IgM Antibody Detection as a Diagnostic Marker for Acute Toxoplasmosis: Current Status of Studies and Main Limitations
Abstract
1. Introduction
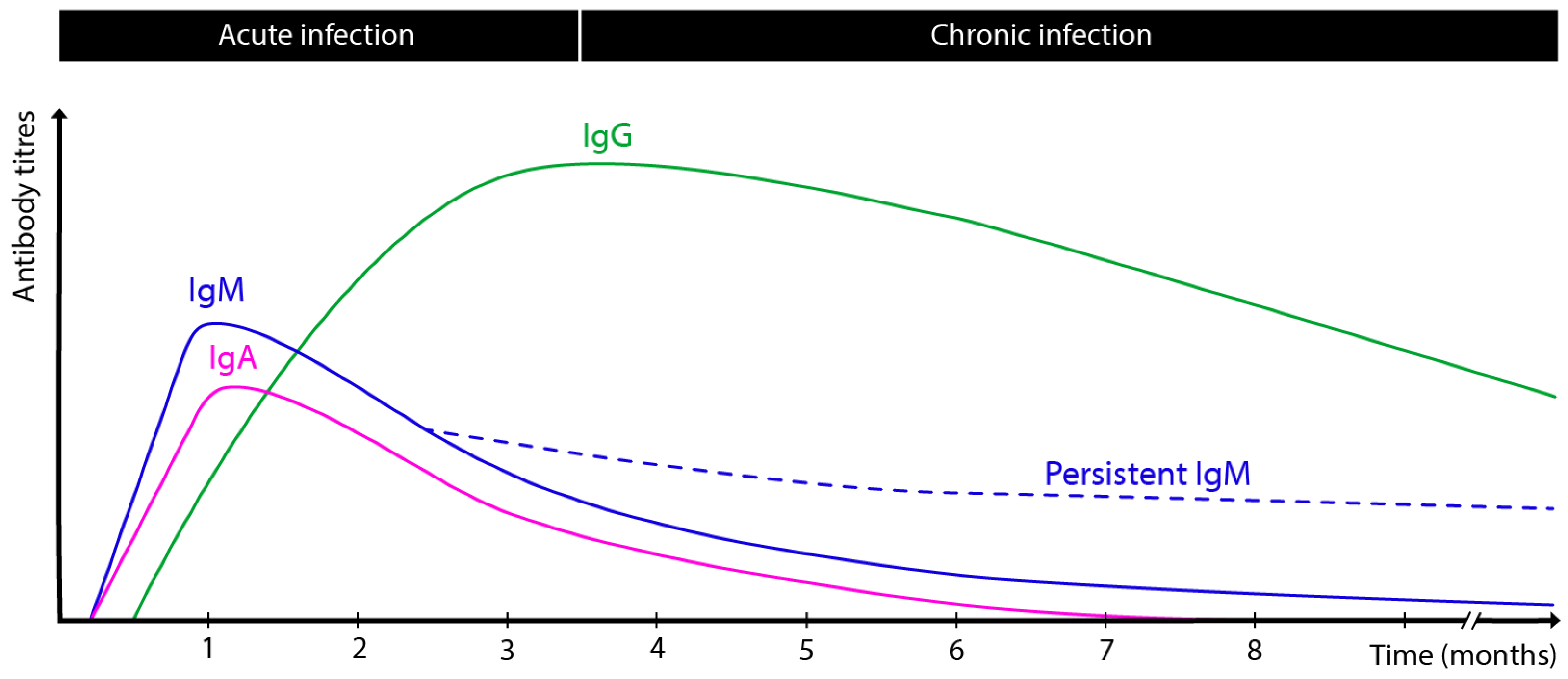
2. Kinetics of Antibody Response During T. gondii Infection
3. Current Methods for IgM Antibody Detection
4. Recombinant Antigens in IgM Detection
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From Animals to Humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.-L. Epidemiology of and Diagnostic Strategies for Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, S.K.; Rinkenberger, N.; Dunay, I.R.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Its Implications within the Central Nervous System. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, A.K.; Fong, C.; Naqvi, A.; Lu, J.-Q. Toxoplasmosis of the Central Nervous System: Manifestations Vary with Immune Responses. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 420, 117223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, W.J.; Jeffers, V. Mechanisms of Toxoplasma gondii Persistence and Latency. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malki, E.S. Toxoplasmosis: Stages of the Protozoan Life Cycle and Risk Assessment in Humans and Animals for an Enhanced Awareness and an Improved Socio-Economic Status. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Villena, I. Congenital Toxoplasmosis in Humans: An Update of Worldwide Rate of Congenital Infections. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollani, L.; Auriti, C.; Achille, C.; Garofoli, F.; De Rose, D.U.; Meroni, V.; Salvatori, G.; Tzialla, C. Congenital Toxoplasmosis: The State of the Art. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 894573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, F.; Lobry, J.R.; Musset, K.; Ferrandiz, J.; Gomez-Marin, J.E.; Petersen, E.; Meroni, V.; Rausher, B.; Mercier, C.; Picot, S.; et al. Serotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in Chronically Infected Pregnant Women: Predominance of Type II in Europe and Types I and III in Colombia (South America). Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.d.M.; Vitor, R.W.A.; Carneiro, A.C.A.V.; Brandão, G.P.; Melo, M.N. Genetic Variability of Brazilian Toxoplasma gondii Strains Detected by Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RAPD-PCR) and Simple Sequence Repeat Anchored-PCR (SSR-PCR). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2004, 4, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Majumdar, D.; Pena, H.F.J.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Geographical Patterns of Toxoplasma gondii Genetic Diversity Revealed by Multilocus PCR-RFLP Genotyping. Parasitology 2014, 141, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhaes, L.; Ajzenberg, D.; Sicot, B.; Bourgeot, P.; Dardé, M.-L.; Dei-Cas, E.; Houfflin-Debarge, V. Severe Congenital Toxoplasmosis Due to a Toxoplasma gondii Strain with an Atypical Genotype: Case Report and Review. Prenat. Diagn. 2010, 30, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, M.; Trotta, A.; Spataro, E.; Giache, S.; Borchi, B.; Zammarchi, L.; Campolmi, I.; Galli, L.; Pasquini, L. Primary Toxoplasmosis Acquired during Early Pregnancy: Is It Currently Overestimated? Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 267, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Bailly, S.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.-P.; Dard, C.; Jean, D.; Coston, A.-L.; Garnaud, C.; Pelloux, H. How to Estimate Time of Infection with Toxoplasma gondii in Pregnant Women. Use of Specific IgG and IgM Kinetics by 7 Techniques on 691 Sera. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 114987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.L. Immunoglobulin M for Acute Infection: True or False? Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, S.; Racsa, L.; Alatoom, A. Implications of False Positive Serology of Toxoplasma gondii in a Pre-Transplant Patient. Lab. Med. 2014, 45, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, L.; Gilbert, R.E.; Wallon, M.; Peyron, F.; Cortina-Borja, M. Duration of the IgM Response in Women Acquiring Toxoplasma gondii during Pregnancy: Implications for Clinical Practice and Cross-Sectional Incidence Studies. Epidemiol. Infect. 2004, 132, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Villavicencio, J.A.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Correa, D. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM Long Persistence: What Are the Underlying Mechanisms? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazas, M.I.; Salamanca-Marin, J.; Torres-Morales, E.; Londoño, J.C.; Celis-Giraldo, D.; Gomez-Marin, J.E. Frequency of Natural Antibodies and Concordance Analysis for Anti-Toxoplasma IgM Tests in Colombian Sera of Pregnant Women. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 103, 115733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gussetti, N.; D’Elia, R.; Mottola, A.; Rigoli, E. Natural Immunoglobulin M Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii during Pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1990, 162, 1359–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G.; Tathineni, N.J.; Davis, M.; Brown, B.W.; Cobb, K.L.; Parsonnet, J.; Remington, J.S. Confirmatory Serologic Testing for Acute Toxoplasmosis and Rate of Induced Abortions among Women Reported to Have Positive Toxoplasma Immunoglobulin M Antibody Titers. