Intravenous Immune Globulin Uses in the Fetus and Neonate: A Review
Abstract
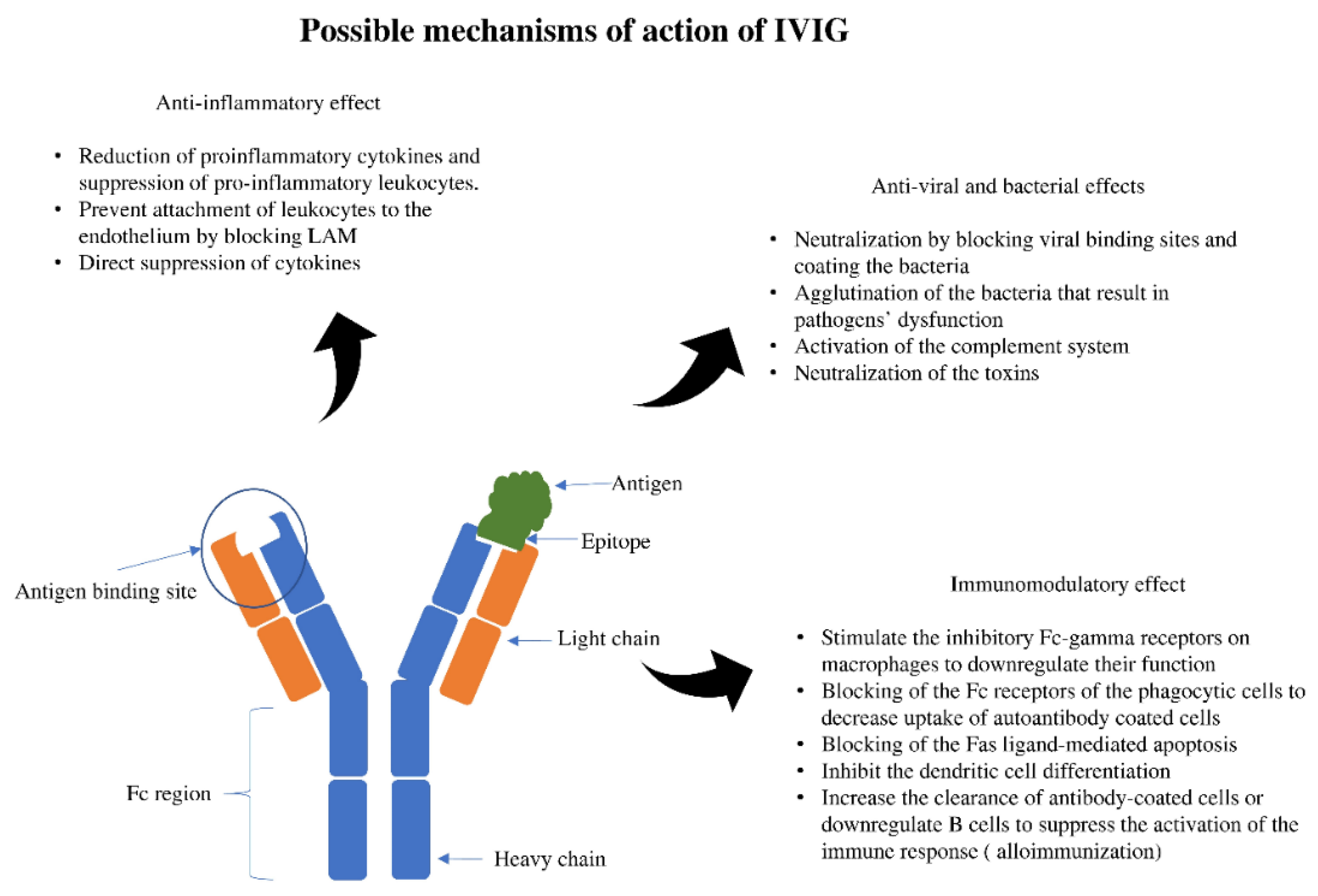
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Use in Fetuses and Neonates
2.1. Alloimmune Hemolytic Disease in Neonates
2.2. Neonatal and Fetal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia
| Clinical Indication | Suggested IVIG Dose | Strength of Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Alloimmune hemolytic disease of the newborn | 0.5–1 gm/kg per dose can be repeated if needed [53] | Recommended by AAP |
| Neonatal and fetal alloimmune thrombocytopenia | ||
| Antenatal management | 0.5 gm/kg/week starts at 24 weeks (standard risk) [65] 1 gm/kg/week starts at 12–16 weeks (high risk) [65] | Recommended by ACOG. Risk stratification is based on the previous history of intracranial hemorrhage in affected siblings; no siblings with ICH (standard risk), a sibling with ICH (high risk) |
| Postnatal management | 1 gm/kg [70] | Limited evidence |
| Neonatal thrombocytopenia due to maternal ITP (postnatal management) | 1 gm/kg/dose [72] | The best approach is to give IVIG after the first platelet transfusion if the platelet count is <50 × 109/L |
| Neonatal thrombocytopenia due to maternal autoimmune disease | 1 gm/kg/dose daily for 2 days or 0.5 gm/kg/dose daily for 4 days [73] | Limited evidence |
| Neonatal infections: | ||
| Sepsis treatment | 0.5 gm/kg/dose [74] | Not recommended |
| Sepsis prophylaxis | 0.5–1gm/kg/dose [75] | Limited evidence |
| Enterovirus infection | 750 mg/kg/dose [76] | Limited evidence |
| Parvovirus infection | 1 gm/kg q3 weeks [77,78] | Limited evidence |
| Neonatal COVID-19 | 2 gm/kg [79] | Limited evidence |
| Neonatal hemochromatosis | ||
| Antenatal management | 1 gm/kg/week starts at 14–18 weeks of gestation [80] | Recommended |
| Postnatal management | 1 gm/kg [81] | Recommended. Given immediately after double volume exchange transfusion |
| Primary immunodeficiency | Varies between studies to achieve Ig level of 800–1000 mg/dl [82] | Limited evidence |
| Neonatal Kawasaki | 2 gm/kg [83] | In addition to high-dose aspirin. Evidence derived from the pediatric population |
2.3. Neonatal Infections
2.3.1. Neonatal Sepsis Treatment and Prophylaxis
2.3.2. Neonatal Enterovirus Infection
2.3.3. Neonatal Parvovirus Infection
2.3.4. Neonatal Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
2.3.5. Neonatal Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV)
2.4. Neonatal Hemochromatosis
2.5. Primary Immunodeficiency
2.6. Kawasaki Disease
2.7. Neonatal Lupus
3. Safety of IVIG Use in Neonates
3.1. Necrotizing Enterocolitis
3.2. Thrombosis
3.3. Anaphylaxis
3.4. Apnea and Cardiac Arrhythmia
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, P.H.; White, K.M. Impact of immunoglobulin therapy in pediatric disease: A review of immune mechanisms. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 51, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahona Afonso, A.F.; João, C.M.P. The production processes and biological effects of intravenous immunoglobulin. Biomolecules 2016, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaigne, B.; Mouthon, L. Mechanisms of action of intravenous immunoglobulin. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2017, 56, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.R.; Padlan, E.A.; Sheriff, S. Antibody-antigen complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1990, 59, 439–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplyakov, A.; Obmolova, G.; Malia, T.J.; Luo, J.; Muzammil, S.; Sweet, R.; Almagro, J.C.; Gilliland, G.L. Structural diversity in a human antibody germline library. MAbs Taylor Fr. 2016, 8, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- João, C.; Negi, V.S.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Bayry, J.; Kaveri, S.V. Passive serum therapy to immunomodulation by IVIG: A fascinating journey of antibodies. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1957–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ranieri, D. Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Its Clinical Applications. Pediatr. Ann. 2017, 46, e6–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Chaudhary, S. Intravenous immunoglobulin in pediatrics: A review. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2014, 70, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro, M.; Negre, S.; Golombek, S.; Matoses, M.L.; Vento, M. Intravenous immune globulin: Clinical applications in the newborn. NeoReviews 2010, 11, e370–e378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.C.; Jain, S.