Abstract
Due to their unique characteristics, Lanthanides series (15 elements) together with scandium and yttrium are used as critical metals in numerous applications such as energy sources, catalysts, hybrid cars, medical technology, and military industry. The significance of rare earth elements has been continuously increasing because the global demand for producing high-tech devices is continuously rising. The recovery of rare earth oxide from concentrate based on eudialyte and steenstrupine was performed using a hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical method. Eudialyte and steenstrupine are a complex Na-Ca-zirconosilicate mineral containing rare earth elements (REEs), Zr, Hf and Nb, thus serving as a potential source of Zr. Because of the presence of silica in eudialyte, the main challenge in its processing is avoiding silica gel formation, which is an unfilterable solid residue. The influence of leaching temperature, time and solid–liquid ratio on leaching efficiency was studied in laboratory conditions. A new research strategy was developed in order to recover rare earth elements using hydrochloric acid, avoiding silica gel formation.
1. Introduction
The unit hydrometallurgical operations (leaching, neutralization, filtration, precipitation, solvent extraction) and pyrometallurgical technique (thermal decomposition, molten salt pyrolysis) were mostly used in China for the treatment of bastnasite, monazite, xenotime and apatite minerals containing rare earth elements under atmospheric pressure [1,2,3,4,5]. Stopic et al. [6] mentioned two strategies for treatment of bastnasite concentrate: (1) direct leaching process and (2) reductive smelting and a subsequent leaching of produced slag. Due to modern higher leachability, silicate minerals such as eudialyte and steenstrupine are the most promising raw materials for Zr, Hf and REE production in comparison to bastnasite. The main reasons for the processing of eudialyte are: (1) high chemical activity of eudialyte, (2) high amounts of Zr, Nb and Hf (enriched with yttrium), (3) very low radioactivity level (most of the radioactivity is concentrated in the loparite, which is not activated during eudialyte leaching and (4) low cost of the concentrate in comparison with other concentrates containing Zr. In comparison to eudialyte, steenstrupine contains radioactive uranium and thorium, which it is necessary to separate in a beneficiation process. The raw material extracted from a Kvanefjeld mineral deposit is treated by Krebs and Furfaro [7] in order to separate uranium and thorium from rare earth elements. First of all, the main aim was the production of an intermediate product based on zinc and uranium. Then, after a hydrometallurgical treatment via leaching, filtration and precipitation, the rare earth carbonate was finally produced, as mentioned by van Wyngaardt [8], Greenland Minerals and Energy (GMEL), looking to simplify refining at Kvanefjeld rare earths project [8]. This aimed to reduce project infrastructure in Greenland, reduce the number of processing steps and equipment sizing, and to best align intermediate product with downstream separation technology. GMEL reported that a testwork had been highly successful in validating the enhanced and simplified leaching method.
The main difficulty during the processing of the eudialyte and steenstripine arises from high silica content, which leads to the gelling of the liquid phase of the process hindering solid–liquid separation. Eudialyte has been mostly used as the raw material of Zr production for a long time, although it is also regarded as a potential tantalum, niobium and REE resource, and studied widely, but mainly in Russia by Lebedev [9,10] using sulphuric acid technology. New technological strategies like decomposition with sulfuric and hydrochloric acid have already been suggested and partly researched in the laboratory and used in industry. Normally, for recovery of Zr, the degree of eudialyte concentrate decomposition cannot be too high: 65–80 wt%. Lebedev concluded that the irregular structure of eudialyte crystal and the presence of niobium and titanium were the reasons that eudialyte concentrate could not be completely decomposed. However, the research contradicted this and pointed out that the appearance of altered eudialyte, due to hydrothermal processes in normal eudialyte and the dense silica layer covers Zr, are the real reasons that eudialyte concentrate can’t be fully opened with sulfuric and hydrochloric acid in any severe treatment conditions, excluding hydrofluoric acid. Furthermore, it is only possible to extract Zr (IV) into solution with manifold excess of an acid under completely rigorous conditions or with the introduction of fluorides ions. Among these methods, sulfuric acid has been studied for Zr recovery because of its advantages like low cost, volatility and corrosion activity and its higher degree of decomposition compared with other acids. Hydrochloric acid treatment is characterized by its small volume flows due to the low molecular mass of HCl and recovery of HCl, but, on the other hand, too high volatility, due to the low molecular mass of hydrochloric acid the volume of solutions, decreases from 1.3 to 1.4 times less than when using sulphuric acid as a leaching agent.
Davris et al. [11] have reported some difficulties in treating with this kind of silicate ore, because of the formation of silica gel that prevents filtration and thus stops the whole experiment process. In his previous study, the dry digestion treatment (called “fuming” process) at 100 °C was successfully used to prevent the formation of silica gel, providing a high leaching efficiency of rare earth elements. In a subsequent leaching process, the rare earth elements were additionally dissolved with water.
Vossenkaul [12] has studied a hydrometallurgical processing of eudialyte-bearing concentrates using hydrochloric acid to recover rare earth elements via low-temperature dry digestion to prevent silica gel formation. Dissolution with high concentrated acid (10−12 mol/L) at room temperature was followed with an exothermic reaction, which was sufficient for the dissolution of eudialyte minerals. Stopic et al. [13,14,15] have studied the optimization of dry digestion of eudialyte concentrate with hydrochloric acid using regression analysis and an artificial neural network. They performed a scale-up of the dry digestion process producing new concentrate based on rare earth carbonate from the Tanbreez eudialyte concentrate containing 31% rare earth elements. Additionally, Ma et al. [15] have developed a new strategy for an extraction of zirconium oxychloride (ZrOCl2) using dry digestion, ion exchange and precipitation method.
Generally, from 2013, several research projects have started in Europe (EREAN, REDMUD; EURARE, SCALE and REMOVAL) in order to study the prevention of silica gel formation and reach a high extraction of rare earth elements from eudialyte, red mud and slags after the smelting of red mud [16,17,18,19,20]. This work belongs to the EURARE project that focuses on producing REE within Europe and reducing the external supply [16]. An extraction of scandium from red mud was studied by Alkan et al. [16,17,18,19,20], confirming that dry digestion was successfully used to prevent a silica gel formation, simultaneously providing a high leaching efficiency of the rare earth elements.
Considering dry digestion process at room temperature, the aim of this work is to study the hydrometallurgical processing of Kvanefjeld concentrate after beneficiation process via flotation. This study was performed using hydrochloric acid in laboratory conditions in order to establish the influence of reaction parameters on the leaching efficiency of the rare earth elements from a steenstrupine concentrate.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
The solid sample was first analysed by X-ray fluorescence (Axios FAST, Malvern Panalytical GmbH, Germany), as shown in Table 1. An additional analysis of rare earth elements was performed by inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis (SPECTRO ARCOS, SPECTRO Analytical Instruments GmbH, Kleve, Germany), as shown in Table 2.

