Abstract
In recent years, mineral resources near the surface are becoming scarce, causing focused mineral exploration on concealed deposits in covered terrains. In northern China, covered terrains are widespread and conceal bedrock sequences and mineralization. These represent geochemical challenges for mineral exploration in China. As a deep-penetrating geochemical technology that can reflect the information of deep anomalies, the fine-grained soil prospecting method has achieved ideal test results in arid Gobi Desert covered terrain, semi-arid grassland covered terrain, and alluvium soil covered terrain of northern China. The anomaly range indicated by the fine-grained soil prospecting method is very good with the known ore body location. The corresponding relationship can effectively indicate deep ore bodies and delineate anomalies in unknown areas. Overall, the fine-grained soil prospecting method can be applied to geochemical prospecting and exploration in covered terrains.
1. Introduction
As mineral resources near the surface are becoming scarce, deep-penetrating geochemistry for finding concealed deposits has attracted significant attention and obtained favorable results [1,2,3]. The fine-grained soil prospecting method is a deep-penetrating geochemical technology developed over the past ten years. The clay minerals of the fine-grained soil are ideal carriers for active metal elements as their surface is large and charged. In addition, iron-manganese oxides exist in large quantities in the soil. As the soil particle size becomes smaller, the specific surface area of iron-manganese oxides increases exponentially, and its ability to adsorb active metal elements increases. The fine-grained substances in the soil are natural “trapping wells” for active elements. The fine-grained soil prospecting method separates the fine-grained components in the soil, enriches the active metal elements, and identifies the deep concealed ore body [2,4,5,6]. At present, the method has made some successful cases in China’s loess covered area [7], volcanic rock covered area [8], semi-arid grassland covered area [6,9], Gobi Desert covered area [2,10], and Western Australia’s transported regolith covered area [4,5]. Compared with other deep-penetrating geochemical methods, the fine-grained soil prospecting method is simpler to operate in field sampling and laboratory analysis, making it easier to master and promote [6,7]. Whether it is for the general survey and detailed investigation of concealed mines on the deposit scale, or the rapid geochemical survey of the coverage area, the fine-grained soil prospecting method is highly suitable [4,7].
Conventional stream sediment sampling and rock debris sampling have been successful by delineating the surface secondary dispersion halo and dispersion train in outcropping regions [11,12,13,14]. The National Geochemical Mapping Project in China, the Regional Geochemistry-National Reconnaissance (RGNR) project, has been running for 40 years since its establishment in 1979. The project, covering an area of nearly 7 million km2, has been playing a leading role in the discovery of mineral deposits [13,14,15,16]. However, these approaches have not been applied to covered terrains in China due to the masked presence of both the surface secondary anomalies and the primary halo [2,13]. In this paper, experiments were conducted in three typically covered terrains (arid Gobi Desert coverage area, semi-arid grassland coverage area, and alluvium soil coverage area; Figure 1) in northern China to verify the applicability of the fine-grained soil prospecting method.
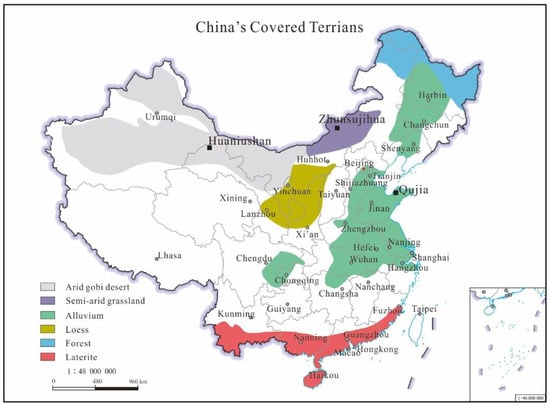
Figure 1.
China’s covered terrains (modified after Wang et al. [2]) and location of the deposit fields.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geological Setting
2.1.1. The Huaniushan Deposit in the Arid Gobi Desert Covered Terrain
The arid Gobi Desert covered terrain is located in the northwest of China, between 40° and 50° north latitude, comprising a total area of about 1,435,000 km2 [17]. Geologically, it belongs to the Paleo-Asian metallogenic domain, and the three polymetallic metallogenic belts of the Tianshan, Beishan, and Qilian mountains pass through it. Here, the ore-forming conditions are superior, and the potential for prospecting, especially for concealed mines, is enormous [2,18]. The selected mining area is the Huaniushan lead-zinc mine, located 91 km northwest of Anxi County, Gansu Province, in the mid-west of the Beishan orogenic belt. The geotectonic location is in the Early Paleozoic Shuangyingshan rift at the northern margin of the Dunhuang block in the northeastern Tarim Paleo-land. The exposed stratum in the mining area is mainly the Sinian Xichangjing Group. The lithology is a set of metamorphic rocks mainly composed of marble, phyllite, and slate, and Quaternary alluvial gravel and sandy clay exist in low-lying terrain. The magmatic activity is intense and frequent, mainly manifested as the large-scale magmatic intrusion of Indosinian syenite, monzonitic granite, and fine-grained porphyritic granite [18,19].
2.1.2. The Zhunsujihua Deposit in the Semi-Arid Grassland Covered Terrain
The semi-arid grassland coverage area is distributed in the middle eastern part of inner Mongolia, roughly 106°–120° east longitude and 40°–50° north latitude, north of the Yinshan Mountains and west of the Greater Hinggan Mountains, covering an area of about 323,900 km2 [17]. It is an important polymetallic metallogenic belt in inner Mongolia. The selected mining area is the Zhunsujihua copper-molybdenum deposit, northwest of Sonid Zuoqi, Xilin gol League, in the inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. It is located in the Late Paleozoic continental marginal accretion belt of the southeastern continental margin of the Siberian Plate. It belongs to a part of the Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic metallogenic belt of Erlian-Dongwuqi, Mongolia-Daxinganling Metallogenic Province, Paleo-Asian metallogenic domain [20]. The exposed strata around the study area are Carboniferous-Permian clastic rocks and Holocene residual slope deposits. The Carboniferous-Permian strata are mainly metamorphic feldspar quartz sandstone and silty slate. The Quaternary stratum is mainly clay, sand, and gravel, with aeolian sand in some parts. The exposed magmatic rocks in the study area are mainly Variscan granodiorite, closely related to Cu and Mo mineralization [20,21].
