Mineral Composition and Structural Characterization of the Clinoptilolite Powders Obtained from Zeolite-Rich Tuffs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Macroscopic Analysis
2.2. X-ray Analysis
2.3. X-ray Fluorescence
2.4. Thermal Analysis
2.5. SEM Analysis
2.6. Particle Size Distribution
2.7. Textural and Physical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Macroscopic and Microscopic Analysis
3.2. XRD Analysis
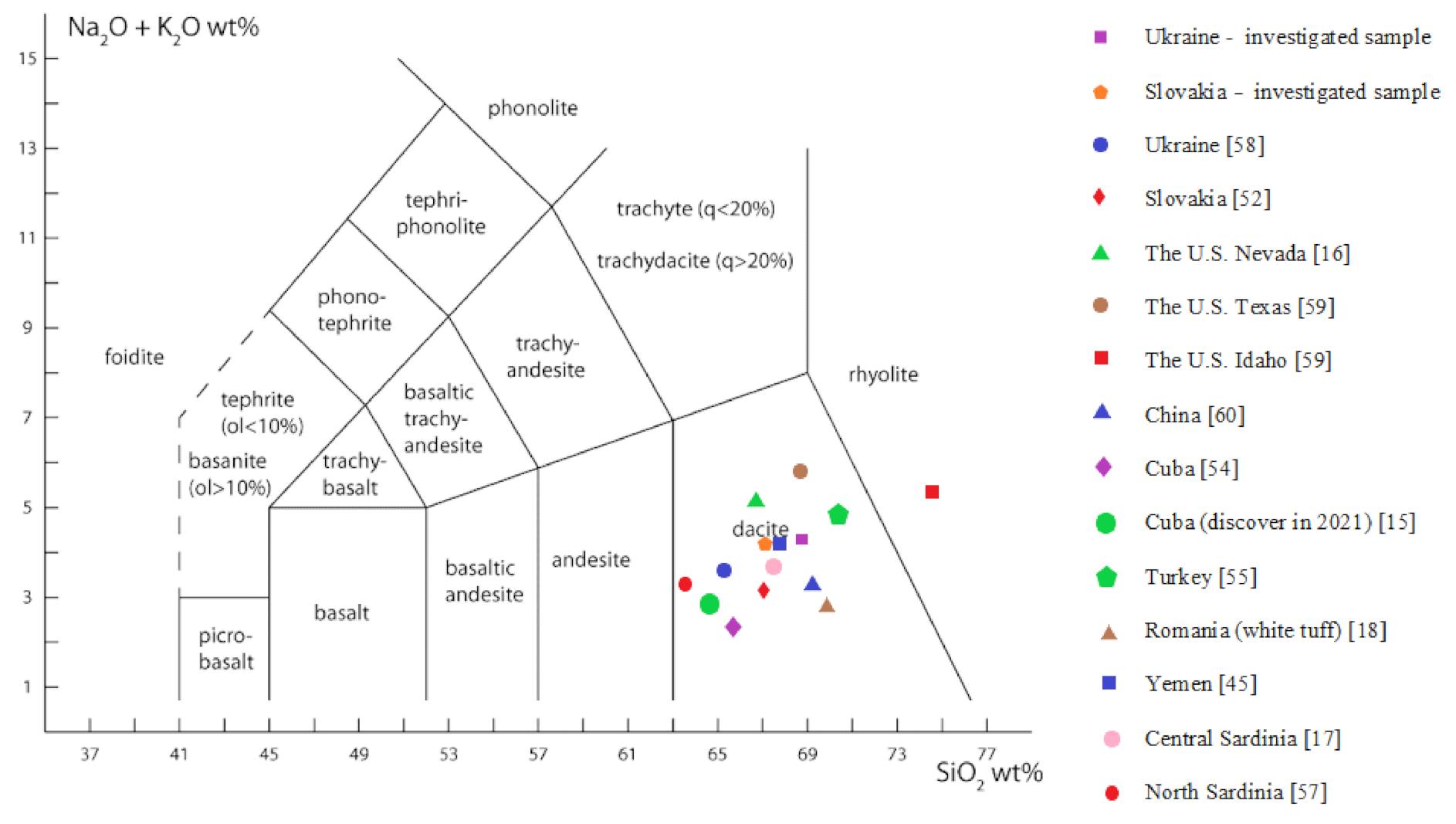
3.3. X-ray Fluorescence
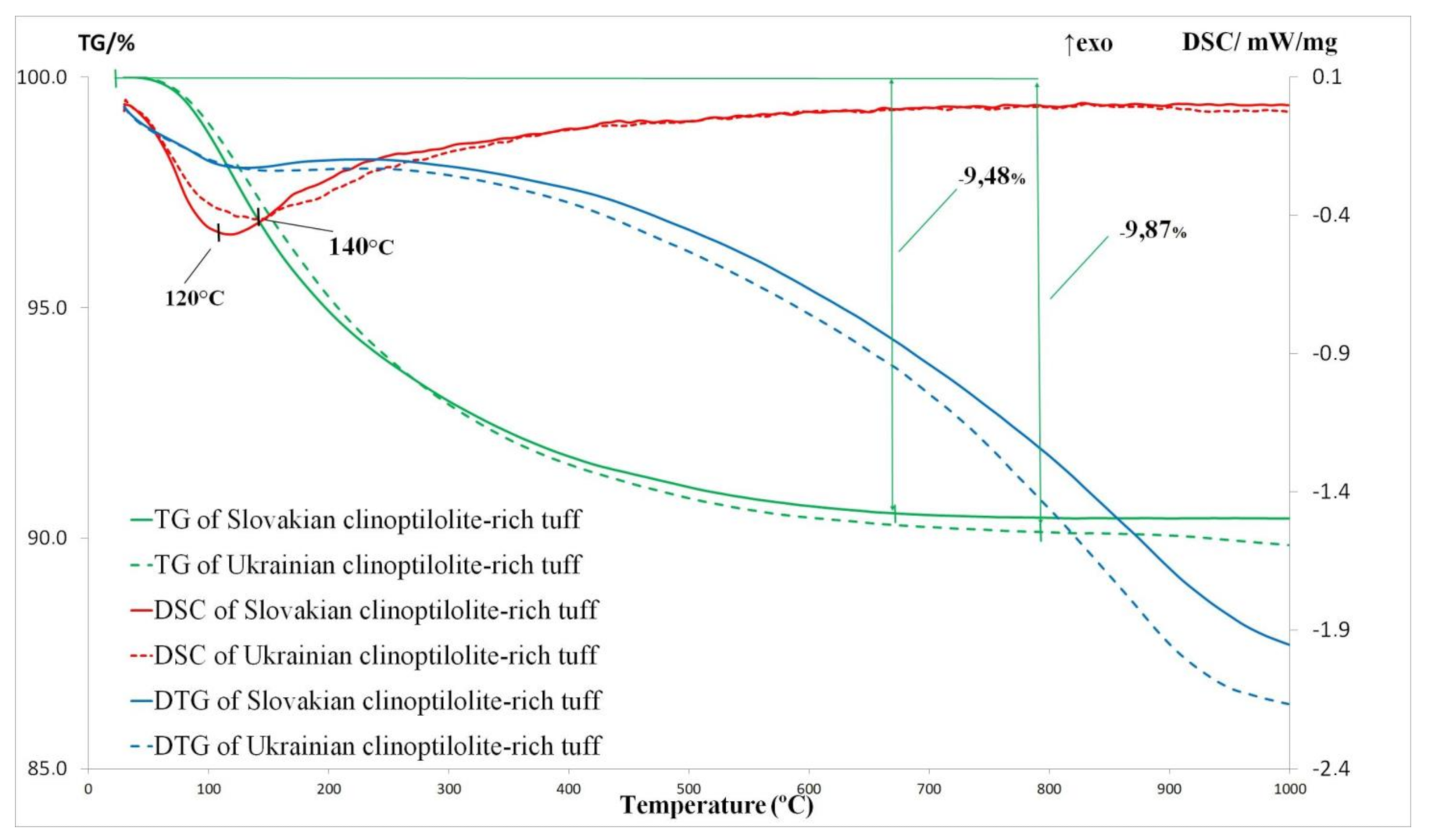
3.4. Thermal Analysis
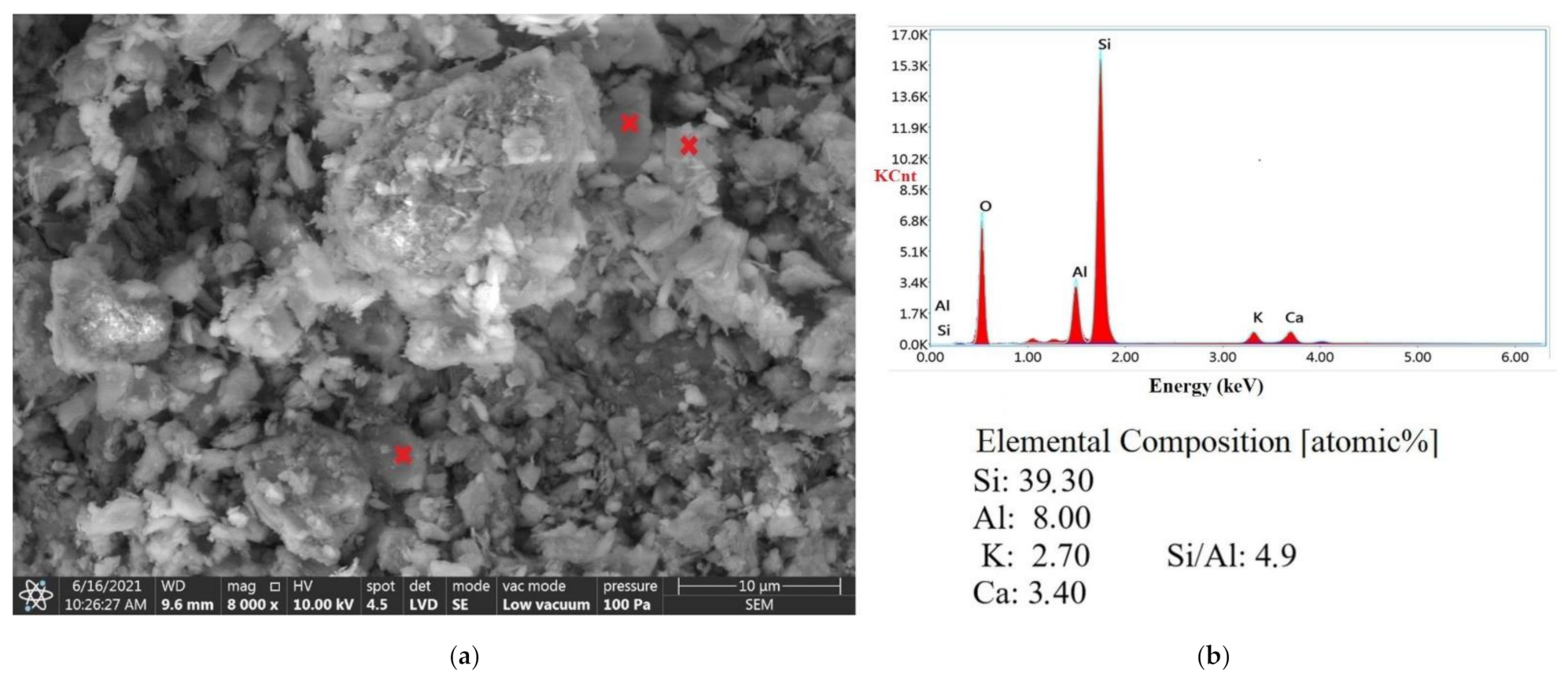
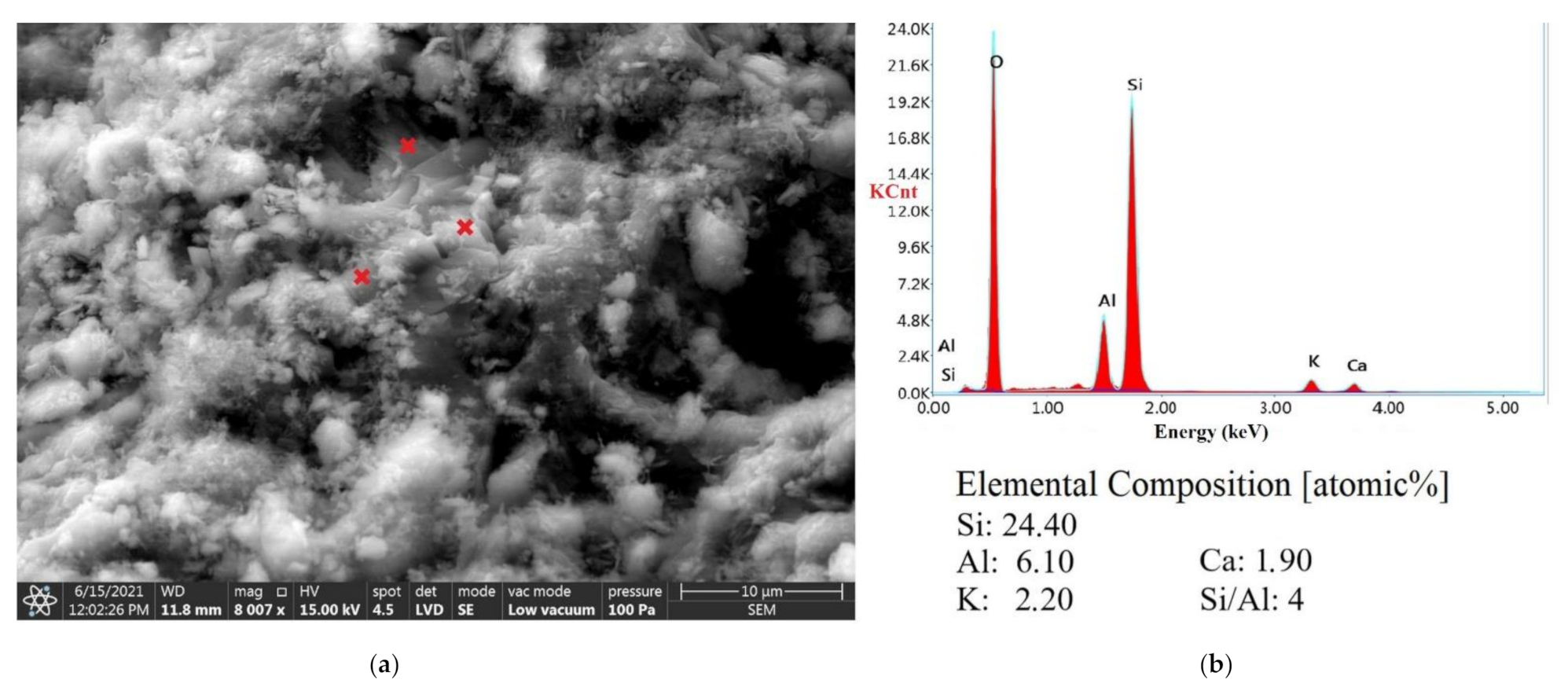
3.5. SEM Analysis
3.6. Particle Size Distribution
3.7. Textural and Physical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Auerbach, S.M.; Carrado, K.A.; Dutta, P.K. Handbook of Zeolite Science and Technology Copyright Year 2003; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 9780824740207. [Google Scholar]
- Breck, D.W. Zeolite Molecular Sieves: Structure, Chemistry and Use; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Ciciszwili, G.W.; Andronikaszwili, T.G.; Kirow, G.N.; Filizowa, D.Ł. Zeolity Naturalne; Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mozgawa, W. Spektroskopia Oscylacyjna Zeolitów; Uczelniane Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Dydaktyczne AGH: Kraków, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, N.; Rikhtegar, N.; Panahi, S.H.; Atabi, F.; Shahraki, B.K. Porosity, characterization and structural properties of natural zeolite—Clinoptilolite—As a sorbent. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2013, 39, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Földvári, M. Handbook of Thermogravimetric System of Minerals and Its Use in Geological Practice; Geological Institute of Hungary: Budapest, Hungary, 2011; ISBN 978-963-671-288-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, T. Zeolity—Kopaliny XXI wieku. Przegląd Geol. 1994, 9, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, V.C.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; De Araújo, M.J.G.; Sapag, K.; Pergher, S.B.C. Basic Treatment in Natural Clinoptilolite for Improvement of Physicochemical Properties. Minerals 2018, 8, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boles, J.R. Composition, optical properties, cell dimensions and thermal Stability of some heulandite group zeolites. Am. Mineral. 1972, 57, 1463–1493. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, K.; Takeuchi, Y. Clinoptilolite: The distribution of potassium atoms and its role in thermal stability. Z. Kristall. 