Purification and Characterization of Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) Targeting Surface Antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioethics
2.2. T. gondii Tachyzoites for Cytometry and Crude Extract Preparation
2.3. Recombinant SAG1 (rSAG1) and E. coli Crude Extract
2.4. Hen Immunization and Egg Collection
2.5. Purification of IgY from Egg Yolks Using Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) 6000
2.6. ELISA for IgY Anti-SAG1
2.7. IgY Anti-SAG1 Detection by Western Blot
2.8. IgY Anti-SAG1 Alexa Fluor 488 Labeling and SAG1 Detection in Tachyzoites by Flow Cytometry
3. Results
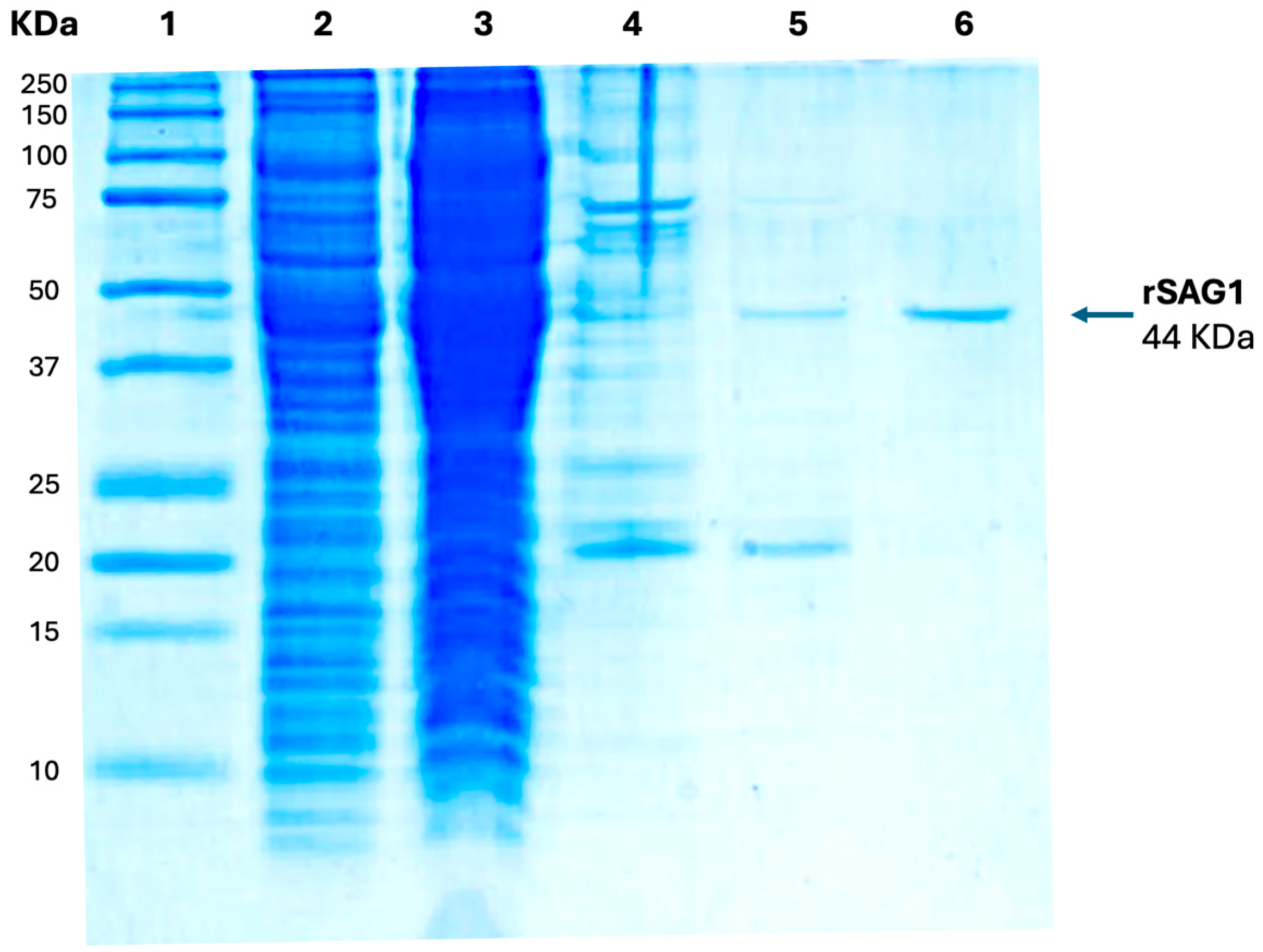
3.1. Recombinant SAG1 (rSAG1) Production in E. coli
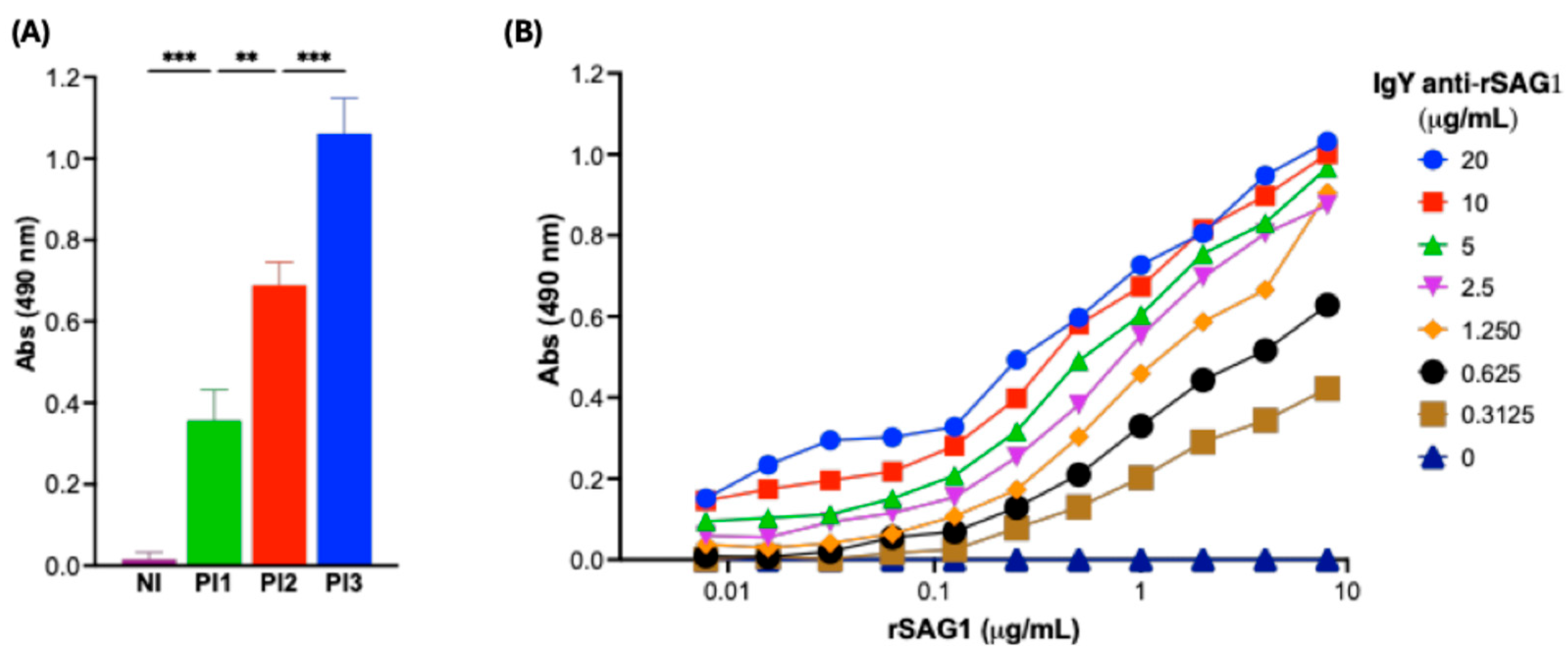
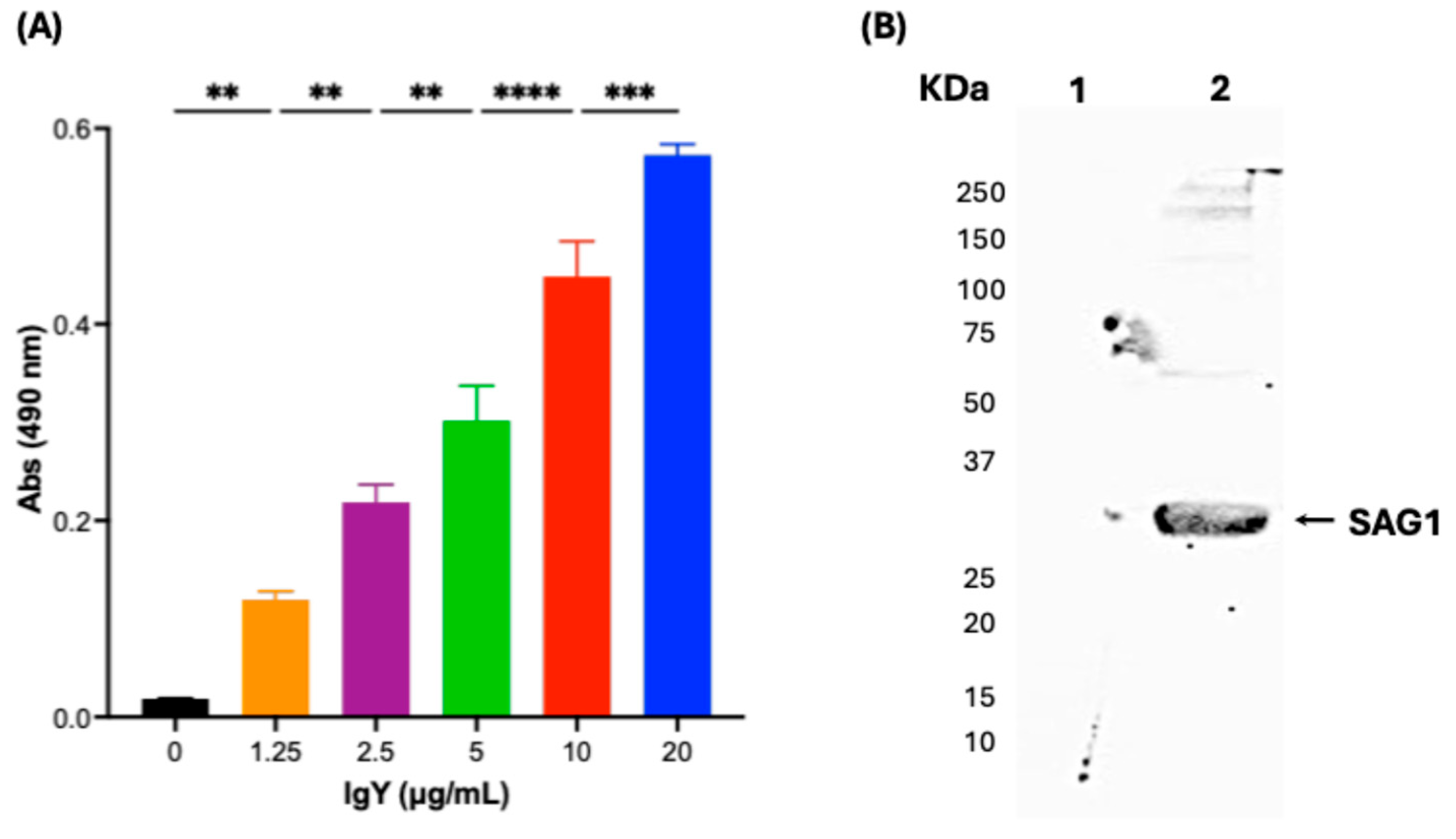
3.2. Anti-SAG1 IgY Production, Purification from Egg Yolks, and Characterization
3.3. Anti-SAG1 IgY Can Detect Recombinant SAG1 (rSAG1) from RH T. gondii
3.4. Anti-SAG1 IgY Can Detect Native SAG1 Present in the RH T. gondii Crude Extract
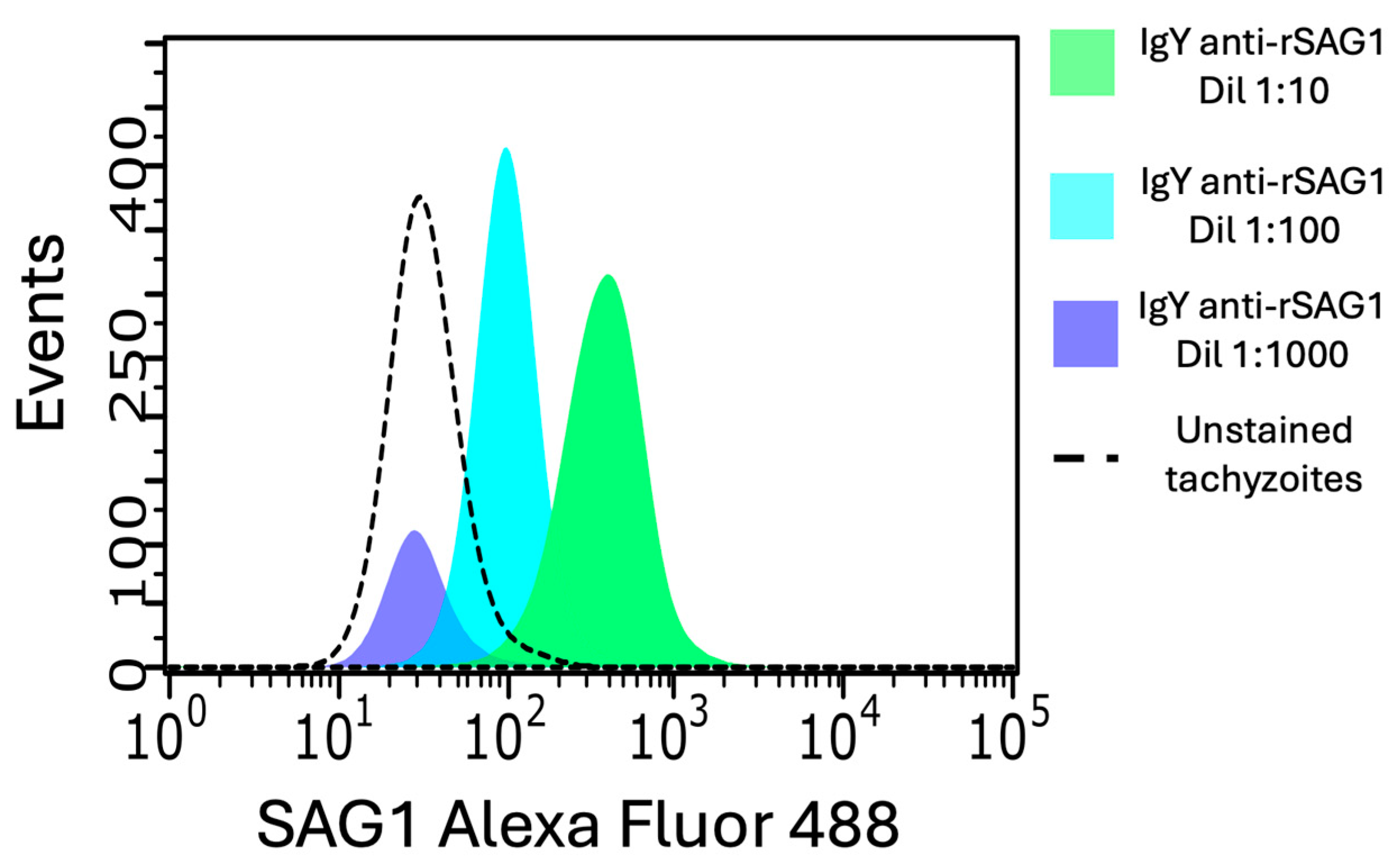
3.5. Anti-SAG1 IgY Can Detect Native SAG1 on the Surface of RH Tachyzoites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attias, M.; Teixeira, D.E.; Benchimol, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Crepaldi, P.H.; De Souza, W. The life-cycle of Toxoplasma gondii reviewed using animations. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, D.; Shaghlil, A.; Sobh, E.; Hamie, M.; Hassan, M.E.; Moumneh, M.B.; Itani, S.; El Hajj, R.; Tawk, L.; El Sabban, M.; et al. Comprehensive Overview of Toxoplasma gondii-Induced and Associated Diseases. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallon, M.; Peyron, F. Congenital Toxoplasmosis: A Plea for a Neglected Disease. Pathogens 2018, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougier, S.; Montoya, J.G.; Peyron, F. Lifelong Persistence of Toxoplasma Cysts: A Questionable Dogma? Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Ortega, H.; Uribe-Salas, F.J.; Conde-Glez, C.J.; Cedillo-Pelaez, C.; Vargas-Villavicencio, J.A.; Luna-Pasten, H.; Canedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegria, L.B.; Correa, D. Seroprevalence and national distribution of human toxoplasmosis in Mexico: Analysis of the 2000 and 2006 National Health Surveys. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 106, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan-Ramirez Mde, L.; Troyo, R.; Roman, S.; Calvillo-Sanchez, C.; Bernal-Redondo, R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of Toxoplasma gondii infection among the Mexican population. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, R.A.M.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Marciano, M.A.M.; Mazuz, M.L.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L.; Fux, B. Toxoplasmosis in Human and Animals Around the World. Diagnosis and Perspectives in the One Health Approach. Acta Trop. 2022, 231, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Toscano, V.; Linares-López, K.A.; Arce-Estrada, G.E.; Figueroa-Damián, R.; Barrios Bautista, D.M.; Hernández-Luengas, L.; Bonilla-Ríos, C.; Tecuatl-Herrada, B.