2.1.3. The Qujia Deposit in the Alluvium Soil Covered Terrain
The alluvial soil covered terrain is distributed in China’s central and eastern plains, covering approximately 996,200 km2 [17]. Here, Jiaodong is chosen as the experimental area. Jiaodong is one of the only three gold mining provinces globally with proven gold resources of more than 5000 tons. Covering less than 0.2% of the country’s land area, more than 200 gold deposits have been discovered in Jiaodong, accounting for approximately one-third of China’s known gold resources [22,23]. There are fewer surface and shallow mines in this area with the continuous increase in geological exploration, and gold prospecting is becoming more difficult. Deep exploration of blindness and coverage areas has become the focus of prospecting in this area [24]. The area between the Sanshandao fault zone and the Jiaojia fault zone is covered by alluvial soil of the Quaternary system, and the farmland is widely spread. The traditional geochemical exploration methods are limited in the covered area. Jiaojia gold belt is mainly distributed along the Jiaojia fault zone, which is about 60 km long and up to 1000 m wide at the widest point. This metallogenic belt includes Jiaojia, Xincheng, Sizhuang, Zhuguolijia, Shaling, and Qianchen, with large to super-large gold deposits [25]. The Qujia concealed gold mining area was used as a test area to detect the exploration effect of the fine-grained soil prospecting method. The mining area is located in the middle section of the Jiaojia gold metallogenic belt. It is the deep extension of the Xincheng and Dongji gold deposits. The NNE-NEE-trending Jiaojia fault structure controls it, and there are a large number of secondary faults, joints, fissures, and mineralized alteration zones developed on both sides of the main fault. The alteration zone extends in a slow wavy shape both in plane and section, and the Quaternary is widely distributed on the surface of the area. Below the Quaternary are monzonitic granites of the Cuizhao unit of Linglong sequence in the early Yanshanian and the porphyritic granodiorite of the Guojialing sequence in the late Yanshanian [26].
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.2.1. Sampling and Analysis of the Huaniushan Deposit
A total of 26 survey lines were laid out along the exploration lines of the Huaniushan lead-zinc mine, with a sampling point distance of 50 m (Figure 2). The sampling depth in the arid Gobi Desert covered area is 10–30 cm [27]. The fine-fraction soil samples (<76 μm) composed of 3 to 5 subsamples within a 5 m radius around the sampling point were collected along the survey lines. Lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), and other elements were analyzed following the strict requirements and specifications in the Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration (IGGE). The standardized quality control procedures consisted of (1) the collection of 3% field duplicate samples, (2) a blank insertion, equivalent to 10% of the laboratory replicate samples, and (3) the insertion of 4 standard reference materials into each batch of 50 routine samples. The standard reference materials used in the research include GSS-1, GSS-2, GSS-17, GSS-19, GSS-25, GAu9a, GAu9b, GAu10a, and GAu10b [28,29]. The analytical scheme and quality monitoring procedures have been previously described in greater detail by Zhang et al. [30]. Lead and zinc were analyzed by plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The detection limit was 2 ppm, and the reporting rate was 100%. The qualified rate of the standard reference materials and the blank samples was 100%, and that of the duplicate samples was 98%.
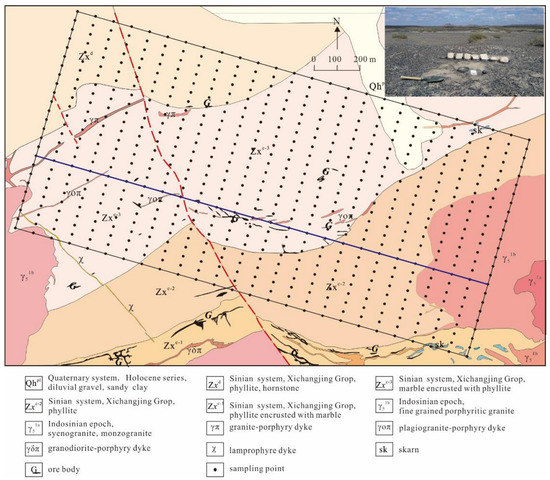
Figure 2.
Geological sketch map (modified after Liu et al. [27]) and sampling sites of the Huaniushan Pb-Zn deposit.
2.2.2. Sampling and Analysis of the Zhunsujihua Deposit
A total of 11 survey lines were laid out along the exploration lines of the Zhunsujihua copper-molybdenum mine, with a sampling point distance of 80 m (Figure 3). The sampling depth in the semi-grassland covered area is 5–30 cm. Fine-fraction soil samples (<76 μm) composed of 3 to 5 subsamples within 5 m around the sampling point were collected along the survey lines. Copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), and other elements were analyzed following the strict requirements and specifications listed by the IGGE. The quality control of samples was conducted, as described above in Section 2.2.1. Copper and molybdenum were analyzed by plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), with a reporting rate of 100%. The detection limit of Cu was 1 ppm, and that of Mo was 0.2 ppm. The qualified rate of the standard reference materials, the blank samples, and the duplicate samples was 100%.
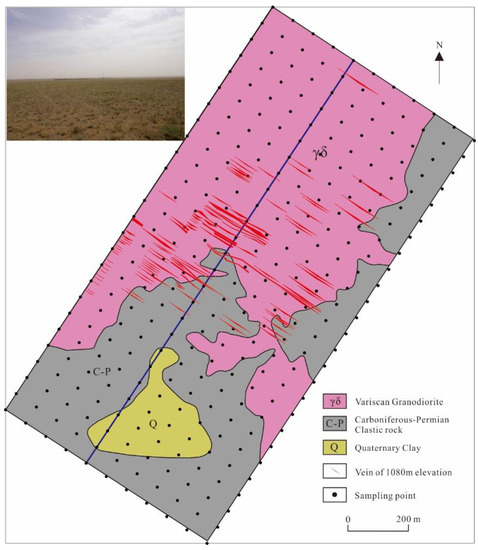
Figure 3.
