Autoantibodies, Oxidative Stress, and Nutritional State in Anorexia Nervosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment and Enrollment
2.2. ELISA Protocol for Anti-Hypothalamus Autoantibodies Detection
2.3. ELISA Test for Uric Acid and Total Antioxidant Capacity Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Anti-Hypothalamus Autoantibodies
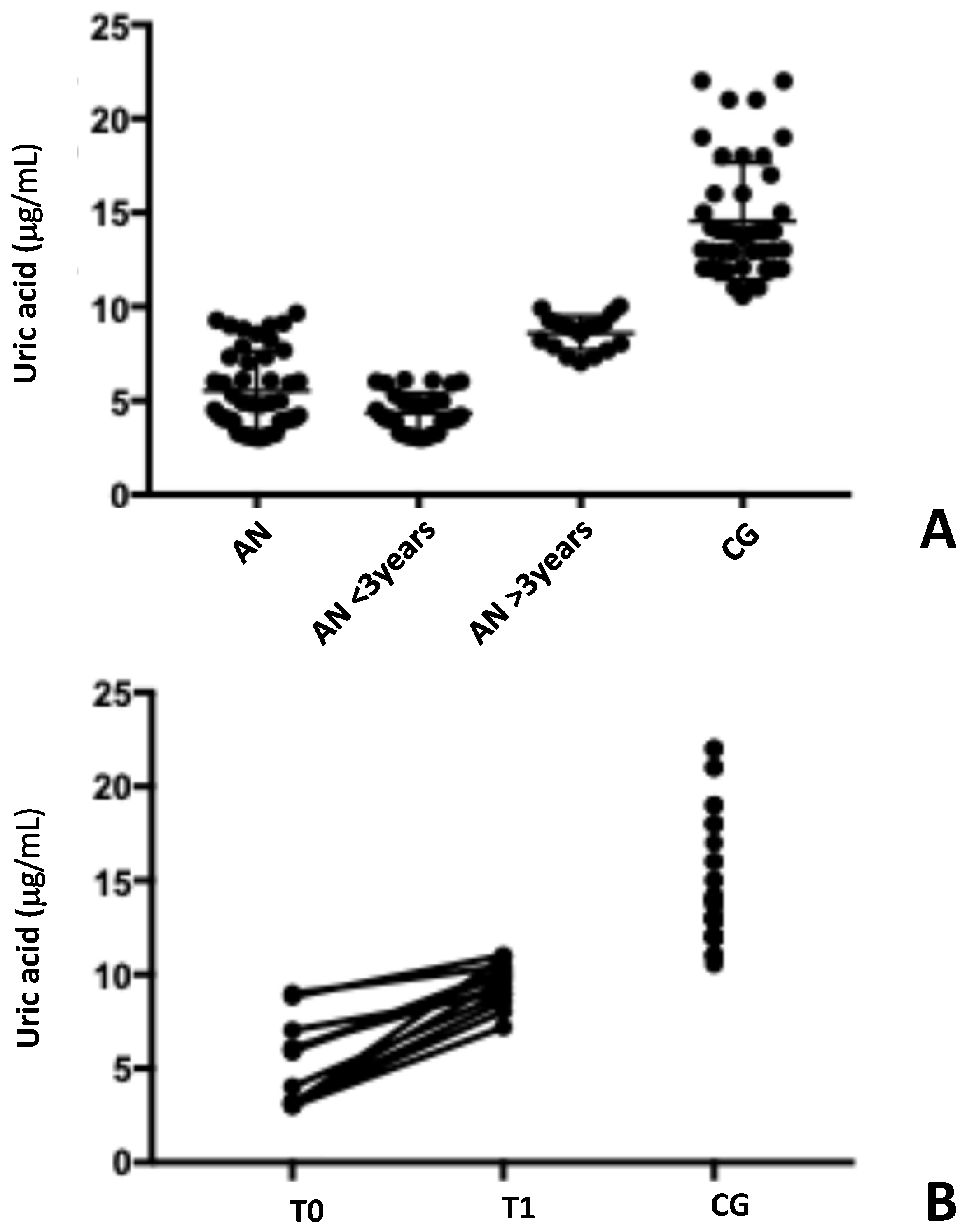
3.3. Oxidative Status Evaluation: Uric Acid and Total Oxidative Content
3.4. Investigation of a Possible Correlation Between Autoantibody Levels and Oxidative Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, B.; Uher, R.; Dragomirecka, E.; Papezova, H. Trends in hospital admissions for eating disorders in a country undergoing a socio-cultural transition, the Czech Republic 1981–2005. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2010, 45, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalski-Bednarz, S.B.; Hillert, A.; Surzykiewicz, J.; Riedl, E.; Harder, J.P.; Hillert, S.M.; Adamczyk, M.; Uram, P.; Konaszewski, K.; Rydygel, M.; et al. Longitudinal Impact of Disordered Eating Attitudes on Depression, Anxiety, and Somatization in Young Women with Anorexia and Bulimia. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, N.; Potter, B.J.; Ukah, U.V.; Low, N.; Israël, M.; Steiger, H.; Healy-Profitós, J.; Paradis, G. Anorexia nervosa and the long-term risk of mortality in women. World Psychiatry 2021, 20, 448–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escelsior, A.; Cogorno, L.; Sukkar, S.G.; Amerio, A.; Donini, L.M.; Bellomo, M.; Iervasi, E.; Amore, M.; Saverino, D. Anti-hypothalamus autoantibodies in anorexia nervosa: A possible new mechanism in neuro-physiological derangement? Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 2481–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, A.F.; Attia, E. Psychopharmacologic Management of Eating Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2022, 24, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, B.; Bartholdy, S.; Robinson, L.; Solmi, M.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Breen, G.; Schmidt, U.; Himmerich, H. A meta-analysis of cytokine concentrations in eating disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 103, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesas-Fernández, A.; Bodner, E.; Hilke, F.J.; Meier, K.; Ghoreschi, K.; Solimani, F. Interleukin-21 in autoimmune and inflammatory skin diseases. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 54, e2250075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerio, A.; Escelsior, A.; Martino, E.; Strangio, A.; Giacomini, C.; Montagna, E.; Aguglia, A.; Bellomo, M.; Sukkar, S.G.; Saverino, D. Dysfunction of Inflammatory Pathways and Their Relationship with Anti-Hypothalamic Autoantibodies in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetissov, S.O.; Déchelotte, P. The putative role of neuropeptide autoantibodies in anorexia nervosa. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2008, 11, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, D.; Mehler, P.S. Anorexia Nervosa and the Immune System-A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.M.; Magnanimi, L.M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Anorexia nervosa and autoimmune comorbidities: A bidirectional route? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amerio, A.; Escelsior, A.; Martino, E.; Strangio, A.; Aguglia, A.; Marcatili, M.; Conio, B.; Sukkar, S.G.; Saverino, D. The Association between Blood SIRT1 and Ghrelin, Leptin, and Antibody Anti-Hypothalamus: A Comparison in Normal Weight and Anorexia Nervosa. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, J.R.; Graell, M.; Navalón, A.; MacDowell, K.S.; Gutiérrez, S.; Soto, M.; Leza, J.C.; Carrasco, J.L.; Marsá, M.D. Dysfunction of inflammatory pathways in adolescent female patients with anorexia nervosa. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 96, 109727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, M.M.; Murlanova, K.; Macias, L.K.; Sabir, A.I.; O'Brien, S.C.; Bhasin, H.; Tamashiro, K.L.; Pletnikov, M.V.; Moran, T.H. Activity-based anorexia disrupts systemic oxidative state and induces cortical mitochondrial fission in adolescent female rats. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalčíková, A.G.; Tichá, Ľ.; Šebeková, K.; Celec, P.; Čagalová, A.; Sogutlu, F.; Podracká, Ľ. Oxidative status in plasma, urine and saliva of girls with anorexia nervosa and healthy controls: A cross-sectional study. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Luchini, C.; Manzato, E.; Sergi, G.; Favaro, A.; Santonastaso, P.; Correll, C.U. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Levels in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa after Oral Re-alimentation: A Systematic Review and Exploratory Meta-analysis. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2016, 24, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, A.; Matsunaga, Y.; Hayashida, K.; Takahashi, N. Role of Oxidative Stress and Ca2+ Signaling in Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 615569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeunovic Ostojic, M.; Maas, J. Anorexia nervosa and uric acid beyond gout: An idea worth researching. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 51, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, M.A. Tests based on EDF statistics. In Goodness-of-Fit Techniques; D’Agostino, R.B., Stephens, M.A., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, M.; Tsai, P.; Anderson, E.J.; Hubbard, J.L.; Gallagher, K.; Soyka, L.A.; Miller, K.K.; Herzog, D.B.; Klibanski, A. Nutrient intake in community-dwelling adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa and in healthy adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadigan, C.M.; Anderson, E.J.; Miller, K.K.; Hubbard, J.L.; Herzog, D.B.; Klibanski, A.; Grinspoon, S.K. Assessment of macronutrient and micronutrient intake in women with anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2000, 28, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveras-López, M.J.; Ruiz-Prieto, I.; Bolaños-Ríos, P.; De la Cerda, F.; Martín, F.; Jáuregui-Lobera, I. Antioxidant activity and nutritional status in anorexia nervosa: Effects of weight recovery. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2193–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ghoch, M.; Calugi, S.; Lamburghini, S.; Dalle Grave, R. Anorexia nervosa and body fat distribution: A systematic review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3895–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurel, L.; MacKean, M.; Lacey, J.H. Factors predicting long-term weight maintenance in anorexia nervosa: A systematic review. Eat. Weight Disord. 2024, 29, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldiroli, A.; La Tegola, D.; Affaticati, L.M.; Manzo, F.; Cella, F.; Scalia, A.; Capuzzi, E.; Nicastro, M.; Colmegna, F.; Buoli, M.; et al. Clinical and Peripheral Biomarkers in Female Patients Affected by Anorexia: Does the Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Affect Severity? Nutrients 2023, 15, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Syrmou, V.; Lioliopoulou, M.L.; Gkiouras, K.; Simopoulou, T.; Katsiari, C.G.; Vassilakou, T.; Bogdanos, D.P. Anorexia Nervosa in Juvenile Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A Causality Dilemma. Children 2023, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivantürk Kızılkan, M.; Kanbur, N.; Akgül, S.; Alikaşifoğlu, A. An Adolescent Boy with Comorbid Anorexia Nervosa and Hashimoto Thyroiditis. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2016, 8, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatly Latzer, I.; Lerner-Geva, L.; Stein, D.; Weiss, B.; Pinhas-Hamiel, O. Disordered eating behaviors in adolescents with celiac disease. Eat. Weight Disord. 2020, 25, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, L.; Nakano, E.Y.; Raposo, A.; Alturki, H.A.; Alarifi, S.N.; Chaves, C.; Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Romão, B. Eating Attitudes of Patients with Celiac Disease in Brazil: A Nationwide Assessment with the EAT-26 Instrument. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.M. Eating Disorders in Youth with Chronic Health Conditions: Clinical Strategies for Early Recognition and Prevention. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Wu, M.; Liang, J.; An, Z. Anorexia and bulimia in relation to ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1400713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medovic, M.V.; Jakovljevic, V.L.; Zivkovic, V.I.; Jeremic, N.S.; Jeremic, J.N.; Bolevich, S.B.; Ravic Nikolic, A.B.; Milicic, V.M.; Srejovic, I.M. Psoriasis between Autoimmunity and Oxidative Stress: Changes Induced by Different Therapeutic Approaches. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 2249834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumurcu, B.E.; Ozyurt, H.; Etikan, I.; Demir, S.; Karlidag, R. Total antioxidant capacity and total oxidant status in patients with major depression: Impact of antidepressant treatment. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 63, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolling, J.; Scherer, E.B.; da Cunha, A.A.; da Cunha, M.J.; Wyse, A.T. Homocysteine induces oxidative-nitrative stress in heart of rats: Prevention by folic acid. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2011, 11, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Lee, S.G.; Davis, C.G.; Koo, S.I.; Chun, O.K. Dietary total antioxidant capacity is associated with diet and plasma antioxidant status in healthy young adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Lim, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kwon, O. Daily nutritional dose supplementation with antioxidant nutrients and phytochemicals improves DNA and LDLstability: A double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients 2013, 5, 5218–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashayee-Khamene, F.; Hajimohammadebrahim-Ketabforoush, M.; Heidari, Z.; Yari, Z.; Karimi, S.; Saber-Firoozi, M.; Hatami, B.; Hekmatdoost, A. Dietary total antioxidant capacity in relation to disease severity and risk of mortality in cirrhosis; results from a cohort study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chung, S.J.; Floegel, A.; Song, W.O.; Koo, S.I.; Chun, O.K. Dietary antioxidant capacity is associated with improved serum antioxidant status and decreased serum C-reactive protein and plasma homocysteine concentrations. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, H.D.; Sheta, H.M.; Morillon, M.B.; Hansen, I.M. Tophaceous Gout in an Anorectic Patient Visualized by Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT). Am. J. Case Rep. 2016, 17, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirken-Heukensfeldt, K.J.; Teunissen, T.A.; van de Lisdonk, H.; Lagro-Janssen, A.L. “Clinical features of women with gout arthritis”. A systematic review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.A.; Crowe, F.L.; Appleby, P.N.; Key, T.J.; Travis, R.C. Serum uric acid concentrations in meat eaters, fish eaters, vegetarians and vegans: A cross-sectional analysis in the EPIC-Oxford cohort. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijailovic, N.R.; Vesic, K.; Borovcanin, M.M. The Influence of Serum Uric Acid on the Brain and Cognitive Dysfunction. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 828476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, M.; Fukuuchi, T.; Aoki, Y.; Mizuta, E.; Ouchi, M.; Kurajoh, M.; Maruhashi, T.; Tanaka, A.; Morikawa, N.; Nishimiya, K.; et al. Exploring the Multifaceted Nexus of Uric Acid and Health: A Review of Recent Studies on Diverse Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocco, C.; Brancia, C.; Corda, G.; Ferri, G.-L. The Hypothalamic–Pituitary Axis and Autoantibody Related Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Gonzalez, E.; Le Loc'h, G.; Al Husni Al Keilani, M.; Delvenne, V. Early Onset Anorexia Nervosa in Children Aged 8 to 12 Years: A Retrospective Study. Psychiatr. Danub. 2024, 36 (Suppl. S2), 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- Solmi, M.; Monaco, F.; Højlund, M.; Monteleone, A.M.; Trott, M.; Firth, J.; Carfagno, M.; Eaton, M.; De Toffol, M.; Vergine, M.; et al. Outcomes in people with eating disorders: A transdiagnostic and disorder-specific systematic review, meta-analysis and multivariable meta-regression analysis. World Psychiatry 2024, 23, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, S.; Pathak, A.; Dalal, V.; Paul, A.; Biswas, S. Oxidative Stress in Autoimmune Diseases: An Under Dealt Malice. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 21, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorice, M.; Profumo, E.; Capozzi, A.; Recalchi, S.; Riitano, G.; Di Veroli, B.; Saso, L.; Buttari, B. Oxidative Stress as a Regulatory Checkpoint in the Production of Antiphospholipid Autoantibodies: The Protective Role of NRF2 Pathway. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Positive | Negative | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anorexia nervosa | 48 (a) | 0 (b) | 48 |
| Control group | 6 (c) | 42 (d) | 48 |
| Total | 54 | 42 | 56 |
| Anorexia Nervosa (N = 48) | Control Group (N = 48) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (male/female) | 2/46 | 4/44 | - |
| Age (years) | 20.8 ± 9.1 | 23.1 ± 4.61 | 0.45 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 15.2 ± 1.9 | 22.3 ± 0.7 | <0.001 |
| Serum markers | |||
| IgG autoantibody to hypothalamic cells (ng/mL) | 8522 ± 1978 | 144.2 ± 283.1 | <0.001 |
| Uric acid (μg/mL) | 5.5 ± 2.1 | 14.6 ± 3.1 | <0.001 |
| TAC (μmol/L) | 399.4 ± 164.0 | 1575 ± 273.2 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amerio, A.; Martino, E.; Strangio, A.; Aguglia, A.; Escelsior, A.; Conio, B.; Sukkar, S.G.; Saverino, D. Autoantibodies, Oxidative Stress, and Nutritional State in Anorexia Nervosa. Antibodies 2025, 14, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14010001
Amerio A, Martino E, Strangio A, Aguglia A, Escelsior A, Conio B, Sukkar SG, Saverino D. Autoantibodies, Oxidative Stress, and Nutritional State in Anorexia Nervosa. Antibodies. 2025; 14(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmerio, Andrea, Eleonora Martino, Antonella Strangio, Andrea Aguglia, Andrea Escelsior, Benedetta Conio, Samir Giuseppe Sukkar, and Daniele Saverino. 2025. "Autoantibodies, Oxidative Stress, and Nutritional State in Anorexia Nervosa" Antibodies 14, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14010001
APA StyleAmerio, A., Martino, E., Strangio, A., Aguglia, A., Escelsior, A., Conio, B., Sukkar, S. G., & Saverino, D. (2025). Autoantibodies, Oxidative Stress, and Nutritional State in Anorexia Nervosa. Antibodies, 14(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib14010001











