Discovery of Antibodies Against Endemic Coronaviruses with NGS-Based Human Fab Phage Display Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phage Display Library Panning
2.2. Subcloning, Screening, Sanger Sequencing, and Identification of Antigen-Specific Bivalent Fabs Using Traditional Approach
2.3. Long Read NGS
2.4. Conversion and Production of Full-Length Human IgG1
2.5. ELISA
2.6. Pseudovirus Neutralization Plaque Assay
2.7. Wild-Type Virus Neutralization Plaque Assay
2.8. Biolayer Interferometry Binding Affinity Measurements
3. Results
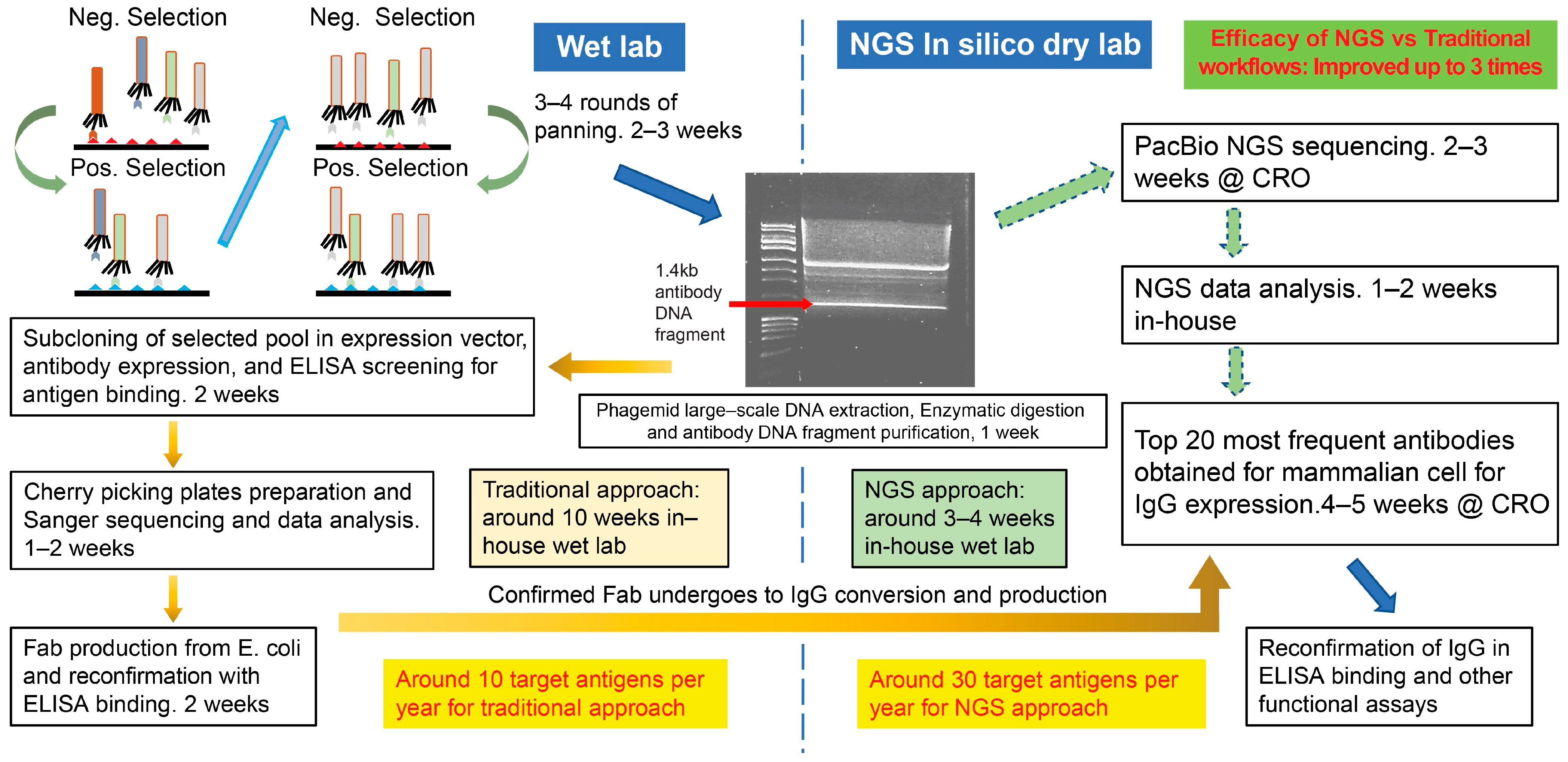
3.1. Traditional Phage-Panning Workflow vs. Long-Read NGS Workflow
3.2. Antibody Gene Sequences Identified Through Traditional vs. NGS Platforms
3.3. Antibody Binding Confirmation ELISA Against Their Respective Antigens
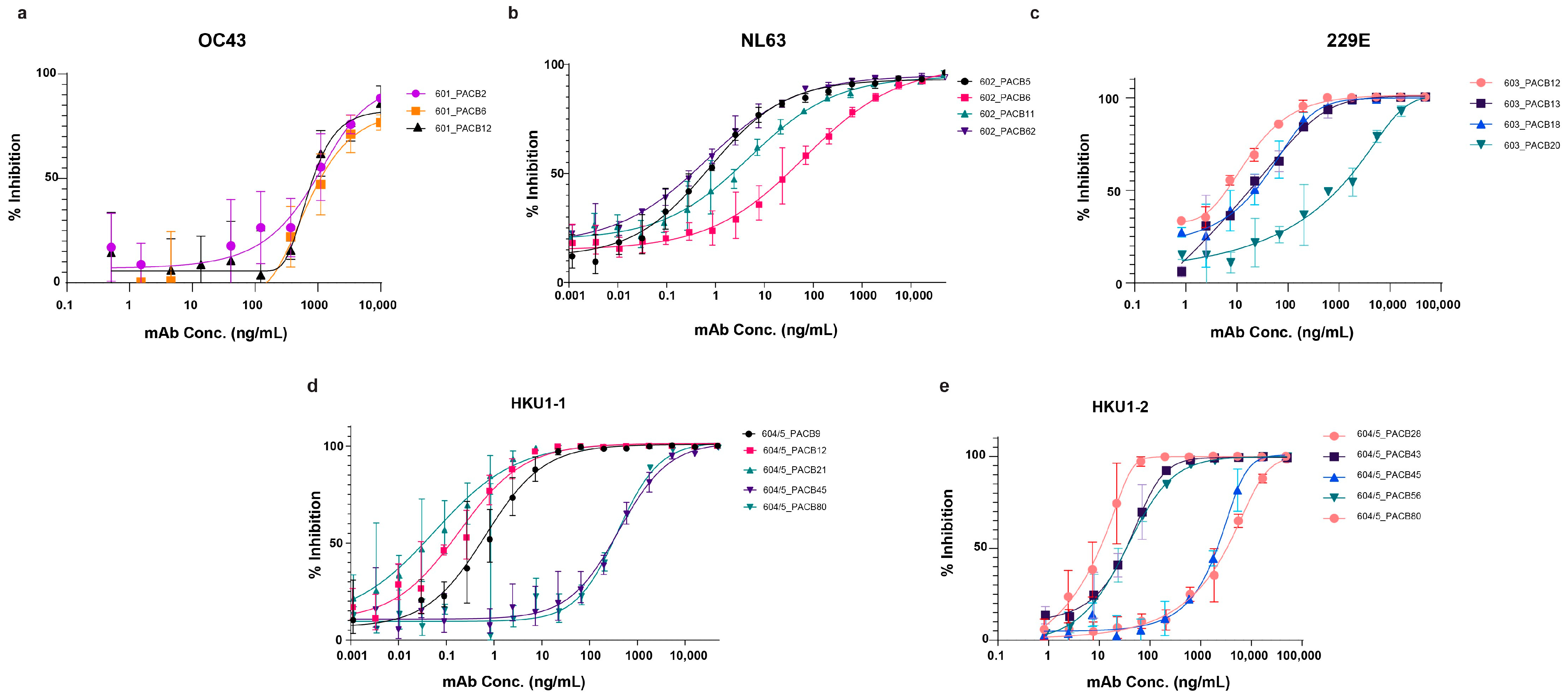
3.4. Pseudovirus Neutralization
3.5. Wild-Type Virus Neutralization
3.6. Biolayer Interferometry (BLI) Affinity Assessment
3.7. Neutralizing Antibody Germline Sequence Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corman, V.M.; Muth, D.; Niemeyer, D.; Drosten, C. Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2018, 100, 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Huang, Y.; Yuen, K.-Y. Coronavirus Diversity, Phylogeny and Interspecies Jumping. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 234, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Chen, D.; Zhu, A.; Li, F.; Zhuang, Z.; Mok, C.K.P.; Dai, J.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.; et al. Mouse models susceptible to HCoV-229E and HCoV-NL63 and cross protection from challenge with SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2202820120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- V’Kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, K.; Dees, J.H.; Becker, W.B.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Chanock, R.M. Recovery in tracheal organ cultures of novel viruses from patients with respiratory disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1967, 57, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulswit, R.J.G.; Lang, Y.; Bakkers, M.J.G.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Schouten, A.; Ophorst, B.; Van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Boons, G.-J.; Bosch, B.-J.; et al. Human coronaviruses OC43 and HKU1 bind to 9-O-acetylated sialic acids via a conserved receptor-binding site in spike protein domain A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatori, G.; Luberto, L.; Maffei, M.; Aurisicchio, L.; Roscilli, G.; Palombo, F.; Marra, E. SARS-CoV-2 SPIKE PROTEIN: An optimal immunological target for vaccines. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.P. Filamentous Fusion Phage: Novel Expression Vectors That Display Cloned Antigens on the Virion Surface. Science 1985, 228, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.K.; Smith, G.P. Searching for Peptide Ligands with an Epitope Library. Science 1990, 249, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitling, F.; Dübel, S.; Seehaus, T.; Klewinghaus, I.; Little, M. A surface expression vector for antibody screening. Gene 1991, 104, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbas, C.F.; Kang, A.S.; Lerner, R.A.; Benkovic, S.J. Assembly of combinatorial antibody libraries on phage surfaces: The gene III site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7978–7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCafferty, J.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G.; Chiswell, D.J. Phage antibodies: Filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature 1990, 348, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. Evolution of phage display libraries for therapeutic antibody discovery. mAbs 2023, 15, 2213793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, T.; Schuster, I.; Deppe, D.; Siegers, K.; Strohner, R.; Herrmann, T.; Berenguer, M.; Poujol, D.; Stehle, J.; Stark, Y.; et al. A fully synthetic human Fab antibody library based on fixed VH/VL framework pairings with favorable biophysical properties. mAbs 2013, 5, 445–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phage Display. Methods in Molecular Biology; Hust, M., Lim, T.S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ravn, U.; Didelot, G.; Venet, S.; Ng, K.T.; Gueneau, F.; Rousseau, F.; Calloud, S.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.; Fischer, N. Deep sequencing of phage display libraries to support antibody discovery. Methods 2013, 60, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschaght, P.; Vintém, A.P.; Logghe, M.; Conde, M.; Felix, D.; Mensink, R.; Gonçalves, J.; Audiens, J.; Bruynooghe, Y.; Figueiredo, R.; et al. Large Diversity of Functional Nanobodies from a Camelid Immune Library Revealed by an Alternative Analysis of Next-Generation Sequencing Data. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.B.; Naciri, J.; Liu, J.L.; Anderson, G.P.; Goldman, E.R.; Zabetakis, D. Next-Generation Sequencing of a Single Domain Antibody Repertoire Reveals Quality of Phage Display Selected Candidates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada-Masuta, T.; Takeda, H.; Uchida, K. Novel Approach for Obtaining Variable Domain of New Antigen Receptor with Different Physicochemical Properties from Japanese Topeshark (Hemitriakis japanica). Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövgren, J.; Pursiheimo, J.P.; Pyykkö, M.; Salmi, J.; Lamminmäki, U. Next generation sequencing of all variable loops of synthetic single framework scFv-Application in anti-HDL antibody selections. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanville, J.; D’Angelo, S.; Khan, T.; Reddy, S.; Naranjo, L.; Ferrara, F.; Bradbury, A. Deep sequencing in library selection projects: What insight does it bring? Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 33, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekosky, B.J.; Kojima, T.; Rodin, A.; Charab, W.; Ippolito, G.C.; Ellington, A.D.; Georgiou, G. In-depth determination and analysis of the human paired heavy- and light-chain antibody repertoire. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio Sequencing and its Applications. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemadou, A.; Giudicelli, V.; Smith, M.L.; Lefranc, M.-P.; Duroux, P.; Kossida, S.; Heiner, C.; Hepler, N.L.; Kuijpers, J.; Groppi, A.; et al. Pacific Biosciences Sequencing and IMGT/HighV-QUEST Analysis of Full-Length Single Chain Fragment Variable from an In Vivo Selected Phage-Display Combinatorial Library. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, F.; Senicar, L.; Parekh, F.; Kong, K.J.; Kinna, A.; Bughda, R.; Sillibourne, J.; Hu, X.; Ma, B.; Bai, Y.; et al. Combining phage display with SMRTbell next-generation sequencing for the rapid discovery of functional scFv fragments. mAbs 2021, 13, 1864084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.Y.; Antoine, A.; Howard, D.; Chang, B.; Chang, W.S.; Slein, M.; Deikus, G.; Kossida, S.; Duroux, P.; Lefranc, M.P.; et al. Coupling of Single Molecule, Long Read Sequencing with IMGT/HighV-QUEST Analysis Expedites Identification of SIV gp140-Specific Antibodies from scFv Phage Display Libraries. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prassler, J.; Thiel, S.; Pracht, C.; Polzer, A.; Peters, S.; Bauer, M.; Nörenberg, S.; Stark, Y.; Kölln, J.; Popp, A.; et al. HuCAL PLATINUM, a Synthetic Fab Library Optimized for Sequence Diversity and Superior Performance in Mammalian Expression Systems. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 413, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tang, A.; Callahan, C.; Pristatsky, P.; Swoyer, R.; Cejas, P.; Nahas, D.; Galli, J.; Cosmi, S.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of Phage Display-Derived Human Monoclonal Antibodies against RSV F Glycoprotein. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tzarum, N.; Wilson, I.A.; Law, M. VH1-69 antiviral broadly neutralizing antibodies: Genetics, structures, and relevance to rational vaccine design. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Potthoff, J.; Bizu, S.; Labuhn, M.; Dold, L.; Schoofs, T.; Horning, M.; Ercanoglu, M.S.; Kreer, C.; Gieselmann, L.; et al. Analysis of antibodies from HCV elite neutralizers identifies genetic determinants of broad neutralization. Immunity 2022, 55, 341–354.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bollas, A.; Wang, Y.; Au, K.F. Nanopore sequencing technology, bioinformatics and applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1348–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Calvo, E.; García-García, A.; Rodríguez, S.; Farrais, S.; Martín, R.; García, T. Construction of a Fab Library Merging Chains from Semisynthetic and Immune Origin, Suitable for Developing New Tools for Gluten Immunodetection in Food. Foods 2022, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| OC43 mAbs | HKU1-1/1-2 mAbs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGS Rank | Sanger Rank | VH Germline | VL Germline | NGS Rank | Sanger Rank | VH Germline | VL Germline |