Geological sketch map (modified after Zhang et al. [21]) and sampling sites of the Zhunsujihua Cu-Mo deposit.
2.2.3. Sampling and Analysis of the Qujia Deposit
A total of 9 survey lines were laid out along the −8, −6, −5, −3, −1, 1, 3, 5, and 7 exploration lines of the Qujia concealed gold mine, with a sampling point distance of 80 m (Figure 4). Fine-fraction soil samples (<125 μm) composed of 3 to 5 subsamples within a 5 m radius of the sampling point were collected along the survey lines. Gold (Au), silver (Ag), and other elements were analyzed following the strict requirements and specifications in the IGGE. The quality control was conducted, as described above in Section 2.2.1. Gold was analyzed by flameless atomic absorption spectrometry (AAN) with a detection limit of 0.2 ppb, and Ag was analyzed by plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) with a detection limit of 20 ppb. The reporting rate was 100%. The qualified rate of the standard reference materials and the blank samples was 100%, and the qualified rate of the duplicate samples was 97.4%.
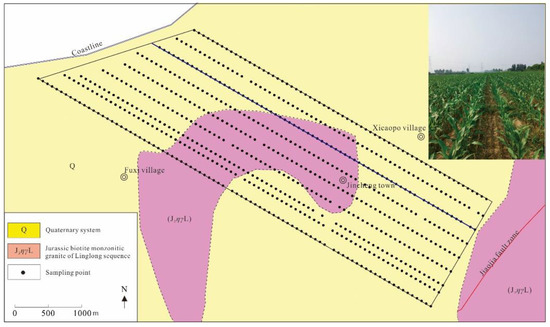
Figure 4.
Geological sketch map and sampling sites of Qujia Au deposit.
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Huaniushan Deposit in the Arid Gobi Desert Covered Terrain
The main ore-forming elements in the Huaniushan test area are Pb and Zn. The Pb content of the fine-grained soil prospecting method ranges between 52.7 and 7806.6 ppm, with a median value of 406.4 ppm and an average value of 779.5 ppm, which are significantly higher than that in the arid Gobi Desert coverage area (a median value of 14.1 ppm and an average value of 15.5 ppm) [31]. The Zn content range between 86.1 and 5807.4 ppm, with a median value of 300.9 ppm and an average value of 525.5 ppm, which is also significantly higher than that in the arid Gobi Desert coverage area (a median value of 45.2 ppm and an average value of 49.7 ppm) [31].
The particle size test in the Huaniushan test area shows that the element content of fine-grained samples is significantly higher than that in coarse-grained samples (Figure 5). In the finer soil fraction, the Pb contents are 5066 ppm in the 120–150 μm, 4879 ppm in the 76–120 μm, and 4432 ppm in the <76 μm fractions, respectively. The Pb contents of the coarser fraction are 1295 ppm in the 840–4800 μm, and 1529 ppm in the 380–840 μm fractions, respectively. Collectively, the Pb content of the fine fraction is higher than that of the coarse fraction. The Zn, Ag, and Au also exhibit a similar pattern. Specifically, the Pb, Zn, Ag, and Au content of fine-grained soil is about 3.40, 4.45, 3.97, and 1.78 times that of coarse-grained soil, respectively. These results show that the fine-fraction soil is a good sampling medium for geochemical surveying in arid Gobi Desert covered areas.
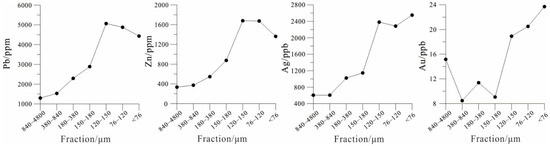
Figure 5.
Pb, Zn, Ag, and Au line chart in different sized soil fractions in the Huaniushan test area.
The line chart of Pb and Zn in the fine fraction of soil (<76 μm) across the concealed mineralized zone (the survey line is marked with a blue line in Figure 2) is shown in Figure 6. The sample No. 17 (800 m) above the ore body contains the highest Pb content, 11,637 ppm, which is about 40 times the Pb content in the background area (about 300 ppm in sample No. 1–4, and No. 20–26). The second highest Pb content is 6891 ppm (Sample No. 12), which also appeared above the ore body (550 m) and is about 20 times that in the background area. Similarly, other high Pb content values also appear above the ore body. A similar distribution is also observed with Zn. These results demonstrate that using the fine fraction of soil can indicate Pb and Zn mineralization in arid Gobi Desert covered areas.
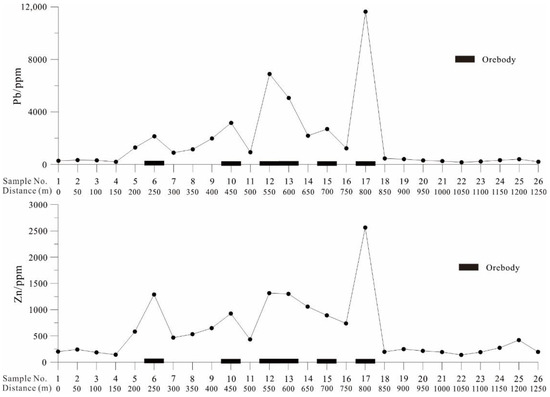
Figure 6.
Pb and Zn line chart of fine-fraction soil samples (<76 μm) across the concealed ore body in the Huaniushan deposit.
