Developing a 3D Model Culture of an EBV+/CD30+ B-Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Cell Line to Assay Brentuximab Vedotin Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines Culture
2.2. Short Tandem Repeat Analysis
2.3. Cytogenetics Analysis of D430B Cell Line
2.4. Analysis of the D430B Cell Line Phenotype and of the Brentuximab Vedotin and Rituximab Binding via Flow Cytometry
2.5. Evaluation of Brentuximab Vedotin Cytotoxic Activity in Conventional 2D Model by DioC6 and the Alamar Blue Assay
2.6. Preparation of Spheroids
2.7. Brentuximab Vedotin Cytotoxicity in a 3D Culture Model
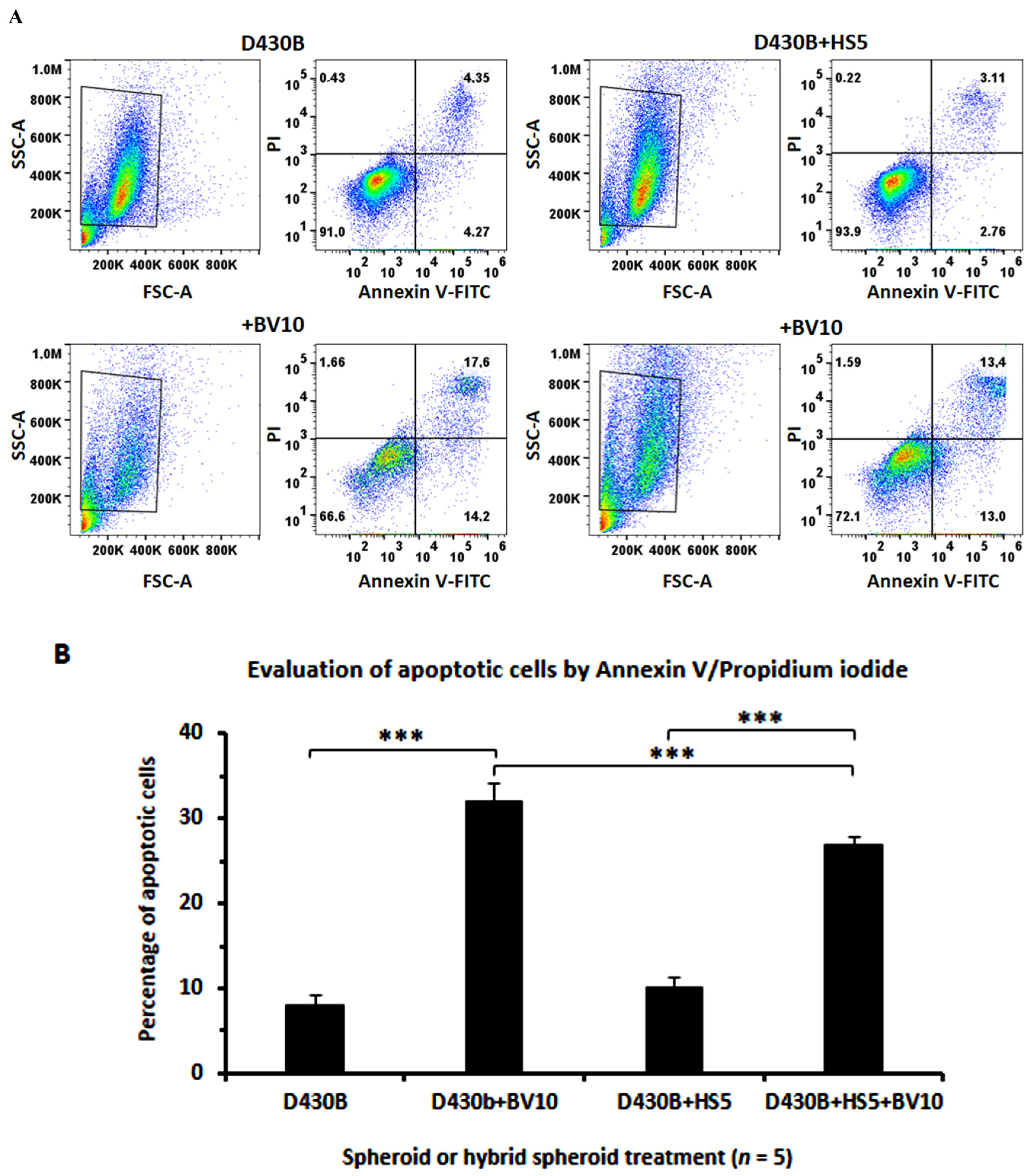
2.8. Evaluation of Apoptosis in Spheroids via AnnexinV/PI Staining
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
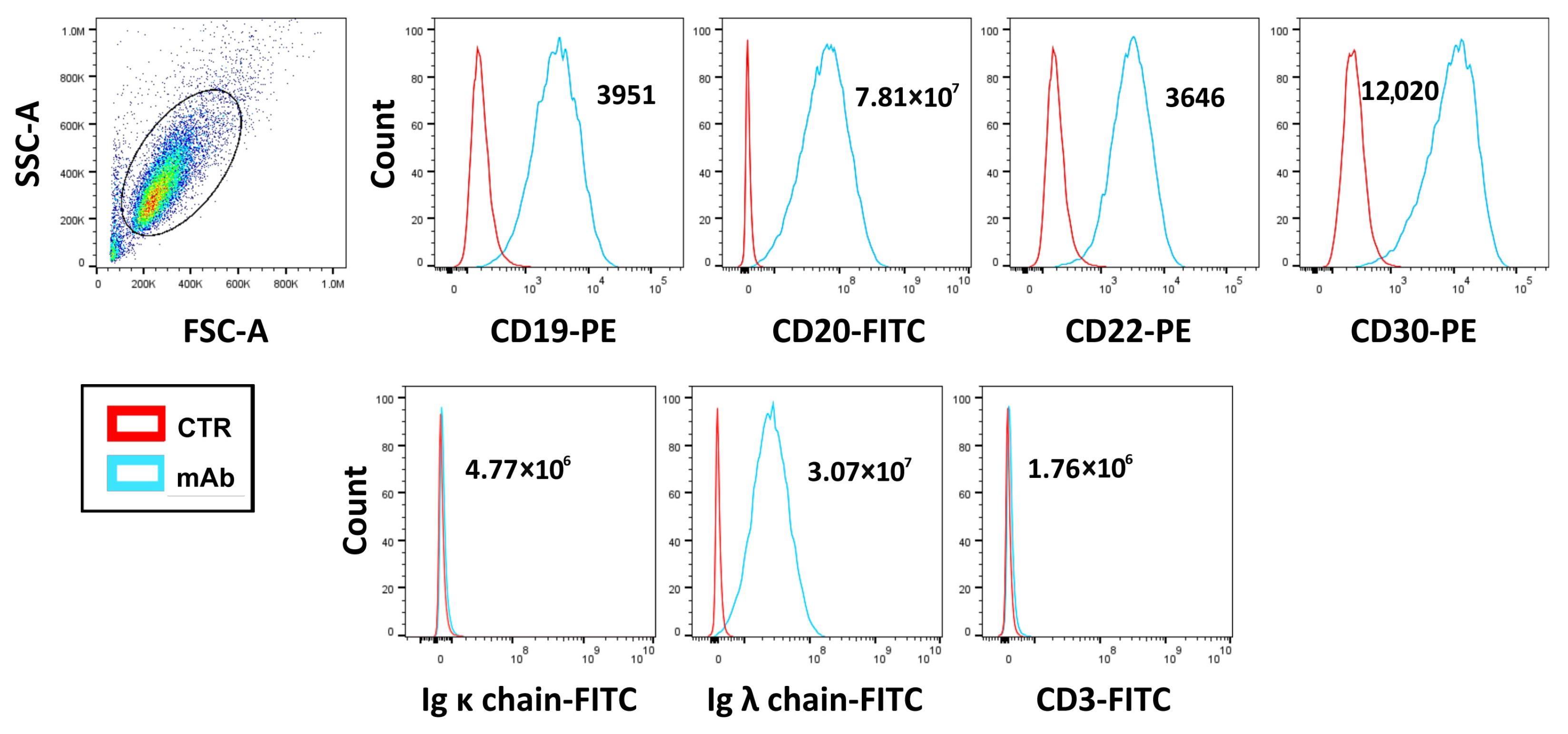
3.1. Determination of CD30 Antigen Expression Level in D430B Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Cells via Flow Cytometry Analysis
3.2. Authenticity of the D430B Cell Line
3.3. Cytogenetics of the D430B Cell Line
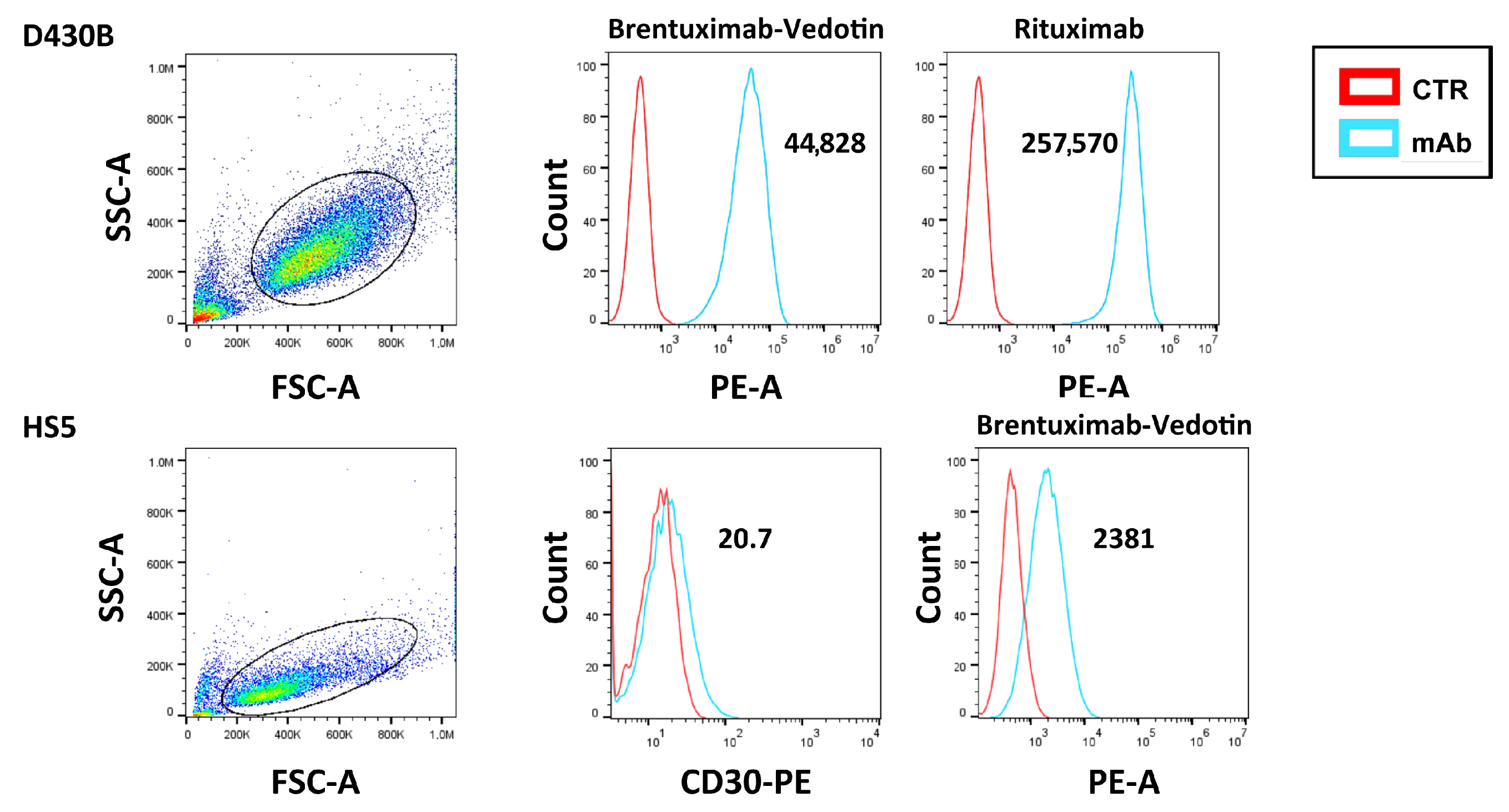
3.4. Cytofluorimetric Analysis of the Binding of Brentuximab Vedotin and Rituximab to D430B Cells
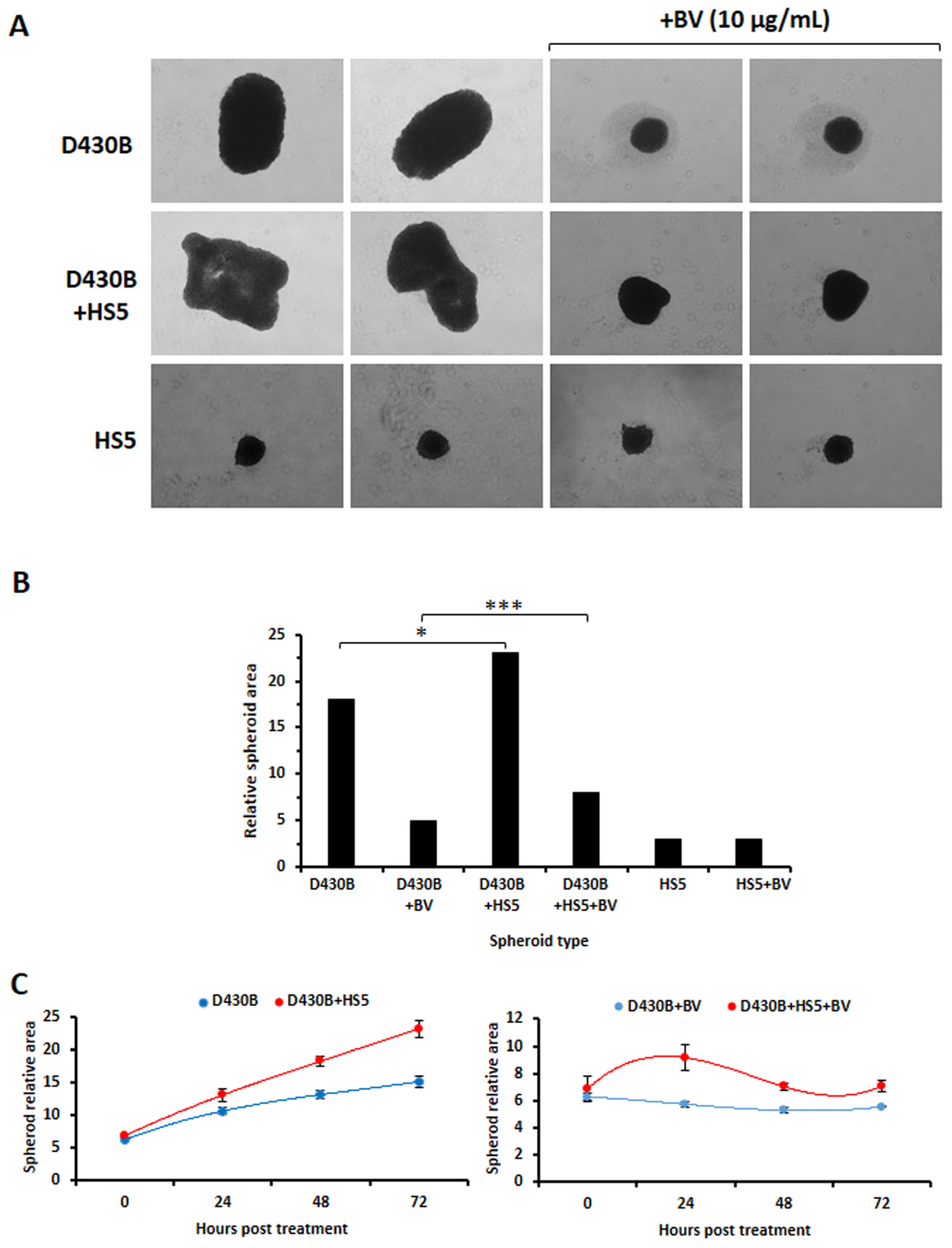
3.5. Establishment of D430B Spheroids
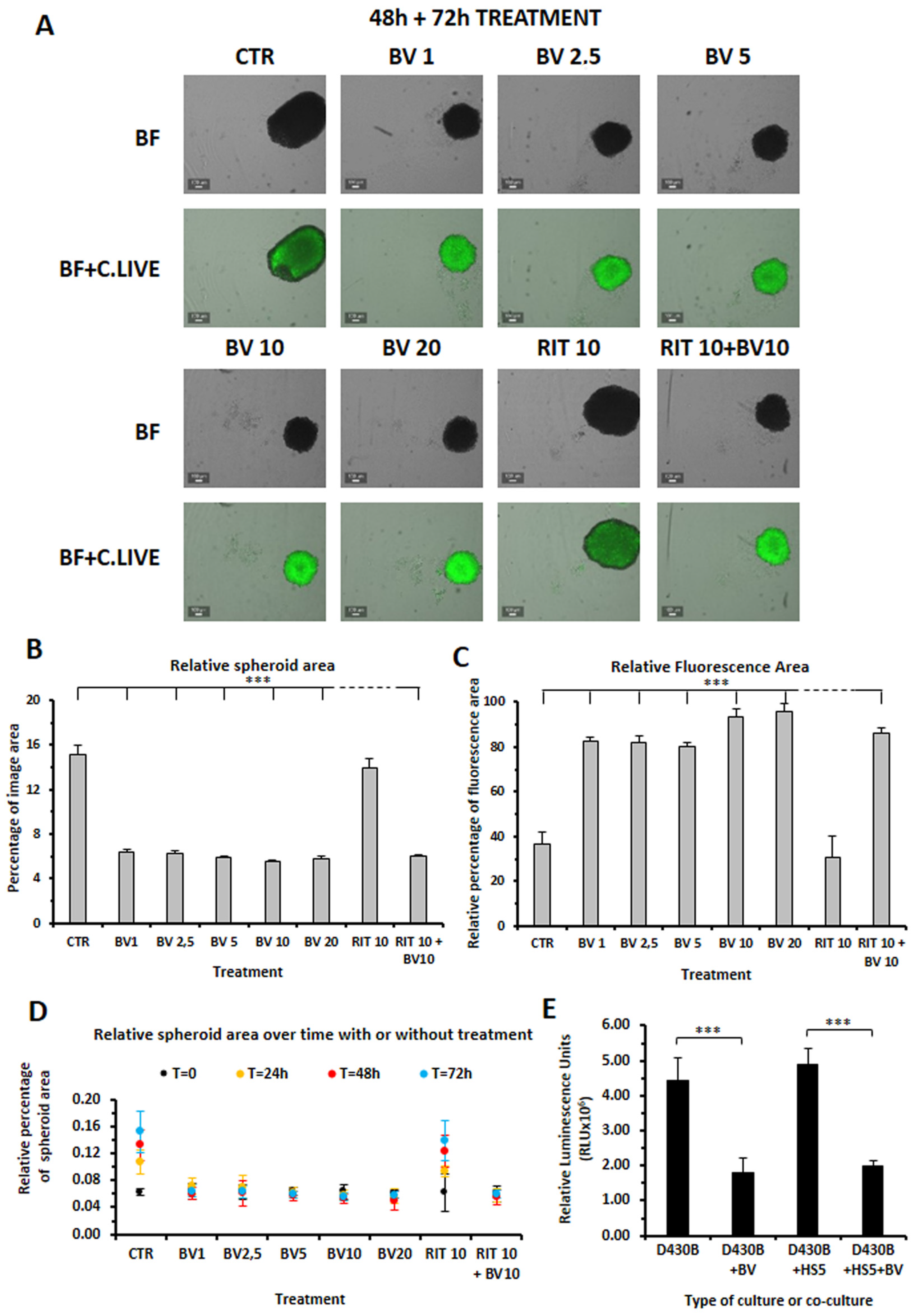
3.6. Brentuximab Vedotin and Rituximab Cytotoxic Effect on D430B Spheroids
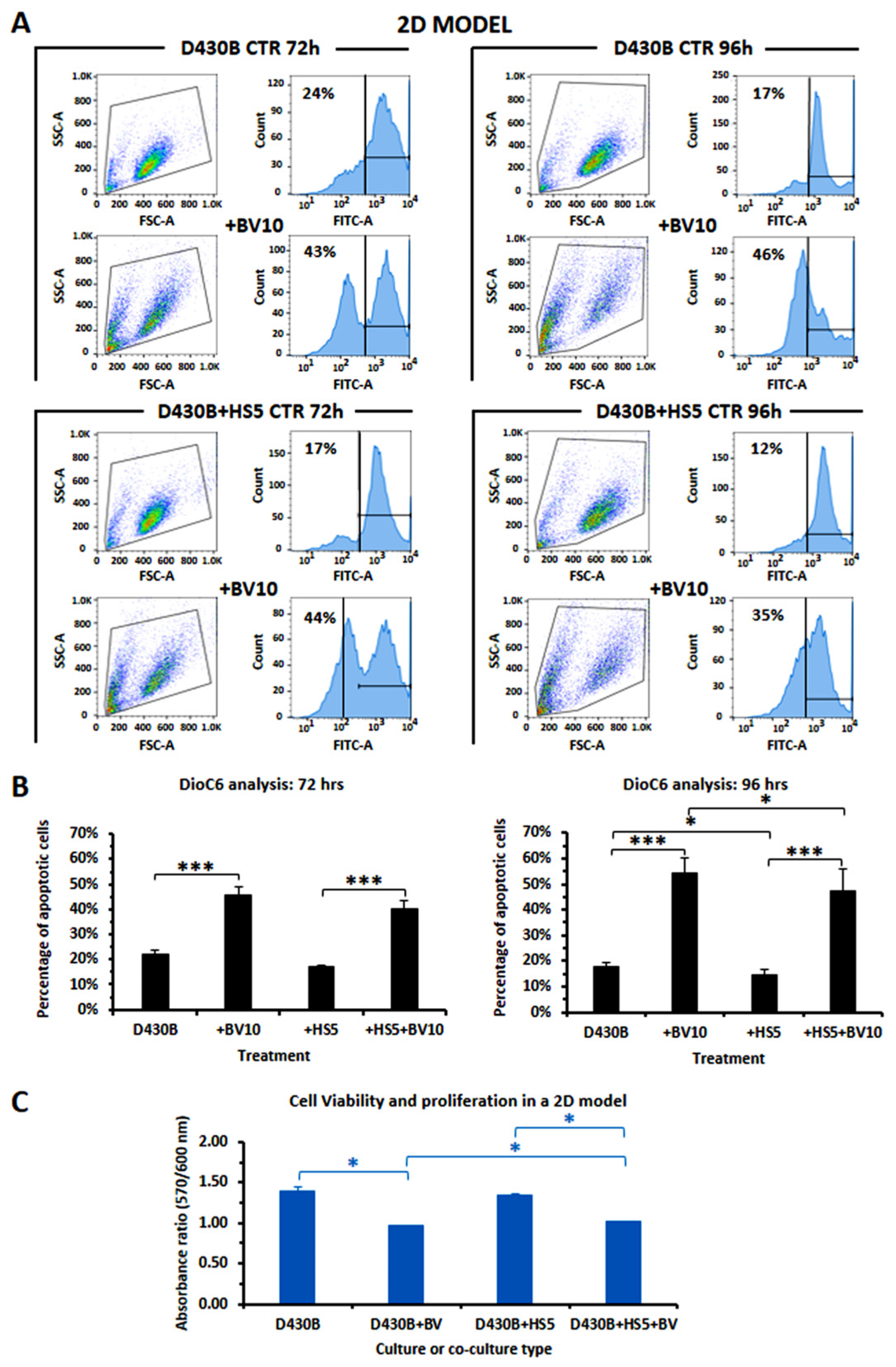
3.7. Determination of Brentuximab Vedotin’s Cytotoxicity on D430B Cells Co-Cultured with Stromal HS5 Cells in 2D and in 3D Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doronina, S.O.; Toki, B.E.; Torgov, M.Y.; Mendelsohn, B.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Chace, D.F.; DeBlanc, R.L.; Gearing, R.P.; Bovee, T.D.; Siegall, C.B.; et al. Development of potent monoclonal antibody auristatin conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, J.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Meyer, D.L.; Mixan, B.J.; Klussman, K.; Chace, D.F.; Rejniak, S.X.; Gordon, K.A.; DeBlanc, R.; Toki, B.E.; et al. cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood 2003, 102, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeley, N.M.; Miyamoto, J.B.; Zhang, X.; Sanderson, R.J.; Benjamin, D.R.; Sievers, E.L.; Senter, P.D.; Alley, S.C. Intracellular