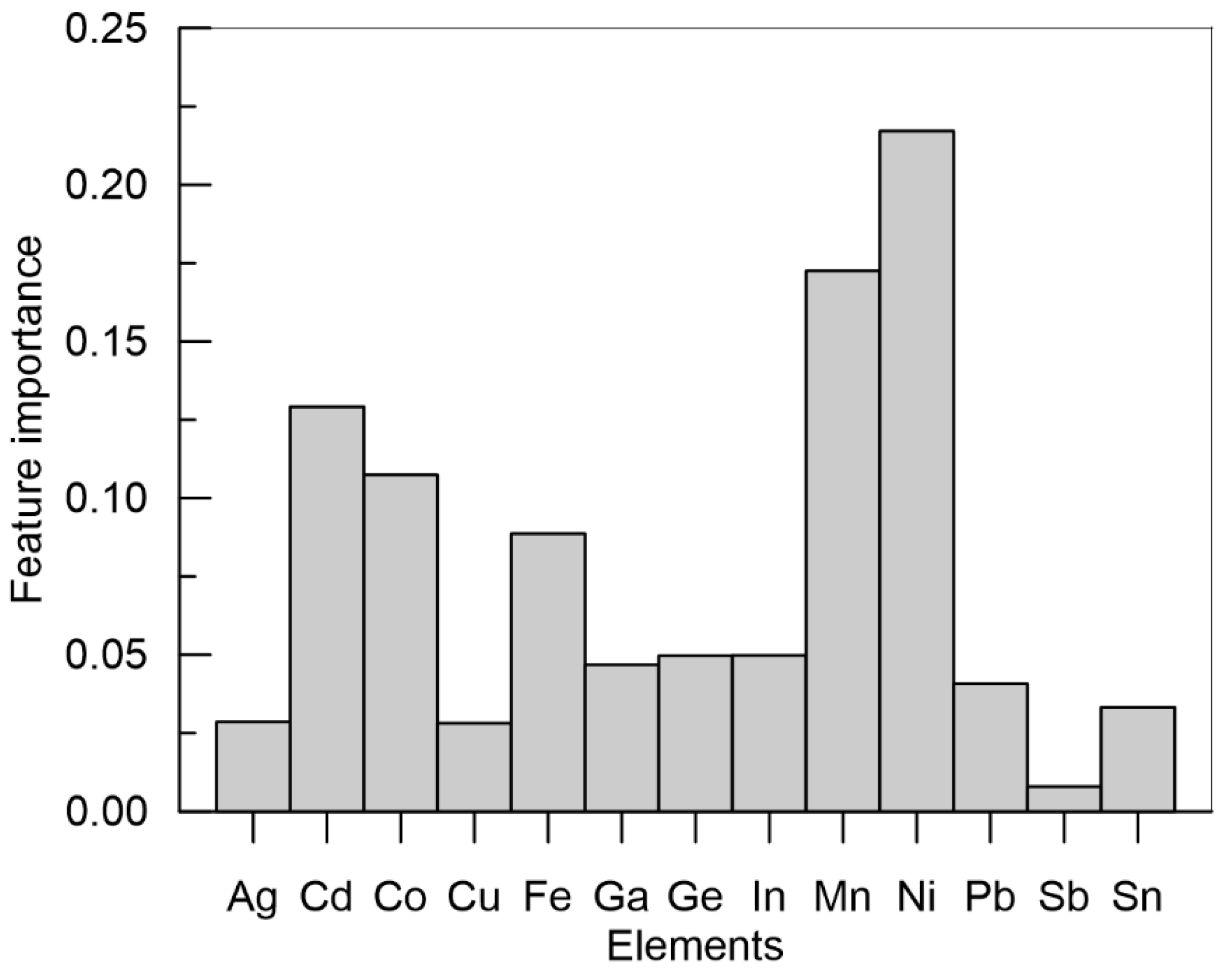
4.2. Feature Importances
4.3. Accuracies of the DT and RF Classifiers
5. Discussion
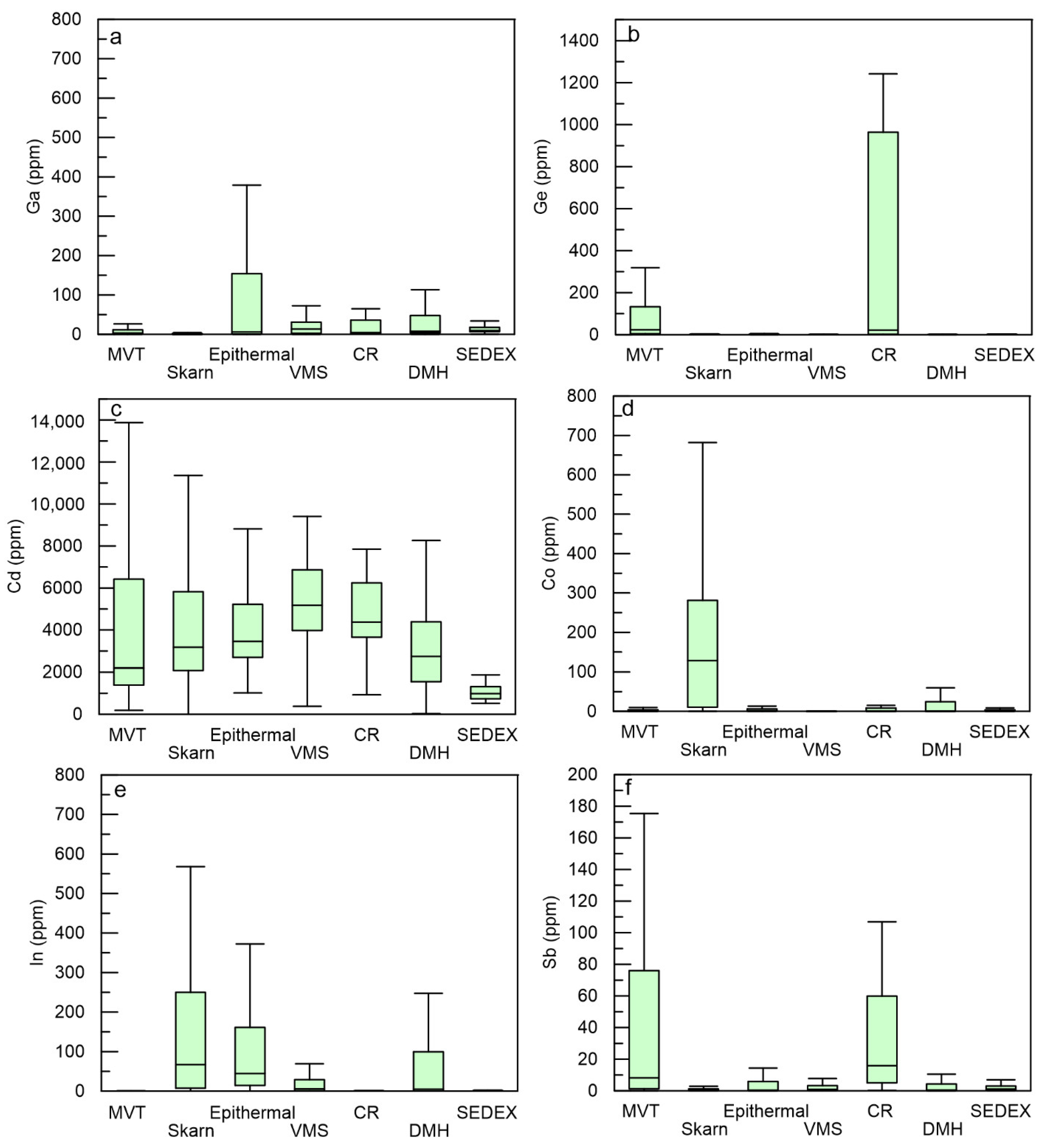
5.1. Critical Metals in Sphalerite
5.2. Assessment of Different ML Methods for Sphalerite LA–ICP–MS Data
5.3. Statistical Element Characteristics of Different Types of Pb–Zn Deposits
5.4. Sphalerite Prediction Application
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Pring, A.; Skinner, W.; Shimizu, M.; Danyushevsky, L.; Saini-Eidukat, B.; Melcher, F. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite: A LA-ICPMS study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4761–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Yuping, L.; Qian, Z.; Tiegeng, L.; Wei, G.; Yulong, Y.; Danyushevskiy, L. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite from base metal deposits in South China: A LA-ICPMS study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 39, 188–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, M.; Hirsch, T.; Gutzmer, J. Gallium, germanium, indium, and other trace and minor elements in sphalerite as a function of deposit type—A meta-analysis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 76, 52–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lary, D.J.; Alavi, A.H.; Gandomi, A.H.; Walker, A.L. Machine learning in geosciences and remote sensing. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, D.D.; Cracknell, M.J.; Large, R.R.; McGoldrick, P.; Kuhn, S.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Baker, M.J.; Fox, N.; Belousov, I.; Figueroa, M.C.; et al. Distinguishing Ore Deposit Type and Barren Sedimentary Pyrite Using Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry Trace Element Data and Statistical Analysis of Large Data Sets. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, K.-F.; Müller, A.; Hou, Z.-L.; Zhu, Z.-H.; Yu, H.-C. Machine Learning Prediction of Quartz Forming-Environments. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2021JB021925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Deng, Y.; Li, W.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Cracknell, M.J.; Belousov, I.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. Revealing the multi-stage ore-forming history of a mineral deposit using pyrite geochemistry and machine learning-based data interpretation. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Hu, M.Y. Trace and Minor Elements in Sphalerite from the Mayuan Lead-Zinc Deposit, Northern Margin of the Yangtze Plate: Implications from LA-ICP-MS Analysis. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2014, 34, 461–468, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.H. Study on Mineralization of Qixiashan Pb-Zn Deposit, Nanjing, China. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2016. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xing, B.; Zheng, W.; Ouyang, Z.X.; Wu, X.D.; Lin, W.P.; Tian, Y. Sulfide microanalysis and S isotope of the Miaoshan Cu polymetallic deposit in western Guandong Province, and its constraints on the ore genesis. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 971–986, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.C. In situ LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of sulfides from Weilasituo polymetallic deposit and its significance. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xing, B.; Xiang, J.F.; Ye, H.S.; Chen, X.D.; Zhang, G.S.; Yang, C.Y.; Jin, X.; Hu, Z.Z. Genesis of Luotuoshan sulfur polymetallic deposit in western Henan Province: Evidence from trace elements of sulfide revealed by using LA-ICP-MS in lamellar ores. Miner. Depos. 2017, 36, 83–106, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.B.; Shao, Y.J.; Yang, Z.A.; Liu, Z.F.; Wang, W.X.; Ren, X.M. LA-ICP-MS analysis of trace elements in sphalerite from the Huanggangliang Fe-Sn deposit, Inner Mongolia, and its implications. Acta Petrol. Miner. 2017, 36, 360–370, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Ding, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y. Element enrichment characteristics: Insights from element geochemistry of sphalerite in Daliangzi Pb–Zn deposit, Sichuan, Southwest China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 186, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Zhou, J.X.; Wang, D.; Yang, G.S.; Lv, C.L. Trace elemental and S-Pb isotopic geochemistry of the Fule Pb-Zn deposit, NE Yunnan Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 3493–3505, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.J.; Yang, Z.S.; Zhuang, L.L.; Ma, W. Genesis of Narusongduo Pb-Zn deposit, Tibet: Constraint from in-situ LA-ICPMS analyses of minor and trace elements in sphalerite. Miner. Depos. 2019, 38, 1365–1378, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fard, M.; Hou, Z. Major and trace elements and sulfur isotopes in two stages of sphalerite from the world-class Angouran Zn–Pb deposit, Iran: Implications for mineralization conditions and type. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 109, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lü, X.; Wang, X. Textural, Chemical, Isotopic and Microthermometric Features of Sphalerite from the Wunuer Deposit, Inner Mongolia: Implications for Two Stages of Mineralization from Hydrothermal to Epithermal. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 6936–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ni, P.; Yang, Y.; Chi, Z.; Jing, S. Constraints on the Genesis of the Qixiashan Pb-Zn Deposit, Nanjing: Evidence from Sulfide Trace Element Geochemistry. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 31, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zeng, Q.; Zhou, J.-X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, P. Genesis of the Xinling vein-type Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, Liaodong Peninsula, China: Evidence from texture, composition and in situ S-Pb isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Deng, T.; Zou, S. Genesis of the Taolin Pb-Zn deposit in northeastern Hunan Province, South China: Constraints from trace elements and oxygen-sulfur-lead isotopes of the hydrothermal minerals. Min. Depos. 