Table 1.
X-ray fluoroscency-analysis of Kvanefjeld concentrate (in weights %).

Table 2.
Inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis of REE in steenstrupine concentrate (in weights %).
According to the presence of eudialyte Na15Ca6Fe3Zr3Si(Si25O73)(O,OH,H2O)3(OH,Cl)2 and steenstrupine Na14Ce6Mn2Fe2(Zr, Th, U)(PO4)7Si12O36)(OH)2 ∙3 H2O in initial material, the amount (in weight %) of the most present oxides in structure are SiO2 (36.4), Na2O (13.2) and Fe2O3 (10.2), respectively. An additional ICP OES analysis detected 14.54% of rare earth elements, as shown in Table 2. The maximal content was for light rare elements: cerium, lanthanum and neodymium (11.8%)
2.2. Methods
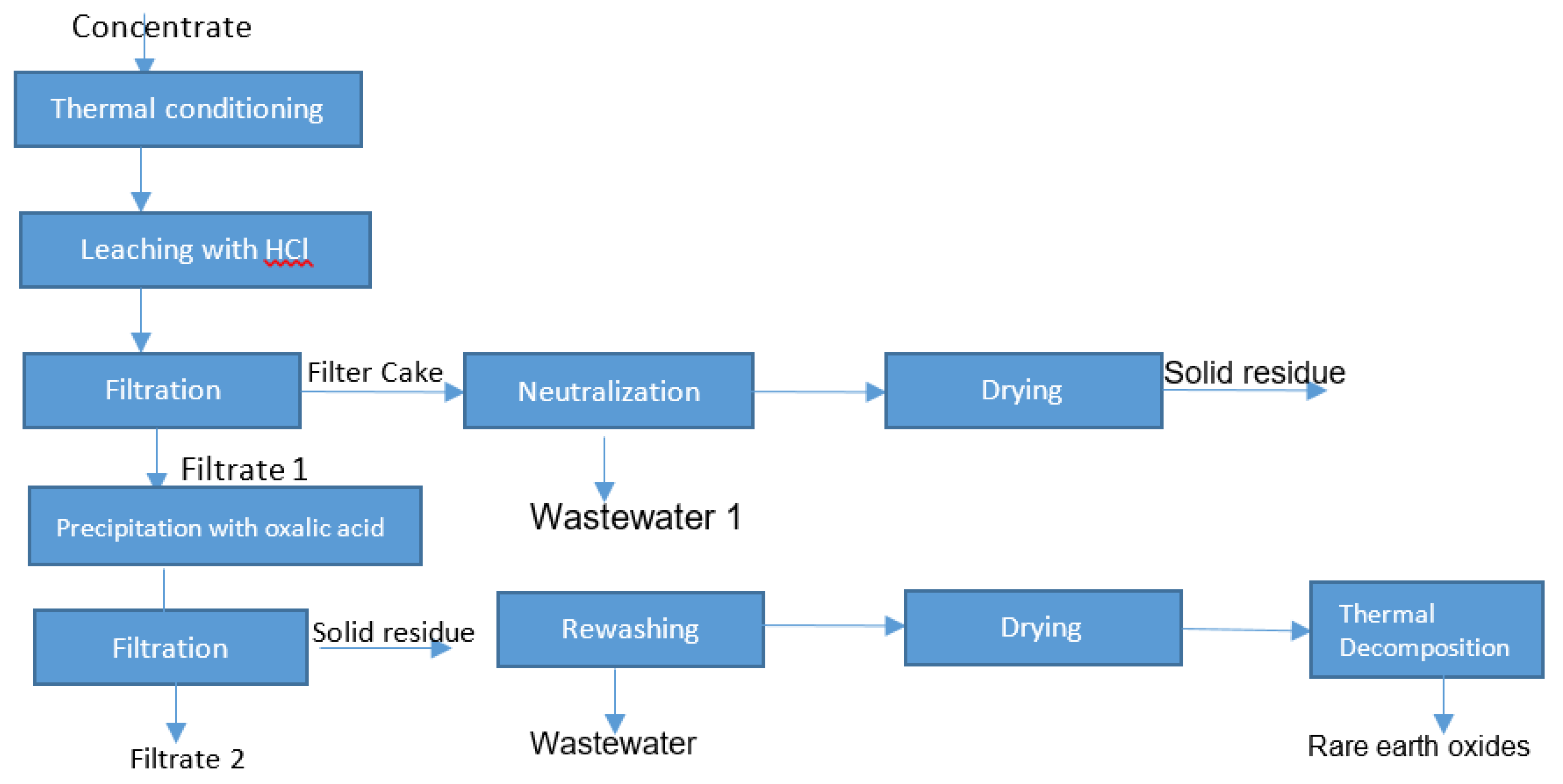
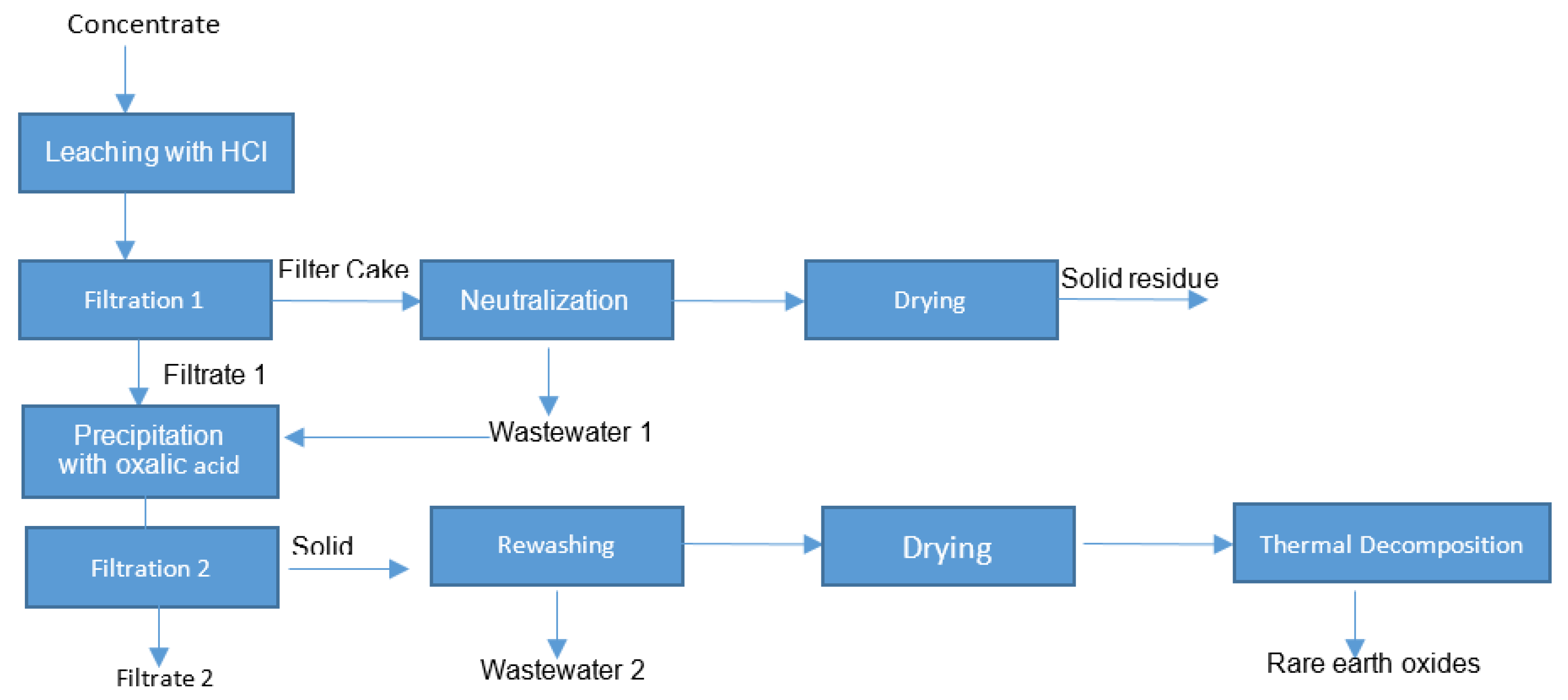
The tested strategy contains a combination of hydrometallurgical operations (leaching under an atmospheric pressure, neutralization, filtration, rewashing and precipitation) and pyrometallurgical steps: thermal conditioning, drying and thermal decomposition in a muffle furnace, as shown in Figure 1. The first aim was to prevent the formation of silica gel, which is possible via the following chemical reactions:
SiO2 + 2 H2O = Si(OH)4
SiCl4 + 4 H2O = Si(OH)4 + 4 HCl
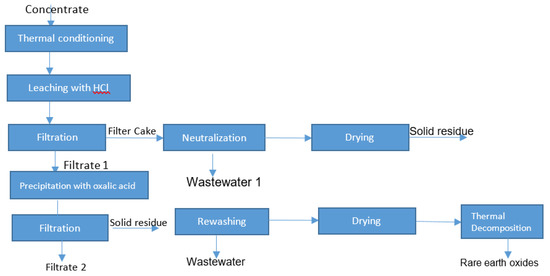
Figure 1.
Research strategy for the preparation of rare earth oxide.
The next step is polymerization of the formed product and formation of silica gel, as shown in Equations (3) and (4).
2 Si(OH)4 = (HO)3Si-O-Si(OH)3 + H2O
(HO)3-Si-O-Si(OH)3 + Si(OH)4 = (HO)3Si-O-Si(OH)2-O-Si(OH)3 + H2O
2.2.1. Thermal Conditioning
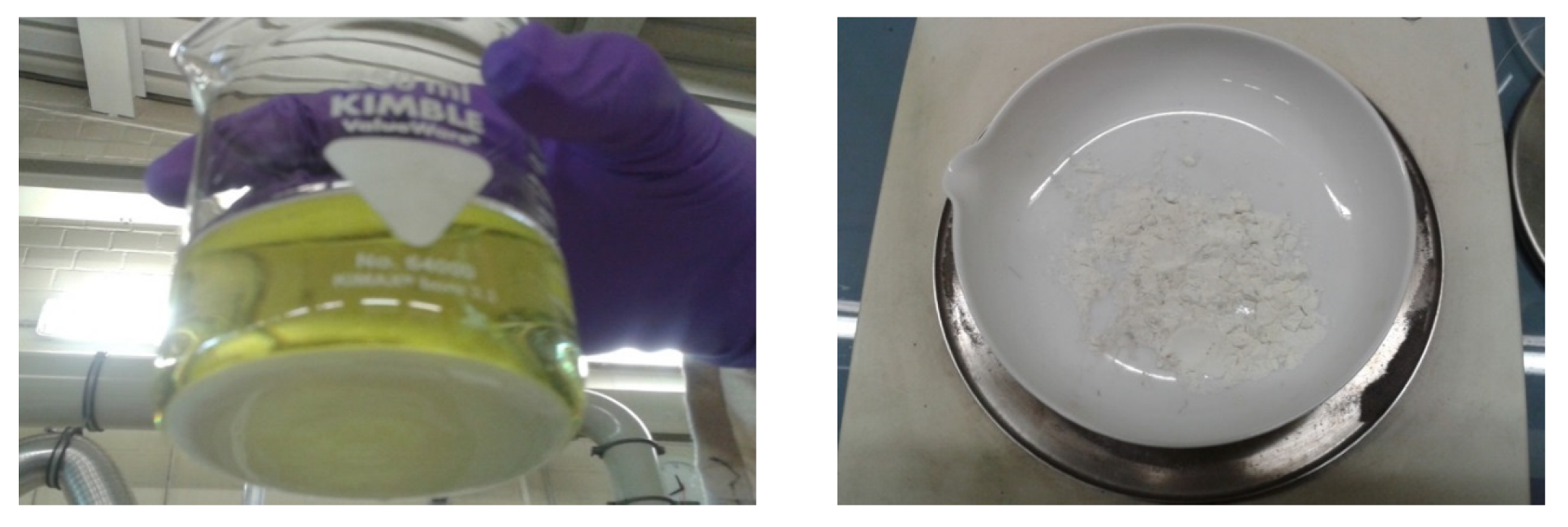
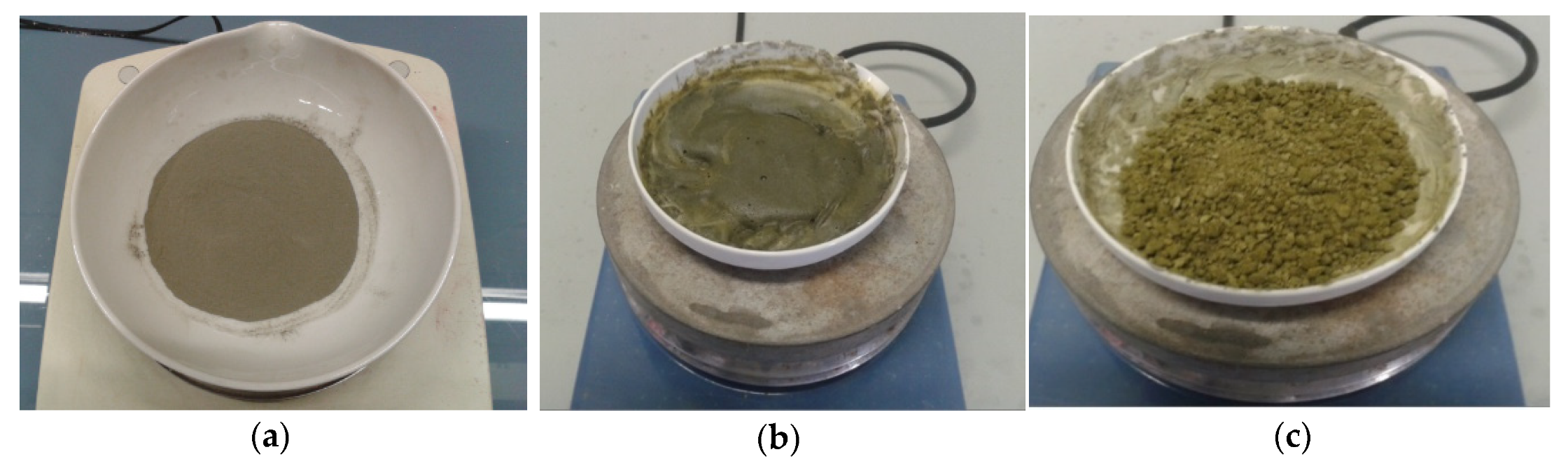
The prevention of silica gel formation was performed at 110 °C with a slow injection of 100 mL 2M hydrochloric acid to 20 g steenstrupine concentrate. the evaporation of added hydrochloric acid took 150 min. The sample used for conditioning and the produced powder iare shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
(a) Inital sample, (b) Conditioning of initial sample, (c) final product.