activation of SGN-35, a potent anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkop, H.; Latza, U.; Hummel, M.; Eitelbach, F.; Seed, B.; Stein, H. Molecular cloning and expression of a new member of the nerve growth factor receptor family that is characteristic for Hodgkin’s disease. Cell 1992, 68, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, U.; Stein, H.; Gerdes, J.; Lemke, H.; Kirchner, H.; Schaadt, M.; Diehl, V. Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin’s disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature 1982, 299, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Gruss, H.J.; Davis, T.; Anderson, D.; Farrah, T.; Baker, E.; Sutherland, G.R.; Brannan, C.I.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; et al. CD30 antigen, a marker for Hodgkin’s lymphoma, is a receptor whose ligand defines an emerging family of cytokines with homology to TNF. Cell 1993, 73, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, H.M.; Hutchings, M.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Advani, R. Anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate therapy in lymphoma: Current knowledge, remaining controversies, and future perspectives. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarting, R.; Behling, E.; Allen, A.; Arguello-Guerra, V.; Budak-Alpdogan, T. CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders as Potential Candidates for CD30-Targeted Therapies. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2022, 146, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyri, M.; Spano, J.P.; Le Bras, F.; Marcelin, A.G.; Todesco, E. CD30 as a therapeutic target in adult haematological malignancies: Where are we now? Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 201, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, A.; Tazzari, P.L.; Legname, G.; Olivieri, F.; Modena, D.; Conte, R.; Stirpe, F. Anti-CD30 immunotoxins with native and recombinant dianthin 30. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 1995, 40, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietlein, M.; Borner, S.M.; Fischer, T.; Hansen, H.; Schnell, R.; Zimmermanns, B.; Tawadros, S.; Engert, A.; Staak, O.; Pogge von Strandmann, E.; et al. Development of anti-CD30 radioimmunoconstructs (RICs) for treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Studies with cell lines and animal studies. Nuklearmedizin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 49, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Wasik, M.; Teicher, B.A.; Flenghi, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F.; Polito, L.; Falini, B.; Kadin, M.E. Antitumor activity of anti-CD30 immunotoxin (Ber-H2/saporin) in vitro and in severe combined immunodeficiency disease mice xenografted with human CD30+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 1995, 85, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforzini, S.; de Totero, D.; Gaggero, A.; Ippoliti, R.; Glennie, M.J.; Canevari, S.; Stein, H.; Ferrini, S. Targeting of saporin to Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells by anti-CD30 and anti-CD25 bispecific antibodies. Br. J. Haematol. 1998, 102, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazzari, P.L.; Bolognesi, A.; de Totero, D.; Falini, B.; Lemoli, R.M.; Soria, M.R.; Pileri, S.; Gobbi, M.; Stein, H.; Flenghi, L.; et al. Ber-H2 (anti-CD30)-saporin immunotoxin: A new tool for the treatment of Hodgkin’s disease and CD30+ lymphoma: In vitro evaluation. Br. J. Haematol. 1992, 81, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Yi, S.; Sun, Q. Advancements in targeting CD30 for lymphoma therapy: A historical perspective and future directions. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2025, 18, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, G.; Maddocks, K.; Christian, B. CD30 and CD30-Targeted Therapies in Hodgkin Lymphoma and Other B cell Lymphomas. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2016, 11, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Qin, W.; Huo, Y.J.; Li, X.; Shi, Q.; Rasko, J.E.J.; Janin, A.; Zhao, W.L. Advances in targeted therapy for malignant lymphoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Li, X. Challenges of CD30 expression and its impact on targeted treatment responses in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: New perspectives for evaluation and validation. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2025, 272, 156098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazzari, P.L.; de Totero, D.; Bolognesi, A.; Testoni, N.; Pileri, S.; Roncella, S.; Reato, G.; Stein, H.; Gobbi, M.; Stirpe, F. An Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphoblastoid cell line (D430B) that grows in SCID-mice with the morphologic features of a CD30+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and is sensitive to anti-CD30 immunotoxins. Haematologica 1999, 84, 988–995. [Google Scholar]
- Haralambieva, E.; Pulford, K.A.; Lamant, L.; Pileri, S.; Roncador, G.; Gatter, K.C.; Delsol, G.; Mason, D.Y. Anaplastic large-cell lymphomas of B-cell phenotype are anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) negative and belong to the spectrum of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 109, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, H.; Foss, H.D.; Durkop, H.; Marafioti, T.; Delsol, G.; Pulford, K.; Pileri, S.; Falini, B. CD30(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A review of its histopathologic, genetic, and clinical features. Blood 2000, 96, 3681–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killock, D. Adding brentuximab vedotin to lenalidomide and rituximab improves OS in R/R DLBCL. Nat. rev. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 22, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Hahn, U.; Kim, W.S.; Fleury, I.; Laribi, K.; Bergua, J.M.; Bouabdallah, K.; Forward, N.; Bijou, F.; MacDonald, D.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin Combination for Relapsed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Hahn, U.; Kim, W.S.; Fleury, I.; Laribi, K.; Bergua, J.M.; Bouabdallah, K.; Forward, N.; Bijou, F.; MacDonald, D.; et al. Plain language summary of the ECHELON-3 study: Brentuximab vedotin combination treatment in people with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Future Oncol. 2025, 21, 1965–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, A.; Delfino, P.; Gatti, A.; Bonato, A.; Takam Kamga, P.; Bazzoni, R.; Ugel, S.; Mercuri, A.; Caligola, S.; Krampera, M. HS-5 and HS-27A Stromal Cell Lines to Study Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Mediated Support to Cancer Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 584232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, P.; Parodi, F.; Parodi, B.; Casarino, L.; Romano, P.; Buccarelli, M.; Pallini, R.; D’Alessandris, Q.G.; Montori, A.; Pilozzi, E.; et al. Short tandem repeat profiling for the authentication of cancer stem-like cells. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karger Publisher. ISCN 2024—An International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (2024). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2024, 164, 1–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, N.L.; Moore, S.; Hastings, R.J. ISCN 2024: Summary of Revisions and New Nomenclature. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2025, 165, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, P.B.; Jambhekar, N.A.; Kumar, R.; Prabhash, K.; Pramesh, C.S.; Desai, S.B.; Noronha, V.; Karimundackal, G.; Shah, A.; Joshi, A.; et al. A comparative analysis of immunohistochemistry and fluorescent in situ hybridization assay to detect anaplastic lymphoma kinase status in lung adenocarcinoma cases: A search for a testing algorithm. Indian J. Cancer 2017, 54, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Totero, D.; Meazza, R.; Zupo, S.; Cutrona, G.; Matis, S.; Colombo, M.; Balleari, E.; Pierri, I.; Fabbi, M.; Capaia, M.; et al. Interleukin-21 receptor (IL-21R) is up-regulated by CD40 triggering and mediates proapoptotic signals in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 2006, 107, 3708–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foty, R. A simple hanging drop cell culture protocol for generation of 3D spheroids. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2011, 51, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, J.M.; Timmins, N.E.; Brown, C.J.; Fussenegger, M.; Nielsen, L.K. Method for generation of homogeneous multicellular tumor spheroids applicable to a wide variety of cell types. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 83, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, M.; Safari, F.; Kanani, M.H.; Ahvati, H. Principles of Hanging Drop Method (Spheroid Formation) in Cell Culture. Methods Mol. Biol. 2025, 2879, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, R.; Watanabe, T. CD30: Expression and function in health and disease. Semin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoli, R.M.; Tazzari, P.L.; Fortuna, A.; Bolognesi, A.; Gulati, S.C.; Stirpe, F.; Tura, S. Positive selection of hematopoietic CD34+ stem cells provides ‘indirect purging’ of CD34- lymphoid cells and the purging efficiency is increased by anti-CD2 and anti-CD30 immunotoxins. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1994, 13, 465–471. [Google Scholar]
- Natesh, N.R.; Varghese, S. Advances and Challenges in Human 3D Solid Tumor Models. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2419912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutgens, F.; Clevers, H. Human Organoids: Tools for Understanding Biology and Treating Diseases. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; D’Souza, G.G.M. Modeling Tumor Microenvironment Complexity In Vitro: Spheroids as Physiologically Relevant Tumor Models and Strategies for Their Analysis. Cells 2025, 14, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo-Ayala, F.; Dobano-Lopez, C.; Valero, J.G.; Nadeu, F.; Gava, F.; Faria, C.; Norlund, M.; Morin, R.; Bernes-Lasserre, P.; Serrat, N.; et al. A novel patient-derived 3D model recapitulates mantle cell lymphoma lymph node signaling, immune profile and in vivo ibrutinib responses. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, C.; Dobano-Lopez, C.; Perez-Galan, P.; Bezombes, C. Goodbye flat lymphoma biology. FEBS Lett. 2025, 599, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, C.; Gava, F.; Gravelle, P.; Valero, J.G.; Dobano-Lopez, C.; Van Acker, N.; Quelen, C.; Jalowicki, G.; Morin, R.; Rossi, C.; et al. Patient-derived lymphoma spheroids integrating immune tumor microenvironment as preclinical follicular lymphoma models for personalized medicine. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselager, M.V.; van Driel, B.F.; Perelaer, E.; de Rooij, D.; Lashgari, D.; Loos, R.; Kater, A.P.; Moerland, P.D.; Eldering, E. In Vitro 3D Spheroid Culture System Displays Sustained T Cell-dependent CLL Proliferation and Survival. HemaSphere 2023, 7, e938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pece, R.; Tavella, S.; Costa, D.; Varesano, S.; Camodeca, C.; Cuffaro, D.; Nuti, E.; Rossello, A.; Alfano, M.; D’Arrigo, C.; et