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Macías-Parra, M.; et al. Toxoplasmosis congénita en el Valle de México: Resultados de una serie de casos (congenital toxoplasmosis in the Valley of Mexico. Results of a case series). Acta Pediatr. Mex. 2018, 39, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela-Amieva, M.; Canedo-Solares, I.; Gutierrez-Castrellon, P.; Perez-Andrade, M.; Gonzalez-Contreras, C.; Ortiz-Cortes, J.; Ortega-Velazquez, V.; Galvan-Ramirez Mde, L.; Ruiz-Garcia, M.; Saltigeral-Simentel, P.; et al. Short report: Neonatal screening pilot study of Toxoplasma gondii congenital infection in Mexico. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, M.; Tartaglia, S.; Apicella, M.; Visconti, D.; Noia, G.; Valentini, P.; Lanzone, A.; Santangelo, R.; Masini, L. The prevention of congenital toxoplasmosis using a combination of Spiramycin and Cotrimoxazole: The long-time experience of a tertiary referral centre. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2024, 29, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarch-Ibanez, B.; Carreras-Abad, C.; Frick, M.A.; Blazquez-Gamero, D.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; Fuentes, I.; the Spanish Research Network of Congenital Toxoplasmosis (REIV-TOXO) Group; Soler-Palacin, P. REIV-TOXO Project: Results from a Spanish cohort of congenital toxoplasmosis (2015–2022). The beneficial effects of prenatal treatment on clinical outcomes of infected newborns. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.X.; Wei, S.S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Peng, H.J. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Medicines in Humans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Chavez, F.; Canedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegria, L.B.; Flores-Garcia, Y.; Figueroa-Damian, R.; Luna-Pasten, H.; Gomez-Toscano, V.; Lopez-Candiani, C.; Arce-Estrada, G.E.; Bonilla-Rios, C.A.; et al. A Proinflammatory Immune Response Might Determine Toxoplasma gondii Vertical Transmission and Severity of Clinical Features in Congenitally Infected Newborns. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Chávez, F.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Flores-García, Y.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Figueroa-Damián, R.; Mora-González, J.C.; Correa, D. Maternal Immune Response During Pregnancy and Vertical Transmission in Human Toxoplasmosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Solares, I.; Correa, D.; Luna-Pasten, H.; Ortiz-Alegria, L.B.; Gómez-Chávez, F.; Xicotencatl-Garcia, L.; Diaz-Garcia, L.; Canfield-Rivera, C.E. Maternal anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies IgG2, IgG3 and IgG1 are markers of vertical transmission and clinical evolution of toxoplasmosis in the offspring. Acta Trop. 2023, 243, 106943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Villavicencio, J.A.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Correa, D. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM Long Persistence: What Are the Underlying Mechanisms? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Mauricio, A.; Caballero-Ortega, H.; Gómez-Chávez, F. Congenital Toxoplasmosis Diagnosis: Current Approaches and New Insights. Acta Parasitol. 2023, 68, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.J.; Peng, J.; Chen, M.; Yao, L.J.; Zou, W.H.; He, C.Y.; Peng, H.J. Toxoplasma gondii SAG1 targeting host cell S100A6 for parasite invasion and host immunity. iScience 2021, 24, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicotencatl-Garcia, L.; Enriquez-Flores, S.; Correa, D. Testing New Peptides From Toxoplasma gondii SAG1, GRA6, and GRA7 for Serotyping: Better Definition Using GRA6 in Mother/Newborns Pairs With Risk of Congenital Transmission in Mexico. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chen, X.-G.; Li, H.; Yan, H.; Yang, P.-L.; Lun, Z.-R.; Zhu, X.-Q. Diagnosis of human toxoplasmosis by using the recombinant truncated surface antigen 1 of Toxoplasma gondii. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 64, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decoster, A.; Darcy, F.; Caron, A.; Vinatier, D.; De L’Aulnoit, D.H.; Vittu, G.; Niel, G.; Heyer, F.; Lecolier, B.; Delcroix, M. Anti—P30 IgA antibodies as prenatal markers of congenital toxoplasma infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1992, 87, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülow, R.; Boothroyd, J. Protection of mice from fatal Toxoplasma gondii infection by immunization with p30 antigen in liposomes. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 3496–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debard, N.; Buzoni-Gatel, D.; Bout, D. Intranasal immunization with SAG1 protein of Toxoplasma gondii in association with cholera toxin dramatically reduces development of cerebral cysts after oral infection. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2158–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, I.; Darcy, F.; Deslee, D.; Dessaint, J.; Capron, A. Isotypic profiles of antibody responses to Toxoplasma gondii infection in rats and mice: Kinetic study and characterization of target antigens of immunoglobulin A antibodies. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 2446–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Ely, K.; Kasper, L. A purified parasite antigen (p30) mediates CD8+ T cell immunity against fatal Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 3501–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundén, A.; Lövgren, K.; Uggla, A.; Araujo, F.G. Immune responses and resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in mice immunized with antigens of the parasite incorporated into immunostimulating complexes. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, H. Research progress on surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Tommaso, A.; Juste, M.O.; Lakhrif, Z.; Mevelec, M.N.; Borowczyk, C.; Hammeni, P.; Desoubeaux, G.; Van Langendonck, N.; Debierre-Grockiego, F.; Aubrey, N.; et al. Engineering and Functional Evaluation of Neutralizing Antibody Fragments Against Congenital Toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, T.; Ai, J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, H.; Kang, M.; You, X.; Li, J. Application of Toxoplasma gondii-specific SAG1, GRA7 and BAG1 proteins in serodiagnosis of animal toxoplasmosis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1029768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harning, D.; Spenter, J.; Metsis, A.; Vuust, J.; Petersen, E. Recombinant Toxoplasma gondii surface antigen 1 (P30) expressed in Escherichia coli is recognized by human Toxoplasma-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibodies. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1996, 3, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A.; Balow, R.M.; Lindahl, T.L.; Forsberg, P.O. Chicken antibodies: Taking advantage of evolution—A review. Poult. Sci. 1993, 72, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeifard, M.; Solhi, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Abbasi, E.; Aminian, M. Production of IgY polyclonal antibody against diphtheria toxin and evaluation of its neutralization effect by Vero cell assay. BMC Biotechnol. 2021, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarez-Estrada, M.A.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Sanchez-Godoy, F.D.; Alonso-Morales, R.A. Immunotherapy With Egg Yolk Eimeria sp.-Specific Immunoglobulins in SPF Leghorn Chicks Elicits Successful Protection Against Eimeria tenella Infection. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 758379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, R.K.; Reddy, P.N.; Sreerama, K. Application of IgY antibodies against staphylococcal protein A (SpA) of Staphylococcus aureus for detection and prophylactic functions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9387–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Hu, Q.; Jiao, L.; Cui, X.; Wu, P.; He, P.; Xia, N.; Lv, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, S. Production of anti-Trichophyton rubrum egg yolk immunoglobulin and its therapeutic potential for treating dermatophytosis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Núñez, D.; Vizcaíno-López, M.F.; Escorcia, M.; Correa, D.; Pérez-Hernández, E.; Gómez-Chávez, F. IgY Antibodies as Biotherapeutics in Biomedicine. Antibodies 2022, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aluja, A.S. [Laboratory animals and official Mexican norms (NOM-062-ZOO-1999)]. Gac. Med. Mex. 2002, 138, 295–298. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12096401/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Underwood, W.; Anthony, R. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://olaw.nih.gov/policies-laws/avma-guidelines-2020.htm (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Figueroa-Castillo, J.A.; Duarte-Rosas, V.; Juarez-Acevedo, M.; Luna-Pasten, H.; Correa, D. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) from Mexico. J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burg, J.L.; Perelman, D.; Kasper, L.H.; Ware, P.L.; Boothroyd, J.C. Molecular analysis of the gene encoding the major surface antigen of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 1988, 141, 3584–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homan, W.L.; Vercammen, M.; De Braekeleer, J.; Verschueren, H. Identification of a 200- to 300-fold repetitive 529 bp DNA fragment in Toxoplasma gondii, and its use for diagnostic and quantitative PCR. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcial-Quino, J.; Fierro, F.; De la Mora-De la Mora, I.; Enriquez-Flores, S.; Gomez-Manzo, S.; Vanoye-Carlo, A.; Garcia-Torres, I.; Sierra-Palacios, E.; Reyes-Vivas, H. Validation of housekeeping genes as an internal control for gene expression studies in Giardia lamblia using quantitative real-time PCR. Gene 2016, 581, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Ochoa, B.; Gomez-Manzo, S.; Alcaraz-Carmona, E.; Serrano-Posada, H.; Centeno-Leija, S.; Arreguin-Espinosa, R.; Cuevas-Cruz, M.; Gonzalez-Valdez, A.; Mendoza-Espinoza, J.A.; Acosta Ramos, M.; et al. Gene Cloning, Recombinant Expression, Characterization, and Molecular Modeling of the Glycolytic Enzyme Triosephosphate Isomerase from Fusarium oxysporum. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.; Marcial-Quino, J.; Gómez-Manzo, S.; Enríquez-Flores, S.; Nequiz-Avendaño, M.; Cortes, A.; De la Luz León-Avila, G.; Saavedra, E.; Pérez-Tamayo, R.; Olivos-García, A. Functional characterization and subcellular distribution of two recombinant cytosolic HSP70 isoforms from Entamoeba histolytica under normal and stress conditions. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Chacana, P.A.; Calzado, E.G.; Brembs, B.; Schade, R. IgY technology: Extraction of chicken antibodies from egg yolk by polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, e3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegria, L.B.; Figueroa-Damian, R.; Bustos-Bahena, M.L.; Gonzalez-Henkel, H.; Calderon-Segura, E.; Luna-Pasten, H.; Correa, D. Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy: Determination of IgM, IgG and avidity in filter paper-embedded blood. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, J.D.; Beatty, B.G.; Vlahos, W.G. Measurement of monoclonal antibody affinity by non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 100, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizhanov, G.; Vyshniauskis, G. A Comparison of Three Methods for Extracting IgY from the Egg Yolk of Hens Immunized with Sendai Virus. Vet. Res. Commun. 2000, 24, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, B.S.; Abhijith, K.S.; Rastogi, N.K.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.; Thakur, M.S. Integrated Approach for the Extraction and Purification of IgY from Chicken Egg Yolk. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigna, J.J.; Tochie, J.N.; Tounouga, D.N.; Bekolo, A.O.; Ymele, N.S.; Youda, E.L.; Sime, P.S.; Nansseu, J.R. Global, regional, and country seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pregnant women: A systematic review, modelling and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zhou, D.Q.; Ruan, W.; Wu, L.G.; Zhang, H.Z. Preparation of mouse anti-recombinant SAG1 antigen monoclonal antibody of Toxoplasma gondii by intrasplenic immunization. Fudan Univ. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 37, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Hendriksen, C.F. A call for a European prohibition of monoclonal antibody production by the ascites procedure in laboratory animals. Altern. Lab. Anim. 1998, 26, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.N.; Brum, B.C.; Cruz, P.B.; Molinaro, C.M.; Silva, V.L.; Chaves, S.A.d.M. Production and Characterization of IgY against Canine IgG: Prospect of a New Tool for the Immunodiagnostic of Canine Diseases. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2014, 57, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Syed Atif, A.; Tan, S.C.; Leow, C.H. Insights into the chicken IgY with emphasis on the generation and applications of chicken recombinant monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 447, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassl, A.; Aspock, H.; Flamm, H. Comparative studies on the purity and specificity of yolk immunoglobulin Y isolated from eggs laid by hens immunized with Toxoplasma gondii antigen. Zentralbl Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. A 1987, 267, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Junior, A.; Santiago, F.M.; Silva, M.V.; Ferreira, F.B.; Macedo Junior, A.G.; Mota, C.M.; Faria, M.S.; Silva Filho, H.H.; Silva, D.A.; Cunha-Junior, J.P.; et al. Production, characterization and applications for Toxoplasma gondii-specific polyclonal chicken egg yolk immunoglobulins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartati, S.; Kusumawati, A.; Wuryastuti, H.; Widada, J.S. Primary structure of mature SAG1 gene of an Indonesian Toxoplasma gondii and comparison with other strains. J. Vet. Sci. 2006, 7, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puspitasari, H.; Praptiwi, Y.; Suwanti, L. Production and Characterization of Immunoglobuline Yolk as anti antigen membrane Toxoplasma gondii. Indones. J. Trop. Infect. Dis. 2016, 6, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir-Koc, R. Production of anti-SAG1 IgY antibody against Toxoplasma gondii parasites and evaluation of antibody activity by ELISA method. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2947–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, M.; Cakir Koc, R.; Budama Kilinc, Y. Novel Fitc-Labeled Igy Antibody: Fluorescence Imaging Toxoplasma Gondii In Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhard, M.H.; Schmidt, P.; Hofmann, A.; Bergmann, J.; Mittermeier, P.; Kaufmann, P.; Wiesmiiller, K.