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Kim, K.K.; Burns, J.C.; Anand, V.; Anderson, M.; Ang, J.; Ansusinha, E.; Arditi, M.; et al. The Kawasaki Disease Comparative Effectiveness (KIDCARE) trial: A phase III, randomized trial of second intravenous immunoglobulin versus infliximab for resistant Kawasaki disease. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2019, 79, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mack, C.L.; Spino, C.; Alonso, E.M.; Bezerra, J.A.; Moore, J.; Goodhue, C.; Ng, V.L.; Karpen, S.J.; Venkat, V.; Loomes, K.M.; et al. A phase I/IIa trial of intravenous immunoglobulin following portoenterostomy in biliary atresia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantha, S.S. A centennial review; the 1890 tetanus antitoxin paper of von Behring and Kitasato and the related developments. Keio J. Med. 1991, 40, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flexner, S. Experimental cerebro-spinal meningitis in monkeys. J. Exp. Med. 1907, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flexner, S. Concerning a serum-therapy for experimental infection with diplococcus intracellularis. J. Exp. Med. 1907, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, C.F.; Chu, F.T. Use of placental extract in prevention and modification of measles. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1933, 45, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruton, O.C. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics 1952, 9, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- HYPOGAMMAGLOBULINAEMIA MWPO. Hypogammaglobulinaemia in the United Kingdom; Her Majesty’s Stationery Office: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Eibl, M. Treatment of defects of humoral immunity. Birth Defects Orig. Artic. Ser. 1983, 19, 193. [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson, J.; Alving, B. Overview of potential uses for imunoglobulin preparations, possible etiologies of adverse reactions, and ideal characteristics of intravenous preparations. In Immunoglobulins: Characteristics and Uses of Intravenous Preparations Department of Health and Human Services; Bethesda: Rockville, MD, USA, 1979; pp. 133–229. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Hara, T.; Kondo, T.; Iwao, H.; Honda, S.; Ueda, K. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin therapy for neonatal immune haemolytic jaundice due to blood group incompatibility. Acta Paediatr. 1991, 80, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibl, M.M. History of immunoglobulin replacement. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2008, 28, 737–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, E.E.; Orange, J.S.; Bonilla, F.; Chinen, J.; Chinn, I.K.; Dorsey, M.; El-Gamal, Y.; Harville, T.O.; Hossny, E.; Mazer, B.; et al. Update on the use of immunoglobulin in human disease: A review of evidence. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S1–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shemer, A.; Kivity, S.; Shoenfeld, Y. Clinical indications for intravenous immunoglobulin utilization in a tertiary medical center: A 9-year retrospective study. Transfusion 2018, 58, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, A.; Wilkes, J.; Thorell, E.; Pavia, A.; Sherwin, C.M.; Enioutina, E.Y. Changing trends in IVIG use in pediatric patients: A retrospective review of practices in a network of major USA pediatric hospitals. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, C.; Shih, A.W.; Jamula, E.; Heddle, N.M.; Parvizian, M.; Hillis, C.M. Impact of organizational interventions on reducing inappropriate intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) usage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2018, 57, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbat, E.; Ali, F.; Al-Niaimi, F. Intravenous immunoglobulins in dermatology. Part 2: Clinical indications and outcomes. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 43, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzi, M.; Yazdanmehr, R.; Eliasy, H.; Birjandi, M.; Goudarzi, A.; Almasian, M. The prevalence of the ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn and its complications in an Iranian population. Iran. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 8, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, S.H.; Nafea, L.T.; Abbas, R.S. Prevalence of ABO Incompatibility and its effect on Neonates Hyperbilirubinemia. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2020, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, R.A.; Khan, J.; Andrews, J.; Mayock, D.; Billimoria, Z.; Pagano, M.B. Severe ABO Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn Requiring Exchange Transfusion. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 41, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watchko, J.F. Neonatal indirect hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus. In Avery’s Diseases of the Newborn; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1198.e5–1218.e5. [Google Scholar]