The areal measurement results of the fine-grained soil prospecting method of the Huaniushan lead-zinc mine are shown in Figure 7. The value corresponding to 85% quantile is classified as the outlier, and the anomalous area is shown as orange to deep red coloration on the geochemical map. The horizontal section of the ore body is superimposed on the contour map to show the geochemical distribution characteristics of the elements and the positional relationship between the element anomalies (orange to deep red in Figure 7) and the ore body. The results show that the geochemical maps of the main ore-forming elements (Pb and Zn) and indicator elements (Ag, Au, Sb, and Hg) are similar, and the multi-element anomalous combinations are mainly concentrated in the middle of the experimental area, spreading east-west, with a high concentration center. The anomaly is continuous and corresponds very well to the No. 2 ore body. At the same time, the anomaly is not closed in the experimental area and corresponds to the No. 3 ore body outside the experimental area. As such, the fine-grained soil prospecting method can effectively indicate deep concealed ore bodies and can be used as an effective method for finding deposits in the arid Gobi Desert area.
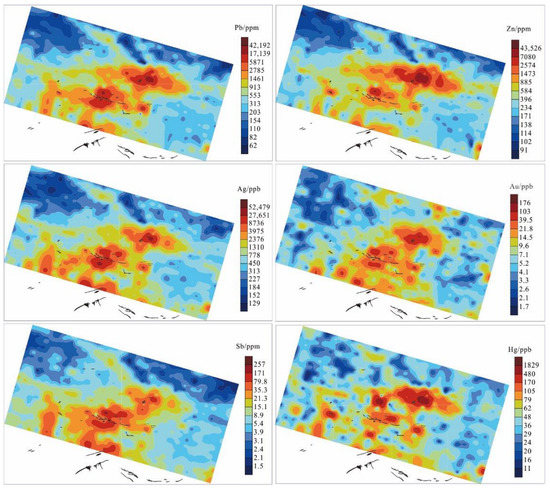
Figure 7.
Geochemical map of the fine-grained soil prospecting method in Huaniushan Pb-Zn deposit.
3.2. Results of the Zhunsujihua Deposit in the Semi-Arid Grassland Covered Terrain
The main ore-forming elements in the Zhunsujihua working area are Mo and Cu. The Mo content of the fine-grained soil prospecting method ranges from 0.93 to 5.69 ppm, with a median value of 1.77 ppm and an average value of 1.97 ppm, which is significantly higher than that in the semi-arid grassland coverage area (median value is 0.75 ppm and average value is 0.99 ppm) [31]. The Cu content ranges from 13.1 to 43.1 ppm, with a median value of 23.8 ppm and an average value of 24.9 ppm, which is also significantly higher than that in the semi-arid grassland coverage area (median value of 12.1 ppm and average value of 15.1 ppm) [31].
The results of the particle size test are shown in Figure 8. The Cu content is 23.5 ppm in the finest fraction (<76 μm) of soil and 8.40 ppm in the coarsest fraction (840–4800 μm). The higher elemental content in the fine fraction and the lower elemental content in the coarse fraction were also recapitulated by Mo and As. The Cu, Mo, and As content of fine-grained soil were about 2.79, 1.65, and 2.36 times that of coarse-grained soil, respectively. As such, the fine-fraction soil is a suitable sampling medium for geochemical surveying in the semi-arid grassland covered area. The result is similar to that of the arid Gobi Desert covered area.
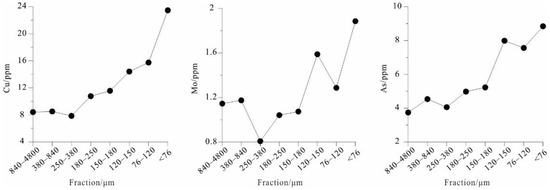
Figure 8.
Line chart showing the concentrations of Cu, Mo, and As in different sized fractions of soil in the Zhunsujihua deposit.
The line chart of Cu and Mo of the fine-fraction soil (<76 μm) across the concealed mineralized zone and background area (the survey line is marked with a blue line in Figure 3) is shown in Figure 9. Sample No. 15 (1120 m) has the highest Cu content of 34.92 ppm, followed by sample No. 17 (1280 m) at 34.08 ppm. Both samples were taken from above the deposit. Even the lowest Cu content of 17.4 ppm (Sample No. 5, at 320 m) is only half the highest value. The Cu content tends to be higher above the ore body and lower far away from the ore body. This trend is also observed with Mo. These results demonstrate that using the fine fraction of soil can indicate Cu and Mo mineralization in semi-arid grassland covered areas. The result is similar to that of the arid Gobi Desert covered area.
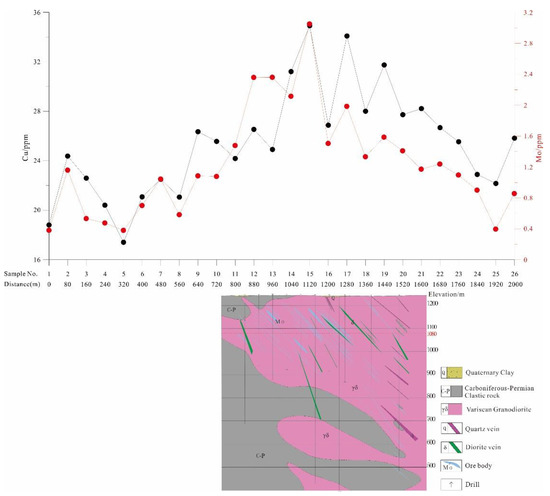
Figure 9.
Cu and Mo line chart of fine-fraction soil samples (<76 μm) across the concealed ore body in the Zhunsujihua deposit.
The areal measurement results of the fine-grained soil prospecting method in the Zhunsujihua copper-molybdenum mine are shown in Figure 10. The Cu and Mo anomalies (orange to deep red in Figure 10) are distributed in the middle of the study area in an irregular strip shape. The anomalies are completely consistent with the vertical projection area of 1080 molybdenum ore body, which is surrounded by the anomalies. At the same time, larger ring-shaped Cu and Mo anomalies also appear in the northeast corner. The anomalous distribution of Cu and Mo is more consistent with the distribution of ore bodies, particularly Mo, indicating that this method can effectively delineate Cu and Mo concealed ore bodies. Overall, the fine-grained soil prospecting method can be used as an effective method for finding deposits in semi-arid grassland areas.