During thermal conditioning, a silica gel was not formed, which is very important for the subsequent step-leaching.
2.2.2. Leaching with Hydrochloric Acid and Filtration
The formed product was dissolved with 2 M hydrochloric acid in order to transfer the rare earth elements (Ln) to the water solution. The following chemical reactions took place:
LnPO4 + 3 HCl = Ln3+(aq) + 3 Cl−(aq) + 3 H+(aq)+ PO4−(aq)
Ln(SiO3)3 + 6 HCl = 2Ln3+(aq) + 6 Cl−(aq) +3 H2SiO3
(Al, Fe)2O3 + 6 HCl = 2 (Al, Fe)3+(aq)+ 6 Cl−(aq) + 3 H2O
(Na, K)2O + 2 HCl = 2 (Na, K)+(aq)+ 2 Cl−(aq) + H2O
ThO2 + 4 HCl = Th4+ + 4 Cl− + 2 H2O
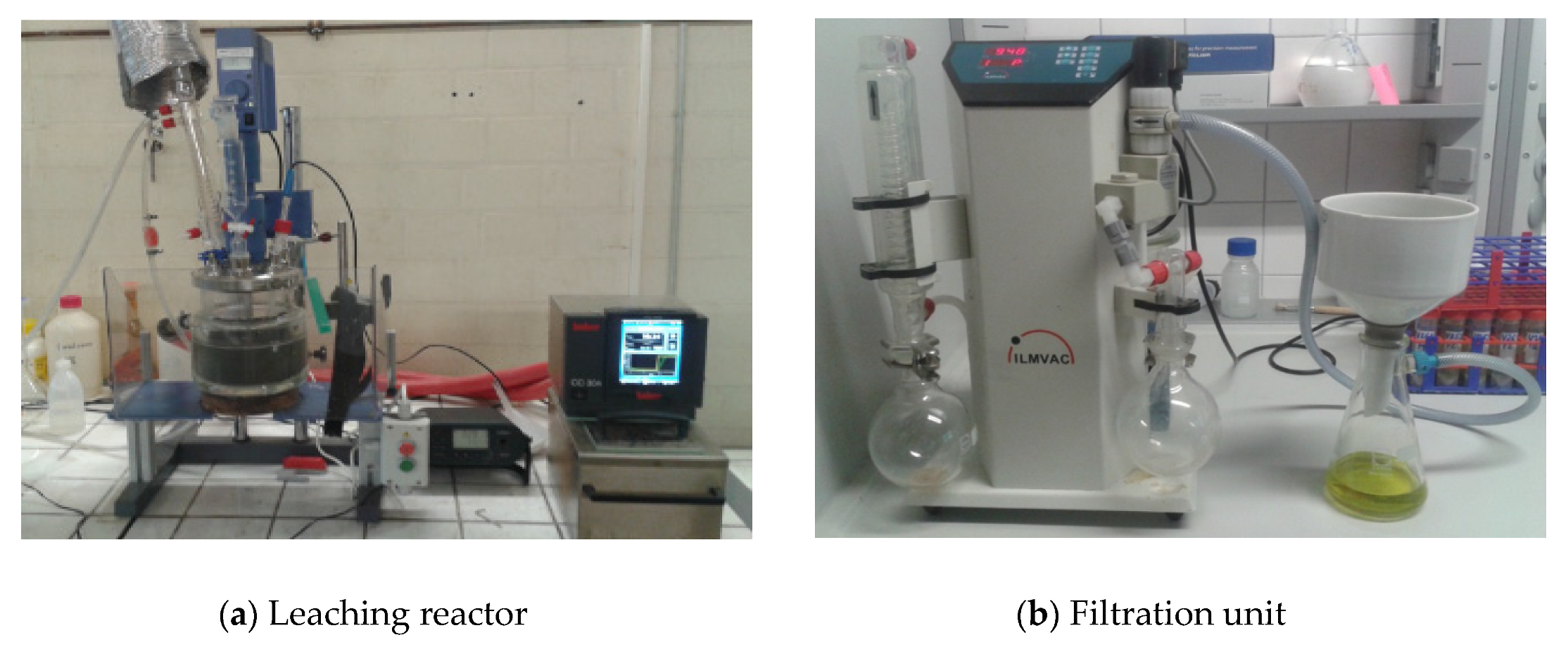
Experiments were performed in a 2 L Reactor (as shown in Figure 3a) in laboratory conditions.

Figure 3.
Leaching reactor and Filtration unit.
A 2 L beaker was placed on top of a heating induction plate and filled with one liter of the previously prepared diluted acid. A temperature measuring device was connected to the induction plate for adequate temperature control. The filtration unit is shown in Figure 3b.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Influence of Temperature on a Leaching Efficiency
The temperature was set between 30 and 90 °C. The stirring equipment was fixed to a clamp above the beaker and connected at a rotation speed of 400 rpm. An anchor stirrer was used instead of magnetic stirrers because of the magnetic nature of the concentrate. The performed experiments are shown in Table 3. The aim was to check the influence of a leaching temperature after the conditioning of steenstrupine concentrate on the leaching efficiency of rare earth elements.