- Alcock, G.S.; Liley, H. Immunoglobulin infusion for isoimmune haemolytic jaundice in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottstein, R.; Cooke, R.W.I. Systematic review of intravenous immunoglobulin in haemolytic disease of the newborn. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003, 88, F6–F10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, B. Neonatal Immune Incompatibilities between Newborn and Mother. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasethu, J.; Luban, N.L. Alloimmune hemolytic disease of the newborn. In Williams Hematology, 7th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 751–765. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, M.B.; de Alarcon, P. Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. NeoReviews 2013, 14, e83–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, P.; McLaughlin, N. Rh Isoimmunization. In Obstetrics in Family Medicine: A Practical Guide; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sperling, J.D.; Dahlke, J.D.; Sutton, D.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Chauhan, S.P. Prevention of RhD alloimmunization: A comparison of four national guidelines. Am. J. Perinatol. 2018, 35, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, Y.; Pavan Kumar, C. Morbidity of ABO haemolytic disease in the newborn. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2012, 32, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, Y.; Sakakibara, H.; Suzuki, S.; Yuza, Y. Anemia Due to ABO Incompatibility in a Neonate. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 810–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, V.; darshini Avulakunta, I. Hemolytic Diseases of the Newborn; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson, J.E.; Delaney, M. Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn: Modern practice and future investigations. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2016, 30, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiers, C.; van Kamp, I.; Oepkes, D.; Lopriore, E. Intrauterine transfusion and non-invasive treatment options for hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn–review on current management and outcome. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkén, J.; Håkansson, S.; Ekéus, C.; Gustafson, P.; Norman, M. Rates of extreme neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus in children and adherence to national guidelines for screening, diagnosis, and treatment in Sweden. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e190858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, V.; Johnson, L. A proposal to prevent severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, S61–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhutani, V.K.; Johnson, L.H.; Maisels, M.J.; Newman, T.B.; Phibbs, C.; Stark, A.R.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M. Kernicterus: Epidemiological strategies for its prevention through systems-based approaches. J. Perinatol. 2004, 24, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, J.-B.L.; Riordan, S.M.; Watchko, J.; Shapiro, S.M. The neurological sequelae of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: Definitions, diagnosis and treatment of the kernicterus spectrum disorders (KSDs). Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2017, 13, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Bhutani, V.K.; Maisels, M.J.; Stark, A.R.; Buonocore, G. Management of jaundice and prevention of severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in infants≥ 35 weeks gestation. Neonatology 2008, 94, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Rahman, K.; Hedayati, M. Hyperbilirubinemia in neonates: Types, causes, clinical examinations, preventive measures and treatments: A narrative review article. Iran. J. Public Health 2016, 45, 558. [Google Scholar]
