Abstract
Urban agriculture, a dynamic multifunctional phenomenon, affects the spatial diversification of urban land use, its valorization and its governance. Literature acknowledges its contribution to the development of sustainable cities. The dimension and extent of this contribution depends significantly on the particular form and function of urban agriculture. However, the complexity of interests and dimensions is insufficiently covered by theory. This paper proposes a typology for urban agriculture, supporting both theory building and practical decision processes. We reviewed and mapped the diversity of the types of agriculture found along three beneficial dimensions (self-supply, socio-cultural, commercial) for product distribution scale and actors. We distinguish between ideal types, subtypes and mixed types. Our intention is to include a dynamic perspective in the typology of urban agricultural land use because transition processes between types are observable due to the existence of complex motivations and influences. In a pilot study of 52 urban agriculture initiatives in Germany, we tested the validity of the typology and discussed it with stakeholders, proving novelty and relevance for profiling discussions.
1. Introduction
1.1. Forms and Motivations of Urban Agriculture
The term ‘urban agriculture’ (UA) is spreading across developed and developing countries worldwide. In the Global North, it refers to a specific form of agriculture that fits the requirements of certain urban lifestyles and is adapted to basic conditions of land and landscape in urban areas [1,2]. Following Berges et al. [3] and Opitz et al. [4], we define UA as “plant and animal production on comparably small inner-city areas, where practitioners often do not have a professional education in agriculture, usually are non-profit oriented and distribute their produce along short supply chains. Examples are allotments, house gardens, balconies and increasingly, community gardens and start-up entrepreneurs such as new entrants into commercial farming. These initiatives make use of currently unused spaces, combining multiple objectives in new ways and developing new concepts and techniques” [4]. These adoptions lead in some cases to new forms of food production that can be highly independent of agro-economic site conditions like soil fertility and climate conditions. Techniques such as mobile seedbeds, the substitution of nutrients in aquaculture and the substitution of sunlight with lamps or greenhouses offer future possibilities of achieving small-scale food production in areas with high population density [5,6]. Furthermore, growing fruits and vegetables is described as a form of self-empowerment, particularly within a community, which can enhance social inclusivity [7,8,9]. Especially in areas with high population density, UA can become a driving factor for the community and connect people from different cultures and social backgrounds [10,11,12,13,14]. Though being not an innovation per se, these new forms of urban land use introduce fresh social learning processes thereby opening opportunities for working towards societal change [15]. However, UA can also be a driver for economic success, create new forms of income in urban areas such as apiculture and self-harvesting gardens and lead to new modes of recreation and work/leisure time balance. It can generate new approaches for individual self-supply and can contribute to short food-chain supply, for example, restaurants that seek marketing niches through growing salads and herbs visibly for guests and allowing full transparency of their crops [16,17,18].
Even though literature describes a wide variety of forms and purposes, some scholars highlight certain aspects of relevance for development strategies and policy discussions. Urban agriculture can be viewed in three ways: as sustainable intensification of productive land use in cities; as land-use diversification; and relatedly, often as a qualitative upgrading of land. The orientation towards productive-output is also coupled with low-input management practices. Often, organic-farming related management principles are applied [3,19]. The outreach of related land-use changes can even generate impacts on the surrounding areas. UA is frequently grounded in a critical position against agri-industrial production and its impacts [20,21]. Additional foundations are transformation, citizen empowerment and the co-creation movement [22]. UA might improve the sustainability of the local food system and its interaction with larger nested systems [23,24] through a better understanding of the complete food chain, including its organization and governance, in a socio-cultural and spatio-environmental context [25,26] and of the nexus between land, energy and water [27].
A multitude of different groups of actors are involved in urban agriculture [28] and the motivations behind their engagement is complex. The fact that the framework conditions of UA have a higher degree of independence from traditional agricultural production factors, leads to a large diversity of initiatives and activities. This diversity occurs on the level of individual interests as well as on a supra-individual level. In contrast to traditional forms, UA is regarded as a phenomenon with a broad range of direct societal impacts: methods such as home gardening [29,30], individuals farming in their leisure time [31], community gardens [32,33] and school gardens [34,35,36] range from individual self-supply to socio-cultural exchange. UA deals with many factors of social and economic life. Gardening activities within communities are described as giving potential to societal restructuring and self-improvement [37] and providing cultural (ecosystem) services. UA is discussed as an economic factor with regards to food security [38,39,40,41,42,43], which is more than food provision [44]. Municipalities’ food strategies become important drivers for innovation [45]. UA can be a driver for local economies [46] through contributing to the establishment of new business [47] and also positively affecting property values [48]. UA contributes to diversifying the city economy, which can lead to better resilience [49]. Impacts on public health [50] and on public awareness that build towards achieving sustainable and local food [51,52,53,54] are part of an economic perspective, too.
1.2. Objective and Structure of the Paper
The objective of this paper is to contribute to a better understanding of the different concepts of UA, by disentangling the complexity of the different forms and motivations behind it. In particular, we introduce a dynamic dimension resulting from transitions in individual motivation patterns and characteristics of UA properties. In order to do so, we develop a typology of UA including a dynamic dimension, which is not part of existing typologies. It also enables us to prove its validity through statistical analysis of an empirical data set and we discuss its value with stakeholders and administrators. It is assumed that such a typology can contribute to facilitating stakeholders’ and decision makers’ strategic objective setting. The paper presents the methods and materials applied in Section 2. Results are presented in Section 3: first the proposed typology and the related levels of information, secondly the empirical results and thirdly, the results of a stakeholder workshop evaluating the typology. Section 4 discusses the results with findings from other research and from an integrated perspective in the light of our objective setting. Finally we conclude with the novelty and the value our research adds for theory building and practical operationalization.
2. Theory Building and Benefits for Decision-Making
2.1. Theory Building on Urban Agriculture and the Role of Typologies
In other research fields like organization and management sciences, typologies have been described as an approach that meets the criteria of theory building [55,56]. Doty and Glick [55] argue that typologies can be seen as complex theories contributing to an improved understanding of the subject of research, in particular when connected with empirical testing linked to model development and application. Meredith [57] describes theory building as a result of a research cycle with iterative steps of description, explanation and testing. In this context, typologies are regarded as basic conceptual models which are typically mixed with other methodological approaches, like classifications, contingency, associative and functional levels propositions [58].
Beyond their value for theory building, typologies have also been developed for a direct operational purpose. With regard to practical decision processes, classification of knowledge and data is essential for the analysis, summary and communication of the complexity of ecological and socio-economic systems [59]. Land-use and land-cover classifications and typologies for example, have a well-established position in informing decision makers and planners on allocation of land use to multiple functions and needs (e.g., [60]), in facilitating the representative selection of case studies, or for reporting [59]. Typologies built upon socio-economic data have been described as suitable concepts for e.g., identifying target groups of rural development measures by allowing better understanding of the motivations and behavioral patterns of beneficiaries [61].
Meanwhile, there is a broad body of literature seeking to explain specific aspects of UA like motivations, community action, innovation and impacts, mostly based on evidence from case study analysis. However, publications that explicitly claim to contribute to theory building on UA in form of concepts and frameworks are rare.
Table 1 provides an overview of relevant typologies for UA. Those typologies either describe the relationship of UA to the three dimensions of sustainability (social, ecological, economic) [1,62,63] or are based on a distinction of existing initiatives within the wide range of UA with several relevant attributes for differentiation [6,64,65]. These typologies provide a good overview of the main reasons for UA and the main types that can be found within the rapidly spreading field of urban agriculture initiatives. However, the concentration on the existing initiatives does not include shifts between different types of UA. To include these shifts, we enhance existing typologies by including the distribution level of the produce. We therefore base the presented typology on the relevant dimensions as presented by Van der Schans & Wiskerke, Cabannes and FAO [1,62,63] with regard to the distribution. Thereby, we provide the typologies with a dynamic component that allows transitions within UA to be described based on changes in the distribution level and on the main focus of interests.

Table 1.
Typologies for Urban Agriculture (UA), Including Interests of UA and Their Relevant Features and Attributes.
2.2. Governance Issues that Could Benefit from a Typology
The term ’governance’ describes new forms of social, economic and political regulation, coordination and control in complex institutional structures in which mostly, a wide variety of public and private participants interact in different ways and forms [66,67]. As UA is a form of land use that occurs in public spaces, there are direct implications on the spatial dimension of cities and the perception of that dimension. Accordingly, UA is a relevant issue for governance and a topic on the policy and planning agenda [68,69,70,71,72]. In the ongoing discussion on spatial policies, planning and strategy development across sectors, UA is a subject well addressed to steering needs, as well as a concept that contributes to solutions that help to meet current major societal challenges (food security, climate change, ecosystem services).