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 184, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villard, O.; Cimon, B.; L’Ollivier, C.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Godineau, N.; Houze, S.; Paris, L.; Pelloux, H.; Villena, I.; Candolfi, E. Serological Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection: Recommendations from the French National Reference Center for Toxoplasmosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 84, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.S.; Suzuki, L.A.; Rossi, C.L. Assessment of the Value of Detecting Specific IgA Antibodies for the Diagnosis of a Recently Acquired Primary Toxoplasma Infection. Prenat. Diagn. 2008, 28, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.; Kanno, R.; Bessho, T.; Koshizuka, T.; Suzutani, T. Evaluation of Toxoplasma gondii IgG Avidity Assays through a Comparison of IgM Serostatus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 105, 115901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec-Gąsior, L.; Sołowińska, K. IgG Avidity Test as a Tool for Discrimination between Recent and Distant Toxoplasma gondii Infection—Current Status of Studies. Antibodies 2022, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, V.; Genco, F.; Tinelli, C.; Lanzarini, P.; Bollani, L.; Stronati, M.; Petersen, E. Spiramycin Treatment of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnant Women Impairs the Production and the Avidity Maturation of T. gondii-Specific Immunoglobulin G Antibodies. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, G.B.; Lemos, E.M.; E Silva-Dos-Santos, P.P.; Dietze, R.; Zandonade, E.; Mineo, J.R.; de Oliveira Silva, D.A.; Pajuaba, A.C.M.; de Souza Gomes, M.; do Amaral, L.R.; et al. Proposed Panel of Diagnostic Tools for Accurate Temporal Classification of Symptomatic T. gondii Infection. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 451, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olariu, T.R.; Blackburn, B.G.; Press, C.; Talucod, J.; Remington, J.S.; Montoya, J.G. Role of Toxoplasma IgA as Part of a Reference Panel for the Diagnosis of Acute Toxoplasmosis during Pregnancy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01357-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévêque, M.F.; Albaba, S.; Arrada, N.; Avignon, M.; Sasso, M.; Fillaux, J.; Lachaud, L. Diagnosis of Congenital Toxoplasmosis: No Benefit of IgA Antibody Detection by Platelia ELISA in a Tricentric Evaluation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0011622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guegan, H.; Stajner, T.; Bobic, B.; Press, C.; Olariu, R.T.; Olson, K.; Srbljanovic, J.; Montoya, J.G.; Djurković-Djaković, O.; Robert-Gangneux, F. Maternal Anti-Toxoplasma Treatment during Pregnancy Is Associated with Reduced Sensitivity of Diagnostic Tests for Congenital Infection in the Neonate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañedo-Solares, I.; Correa, D.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Gómez-Chávez, F.; Xicoténcatl-García, L.; Díaz-García, L.; Canfield-Rivera, C.E. Maternal Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies IgG2, IgG3 and IgG1 Are Markers of Vertical Transmission and Clinical Evolution of Toxoplasmosis in the Offspring. Acta Trop. 2023, 243, 106943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remington, J.S.; Thulliez, P.; Montoya, J.G. Recent Developments for Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, J.; Lemoine, J.-P.; L’ollivier, C.; Deleplancque, A.-S.; Fricker Hidalgo, H.; Pelloux, H.; Pomares, C.; Cimon, B.; Paris, L.; Houzé, S.; et al. Contribution of Serology in Congenital Toxoplasmosis Diagnosis: Results from a 10-Year French Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2023, 61, e00354-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villard, O.; Cimon, B.; L’Ollivier, C.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Godineau, N.; Houze, S.; Paris, L.; Pelloux, H.; Villena, I.; Candolfi, E. Help in the Choice of Automated or Semiautomated Immunoassays for Serological Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis: Evaluation of Nine Immunoassays by the French National Reference Center for Toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.; Borobio, M.V.; Guy, E.; Liesenfeld, O.; Meroni, V.; Naessens, A.; Spranzi, E.; Thulliez, P. European Multicenter Study of the LIAISON Automated Diagnostic System for Determination of Toxoplasma gondii-Specific Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM and the IgG Avidity Index. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay-Andrieu, F.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Sickinger, E.; Espern, A.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.-P.; Braun, H.-B.; Pelloux, H. Comparative Evaluation of the ARCHITECT Toxo IgG, IgM, and IgG Avidity Assays for Anti-Toxoplasma Antibodies Detection in Pregnant Women Sera. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 65, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderaro, A.; Piccolo, G.; Peruzzi, S.; Gorrini, C.; Chezzi, C.; Dettori, G. Evaluation of Toxoplasma gondii Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM Assays Incorporating the NewVidia Analyzer System. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theel, E.S.; Yarbrough, M.L.; Hilgart, H.; Gronowski, A.M. Evaluation of the Bio-Rad BioPlex 2200 Toxoplasma gondii IgM Multiplex Flow Immunoassay. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2019, 3, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Bourhis, C.; Chevrier, S.; Gangneux, J.-P. Evaluation of DPC Immulite 2000 Toxoplasma Quantitative IgG/IgM Kits for Automated Toxoplasmosis Serology with Immulite 2000. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2009, 23, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genco, F.; Sarasini, A.; Parea, M.; Prestia, M.; Scudeller, L.; Meroni, V. Comparison of the LIAISON®XL and ARCHITECT IgG, IgM, and IgG Avidity Assays for the Diagnosis of Toxoplasma, Cytomegalovirus, and Rubella Virus Infections. New Microbiol. 2019, 42, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasper, D.C.; Prusa, A.R.; Hayde, M.; Gerstl, N.; Pollak, A.; Herkner, K.R.; Reiter-Reisacher, R. Evaluation of the Vitros ECiQ Immunodiagnostic System for Detection of Anti-Toxoplasma Immunoglobulin G and Immunoglobulin M Antibodies for Confirmatory Testing for Acute Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnant Women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusa, A.-R.; Hayde, M.; Unterasinger, L.; Pollak, A.; Herkner, K.R.; Kasper, D.C. Evaluation of the Roche Elecsys Toxo IgG and IgM Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay for the Detection of Gestational Toxoplasma Infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 68, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Remington, J.S.; Clavet, C.; Varney, G.; Press, C.; Ware, D. Evaluation of Six Commercial Kits for Detection of Human Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. The FDA Toxoplasmosis Ad Hoc Working Group. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 3112–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PLATELIA™ TOXO IgM (BIO-RAD). Available online: https://commerce.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/inserts/CDG/en/Literature/inserts/72841_881043_GB.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- FDA 510(k) Substantial Equivalence Determination Decision Summary: K142826. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K142826.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- FDA 510(k) Substantial Equivalence Determination Decision Summary: K131441. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K131441.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- FDA 510(k) Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Information Supporting A. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf/K954576.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Dave, J.; Balfour, A.H.; Perkin, J. Evaluation of the VIDAS Toxo Competition Assay for the Detection of Antibodies Specific to Toxoplasma gondii in Human Sera. Serodiagn. Immunother. Infect. Dis. 1994, 6, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigue, N.; Menotti, J.; Hamane, S.; Derouin, F.; Garin, Y.J.-F. Performance of the BioPlex 2200 Flow Immunoassay in Critical Cases of Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, W.E.; Martins, T.B.; Litwin, C.M.; Roberts, W.L. Performance Characteristics of Six IMMULITE 2000 TORCH Assays. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 126, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA 510(k) Substantial Equivalence Determination Decision Summary: K24095. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K242095.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Zhang, K.; Lin, G.; Han, Y.; Li, J. Serological Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis and Standardization. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2016, 461, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, M.G.; Lunde, M.N.; Hajkowski, R.; McMahon, J. Determination of IgM and IgG Antibodies to Toxoplasma Using the IFA Test, ELISA, and Dot-ELISA Procedures. Vet. Parasitol. 1986, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ybañez, R.H.D.; Ybañez, A.P.; Nishikawa, Y. Review on the Current Trends of Toxoplasmosis Serodiagnosis in Humans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, M.; Borchi, B.; Zammarchi, L.; Sterrantino, G.; Brogi, M.; Kiros, S.T.; Lorini, C.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Colao, M.G.; Bartoloni, A. Immunoglobulin M Indirect-Fluorescent Antibody Test for the Diagnosis of Acute Toxoplasmosis during Pregnancy in the Avidity Era: A 14-Year Experience at the Tuscany Reference Center for Infectious Diseases in Pregnancy, Florence, Italy. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2016, 42, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avignon, M.; Lévêque, M.F.; Guemas, E.; Sasso, M.; Albaba, S.; Lachaud, L.; Fillaux, J. Diagnosis of Congenital Toxoplasmosis: Performance of Four IgG and IgM Automated Assays at Birth in a Tricentric Evaluation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0011522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.G. In Defense of Children’s Brain: Reshuffling the Laboratory Toolbox for the Diagnosis of Congenital Toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 62, e01697-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhis, S.; Rouges, C.; Dahane, N.; Guegan, H.; Yéra, H.; Robert-Gangneux, F. Could PLATELIA Toxo IgM Be the New Gold Standard for the Serological Diagnosis of Congenital Toxoplasmosis: A French Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 62, e01222-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleplancque, A.