- Ballow, M. The IgG molecule as a biological immune response modifier: Mechanisms of action of intravenous immune serum globulin in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergaz, Z.; Arad, I. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in neonatal immune hemolytic jaundice. J. Perinat. Med. Off. J. WAPM 1993, 21, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voto, L.S.; Sexer, H.; Ferreiro, G.; Tavosnanska, J.; Orti, J.; Mathet, E.R.; Margulies, M.; Margulies, M. Neonatal administration of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in rhesus hemolytic disease. J. Perinat. Med. Off. J. WAPM 1995, 23, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyer, G.; Siklar, Z.; Dallar, Y.; Yildirmak, Y.; Trias, Ü. Brief report. Multiple dose IVIG treatment in neonatal immune hemolytic jaundice. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2001, 47, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soukka, H.; Halkola, L.; Aho, H.; Rautanen, M.; Kero, P.; Kääpä, P. Methylprednisolone attenuates the pulmonary hypertensive response in porcine meconium aspiration. Pediatr. Res. 1997, 42, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyperbilirubinemia AAoPSo. Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwiers, C.; Scheffer-Rath, M.E.A.; Lopriore, E.; de Haas, M.; Liley, H.G. Immunoglobulin for alloimmune hemolytic disease in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Fekey, S.W.I.; El-Sharkawy, H.M.; Ahmed, A.A.-E.E.; Nassar, M.A.-E.; Elgendy, M.M. Effect of Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Reducing Bilirubin Levels in Hemolytic Disease of Newborn. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2019, 74, 957–968. [Google Scholar]
- Al-lawama, M.; Badran, E.; Ala’Elrimawi, A.B.M.; Alkhatib, H. Intravenous Immunoglobulins as Adjunct Treatment to Phototherapy in Isoimmune Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2019, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, D.; More, K.; Oberoi, S.; Shah, P.S. Intravenous immunoglobulin in isoimmune haemolytic disease of newborn: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014, 99, F325–F331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haas, M.; Thurik, F.F.; Koelewijn, J.M.; van der Schoot, C.E. Haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Vox Sang. 2015, 109, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, B.; Smart, E. Haemolytic diseases. ISBT Sci. Ser. 2008, 3, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits-Wintjens, V.E.H.J.; Walther, F.J.; Rath, M.E.A.; Lindenburg, I.T.M.; Pas, A.B.T.; Kramer, C.M.; Oepkes, D.; Brand, A.; Lopriore, E. Intravenous immunoglobulin in neonates with rhesus hemolytic disease: A randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zdravic, D.; Yougbare, I.; Vadasz, B.; Li, C.; Marshall, A.H.; Chen, P.; Kjeldsen-Kragh, J.; Ni, H. Fetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. In Seminars in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brojer, E.; Husebekk, A.; Dębska, M.; Uhrynowska, M.; Guz, K.; Orzińska, A.; Dębski, R.; Maślanka, K. Fetal/neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: Pathogenesis, diagnostics and prevention. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2016, 64, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kjær, M.; Bertrand, G.; Bakchoul, T.; Massey, E.; Baker, J.M.; Lieberman, L.; Tanael, S.; Greinacher, A.; Murphy, M.F.; Arnold, D.M.; et al. Maternal HPA-1a antibody level and its role in predicting the severity of Fetal/Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia: A systematic review. Vox Sang. 2019, 114, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelhorst, D.; Oepkes, D. Foetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 58, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelhorst, D.; Murphy, M.; Greinacher, A.; Shehata, N.; Bakchoul, T.; Massey, E.; Baker, J.; Lieberman, L.; Tanael, S.; Hume, H.; et al. Antenatal management in fetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: A systematic review. Blood 2017, 129, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bussel, J.B.; Zabusky, M.R.; Berkowitz, R.L.; McFarland, J.G. Fetal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, L.D.; Berkowitz, R.L.; Moise, K.J., Jr.; Bussel, J.B.; McFarland, J.G.; Saade, G.R. Fetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: A management algorithm based on risk stratification. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 118, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, K.Q.; Lehman, K.J.; O’Shaughnessy, R.W. Effects of antepartum therapy for fetal alloimmune thrombocytopenia on maternal lifestyle. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.M.; on behalf of the International Collaboration for Transfusion Medicine Guidelines (ICTMG); Shehata, N.; Bussel, J.; Murphy, M.F.; Greinacher, A.; Bakchoul, T.; Massey, E.; Lieberman, L.; Landry, D.; et al. Postnatal intervention for the treatment of FNAIT: A systematic review. J. Perinatol. Off. J. Calif. Perinat. Assoc. 