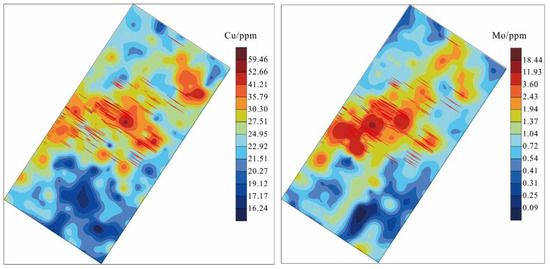
Figure 10.
Geochemical map of the fine-grained soil prospecting method in Zhunsujihua Cu-Mo deposit.
3.3. Results of the Qujia Deposit in the Alluvium Soil Covered Terrain
The main ore-forming element in the study area is Au. The Au content of the fine-grained soil prospecting method ranges from 0.37 to 249.56 ppb, with a median value of 5.44 ppb and an average value of 21.06 ppb, which is significantly higher than that in China (1.40 ppb) [32], Shandong Province (1.53 ppb) [33], and Yantai City, Shandong Province (1.91 ppb) [34].
Figure 11 shows the line chart of Au, Ag, Co, and Cr across the concealed mineralized zone and into unknown areas (the survey line is marked with a blue line in Figure 4). The Au content above the ore body (Sample No. 51–57, 4000–4480 m) is 25.7–71.4 ppb, which is 10 to 30 times the Au content of the background area (about 2 ppb, Sample No. 18–37, 1360–2880 m). The Au distribution is highest above the ore body and lower further away from the ore body. The Ag displays a similar distribution to Au. The content of Co and Cr is highest above the basic rock mass and lower further away from the basic rock mass. These results demonstrate that using the fine fraction of soil can indicate Au mineralization and geological background in alluvium soil covered areas.
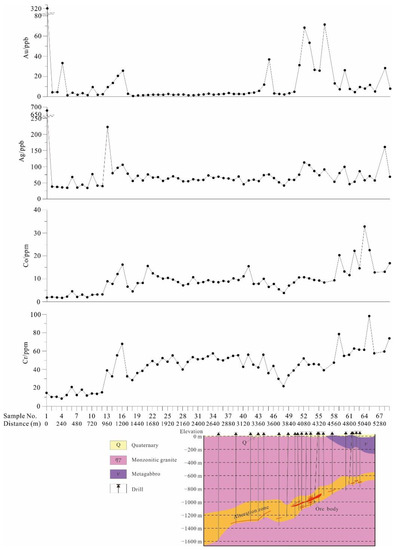
Figure 11.
Au, Ag, Co, and Cr line chart of fine-fraction soil samples (<125 μm) across the concealed ore body in the Qujia deposit.
The Au and Ag geochemical maps (Figure 12) measured by the fine-grained soil prospecting method in the Qujia experimental area are very similar. The anomalous areas (orange to deep red in Figure 12) are mainly distributed in the southeast of the experimental area, corresponding to deep ore bodies [26]. The anomaly area is large and of high intensity. The anomaly is not closed in the test area and extends to the southwest, consistent with the neighboring Zhaoxian exploration area [35]. The anomaly also appears in the northwest of the test area with high intensity, thus not enclosed inside the test area. The test results show that the surface geochemical anomalies correspond to known ore bodies and new anomalies in unknown areas, confirming that the fine-grained soil prospecting method can effectively indicate deep concealed ore bodies and be used as an effective method for finding deposits in the alluvial soil covered terrain.
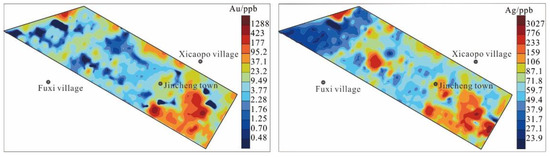
Figure 12.
Geochemical map of the fine-grained soil prospecting method in Qujia Au deposit.
4. Discussion
In northern China, many areas are covered by aeolian sand and some other transported cover (alluvial soil, etc.). These can travel long distances and deposit far from the source region, influencing the effectiveness of metal migration mechanisms in and through the cover and selecting the best sample media for exploration [6,36]. The mineral composition and mobility of the foreign substances make it the most interfering substance for geochemical mapping in northern China, not only in the outcrop area but also in the covered area [6]. The fine-grained soil prospecting method has achieved optimal results in the covered terrains.
Scholars have proposed a variety of theories for the migration of metal elements through the covering layer. These include the physical and chemical release of elements during the weathering process, dissolved elements in the groundwater cycle being brought to the surface, ion diffusion, oxidation-reduction potential, evaporation, absorbance of the root system of the plant, the gas diffuses, and elements carried by the gas [1,37,38,39]. Anand et al. [40] have summarized the mechanisms for metal transfer upwards through transported cover, as well as pitfalls of these mechanisms (Table 1). Xie and Wang [39,41] have proposed a multi-agent migration mechanism based on earth-gas. It is hypothesized that in the arid Gobi terrain, the mineralization information under the cover can be driven by multiple forces to reach the surface through the overburden in the form of nano- and micro-levels. Elements are released from the ore body and associated altered rocks during weathering. Due to the arid terrain of the Gobi, the water-table is hundreds of meters deep and vegetation is sparse. Water and vegetation would therefore seem to play a very limited role in the transport of elements upwards to the surface, despite evaporation and capillary action of plants potentially contributing to mineral uptake during rainfall events. Hence, the migration process relies on multiple agents, with gas being regarded as the main medium for vertical migration of the elements [2,42]. Potent evidence is obtained by detailed studies on earth-gas and soil above ore bodies with transmission electron microscope (TEM) equipped with energy dispersive spectroscopy. This technology enables characterization of complex nano-metal particles in the ore, geo-gas, and soil within a scale of a few tens to hundreds of nanometers [3,43,44,45,46,47]. This has also been confirmed in the arid environment of Australia and Chile [1,48,49,50].