2020, 55, 1467–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xu, D.; Wang, Z.; Xu, K.; Huang, Q.; Zou, S.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, T. Trace element geochemistry and O-S-Pb-He-Ar isotopic systematics of the Lishan Pb-Zn-Cu hydrothermal deposit, NE Hunan, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Li, X.; Kontonikas-Charos, A.; Gilbert, S.; Lv, Y. Indium distribution in sphalerite from sulfide–oxide–silicate skarn assemblages: A case study of the Dulong Zn–Sn–In deposit, Southwest China. Min. Depos. 2021, 56, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ye, L.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Danyushevsky, L.; Wang, H. LA-ICP-MS analyses of trace elements in base metal sulfides from carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposits, South China: A case study of the Maoping deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 130, 103945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.P.; Pati, P.; Dora, M.L.; Baswani, S.R.; Meshram, T.; Shareef, M.; Pattanayak, R.S.; Suryavanshi, H.; Mishra, M.; Raza, M.A. Trace-element systematics and isotopic characteristics of sphalerite-pyrite from volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits of Betul belt, central Indian Tectonic Zone: Insight of ore genesis to exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 134, 104149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Tian, H.; Zhao, J.; Tong, X.; Chen, X. Trace element and S isotope characterization of sulfides from skarn Cu ore in the Laochang Sn-Cu deposit, Gejiu district, Yunnan, China: Implications for the ore-forming process. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 134, 104155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Mao, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, H.; Jia, F.; Wang, S.; Huang, W.; Li, H. Genetic discrimination of the Dingjiashan Pb-Zn deposit, SE China, based on sphalerite chemistry. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 135, 104212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benites, D.; Torró, L.; Vallance, J.; Kouzmanov, K.; Chelle-Michou, C.; Fontboté, L. Distribution of indium, germanium, gallium and other minor and trace elements in polymetallic ores from a porphyry system: The Morococha district, Peru. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 136, 104236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, S.; Lv, C.; Dai, Z. Genesis of the sediment-hosted Haerdaban Zn-Pb deposit, Western Tianshan, NW China: Constraints from textural, compositional and sulfur isotope variations of sulfides. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, G.; Xue, X.; Li, H.; Shah, S.A.; Wang, N.; Chen, X. LA-ICP-MS trace element geochemistry of sphalerite: Metallogenic constraints on the Qingshuitang Pb–Zn deposit in the Qinhang Ore Belt, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 141, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torró, L.; Benites, D.; Vallance, J.; Laurent, O.; Ortiz-Benavente, B.A.; Chelle-Michou, C.; Proenza, J.A.; Fontboté, L. Trace element geochemistry of sphalerite and chalcopyrite in arc-hosted VMS deposits. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 232, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brijain, M.; Patel, R.; Kushik, M.; Rana, K. A Survey on Decision Tree Algorithm for Classification. Int. J. Eng. Dev. Res. 2014, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, M.A.; Brodley, C.E. Decision tree classification of land cover from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavian, S.R.; Landgrebe, D. A survey of decision tree classifier methodology. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1991, 21, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRoberts, R.E.; Tomppo, E.O.; Finley, A.O.; Heikkinen, J. Estimating areal means and variances of forest attributes using the k-Nearest Neighbors technique and satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Lopez, H.; Ek, A.R.; Bauer, M.E. Estimation and mapping of forest stand density, volume, and cover type using the k-nearest neighbors method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 77, 251–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, O. (Ed.) K-Nearest Neighbors. In Dimensionality Reduction with Unsupervised Nearest Neighbors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lowd, D.; Domingos, P. Naive Bayes models for probability estimation. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Bonn, Germany, 7–11 August 2005; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, W.S. What is a support vector machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Zeng, Q.; Zhou, J.-X. Machine learning coupled with mineral geochemistry reveals the origin of ore deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 142, 104753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.M. The geochemistry of gallium, indium, thallium—A review. Phys. Chem. Earth 1957, 2, 164–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, Z. Indium and germanium in the structure of sphalerite: An example of coupled substitution with copper. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 39, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, B.; Lilly, R.; Hong, W. The Effect of Co-Crystallising Sulphides and Precipitation Mechanisms on Sphalerite Geochemistry: A Case Study from the Hilton Zn-Pb (Ag) Deposit, Australia. Minerals 2020, 10, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Hou, Z.Q.; Yue, L.L.; Ma, W.; Tang, B.L. Critical metals in sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 406–424, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondillo, N.; Herrington, R.; Boyce, A.J.; Wilkinson CSantoro, L.; Rumsey, M. Critical elements in nonsulphide Zn deposits: A re-analysis of the Kabwe Zn-Pb ores. Mineral. Mag. 2018, 82 (Suppl. S1), 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, S. Indium, Germanium and Gallium in Volcanic-and Sediment-Hosted Base-Metal Sulphide Deposits; British Columbia Ministry of Energy and Mines: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2015; pp. 