UA should be within the purview of city management, as there is an expressed demand to determine the role of UA in city structure [47]. Many UA initiatives are not regulated by market systems and have a bottom-up character. Their influence on a city’s economy is recognized but at the same time rather uneven and unpredictable. Hence the role of policy makers in balancing benefits and costs of UA is significant [49]. Particularly for the USA, a diverse mix of UA strategies from policy makers is reported, ranging from attempts to stimulate economic development, to initiatives to increase food security and access, through to efforts to combat obesity and diabetes [73]. Also, a wide number of U.S. cities intend to develop urban food production for purposes of recreation, self-supply and/or profit [46]. However, the success of governance is, beside institutional factors, determined by local UA settings (e.g., the actors involved and their motivations and values, alongside various types of networks and local societal constraints with UA practices) as Cohen [74] identified in five U.S. case studies.
New tools are required to identify gaps in the spatial food system, such as mapping existing sites, locations and forms and to adapt new initiatives to sociodemographic and environmental conditions [73]. Creating and applying a typology of UA can be a first step towards handling all the different forms and characteristics of UA and determining their potential for agricultural production in a city.
Relevant dimensions for governance in this context are the distribution level of the goods produced and the specific interests of the kinds of actors involved in these initiatives [1,64]. Our assumption is that a typology can be used to sharpen the governance perspective of UA initiatives, particularly as UA proves to be multifunctional, multi-purpose and multi-actor constellation, which is implicitly related to a broad diversity of development options. Here, planning and multi-level governance has to develop consensus-oriented, multi-objective strategies. Spatial considerations, might urge prioritization of certain forms of UA for particular locations or purposes. Here the typology supports (self-) profiling of UA initiatives.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Development of a Typology
The first procedural step towards developing the typology was the description of interests and attributes. These were identified based on a previous literature review [4]. The typology was built as a conceptual model aiming to provide improved understanding of the interrelations between the interests and the main distinguishing attributes (Table 2).

Table 2.
Procedural Approach Applied for the Typology Development, Structured Along Research Steps in Framework and Theory Building.
Following Cabannes, van der Schans and Wiskerke and FAO [1,62,63] we identified three main interests. The first interest, “self-supply”, refers to UA by which actors support their own livelihoods. These activities usually do not generate money but provide food that reduces the actor’s expenses. We decided to use the term self-supply instead of subsistence to avoid confusion. Subsistence usually refers to self-production to ensure a basic standard of living. In the context of this typology, self-supply refers to an additional own production that may improve the standard of living but is not necessary to ensure it. The second interest, “socio-cultural”, refers to UA that is undertaken to restore the communal relationships between urban citizens, to raise awareness of environmental issues and to provide more experience with the food production cycle. The third interest, “commercial”, refers to market-oriented activities such as family-based micro-enterprises and larger cooperatives or producers. The products are sold commercially, directly by the producer or through intermediaries. These interests build the core of the typology.
In order to provide a typology that can be used to distinguish initiatives with similar interests, we added some of the main attributes to the typology. Related to Pearson et al. [64] we included different scales in the typology. In contrast to Pearson et al. [64] we concentrated on the distribution level, which allows us to distinguish not only by initiatives but also between similar initiatives that use a different level of distribution. Furthermore, we included the practitioners of UA to include difference in the ownership.
3.2. Empirical Test of Validity of the Typology
To verify the validity of typology we used a dataset consisting of 281 UA initiatives in Germany. Data was retrieved from the online platform Stadtacker.net (www.stadtacker.net) where initiatives can register their profile using a systematic approach and format. Since the main initiatives and the association for urban agriculture in Germany are part of the cooperation that started the database, it is popular within the urban agriculture initiatives, even if registration is voluntary. For the test of validity, we included all initiatives that were registered with a complete profile in the subcategory ‘Fields and Gardens’. The data obtained included results from comparative rankings on the relevance of social and economic aspects about the use and distribution of the goods produced, sources of income and about the legal status and the form of the initiative. We only retrieved data from self-edited and checked entries from the initiatives themselves. Since the database being developed is an ongoing process, the population of our dataset is not representative. Through the approach we used, datasets with missing values were excluded listwise, meaning that the number of remaining initiatives was limited to 52 of the registered initiatives in the database. In addition, agriculture on private land by individuals and private households is not part of the database and therefore, it is not possible to find examples for the ideal type of self-supply. However, the variety of different initiatives allows us to make estimates of distributions within the typology settings.
As proxy, variables for the interests of the initiatives the self-assessment statements of the initiatives on the relevance of social and economic issues were used. Since it is not possible to differentiate between economic interests for self-supply or market-based economic interests, we used the statement, “Do you consume all the goods you produce yourself?” as an indicator of self-supply and market-based economic interests. We assume that if an initiative consumes all the goods it produces, it cannot have any commercial interest. The variables were implemented on a five-point Likert scale, ranging from unimportant to important.
We applied a two-step cluster analysis to divide the data in different groups on a scale from purely social interests, to purely economic interests. The cluster analysis allows to group a set of objects to clusters that are homogenous within a cluster and heterogeneous to the other clusters [75]. These groups were subdivided again depending on whether they consumed the goods they produce themselves. If they consumed all the goods, we assumed self-supply, if not, we assumed a commercial interest. This approach allowed us to categorize all types of the typology except the non-sociocultural mixed type. The results of the calculations were compared with the typology according to legal status and the kind of initiative. The data analysis was conducted by using SPSS 21.
3.3. Stakeholder Workshop on the Operational Value of the Typology
In order to discuss and evaluate the operational value of the typology, we presented it at a stakeholder workshop in Berlin, Germany, in October 2014. The participants (n = 14) have the following backgrounds: urban agriculture and urban gardening advocacy organization, gardeners, public administration (urban development, nature protection), research and research funding and management, rooftop gardening and education for UA. Structured along two guiding questions: “Which types of UA are of specific relevance for Berlin?” and “How can they be supported?”, a round table discussion applying visualization methods was carried out. The question “How relevant is the presented typology of UA for your work?” was answered by setting a mark in a 5 point Likert scale (irrelevant—less relevant—neutral—relevant—highly relevant). The results were obtained through descriptive analysis.
4. Results
4.1. Typology for Urban Agriculture
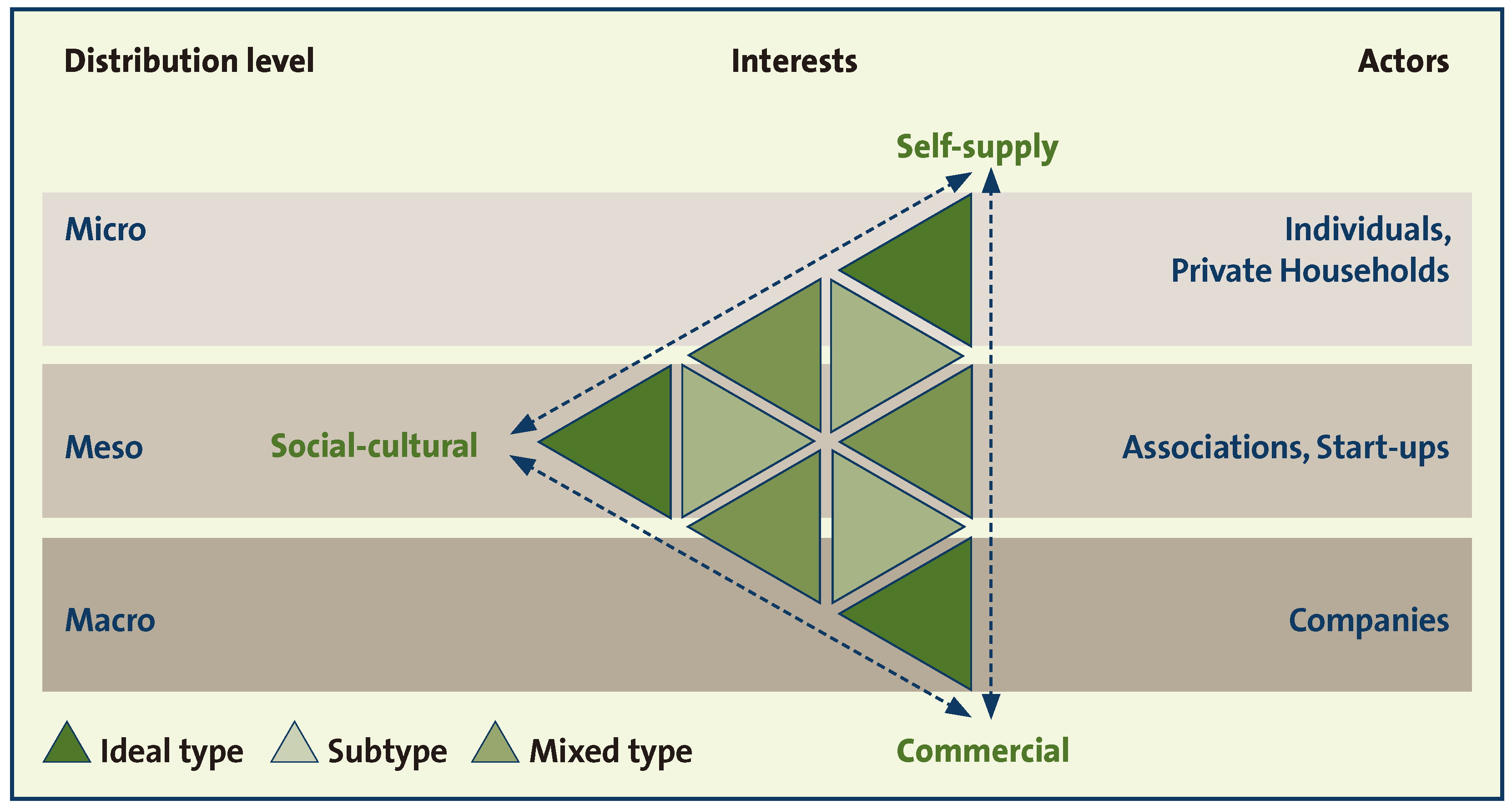
The proposed typology is based on three different attributes: the distribution level of produced goods, the actors involved and the interests behind the initiatives (see Table 2). Distribution level and actors are strongly related to each other so they create one of the criteria divided by different interests. The interests behind the initiatives are based on the main types of urban farming as presented by FAO [1] but with the distribution level, we focused more on the beneficiaries of the produced goods. An additional value of the typology can be found in the inclusion of additional intentions than generating food, like work-leisure-time balance and social communities.