-S.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Pomares, C.; L’Ollivier, C.; Lemoine, J.-P.; Cimon, B.; Paris, L.; Houzé, S.; Villena, I.; Pelloux, H.; et al. Comparative Performance of ISAGA IgM and ELISA Assays for the Diagnosis of Maternal and Congenital Toxoplasma Infections: Which Technique Could Replace ISAGA IgM? Parasite 2024, 31, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, B.; Migliorini, L. Western Blotting for the Diagnosis of Congenital Toxoplasmosis. New Microbiol. 2011, 34, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Meroni, V.; Genco, F.; Scudeller, L.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.-P.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; L’Ollivier, C.; Paris, L.; Pelloux, H. Diagnostic Accuracy of LDBIO-Toxo II IgG and IgM Western Blot in Suspected Seroconversion in Pregnancy: A Multicentre Study. Pathogens 2022, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imen, K.; Nada, B.; Chouaieb, H.; Fathallah, A. Contribution of the “Recomline Toxoplasma IgM” Kit in the Distinction between Toxoplasmic IgM and Natural IgM. Int. J. Pharm. Phytopharm. Res. 2021, 11, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Infectious Diseases: From Methods to Devices. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begeman, I.J.; Lykins, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lai, B.S.; Levigne, P.; El Bissati, K.; Boyer, K.; Withers, S.; Clouser, F.; Noble, A.G.; et al. Point-of-Care Testing for Toxoplasma gondii IgG/IgM Using Toxoplasma ICT IgG-IgM Test with Sera from the United States and Implications for Developing Countries. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Noordin, R. Serological and Molecular Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Toxoplasma Infection in Humans and Animals. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, C.A.; Budvytyte, L.N.; Press, C.; Zhou, L.; McLeod, R.; Maldonado, Y.; Montoya, J.G.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.G. Evaluation of Three Point-of-Care Tests for Detection of Toxoplasma Immunoglobulin IgG and IgM in the United States: Proof of Concept and Challenges. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapey, E.; Wallon, M.; Peyron, F. Evaluation of the LDBIO Point of Care Test for the Combined Detection of Toxoplasmic IgG and IgM. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2017, 464, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotresha, D.; Noordin, R. Recombinant Proteins in the Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis. APMIS 2010, 118, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferra, B.T.; Chyb, M.; Sołowińska, K.; Holec-Gąsior, L.; Skwarecka, M.; Baranowicz, K.; Gatkowska, J. The Development of Toxoplasma gondii Recombinant Trivalent Chimeric Proteins as an Alternative to Toxoplasma Lysate Antigen (TLA) in Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for the Detection of Immunoglobulin G (IgG) in Small Ruminants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, A.; Abbaszadeh Afshar, M.J.; Mohtasebi, S.; Jafarpour Azami, S.; Alimi, R.; Keshavarz, H. Assessment of an In-House Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and IgG Avidity Test Based on SAG1 and GRA7 Proteins for Discriminating between Acute and Chronic Toxoplasmosis in Humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0041621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec, L.; Gasior, A.; Brillowska-Dabrowska, A.; Kur, J. Toxoplasma gondii: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Using Different Fragments of Recombinant Microneme Protein 1 (MIC1) for Detection of Immunoglobulin G Antibodies. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenter, A.M.; Johnson, A.M. Recognition of Recombinant Toxoplasma gondii Antigens by Human Sera in an ELISA. Parasitol. Res. 1991, 77, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dard, C.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.-P.; Pelloux, H. Relevance of and New Developments in Serology for Toxoplasmosis. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec-Gasior, L. Toxoplasma Gondii Recombinant Antigens as Tools for Serodiagnosis of Human Toxoplasmosis: Current Status of Studies. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Karanis, P.; Fallahi, S. Advances in Serological, Imaging Techniques and Molecular Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Infection 2018, 46, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potasman, I.; Araujo, F.G.; Desmonts, G.; Remington, J.S. Analysis of Toxoplasma gondii Antigens Recognized by Human Sera Obtained before and after Acute Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 154, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafid, J.; Tran Manh Sung, R.; Akono, Z.Y.; Pozzetto, B.; Jaubert, J.; Raberin, H.; Jana, M. Toxoplasma gondii Antigens: Analysis by SDS-PAGE and Immunoblotting; Relation with Circulating Antigens. Eur. J. Protistol. 