Table 1.
Summary of different mechanisms of transfer metals upwards through transported cover (Anand et al., 2016 [40]).
After the active metal elements migrate from deep ore bodies to the surface, they will inevitably occur in the surface medium in various forms, including ionic compounds, complexes, soluble salts, colloids, elemental particles, and alloy mineral particles [7,51]. No matter what form it exists in, active metal elements are often positively charged, so they are readily adsorbed by negatively charged clay minerals and/or iron-manganese oxides. Clay minerals are the most important secondary minerals in the soil, mainly secondary crystalline layered silicate, including kaolin, montmorillonite, illite, chlorite, hydromica, and vermiculite. The colloidal surface of clay minerals is charged and has a large specific surface area [52], so it is an ideal carrier for the active metal elements, and clay minerals mainly exist in the fine-grained soil components. In addition, iron and manganese oxides are abundant in surface soil, and iron and manganese oxide films often cover the surface of mineral particles. The specific surface area of iron-manganese oxide in the soil increases exponentially with the decrease of the sample size (Figure 13). The larger the specific surface area, the stronger its ability to adsorb active metal elements. Therefore, the physical separation of the soil’s fine particle components can effectively enrich the active metal elements. For example, in the arid Gobi Desert covered areas, as the soil particle size decreases, elements such as Al2O3, Fe2O3, and Mn, representing clay minerals and iron-manganese oxides, increase. Simultaneously, the content of ore-forming elements also increases (Figure 14). It can be seen from the above that fine-grained substances are natural “trapping wells” for active metal elements because of their strong adsorption and exchangeability properties.
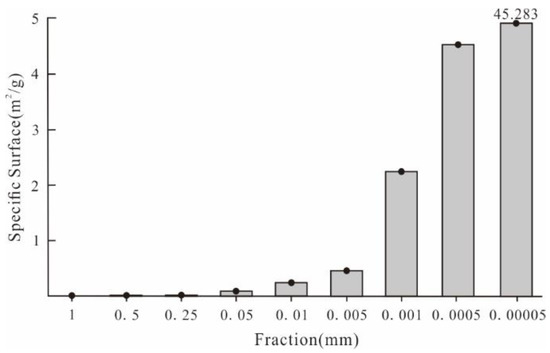
Figure 13.
Specific surface of different grain size fractions in soil [44].
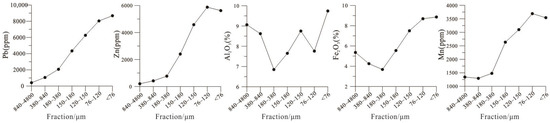
Figure 14.
Pb, Zn, Al2O3, Fe2O3, and Mn line chart in different size fractions of soil in the arid Gobi Desert covered areas.
In the arid Gobi Desert area, aeolian sand is the main factor that interferes with the sampling medium for geochemical exploration. Aeolian sand accounts for a very low proportion in the >830 and <120 μm particle sizes, and more than 90% of aeolian sand is concentrated in 120–830 μm. Therefore, coarse-grained soil (>830 μm) and fine-grained soil (<120 μm) are not disturbed by aeolian sand, and both may be effective sampling media for geology and mineralization studies [53]. The coarser fraction of soils (weight percentage is 21.9%) consists largely of quartz and feldspar, followed by gypsum and calcite. The intermediate fraction (120–830 μm) is dominated by quartz, gypsum, feldspar, and calcite, with small amounts of clay minerals, and its weight percentage is 58.6%. The fine fraction (weight percentage is 19.5%) consists largely of calcite and clay minerals, including illite, kaolinite, and chlorite [42]. As the particle size of the sample changes from large to small, a few trends were observed: (1) the content of quartz and feldspar gradually decreases—the coarser fraction of soils contains 32.4% quartz and 33% feldspar, while the fine fraction contains 13.6% quartz and 9.4% feldspar, respectively, and (2) the content of clay minerals gradually increases, and the content of clay minerals in the coarser fraction of soils is 7.7%, and 40.3% in the fine fraction. In addition, the alkaline soil (with a pH value of 7.5–9.5) might arise because evaporation exceeds rainfall in this region and the rock-based material in the overburdened soil accumulates on the surface under the effect of evaporation, making the surface soil alkaline [54]. The Eh negatively correlates with the pH. When the pH changes within a certain range, the amount of zeta potential on the surface of clay minerals also changes. Under alkaline conditions, the amount of negative charge on the surface of clay minerals is increased [55]. This is also confirmed in the experiment of kaolinite and halloysite adsorption of rare earth elements [55]. Additionally, the electrical conductivity of fine-grained samples in surface soil was significantly higher than that of coarse-grained samples [54]. These may make positively charged metal ions more easily adsorbed by fine-grained samples.
In this study, the experimental work of the fine-grained soil prospecting method is introduced to three mining areas. Additionally, the effectiveness of the method is evaluated by discussing ore-forming elements (Pb and Zn in the Huaniushan Pb-Zn deposit, Co and Mo in Zhunsujihua Cu-Mo deposit, and Au and Ag in Qujia Au deposit) in each experimental area. The method is also suitable and applicable for other elements’ deposits, such as copper and nickel ore [10], as well as rare metal ores [56], and even uranium ore [47]. In recent years, our team also carried out regional scale geochemical surveys (1:200,000 or 1:1 million) using the fine-grained soil prospecting method. For example, Wang et al. [57] effectively delineated the strategic target area of large-scale in situ leachable sandstone-type uranium deposits in the Turpan-Hami Basin in the arid desert area. Liu et al. [9] effectively delineated the known Pb-Zn deposit in the semi-arid grassland covered area, and provided a new target. Zhang et al. [58] confirmed the effectiveness of the fine-grained exploration technology in the Zhou’an copper-nickel mine in the alluvial soil coverage area. Zhang et al. [6] indicated that geochemical anomalies of uranium in the soil have a corresponding relationship with uranium-bearing geological bodies, including concealed uranium ore mineralization and granitic intrusions in the semi-arid grassland coverage area. A series of similar tests carried out internationally verified the applicability of the fine-grained soil prospecting method and yielded promising results [4,5,48,59].