-H.; Bessler, W.G.; Lösch, U. The Lipopeptide, Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4: An Alternative Adjuvant to Freund’s Adjuvant for the Immunisation of Chicken to Produce Egg Yolk Antibodies. Altern. Lab. Anim. 1997, 25, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Li, X.; Teng, Y.; Liang, Y.; Peng, B.; Fang, F.; Chen, Z. Comparison of Adjuvant Efficacy of Chitosan and Aluminum Hydroxide for Intraperitoneally Administered Inactivated Influenza H5N1 Vaccine. DNA Cell Biol. 2010, 29, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Min, M.; Du, N.; Gu, Y.; Hode, T.; Naylor, M.; Chen, D.; Nordquist, R.E.; Chen, W.R. Chitin, Chitosan, and Glycated Chitosan Regulate Immune Responses: The Novel Adjuvants for Cancer Vaccine. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 387023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Omer, S.B. Why and How Vaccines Work. Cell 2020, 183, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshager, D.; Tesfaye, S.; Fikre, Z.; Mu-uz, G.; Yimer, M. The potential application of avian egg antibodies with emphasis on immunotherapeutic and immunodiagnostic purpose. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Health 2015, 7, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criste, A.; Urcan, A.C.; Corcionivoschi, N. Avian IgY antibodies, ancestors of mammalian antibodies—Production and application. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 25, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korah, M.C.; Hima, S.; V, S.R.; Anil, A.; Harikrishnan, V.; Krishnan, L.K. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Avian Egg-Yolk Derived Pure Anti-Snake Venom in Healthy and Disease Animal-Model. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Dias, A.C.P.; Zhang, X. Chimerism of avian IgY—scFv and truncated IgG—Fc: A novel strategy in cross—Species antibody generation and enhancement. Immunology 2024, 172, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, C.L.; Gallardo, M.J.; Casanova, N.; Terzolo, H.; Chacana, P. IgY-technology (egg yolk antibodies) in human medicine: A review of patents and clinical trials. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, C.; Lyu, J.; Yi, P.; Shen, X.; Tang, B.; Zhao, H.; Ren, B.; Kuang, Y.; Zhou, L.; et al. Egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY) targeting SARS-CoV-2 S1 as potential virus entry blocker. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 2421–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Xicoténcatl-García, L.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Rico-Torres, C.P.; Gómez-Chávez, F. The FcRn from gene to protein and function: Comparison between species. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1608426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, P.; Malave, C.; Zerpa, N.; Vazquez, H.; D’Suze, G.; Montero, Y.; Castillo, C.; Alagon, A.; Sevcik, C. IgY pharmacokinetics in rabbits: Implications for IgY use as antivenoms. Toxicon 2014, 90, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevcik, C.; Diaz, P.; D’Suze, G. On the presence of antibodies against bovine, equine and poultry immunoglobulins in human IgG preparations, and its implications on antivenom production. Toxicon 2008, 51, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torche, A.M.; Le