2019, 39, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelhorst, D.; Oostweegel, M.; Porcelijn, L.; Middelburg, R.A.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Oepkes, D.; Van Der Bom, J.G.; De Haas, M.; Lopriore, E. Treatment and outcomes of fetal/neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: A nationwide cohort study in newly detected cases. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Lugt, N.M.; van Kampen, A.; Walther, F.J.; Brand, A.; Lopriore, E. Outcome and management in neonatal thrombocytopenia due to maternal idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Vox Sang. 2013, 105, 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, I.; Murray, N. Neonatal thrombocytopenia: Causes and management. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003, 88, F359–F364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohlsson, A.; Lacy, J.B. Intravenous immunoglobulin for suspected or proven infection in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, CD001239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, A.; Lacy, J.B. Intravenous immunoglobulin for preventing infection in preterm and/or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD000361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abzug, M.J.; Keyserling, H.L.; Lee, M.L.; Levin, M.J.; Rotbart, H.A. Neonatal enterovirus infection: Virology, serology, and effects of intravenous immune globulin. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 20, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugolotto, S.; Padovani, E.M.; Sanna, A.; Chiaffoni, G.P.; Marradi, P.L.; Borgna-Pignatti, C. Intrauterine anemia due to parvovirus B19: Successful treatment with intravenous immunoglobulins. Haematologica 1999, 84, 668–669. [Google Scholar]
- Manchanda, A.; Datta, V.; Jhunjhunwala, K.; Saili, A.; Kumar, A.; Agarwal, N. Parvovirus B19 nonimmune hydrops in a neonate. Indian J. Pediatr. 2007, 74, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, Z.S.; Zhang, F.R.; Xiong, R.H.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, X.F.; Wang, W.Y.; Ren, J. Frist case of severe childhood novel coronavirus pneumonia in China. Zhonghua er ke za zhi Chin. J. Pediatr. 2020, 58, E005. [Google Scholar]
- Whitington, P.F.; Kelly, S.; Taylor, S.A.; Nóbrega, S.; Schreiber, R.A.; Sokal, E.M.; Hibbard, J.U. Antenatal Treatment with Intravenous Immunoglobulin to Prevent Gestational Alloimmune Liver Disease: Comparative Effectiveness of 14-Week versus 18-Week Initiation. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2018, 43, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, E.B.; Karpen, S.J.; Kelly, S.; Mack, C.L.; Malatack, J.J.; Sokol, R.J.; Whitington, P.F. treatment of neonatal hemochromatosis with exchange transfusion and intravenous immunoglobulin. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartier, P.; Debré, M.; De Blic, J.; De Sauverzac, R.; Sayegh, N.; Jabado, N.; Haddad, E.; Blanche, S.; Casanova, J.-L.; Smith, C.E.; et al. Early and prolonged intravenous immunoglobulin replacement therapy in childhood agammaglobulinemia: A retrospective survey of 31 patients. J. Pediatr. 1999, 134, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement for Health Professionals From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e927–e999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdan, K.; Pilz, G.; Bujdoso, O.; Fraunberger, P.; Neeser, G.; Schmieder, R.E.; Viell, B.; Marget, W.; Seewald, M.; Walger, P.; et al. Score-based immunoglobulin G therapy of patients with sepsis: The SBITS study. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar]
- Alejandria, M.M.; Lansang, M.A.; Dans, L.F.; Mantaring, J.B., III. Intravenous immunoglobulin for treating sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, Cd001090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubron, C.; Berteau, F.; Sparrow, R.L. Intravenous immunoglobulin for adjunctive treatment of severe infections in ICUs. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Y. Evaluation of the Effect of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Dosing on Mortality in Patients with Sepsis: A Network Meta-analysis. Clin. Ther. 2019, 41, 1823.e4–1838.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, B.J.; Gordon, T.; Korones, S.B.; Shankaran, S.; Tyson, J.E.; Bauer, C.R.; Fanaroff, A.A.; Lemons, J.A.; Donovan, E.F.; Oh, W.; et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: A report from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. J. Pediatr. 