Therefore, the above findings demonstrate that the fine-grained soil prospecting method can indicate concealed ore bodies and be used for coverage area surveys.
5. Conclusions
With the continuous improvement of the degree of mineral exploration work, the possibility of discovering new deposits in outcropping areas has become less and the search for concealed mines in the covered terrains has become a focus of attention. As a deep-penetrating geochemical technology that can reflect the information of deep anomalies, the fine-grained soil prospecting method has achieved ideal test results in arid Gobi Desert covered terrain, semi-arid grassland covered terrain, and alluvium soil covered terrain of northern China. The fine-grained soil is rich in clay minerals and iron-manganese oxides, with a large specific surface area and strong adsorption capacity, which can effectively enrich active metal elements. Therefore, the anomaly range indicated by the fine-grained soil prospecting method is very good with the known ore body location. The corresponding relationship can effectively indicate deep ore bodies and delineate anomalies in unknown areas. As such, the fine-grained soil prospecting method can be applied to geochemical prospecting and exploration in the coverage terrains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W. and B.Z. (Bimin Zhang); methodology, B.Z. (Bimin Zhang) and H.L.; software, H.L.; validation, X.W., B.Z. (Bimin Zhang) and H.L.; formal analysis, H.L.; investigation, H.L., Z.H. and B.Z. (Baoyun Zhang); resources, H.L.; data curation, H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L.; writing—review and editing, H.L., G.Y. and B.Z. (Bimin Zhang); visualization, H.L.; supervision, B.Z. (Bimin Zhang); project administration, H.L.; funding acquisition, H.L. and G.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41903071), the State Key Research and Development Project of China (2016YFC0600600, 2018YFC0604106), and the China Geological Survey Project (DD20190450, DD20190451).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks are given to all participants involved in this research for their hard work in field sampling, laboratory analysis, and data processing. The constructive comments and suggestions of anonymous reviewers made this paper more readable and robust.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cameron, E.M.; Hamilton, S.M.; Leybourne, M.I.; Hall, G.E.M.; McClenaghan, M.B. Finding deeply buried deposits using geochemistry. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2004, 4, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wen, X.; Rong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S.; Shi, S.; Wei, H. Vertical variations and dispersion of elements in arid desertregolith: A case study from the Jinwozi gold deposit, northwestern China. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2007, 7, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Han, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Feng, H. Metal-bearing nanoparticles observed in soils and fault gouges over the Shenjiayao gold deposit and their significance. Minerals 2019, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, P.A. Fine fraction regolith chemistry from the East Wongatha area, Western Australia: Tracing bedrock and mineralization through thick cover. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2013, 13, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.R.P.; Morris, P.A.; Anand, R.R.; Lau, I.C.; Pinchand, G.T. Application of ultrafine fraction soil extraction and analysis for mineral exploration. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2020, 20, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Han, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, B.; Dou, B. Regional geochemical survey of concealed sandstone-type uranium deposits using fine-grained soil and groundwater in the Erlian basin, north-east China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 216, 106573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Ye, R.; Yao, W.; Wang, W. Fine-grained soil prospecting method for mineral exploration in loess covered areas and discussion on the origin of geochemical anomalies. J. Guilin. Univ. Technol. 2019, 39, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Ye, R.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Han, Z.; Lin, X.; Wang, Z. Geochemical exploration for concealed deposits at the periphery of the Zijinshan copper-gold mine, southeastern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 157, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chi, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J. Geochemical methods for grassland-covered hilly terrains in central-eastern inner Mongolia. Geophy. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 37, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D.; Chi, Q. The application of debris and soil geochemical measurement methods to the Shaquanzi Cu-Ni deposit, Xinjiang. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 39, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Lombard, M.; de Bruin, D.; Elsenbroek, J. High-density regional geochemical mapping of soils and stream sediments in South Africa. J. Geochem. Explor. 1999, 66, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Xia, X.; Liu, N. Research progress of applied geochemsity during the decade of 2011 to 2020 in China. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2020, 39, 927–944. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Ren, T.; Xi, X.; Zhang, L. The implementation of the Regional Geochemistry-National Reconnaissance Program (RGNR) in China in the past thirty years. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2009, 30, 700–716. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Sun, H.; Ren, T. Regional Geochemistry-National Reconnaissance project in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 1989, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. A decade of exploration geochemistry. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2013, 32, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Mu, X.; Ren, T. Geochemical mapping in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 60, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Xu, S.; Yao, W.; Ye, R. Geochemical challenges of diverse regolith-covered terrains for mineral exploration in China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 73, 417–431. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W. Metallogenic study of Huaniushan Au-Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, Beishan area, Gansu province. Geol. Miner. Res. South China 2010, 3, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhai, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, C.; Wang, X.; Lei, Y. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of basalt and its geological significance in Huaniushan Pb-Zn deposit, Beishan area, Gansu, China. Geol. Bull. China 2010, 29, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, R.; Lang, H.; Tao, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, P. Geophysical and geochemical anomalous features of molybdenum deposit in Zhunsujihua, Inner Mongolia and its geological significance. Geoscience 2011, 25, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; He, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H. Geochemical exploration for concealed deposits on semi-arid grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 37, 804–810. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q. Gold mineralization in china: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Res. 2016, 36, 219–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, R.; Gao, X.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, L. A preliminary study of extreme enrichment of critical elements in the Jiaodong gold deposits, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2020, 36, 1285–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Cui, S.