For the distribution of the produced goods, we proposed three different levels [64,76]. On the micro level no distribution or circulation from the producer to other persons except nearby environments, such as relatives and friends, takes place. This level is represented mostly by individuals and private households. On the meso level, the produced goods are shared between friends and peers or sold to known consumers. The goods are circulating between a definable community and known persons on a submarket. Formal and informal associations and start-ups are the main actors involved on this level. On the macro level, the distribution of the produced goods does not refer to a specific group. On this level, the consumers are not in a defined relationship to the producers and the produced goods are part of the market. The macro level is represented by companies.
The interests and motivations behind the UA initiatives are at the center of the typology. We propose an approach that covers the scope of social and cultural (multifunctional), self-supply and commercial interest [1].
Social and cultural interests are motivations that result from the urban environment and have little or no economic incentives. The multifunctional interests can be affected by health motivations, work/leisure time balance, or social inclusion. Growing food and its consumption in a community, meeting people in leisure time and sharing knowledge on different gardening practices can be drivers for UA for individuals. These forms of social inclusion can be found in allotment gardens, gardening associations and community gardens. Another motivation can be found in cultural exchange. It appears that the production of specific agricultural products can be a driver for participation in UA initiatives or for individual crop growing. This form of motivation can refer to specific agricultural products that are not available in local grocery stores. This kind of production can be heirloom products grown from old, often local varieties, or products that are necessary for traditional cooking. Cultural gardens and school gardens often provide education about foreign growing practices.
The individual interests mainly consist of self-supply. The term self-supply in the typology includes any form of personal requirements that are based on individual interests. It can refer to pure self-supply but also to casual earnings when individuals or private households grow their own food to save money. It can also include different forms of recreation and work-leisure time balance that lead to a benefit for the individual conditions of the practitioner of UA. In this case, self-supply implies different forms of personal benefits that occur for an individual when implementing UA. These benefits can appear either as a financial benefit through savings and self-supply or as physical or mental benefits through better self-awareness or recreation measures.
Commercial interests refer to the usage of produced goods for financial benefits. These are neither social nor cultural motivations, nor interest in self-supply. The goods produced are sold to the market. In order to achieve financial success, they need to meet the demand of the local population. UA can fill gaps in niche markets like direct marketing in the city that is independent from carbon intensive transport systems and fulfills the basic ideas of sustainability. It can also refer to specific goods like honey that was produced in the city or food that is directly processed and served in a restaurant. Due to the higher density of the urban population, niche markets can exist that require agricultural products that would not be lucrative in rural areas.
4.1.1. Ideal Types
Based on the typology (Figure 1), we can identify nine different types of UA. These types can be clustered in ideal types and subtypes of each main interest and mixed-types that are distinguished by the lack of one specific interest.
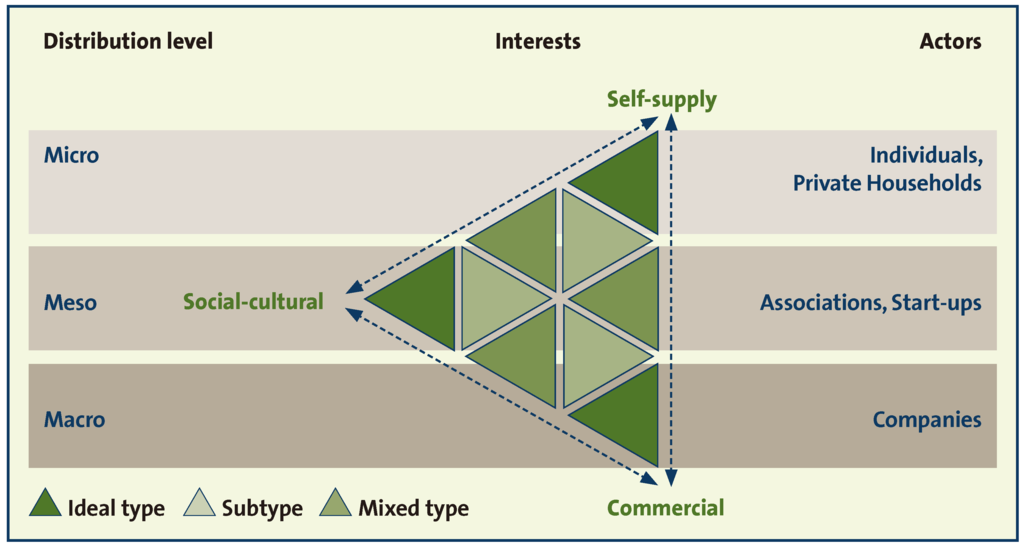
Figure 1.
Triangle graph of ideal, subtypes and mixed types of UA, according to the distribution level of the produce, the involved actors and the predominant interests.
Ideal Type: Self-Supply
Self-supply is the driver for this type of UA. Individuals and private households implement it on private land or space. The produce is consumed on a micro level, meaning that the goods remain in the household or are used by the individual producer. The goods are used for self-supply and the agricultural activities are a kind of recreation. No other individual, group or community is affected during the process of cultivating the vegetables and herbs. In many cases, the producer holds all the property rights to the land and space that is used for the urban agriculture initiative (UAI). There is no interest in using the produced goods commercially or for social or cultural exchange. Typical forms of this kind of UA are the growing of vegetables, fruits and herbs on a private balcony or in a private garden.
Ideal Type: Sociocultural
The actors in sociocultural UA initiatives are driven by the need for social inclusion, cultural exchange or educational factors. The consumption of vegetables and herbs is only a marginal part of motivation for involvement in this kind of UA. The main interests are the need for affiliation and close and friendly communication with other members of the initiative or learning to experience nature and self-awareness at school. Food is produced to be shared with the other members of the community. Gardening is more like a foundation for shared activities that are performed on communal land or is practiced to gain knowledge about cultivating food. There is lively exchange of ideas and seeds among members and mutual support. Typically, formal or informal associations and educational institutions implement this kind of UA. Community and cultural gardens focused on community building and social exchange, as well as school gardens and gardens at adult education centers belong to this type of UA.
Ideal Type: Commercial
Market-based and for-profit interests define the commercial ideal type. Motivation does not come from the need for social or cultural exchange and there is no intention to use the goods produced for self-supply. The goods are cultivated on private land and sold to a professional market made up of anonymous consumers. The drivers for the producers are strictly financial interests, either as the owner of the UA initiative or as an employee. A typical form of these initiatives is private companies that produce goods for a market. These markets can be niche conventional supermarkets or markets like specific restaurants selling local urban-grown food.
4.1.2. Subtypes
In addition to these ideal types, we want to introduce subtypes that are highly related to the ideal types, but imply some additional characteristics that are not part of the ideal types (see Figure 1).