| 1 | 1 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV1S17 | 1 | 7 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV3-1 |
| 2 | 2 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 2 | 2 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 |
| 3 | 7 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-12 | 3 | 1 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV2-14 |
| 4 | 4 | IGHV1-2 | IGLV3-1 | 4 | 4 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV1-16 |
| 5 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 5 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV3-1 | ||
| 6 | IGHV1-2 | IGKV1-39 | 6 | 2 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV3-1 | |
| 7 | 4 | IGHV1-69 | IGLV3-1 | 7 | 7 | IGHV1-69 | IGLV3-1 |
| 8 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV1S22 | 8 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV3-11 | |
| 9 | 7 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 8 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1S8 |
| 10 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV1-44 | 9 | 11 | IGHV1-2 | IGKV3-11 | |
| 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 10 | IGHV1-2 | IGKV1-39 | ||
| 12 | 9 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV1-8 | 11 | IGHV5-10-1 | IGKV1S8 | |
| 13 | 3 | IGHV1-69 | IGLV2-14 | 12 | 11 | IGHV1-2 | IGKV1-39 |
| 14 | 9 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV3-1 | 13 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 |
| 15 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 14 | IGHV1-2 | IGKV1-39 | ||
| 16 | 9 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 15 | 4 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV3-11 |
| 17 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV2-28 | 16 | 11 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV2-14 | |
| 18 | 9 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV1-39 | 17 | 11 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV1-47 |
| 19 | 4 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV3-11 | 18 | 11 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV1-40 |
| 20 | 9 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 19 | 10 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 |
| 20 | 11 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV3-1 | ||||
| NL63 mAbs | 21 | 11 | IGHV1-2 | IGKV3-11 | |||
| NGS Rank | Sanger Rank | VH germline | VL germline | 22 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV2-14 | |