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, H.; Ishihara, S. Trace elements of Indium-bearing sphalerite from tin-polymetallic deposits in Bolivia, China and Japan: A femto-second LA-ICPMS study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 53, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Indium Mineralization in a Sn-Poor Skarn Deposit: A Case Study of the Qibaoshan Deposit, South China. Minerals 2017, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, X.F. Spatial and temporal distributions, metallogenic backgrounds and processes of indium deposits. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 3611–3626, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.F.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.T.; Lv, Y.H. Critical minerals of indium: Major ore types and scientific issues. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 3292–3302, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, M.E.; Seifert, T.; Burisch, M.; Krause, J.; Richter, N.; Gutzmer, J. Indium-bearing sulfides from the Hämmerlein skarn deposit, Erzgebirge, Germany: Evidence for late-stage diffusion of indium into sphalerite. Min. Depos. 2019, 54, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, F.D.; Bernardini, G.P.; Costagliola, P.; Plant, D.; Vaughan, D.J. Compositional zoning in sphalerite crystals. Am. Mineral. 2005, 90, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.E.; Burisch, M.; Ostendorf, J.; Krause, J.; Frenzel, M.; Seifert, T.; Gutzmer, J. Trace element geochemistry of sphalerite in contrasting hydrothermal fluid systems of the Freiberg district, Germany: Insights from LA-ICP-MS analysis, near-infrared light microthermometry of sphalerite-hosted fluid inclusions, and sulfur isotope geochemistry. Min. Depos. 2019, 54, 237–262. [Google Scholar]
- Belissont, R.; Boiron, M.-C.; Luais, B.; Cathelineau, M. LA-ICP-MS analyses of minor and trace elements and bulk Ge isotopes in zoned Ge-rich sphalerites from the Noailhac—Saint-Salvy deposit (France): Insights into incorporation mechanisms and ore deposition processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 126, 518–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Brugger, J.; Etschmann, B.; Howard, D.L.; de Jonge, M.D.; Ryan, C.; Paterson, D. Determination of the oxidation state of Cu in substituted Cu-In-Fe-bearing sphalerite via μ-XANES spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Lin, C.-J. A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leach, D.L.; Sangster, D.F.; Kelley, K.D.; Large, R.R.; Garven, G.; Allen, C.R.; Gutzmer, J.; Walters, S. Sediment-Hosted Lead-Zinc Deposits: A Global Perspective. In Economic Geology: One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brannon, J.C.; Podosek, F.A.; McLimans, R.K. Alleghenian age of the Upper Mississippi Valley zinc–lead deposit determined by Rb–Sr dating of sphalerite. Nature 1992, 356, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, D.L.; Sangster, D.F. Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc deposits. Geol. Assoc. Can. Spec. Pap. 1993, 40, 289–314. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini, G.P.; Borgheresi, M.; Cipriani, C.; Di Benedetto, F.; Romanelli, M. Mn distribution in sphalerite: An EPR study. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2004, 31, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.M.; Gibson, H.L.; Jonasson, I.R.; Galley, A.G. Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits. In Economic Geology: One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannington, M.D.; Ronde, C.E.J.D.; Petersen, S. Sea-Floor Tectonics and Submarine Hydrothermal Systems. In Economic Geology: One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannington, M.D.; Poulsen, K.H.; Thompson, J.F.H.; Sillitoe, R.H. Volcanogenic Gold in the Massive Sulfide Environment. In Reviews in Economic Geology: Volcanic Associated Massive Sulfide Deposits: Processes and Examples in Modern and Ancient Settings; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, L.D. Skarns and Skarn Deposits. Geosci. Can. 1992, 19, 145–162. [Google Scholar]
- Meinert, L.D.; Dipple, G.M.; Nicolescu, S. World Skarn Deposits. In Economic Geology: One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bralia, A.; Sabatini, G.; Troja, F. A revaluation of the Co/Ni ratio in pyrite as geochemical tool in ore genesis problems. Miner. Depos. 1979, 14, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, Q.; Liang, K. Metallogenic model for the Laochang Pb–Zn–Ag–Cu volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit related to a Paleo-Tethys OIB-like volcanic center, SW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 578–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ye, L.; Huang, Z.; Gao, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Ore Genesis and Geodynamic Setting of Laochang Ag-Pb-Zn-Cu Deposit, Southern Sanjiang Tethys Metallogenic Belt, China: Constraints from Whole Rock Geochemistry, Trace Elements in Sphalerite, Zircon U-Pb Dating and Pb Isotopes. Minerals 2018, 8, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-D.; Li, J.-W.; Zhao, X.-F.; Wang, H.-Q.; Qi, L. Re–Os and U–Pb geochronology of the Laochang Pb–Zn–Ag and concealed porphyry Mo mineralization along the Changning–Menglian suture, SW China: Implications for ore genesis and porphyry Cu–Mo exploration. Min. Depos. 2016, 51, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, J.-X.; Long, H.-S.; Zhou, L.; Luo, K. Vertical evolution of Ag-Pb-Zn-(Cu)-Mo in porphyry system: A case study from the Laochang deposit, SW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
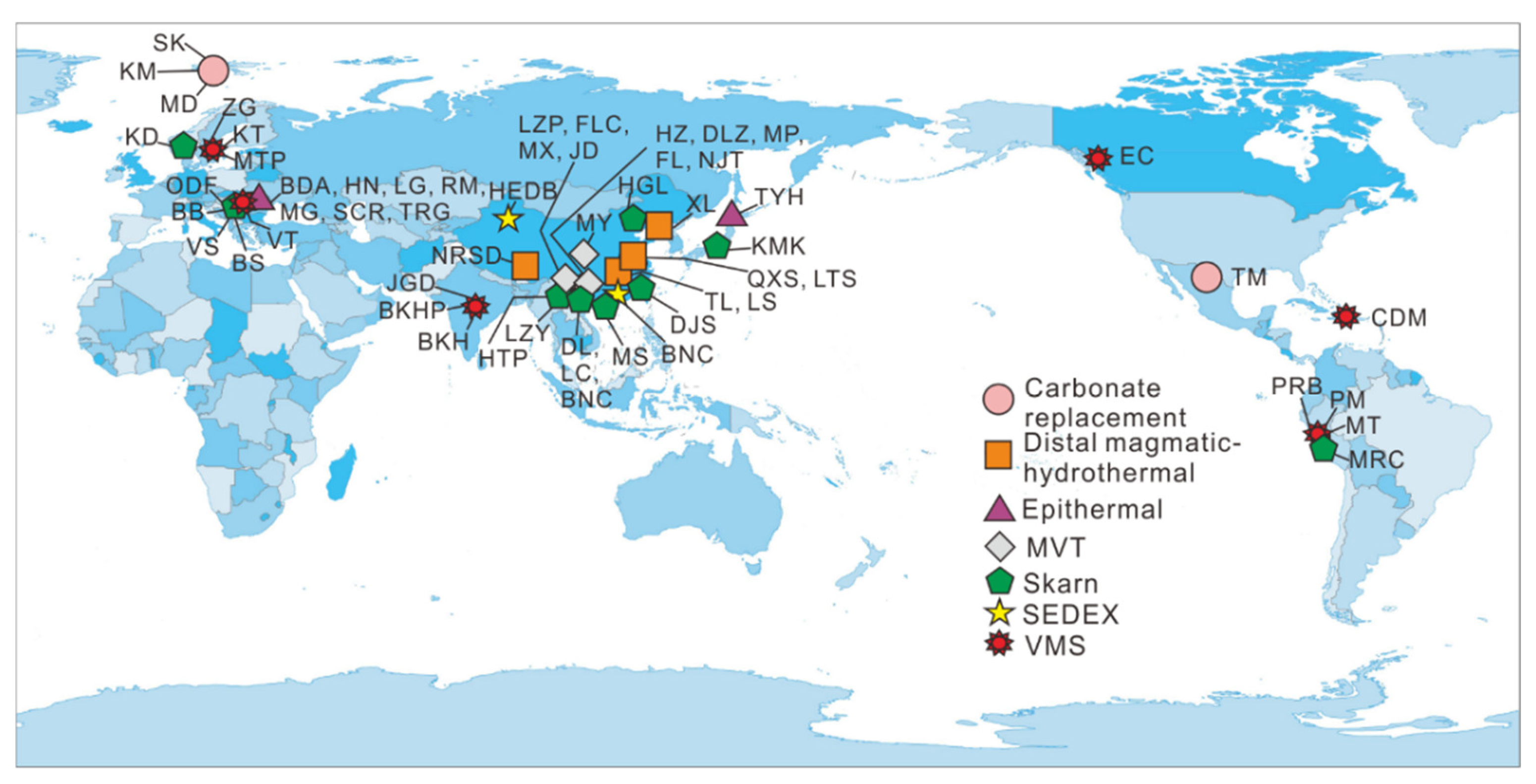

| Deposit | Country | Type | Number | References | Deposit | Country | Type | Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tres Marias | Mexico | CR | 22 | [1] | Mayuan | China | MVT | 50 | [8] |
| Sinkholmen | Norway | CR | 8 | [1] | Hetaoping | China | Skarn | 24 | [7] |
| Kapp Mineral | Norway | CR | 10 | [1] | Luziyuan | China | Skarn | 24 | [7] |
| Melandsgruve | Norway | CR | 8 | [1] | Majdanpek | Serbia | Skarn | 8 | [1] |
| Taolin | China | DMH | 64 | [21] | Ocna de Fier | Romania | Skarn | 37 | [1] |
| Xinling | China | DMH | 25 | [20] | Baita Bihor | Romania | Skarn | 30 | [1] |
| Luotuoshan | China | DMH | 35 | [12] | Valea Seaca | Romania | Skarn | 6 | [1] |