Subtype: Self-Supply
This type is defined by non-commercial motivations and a lack of social or cultural interests. The incentives for the UAIs can be found in self-supply, in a sense of the importance of homegrown food and work-leisure time balance. In contrast to the self-supply ideal type, actors who implement this type of UA do not grow their produce on their own private land. They are part of a formal or informal association that provides the actors with land or space. The interaction between the participants of this form of UA is based on a formal structure. There are no common vegetable beds or collective activities. Producers keep their goods for private consumption or trade their goods for fruits, vegetables or seeds with other gardeners in the UAI. Typical forms of this kind of UAI are allotment gardens where collective activities of members are less relevant compared to active, community-action-centered forms.
Subtype: Sociocultural
This type of UA is defined by a lack of interest in economic factors, be they financial or for the purposes of self-supply in terms of savings. For the participants, the social and cultural exchanges are what drives them to join these initiatives. In contrast to the sociocultural ideal type, the production of goods has a higher value for the operators. While the social and cultural exchange is of significant importance, the chance to grow one’s own food is an additional and important purpose of the activity. Work/leisure time balance and the feeling of self-empowerment are also central motivations. These UAIs may intend to promote social inclusion and cultural exchange but these are not the only reasons for joining them. The produced goods are cultivated for collective consumption, but can also be consumed on an individual basis. Community gardens with loose social activities are part of this subtype.
Subtype: Commercial
The commercial subtype is based on pure financial interests, in line with the commercial ideal type. The goods are produced for the market. In contrast to the commercial ideal type, distribution of the agricultural products does not only take place at the macro level. Direct marketing in a shop or at a weekly market is a necessary way to sell the products. These forms of distribution lead to closer contact with a definable group of consumers, building the foundation for financial earnings from UA. Initiatives such as start-ups or organic producers that are part of community-supported agriculture (CSA) or self-harvesting gardens are typical forms of this subtype.
4.1.3. Mixed Types
Besides the ideal types and the associated subtypes we can find three additional types that are defined by a combination of two major interests and by the lack of a third interest. These types are named according to the lacking interest.
Non-Commercial Mixed Type
The non-commercial mixed type combines the needs for social and cultural exchange with the interest of growing food for own consumption and work-leisure time balance. In this type, both interests come together. The driver for joining such an initiative might be an interest in new methods of growing or a demand for uncommon vegetables or herbs for a specific cultural cuisine. In this kind of initiative, the produce is used for self-supply but also swapped among the operators. Forms of this UA type include gardens where members keep most of their produce for their own consumption but also define themselves by community activities. The absence of commercial interests is the key feature.
Non-Self-Supply Mixed Type
The non-self-supply mixed type combines commercial and sociocultural aspects. In this type, the producers may have commercial interests but they also have social or cultural ones. The actors here are social entrepreneurs, companies with a high level of social responsibility and start-ups trying to establish an ongoing enterprise from a community-based UA. The food produced is sold on markets at the meso and macro levels and is cultivated on public or private land or space. The enterprises are community-based and organize social events to keep in touch with the consumers. Backyard parties, seminars about sustainable gardening and other forms of social and cultural events are organized to keep in touch with some consumers and to achieve social and cultural goals. City farms and self-harvesting gardens with a broad educational program belong to this mixed type.
Non-Sociocultural Mixed Type
The UAIs in this mixed type have no sociocultural interests. They are defined by economic motivations. The producer offers special kinds of products to a well-defined circle of consumers. Forms that can be found in this mixed type include beekeepers selling honey that they had formerly used for self-supply purposes. Another example might be farmers who start to rent out land and offer a service to help gardeners to cultivate this land. Entrepreneurs attempting to establish new innovative forms of UA that sell goods to peers and known persons belong to this type of UA. Direct marketing and a larger circle of peers have increased the number of consumers and buyers. New forms of enterprises, such as self-harvesting gardens without an educational program, belong to this type of UAI.
4.1.4. Dynamics within Urban Agriculture
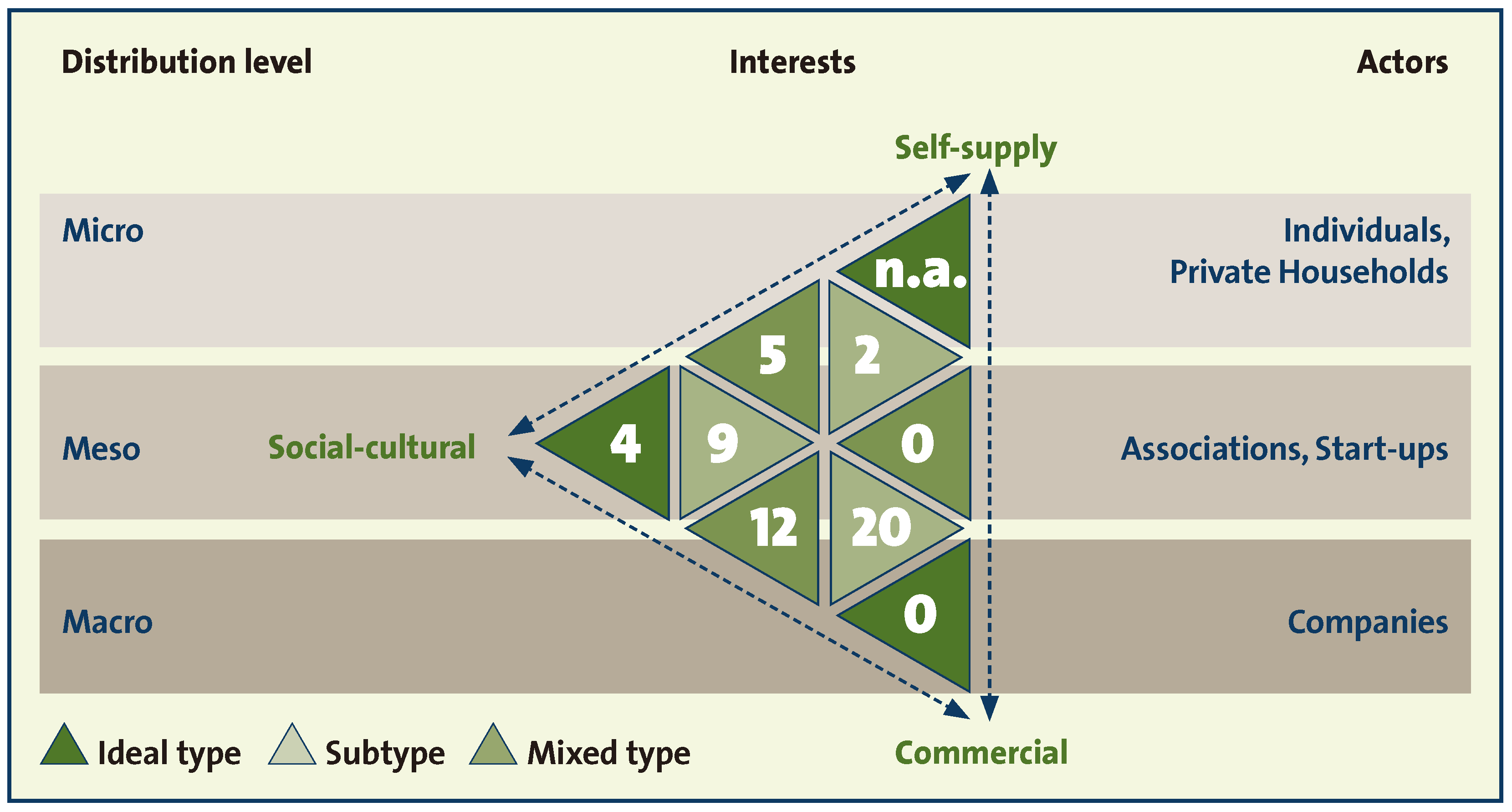
Besides the different types of urban agriculture defined by the three main interests, the scale level of distribution and the actors mentioned above, the typology also includes dynamics between these types. In Figure 2, these dynamics are represented by the arrows between the ideal types. Within the typology, we can distinguish three spheres: (1) The non-commercial sphere; (2) the non-self-supply sphere; (3) the commercial sphere, which is based on neither social nor cultural interests. The transitions within these spheres are just small shifts between the different types of urban agriculture. We assume that changes usually occur between direct neighbors in the typology. As an example for the transition within the non-commercial sphere, individuals who start agriculture on their balcony might join an allotment garden to expand their activities and benefit from a higher value of recreation. On the other hand, as an example for the transition within the commercial sphere, individuals such as apiculturists who produce honey for themselves and their friends could start selling honey to local markets or on farmers markets to obtain casual earnings and move within the distribution level from meso to macro and from the self-supply subtype to the commercial subtype.