Table 3.
The first trials (duration 2 h, pH = 0.1, 0.73 g HCl/g concentrate).
After reaching the desired temperature, the weighed 20 g of steenstrupine concentrate was added, and the stop watch started. A cover was placed over the beaker to avoid excessive evaporation at temperatures above 70 °C. Samples were taken from the leaching mixture by means of a syringe after 2 h. The taken samples were filtered using previously weighed fine filter papers and the leachate was collected in test tubes. The used filter papers were then placed over a vacuum filtering machine where they were neutralized with distilled water before being introduced in a drying cabin at 105 °C for three hours.
After the 2 h sample was taken, the stirrer and heating plate were disconnected and the beaker content was filtered using the above-mentioned filtering machine. The filtrate was collected in a bottle and the neutralizing of the solid residue and filter was carried out before drying in the same conditions as the rest of the samples. After the drying time had elapsed, the solid residue was weighed and results were noted down.
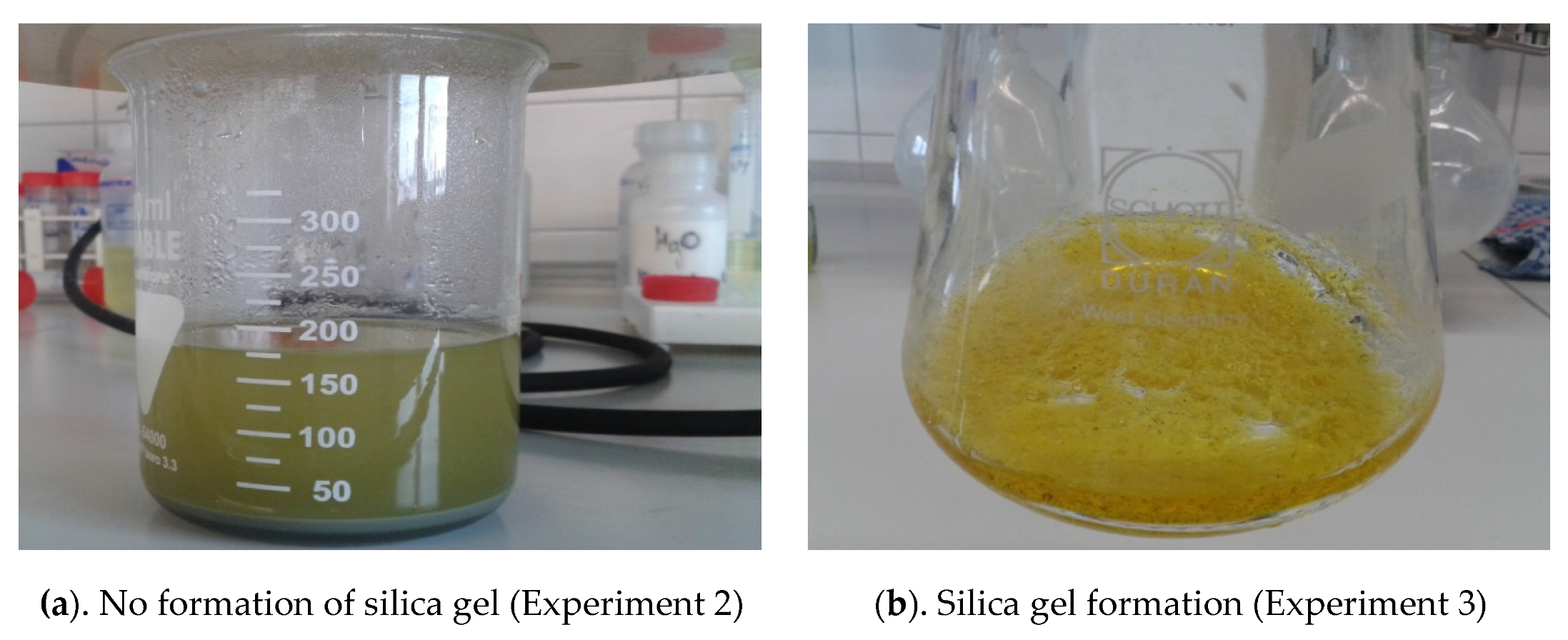
The obtained results confirmed that not only thermal conditioning (Experiment 2), but also an increase temperatures up to 70 °C in a closed reactor (Experiments 4 and 5), prevent the formation of a silica gel, as shown at Figure 4a.

Figure 4.
Experiment 2 and Experiment 3.
The formation of gel was confirmed at room temperature and at 70 °C, where the reactor was opened and an evaporation of the used hydrochloric acid was observed, as shown in Figure 4b. The maximal leaching efficiency was obtained at 90 °C in a duration of 2 h (Experiment 5).