al. Inhibitors of ADAM10 reduce Hodgkin lymphoma cell growth in 3D microenvironments and enhance brentuximab-vedotin effect. Haematologica 2022, 107, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbrana, F.V.; Pinos, R.; Barbaglio, F.; Ribezzi, D.; Scagnoli, F.; Scarfo, L.; Redwan, I.N.; Martinez, H.; Fare, S.; Ghia, P.; et al. 3D Bioprinting Allows the Establishment of Long-Term 3D Culture Model for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 639572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scielzo, C.; Ghia, P. Modeling the Leukemia Microenviroment In Vitro. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 607608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobano-Lopez, C.; Valero, J.G.; Araujo-Ayala, F.; Nadeu, F.; Gava, F.; Faria, C.; Norlund, M.; Morin, R.; Bernes-Lasserre, P.; Arenas, F.; et al. Patient-derived follicular lymphoma spheroids recapitulate lymph node signaling and immune profile uncovering galectin-9 as a novel immunotherapeutic target. Blood Cancer J. 2024, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxall, R.; Narang, P.; Glaysher, B.; Hub, E.; Teal, E.; Coles, M.C.; Ashton-Key, M.; Beers, S.A.; Cragg, M.S. Developing a 3D B Cell Lymphoma Culture System to Model Antibody Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 605231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, M.; Locatelli, I.; D’Arrigo, C.; Mora, M.; Vozzi, G.; De Acutis, A.; Pece, R.; Tavella, S.; Costa, D.; Poggi, A.; et al. Lysyl-Oxidase Dependent Extracellular Matrix Stiffness in Hodgkin Lymphomas: Mechanical and Topographical Evidence. Cancers 2022, 14, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dus-Szachniewicz, K.; Gdesz-Birula, K.; Rymkiewicz, G. Development and Characterization of 3D Hybrid Spheroids for the Investigation of the Crosstalk Between B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas and Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2022, 15, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, M.; Schmitt, S.; Cyprys, P.; Kasper, M.A.; Mai, I.; Klanova, M.; Maiser, A.; Leonhardt, H.; Hackenberger, C.P.R.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.R.; et al. TUB-010, a novel anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate based on Tub-tag technology, widens the therapeutic window by reducing toxicity while maintaining high efficacy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2025, OF1–OF14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| STR Locus | D430B |