1977, 145, 216–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M. Natural vs. Synthetic zeolites. Crystals 2020, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manecki, A.; Muszyński, M. Przewodnik do Petrografii; Uczelniane Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Dydaktyczne AGH: Kraków, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mastinu, A.; Kumar, A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Bonini, S.A.; Premoli, M.; Aria, F.; Gianoncelli, A.; Memo, M. Zeolite Clinoptilolite: Therapeutic Virtues of an Ancient Mineral. Molecules 2019, 24, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flanagan, D.M. Zeolites (Natural). Miner. Commod. Summ. 2020, 188–189. [Google Scholar]
- Costafreda, J.L.; Martín, D.A. New Deposit of Mordenite–Clinoptilolite in the Eastern Region of Cuba: Uses as Pozzolans. Molecules 2021, 26, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Product Data Sheet; KMI Zeolite Inc.: Amargosa Valley, NV, USA; Available online: https://www.kmizeolite.com/technical-data/ (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Mormone, A.; Piochi, M. Mineralogy, Geochemistry and Genesis of Zeolites in Cenozoic Pyroclastic Flows from the Asuni Area (Central Sardinia, Italy). Minerals 2020, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bojar, A.-V.; Barbu, V.; Wojtowicz, A.; Bojar, H.-P.; Hałas, S.; Duliu, O.G. Miocene Slănic Tuff, Eastern Carpathians, Romania, in the Context of Badenian Salinity Crisis. Geosciences 2018, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tschegg, C.; Rice, A.H.N.; Grasemann, B.; Matiasek, E.; Kobulej, P.; Dzivák, M.; Berger, T. Petrogenesis of a Large-Scale Miocene Zeolite Tuff in the Eastern Slovak Republic: The Nižný Hrabovec Open-Pit Clinoptilolite Mine. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondale, K.D.; Carland, R.M.; Aplan, F.F. The comparative ion exchange capacities of natural sedimentary and synthetic zeolites. Miner. Eng. 1995, 8, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M.; White, E.A.D. The hydrothermal chemistry of silicates. Part II. Synthetic crystalline sodium aluminosilicate. J. Chem. Soc. 1952, 286, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Yokoyama, H.; Iwamoto, Y.; Iwamoto, Y. Characterization of zeolite in zeolite-geopolymer hybrid bulk materials derived from kaolinitic clays. Materials 2013, 6, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bandura, L.; Franus, M.; Józefaciuk, G.; Franus, W. Synthetic zeolites from fly ash as effective mineral sorbents for land-based petroleum spills cleanup. Fuel 2015, 147, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rożek, P.; Król, M.; Mozgawa, W. Geopolymer-zeolite composites: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, K.M.; Król, M.; Bajda, T.; Mozgawa, W. Sorption of heavy metal cations on mesoporous ZSM-5 and mordenite zeolites. Materials 2019, 12, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohács, K.; Faitli, J.; Bokányi, L.; Mucsi, G. Control of Natural Zeolite Properties by Mechanical Activation in Stirred Media Mill. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivashankari, L.; Rajkishore, S.K.; Lakshmanan, A.; Subramanian, K.S. Optimization of Dry Milling Process for Synthesizing Nano Zeolites. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Şükrü, U.; Musa, S.; Soner, T.; İrfan, T. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater solution using a mechanically activated novel zeolitic material. J. Min. Sci. 2020, 56, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Wakihara, T.; Ichikawa, R.; Tatami, J.; Endo, A.; Yoshida, K.; Sasaki, Y. Bead-Milling and Postmilling Recrystallization: An Organic Template-free Methodology for the Production of Nano-zeolites. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejhieh, A.N.; Khorsandi, S. Photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol with ZnO supported nano-clinoptilolite zeolite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolzaya, T.; Davaabal, B.; Ochirbat, Z.; Oyun-Erdene, G.; Min-jigmaa, A.; Temuujin, J. The mechanochemical activation study of Tsagaan-tsav zeolite. Mong. J. Chem. 2011, 12, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikashina, V.; Streletskii, A.; Kolbanev, I.; Meshkova, I.; Grinev, V.; Serova, I.; Yusupov, T.; Shumskaya, L. Effect of mechanical activation on the properties of natural zeolites. Inorg. Mater. 2011, 47, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.R.; Lecus, A.; Gajdardziska-Josifovska, M.; Schofield, M.; Virnoche, M.; Chang, J.; Chen, J.; Garman, D. Graphene-oxide loading on natural zeolite particles for enhancement of adsorption properties. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 4589–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.; Singh, B.K.; Um, W. Efficient radon removal using fluorine-functionalized natural zeolite. J. Environ. Radioact. 2021, 233, 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtu, Y.D.; Melak, F.; Yitbarek, M.; Astatkie, H. Aluminum Coated Natural Zeolite for Water Defluoridation: A Mechanistic Insight; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Reeve, P.J.; Fallowfield, H.J. Natural and surfactant modified zeolites: A review of their applications for water remediation with a focus on surfactant desorption and toxicity towards microorganisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 205, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, E.A.; Buamah, R.; Kwakye-Awuah, B. Defluorination of drinking water using surfactant modified zeolites. J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowman, R.S. Applications of surfactant-modified zeolites to environmental remediation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Xie, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, H. Adsorption of organic pollutants by surfactant modified zeolite as controlled by surfactant chain length. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 179, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghash, A.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A. Comparison of the efficiency of modified clinoptilolite with HDTMA and HDP surfactants for the removal of phosphate in aqueous solutions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Viet, P.V.; Chao, H.P. Surfactant modified zeolite as amphiphilic and dual-electronic adsorbent for removal of cationic and oxyanionic metal ions and organic compounds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, E.J.; Hunter, D.B.; Bowman, R.S. Fourier transform Raman spectroscopy of sorbed HDTMA and the mechanism of chromate sorption to surfactant-modified clinoptilolite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashaqbeh, O.A.; Alsafadi, D.A.; Alsalhi, L.Z.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L.; Snow, D.D. Removal of Carbamazepine onto Modified Zeolitic Tuff in Different Water Matrices: Batch and Continuous Flow Experiments. Water 2021, 13, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, V.L.B.; Bruj, G.; Dordai, L.; Roman, M.; Cadar, O.; Becze, A. Evaluation of the Impact of Different Natural Zeolite Treatments on the Capacity of Eliminating/Reducing Odors and Toxic Compounds. Materials 2021, 14, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Xinghu, W.; Dawood, A.S.; Xin, C.; Yan, C.; Assabri, A.M. Characterization of Yemeni Natural Zeolite (Al-Ahyuq Area) and its Environment Applications: A Review. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschegg, C.; Hou, Z.; Rice, A.H.N.; Fendrych, J.; Matiasek, E.; Berger, T.; Grasemann, B. Fault zone structures and strain localization in clinoptilolite-tuff (Nižný Hrabovec, Slovak Republic). J. Struct. Geol. 2020, 138, 104090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Maitre, R.W.; Bateman, P.; Dudek, A.; Keller, J.; Lameyre, J.; Le Bas, M.J.; Sabine, P.A.; Schmid, R.; Sorensen, H.; Strekeisen, A.; et al. A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms: Recommendations of the InternationalUnion of Geological Sciences, Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks. Int. Union Geol. Sci. 1989, 552, 193. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 13320 Particle Size Analysis—Laser Diffraction Methods; The International Organization for Standarization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Vasylechko, V.O.; Gryshchouk, G.V.; Kuz’ma, Y.B.; Zakordonskiy, V.P.; Vasylechko, L.O.; Lebedynets, L.O.; Kalytovs’ka, M.B. Adsorption of cadmium on acid-modified Transcarpathian clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 60, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynsky, M.; Golembiewski, R.; Trykowski, G.; Buszewski, B. Heterogeneity and hierarchy of clinoptilolite porosity. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçmaz, H. Mineralogical and petrographic study of zeolitic tuffs from Yenice-Saraycık (Demirci, Manisa), Turkey. Muhendis. Fak. Muhendis. 2018, 20, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewská, E.; Tylus, W.; Drábik, M.; Majzlan, J.; Kravčak, J.; Williams, C.; Čaplovičová, M.; Čaplovič, L. Structure investigation of nano-FeO(OH) modified clinoptilolite tuff for antimony removal. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 248, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, B.; Matusik, J.; Bajda, T. New insights into alkylammonium-functionalized clinoptilolite and Na-P1 zeolite: Structural and textural features. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 361, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervini-Silva, J.; Nieto-Camacho, A.; Kaufhold, S.; Ufer, K.; Palacios, E.; Montoya, A.; Dathe, W. Antiphlogistic effect by zeolite as determined by a murine inflammation model. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 228, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gennaro, B.; Aprea, P.; Liguori, B.; Galzerano, B.; Peluso, A.; Caputo, D. Zeolite-Rich Composite Materials for Environmental Remediation: Arsenic Removal from Water. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalebić, B.; Pavlović, J.; Dikić, J.; Rečnik, A.; Gyergyek, S.; Škoro, N.; Rajić, N. Use of Natural Clinoptilolite in the Preparation of an Efficient Adsorbent for Ciprofloxacin Removal from Aqueous Media. Minerals 2021, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, P.; Santona, L.; Cozza, C.; Giuliano, V.; Abbruzzese, C.; Nastro, V.; Melisa, P. Thermal and spectroscopic studies of zeolites exchanged with metal cations. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 734, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciezkowska, M.; Bajda, T.; Decewicz, P.; Dziewit, L.; Drewniak, L. Effect of Clinoptilolite and Halloysite Addition on Biogas Production and Microbial Community Structure during Anaerobic Digestion. Materials 2020, 13, 4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, L.E.; Juenger, M.C.G. Effect of calcination on the reactivity of natural clinoptilolite zeolites used as supplementary cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-F.