| Narusongduo | China | DMH | 66 | [16] | Baisoara | Romania | Skarn | 20 | [1] |
| Qixiashan | China | DMH | 122 | [9,19] | Lefevre | Canada | Skarn | 8 | [1] |
| Morococha | Peru | DMH | 323 | [28] | Konnerudkollen | Norway | Skarn | 5 | [1] |
| Weilasituo | China | DMH | 22 | [11] | Kamioka | Japan | Skarn | 8 | [1] |
| Lishan | China | DMH | 27 | [21] | Dulong | China | Skarn | 57 | [23] |
| Baia de Aries | Romania | Epithermal | 6 | [1] | Laochang | China | Skarn | 16 | [26] |
| Hanes | Romania | Epithermal | 8 | [1] | Miaoshan | China | Skarn | 10 | [10] |
| Larga | Romania | Epithermal | 8 | [1] | Huanggangliang | China | Skarn | 2 | [13] |
| Rosia Montana | Romania | Epithermal | 20 | [1] | Dingjiashan | China | Skarn | 52 | [27] |
| Magura | Romania | Epithermal | 8 | [1] | Morococha | Peru | Skarn | 52 | [28] |
| Sacaramb | Romania | Epithermal | 11 | [1] | Bainiuchang | China | Skarn | 18 | [7] |
| Toroiaga | Romania | Epithermal | 6 | [1] | Dabaoshan | China | SEDEX | 26 | [7] |
| Toyoha | Japan | Epithermal | 22 | [1] | Haerdaban | China | SEDEX | 173 | [29] |
| Wunuer | China | Epithermal | 82 | [18] | Vorta | Romania | VMS | 8 | [1] |
| Xinling | China | Epithermal | 19 | [20] | Eskay Creek | Canada | VMS | 12 | [1] |
| Morococha | Peru | Epithermal | 7 | [28] | Zinkgruvan | Sweden | VMS | 5 | [1] |
| Daliangzi | China | MVT | 85 | [14] | Kaveltorp | Sweden | VMS | 8 | [1] |
| Huize | China | MVT | 24 | [7] | Marketorp | Sweden | VMS | 8 | [1] |
| Mengxing | China | MVT | 18 | [7] | Sauda Sa | Norway | VMS | 10 | [1] |
| Liziping | China | MVT | 67 | [30] | Banskhapa | Indian | VMS | 5 | [25] |
| Fulongchang | China | MVT | 48 | [30] | Jangaldehri | Indian | VMS | 10 | [25] |
| Angouran | Iran | MVT | 43 | [17] | Biskhan | Indian | VMS | 11 | [25] |
| Niujiaotang | China | MVT | 26 | [7] | María Teresa | Peru | VMS | 141 | [31] |
| Jinding | China | MVT | 24 | [7] | Perubar | Peru | VMS | 50 | [31] |
| Maoping | China | MVT | 49 | [24] | Palma | Peru | VMS | 37 | [31] |
| Fule | China | MVT | 22 | [15] | Cerro de Maimón | Dominican Republic | VMS | 17 | [31] |
| Classifiers | DT Classifier | RF Classifier | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types | CR | DMH | Epithermal | MVT | SEDEX | Skarn | VMS | CR | DMH | Epithermal | MVT | SEDEX | Skarn | VMS | ||
| Percision | 1 | 0.353 | 0.835 | 0.830 | 0.872 | 0.917 | 0.795 | 0.969 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.976 | 0.966 | 0.935 | 1.000 | 0.975 | 1.000 |
| 2 | 0.692 | 0.921 | 0.825 | 0.917 | 0.963 | 0.870 | 0.960 | 2 | 1.000 | 0.975 | 0.966 | 0.963 | 1.000 | 0.968 | 0.990 | |
| 3 | 0.571 | 0.932 | 0.764 | 0.919 | 0.923 | 0.826 | 0.854 | 3 | 1.000 | 0.986 | 0.965 | 0.956 | 1.000 | 0.928 | 0.989 | |
| 4 | 0.750 | 0.911 | 0.800 | 0.886 | 0.849 | 0.860 | 0.906 | 4 | 1.000 | 0.952 | 1.000 | 0.914 | 0.980 | 0.972 | 0.989 | |
| 5 | 0.667 | 0.868 | 0.818 | 0.954 | 0.963 | 0.898 | 0.920 | 5 | 1.000 | 0.941 | 0.948 | 0.970 | 1.000 | 0.939 | 0.989 | |
| Mean | 0.607 | 0.894 | 0.807 | 0.910 | 0.923 | 0.850 | 0.922 | Mean | 1.000 | 0.966 | 0.969 | 0.948 | 0.996 | 0.956 | 0.992 | |