| 1 | 1 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 23 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV3-1 | |
| 2 | 16 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1S8 | 24 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | |
| 3 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 25 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV1-44 | ||
| 4 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 26 | 11 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV1-40 | |
| 5 | 2 | IGHV5-51 | IGLV1-47 | 27 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 |
| 6 | 10 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV1-39 | 28 | 10 | IGHV5-10-1 | IGKV1-39 |
| 7 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 29 | 11 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV3-1 | |
| 8 | 16 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 30 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV3-1 | |
| 9 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 35 | 11 | IGHV1-2 | IGLV3-1 | |
| 10 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 36 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | |
| 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 37 | 11 | IGHV3-15 | IGKV1-39 | |
| 12 | IGHV1-69 | IGLV3-1 | 41 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | |
| 13 | 16 | IGHV1-2 | IGKV1-16 | 43 | 4 | IGHV6-1 | IGKV1-39 |
| 14 | 6 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 45 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-12 |
| 15 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 49 | 11 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV3-1 | |
| 16 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 51 | 11 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV3-1 | |
| 17 | 6 | IGHV1-2 | IGLV3-1 | 56 | 11 | IGHV5-51 | IGKV1-39 |
| 18 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 58 | 7 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV1-39 | |
| 19 | 16 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | 67 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGLV1-40 |
| 20 | 3 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV3-1 | 71 | 11 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV3-1 |
| 62 | 3 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV3-11 | 80 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV3-11 |
| 84 | 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGLV3-1 | ||||
| 229E mAbs | 93 | 11 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV1-40 | |||
| NGS Rank | Sanger Rank | VH germline | VL germline | 97 | 11 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV2-28 |
| 1 | 1 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV3-11 | 99 | 11 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV3-1 |
| 2 | 2 | IGHV5-51 | IGKV1-39 | ||||
| 3 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | |||||
| 4 | 5 | IGHV3-15 | IGKV3-11 | ||||