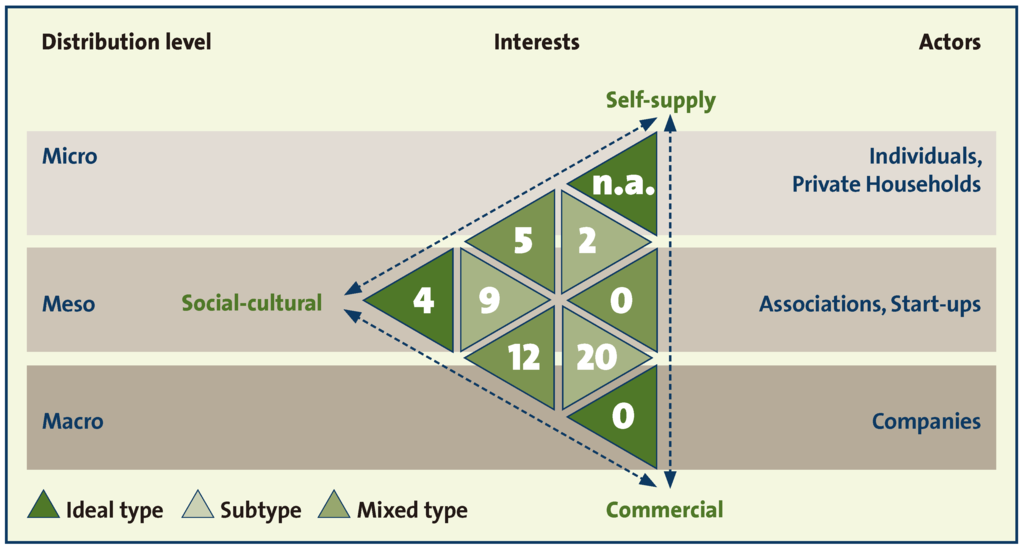
Figure 2.
Calculated frequency distribution of urban agriculture types in the sample of German UA initiatives retrieved from Stadtacker.net (n = 52).
4.2. Empirical Test of Validity
Pilot Study
For the test of validity we used a sample of 52 initiatives on stadtacker.net. We conducted a two-step cluster analysis based on variables for the social and economic relevance of the initiative. The analysis indicates a four-cluster solution for our approach. The silhouette measure of cohesion and separation is 0.8 and indicates very satisfying results [75]. The results show four clusters that differentiate the importance of social and economic issues, according to the self-assessment feedback in the stadtacker.net profile (Table 3). Cluster one is purely focused on social issues and represents the ideal sociocultural type. In the dataset, this cluster represents 8.2% of the population. In cluster two, social relevance is predominant and economic issues are less relevant. According to the typology, this cluster would represent the sociocultural subtype. Cluster three shows a slight predominance of social issues but also indicates commercial interests. Considering that the statements of cluster two represent the overall mean of the total number of answers, this cluster can be defined as a mixed type between social and commercial interests. Cluster four represents commercial subtypes with an overrepresentation of economic issues but also with some social interests.

Table 3.
Results of Two-Step Cluster Analysis Using Variables for Social and Economic Relevance.
In the next step, these clusters were combined with the variable for self-consumption of produced goods. If members of the initiatives stated that they consumed all goods by themselves, we assumed that there is no market interest, so that economic interests lead to interests in self-supply. Following this assumption, these initiatives were transferred to the non-economic sphere, while the other initiatives constitute the non-self-supply sphere. Using this approach resulted in 52 initiatives divided into six types of the typology. The social-cultural ideal type is represented by four initiatives, the social-cultural subtype by nine, the commercial subtype by 20 and the subsistence subtype by two initiatives. The mixed types are represented by five initiatives in the non-commercial mixed type and by 12 initiatives in the non-self-supply mixed type. The self-supply ideal type is not part of the database. The data did not contain an initiative belonging to the commercial ideal type. Thus our approach did not allow us to identify any representative for the non-sociocultural mixed type; we can only assume that some initiatives of the commercial subtype could also belong to this mixed type (Figure 2).
The validity of these results was checked against the variable for sources of income. No initiative in the non-commercial sphere sells produced goods and no initiative in the non-self-supply sphere stated self-supply as a source of income.
To test the validity of the typology in this real-world approach, we mapped the legal status and the self-designation of the initiatives with the calculated types and compared them to the typology. Table 4 shows the frequency distribution. Social ideal and subtype consist of registered associations and other non-registered initiatives. The majority of the initiatives in both cases are community gardens. The commercial subtype consists of registered associations and one limited company that mainly manages self-harvesting sites.

Table 4.
Mapping of Legal Status and Self-Designation to Calculated Types with IT = Ideal Type, ST = Subtype and MT = Mixed Type.
4.3. Operational Value for Stakeholders
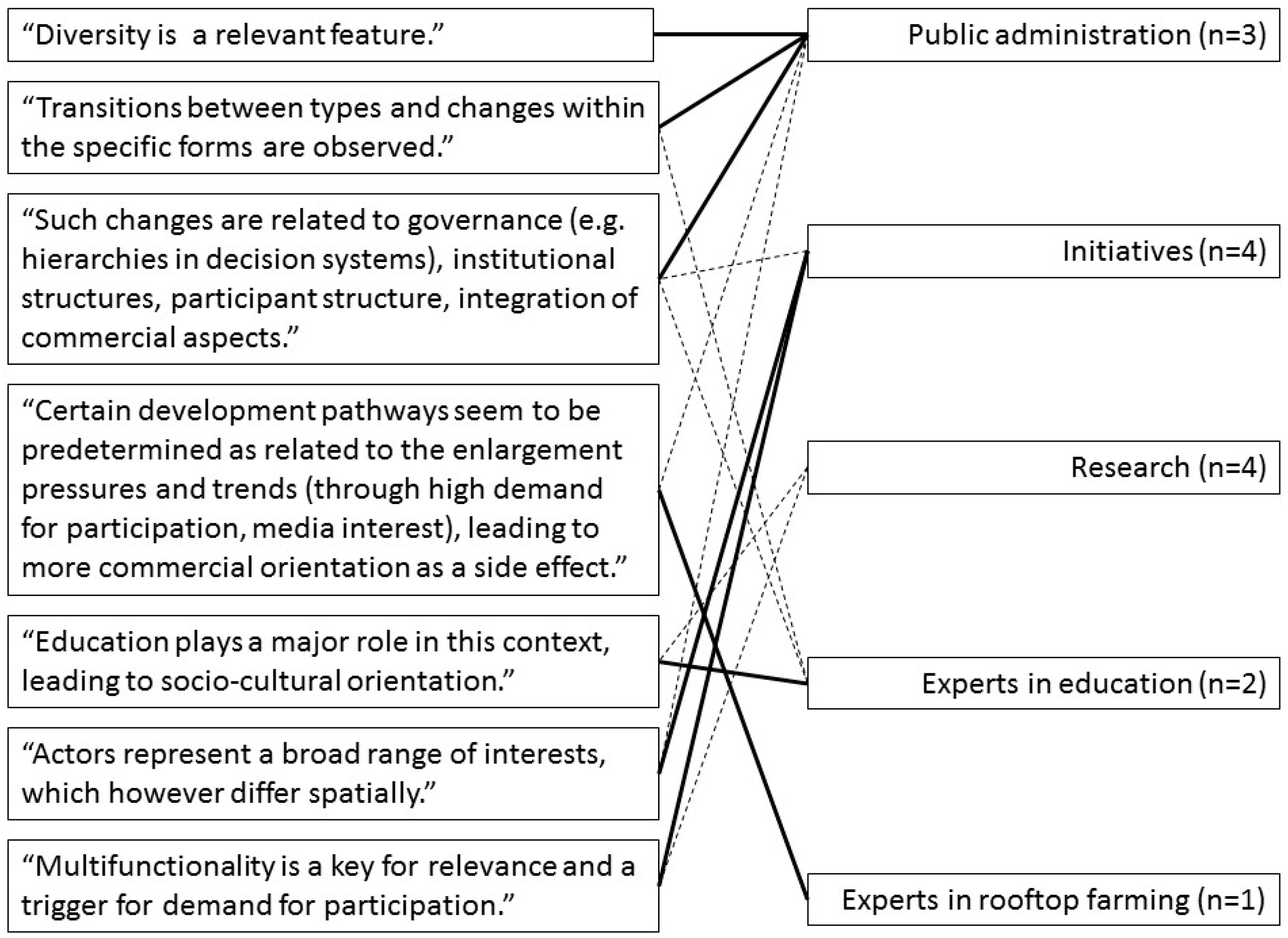
The key statements by the participants of the stakeholder workshop in Berlin regarding the questions: “Which types of UA are of specific relevance for Berlin from your point of view?” and “How can they be supported?” are summarized in Figure 3.