| SD | 0.139 | 0.037 | 0.024 | 0.028 | 0.042 | 0.036 | 0.041 | SD | 0.000 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.019 | 0.004 | |
| Recall | 1 | 0.375 | 0.921 | 0.650 | 0.848 | 0.902 | 0.789 | 0.939 | 1 | 0.563 | 0.990 | 0.950 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.953 | 0.970 |
| 2 | 0.600 | 0.907 | 0.825 | 0.905 | 0.963 | 0.934 | 0.941 | 2 | 0.667 | 0.990 | 0.889 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.984 | 0.980 | |
| 3 | 0.571 | 0.894 | 0.689 | 0.895 | 0.923 | 0.905 | 0.936 | 3 | 0.571 | 0.986 | 0.902 | 1.000 | 0.969 | 0.981 | 0.979 | |
| 4 | 0.429 | 0.939 | 0.727 | 0.918 | 0.918 | 0.860 | 0.897 | 4 | 0.381 | 1.000 | 0.818 | 0.994 | 0.980 | 0.991 | 0.969 | |
| 5 | 0.750 | 0.952 | 0.652 | 0.901 | 1.000 | 0.882 | 0.939 | 5 | 0.625 | 0.990 | 0.797 | 0.988 | 1.000 | 0.973 | 0.949 | |
| Mean | 0.545 | 0.923 | 0.709 | 0.893 | 0.941 | 0.874 | 0.930 | Mean | 0.561 | 0.991 | 0.871 | 0.996 | 0.990 | 0.976 | 0.969 | |
| SD | 0.133 | 0.021 | 0.065 | 0.024 | 0.036 | 0.049 | 0.017 | SD | 0.098 | 0.005 | 0.056 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.011 | |
| F1-score | 1 | 0.364 | 0.876 | 0.729 | 0.860 | 0.909 | 0.792 | 0.954 | 1 | 0.720 | 0.983 | 0.958 | 0.967 | 1.000 | 0.967 | 0.985 |
| 2 | 0.643 | 0.914 | 0.825 | 0.911 | 0.963 | 0.901 | 0.950 | 2 | 0.800 | 0.982 | 0.926 | 0.981 | 1.000 | 0.976 | 0.985 | |
| 3 | 0.571 | 0.913 | 0.724 | 0.907 | 0.923 | 0.864 | 0.893 | 3 | 0.727 | 0.986 | 0.932 | 0.977 | 0.984 | 0.954 | 0.984 | |
| 4 | 0.545 | 0.925 | 0.762 | 0.902 | 0.882 | 0.860 | 0.902 | 4 | 0.552 | 0.975 | 0.900 | 0.952 | 0.980 | 0.981 | 0.979 | |
| 5 | 0.706 | 0.908 | 0.726 | 0.927 | 0.981 | 0.890 | 0.929 | 5 | 0.769 | 0.965 | 0.866 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.955 | 0.969 | |
| Mean | 0.566 | 0.907 | 0.753 | 0.901 | 0.932 | 0.861 | 0.926 | Mean | 0.714 | 0.978 | 0.916 | 0.971 | 0.993 | 0.967 | 0.980 | |
| SD | 0.116 | 0.017 | 0.039 | 0.022 | 0.036 | 0.038 | 0.025 | SD | 0.086 | 0.008 | 0.031 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.006 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, G.-T.; Zhou, J.-X. Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Classification of Pb–Zn Deposit Types Using LA–ICP–MS Data of Sphalerite. Minerals 2022, 12, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101293
Sun G-T, Zhou J-X. Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Classification of Pb–Zn Deposit Types Using LA–ICP–MS Data of Sphalerite. Minerals. 2022; 12(10):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101293
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Guo-Tao, and Jia-Xi Zhou. 2022. "Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Classification of Pb–Zn Deposit Types Using LA–ICP–MS Data of Sphalerite" Minerals 12, no. 10: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101293
APA StyleSun, G.-T., & Zhou, J.-X. (2022). Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Classification of Pb–Zn Deposit Types Using LA–ICP–MS Data of Sphalerite. Minerals, 12(10), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101293