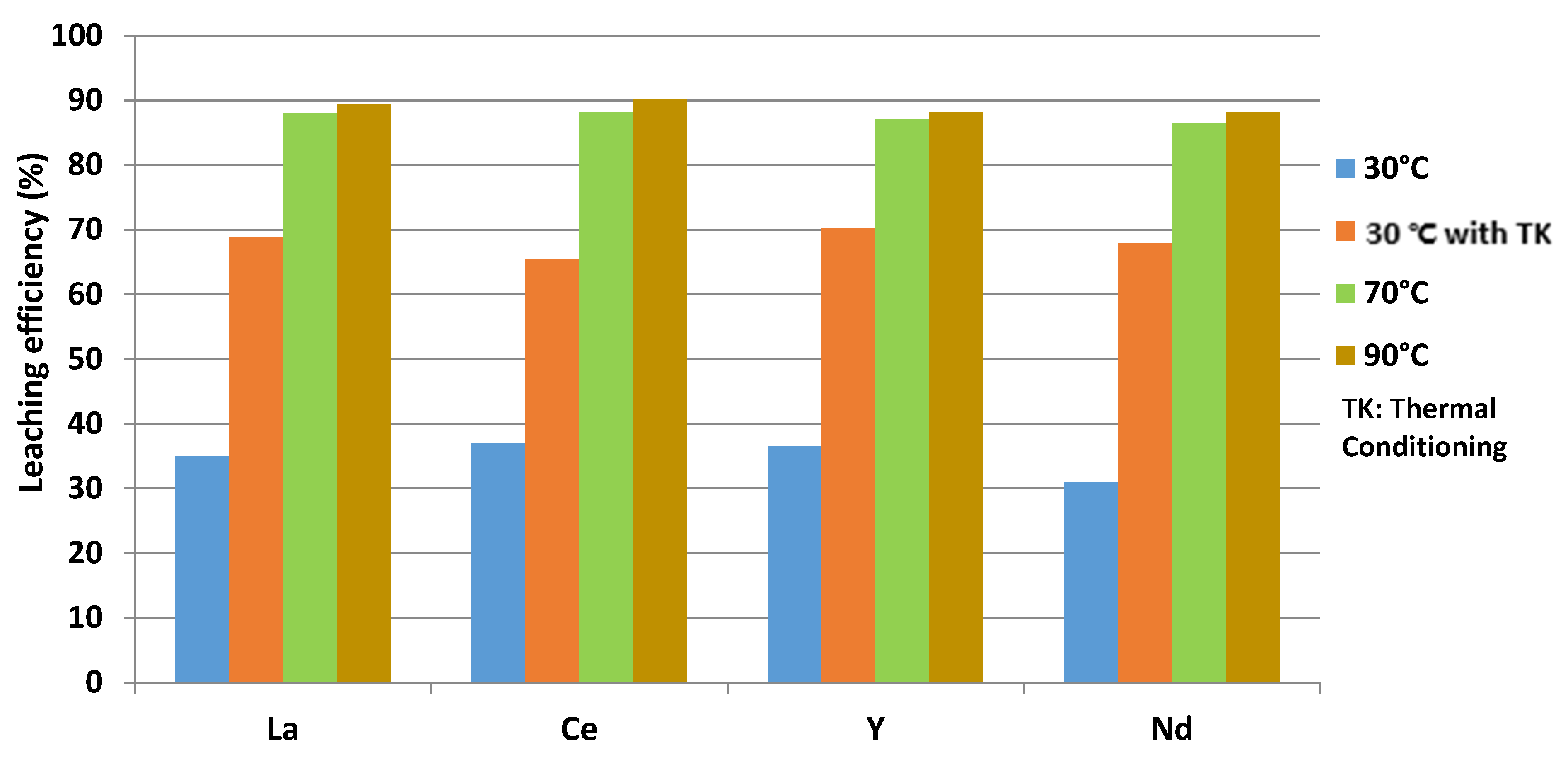
The maximal leaching efficiency is about 90% for La, Ce, Y and Nd for a solid/liquid ratio of 0.08, as shown in Figure 5.
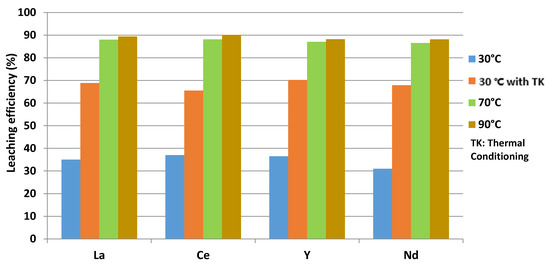
Figure 5.
Leaching efficiency of La, Ce, Y and Nd.
3.2. The Influence of Liquid/Solid Ratio at a Leaching Efficiency
A study of an influence of the solid/liquid ratio on the leaching efficiency of yttrium was performed at 90 °C, as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The influence of solid/liquid ratio on the leaching efficiency of yttrium (90 °C, 2 h).
According to the results in Table 4, an increase in solid/liquid ratio leads to the prevention of silica gel formation, in contrast with our expectation regarding an increase of the content of silica with the increased S/L ratio of a tested concentrate. Generally, in 0.91 g HCl/g concentrate an increase in the solid/liquid ration does not show any influence on the leaching efficiency. In order to avoid silica gel formation, a solid/liquid ratio of 20 g/250 mL (0.91 g HCl/g concentrate) was chosen as an optimal value.
3.3. The Influence of Leaching Time on a Leaching Efficiency
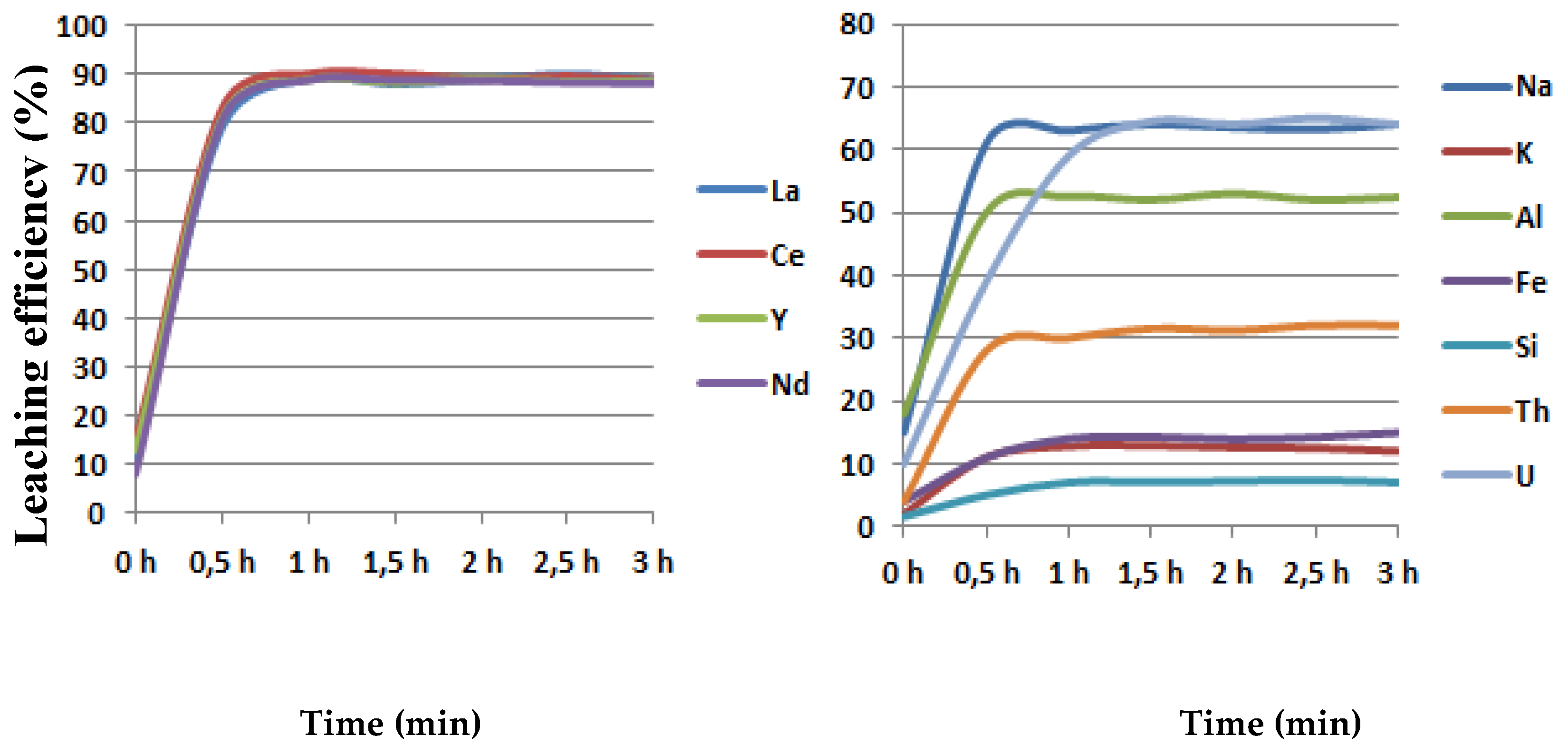
In order to investigate the influence of leaching time on the leaching efficiency, the trials were performed under optimal conditions: 90 °C, 2 h, 400 rpm, solid/liquid ratio 20 g/250 mL (0.91 g HCl/g concentrate) in maximal duration to 300 min. The obtained results have confirmed that, after 30 min, there is no influence on the leaching efficiency of rare earth elements (La, Ce, Y, Nd) and impurities such as Fe, Al. K, N, Th, U.