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yang, C.; Jiao, X. Great progress and far-reaching significance of deep exploration in the Jiaojia metallogenic belt, Shandong province. Geol. Prospect. 2008, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Li, D.; Tian, J.; Shan, W.; Li, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Luo, W.; Xiong, Y. Progress of deep exploration and theoretical innovation of metallogenic of gold deposits in Shandong province. Shandong Land Resour. 2018, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shu, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, P.; Chi, N. A study of geochemical Zonation of primary halos in the Qujia gold deposit, Laizhou, Shandong province, and its geological significance. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 337–356. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Z. The application of soil geochemical measurement method to the Huaniushan Pb-Zn deposit, Gansu Province. Geophy. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 40, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Yan, M.; Li, L.; Shen, H. Usable values for Chinese standard reference samples of stream sediment, soil and rocks GSD 9-12, GSS 1-8 and GSR 1-6. Geostand. Newslett. 1985, 9, 227–280. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Wang, C.; Cao, Q.; Gu, T.; Chi, Q. Eleven gold geochemical reference samples (GAu 8-18). Geostand. Newslett. 1995, 19, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bai, J.; Wang, Y. Analytical scheme and quality monitoring system for China Geochemcial Baselines. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Mou, X.; Ren, T.; Ma, Z.; Liu, R.; Gong, Q.; Wang, M.; Gong, J.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. Research on Application of Geochemical Exploration Data for Evaluation of National Mineral Resources Potential; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Q.; Yan, M. Handbook of Elemental Abundance for Applied Geochemistry; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Dai, J.; Hu, X.; Song, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Background values of soil geochemistry in Shandong province. Shandong Land Resour. 2018, 34, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Dai, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Yu, C.; Han, L.; Ren, T.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Soil geochemical background value of 17 cities in Shandong province. Shandong Land Resour. 2019, 35, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Liu, H.; Hou, J.; Gao, H. Characteristics of ore bodies and prospecting potential of Zhaoxian gold deposit in Laizhou city of Shandong province. Shandong Land Resour. 2018, 34, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, W.; Anand, R.; Bohu, T. Biochemical and mechanical dispersion mechanisms of Au and As in areas covered by Permian glacial sediments and aeolian sand. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2019, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, D.L.; Kelley, K.D.; Coker, W.B.; Caughlin, B.; Doherty, M. Beyond the obvious limits of ore deposits: The use of mineralogical, geochemical and biological features for the remote detection of mineralization. Econ. Geol. 2006, 101, 729–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, L.; Kristiansson, K. Experimental evidence for an ascending microflow of geogas in the ground. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 70, 407–416. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Conceptual model of deep-penetrating geochemical migration. Geol. Bull. China 2005, 24, 892–896. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, R.R.; Aspandiar, M.F.; Noble, R.R.P. A review of metal transfer mechanisms through transported cover with emphasis on the vadose zone within the Australian regolith. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 73, 394–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, X. Recent developments on deep-penetrating geochemistry. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Chi, Q.; Yao, W.; Liu, H.; Lin, X. Three-dimensional geochemical patterns of regolith over a concealed gold deposit revealed by overburden drilling in desert terrains of northwestern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 164, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. Characteristics, formation and migration of the particles carried by ascending gas flow from the concealed metal deposit. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X. Nanogeochemistry: Deep-penetrating geochemical exploration through cover. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Ye, R. Nanoparticles observed by TEM from gold, copper-nickel, and silver deposits and implications for mineral exploration in covered Terrains. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 6014–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, S. Microscopic characterization of metallic nanoparticles in ore rocks, fault gouge and geogas from the Shanggong gold deposit, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 217, 106562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ye, R.; Zhang, B. Source identification of the geochemical anomaly from the fine-grained soil survey in the Nuheting sandstone-type uranium deposit, Erlian Basin, north China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 227, 106797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.R.; Lintern, M.; Noble, R.R.P.; Aspandiar, M.; Macfarlane, C.; Hough, R.; Stewart, A.; Wakelin, S.; Townley, B.; Reid, N. Geochemical dispersion through transported cover in regolith-dominated terrains-toward an understanding of process. SEG Spec. Publ. 2014, 18, 97–126. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, R.R.P.; Lintern, M.; Townley, B.; Anand, R.R.; Reid, N. Metal migration at the North Miitel Ni sulphide deposit in the southern Yilgarn craton: Part 3. Gas and overview. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2013, 13, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Lu, Y.; Yao, W.; Bai, J. Further study on deep penetrating geochemistry over the Spence porphyry copper deposit, Chile. Geosci. Front. 2011, 2, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Leaching of mobile forms of metals in overburden: Development and application. J. Geochem. Explor. 1998, 61, 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L. Environmental Soil Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X. Comparative Interpretation of Multi-Element Regional Geochemistry in Gobi Desert, Eastern Tianshan, NW China; Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B. Deep-Penetrating Geochemistry: Mechanism and Methods in Gobi Areas; Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Liang, X.; Ma, L.; Huang, J.; He, H.; Zhu, J. Adsorption of REEs on kaolinite and halloysite: A link to the REE distribution on clays in the weathering crust of granite. Chem. Geol. 2019, 525, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; Hu, B. Geogas field characteristics of the Kalu’an pegmatite lithium deposit and its prospecting significance. Acta Petrol. Miner. 2019, 38, 570–578. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S. Deep-penetrating geochemistry for sandstone-type uranium deposits in the Turpan–Hami basin, north-western China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Yao, W.; Ye, R. Models and case history studies of deep-penetrating geochemical exploration for concealed deposits in basins. Geol. China 2016, 43, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar]
- van Geffen, P.W.G.; Kyser, K.T.; Oates, C.J.; Ihlenfeld, C. Till and vegetation geochemistry at the Talbot VMS Cu–Zn prospect, Manitoba, Canada: Implications for mineral exploration. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2012, 12, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).