|---|---|
| D5S818 | 12,13 |
| D13S317 | 11,12 |
| D7S820 | 10,11 |
| D16S539 | 12 |
| VWA | 18 |
| TH01 | 6,10 |
| AM | x,y |
| TPOX | 9,11 |
| CSF1PO | 10,11 |
| D21S11 | 30,32.2 |
| D3S1358 | 15,17 |
| D18S51 | 15,17 |
| Penta E | 7,12 |
| Penta D | 10 |
| D8S1179 | 13,15 |
| FGA | 21,22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannoni, P.; Pietra, G.; Izzo, O.; Fugazza, G.; Benelli, R.; Poggi, A.; Krampera, M.; Utzeri, C.; Marchese, M.; Musso, M.; et al. Developing a 3D Model Culture of an EBV+/CD30+ B-Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Cell Line to Assay Brentuximab Vedotin Treatment. Antibodies 2025, 14, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040098
Giannoni P, Pietra G, Izzo O, Fugazza G, Benelli R, Poggi A, Krampera M, Utzeri C, Marchese M, Musso M, et al. Developing a 3D Model Culture of an EBV+/CD30+ B-Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Cell Line to Assay Brentuximab Vedotin Treatment. Antibodies. 2025; 14(4):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040098
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannoni, Paolo, Gabriella Pietra, Orlando Izzo, Giuseppina Fugazza, Roberto Benelli, Alessandro Poggi, Mauro Krampera, Chiara Utzeri, Monica Marchese, Marco Musso, and et al. 2025. "Developing a 3D Model Culture of an EBV+/CD30+ B-Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Cell Line to Assay Brentuximab Vedotin Treatment" Antibodies 14, no. 4: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040098
APA StyleGiannoni, P., Pietra, G., Izzo, O., Fugazza, G., Benelli, R., Poggi, A., Krampera, M., Utzeri, C., Marchese, M., Musso, M., Visconti, P., & de Totero, D. (2025). Developing a 3D Model Culture of an EBV+/CD30+ B-Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Cell Line to Assay Brentuximab Vedotin Treatment. Antibodies, 14(4), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040098