The maximal leaching for all rare earth elements amounted to 90% in 30 min. Minimal leaching efficiency (in %) was, for silicon, 6, and for potassium and iron, 6, 12, and 15, respectively. The dissolution of thorium and uranium amounted to 30% and 62%, respectively. The maximal leaching of impurities was, for sodium and aluminium, 62% and 52%, respectively, as shown in Figure 6.
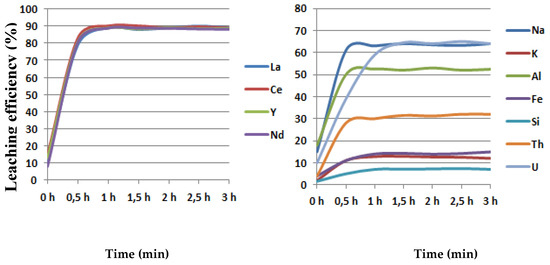
Figure 6.
The influence of leaching time on the leaching efficiency.
3.4. Solid/Liquid Separation
After experiment No. 6 under optimal parameters (90 °C, 2 h, 0.91 g HCl/g concentrate), a filtration was performed. The obtained results are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Metal distribution in filtrate, wastewater from filter cake and solid residue.
The obtained results have confirmed the loss of rare earth elements in wastewater. Due to this fact, the research strategy was optimized, as shown in Figure 7.
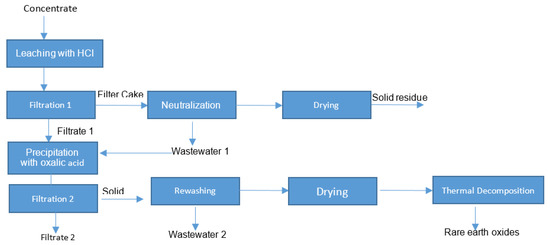
Figure 7.
The optimized strategy for the leaching (without thermal conditioning).
After using the optimized strategy for the treatment of steenstrupine concentrate (without thermal conditioning), the leaching efficiency was increased to 96%, which is a sufficient result (Table 6).

Table 6.
The rare earth elements distribution in filtrate, wastewater 2 and solid residue (Experiment. 6).
3.5. Precipitation with Oxalic Acid
The precipitation process was performed using 1M H2C2O4 ∙2 H2O (Oxalic acid, VWR, Germany), as shown in Equation (10).
2 Ln3+(aq) + 3 H2C2O4 + n H2O = Ln2(C2O4)3 · n H2O↓ + 6 H+(aq)
The obtained results are shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8.
The obtained powder after precipitation with oxalic acid, filtration and washing.
Using the relationship between the element concentration in water solution (before and after precipitation), the precipitation efficiency was calculated and shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Precipitation efficiency (%).
As shown in Table 7, the maximal precipitation efficiency was obtained for rare earth elements, but also for thorium (95.59), which shows that a separation process must be included in this strategy.
3.6. Thermal Decomposition of Rare Earth Oxalate
The final step in research strategy is thermal decomposition of rare earth oxalate at 900 °C for 2 h in a muffle furnace. The expected reactions are presented via Equations (11)–(16):
Ln2(C2O4)3 · n H2O = Ln2(C2O4)3 + n H2O↑
Ln2(C2O4)3 = Ln2(C2O4)(CO3)2 + 2 CO↑
Ln2(C2O4)(CO3)2 = Ln2(CO3)3 + CO↑
Ln2(CO3)3= Ln2O(CO3)2 + CO2↑
Ln2O(CO3)2 = Ln2O2CO3 + CO2↑
Ln2O2CO3 = Ln2O3 + CO2↑
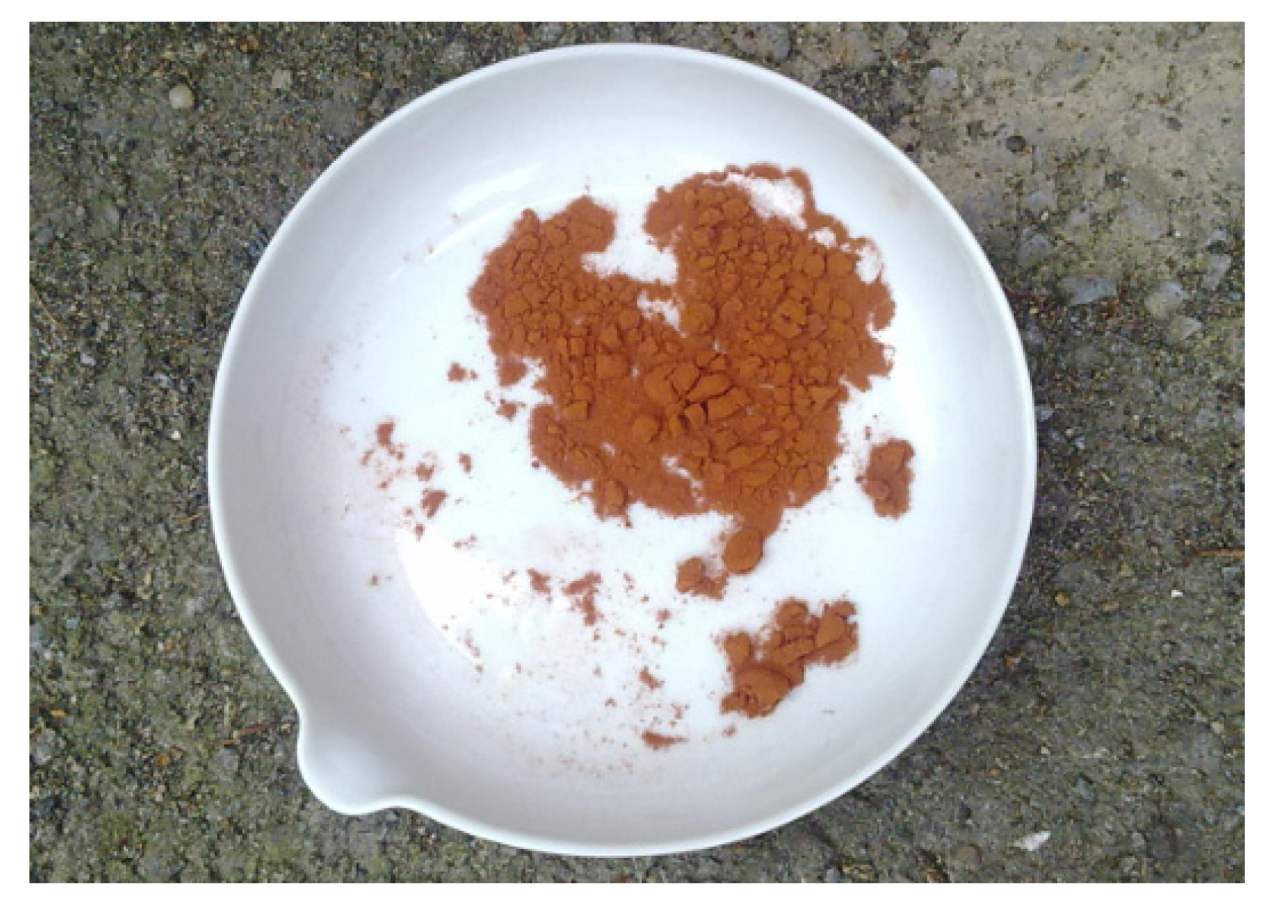
The obtained product based on rare earth elements is shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9.