| 5 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV1-44 | |||||
| 6 | 8 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV2-14 | ||||
| 7 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | |||||
| 8 | 4 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | ||||
| 9 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV2-14 | |||||
| 10 | 3 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | ||||
| 11 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | |||||
| 12 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | |||||
| 13 | IGHV6-1 | IGKV1-39 | |||||
| 14 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV2-14 | |||||
| 15 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-16 | |||||
| 16 | IGHV2-70 | IGLV3-1 | |||||
| 17 | 5 | IGHV3-15 | IGKV1-39 | ||||
| 18 | IGHV3-23 | IGLV1-8 | |||||
| 19 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV3-1 | |||||
| 20 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV3-11 | |||||
| 23 | 8 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | ||||
| 37 | 5 | IGHV3-23 | IGKV1-39 | ||||
| 66 | 10 | IGHV1-69 | IGKV1-39 | ||||
| 77 | 10 | IGHV3-15 | IGLV3-1 |
| OC43 | NL63 | 229E | HKU1-1 | HKU1-2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lowest EC50 (ng/mL) | 6 | 18 | 10 | 5 | 7 |
| Median EC50 (ng/mL) | 14 | 41 | 26 | 10 | 16 |
| Highest EC50 (ng/mL) | 27 | 183 | 2935 | 713 | 977 |
| Number of EC50 values in analysis | 20 | 21 | 24 | 39 | 16 |
| HCoV | mAb ID | ELISA EC50 (ng/mL) | Pseudovirus Neutralization IC50 (ng/mL) | Wild-Type Virus Neutralization IC50 (ng/mL) | Apparent KD (M) | Kon (1/Ms) | Koff (1/s) | VH Germline | VL Germline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC43 | 601_PACB2 (601_1A1) | 13 | 994 | 438 | 1.6 × 10−9 | 9.0 × 104 | 1.4 × 10−4 | hu IGHV1-69 | hu IGKV1-39 |
| 601_PACB6 | 17 | 924 | 552 | <1.0 × 10−12 | 2.1 × 105 | 1.7 × 10−7 | hu IGHV1-2 | hu IGKV1-39 | |
| 601_PACB12 | 14 | 1129 | 940 | 2.7 × 10−12 | 7.0 × 104 | 1.9 × 10−7 | hu IGHV3-23 | hu IGLV1-40 | |
| NL63 | 602_PACB5 (602_1B10) | 18 | 0.7 | 51 | 3.0 × 10−9 | 5.1 × 105 | 1.5 × 10−3 | hu IGHV5-51 | hu IGLV1-47 |
| 602_PACB6 | 29 | 65 | 822 | 6.5 × 10−12 | 6.6 × 104 | 4.3 × 10−7 | hu IGHV3-23 | hu IGKV1-39 | |
| 602_PACB11 | 41 | 5 | 174 | 3.5 × 10−12 | 1.3 × 105 | 4.5 × 10−7 | hu IGHV1-69 | hu IGKV1-39 | |
| 602_PACB62 (602_1B1) | 26 | 0.7 | 1183 | 5.1 × 10−12 | 9.7 × 104 | 4.9 × 10−7 | hu IGHV1-69 | hu IGKV3-11 | |
| 229E | 603_PACB12 | 14 | 5 | n.d. | 6.5 × 10−12 | 6.7 × 104 | 4.4 × 10−7 | hu IGHV1-69 | hu IGKV1-39 |
| 603_PACB13 | 27 | 17 | n.d. | 5.9 × 10−12 | 8.4 × 104 | 4.9 × 10−7 | hu IGHV6-1 | hu IGKV1-39 | |
| 603_PACB18 | 132 | 23 | n.d. | 1.0 × 10−11 | 3.8 × 104 | 3.9 × 10−7 | hu IGHV3-23 | hu IGLV1-47 | |
| 603_PACB20 | 22 | 866 | n.d. | 3.0 × 10−10 | 2.5 × 106 | 7.5 × 10−4 | hu IGHV1-69 | hu IGKV3-11 | |
| HKU1-1 | 604/5_PACB9 (604_1A12) | 11 | 0.7 | n.d. | 4.0 × 10−12 | 4.0 × 106 | 1.6 × 10−5 | hu IGHV1-2 | hu IGKV1-39 |