1996, 129, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, A.; Lacy, J.B. Intravenous immunoglobulin for preventing infection in preterm and/or low-birth-weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, CD000361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baley, J.E. Neonatal sepsis: The potential for immunotherapy. Clin Perinatol. 1988, 15, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Wolkowiez, M.; Benjamin, D.K., Jr.; Capparelli, E. Immunotherapy in neonatal sepsis: Advances in treatment and prophylaxis. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2009, 21, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocklehurst, P.; Farrell, B.; King, A.; Juszczak, E.; Darlow, B.; Haque, K.; Salt, A.; Stenson, B.; Tarnow-Mordi, W. Treatment of neonatal sepsis with intravenous immune globulin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Capasso, L.; Borrrelli, A.C.; Parrella, C.; Lama, S.; Ferrara, T.; Coppola, C.; Catania, M.; Iula, V.D.; Raimondi, F. Are IgM-enriched immunoglobulins an effective adjuvant in septic VLBW infants? Ital. J. Pediatr. 2013, 39, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bancalari Molina, A.; Muñoz Pérez, T.; Martínez Bengoechea, P. Prolonged intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in very low birth weight infants with late onset sepsis. J. Neonatal-Perinat. Med. 2019, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, J.; Seed, P.; Cotten, C. Does IVIg administration yield improved immune function in very premature neonates? J. Perinatol. 2010, 30, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Togawa, Y.; Kouwaki, M.; Koyama, N.; Saitoh, S. Echovirus type 7 virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in a neonate successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: A case report. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.M.; Overall, J.C., Jr. Intravenous immunoglobulin in disseminated neonatal echovirus 11 infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1989, 8, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yen, M.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Cheng-Hsun, C.; Liu, C.-C.; Chiu, N.-C.; Lien, R.; Chang, L.-Y.; Chiu, C.-H.; Tsao, K.-C.; Lin, T.-Y. Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin for neonates with severe enteroviral infections with emphasis on the timing of administration. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 64, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S. History in a Crisis—Lessons for Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1681–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauci, A.S.; Lane, H.C.; Redfield, R.R. Covid-19—Navigating the Uncharted. N. Engl. J. 2020, 382, 1268–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, T.M.; Currie, D.W.; Clark, S.; Pogosjans, S.; Kay, M.; Schwartz, N.G.; Lewis, J.; Baer, A.; Kawakami, V.; Lukoff, M.D.; et al. Epidemiology of Covid-19 in a Long-Term Care Facility in King County, Washington. N. Engl. J. 2020, 382, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubiana, J.; Poirault, C.; Corsia, A.; Bajolle, F.; Fourgeaud, J.; Angoulvant, F.; Debray, A.; Basmaci, R.; Salvador, E.; Biscardi, S.; et al. Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children during the covid-19 pandemic in Paris, France: Prospective observational study. BMJ (Clin. Res.) 2020, 369, m2094. [Google Scholar]
- Viner, R.M.; Whittaker, E. Kawasaki-like disease: Emerging complication during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1741–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Xia, S.; Yuan, W.; Yan, K.; Xiao, F.; Shao, J.; Zhou, W. Neonatal Early-Onset Infection With SARS-CoV-2 in 33 Neonates Born to Mothers With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakoulas, G.; Geriak, M.; Kullar, R.; Greenwood, K.; Habib, M.; Vyas, A.; Ghafourian, M.; Dintyala, V.N.K.; Haddad, F. Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) Significantly Reduces Respiratory Morbidity in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Prospective Randomized Trial. A Prospect. Randomized Trial 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghazadeh, A.; Rezaei, N. Towards treatment planning of COVID-19: Rationale and hypothesis for the use of multiple immunosuppressive agents: Anti-antibodies, immunoglobulins, and corticosteroids. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cao, S.; Dong, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, E.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Fu, S.; Wang, R. Effect of regular intravenous immunoglobulin therapy on prognosis of severe pneumonia in patients with COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rose, D.U.; The Study Group of Neonatal Infectious Diseases of The Italian Society of Neonatology (SIN); Piersigilli, F.; Ronchetti, M.P.; Santisi, A.; Bersani, I.; Dotta, A.; Danhaive, O.; Auriti, C. Novel Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in newborns and infants: What we know so far. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2020, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Fang, C.; Peng, S.; Zhang, L.; Chang, G.; Xia, S.; Zhou, W. Clinical analysis of 10 neonates born to mothers with 2019-nCoV pneumonia. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, P. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Neonates and Children From China: A Review. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, N.; Morioka, I. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Epidemiology, prediction, diagnosis, and emerging treatment options for symptomatic infants. Expert Opin. Orphan Drugs 2020, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revello, M.G.; Lazzarotto, T.; Guerra, B.; Spinillo, A.; Ferrazzi, E.; Kustermann, A.; Guaschino, S.; Vergani, P.; Todros, T.; Frusca, T.; et al. A randomized trial of hyperimmune globulin to prevent congenital cytomegalovirus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanimura, K.; Tairaku, S.; Deguchi, M.; Sonoyama, A.; Morizane, M.; Ebina, Y.; Morioka, I.; Yamada, H. Prophylactic intravenous immunoglobulin injections to mothers with primary cytomegalovirus infection. Kobe J. Med. Sci. 2014, 60, E25–E29. [Google Scholar]
- Kasko, O.; Klose, E.; Rama, G.; Newberry, D.; Jnah, A. Gestational Alloimmune Liver Disease: A Case Study. Neonatal Netw. 2018, 37, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.A.; Kelly, S.; Alonso, E.M.; Whitington, P.F. The Effects of Gestational Alloimmune Liver Disease on Fetal and Infant Morbidity and Mortality. J. Pediatr. 2018, 196, 123.e1–128.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitington, P.F.; Pan, X.; Kelly, S.; Melin-Aldana, H.; Malladi, P. Gestational alloimmune liver disease in cases of fetal death. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, N.; Sasaki, A.; Saito, J.; Mitani, Y.; Yachie, A.; Takahashi, H.; Matsubara, S.; Tenkumo, C.; Tanaka, H.; Hata, T.; et al. The Japanese experience and pharmacokinetics of antenatal maternal high-dose immunoglobulin treatment as a prophylaxis for neonatal hemochromatosis in siblings. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.; Kumar, V.H.S. Liver Failure and Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in a Preterm Neonate: Role of Early IVIG and Exchange Transfusion. AJP Rep. 2018, 8, e95–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roos Mariano da Rocha, C.; Rostirola Guedes, R.; Kieling, C.O.; Rossato Adami, M.; Cerski, C.T.; Gonçalves Vieira, S.M. Neonatal Liver Failure and Congenital Cirrhosis due to Gestational Alloimmune Liver Disease: A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Rep. Pediatr. 2017, 2017, 7432859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeira, P.; Quinello, C.; Silveira-Lessa, A.L.; Zago, C.A.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M. IgG placental transfer in healthy and pathological pregnancies. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 985646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, J.S.; Grossman, W.J.; Navickis, R.J.; Wilkes, M.M. Impact of trough IgG on pneumonia incidence in primary immunodeficiency: A meta-analysis of clinical studies. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 137, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, S.M.; Van Stijn, D.; Burgner, D.; Levin, M.; Kuipers, I.M.; Hutten, B.A.; Kuijpers, T.W. Dissecting Kawasaki disease: A state-of-the-art review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 176, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanley, T.V.; Grimwood, K. Classical Kawasaki disease in a neonate. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2002, 86, F135–F136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, S.; Yamanaka, T.; Tsuchida, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Yanagawa, H. Epidemiology of infant Kawasaki disease with a report of the youngest neonatal case ever reported in Japan. Acta Paediatr. 1996, 85, 995–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.C.; Wiggins, J.W.; Toews, W.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Leung, D.; Wilson, H.; Glodé, M.P. Clinical spectrum of Kawasaki disease in infants younger than 6 months of age. J. Pediatr. 