The obtained powder based on rare earth oxide.
The chemical composition of the obtained powder is shown in Table 8.

Table 8.
ICP-OES analysis of the obtained product.
4. Conclusions
The valorization of rare earth elements from a steenstrupine concentrate via combined hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical process was successfully performed using an optimized strategy with a rewashing process enabling maximal efficiency for rare earth elements (Ce, La, Nd, Y) approximately 96%. This study has revealed that this treatment is possible without thermal conditioning of initial sample. The optimal parameter for leaching are: 90 °C, 2 h, 400 rpm, solid/liquid ratio of 20 g/250 mL and a duration of 30 min. In comparison to dry digestion processes, it takes place within the same time of 30 min, but at an increased temperature of 90 °C and small solid/liquid ratio, which is a disadvantage. The obtained rare earth oxides contains some impurities, which leads to the involvement of solvent extraction as an important step for this work.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, investigation and experimental design (Y.Y.); Methodology and writing of paper (S.S.); supervision and funding acquisation (B.F.). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
“The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme ([FP7/2007-2013]) under grant agreement n 309373. This publication reflects only the author’s view, exempting the Community from any liability”. Project web site: www.eurare.eu. Authors are thankful to Greenland Minerals and Energy, Australia for providing Kvanefjeld steentrupine concentrate samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, G.; Huang, W. Bastnaesite smelting process review. Rare Met. 1997, 21, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Guocai, Z.; Jun, T. Rare earth extraction from bastnaesite with green chemistry method. Chemistry 2000, 12, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Spear, S.F.; Pyle, M.J. Apatite, monazite, and xenotime in metamorphic rocks. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 48, 293–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Xue, X.; Zhang, G. Development Status and Research Progress in Rare Earth Industry in China. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2007, 31, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhengfu, S. Study on the utilization of monazite resource. World Nonferrous Met. 2014, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Stopić, S.; Friedrich, B. Leaching of rare earth elements with sulfuric acid from bastnasite ores. Mil. Tech. Cour. 2018, 66, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furfaro, D.; Krebs, J. Removal of Uranium and Thorium from Kvanefjeld, Rare Earth İntermediate Product; Greenland Minerals and Energy Limited: Perth, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyngaardt, M. GMEL looking to simplify refining at Kvanefjeld rare earths project. In Creamer Medias Mining Weekly; Creamer Media: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, V.N. Sulfuric Acid Technology for Processing of Eudialyte Concentrate. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2003, 76, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.N.; Shchur, T.E.; Maiorov, D.V.; Popova, L.A.; Serkova, R.P. Specific Features of Acid Decomposition of Eudialyte and Certain Rare-Metal Concentrates from Kola Peninsula. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2003, 76, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davris, P.; Stopic, S.; Balomenos, E.; Panias, D.; Paspaliaris, I.; Friedrich, B. Leaching of rare earth elements from Eudialyte concentrate by supressing silicon dissolution. Miner. Eng. 2017, 108, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voßenkaul, D.; Birich, A.; Müller, N.; Stoltz, N.; Friedrich, B. Hydrometallurgical processing of eudialyte bearing concentrates to recover rare earth elements via low-temperature dry digestion to prevent the silica gel formation. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopic, S.; Ma, Y.; Friedrich, B. Leaching of Eudialyte concentrate and REE-Precipitation. In Proceedings of the 9th European Metallurgical Conference EMC 2017, Leipzig, Germany, 25–28 June 2017; Volume 2, pp. 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Stopic, S.; Gronen, L.; Obradovic, S.; Milivojevic, M.; Friedrich, B. Neural Network Modeling for the Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Eudialyte Concentrate by Dry Digestion and Leaching. Metals 2018, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Hydrometallurgical Treatment of a Eudialyte Concentrate for Preparation of Rare Earth Carbonate. Johns. Matthey Technol. Rev. 2019, 63, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Selective Recovery and separation of Zr and Hf from sulfuric acid leach solution using anionic exchange resin. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balomenos, E.; Davris, P.; Deady, E.; Yang, J.; Panias, D.; Friedrich, B.; Binnemans, K.; Seisenbaeva, G.; Dittrich, C.; Kalvig, P.; et al. The EURARE Project: Development of a Sustainable Exploitation Scheme for Europe’s Rare Earth Ore Deposits. Johns. Matthey Technol. Rev. 2017, 61, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, G.; Diaz, F.; Gronen, L.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. A mineralogical assessment on bauxite residue (red mud) leaching for titanium recovery. Metals 2017, 7, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.; Peters, E.; Forsberg, K.; Dittrich, C.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Scandium Recovery from an Ammonium Fluoride Strip Liquor by Anti-Solvent Crystallization. Metals 2018, 8, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, G.; Yagmurlu, B.; Friedrich, B.; Ditrich, C.; Gronen, L.; Stopic, S.; Ma, Y. Selective Silica gel Scandium Extraction from, Iron–depleted Red Mud Slags by Dry Digestion. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).