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, B.-H.; Yoshiyuki, I.; Liou, S.Y.-H.; Huang, R.-T. A Further Investigation of NH4+ Removal Mechanisms by Using Natural and Synthetic Zeolites in Different Concentrations and Temperatures. Minerals 2018, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franus, W.; Woszuk, A.; Bandura, L.; Zofka, A. Właściwości zeolitu naturalnego i syntetycznego oraz ich wpływ na efekt spienienia asfaltu. Mater. Bud. 2017, 8, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkuna, O.; Leboda, R.; Skubiszewska-Ziemba, J.; Vrublevska, T.; Gunko, V.M.; Ryczkowski, J. Structural and physicochemical properties of natural zeolites: Clinoptilolite and mordenite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 87, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.V.; Arellano, J.J.C.; Ramırez, H.B. Characterization and preparation of porous membranes with a natural Mexican zeolite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewská, E.; Tylus, W.; Bujdoš, M. Study of Mono- and Bimetallic Fe and Mn Oxide-Supported Clinoptilolite for Improved Pb(II) Removal. Molecules 2021, 26, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvarcı, Ö.Ç.; Akdeniz, Y.; Özmıhçı, F.; Ülkü, S.; Balköse, D.; Çiftçioğlu, M. Thermal behaviour of a zeolitic tuff. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stocker, K.; Ellersdorfer, M.; Lehner, M.; Raith, J.G. Characterization and Utilization of Natural Zeolites in Technical Applications. Berg. Huettenmaenn Monatsh 2017, 162, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, E.; Polcaro, C.M.; Ciccioli, P.; Galli, E. The comparative study of a laccase-natural clinoptilolite-based catalyst activity and free laccase activity on model compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 289, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woszuk, A.; Wróbel, M.; Franus, W. Influence of Waste Engine Oil Addition on the Properties of Zeolite-Foamed Asphalt. Materials 2019, 12, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Güngör, D.; Özen, S. Development and characterization of clinoptilolite-, mordenite-, and analcime-based geopolymers: A comparative study. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holub, M.; Balintova, M.; Demcak, S.; Hurakova, M. Characterization of Natural Zeolite and Determination Its Adsorption Properties. Czas. Inżynierii Lądowej Sr. Archit. 2016, 63, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czuma, N.; Panek, R.; Baran, P.; Zarębska, K. The influence of binders for the pelletization of fly ash zeolites on sulfur dioxide sorption properties. Clay Miner. 