1986, 109, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D.M.; Llanos, C.; Izmirly, P.M.; Brock, B.; Byron, J.; A Copel, J.; Cummiskey, K.; Dooley, M.A.; Foley, J.; Graves, C.; et al. evaluation of fetuses in a study of intravenous immunoglobulin as preventive therapy for congenital heart block: Results of a multicenter, prospective, open-label clinical trial. Arthr. Rheum. 2010, 62, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffatti, A.; Cerutti, A.; Favaro, M.; Del Ross, T.; Calligaro, A.; Hoxha, A.; Marson, P.; Leoni, L.; Milanesi, O. Plasmapheresis, intravenous immunoglobulins and bethametasone-a combined protocol to treat autoimmune congenital heart block: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 706–713. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, R.D.; Hardman, T.; Thornton, J.; Hill, H.R. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation of the safety of intravenous immune globulin administration to preterm neonates. J. Perinatol. Off. J. Calif. Perinat. Assoc. 1989, 9, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, M.; Negre, S.; Matoses, M.L.; Golombek, S.G.; Vento, M. Necrotizing enterocolitis following the use of intravenous immunoglobulin for haemolytic disease of the newborn. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.R.; Barr, A.L.; French, N.P.; Lown, J.A.; Knowles, S. A fatal case of necrotizing enterocolitis in a neonate with polyagglutination of red blood cells. J. Paediatr. Child Health 1993, 29, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, L.; Spradbrow, J.; Keir, A.; Dunn, M.; Lin, Y.; Callum, J. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in neonates at a tertiary academic hospital: A retrospective 11-year study. Transfusion 2016, 56, 2704–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, J.J.; Zhou, X.G.; Zhou, X.Y.; Cheng, R.; Hu, Y.H. The effect of immunoglobulin treatment for hemolysis on the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis—A meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 3902–3910. [Google Scholar]
- Louis, D.; Patil, S.; Saini, S.S.; Kumar, P. A Doppler velocimetry evaluation of intestinal blood flow characteristics in neonates receiving intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: A prospective observational study. Indian J. Pediatr. 2015, 82, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanges, M.; Spadaro, G.; Miniero, M.; Mattera, D.; Sollazzo, R.; D’Armiento, F.P.; De Palma, G.D.; Pecoraro, A.; Borrelli, F.; Genovese, A.; et al. Efficacy of subcutaneous immunoglobulins in primary immunodeficiency with Crohn’s-like phenotype: Report of a case. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 2641–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Wittstock, M.; Benecke, R.; Zettl, U.K. Therapy with intravenous immunoglobulins: Complications and side-effects. Eur. Neurol. 2003, 50, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, A.R.; Saxonhouse, M. Neonatal thrombosis after antenatal treatment of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia with intravenous immunoglobulin. J. Clin. Neonatol. 2019, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufekci, S.; Coban, A.; Bor, M.; Yasa, B.; Nisli, K.; Ince, Z. Cardiac rhythm abnormalities during intravenous immunoglobulin G (IVIG) infusion in two newborn infants: Coincidence or association? Clin. Case Rep. 2015, 3, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kapoor, R.; Basu, S. Apnea as a complication of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in a neonate. Indian J. Pediatr. 2014, 81, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Alloimmune hemolytic disease of the newborn |
| Fetal and Neonatal immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (FNAIT and ITP) |
| Neonatal infections: Sepsis treatment and prophylaxis Enterovirus infection Parvovirus infection COVID-19 related neonatal disease Congenital CMV |
| Neonatal hemochromatosis (GALD) |
| Primary immunodeficiency |
| Neonatal Kawasaki disease |
| Neonatal lupus |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsaleem, M. Intravenous Immune Globulin Uses in the Fetus and Neonate: A Review. Antibodies 2020, 9, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040060
Alsaleem M. Intravenous Immune Globulin Uses in the Fetus and Neonate: A Review. Antibodies. 2020; 9(4):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040060
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsaleem, Mahdi. 2020. "Intravenous Immune Globulin Uses in the Fetus and Neonate: A Review" Antibodies 9, no. 4: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040060
APA StyleAlsaleem, M. (2020). Intravenous Immune Globulin Uses in the Fetus and Neonate: A Review. Antibodies, 9(4), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040060