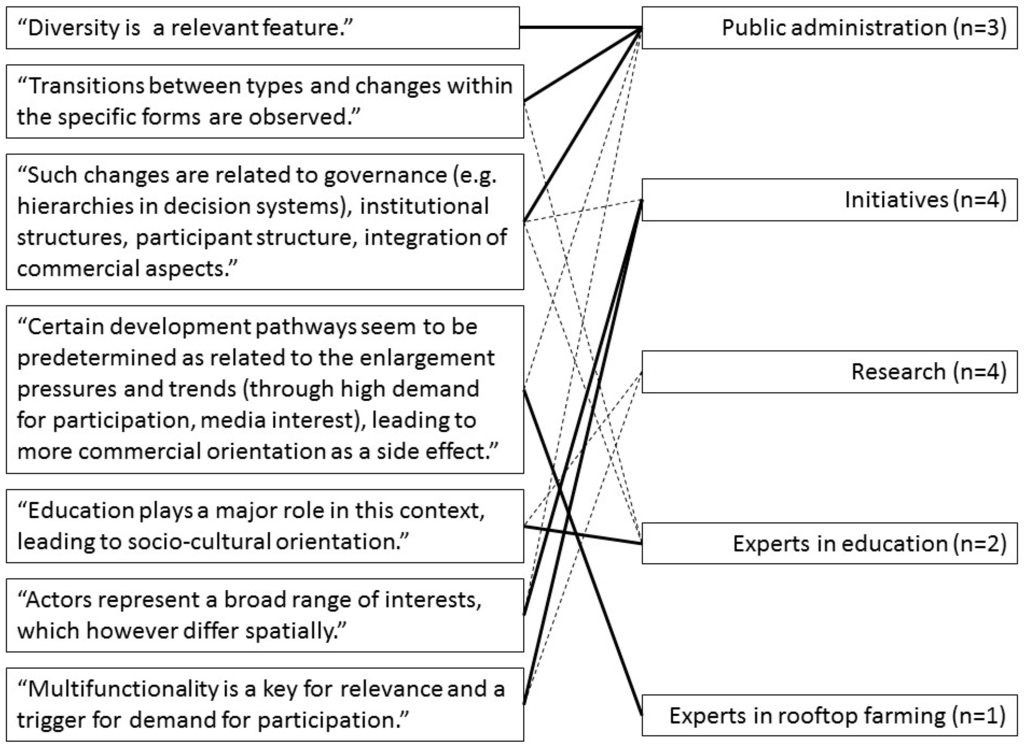
Figure 3.
Statements from the stakeholder workshop. Solid lines connect the statements to the original contributor of that statement, dotted lines represent groups who confirmed and expanded on the statement.
All types were assessed as relevant by the stakeholders. The existence of different types and of transitions between them was confirmed by observation and experience, e.g., that socially motivated people move from cooperation in community gardens to allotment gardens and hence contribute to changing the primary self-supply orientation of this gardening type.
It was discussed that the relevance of a certain type is not synonymous with the level of demand for it. Therefore, the existence of waitlists is not considered an appropriate indicator. Demand is neither specifically related to social milieus or to the abundance of available spaces, though preferences for inner-city locations exist. Co-creation of urban green and urban life is agreed to be a central motivation of many practitioners. The diversity of urban society is reflected in the diversity of the UA types. The typology should not be used to set socio-cultural benefits off against commercial ones in the sense of competiveness. Accordingly it should not be applied for funding preferences, but rather should consider whether institutional ties and individual concepts are convincing: “Basically the fit to the plot of land is the nucleus.”
The questions: “How relevant is the presented typology of UA for your work?” resulted in comparably homogeneous medium-ranked assessments, which indicate a limited direct operational relevance. In contrast to participants from academia who clearly supported the relevance, for both groups of actors from practice (administration and stakeholders), the relevance of the typology was evaluated as relevant (60%) or less relevant (40%).
5. Discussion
Aiming at sustainability, implementing new forms of governance and the commitment to apply organic farming principles belong to the fundamental communality of new developments within urban agriculture [3]. Though explicitly recognizing its complexity, up to now this phenomenon of increasing public and scientific perception is either discussed against the background of its forms or its functions. With the development of a typology for UA we pursued a twofold strategy: to improve the understanding of UA and to provide an approach with relevance for operational decision making for stakeholders, planners and policymakers. Therefore, with an approach that takes the multiple features as a given concept, elaborates on the relevant dimensions and contributes in a structured way towards a typology, we believe we have made a novel contribution to theory building on UA. The basic requirements for theory building according to Dubin [77] have been addressed as follows: The typology allows prediction or increased understanding by integrating the views of multiple scales and actors, as well as interests and motivations. With this, the typology also includes attributes or variables and their interactions. The typology avoids inclusion of ‘composite’ variables by breaking down the attributes of interests and motivations into the clearly defined variables of self-supply, socio-cultural and commercial as also found by other authors [1,62,63]. An important aspect of the typology is the dynamic component, which allows allocation of specific types representing stages of shifts between types, which are typical for the multi-objective orientation of the phenomenon [8,11,13]. Finally, the typology includes boundary criteria which are stated in the definition of UA in the introduction, following Berges et al. [3] and Opitz et al. [4]. In these boundaries the proposed typology makes a relevant distinction from other existing typologies of UA. In line with Opitz et al. [4], we regard professional farming, also when located in or associated with urban areas, as being beyond the boundaries of the definition of UA underlying this typology. We assume an urban context as conditional. So, we define the operational scope of our contribution in a more limited way than the broader FAO definition [1]. These boundaries theoretically separate established forms of agriculture with defined operational and steering scopes and instruments from the new and highly informal phenomenon of UA.
In typology development, conceptual model building and empirical testing are two steps. In their interrelated and if possible, iterative nature both steps are essential to prove the validity of a typology and give evidence for adaptations. The empirical grounding of the typology was carried out based on a database of German UA initiatives, obtained from an online platform, which had been established within a concerted activity between a research project and several advocacy organizations for UA since 2010 [3]. As system boundaries are identical with the above-mentioned ones and in addition, an underrepresentation of private and traditional allotment gardens is recorded, this limitation has to be regarded critically when discussing the reliability of the empirical pilot study results as a test of validity. Nevertheless, most of the common initiatives that were described by other authors could be found in the database and be assigned to a matching type [9,26,34,65]. The advantage of this approach can be seen in the fact that every initiative is part of the result. Through this, we can estimate if the classification of each initiative fits to the type we defined during the developing process of the typology. On the other hand, the sample size is limited and includes only initiatives in Germany. The figures shown in Figure 2, based on a sample size of 52 initiatives only, definitely should not be understood as a statement of frequency distribution of the different types and subtypes within UA in general or in German UA initiatives specifically. Yet, the result is presented to provide evidence for the applicability of the typology to the real world.
The latter was discussed with stakeholders from UA practice, associations, public administration and research in Berlin. To qualify this, here the non-representativeness and limited number of participants (n = 14) should also be noted. Since all stakeholder came from Berlin, we cannot make statements about the perception in other urban areas. Discussions with stakeholders strengthen the assumption that the typology is useful in identifying different groups of UA initiatives and in clarifying the field of UA with its huge diversity. A lesson learnt from the stakeholder workshop is that the typology can be more than an instrument that facilitates grouping or understanding. It can be seen as tool for guiding discussions towards clarifying roles. Limited is its feasibility as a direct support for daily work processes of those who take decisions related to different forms of UA and their requirements; the developers of the typology had initially assumed that this would be an application. In the workshop the stakeholders highlight the high commitment towards ensuring diversity as a major strategy and reject the usability of the typology for influencing spatial or group targeted priority setting in planning, decision and policy making. We nevertheless recommend that the typology should be tested in a practical context for discussion and profiling purposes. One reservation towards applying the typology as a planning tool was seen in the risk of it leading to a standardization of requirements (e.g., priority for access to gardening spaces) and development pathways that are on a second level agenda, e.g., towards commercialization. The system boundaries (as described above) had been introduced and accepted by the stakeholders. However, one criticism is that the categorization lacks definition and accuracy, particularly with regards to its grounding in economic theory, which might not take the sharing economy into account, which is at least part of the theoretical pillars of the bottom-up and transition movements that UA advocates perceive themselves to be part of. System boundaries also fail to refer to urban-rural interactions, such as the positive impacts of UA on rural viability.