2020, 55, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembenek, M.; Hryniewicz, M. Badania i Opracowanie Metody Doboru Układu Zagęszczania Prasy Walcowej; Wydawnictwo AGH: Kraków, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kłassiena, P.W.; Griszajew, I.G. Podstawy Techniki Granulacji; Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Izak, P. Reologia w Ceramice, Wydanie Drugie Uzupełnione; Wydawnictwo AGH: Kraków, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, B.; Bajda, T. Organically modified zeolites in petroleum compounds spill cleanup—Production, efficiency, utilization. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 149, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Sing Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
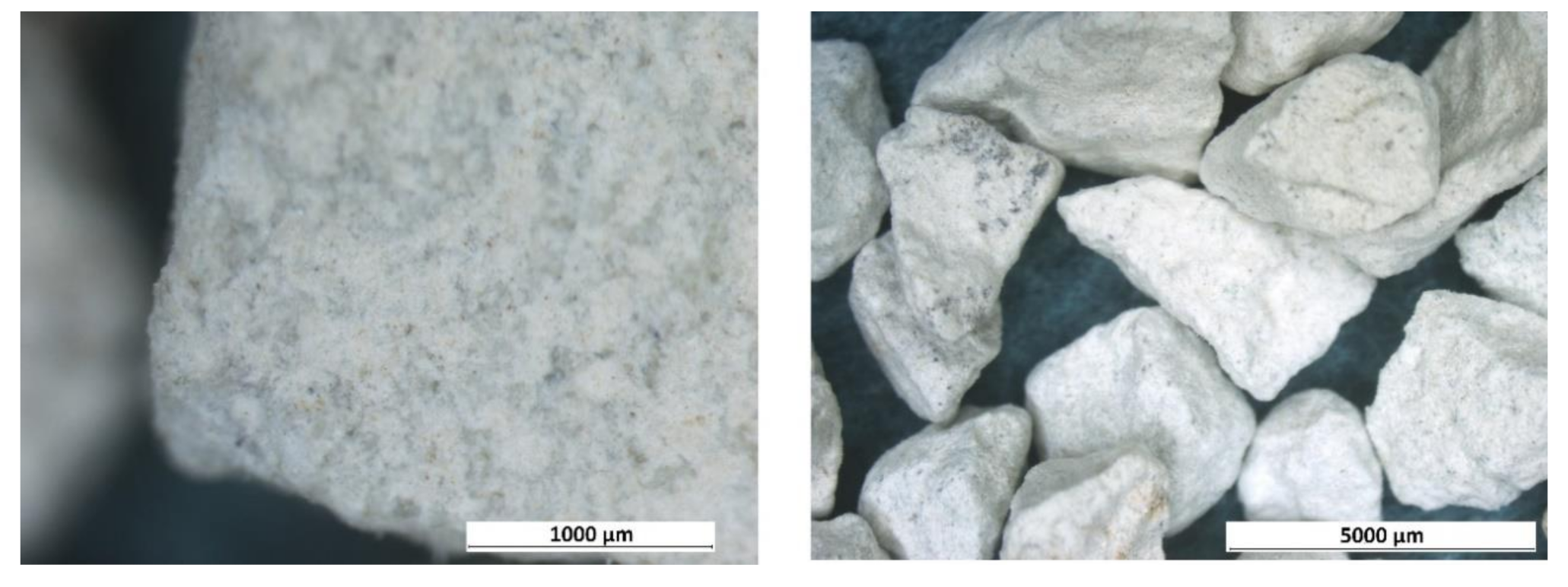
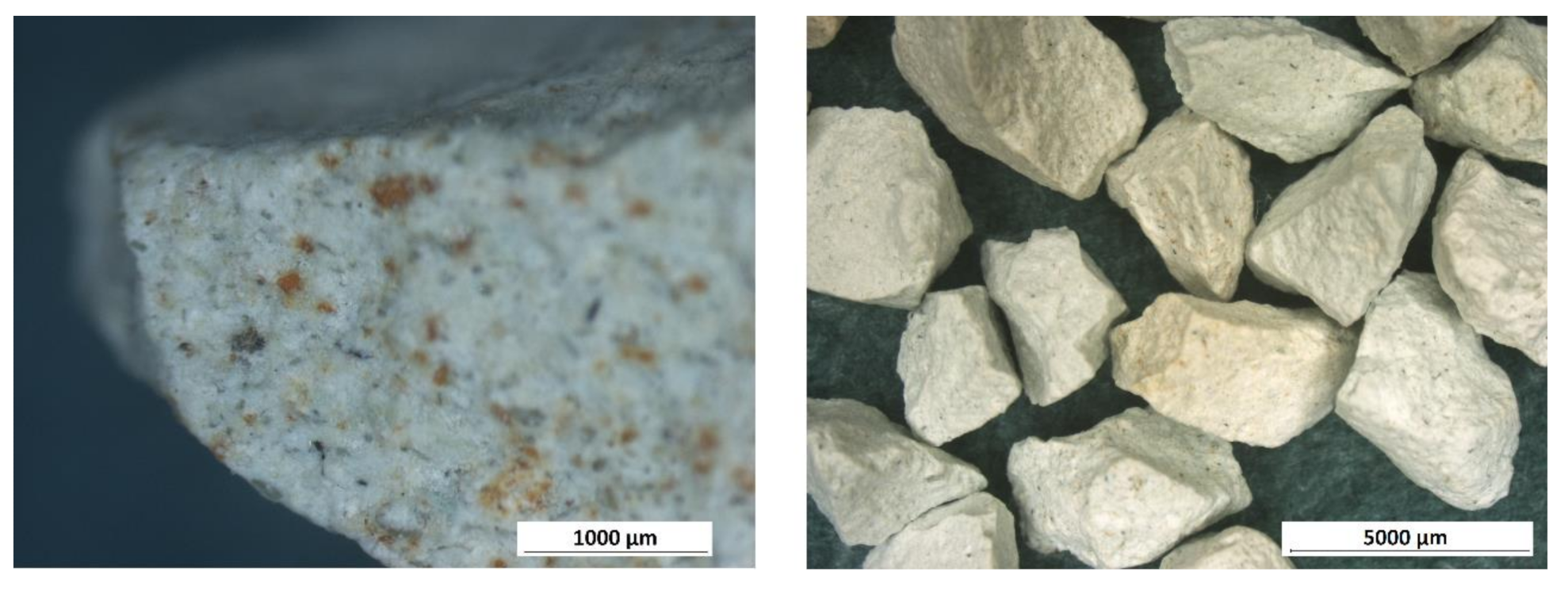
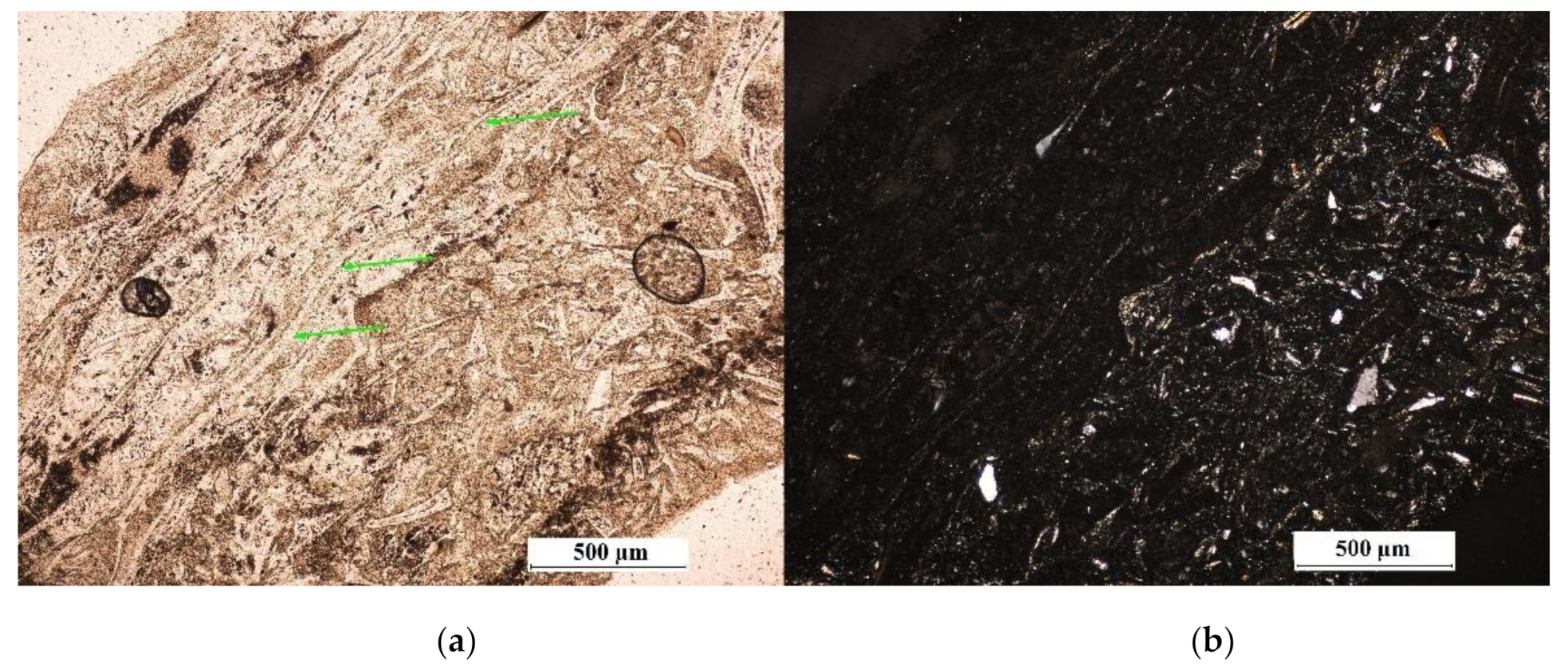


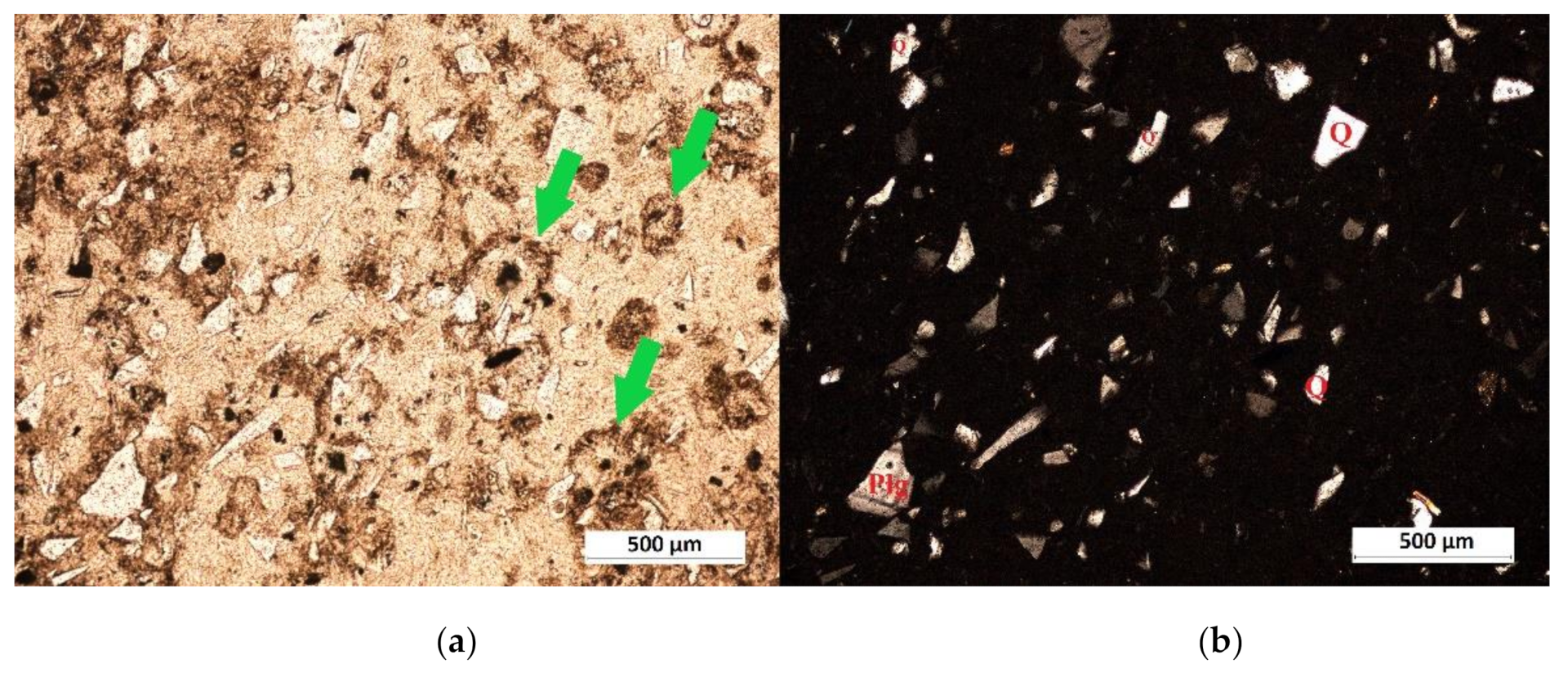


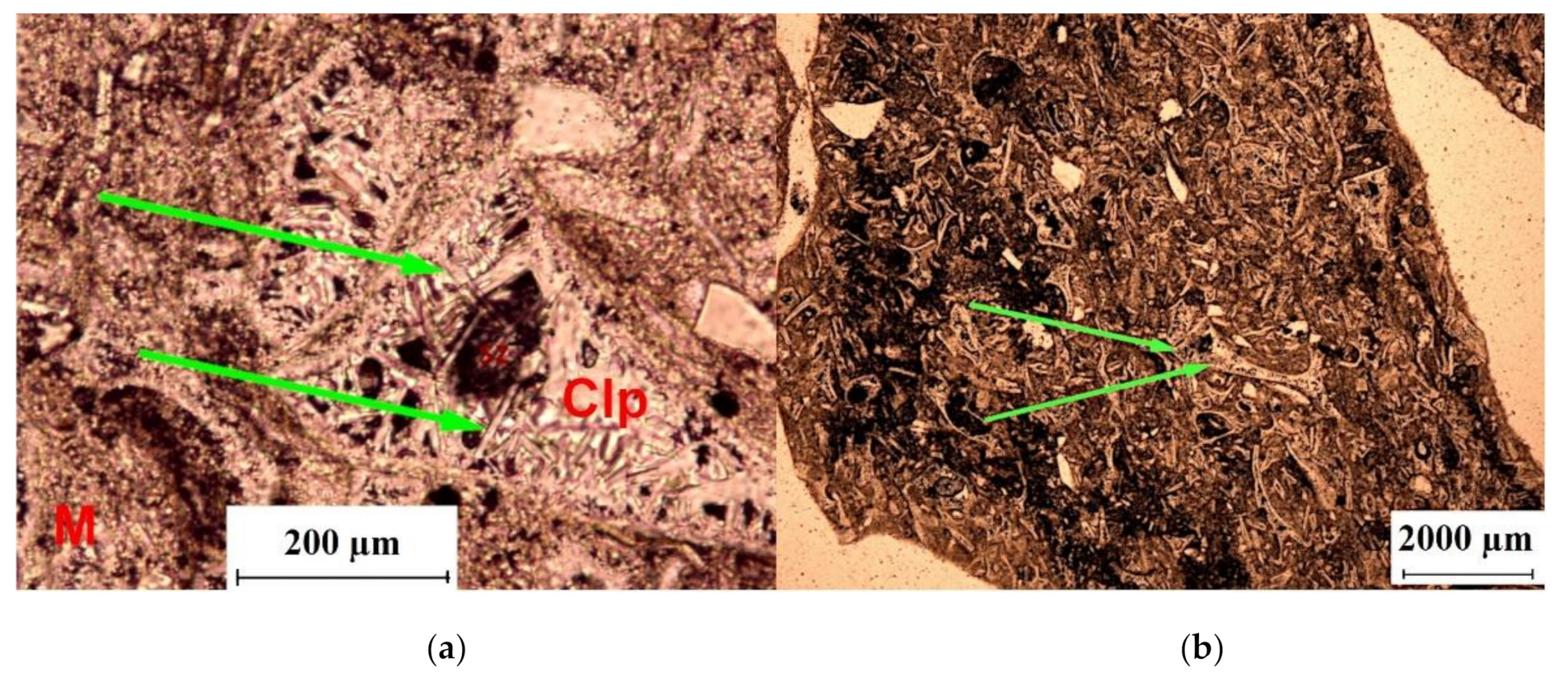
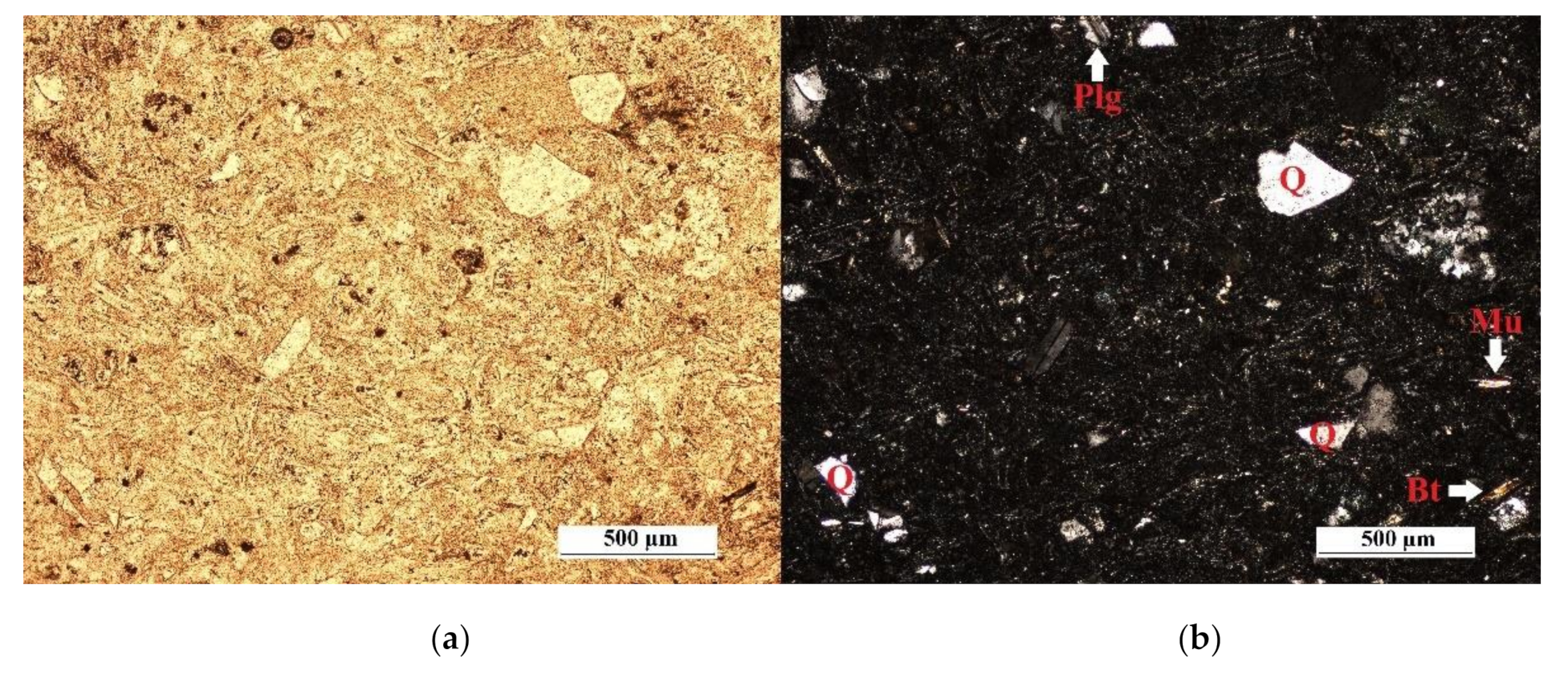
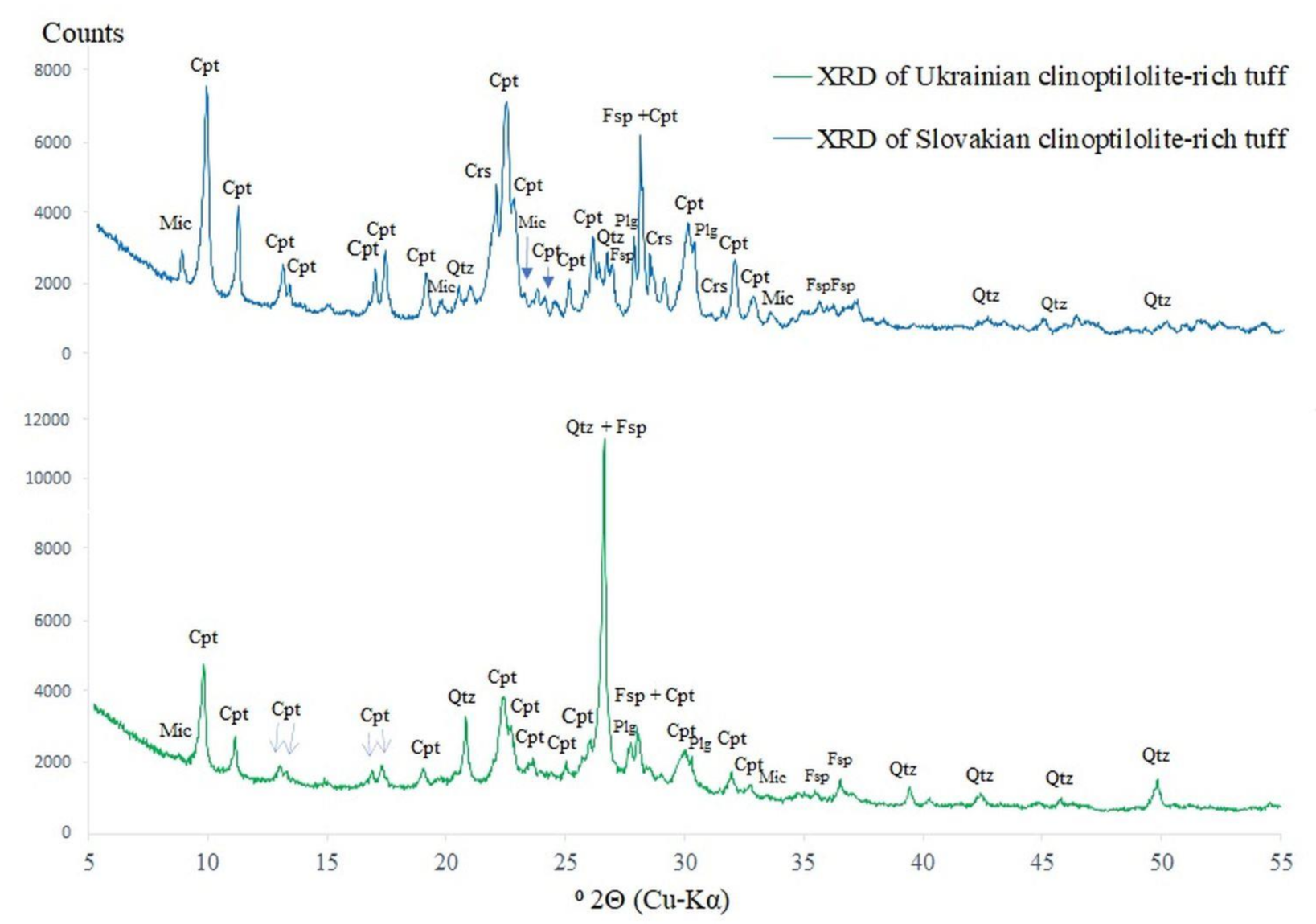
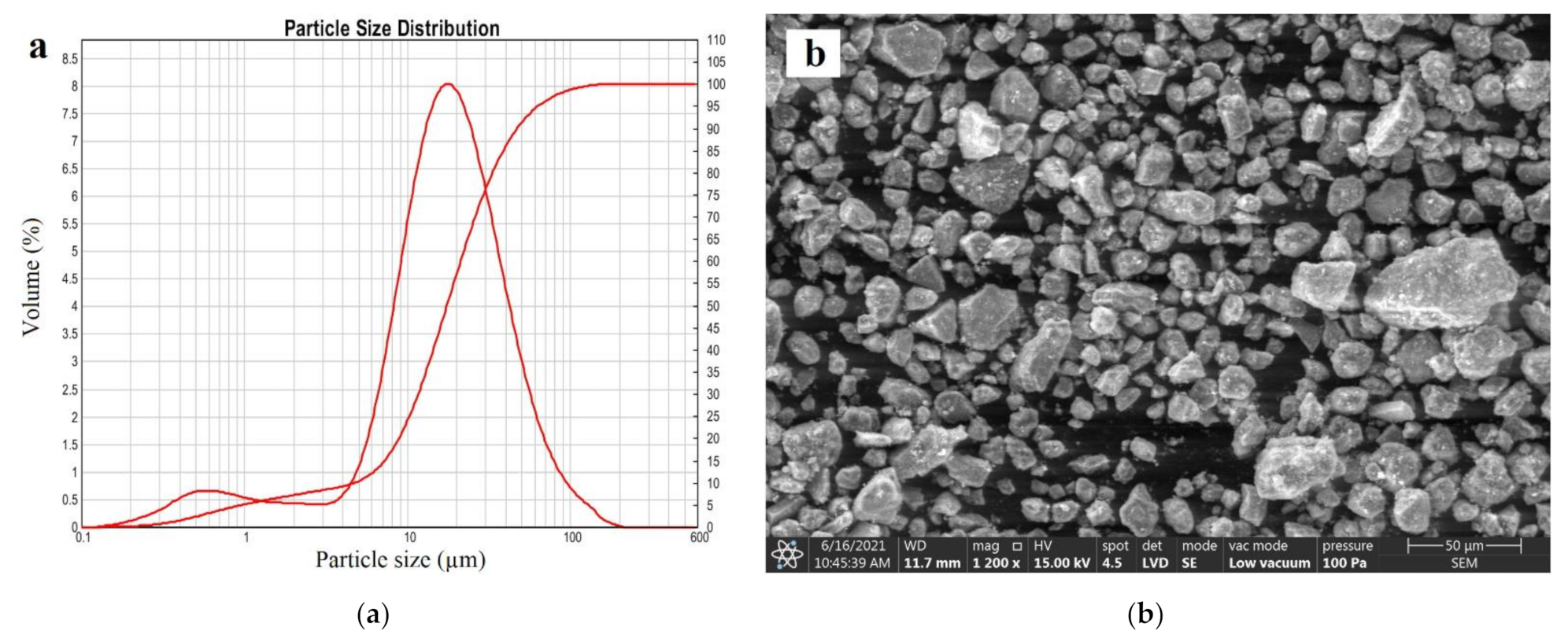
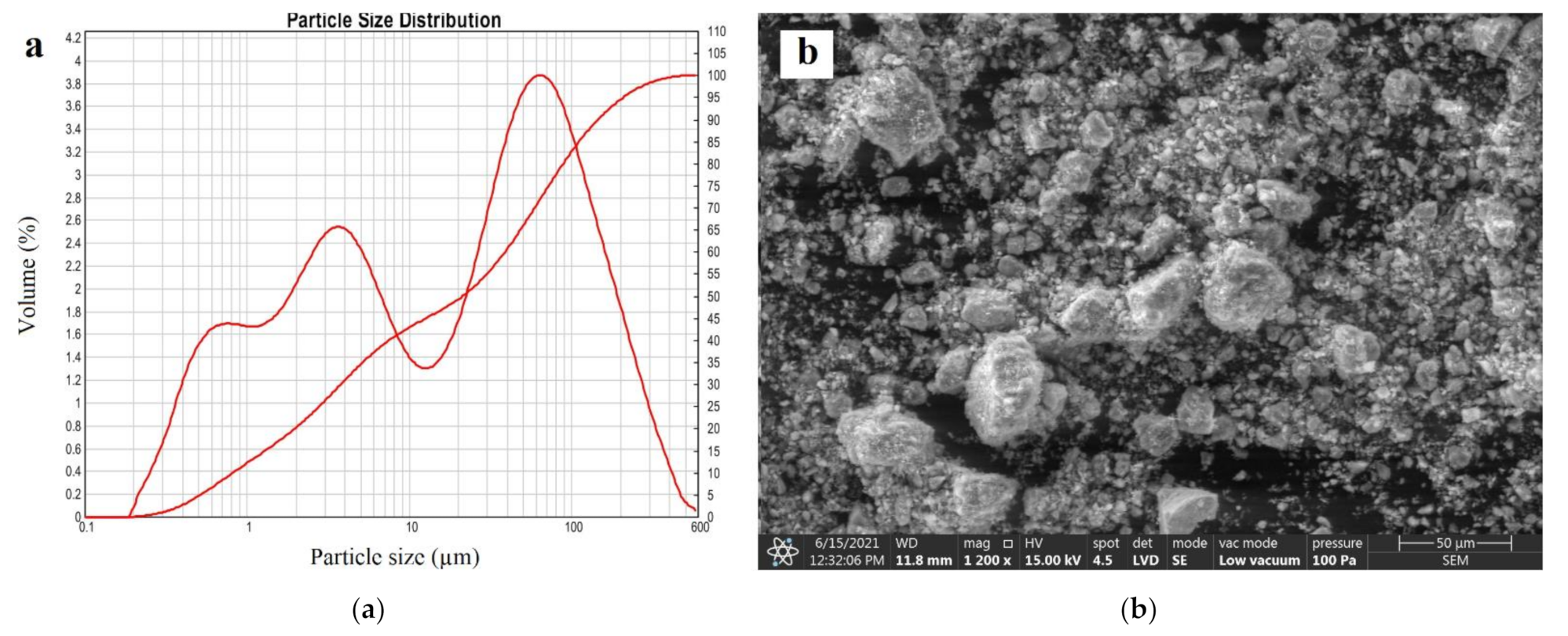

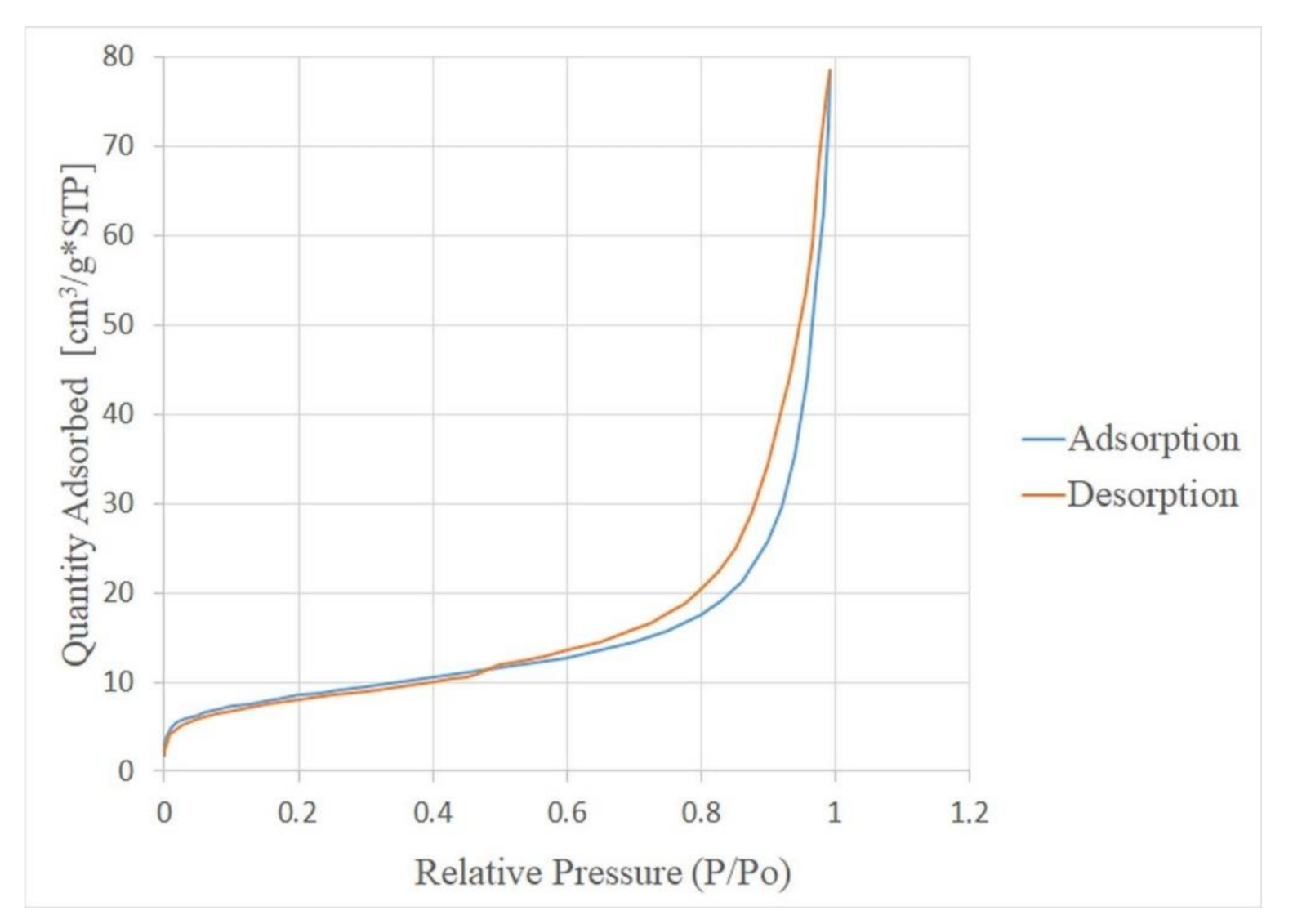
| Deposit | Type of Clinoptilolite-Bearing Rock | Clinoptilolite Content (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| Ukraine-investigated sample | Volcanic tuff | ≈70 |
| Slovakia-investigated sample | Volcanic tuff | ≈85 |
| Slovakia [52] | Volcanic tuff | 70 to 85 |
| Ukraine [53] | Volcanic tuff | ≈75 |
| The U.S. Nevada [16] | Volcanic tuff | 97 |
| Cuba [54] | Volcanic tuff | 65 |
| Turkey [55] | Volcanic tuff | 79 |
| Yemen [45] | Volcanic tuff | 68 to 72 |
| Serbia [56] | Volcanic tuff | >80 |
| North Sardinia [57] | Volcanic tuff | 63 |
| Deposit | Chemical Composition (wt %) | Si/Al Ratio 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | LOI 1 | ||
| Ukraine-investigated sample | 68.57 | 11.77 | 1.95 | 2.52 | 0.74 | 3.32 | 1.16 | 0.15 | 9.67 | 5.10 |
| Slovakia-investigated sample | 67.15 | 12.39 | 1.43 | 3.36 | 0.56 | 3.63 | 0.95 | 0.17 | 10.27 | 4.90 |
| Ukraine [58] | 65.24 | 12.58 | 1.85 | 3.24 | 0.78 | 2.88 | 0.64 | 0.18 | 12.23 | - 3 |
| Slovakia [52] | 67.16 | 12.30 | 2.30 | 2.91 | 1.10 | 2.28 | 0.66 | 0.17 | 10.90 | - 3 |
| The U.S. Nevada [16] | 66.70 | 11.48 | 0.90 | 1.33 | 0.27 | 3.42 | 1.80 | 0.13 | 13.95 | 5.80 |
| The U.S Texas [59] | 68.07 | 13.59 | 2.43 | 7.97 | 1.12 | 2.69 | 3.30 | - 3 | - 3 | 5.01 |
| The U.S. Idaho [59] | 75.04 | 12.85 | 2.38 | 3.48 | 0.80 | 4.86 | 0.50 | - 3 | - 3 | 5.84 |
| China [60] | 69.14 | 12.82 | - 3 | 3.70 | 0.05 | 1.94 | 1.58 | - 3 | - 3 | 4.58 |
| Cuba [54] | 65.30 | 11.20 | 1.60 | 2.60 | 1.10 | 1.06 | 1.50 | 0.20 | 14.70 | - 3 |
| Cuba (Discover in 2021) [15] | 64.69 | 12.61 | 1.62 | 2.59 | 0.55 | 2.01 | 0.82 | - 3 | 13.16 | 4.62 |