1991, 26, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.D.; Mullenax, J.; Araujo, F.G.; Erlich, H.A.; Remington, J.S. Western Blot Analysis of the Antigens of Toxoplasma gondii Recognized by Human IgM and IgG Antibodies. J. Immunol. 1983, 131, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harning, D.; Spenter, J.; Metsis, A.; Vuust, J.; Petersen, E. Recombinant Toxoplasma gondii Surface Antigen 1 (P30) Expressed in Escherichia coli Is Recognized by Human Toxoplasma-Specific Immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG Antibodies. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1996, 3, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatnia, G.; Ghaffarifar, F.; Khalilpour, A.; Amerizadeh, A.; Rahmah, N. A Toxoplasma gondii 10 KDa in Vitro Excretory Secretory Antigen Reactive with Human IgM and IgA Antibodies. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 28, 606–614. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, A.C.d.A.; de Souza, M.A.; Mineo, J.R. Detection of Antibodies to the 97 KDa Component of Toxoplasma gondii in Samples of Human Serum. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2002, 97, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlich, H.A.; Rodgers, G.; Vaillancourt, P.; Araujo, F.G.; Remington, J.S. Identification of an Antigen-Specific Immunoglobulin M Antibody Associated with Acute Toxoplasma Infection. Infect. Immun. 1983, 41, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.R.; Behnke, M.S.; Mackey, A.J.; Radke, J.B.; Roos, D.S.; White, M.W. The Transcriptome of Toxoplasma gondii. BMC Biol. 2005, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, K.J.; Aliota, M.T.; Knoll, L.J. Dual Transcriptional Profiling of Mice and Toxoplasma gondii during Acute and Chronic Infection. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, D.; Maine, G.T.; Villena, I.; Hunt, J.C.; Howard, L.; Sheu, M.; Brojanac, S.; Chovan, L.E.; Nowlan, S.F.; Pinon, J.M. Recombinant Antigens To Detect Toxoplasma gondii-Specific Immunoglobulin G and Immunoglobulin M in Human Sera by Enzyme Immunoassay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffolano, W.; Beghetto, E.; Del Pezzo, M.; Spadoni, A.; Di Cristina, M.; Petersen, E.; Gargano, N. Use of Recombinant Antigens for Early Postnatal Diagnosis of Congenital Toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5916–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanaliha, K.; Motazedian, M.H.; Kazemi, B.; Shahriari, B.; Bandehpour, M.; Sharifniya, Z. Evaluation of Recombinant SAG1, SAG2, and SAG3 Antigens for Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis. Korean J. Parasitol. 2014, 52, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmley, S.F.; Sgarlato, G.D.; Mark, J.; Prince, J.B.; Remington, J.S. Expression, Characterization, and Serologic Reactivity of Recombinant Surface Antigen P22 of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.E.; Duré, A.B. Effectiveness of Two Sequences of Toxoplasma gondii SAG2 Protein to Differentiate Toxoplasmosis Infection Stages by Measuring IgG, IgA and IgM Antibodies. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 33, 246–259. [Google Scholar]
- Golkar, M.; Azadmanesh, K.; Khalili, G.; Khoshkholgh-Sima, B.; Babaie, J.; Mercier, C.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.-P.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Pelloux, H.; Cesbron-Delauw, M.-F. Serodiagnosis of Recently Acquired Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnant Women Using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays with a Recombinant Dense Granule GRA6 Protein. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selseleh, M.; Keshavarz, H.; Mohebali, M.; Shojaee, S.; Selseleh, M.; Eshragian, M.R.; Mansouri, F.; Modarressi, M.H. Production and Evaluation of Toxoplasma gondii Recombinant GRA7 for Serodiagnosis of Human Infections. Korean J. Parasitol. 2012, 50, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ramirez, R.; Press, C.; Li, S.; Parmley, S.; Thulliez, P.; Remington, J.S. Detection of Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to P35 Antigen of Toxoplasma gondii for Serodiagnosis of Recently Acquired Infection in Pregnant Women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3967–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Wu, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zou, L.; Gao, S.; Lin, M.; Zhou, Y. Toxoplasma gondii: Expression Pattern and Detection of Infection Using Full-Length Recombinant P35 Antigen. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 113, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaie, J.; Miri, M.; Sadeghiani, G.; Zare, M.; Khalili, G.; Golkar, M. Expression and Single-Step Purification of GRA8 Antigen of Toxoplasma gondii in Escherichia coli. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2011, 3, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.G.; Duré, A.B. Immunochemical Evaluation of Two Toxoplasma gondii GRA8 Sequences to Detect Acute Toxoplasmosis Infection. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 100, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.; Arcavi, M.; Santillan, G.; Amendoeira, M.R.; De Souza Neves, E.; Griemberg, G.; Guarnera, E.; Garberi, J.C.; Angel, S.O. Detection of Human Toxoplasma-Specific Immunoglobulins A, M, and G with a Recombinant Toxoplasma gondii Rop2 Protein. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1998, 5, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, T.; Yu, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, A.; Xu, X.; Luo, Q.; Hu, Y.; Song, W.; Lun, Z.; et al. RROP2(186-533): A Novel Peptide Antigen for Detection of IgM Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferra, B.; Holec-Gąsior, L.; Gatkowska, J.; Dziadek, B.; Dzitko, K. Toxoplasma gondii Recombinant Antigen AMA1: Diagnostic Utility of Protein Fragments for the Detection of IgG and IgM Antibodies. Pathogens 2020, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Bruno, L.; Buffolano, W.; Gargano, N. Chimeric Antigens of Toxoplasma gondii: Toward Standardization of Toxoplasmosis Serodiagnosis Using Recombinant Products. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, P.R.B.; Ferreira, A.W. High Diagnostic Efficiency of IgM-ELISA with the Use of Multiple Antigen Peptides (MAP1) from T. gondii ESA (SAG-1, GRA-1 and GRA-7), in Acute Toxoplasmosis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2010, 52, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Jiang, M.; Qu, L.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Gong, L.; Gong, R.; Si, J. Toxoplasma gondii: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Based on a Recombinant Multi-Epitope Peptide for Distinguishing Recent from Past Infection in Human Sera. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 133, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapała, D.; Holec-Gasior, L.; Kur, J. New Recombinant Chimeric Antigens, P35-MAG1, MIC1-ROP1, and MAG1-ROP1, for the Serodiagnosis of Human Toxoplasmosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 82, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferra, B.T.; Holec-Gąsior, L.; Gatkowska, J.; Dziadek, B.; Dzitko, K.; Grąźlewska, W.; Lautenbach, D. The First Study on the Usefulness of Recombinant Tetravalent Chimeric Proteins Containing Fragments of SAG2, GRA1, ROP1 and AMA1 Antigens in the Detection of Specific Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Mouse and Human Sera. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, R.E.; McLeod, R.; Roberts, C.W. Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoite–Bradyzoite Interconversion. Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Galvan, G.; Araujo, F.G.; Suzuki, Y.; Remington, J.S.; Parmley, S. Serodiagnosis of Recently Acquired Toxoplasma gondii Infection Using an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with a Combination of Recombinant Antigens. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2000, 7, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alhajj, M.; Zubair, M.; Farhana, A. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Irving, A.T. Massively-Multiplexed Epitope Mapping Techniques for Viral Antigen Discovery. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1192385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, S.S.; Paiva, V.F.; Carvalho, F.R.; Barros, H.L.S.; Silva, T.L.; Barros, P.S.C.; Pajuaba, A.C.A.M.; Barros, G.B.; Dietze, R.; Mineo, T.W.P.; et al. A Peptide Originated from Toxoplasma gondii Microneme 8 Displaying Serological Evidence to Differentiate Recent from Chronic Human Infection. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 84, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.A.M.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Resende, C.A.A.; Couto, C.A.P.; Gandra, I.B.; dos Santos Barcelos, I.C.; da Silva, J.O.; Machado, J.M.; Silva, K.A.; Silva, L.S.; et al. Recombinant Multiepitope Proteins Expressed in Escherichia coli Cells and Their Potential for Immunodiagnosis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Piao, Y.; Moon, E.-K.; Quan, F.-S. Influenza M1 Virus-like Particles Consisting of Toxoplasma gondii Rhoptry Protein 4. Korean J. Parasitol. 2017, 55, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Mao, J.; Kang, H.-J.; Chu, K.-B.; Quan, F.-S. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Infections Using Virus-like Particles Displaying T. gondii ROP4 Antigen. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Chu, K.-B.; Mao, J.; Kang, H.-J.; Eom, G.-D.; Yoon, K.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Moon, E.-K.; Lee, Y.-H.; Quan, F.-S. Recombinant AMA1 Virus-like Particle Antigen for Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensini, A. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnancy: Opportunities and Pitfalls of Serological Diagnosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G. Systematic Screening and Treatment of Toxoplasmosis during Pregnancy: Is the Glass Half Full or Half Empty? Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 219, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.; Meroni, V.; Vasconcelos-Santos, D.V.; Mandelbrot, L.; Peyron, F. Congenital Toxoplasmosis: Should We Still Care about Screening? Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2022, 27, e00162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, L.; Hamidović, A.; Dardé, M.L.; Mercier, M. Diversity of Toxoplasma gondii Strains at the Global Level and Its Determinants. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazevic, N.; Rogic, D.; Pelajic, S.; Miler, M.; Glavcic, G.; Ratkajec, V.; Vrkljan, N.; Bakula, D.; Hrabar, D.; Pavic, T. YKL-40 as a Biomarker in Various Inflammatory Diseases: A Review. Biochem. Medica 2024, 34, 10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahad, F.A.A.-Z.; Mohammed, A.A.; Jasim, G.A. YKL-40 as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker in Toxoplasmosis. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 29, e61–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria Junior, G.M.; Murata, F.H.A.; Lorenzi, H.A.; Castro, B.B.P.; Assoni, L.C.P.; Ayo, C.M.; Brandão, C.C.; de Mattos, L.C. The Role of MicroRNAs in the Infection by T. gondii in Humans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 670548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-J.; Zhou, D.-H.; Nisbet, A.J.; Huang, S.-Y.; Fan, Y.-F.; Zhu, X.-Q. Characterization of Mouse Brain MicroRNAs after Infection with Cyst-Forming Toxoplasma gondii. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-J.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.-L.; Xu, M.-J.; Zhu, X.-Q. Analysis of MiRNA Expression Profiling in Mouse Spleen Affected by Acute Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 37, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafi, Z.; Ata, T.; Asha, S. CRISPR in Clinical Diagnostics: Bridging the Gap between Research and Practice. Bioanalysis 2025, 17, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyusheva, A.; Brezgin, S.; Babin, Y.; Vasilyeva, I.; Glebe, D.; Kostyushev, D.; Chulanov, V. CRISPR-Cas Systems for Diagnosing Infectious Diseases. Methods 2022, 203, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test | Manufacturer | Type of Test | Principle | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platelia Toxo IgM | Bio-Rad | EIA 1 | Patient IgM antibodies bind to anti-human µ-chain antibodies coated on the microplate wells, followed by incubation with T. gondii antigen and a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated murine monoclonal antibody anti-T. gondii (P30). Detection by chromogenic substrate (TMB). | [45] |
| Architect/Alinity | Abbott | CMIA 2 | μ-Capture chemiluminescent immunoassay. Patient IgM antibodies bind to anti-human IgM-coated paramagnetic microparticles. Detection is achieved by incubating the bound IgM with native T. gondii lysate, pre-complexed with an acridinium-labeled anti-Toxo P30 (SAG1) monoclonal F(ab′)2 fragment. The resulting chemiluminescent signal is measured. | [37] |
| Advia Centaur/Atellica Toxo IgM | Siemens | CMIA | Patient IgM binds to mouse anti-human IgMμ monoclonal antibody covalently coupled to paramagnetic particles. A T. gondii antigen, complexed with an acridinium-labeled anti-p30 F(ab′)2 fragment, then binds to captured IgM. If IgM is present, antibody/antigen complexes form, producing a chemiluminescent signal proportional to IgM concentration. | [46] |
| Liaison | DiaSorin | CMIA | Magnetic particles coated with IgG to human IgM (mouse monoclonal) selectively bind IgM from the patient sample. After incubation with inactivated T. gondii (RH strain) obtained from ruptured and detergent-extracted trophozoite detection is achieved using mouse monoclonal anti- SAG1 antibodies conjugated to an isoluminol derivative. | [47] |
| Elecsys Toxo IgM | Roche Diagnostics GmbH | ECLIA 3 | Patient sample is incubated with a ruthenium-labeled recombinant T. gondii SAG1 antigen, allowing IgM antibodies to bind. Then, biotinylated anti-human IgM antibodies and streptavidin-coated microparticles are added, forming a solid-phase complex via biotin/streptavidin interaction. After washing, the complex is held in an electrochemiluminescence measuring cell using a magnetic field, while unbound components are removed. An electrochemiluminescent reaction is triggered by applying voltage, and the light emission is detected. | [43] |
| VIDIA Toxo IgM | BioMérieux | CMIA | The system uses a two-step enzyme immunoassay on paramagnetic microparticles with a chemiluminescence-based detection step, but to the best of our knowledge, a complete description of the system has not been published. | [38] |
| AxSYM Toxo IgM | Abbott | MEIA 4 | Microparticles are coated with T. gondii antigen (RH strain) derived from HeLa cell culture which captures IgM from serum. After washing, goat anti-human IgM–alkaline phosphatase conjugate binds to any attached IgM. A rheumatoid neutralization buffer reduces rheumatoid factor interference. The alkaline phosphatase reacts with the substrate 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate (MUP) to release a fluorescent product. | [48] |
| Vidas Toxo IgM | BioMérieux | ELFA 5 | Competitive fluorescent detection system, where patient IgM antibodies to T. gondii compete with an anti-p30 monoclonal antibodies. A Solid Phase Receptacle (SPR) serves as both the pipette and solid-phase support; its interior is precoated with T. gondii antigen (RH strain). Patient serum is drawn into the SPR from a reagent strip containing sequential wells for washing, conjugate incubation (alkaline phosphatase-labeled anti-p30 mAb), and fluorescent substrate (MUP). Any bound enzyme conjugate converts the substrate to a fluorescent product (4-methylumbelliferone). | [49] |