| 604/5_PACB12 (604_1B3) | 6 | 0.2 | n.d. | 1.7 × 10−10 | 1.7 × 106 | 2.9 × 10−4 | hu IGHV1-2 | hu IGKV1-39 | |
| 604/5_PACB21 | 9 | 0.06 | n.d. | <1.0 × 10−12 | 7.5 × 105 | <1.0 × 10−7 | hu IGHV1-2 | hu IGKV3-11 | |
| HKU1-2 | 604/5_PACB28 (605_1D10) | 8 | 9 | n.d. | 9.9 × 10−11 | 3.2 × 106 | 3.2 × 10−4 | hu IGHV5-51 | hu IGKV1-39 |
| 604/5_PACB43 (605_1C4) | 18 | 26 | n.d. | 1.3 × 10−12 | 3.8 × 105 | 4.8 × 10−7 | hu IGHV6-1 | hu IGKV1-39 | |
| 604/5_PACB56 | 4 | 32 | n.d. | 5.6 × 10−10 | 4.2 × 105 | 2.3 × 10−4 | hu IGHV5-51 | hu IGKV1-39 |
| HCoV | mAb ID | ELISA EC50 on HKU1-1 (ng/mL) | Pseudovirus Neutralization IC50 HKU1-1 (ng/mL) | Apparent KD on HKU1-1 (M) | HKU1-1 Kon (1/Ms) | HKU1-1 Koff (1/s) | VH Germline | VL Germline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HKU1-1/HKU1-2 | 604/5_PACB45 | 5 | 409 | <1.0 × 10−12 | 1.5 × 106 | <1.0 × 10−7 | hu IGHV1-69 | hu IGKV1D-16 |
| 604/5_PACB80 | 8 | 388 | <1.0 × 10−12 | 3.1 × 105 | <1.0 × 10−7 | hu IGHV1-69 | hu IGKV3-11 | |
| mAb ID | ELISA EC50 on HKU1-2 (ng/mL) | Pseudovirus Neutralization IC50 HKU1-2 (ng/mL) | Apparent KD on HKU1-2 (M) | HKU1-2 kon (1/Ms) | HKU1-2 koff (1/s) | |||
| 604/5_PACB45 | 425 | 1708 | 2.1 × 10−8 | 1.5 × 107 | 3.0 × 10−1 | |||
| 604/5_PACB80 | 977 | 2646 | 8.9 × 10−9 | 4.0 × 104 | 3.5 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, O.C.-C.; Miller, S.; Patel, R.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sarullo, G.; Go, G.; Galli, J.; Hessels, J.; Schlingmann-Molina, B.; Ndashimye, E.; et al. Discovery of Antibodies Against Endemic Coronaviruses with NGS-Based Human Fab Phage Display Platform. Antibodies 2025, 14, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020028
Pan OC-C, Miller S, Patel R, Mukhopadhyay S, Sarullo G, Go G, Galli J, Hessels J, Schlingmann-Molina B, Ndashimye E, et al. Discovery of Antibodies Against Endemic Coronaviruses with NGS-Based Human Fab Phage Display Platform. Antibodies. 2025; 14(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020028
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Oscar Chi-Chien, Sean Miller, Ruchin Patel, Shreya Mukhopadhyay, Giancarlo Sarullo, Gwenny Go, Jennifer Galli, Jamie Hessels, Barbara Schlingmann-Molina, Emmanuel Ndashimye, and et al. 2025. "Discovery of Antibodies Against Endemic Coronaviruses with NGS-Based Human Fab Phage Display Platform" Antibodies 14, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020028
APA StylePan, O. C.-C., Miller, S., Patel, R., Mukhopadhyay, S., Sarullo, G., Go, G., Galli, J., Hessels, J., Schlingmann-Molina, B., Ndashimye, E., Wen, Z., Warren, C., Durr, E., Zhang, L., Vora, K. A., Fridman, A., & Chen, Z. (2025). Discovery of Antibodies Against Endemic Coronaviruses with NGS-Based Human Fab Phage Display Platform. Antibodies, 14(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14020028