Furthermore, stability over time is a key prerequisite for a typology. Institutional arrangements or governance instruments like land-use regulations may guarantee a certain permanence of urban agricultural land use or its orientation. However, the suggested typology seems according to its intentions to be capable of reflecting the evidence for multidimensionality and for transitions in individual motivation pattern and characteristics of UA properties. Though established from a developed countries perspective, it would be worthwhile examining whether this typology holds valid and provides operational value for developing countries in practice as well as in theory. Shifts between types and subtypes in developing countries can be expected to be observed or demanded from distinct development strategic perspectives to those in the global North.
6. Conclusions
Based on a review of the growing field of publications on UA, which exhibits a large complexity of new emerging forms, actors, motivations and interests, we identified the lack of a typology of UA, which is specifically related to the system borders of this phenomenon. This paper presents the typology development following a structured approach, aimed at contributing to better understanding of and theory building on UA, as well as to its application contexts of decision support. The typology divides the field of UA into different types of initiatives based on usage of produced goods and on the actors and their interests. By forming aggregated types of initiatives, a better understanding of the diversity that occurs within urban agriculture is possible. The typology also provides information about the different scales in which actors in the different types are involved: the micro, meso and macro levels. As the concept of UA is increasingly discussed in the context of food security or urban resilience, the integration of this information level makes sense.
A novelty and added value of the typology lies in the fact that the dimensions of multifunctionality which are typical for existing forms can be located within the typology. The validation results in terms of abundance and distribution of the different legal statuses and forms of initiatives amongst the different types can be seen as an indication for the typology’s usability. Also the indicators we used yielded a result that is in line with our prior estimates.
In a workshop with stakeholders and officials from administration that tested the operational value of the typology, it mainly proved its value as a tool for leading informed discussion. This was particularly evident from observations and interpretations of sub-types and mixed types, indicating that forms in which multiple interests coexist prevail. Contrary to our assumption that the typology would be applicable in the context of policy intervention that seeks high effectiveness through clear profiles of UA types related to policy objectives, we learned that there is a large consensus in appreciating diversity and allowing for broad acknowledgement. Therefore, we mainly see the typology as a contribution to theory on UA. The first results indicate its validity for consideration in analytical frameworks and encourage its application in a larger empirical context.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the time and effort that the editor and reviewers have taken to comment on our paper and we want to thank them for their useful suggestions concerning our manuscript. Funding from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany (BMBF) has supported this research carried out within the project INNSULA (funding code FKZ 16I1623). The Leibniz Centre for Agricultural Landscape Research (ZALF) further financially supported the work on this article. ZALF is institutionally funded by the Federal Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Consumer Protection (BMELV) and the Ministry for Science, Research and Culture of the State of Brandenburg (MWFK).
Author Contributions
Thomas Krikser and Annette Piorr conceived and designed the data analysis, and carried out the literature review; Thomas Krikser performed the data analysis and developed the typology; Annette Piorr contributed the governance perspective and the discussion. Regine Berges and Ina Opitz organized the stakeholder workshop.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| UA | Urban Agriculture |
| UAI | Urban Agriculture Initiative |
| CSA | Community-Supported Agriculture |
| IT | Ideal Type |
| SD | Subtype |
| MD | Mixed Type |
References
- FAO. Agricultural Management, Marketing and Finance Occasional Paper 19. Available online: ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/010/a1471e/a1471e00.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Mougeot, L.J.A. Urban Agriculture: Definition, Presence and Potentials and Risks. Growing Cities Growing Food: Urban Agriculture on the Policy Agenda: A Reader on Urban Agriculture; Bakker, N., Dubbeling, M., Guendel, S., Sabel Koschella, U., de Zeeuw, H., Eds.; DSE: Feldafing, Germany, 2001. Available online: http://www.ruaf.org/sites/default/files/Theme1_1_1.PDF (accessed on 19 February 2015).
- Berges, R.; Opitz, I.; Piorr, A.; Krikser, T.; Lange, A.; Bruszewska, K.; Specht, K.; Henneberg, C. Urbane Landwirtschaft—Innovationsfelder für die nachhaltige Stadt? Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung (ZALF) e. V.: Müncheberg, Germany, 2014. Available online: http://project2.zalf.de/innsula/downloads/Berges%20et%20al%202014%20Urbane%20Landwirtschaft%20%E2%80%93%20Innovationsfelder%20f%C3%BCr%20die%20nachhaltige%20Stadt.pdf (accessed on 13 February 2015).
- Opitz, I.; Berges, R.; Piorr, A.; Krikser, T. Contributing to food security in urban areas: Differences between urban agriculture and peri-urban agriculture in the Global North. Agric. Hum. Values. 2016, 33, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, K.; Siebert, R.; Hartmann, I.; Freisinger, U.; Sawicka, M.; Werner, A.; Thomaier, S.; Henckel, D.; Walk, H.; Dierich, A. Urban agriculture of the future: An overview of sustainability aspects of food production in and on buildings. Agric. Hum. Values. 2013, 33, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, P.A. Room for urban agriculture in Rotterdam: defining the spatial opportunities for urban agriculture within the industrialized city. In Sustainable Food Planning: Evolving Theory and Practice; Viljoen, A., Wiskerke, J.S.C., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers Books: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 533–546. [Google Scholar]
- Alkon, A. Paradise or pavement: The social constructions of the environment in two urban farmers' markets and their implications for environmental justice and sustainability. Local. Environ. 2008, 13, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.A. Community resilience and contemporary agri-ecological systems: Reconnecting people and food, and people with people. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2008, 25, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okvat, H.A.; Zautra, A.J. Community gardening: A parsimonious path to individual, community, and environmental resilience. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2011, 47, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonacich, E.; Alimahomed-Wilson, J. Confronting racism, capitalism, and ecological degradation: Urban farming and the struggle for social justice in black Los Angeles. Souls 2011, 13, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, L. Diversity and connections in community gardens: A contribution to local sustainability. Local. Environ. 2004, 9, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyson, T.A. Civic agriculture and community problem solving. Cult. Agric. 2005, 27, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldivar-Tanaka, L.; Krasny, M.E. Culturing community development, neighborhood open space, and civic agriculture: The case of Latino community gardens in New York City. Agric. Hum. Values. 2004, 21, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaline, K.; Hunold, C. Urban agriculture and ecological citizenship in Philadelphia. Local environment. Int. J. Justice. Sustain. 2010, 15, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, I.; Specht, K.; Berges, R.; Siebert, R.; Piorr, A. Toward sustainability: Novelties, areas of learning and innovation in urban agriculture. Sustainability 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, K.R.; Cowee, M.W. Direct marketing local food to chefs: Chef preferences and perceived obstacles. J. Food. Distrib. Res. 2009, 40, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Inwood, S.M.; Sharp, J.S.; Moore, R.H.; Stinner, D.H. Restaurants, chefs and local foods: insights drawn from application of a diffusion of innovation framework. Agric. Hum. Values. 2009, 26, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, R.J.; Westfall, S.J. How the sustainable food movement has created the new farm to table industry. Am. Soci. Bus. Behav. Sci. 2011, 7, 66–78. [Google Scholar]
- Lovell, S.T.; DeSantis, S.; Nathan, C.A.; Olson, M.B.; Méndez, V.E.; Kominami, H.C.; Erickson, D.L.; Morris, K.S.; Morris, W.B. Integrating agroecology and landscape multifunctionality in Vermont: An evolving framework to evaluate the design of agroecosystems. Agric. Sys. 2010, 103, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.A.; Nicholls, C.; Funes, F. The Scaling up of Agroecology: Spreading the Hope for Food Sovereignty and Resiliency; Sociedad Científica Latinoamericana de Agroecología (SOCLA), 2012; pp. 1–20. Available online: http://futureoffood.org/pdfs/SOCLA_2012_Scaling_Up_Agroecology_Rio20.pdf (accessed on 13 February 2015).