| BioPlex 2200 ToRC IgM kit | Bio-Rad | MFI 6 | A multiplex system that simultaneously detects T. gondii, Rubella virus-, and CMV-specific IgM antibodies. Samples are incubated with antigen-coated fluoromagnetic beads carrying a unique fluorescent signature and binding IgM antibodies. Next, a fluorescent anti-human IgM reporter conjugate is added. As the bead mixture passes through a dual-laser flow detector, the first laser classifies each bead type by its embedded dye, while the second laser quantifies the fluorescence signal. | [50] |
| Immulite 2000 | DPC-Siemens | CLIA | A polystyrene bead coated with partially purified T. gondii antigen (RH strain tachyzoites from mouse peritoneum) is incubated with patient serum. After washing, a goat anti-human IgM antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase is added, after which a chemiluminescent substrate (phosphate ester of adamantyl dioxetane) is introduced. To minimize false reactivity, reagents include antibodies to human IgG and rheumatoid factors. | [51] |
| Vitros | Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics | CLIA | Patient IgM is incubated with a biotinylated mouse anti-human IgM antibody, forming an immune complex that is captured by streptavidin on the test wells. Then, an HRP-labeled mouse monoclonal anti-Toxoplasma antibody—complexed with inactivated T. gondii antigen—binds to any Toxoplasma-specific IgM on the well. A luminogenic substrate and an electron transfer agent (a substituted acetanilide which increases the level of light produced and prolongs its emission). | [42] |
| Access | Beckman-Coulter | CMIA | Patient sample is added to paramagnetic microparticles coated with sheep anti-human IgM, allowing T. gondii-specific IgM to bind. A T. gondii antigen complexed with anti-p30 monoclonal antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase is introduced followed by addition of a chemiluminescent substrate. | [52] |
| Antigen Category | Antigen | Number of Tested Sera | Type of ELISA | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface antigens (SAGs) | SAG1 (P30) | 142 | Indirect | 10.6 | ND * | [86] |
| SAG145–196 | 104 | Double sandwich | 65.7 | 95.8 | [87] | |
| SAG1 | 58 | Indirect | 39.3 | 80 | [88] | |
| SAG1 | 138 | Indirect | 89.7 | 96.3 | [71] | |
| P2227–172 (SAG2) | 26 | Indirect | 46 | 100 | [89] | |
| SAG2 | 58 | Indirect | 64.3 | 83.3 | [88] | |
| SAG2L1–188 | 242 | Indirect | 52.3 | 61.4 | [90] | |
| SAG2c27–173 | 81.8 | 42.9 | ||||
| SAG3 | 58 | Indirect | 17.9 | 76.7 | [88] | |
| Dense granule antigens (GRAs) | GRA640–230 | 88 | Indirect | 91.7 | 97.1 | [91] |
| GRA7 (P29) | 142 | Indirect | 50.7 | ND * | [86] | |
| GRA7 | 174 | Indirect | 96 | 90 | [92] | |
| GRA7 | 138 | Indirect | 100.0 | 96.3 | [71] | |
| GRA81–135 (P35) | 69 | Double sandwich | 90 | 100 | [93] | |
| GRA81–135 (P35) | 142 | Indirect | 54.9 | ND * | [86] | |
| GRA8 (P35) | 125 | Double sandwich | 100 | 96 | [94] | |
| GRA823–169 | 68 | Indirect | 60.6 | 97.1 | [95] | |
| GRA8A1–95 | 123 | Indirect | 57.8 | 59.3 | [96] | |
| GRA8B48–145 | 65.2 | 59.3 | ||||
| Rhoptry proteins (ROPs) | ROP1 (P66) | 142 | Indirect | 58.5 | ND * | [86] |
| ROP2196–561 | 103 | Indirect | 62.1 | 100 | [97] | |
| ROP2177–537 (P54) | 142 | Indirect | 12.6 | ND * | [86] | |
| ROP2186–533 | 203 | Indirect | 100 | 100 | [98] | |
| Micronemal proteins (MICs) | MIC2a157–235 | 104 | Double sandwich | 60 | 100 | [87] |
| MIC2b466–610 | 51.4 | 98.6 | ||||
| MIC3234–307 | 31.4 | 100 | ||||
| Other | P68 | 142 | Indirect | 18.3 | ND * | [86] |
| M2AP37–263 1 | 104 | Double sandwich | 48.6 | 98.6 | [87] | |
| AMA1 2 | 156 | Indirect | 80 | 93.8 | [99] |
| Antigen | Number of Tested Sera | Type of ELISA | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC2 (MIC2157–235-MIC3234–307-SAG1182–312) | 157 | Double sandwich | 98 | 100 | [100] |
| EC3 (GRA336–134-GRA724–102-M2AP37–263) | 84 | 100 | |||
| MAP1 1 (SAG1-GRA7-GRA1) | 250 | Indirect | 100 | 100 | [101] |
| MEP 2 (SAG1309–318-SAG2109–118-SAG3347–356) | 161 | Indirect | 96.6 | 100 | [102] |
| P35-MAG1 | 123 | Indirect | 81.8 | 93.4 | [103] |
| MIC1-ROP1 | 72.7 | 95.1 | |||
| MAG1-ROP1 | 59.1 | 96.7 | |||
| SAG231–170-GRA126–190-ROP185–396-AMA1N67–287 | 207 | Indirect | 90.9 | 97.1 | [104] |
| AMA1N67–287-SAG231–170-GRA126–190-ROP185–396 | 84.9 | 99 | |||
| AMA1C287–569-SAG231–170-GRA126–190-ROP185–396 | 92.4 | 91.4 | |||
| AMA168–569-SAG231–170-GRA126–190-ROP185–396 | 95.5 | 99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sołowińska, K.; Holec-Gąsior, L. IgM Antibody Detection as a Diagnostic Marker for Acute Toxoplasmosis: Current Status of Studies and Main Limitations. Antibodies 2025, 14, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020044
Sołowińska K, Holec-Gąsior L. IgM Antibody Detection as a Diagnostic Marker for Acute Toxoplasmosis: Current Status of Studies and Main Limitations. Antibodies. 2025; 14(2):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleSołowińska, Karolina, and Lucyna Holec-Gąsior. 2025. "IgM Antibody Detection as a Diagnostic Marker for Acute Toxoplasmosis: Current Status of Studies and Main Limitations" Antibodies 14, no. 2: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020044
APA StyleSołowińska, K., & Holec-Gąsior, L. (2025). IgM Antibody Detection as a Diagnostic Marker for Acute Toxoplasmosis: Current Status of Studies and Main Limitations. Antibodies, 14(2), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020044