Dimna, M.; Le Corre, P.; Mesplede, A.; Le Gal, S.; Cariolet, R.; Le Potier, M.F. Immune responses after local administration of IgY loaded-PLGA microspheres in gut-associated lymphoid tissue in pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 109, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, C.G.; Bok, M.; Vlasova, A.N.; Chattha, K.S.; Fernandez, F.M.; Wigdorovitz, A.; Parreno, V.G.; Saif, L.J. IgY antibodies protect against human Rotavirus induced diarrhea in the neonatal gnotobiotic piglet disease model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akita, E.M.; Jang, C.B.; Kitts, D.D.; Nakai, S. Evaluation of Allergenicity of Egg Yolk Immunoglobulin Y and Other Egg Proteins by Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis. Food Agric. Immunol. 2010, 11, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, Z.; Shahsavar, S.; Keikha, M.; Ghazvini, K. Chicken immunoglobulin (IgY) as an alternative treatment for bacterial infections, emphasizing advantages, disadvantages and mechanisms. J. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Aguirre, E.A.; León-Núñez, D.; Marcial-Quino, J.; Gómez-Manzo, S.; Reyes-López, C.A.; Medina-Flores, Y.; Mata-Ruíz, O.; Xicotencatl-García, L.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; et al. Purification and Characterization of Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) Targeting Surface Antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii. Antibodies 2025, 14, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040081
Herrera-Aguirre EA, León-Núñez D, Marcial-Quino J, Gómez-Manzo S, Reyes-López CA, Medina-Flores Y, Mata-Ruíz O, Xicotencatl-García L, Luna-Pastén H, Ortiz-Alegría LB, et al. Purification and Characterization of Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) Targeting Surface Antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii. Antibodies. 2025; 14(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040081
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Aguirre, Enrique Adrián, Diana León-Núñez, Jaime Marcial-Quino, Saúl Gómez-Manzo, César Augusto Reyes-López, Yolanda Medina-Flores, Olga Mata-Ruíz, Lizbeth Xicotencatl-García, Hector Luna-Pastén, Luz Belinda Ortiz-Alegría, and et al. 2025. "Purification and Characterization of Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) Targeting Surface Antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii" Antibodies 14, no. 4: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040081
APA StyleHerrera-Aguirre, E. A., León-Núñez, D., Marcial-Quino, J., Gómez-Manzo, S., Reyes-López, C. A., Medina-Flores, Y., Mata-Ruíz, O., Xicotencatl-García, L., Luna-Pastén, H., Ortiz-Alegría, L. B., Pérez-Hernández, N., Escorcia, M., Correa, D., & Gómez-Chávez, F. (2025). Purification and Characterization of Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) Targeting Surface Antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii. Antibodies, 14(4), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14040081