| Turkey [55] | 69.71 | 11.74 | 1.21 | 2.30 | 0.31 | 4.41 | 0.76 | - 3 | 12.80 | - 3 |
| Romania (white tuff) [18] | 70.72 | 10.17 | - 3 | 4.26 | 0.67 | 2.14 | 0.82 | 0.18 | 11.47 | - 3 |
| Yemen [45] | 67.20 | 11.69 | 2.77 | 2.12 | 0.41 | 3.67 | 0.90 | - 3 | 10.23 | - 3 |
| Central Sardinia [17] | 67.27 | 11.66 | 1.97 | 2.82 | 0.97 | 2.91 | 0.93 | 0.39 | 10.90 | - 3 |
| North Sardinia [57] | 63.36 | 12.90 | - 3 | 3.10 | 1.29 | 2.16 | 1.390 | - 3 | 15.71 | 4.17 |
| Clinoptilolite Source Locations | Estimated * Clinoptilolite Structural Decomposition Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| Ukraine-investigated sample | >1000 |
| Slovakia-investigated sample | >1000 |
| The U.S. Nevada [16] | 700 |
| The U.S. Texas [59] | 965 |
| The U.S. Idaho [59] | 965 |
| Cuba [8] | >1000 |
| The U.K. [59] | >920 |
| Turkey [65] | 800 |
| Austria [66] | 720 |
| North Sardinia [57] | 450–500 |
| Italy (Modena) [67] | >1100 |
| Deposit | Molar Si/Al Ratio |
|---|---|
| Ukraine-investigated sample | 4.90 * |
| Slovakia-investigated sample | 4.00 * |
| Slovakia [70] The U.S. Nevada [16] | 5.00 * 5.80–6.40 |
| China [60] | 2.19–5.73 |
| Turkey [69] | 5.25–6.08 |
| Central Sardinia [17] | 4.13–5.42 |
| Serbia [56] | 5.03 * |
| Sample | Textural Properties | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2/g) | VTOT0.99 (cm3/g) | VmicT (cm3/g) | Smic (m2/g) | VmesBJH (cm3/g) | Smes (m2/g) | Vmac (cm3/g) | Ravg (μm) | |
| Ukrainian powder | 12.58 | 0.059 | 0.002 | 3.18 | 0.029 | 9.939 | 0.029 | 0.012 |
| Slovakian powder | 29.91 | 0.122 | 0.003 | 5.68 | 0.064 | 23.815 | 0.055 | 0.011 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pabiś-Mazgaj, E.; Gawenda, T.; Pichniarczyk, P.; Stempkowska, A. Mineral Composition and Structural Characterization of the Clinoptilolite Powders Obtained from Zeolite-Rich Tuffs. Minerals 2021, 11, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11101030
Pabiś-Mazgaj E, Gawenda T, Pichniarczyk P, Stempkowska A. Mineral Composition and Structural Characterization of the Clinoptilolite Powders Obtained from Zeolite-Rich Tuffs. Minerals. 2021; 11(10):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11101030
Chicago/Turabian StylePabiś-Mazgaj, Ewelina, Tomasz Gawenda, Paweł Pichniarczyk, and Agata Stempkowska. 2021. "Mineral Composition and Structural Characterization of the Clinoptilolite Powders Obtained from Zeolite-Rich Tuffs" Minerals 11, no. 10: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11101030
APA StylePabiś-Mazgaj, E., Gawenda, T., Pichniarczyk, P., & Stempkowska, A. (2021). Mineral Composition and Structural Characterization of the Clinoptilolite Powders Obtained from Zeolite-Rich Tuffs. Minerals, 11(10), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11101030