- Sonnino, R.; Marsden, T. Beyond the divide: Rethinking relationships between alternative and conventional food networks in Europe. J. Econ. Geogr. 2006, 6, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, V.E.; Bacon, C.M.; Cohen, R. Agroecology as a transdisciplinary, participatory, and action-oriented approach. Agroecol. Sustain. Food. Sys. 2013, 37, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Dalgaard, T.; Hutchings, N.; Porter, J.R. Agroecology, scaling and interdisciplinarity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 100, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, B.; Berardi, G.; Green, R. Resilience in agriculture: Small-and medium-sized farms in northwest Washington State. Agroecol. Sustain. Food. Syst. 2013, 37, 316–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, C. Social embeddedness and relations of regard: Alternative ‘good food’ networks in south-west Ireland. J. Rural. Stud. 2003, 19, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nost, E. Scaling-up local foods: Commodity practice in community supported agriculture (CSA). J. Rural. Stud. 2014, 34, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repp, A.; Weith, T. Building bridges across sectors and scales: exploring systemic solutions towards a sustainable management of land—Experiences from 4th year status conference on research for sustainable land management. Land 2015, 4, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veenhuizen, R. Cities Farming for the Future—Urban Agriculture for Green and Productive Cities; RUAF Foundation, IDRC and IIRR Publishing: Silang, Philippines, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Comstock, N.; Dickinson, L.M.; Marshall, J.A.; Soobader, M.; Turbin, M.S.; Buchenau, M.; Litt, J.S. Neighborhood attachment and its correlates: Exploring neighborhood conditions, collective efficacy, and gardening. J. Environ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortright, R.; Wakefield, S. Edible backyards: A qualitative study of household food growing and its contributions to food security. Agric. Hum. Values. 2011, 28, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delind, L.B.; Bingen, J. Place and civic culture: re-thinking the context for local agriculture. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics. 2008, 21, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, M.P. Growing what you eat: Developing community gardens in Baltimore, Maryland. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlager, L.; Smith, C. Beliefs, knowledge, and values held by inner-city youth about gardening, nutrition, and cooking. Agric. Hum. Values. 2007, 24, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, D. The child in the garden: An evaluative review of the benefits of school gardening. J. Environ. Educ. 2009, 40, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, E.J. The effects of school gardens on students and schools: Conceptualization and considerations for maximizing healthy development. Health. Educ. Behav. 2007, 34, 846–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skelly, S.M.; Bradley, J.C. The growing phenomenon of school gardens: Measuring their variation and their effect on students' sense of responsibility and attitudes toward science and the environment. Appl. Environ. Educ. Commun. 2007, 6, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudup, M.B. It takes a garden: Cultivating citizen-subjects in organized garden project. Geoforum 2008, 39, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colasanti, K.J.A.; Hamm, M.W. Assessing the local food supply capacity of Detroit, Michigan. J. Agric. Food. Syst. Commun. Dev. 2010, 1, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, P.M.; Mullinix, K.; Fallick, A.; Harcourt, M. Agriculture on the edge: strategies to abate urban encroachment onto agricultural lands by promoting viable human-scale agriculture as an integral element of urbanization. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2010, 8, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, P.; DeLiberty, T.L. Local food practices and growing potential: Mapping the case of Philadelphia. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, R.; Gallant, E.; Patel, S.; Michalak, M.; Bunch, M.; Schaffner, S. Could Toronto Provide 10% of its fresh vegetable requirements from within its own boundaries? Matching consumption requirements with growing spaces. J. Agric. Food. Systs. Community Dev. 2010, 1, 105–127. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf, S.S.; Widener, M.J. Growing Buffalo’s capacity for local food: A systems framework for sustainable agriculture. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, C.R.; Axmann, P.; Vogl-Lukasser, B. Urban organic farming in Austria with the concept of Selbsternte (’self-harvest‘): An agronomic and socio-economic analysis. Renew. Agric. Food. Syst. 2004, 19, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierand, P. Stadtentwicklung Mit Dem Gartenspaten; Selbstverlag: Dortmund, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- EU SCAR. Agricultural Knowledge and Innovation Systems in Transition – A Reflection Paper. 2012. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/research/bioeconomy/pdf/ki3211999enc_002.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2015).
- Grewal, S.S.; Grewal, P.S. Can cities become self-reliant in food? Cities 2012, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.; Maconachie, R.; Binns, T.; Tengbe, P.; Bangura, K. Meeting the urban challenge? Urban agriculture and food security in post-conflict Freetown, Sierra Leone. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 36, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Voicu, I.; Been, V. The effect of community gardens on neighboring property values. Real Estate Economics. 2008, 36, 241–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, R. The Impact of Urban Agriculture on the Household and Local Economies. 2000. Available online: http://wentfishing.net/farmlit/Theme3.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2015).
- Brown, K.H.; Jameton, A.L. Public health implications of Urban Agriculture. J. Public. Heal. Polic. 2000, 21, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, M.K.; Mellor, J.; Crane, L. Buying local food: Shopping practices, place, and consumption networks in defining food as “Local”. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2010, 100, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagan, R. Direct Marketing: Towards sustainable local food systems? Local. Environ. 2008, 13, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerton, S.; Sinclair, A.J. Buying local organic food: A pathway to transformative learning. Agric. Hum. Values. 2010, 27, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfang, G. Avoiding Asda? Exploring consumer motivations in local organic food networks. Local. Environ. 2008, 13, 187–201. [Google Scholar]
- Doty, D.H.; Glick, W.H. Typologies as a unique form of theory building: Toward improved understanding and modelling. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1994, 19, 230–251. [Google Scholar]
- O´Raghallaigh, P.; Sammon, D.; Murphy, G. Theory-building using typologies—A worked example on building a typology of knowledge activities for innovation. In Bridging the Socio-Technical Gap in Decision Support Systems; Respício, A., Adam, F., Phillips-Wren, G.E., Teixeira, C., Telhada, J., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 371–382. [Google Scholar]
- Meredith, J. Theory building through Conceptual Methods. Int. J. Oper. Product. Manag. 1992, 13, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N. Foundations of Social Research; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Hazeu, G.W.; Metzger, M.J.; Mücher, C.A.; Pérez-Soba, M.; Renetzeder, C.; Andersen, E. European environmental stratifications and typologies: An overview. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 142, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.R.; Hardy, E.E.; Roach, J.T.; Witmer, R.E. A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensing Data; United States Government Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976; p. 964.
- Huynh Thanh, H.; Franke, C.; Piorr, A.; Lange, A.; Zasada, I. Target groups of rural development policies: Development of a surveybased farm typology for analysing self-perception statements of farmers. Outlook. Agric. 2014, 43, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabannes, Y. Financing and investment for urban agriculture. In Cities Farming for the Future: Urban Agriculture for Green and Productive Cities; Van Veenhuizen, R., Ed.; RUAF Foundation, IDRC and IIRR Publishing: Silang, Philippines, 2006; pp. 87–123. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Schans, J.W.; Wiskerke, J.S.C. Urban agriculture in developed economies. In Sustainable Food Planning: Evolving Theory and Practice; Viljoen, A., Wiskerke, J.S.C., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Pub: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, L.J.; Pearson, L.; Pearson, C.J. Sustainable urban agriculture: Stocktake and opportunities. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2010, 8, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COST Wiki. Types of Urban Agriculture, 2014. Available online: http://www.urbanagricultureeurope.la.rwth-aachen.de/mediawiki/index.php/Types_of_Urban_Agriculture (accessed on 27 April 2016).
- Benz, A.; Dose, N. Governance—Modebegriff oder nützliches sozialwissenschaftliches Konzept? In Dies. (Hrsg.): Governance-Regieren in Komplexen Regelsystemen. Eine Einführung; Lütz, S., Schimank, U., Eds.; Springer VS Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2010; pp. 13–36. [Google Scholar]
- Vatn, A. Markets in environmental governance. From theory to practice. Ecolog. Econ. 2014, 105, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.C.; Salus, D.A. Community and conservation land trusts as unlikely partners? The case of Troy Gardens, Madison, Wisconsin. Land Use Policy 2003, 20, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez de Molina, M. Agroecology and politics. How to get sustainability? About the necessity for a political agroecology. Agroecol. Sustain. Food. Syst. 2013, 37, 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Lovell, S.T. Multifunctional urban agriculture for sustainable land use planning in the United States. Sustainability 2010, 2, 2499–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Minock, M.; Stockmann, D. Creating a legal framework for urban agriculture: Lessons from Flint, Michigan. J. Agric. Food. Syst. Community Develop. 2010, 1, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, W.; Balmer, K.; Kaethler, T.; Rhoads, A. Using land inventories to plan for urban agriculture: Experiences from Portland and Vancouver. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2008, 74, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.R.; Lovell, S.T. Mapping public and private spaces of urban agriculture in Chicago through the analysis of high-resolution aerial images in Google Earth. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2012, 108, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N. Planning for urban agriculture: Problem recognition, policy formation, and politics. In Sustainable Food Planning; Viljoen, A., Wiskerke, J.S.C., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Pub: Wiskerke, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sarstedt, M.; Erik, M. A concise guide to market research. In The Process, Data, and Methods Using IBM SPSS Statistics; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson, L.-G. “Relationship marketing” and the “markets-as-networks approach”—A comparative analysis of two evolving streams of research. J. Mark. Manag. 1997, 13, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, R. Theory Building; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).